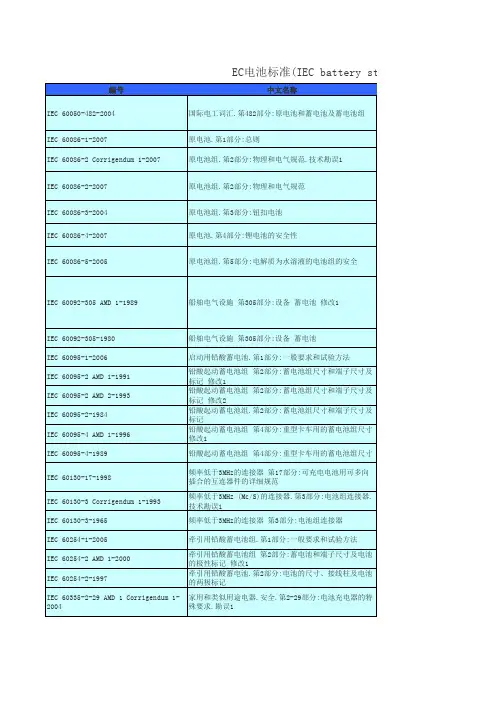
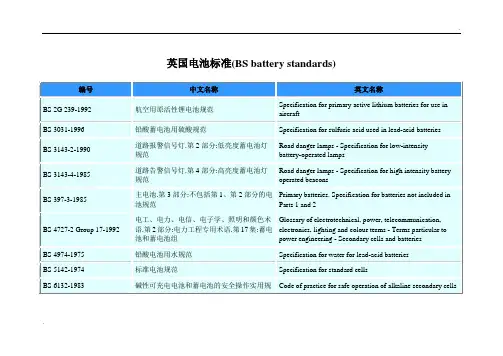
欧洲电池标准(EN battery standards)
- 格式:doc
- 大小:116.00 KB
- 文档页数:6

电池检测标准国际标准As technology advances and the demand for portable electronic devices increases, the need for standardized battery testing becomes crucial. The international standard for battery testing provides manufacturers, consumers, and regulatory bodies with a common set of guidelines to ensure the safety and performance of batteries used in various devices.随着技术的进步和对便携电子设备的需求增加,标准化电池测试的需求变得至关重要。
国际标准对电池测试提供了制造商、消费者和监管机构一个共同的指导方针,以确保各种设备中使用的电池的安全性和性能。
One of the key aspects of battery testing standards is safety. Batteries can be potentially hazardous if not properly tested and certified to meet safety requirements. The international standards outline testing procedures to assess the safety of batteries under various conditions such as overcharging, short-circuiting, and high temperatures.电池测试标准的一个关键方面是安全性。

电池认证标识
电池认证标识是指在电池产品上贴有的特定标志,用于表示该电池产品符合一定的认证标准和规范。
这些认证标识可以提供关于电池产品质量、性能、安全性和环境友好性的信息,帮助用户做出正确的选择。
以下是一些常见的电池认证标识:
1. CE标志:CE标志是欧盟规定的认证标志,表示该电池产品符合欧洲法规的安全、健康和环保要求。
2. UL标志:UL标志是美国Underwriters Laboratories认证的标志,表示该电池产品已经通过UL的安全测试和评估,符合美国安全标准。
3. FCC标志:FCC标志是美国联邦通信委员会认证的标志,表示该电池产品符合无线电频率辐射限制要求,不会干扰无线通信。
4. RoHS标志:RoHS标志表示该电池产品符合欧洲RoHS指令(限制使用某些有害物质)的要求,不含有害物质,对环境友好。
5. ENERGY STAR标志:ENERGY STAR标志是美国能源部和环境保护局共同推出的认证标志,表示该电池产品在能源效率方面达到高水平,节能环保。
6. EPEAT标志:EPEAT标志是电子产品环境评估工具组织认证的标志,表示该电池产品在材料选择、能源效率、产品寿命和循环利用等方面符合环保要求。
这些认证标识的出现可以帮助用户辨识符合认证标准的电池产品,并提供一定的保证,确保产品的质量和安全性。
当购买电池产品时,可以留意这些认证标识并参考其含义。

ÖNORMEN 15194Edition: 2009-06-01Cycles ― Electrically power assisted cycles ― EPACBicyclesFahrräder ― Elektromotorisch unterstützte Räder ― EPAC-FahrräderCycles ― Cycles à assistance électrique ― Bicyclettes EPACICS 43.120; 43.150Identical (IDT) with EN 15194:2009-01Supersedes ÖNORM EN 15194:2009-03 responsibleON-Committee ON-K 038Road vehiclesPublisher and printing Austrian Standards Institute/Österreichisches Normungsinstitut (ON) Heinestraße 38, 1020 WienCopyright © Austrian Standards Institute 2009. All rights reserved! No part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means – electronic, mechanical, photocopying or any other data carries without prior permission! E-Mail: publishing@as-plus.atInternet: www.as-plus.at/nutzungsrechteSale and distribution of national and foreign standards and technical regulations via Austrian Standards plus GmbH Heinestraße 38, 1020 Wien E-Mail: sales@as-plus.at Internet: www.as-plus.at24-Hours-Webshop: www.as-plus.at/shop Tel.: +43 1 213 00-444 Fax.: +43 1 213 00-818A S + S h o p 31.01.2012ÖNORM EN 15194:20092National ForewordDue to some misprints in the German version a new edition has been published. To ensure that the English and German version of ÖNORM EN 15194 have the same date of issue, the English version of ÖNORM EN 15194 will be withdrawn and published again without any modifications and corrections.A S + S h o p 31.01.2012EUROPEAN STANDARD NORME EUROPÉENNE EUROPÄISCHE NORMEN 15194January 2009ICS 43.120; 43.150English VersionCycles - Electrically power assisted cycles - EPAC BicyclesCycles - Cycles à assistance électrique - Bicyclettes EPACFahrräder - Elektromotorisch unterstützte Räder - EPACFahrräderThis European Standard was approved by CEN on 22 November 2008.CEN members are bound to comply with the CEN/CENELEC Internal Regulations which stipulate the conditions for giving this European Standard the status of a national standard without any alteration. Up-to-date lists and bibliographical references concerning such national standards may be obtained on application to the CEN Management Centre or to any CEN member.This European Standard exists in three official versions (English, French, German). A version in any other language made by translation under the responsibility of a CEN member into its own language and notified to the CEN Management Centre has the same status as the official versions.CEN members are the national standards bodies of Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland,France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal,Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and United Kingdom.EUROPEAN COMMITTEE FOR STANDARDIZATION C O M I T É E U R O P ÉE N D E N O R M A LI S A T I O N EUR OP ÄIS C HES KOM ITEE FÜR NOR M UNGManagement Centre: Avenue Marnix 17, B-1000 Brussels© 2009 CENAll rights of exploitation in any form and by any means reserved worldwide for CEN national Members.Ref. No. EN 15194:2009: EA S + S h o p 31.01.2012EN 15194:2009 (E)2Contents PageForeword ..............................................................................................................................................................4 Introduction .........................................................................................................................................................5 1 Scope ......................................................................................................................................................6 2 Normative references ............................................................................................................................6 3Terms and definitions (7)4 Requirements .........................................................................................................................................9 4.1 General ....................................................................................................................................................9 4.2 EPAC specific additional requirements ..............................................................................................9 4.2.1 Electric circuit ........................................................................................................................................9 4.2.2 Batteries ..................................................................................................................................................9 4.2.3 Electric cables and connections ....................................................................................................... 10 4.2.4 Power management ............................................................................................................................ 12 4.2.5 Electro Magnetic Compatibility ......................................................................................................... 13 4.2.6 Maximum speed for which the electric motor gives assistance .................................................... 14 4.2.7 Maximum power measurement ......................................................................................................... 15 5 Marking, labelling................................................................................................................................ 15 6Instruction for use (15)Annex A (informative) Example of recommendation for battery charging ................................................. 16 Annex B (informative) Example of relation between speed/torque/current ............................................... 17 Annex C (normative) Electromagnetic compatibility of EPAC and ESA .................................................... 20 C.1 Conditions applying to vehicles and to electrical/electronic sub-assemblies (ESA) .................. 20 C.1.1 Marking ................................................................................................................................................ 20 C.1.2 Requirements ...................................................................................................................................... 20 C.2 Method of measuring broad-band electromagnetic radiation from vehicles ............................... 24 C.2.1 Measuring equipment ......................................................................................................................... 24 C.2.2 Test method ......................................................................................................................................... 24 C.2.3 Measurement ....................................................................................................................................... 24 C.3 Method of measuring narrow band electromagnetic radiation from vehicles ............................. 25 C.3.1 General ................................................................................................................................................. 25 C.3.2 Antenna type, position and orientation ............................................................................................ 25 C.4 Methods of testing vehicle immunity to electromagnetic radiation .............................................. 25 C.4.1 General ................................................................................................................................................. 25 C.4.2 Expression of results ......................................................................................................................... 25 C.4.3 Test conditions ................................................................................................................................... 25 C.4.4 State of the vehicle during the tests ................................................................................................. 25 C.4.5 Type, position and orientation of the field generator ..................................................................... 26 C.4.6 Requisite test and condition .............................................................................................................. 27 C.4.7 Generation of the requisite field strength ........................................................................................ 28 C.4.8 Inspection and monitoring equipment ............................................................................................. 29 C.5 Method of measuring broad-band electromagnetic radiation from separate technical units(ESA) (29)C.5.1 General ................................................................................................................................................. 29 C.5.2 State of the ESA during the test ........................................................................................................ 29 C.5.3 Antenna type, position and orientation ............................................................................................ 29 C.6 Method of measuring narrow-band electromagnetic radiation from separate technicalunits (ESAs) (30)C.6.1 General (30)A S + S h o p 31.01.2012EN 15194:2009 (E)3C.6.2 Test conditions .................................................................................................................................... 30 C.6.3 State of the ESA during the tests ...................................................................................................... 30 C.6.4 Antenna type, position and orientation ............................................................................................. 30 C.7 Methods of testing the ESA immunity to electromagnetic radiation ............................................. 30 C.7.1 General ................................................................................................................................................. 30 C.7.2 Expression of results .......................................................................................................................... 30 C.7.3 Test conditions .................................................................................................................................... 30 C.7.4 State of the ESA during the tests ...................................................................................................... 30 C.7.5 Requisite test and condition .............................................................................................................. 31 C.7.6 Generation of the requisite field strength ......................................................................................... 31 C.7.7 Inspection and monitoring equipment .............................................................................................. 32 C.8 ESD test ................................................................................................................................................ 32 Annex D (informative) Maximum power measurement - Alternative method ............................................. 33 D.1 Generalities .......................................................................................................................................... 33 D.2 Test conditions .................................................................................................................................... 33 D.3 Test procedure ..................................................................................................................................... 33 Bibliography (35)A S + S h o p 31.01.2012EN 15194:2009 (E)4ForewordThis document (EN 15194:2009) has been prepared by Technical Committee CEN/TC 333 “Cycles”, the secretariat of which is held by UNI.This European Standard shall be given the status of a national standard, either by publication of an identical text or by endorsement, at the latest by July 2009, and conflicting national standards shall be withdrawn at the latest by July 2009.Attention is drawn to the possibility that some of the elements of this document may be the subject of patent rights. CEN [and/or CENELEC] shall not be held responsible for identifying any or all such patent rights. According to the CEN/CENELEC Internal Regulations, the national standards organizations of the following countries are bound to implement this European Standard: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom.A S + S h o p 31.01.2012EN 15194:2009 (E)5IntroductionThis European Standard gives requirements for electric power assisted cycles (EPAC).This European Standard has been developed in response to demand throughout Europe. Its aim is to provide a standard for the assessment of electrically powered cycles of a type which are excluded from type approval by Directive 2002/24/EC.Due to the limitation of the voltage to 48 VDC, there are no special requirements applicable to the EPAC in regard to protection against electrical hazards.EPACs are vehicles which use the same traffic areas as cars, lorries and motorcycles, which is predominantly the street. For this reason the products concerning EMC-testing have the same basic conditions. Chapter 8 of the EC Directive 97/24 contains a very high value concerning the immunity test of electronic components with 30 V/m, nevertheless based on the application area it comes up of the implementation. Manipulation of the electronic system of EPAC by other source of interference in the scope of the public road traffic could signify considerable risks of safety regulations for the user of EPAC. The standards EN 61000-6-1 as well as EN 61000-6-3 are standards for appliances in residential, commercial and light-industrial environments which do not reach the values for the EMC immunity-test necessary in the road traffic area. In these standards the EMC immunity of the electric and electronic systems will be tested only with 3 V/m, which is the tenth part of the requirements in chapter 8 of the EC Directive 97/24. These standards are unsuitable to obtain the urgent and necessary security level.A S + S h o p 31.01.2012。

REGULATIONSCOMMISSION REGULATION (EU) No 1103/2010of 29 November 2010establishing, pursuant to Directive 2006/66/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, rules as regards capacity labelling of portable secondary (rechargeable) and automotive batteries and accumulators(Text with EEA relevance)法规欧盟委员会法规第1103/2010号于2010年11月29日根据欧盟议会和理事会第2006/66/EC号指令,建立可携带二次电池(可充电)和汽车电池与蓄电池的容量标签的法规THE EUROPEAN COMMISSION,Having regard to the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union, Having regard to Directive 2006/66/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 6 September 2006 on batteries and accumulators and waste batteries and accumulators and repealing Directive 91/157/EEC ( 1 ), and in particular Article 21(2) and 21(7) thereof,欧盟理事会考虑到欧盟运作的协定考虑到欧盟议会和理事会于2006年9月6日颁布的2006/66/EC号关于电池和蓄电池、废弃电池及蓄电池以及废止91/157/EEC的指令,尤其是第21(2)和21(7)条款。

根据欧盟废旧电气电子回收指令2002/96/EC(WEEE)电子电气设备废弃物指令 , 凡是于 2005年 8月 13日以后投放欧盟市场的电子电气产品开始要求使用回收图标:打叉的有轮垃圾箱,下有一横条。
图标的设计要求第二条中第 2款提到的辅助图标应由以下内容组成,高度为 h、宽度为 1.2a的实芯条,高度 h与宽度的关系应为 0.3a或 1mm;实芯条应与交叉线和带轮子的垃圾桶图形联用;实芯条内不能有任何文字或信息。
实芯条与交叉线和带轮子的垃圾桶图形的相互关系应符合上图规定。
一.适用范围该规定适用于电气电子设备,有关设计和使用图标的 EN标准 prEN50419将电气电子设备定义为如下产品:指设计用于额定工作电压不超过 1000V交流或 1500V直流的、依靠电流或电磁场正常工作的设备,或产生、转换、测量这类电流和电磁场的设备。
WEEE指令 2002/96/EC中附录IA列出了这类设备。
该标准还定义了生产者,即:指任何从事以下活动的人。
定义的生产者还包括只是出售所用的技术,包括按照欧盟议会于 1997年 5月 20日颁布的有关远程(电子)合同保护消费者指令 97/7/EC指令以远程通信方式出售技术的:a.以自己的品牌制造和销售电气电子产品设备;b.销售由其他供应商制造的、但是标以自己商标的销售商;如果产品上出现的是生产者的商标,则该销售商不能被认为是生产者。
c.在专业领域进口或出口电气电子设备到各成员国。
2006/66/EC电池和蓄电池及电池和蓄电池废弃物指令检测-Battery电池指令检测欧盟(RoHS)已於2006年9月26日正式公告2006/66/EC (Batteries and Accumulators and Waste Batteries and Accumulators Directive)「电池、蓄电池、废电池及废蓄电池」指令,并自2008年9月26日起废止现行之第91/157/EEC号「含有某些危险物质之电池和蓄电池」指令。
cmetus关于电池标准English Answer:Cmetus: Battery Standards.Cmetus is a global organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus standards for the battery industry. These standards are developed through a process of consensus among stakeholders, including battery manufacturers, users, and other interested parties.Cmetus standards cover a wide range of topics, including:Battery safety.Battery performance.Battery testing.Battery materials.Battery recycling.Cmetus standards are used by battery manufacturers, users, and other stakeholders to ensure that batteries are safe, reliable, and environmentally friendly.Benefits of Cmetus Standards.There are many benefits to using Cmetus standards, including:Increased safety: Cmetus standards help to ensure that batteries are safe to use. This is important for both consumers and businesses.Improved performance: Cmetus standards help to ensure that batteries perform as expected. This is important for businesses that rely on batteries to power their products.Reduced environmental impact: Cmetus standards help toreduce the environmental impact of batteries. This is important for everyone who is concerned about the environment.Cmetus Standards for Battery Safety.Cmetus has developed a number of standards for battery safety. These standards address issues such as:Battery fires.Battery explosions.Battery leaks.Battery recalls.Cmetus standards for battery safety are used by battery manufacturers, users, and other stakeholders to help prevent battery accidents.Cmetus Standards for Battery Performance.Cmetus has developed a number of standards for battery performance. These standards address issues such as:Battery capacity.Battery power.Battery life.Battery efficiency.Cmetus standards for battery performance are used by battery manufacturers, users, and other stakeholders to help ensure that batteries perform as expected.Cmetus Standards for Battery Testing.Cmetus has developed a number of standards for battery testing. These standards address issues such as:Battery safety testing.Battery performance testing.Battery life testing.Battery durability testing.Cmetus standards for battery testing are used by battery manufacturers, users, and other stakeholders to help ensure that batteries are safe and reliable.中文回答:Cmetus,电池标准。
en60079电池测试标准
EN 60079 是欧盟制定的一系列电池测试标准,旨在确保电池在特定应用中的安全性和可靠性。
以下是EN 60079 电池测试标准的一些主要内容:
1. 电池类型:EN 60079 标准适用于各种类型的电池,包括锂离子电池、镍镉电池、镍氢电池等。
2. 测试项目:EN 60079 标准包括多项测试项目,如短路测试、过充测试、过放测试、温度循环测试等。
3. 测试条件:EN 60079 标准规定了电池测试的条件,如温度、湿度、电压等。
4. 测试结果:EN 60079 标准要求电池在测试过程中不得出现泄漏、起火、爆炸等安全问题,并且电池的性能指标应符合相关要求。
5. 认证:符合EN 60079 标准的电池可以获得欧盟认证,证明其符合欧盟的安全和环保要求。
EN 60079 电池测试标准是欧盟电池行业的重要标准之一,它为电池的设计、制造和使用提供了统一的规范和要求,有助于确保电池的安全性和可靠性。
欧盟动力电池拆解标准
欧盟对于动力电池的拆解标准主要体现在其最新的《电池法》中。
根据这项法规,动力电池的回收率有明确的要求,旨在提高电池的回收率和再利用程度,减少环境污染。
以下是欧盟动力电池拆解标准的主要要点:
1. 回收率目标:根据新电池法,到2027年,可携式电池的回收率应达到63%,2030年达到73%。
电动车、电动自行车、电动滑板车等轻型交通工具(LMT)的电池回收率在2028年达到51%,2031年达到61%。
2. 关键金属回收率:法案明确规定了钴、锂和镍等关键金属的回收率目标。
到2027年,锂的回收率应达到50%,2031年达到80%。
钴、铜、铅和镍的回收率在2027年应达到90%。
3. 电池护照:自2027年起,出口到欧洲的动力电池需要持有符合要求的“电池护照”。
电池护照记录电池的制造商、材料成分、碳足迹、供应链等信息,有助于提高电池价值链的透明度和数据可信度。
4. 碳排放披露:电池出口企业需披露从上游矿产、材料到电池生产、回收以及再利用各环节的碳排放数据。
5. 可持续性与循环性:新电池法强调电池在整个生命周期内对环境和社会的影响,要求提高可持续性和循环性。
6. 原材料使用比例:新电池法规定,新电池应使用一定比例的回收材料。
例如,钴在法规生效八年后应包含16%,铅为85%,锂和镍为6%。
7. 标准化规则:新电池法要求制定电池产品、工艺、废电池和回收物的标准化规则,以加强内部市场、推进循环经济。
这些标准对动力电池的拆解、回收和再利用提出了较高的要求,旨在促进可持续发展和环境保护。
我国企业出口欧洲的动力电池需要遵循这些标准,以确保产品合规。