头孢他啶使用说明
- 格式:docx
- 大小:13.80 KB
- 文档页数:4


注射用头孢他啶说明书请仔细阅读说明书并在医师指导下使用【药品名称】通用名称:注射用头孢他啶英文名称:Ceftazidime for Injection汉语拼音:Zhusheyong Toubaotading【成份】本品活性成份为头孢他啶,化学名称:(6R, 7R)-7-[[(2-氨基-4-噻唑基)-[(1-羧基-1-甲基乙氧基)亚氨基]乙酰基]氨基]-2-羧基-8-氧代-5-硫杂-1-氮杂双环[4.2.0]辛-2-烯-3-甲基吡啶鎓内盐五水合物。
化学结构式:分子式:C22H22N6O7S2·5H2O分子量:辅料:碳酸钠。
【性状】本品为白色或类白色结晶性粉末。
【适应症】用于敏感革兰氏阴性杆菌所致的败血症、下呼吸道感染、腹腔和胆道感染、复杂性尿路感染和严重皮肤软组织感染等。
对于由多种耐药革兰氏阴性杆菌引起的免疫缺陷者感染、医院内感染以及革兰氏阴性杆菌或铜绿假单胞菌所致中枢神经系统感染尤为适用。
【规格】1.0g(按头孢他啶计)【用法用量】静脉注射或静脉滴注。
剂量依感染的严重程度、微生物敏感性及患者机体状态而定。
成人:1. 败血症、下呼吸道感染、胆道感染等,一日4~6g,分2~3次静脉滴注或静脉注射,疗程10~14日。
2. 泌尿系统感染和重度皮肤软组织感染等,一日2~4g,分2次静脉滴注或静脉注射,疗程7~14日。
对于轻度尿路感染,每12小时~1g即已足够。
3. 对于某些危及生命的感染、严重铜绿假单胞菌感染和中枢神经系统感染,可酌情增量至一日~0.2g/kg,分3次静脉滴注或静脉注射。
儿童:2个月以上婴幼儿常用剂量为一日30~100mg/kg,分2~3次静脉滴注。
对新生儿至2个月婴儿临床经验有限。
肾功能损害患者:因头孢他啶主要经肾脏排泄,对肾功能损害患者应减量使用。
可根据肌酐清除率来计算合适的给药剂量。
透析后患者应重复适当维持剂量。
配制方法:5ml注射用水加入0.5g装瓶中或10ml注射用水加入1g或2g装瓶中,使完全溶解后,于3~5分钟静脉缓慢推注。

头孢他啶-阿维巴坦药品说明书赵锦锦【摘要】头孢他啶-阿维巴坦注射剂由森林实验室(Forest Lab)和阿斯利康制药公司联合开发,现艾尔健和阿斯利康公司分别在北美和世界其它地区拥有其商业化的权利,商品名为AVYCAZ,己于2015年2月25日被FDA快速批准.该复方制剂由一种头孢菌素(头孢他啶)和一种β-内酰胺酶抑制剂(阿维巴坦)组成,用于治疗18岁及以上复杂性腹腔内感染、复杂性尿路感染以及医院获得性细菌性肺炎和呼吸机相关细菌性肺炎,抗菌谱为耐药形势严峻的革兰阴性菌.我们对其说明书进行翻译,包括适应证、用法用量、不良反应、临床药理学、微生物学和临床研究等,以供大家阅读和参考.【期刊名称】《国外医药(抗生素分册)》【年(卷),期】2019(040)002【总页数】13页(P115-127)【关键词】头孢他啶;阿维巴坦;适应证;微生物学;临床研究【作者】赵锦锦【作者单位】复旦大学附属华山医院抗生素研究所,上海200040【正文语种】中文【中图分类】R978.1+11 前言2015年2月25日被食品药品监督管理局(FDA)批准的新药头孢他啶-阿维巴坦注射剂,由半合成头孢菌素头孢他啶五水合物和β-内酰胺酶抑制剂阿维巴坦钠组成,用于治疗革兰阴性菌感染,尤其是耐药菌引起的严重感染,适应证为18岁及以上患者由敏感革兰阴性菌引起的复杂性腹腔内感染(complicated intra-abdominal infections, cIAI)(联合甲硝唑)、复杂性尿路感染(complicated urinary tract infections, cUTI)(包括肾盂肾炎)和医院获得性细菌性肺炎和呼吸机相关细菌性肺炎(hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia , HABP/VABP)。
2 药品说明本药通用名为头孢他啶-阿维巴坦(ceftazidimeavibactam),商品名为AVYCAZ。




头孢克肟分散片是一种抗生素,属于第三代头孢菌素,抗菌谱比较广,对于大部分的革兰阳性菌和阴性菌都有抗菌活性,特别是对于肺炎链球菌、淋球菌、大肠杆菌以及沙雷氏菌等都有较强的抗菌作用。
在临床上可以广泛的用于敏感菌所引起的多部位的感染,包括呼吸系统的感染、泌尿生殖系统的感染、中耳炎、鼻窦炎、胆囊炎、胆管炎等多部位感染的治疗。
头孢克肟分散片在口服时注意可以加水分散之后口服,或者含于口中含服或者吞服,一般成人是一次服用一片,一天服用两次,感染严重的话可以一次服用两片,一天服用两次。
头孢菌素:共性:1.交叉过敏:有β-内酰胺类类药物过敏性休克史者不可应用。
2.本人或双亲、弟兄有易引起支气管哮喘、皮疹、荨麻疹等过敏症状体质患者慎用。
3.经口摄食不足患者或非经口维持营养患者、全身状态不良患者(有时会出现维生素K缺乏症状,故应注意观察)慎用。
4.与氨基糖苷类有协同杀菌作用。
5.与氨基糖苷类药合用可增加肾毒性;与呋塞米等强利尿剂合用可增加肾毒性。
6.对有黄疸的新生儿,使用本品会增加发生疸红素脑病的危险。
7.长期使用可引起菌群失调。
8.服用过多剂量的头孢菌素会导致大脑受刺激及引起惊厥。
9.可能影响肠道菌群,导致雌激素重吸收减少并降低合并使用口服避孕药的疗效。
10.与氨基糖苷类、喹诺酮类、质子泵抑制剂、万古霉素、氨茶碱、氨溴索、维生素B6等有配伍禁忌。
第一代头孢菌素【头孢氨苄】1.脓液药物浓度与血药浓度基本相等,关节腔渗出液中药物浓度为血药浓度的50%,胆汁中药物浓度为血药浓度的1~4倍。
2.口服,一日4次,一日总量不超过4g。
不宜用于重症感染。
3.食物对血药峰浓度和半衰期无明显影响。
【头孢羟氨苄】1.头孢羟氨苄自胃肠道的吸收较头孢氨苄和头孢拉定缓慢,但血药浓度较后二者持久。
2.骨骼、肌肉和滑囊液中的浓度分别为同期血清浓度的23%、31%和43%。
胆汁中浓度一般较血清浓度为低。
3.口服,一日2次,一日总量不超过4g。
4.食物对血药峰浓度和半衰期无明显影响。


1PRODUCT INFORMATIONCEPTAZ®2(ceftazidime for injection)3L-arginine formulation45For Intravenous or Intramuscular Use678DESCRIPTION: Ceftazidime is a semisynthetic, broad-spectrum, beta-lactam antibiotic forparenteral administration. It is the pentahydrate of pyridinium, 1-[[7-[[(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)[(1-910carboxy-1-methylethoxy)imino]acetyl]amino]-2-carboxy-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-11en-3-yl]methyl]-, hydroxide, inner salt, [6R-[6α,7β(Z)]]. It has the following structure:12131415The empirical formula is C22H32N6O12S2, representing a molecular weight of 636.6.CEPTAZ is a sterile, dry mixture of ceftazidime pentahydrate and L-arginine. The L-arginine1617is at a concentration of 349 mg/g of ceftazidime activity. CEPTAZ dissolves without the18evolution of gas. The product contains no sodium ion. Solutions of CEPTAZ range in color from 19light yellow to amber, depending on the diluent and volume used. The pH of freshly constituted 20solutions usually ranges from 5 to 7.5.2122CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: After intravenous (IV) administration of 500-mg and 1-g doses of ceftazidime over 5 minutes to normal adult male volunteers, mean peak serum2324concentrations of 45 and 90 mcg/mL, respectively, were achieved. After IV infusion of 500-mg, 251-g, and 2-g doses of ceftazidime over 20 to 30 minutes to normal adult male volunteers, mean peak serum concentrations of 42, 69, and 170 mcg/mL, respectively, were achieved. The average2627serum concentrations following IV infusion of 500-mg, 1-g, and 2-g doses to these volunteers28over an 8-hour interval are given in Table 1.2930Table 1Ceftazidime Serum Concentrations (mcg/mL)IV Dose 0.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 8 hmg 42 25 12 6 2 500g 60 39 23 11 31g 129 75 42 13 523132The absorption and elimination of ceftazidime were directly proportional to the size of the33dose. The half-life following IV administration was approximately 1.9 hours. Less than 10% of 34ceftazidime was protein bound. The degree of protein binding was independent of concentration.There was no evidence of accumulation of ceftazidime in the serum in individuals with normal3536renal function following multiple IV doses of 1 and 2 g every 8 hours for 10 days.37Following intramuscular (IM) administration of 500-mg and 1-g doses of ceftazidime to38normal adult volunteers, the mean peak serum concentrations were 17 and 39 mcg/mL,39respectively, at approximately 1 hour. Serum concentrations remained above 4 mcg/mL for 6 and 408 hours after the IM administration of 500-mg and 1-g doses, respectively. The half-life of41ceftazidime in these volunteers was approximately 2 hours.42The presence of hepatic dysfunction had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of ceftazidime in 43individuals administered 2 g intravenously every 8 hours for 5 days. Therefore, a dosage44adjustment from the normal recommended dosage is not required for patients with hepatic45dysfunction, provided renal function is not impaired.46Approximately 80% to 90% of an IM or IV dose of ceftazidime is excreted unchanged by the 47kidneys over a 24-hour period. After the IV administration of single 500-mg or 1-g doses,approximately 50% of the dose appeared in the urine in the first 2 hours. An additional 20% was4849excreted between 2 and 4 hours after dosing, and approximately another 12% of the doseappeared in the urine between 4 and 8 hours later. The elimination of ceftazidime by the kidneys5051resulted in high therapeutic concentrations in the urine.52The mean renal clearance of ceftazidime was approximately 100 mL/min. The calculated53plasma clearance of approximately 115 mL/min indicated nearly complete elimination of54ceftazidime by the renal route. Administration of probenecid before dosing had no effect on the 55elimination kinetics of ceftazidime. This suggested that ceftazidime is eliminated by glomerular 56filtration and is not actively secreted by renal tubular mechanisms.57Since ceftazidime is eliminated almost solely by the kidneys, its serum half-life is significantly 58prolonged in patients with impaired renal function. Consequently, dosage adjustments in such59patients as described in the DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section are suggested.60Ceftazidime concentrations achieved in specific body tissues and fluids are depicted in61Table 2.62Table 2: Ceftazidime Concentrations in Body Tissues and Fluids 63Tissue or Fluid Dose/ RouteNo. ofPatientsTime ofSamplePostdoseAverage Tissueor Fluid Level(mcg/mL ormcg/g)Urine 500 mg IM 6 0-2 h 2,100.02 g IV 6 0-2 h 12,000.0Bile 2 g IV 3 90 min 36.4Synovial fluid 2 g IV 13 2 h 25.6Peritoneal fluid 2 g IV 8 2 h 48.6Sputum 1 g IV 8 1 h 9.0Cerebrospinal fluid 2 g q8h IV 5 120 min 9.8(inflamed meninges) 2 g q8h IV 6 180 min 9.4Aqueous humor 2 g IV 13 1-3 h 11.0Blister fluid 1 g IV 7 2-3 h 19.7Lymphatic fluid 1 g IV 7 2-3 h 23.4Bone 2 g IV 8 0.67 h 31.1Heart muscle 2 g IV 35 30-280 min 12.7Skin 2 g IV 22 30-180 min 6.6Skeletal muscle 2 g IV 35 30-280 min 9.4Myometrium 2 g IV 31 1-2 h 18.764Microbiology: Ceftazidime is bactericidal in action, exerting its effect by inhibition of enzymes 65responsible for cell-wall synthesis. A wide range of gram-negative organisms is susceptible to66ceftazidime in vitro, including strains resistant to gentamicin and other aminoglycosides. In67addition, ceftazidime has been shown to be active against gram-positive organisms. It is highly 68stable to most clinically important beta-lactamases, plasmid or chromosomal, which are produced 69by both gram-negative and gram-positive organisms and, consequently, is active against many 70strains resistant to ampicillin and other cephalosporins.71Ceftazidime has been shown to be active against the following organisms both in vitro and in 72clinical infections (see INDICATIONS AND USAGE).7374Aerobes,Gram-negative:Citrobacter spp., including Citrobacter freundii and Citrobacter75diversus; Enterobacter spp., including Enterobacter cloacae and Enterobacter aerogenes;76Escherichia coli; Haemophilus influenzae, including ampicillin-resistant strains; Klebsiella spp.77(including Klebsiella pneumoniae); Neisseria meningitidis; Proteus mirabilis; Proteus vulgaris;78Pseudomonas spp. (including Pseudomonas aeruginosa); and Serratia spp.79Aerobes, Gram-positive:Staphylococcus aureus, including penicillinase- and non–80penicillinase-producing strains; Streptococcus agalactiae (group B streptococci); Streptococcus 81pneumoniae; and Streptococcus pyogenes (group A beta-hemolytic streptococci).Anaerobes:Bacteroides spp. (NOTE: many strains of Bacteroides fragilis are resistant).8283Ceftazidime has been shown to be active in vitro against most strains of the following organisms; however, the clinical significance of this activity is unknown: Acinetobacter spp.,8485Clostridium spp. (not including Clostridium difficile), Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Morganella 86morganii (formerly Proteus morganii), Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Peptococcus spp.,87Peptostreptococcus spp., Providencia spp. (including Providencia rettgeri, formerly Proteus88rettgeri), Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Yersinia89enterocolitica.Ceftazidime and the aminoglycosides have been shown to be synergistic in vitro against9091Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the enterobacteriaceae. Ceftazidime and carbenicillin have also 92been shown to be synergistic in vitro against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.93Ceftazidime is not active in vitro against methicillin-resistant staphylococci, Streptococcus94faecalis and many other enterococci, Listeria monocytogenes, Campylobacter spp., or95Clostridium difficile.96Susceptibility Tests:Diffusion Techniques:Quantitative methods that require measurement of 97zone diameters give an estimate of antibiotic susceptibility. One such procedure1-3 has been98recommended for use with disks to test susceptibility to ceftazidime.99Reports from the laboratory giving results of the standard single-disk susceptibility test with a 30-mcg ceftazidime disk should be interpreted according to the following criteria:100101Susceptible organisms produce zones of 18 mm or greater, indicating that the test organism 102is likely to respond to therapy.Organisms that produce zones of 15 to 17 mm are expected to be susceptible if high dosage 103104is used or if the infection is confined to tissues and fluids (e.g., urine) in which high antibiotic 105levels are attained.106Resistant organisms produce zones of 14 mm or less, indicating that other therapy should be 107selected.108Organisms should be tested with the ceftazidime disk since ceftazidime has been shown by in 109vitro tests to be active against certain strains found resistant when other beta-lactam disks are 110used.111Standardized procedures require the use of laboratory control organisms. The 30-mcg ceftazidime disk should give zone diameters between 25 and 32 mm for Escherichia coli112113ATCC 25922. For Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853, the zone diameters should bebetween 22 and 29 mm. For Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923, the zone diameters should be 114115between 16 and 20 mm.116Dilution Techniques:In other susceptibility testing procedures, e.g., ICS agar dilution or the 117equivalent, a bacterial isolate may be considered susceptible if the minimum inhibitory118concentration (MIC) value for ceftazidime is not more than 16 mcg/mL. Organisms are119considered resistant to ceftazidime if the MIC is ≥64 mcg/mL. Organisms having an MIC value 120of <64 mcg/mL but >16 mcg/mL are expected to be susceptible if high dosage is used or if the 121infection is confined to tissues and fluids (e.g., urine) in which high antibiotic levels are attained. 122As with standard diffusion methods, dilution procedures require the use of laboratory control 123organisms. Standard ceftazidime powder should give MIC values in the range of 4 to 16 mcg/mL 124for Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923. For Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, the MIC range125should be between 0.125 and 0.5 mcg/mL. For Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853, the MIC 126range should be between 0.5 and 2 mcg/mL.127128INDICATIONS AND USAGE: CEPTAZ is indicated for the treatment of patients with129infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated organisms in the following diseases: 1301.Lower Respiratory Tract Infections, including pneumonia, caused by Pseudomonas131aeruginosa and other Pseudomonas spp.; Haemophilus influenzae, including132ampicillin-resistant strains; Klebsiella spp.; Enterobacter spp.; Proteus mirabilis; Escherichiacoli; Serratia spp.; Citrobacter spp.; Streptococcus pneumoniae; and Staphylococcus aureus 133134(methicillin-susceptible strains).1352.Skin and Skin-Structure Infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Klebsiella spp.; 136Escherichia coli; Proteus spp., including Proteus mirabilis and indole-positive Proteus;137Enterobacter spp.; Serratia spp.; Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible strains); and 138Streptococcus pyogenes (group A beta-hemolytic streptococci).1393. Urinary Tract Infections, both complicated and uncomplicated, caused by Pseudomonas140aeruginosa; Enterobacter spp.; Proteus spp., including Proteus mirabilis and indole-positive 141Proteus; Klebsiella spp.; and Escherichia coli.4.Bacterial Septicemia caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella spp., Haemophilus142143influenzae, Escherichia coli, Serratia spp., Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Staphylococcusaureus (methicillin-susceptible strains).1441455. Bone and Joint Infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa,Klebsiella spp., Enterobacter 146spp., and Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible strains).1476.Gynecologic Infections, including endometritis, pelvic cellulitis, and other infections of the 148female genital tract caused by Escherichia coli.1497.Intra-abdominal Infections, including peritonitis caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp.,and Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible strains) and polymicrobial infections150151caused by aerobic and anaerobic organisms and Bacteroides spp. (many strains of Bacteroides 152fragilis are resistant).1538.Central Nervous System Infections, including meningitis, caused by Haemophilus influenzae 154and Neisseria meningitidis. Ceftazidime has also been used successfully in a limited number of 155cases of meningitis due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Streptococcus pneumoniae.156Specimens for bacterial cultures should be obtained before therapy in order to isolate and157identify causative organisms and to determine their susceptibility to ceftazidime. Therapy may be 158instituted before results of susceptibility studies are known; however, once these results become 159available, the antibiotic treatment should be adjusted accordingly.CEPTAZ may be used alone in cases of confirmed or suspected sepsis. Ceftazidime has been 160161used successfully in clinical trials as empiric therapy in cases where various concomitant162therapies with other antibiotics have been used.163CEPTAZ may also be used concomitantly with other antibiotics, such as aminoglycosides, 164vancomycin, and clindamycin; in severe and life-threatening infections; and in the165immunocompromised patient (see COMPATIBILITY AND STABILITY). When such166concomitant treatment is appropriate, prescribing information in the labeling for the otherantibiotics should be followed. The dosage depends on the severity of the infection and the167168patient's condition.169170CONTRAINDICATIONS: CEPTAZ is contraindicated in patients who have shown171hypersensitivity to ceftazidime or the cephalosporin group of antibiotics.172173WARNINGS: BEFORE THERAPY WITH CEPTAZ IS INSTITUTED, CAREFUL INQUIRY 174SHOULD BE MADE TO DETERMINE WHETHER THE PATIENT HAS HAD PREVIOUS 175HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS TO CEFTAZIDIME, CEPHALOSPORINS,176PENICILLINS, OR OTHER DRUGS. IF THIS PRODUCT IS TO BE GIVEN TOPENICILLIN-SENSITIVE PATIENTS, CAUTION SHOULD BE EXERCISED BECAUSE 177178CROSS-HYPERSENSITIVITY AMONG BETA-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS HAS BEENCLEARLY DOCUMENTED AND MAY OCCUR IN UP TO 10% OF PATIENTS WITH A 179180HISTORY OF PENICILLIN ALLERGY. IF AN ALLERGIC REACTION TO CEPTAZ181OCCURS, DISCONTINUE THE DRUG. SERIOUS ACUTE HYPERSENSITIVITY182REACTIONS MAY REQUIRE TREATMENT WITH EPINEPHRINE AND OTHER183EMERGENCY MEASURES, INCLUDING OXYGEN, IV FLUIDS, IV ANTIHISTAMINES, 184CORTICOSTEROIDS, PRESSOR AMINES, AND AIRWAY MANAGEMENT, AS185CLINICALLY INDICATED.186Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with nearly all antibacterial agents,187including ceftazidime, and may range in severity from mild to life threatening. Therefore, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who present with diarrhea subsequent to 188189the administration of antibacterial agents.Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon and may permit190191overgrowth of clostridia. Studies indicate that a toxin produced by Clostridium difficile is one 192primary cause of "antibiotic-associated colitis."After the diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis has been established, appropriate therapeutic 193194measures should be initiated. Mild cases of pseudomembranous colitis usually respond to drug195discontinuation alone. In moderate to severe cases, consideration should be given to management196with fluids and electrolytes, protein supplementation, and treatment with an antibacterial drug197clinically effective against Clostridium difficile colitis.198Elevated levels of ceftazidime in patients with renal insufficiency can lead to seizures,encephalopathy, coma, asterixis, neuromuscular excitability, and myoclonia (see199200PRECAUTIONS).201202PRECAUTIONS:203General: High and prolonged serum ceftazidime concentrations can occur from usual dosages in204patients with transient or persistent reduction of urinary output because of renal insufficiency.205The total daily dosage should be reduced when ceftazidime is administered to patients with renal206insufficiency (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Elevated levels of ceftazidime in thesepatients can lead to seizures, encephalopathy, coma, asterixis, neuromuscular excitability, and 207208myoclonia. Continued dosage should be determined by degree of renal impairment, severity ofinfection, and susceptibility of the causative organisms.209210As with other antibiotics, prolonged use of CEPTAZ may result in overgrowth of211nonsusceptible organisms. Repeated evaluation of the patient's condition is essential. If212superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.213Inducible type I beta-lactamase resistance has been noted with some organisms (e.g.,214Enterobacter spp.,Pseudomonas spp., and Serratia spp.). As with other extended-spectrum215beta-lactam antibiotics, resistance can develop during therapy, leading to clinical failure in some216cases. When treating infections caused by these organisms, periodic susceptibility testing should217be performed when clinically appropriate. If patients fail to respond to monotherapy, anaminoglycoside or similar agent should be considered.218219Cephalosporins may be associated with a fall in prothrombin activity. Those at risk includepatients with renal or hepatic impairment, or poor nutritional state, as well as patients receiving a 220221protracted course of antimicrobial therapy. Prothrombin time should be monitored in patients at222risk and exogenous vitamin K administered as indicated.CEPTAZ should be prescribed with caution in individuals with a history of gastrointestinal 223224disease, particularly colitis.225Arginine has been shown to alter glucose metabolism and elevate serum potassium transiently 226when administered at 50 times the recommended dose. The effect of lower dosing is not known. 227Distal necrosis can occur after inadvertent intra-arterial administration of ceftazidime.228Drug Interactions: Nephrotoxicity has been reported following concomitant administration of 229cephalosporins with aminoglycoside antibiotics or potent diuretics such as furosemide. Renal 230function should be carefully monitored, especially if higher dosages of the aminoglycosides are to 231be administered or if therapy is prolonged, because of the potential nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity of aminoglycosidic antibiotics. Nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity were not noted when ceftazidime 232233was given alone in clinical trials.Chloramphenicol has been shown to be antagonistic to beta-lactam antibiotics, including234235ceftazidime, based on in vitro studies and time kill curves with enteric gram-negative bacilli. Due 236to the possibility of antagonism in vivo, particularly when bactericidal activity is desired, this 237drug combination should be avoided.238Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions: The administration of ceftazidime may result in a239false-positive reaction for glucose in the urine when using CLINITEST® tablets, Benedict'ssolution, or Fehling's solution. It is recommended that glucose tests based on enzymatic glucose 240241oxidase reactions (such as CLINISTIX®) be used.242Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility: Long-term studies in animals have not 243been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential. However, a mouse Micronucleus test and an 244Ames test were both negative for mutagenic effects.245Pregnancy:Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category B. Reproduction studies have been246performed in mice and rats at doses up to 40 times the human dose and have revealed no evidence 247of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to ceftazidime. CEPTAZ at 23 times the human dose 248was not teratogenic or embryotoxic in a rat reproduction study. There are, however, no adequate 249and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are notalways predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly 250251needed.252Nursing Mothers: Ceftazidime is excreted in human milk in low concentrations. It is not knownwhether the arginine component of this product is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs 253254are excreted in human milk and because safety of the arginine component of CEPTAZ in nursing 255infants has not been established, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to 256discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.257Pediatric Use: Safety of the arginine component of CEPTAZ in neonates, infants, and children 258has not been established. This product is for use in patients 12 years and older. If treatment with ceftazidime is indicated for neonates, infants, or children, a sodium carbonate formulation should 259260be used.261262ADVERSE REACTIONS: The following adverse effects from clinical trials were considered to 263be either related to ceftazidime therapy or were of uncertain etiology. The most common were 264local reactions following IV injection and allergic and gastrointestinal reactions. No265disulfiramlike reactions were reported.266Local Effects, reported in fewer than 2% of patients, were phlebitis and inflammation at the site of injection (1 in 69 patients).267268Hypersensitivity Reactions, reported in 2% of patients, were pruritus, rash, and fever.Immediate reactions, generally manifested by rash and/or pruritus, occurred in 1 in 285 patients. 269270Toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and erythema multiforme have also been 271reported with cephalosporin antibiotics, including ceftazidime. Angioedema and anaphylaxis 272(bronchospasm and/or hypotension) have been reported very rarely.273Gastrointestinal Symptoms, reported in fewer than 2% of patients, were diarrhea (1 in 78),274nausea (1 in 156), vomiting (1 in 500), and abdominal pain (1 in 416). The onset of275pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after treatment (see WARNINGS). 276Central Nervous System Reactions (fewer than 1%) included headache, dizziness, and277paresthesia. Seizures have been reported with several cephalosporins, including ceftazidime. In addition, encephalopathy, coma, asterixis, neuromuscular excitability, and myoclonia have been 278279reported in renally impaired patients treated with unadjusted dosage regimens of ceftazidime (see PRECAUTIONS: General).280281Less Frequent Adverse Events (fewer than 1%) were candidiasis (including oral thrush) and 282vaginitis.Hematologic: Rare cases of hemolytic anemia have been reported.283284Laboratory Test Changes noted during ceftazidime clinical trials were transient and included: 285eosinophilia (1 in 13), positive Coombs' test without hemolysis (1 in 23), thrombocytosis (1 in 28645), and slight elevations in one or more of the hepatic enzymes, aspartate aminotransferase287(AST, SGOT) (1 in 16), alanine aminotransferase (ALT, SGPT) (1 in 15), LDH (1 in 18), GGT (1 288in 19), and alkaline phosphatase (1 in 23). As with some other cephalosporins, transient289elevations of blood urea, blood urea nitrogen, and/or serum creatinine were observed290occasionally. Transient leukopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, and291lymphocytosis were seen very rarely.292293POSTMARKETING EXPERIENCE WITH CEPTAZ PRODUCTS: In addition to theadverse events reported during clinical trials, the following events have been observed during 294295clinical practice in patients treated with CEPTAZ and were reported spontaneously. For some of 296these events, data are insufficient to allow an estimate of incidence or to establish causation.297General: Anaphylaxis; allergic reactions, which, in rare instances, were severe (e.g.,298cardiopulmonary arrest); urticaria; pain at injection site.299Hepatobiliary Tract: Hyperbilirubinemia, jaundice.300Renal and Genitourinary: Renal impairment.301Cephalosporin-Class Adverse Reactions: In addition to the adverse reactions listed above that 302have been observed in patients treated with ceftazidime, the following adverse reactions and303altered laboratory tests have been reported for cephalosporin-class antibiotics:304Adverse Reactions:Colitis, toxic nephropathy, hepatic dysfunction including cholestasis, 305aplastic anemia, hemorrhage.306Altered Laboratory Tests:Prolonged prothrombin time, false-positive test for urinary307glucose, pancytopenia.308309OVERDOSAGE: Ceftazidime overdosage has occurred in patients with renal failure. Reactions 310have included seizure activity, encephalopathy, asterixis, neuromuscular excitability, and coma. 311Patients who receive an acute overdosage should be carefully observed and given supportive312treatment. In the presence of renal insufficiency, hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis may aid inthe removal of ceftazidime from the body.313314315DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:Dosage: The usual adult dosage is 1 gram administered intravenously or intramuscularly every 8 316317to 12 hours. The dosage and route should be determined by the susceptibility of the causative 318organisms, the severity of infection, and the condition and renal function of the patient.319The guidelines for dosage of CEPTAZ are listed in Table 3. The following dosage schedule is 320recommended.321Table 3: Recommended Dosage Schedule322DoseFrequency Patients 12 years and older*Usual recommended dosage 1 gram IV or IM q8-12hUncomplicated urinary tract infections 250 mg IV or IM q12hBone and joint infections 2 grams IV q12hComplicated urinary tract infections 500 mg IV or IM q8-12hUncomplicated pneumonia; mild skin and skin- structure infections 500 mg-1 gramIV or IM q8hSerious gynecologic and intra-abdominal infections 2 grams IV q8h Meningitis 2 grams IV q8h Very severe life-threatening infections, especiallyin immunocompromised patients 2 grams IV q8hLung infections caused by Pseudomonas spp. in patients with cystic fibrosis with normal renal function†30-50 mg/kg IVto a maximumof 6 grams per day q8h* This product is for use in patients 12 years and older. If treatment with ceftazidime is323indicated for patients less than 12 years old, a sodium carbonate formulation should324be used.325†Although clinical improvement has been shown, bacteriologic cures cannot be326expected in patients with chronic respiratory disease and cystic fibrosis.327328Impaired Hepatic Function: No adjustment in dosage is required for patients with hepatic 329dysfunction.330Impaired Renal Function: Ceftazidime is excreted by the kidneys, almost exclusively by 331glomerular filtration. Therefore, in patients with impaired renal function (glomerular filtration 332rate [GFR]<50 mL/min), it is recommended that the dosage of ceftazidime be reduced to333compensate for its slower excretion. In patients with suspected renal insufficiency, an initial334loading dose of 1 gram of CEPTAZ may be given. An estimate of GFR should be made to335determine the appropriate maintenance dosage. The recommended dosage is presented in Table 4. 336。
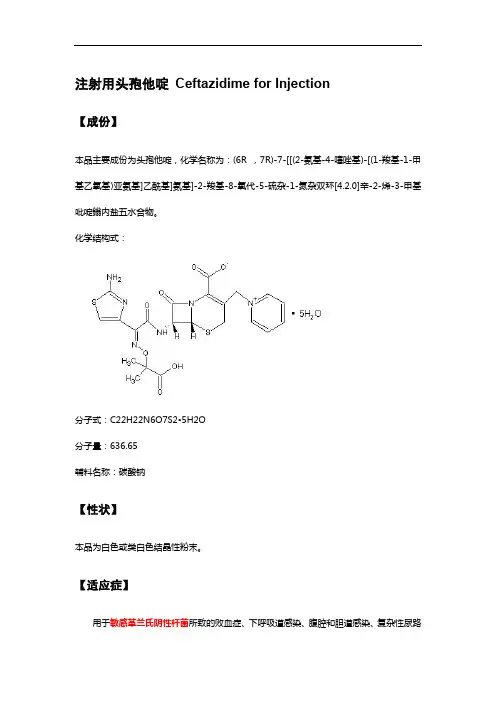
注射用头孢他啶Ceftazidime for Injection【成份】本品主要成份为头孢他啶,化学名称为:(6R ,7R)-7-[[(2-氨基-4-噻唑基)-[(1-羧基-1-甲基乙氧基)亚氨基]乙酰基]氨基]-2-羧基-8-氧代-5-硫杂-1-氮杂双环[4.2.0]辛-2-烯-3-甲基吡啶鎓内盐五水合物。
化学结构式:分子式:C22H22N6O7S2•5H2O分子量:636.65辅料名称:碳酸钠【性状】本品为白色或类白色结晶性粉末。
【适应症】用于敏感革兰氏阴性杆菌所致的败血症、下呼吸道感染、腹腔和胆道感染、复杂性尿路感染和严重皮肤软组织感染等。
对于由多种耐药革兰氏阴性杆菌引起的免疫缺陷者感染、医院内感染以及革兰氏阴性杆菌或铜绿假单胞菌所致中枢神经系统感染尤为适用。
【规格】按C22H22N6O7S2计算1.0g【用法用量】静脉注射或静脉滴注。
1.败血症、下呼吸道感染、胆道感染等,一日4~6g,分2~3次静脉滴注或静脉注射,疗程10~14日。
2.泌尿系统感染和重度皮肤软组织感染等,一日2~4g,分2次静脉滴注或静脉注射,疗程7~14日。
3.对于某些危及生命的感染、严重铜绿假单胞菌感染和中枢神经系统感染,可酌情增量至一日0.15~0.2g/kg,分3次静脉滴注或静脉注射。
4.婴幼儿常用剂量为一日30~100mg/kg,分2~3次静脉滴注。
【不良反应】本品的不良反应少见而轻微。
少数患者可发生皮疹、皮肤瘙痒、药物热;恶心、腹泻、腹痛;注射部位轻度静脉炎;偶可发生一过性血清氨基转移酶酶、血尿素氮、血肌酐值的轻度升高;白细胞、血小板减少及嗜酸性粒细胞增多等。
【禁忌】对头孢菌素类抗生素过敏者禁用。
【注意事项】1.交叉过敏反应:对一种头孢菌素或头霉素(cephamycin)过敏者对其他头孢菌素或头霉素也可能过敏。
对青霉素类、青霉素衍生物或青霉胺过敏者也可能对头孢菌素或头霉素过敏。
对青霉素过敏病人应用头孢菌素时发生过敏反应者达5%~10%;如作过敏试验,则对青霉素过敏病人对头孢菌素过敏者达20%。

临床头孢他啶药物常规用药、剂量调整、给药说明、贮藏、药物警戒、不良反应、禁忌症、注意事项、药物监控及药物过量常规用药头孢他啶是用于肠胃外给药的半合成、广谱、β-内酰胺类抗菌药物。
可用于敏感微生物引起的单一或多重感染。
成人常用剂量头孢他啶可用于治疗由敏感微生物引起的单一或多重感染,具体如下:◆全身性重度感染:由假单胞菌属(包括铜绿假单胞菌)、流感嗜血杆菌(包括氨苄西林耐药菌株)、克雷伯菌属(包括克雷伯菌)、肠杆菌属、变形杆菌属、大肠埃希菌、沙雷氏菌属、枸橼酸杆菌属、肺炎链球菌和金黄色葡萄球菌(甲氧西林敏感菌株)引起的全身性重度感染,例如:败血症、菌血症、腹膜炎、免疫抑制患者的感染和重症监护患者的感染(如烧伤感染)。
◆下呼吸道感染(包括肺炎):由假单胞菌属(包括铜绿假单胞菌)、流感嗜血杆菌(包括氨苄西林耐药菌株)、克雷伯菌属(包括肺炎克雷伯菌)、肠杆菌属、奇异变形杆菌、大肠埃希菌、沙雷氏菌属、枸橼酸杆菌属、肺炎链球菌和金黄色葡萄球菌(甲氧西林敏感菌株)引起。
◆耳鼻喉感染:由假单胞菌属(包括铜绿假单胞菌)、流感嗜血杆菌(包括氨苄西林耐药菌株)、肺炎链球菌、金黄色葡萄球菌(甲氧西林敏感菌株)和酿脓链球菌(A 族β溶血性链球菌)引起。
◆尿路感染:由假单胞菌属(包括铜绿假单胞菌)、肠杆菌属、变形杆菌属(包括奇异变形杆菌和吲哚阳性变形杆菌)、克雷伯菌属和大肠埃希菌引起。
◆皮肤和软组织感染:由铜绿假单胞菌、克雷伯菌属、大肠埃希菌、变形杆菌属(包括奇异变形杆菌和吲哚阳性变形杆菌)、肠杆菌属、沙雷氏菌属、金黄色葡萄球菌(甲氧西林敏感菌株)和酿脓链球菌(A 族β溶血性链球菌)引起。
◆骨和关节感染:由铜绿假单胞菌、克雷伯菌属、肠杆菌属和金黄色葡萄球菌(甲氧西林敏感菌株)引起。
◆妇科感染:包括子宫内膜炎、盆腔蜂窝组织炎和其他由大肠埃希菌引起的女性生殖道感染。
◆胃肠道、胆道和腹部感染:包括由大肠埃希菌、克雷伯菌属和金黄色葡萄球菌(甲氧西林敏感菌株)引起的腹膜炎,以及由需氧和厌氧微生物以及拟杆菌(注意:许多脆弱拟杆菌菌株具有耐药性)引起的多种微生物感染。
头孢他啶注射说明书关于《头孢他啶注射说明书》,是我们特意为大家整理的,希望对大家有所帮助。
在应用药物时,我们除开要遵医嘱以外,还需要细心去看一下药物的使用说明。
头孢他啶注射使用说明上表明该药品能够用以医治支气管炎、肺炎、膀胱炎等感染,禁忌是一些针对头孢克肟及青霉素类药物过敏的病人,有关头孢他啶注射使用说明内的别的相关内容,详细下面。
生产作用主冶疫苗可用以医治单纯性的感染或由二种以上敏感菌造成的混和感染。
临床医学上关键用以败血症、菌血症、支气管炎、肺炎、胸膜炎、腹膜炎、肾盂肾炎、尿道感染、前列腺炎、膀胱炎、耳鼻咽喉感染、皮肤和软组织感染、骨和骨节感染、盆腔炎及烧伤等。
生产成分疫苗为半生成的第三代头孢菌素。
产品为分散酸(五水化合物),并加上一定量的无水碳酸钠,做成注射剂供用。
生产药用价值疫苗本产品为第三代头孢菌素抗生素,抑菌魅力较强,抗菌谱范围广,对革兰呈阳性或阴性菌均具备较强功效。
对革兰阳性菌、阴性菌造成的β内酰胺酶具备高宽比的可靠性,本产品对绿脓杆菌、大肠杆菌、克雷白链球菌、变形杆菌、肠球菌、沙门氏菌、志贺菌、淋病奈瑟菌、脑膜炎奈瑟菌、金葡菌、溶血性链球菌感染、肺炎链球菌及产气杆菌等具备强的抑菌特异性。
生产药品相互影响疫苗1 本产品与以下药品有配伍禁忌,不能同瓶滴注:盐酸阿米卡星、盐酸卡那霉素、盐酸金霉素、盐酸土霉素、盐酸四环素、葡萄糖酸红霉素、盐酸多粘菌素B。
生产副作用疫苗本产品的副作用罕见而轻度。
极少数病人可产生皮疹、皮肤瘙痒、药物热;恶心想吐、腹泻、腹痛;注射位置轻微静脉炎;偶可产生一过性血细胞氨谷丙转氨酶酶、血尿素氮、血肌酐值的轻微上升;白细胞计数、血小板低及嗜酸性粒细胞增加等。
生产禁忌疫苗对头孢菌素抗生素有皮肤过敏的患者禁止使用。
头胞他唳-阿维巴坦药品说明书赵锦锦编译,张菁•校审(复旦大学附属华山医院抗生素研究所,上海200040)摘要:头抱他喘-阿维巴坦注射剂由森林实验室(Forest Lab)和阿斯利康制药公司联合开发,现艾尔健和阿斯利康公司分别在北美和世界其它地区拥有其商业化的权利,商品名为AVYCA 乙已于2015年2月25日被FDA 快速批准。
该复方制剂由一种头 抱菌素(头抱他喘)和一种卜内酰胺酶抑制剂(阿维巴坦)组成,用于治疗18岁及以上复杂性腹腔内感染、复杂性尿路感染以及医院 获得性细菌性肺炎和呼吸机相关细菌性肺炎,抗菌谱为耐药形势严峻的革兰阴性菌。
我们对其说明书进行翻译,包括适应证、用法用量、不良反应、临床药理学、微生物学和临床研究等,以供大家阅读和参考。
关键词:头抱他喘;阿维巴坦;适应证;微生物学;临床研究中图分类号:R978.1-1 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1001-8751(2019)02-0115-131前言2015年2月25日被食品药品监督管理局(FDA)批 准的新药头抱他噪-阿维巴坦注射剂,由半合成头抱菌素头抱他噪五水合物和卜内酰胺酶抑制剂阿维巴坦钠组成,用于治疗革兰阴性菌感染,尤其是耐药 菌引起的严重感染,适应证为18岁及以上患者由敏感革兰阴性菌引起的复杂性腹腔内感染(complicatedintra-abdominal infections, cIAI)(联合甲硝呼)、复杂 性尿路感染(complicated urinary tract infections, cUTI)(包括肾盂肾炎)和医院获得性细菌性肺炎和呼吸机相关细菌性肺炎(hospital-acquired bacterial pneumoniaand ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia , HABP/VABP)…2药品说明本药通用名为头抱他噪-阿维巴坦(ceftazidime-avibactam),商品名为AVYCAZ 。
核准日期: 年 月 日注射用头孢他啶说明书请仔细阅读说明书并在医师指导下使用【药品名称】通用名称:注射用头孢他啶英文名称:Ceftazidime for Injection汉语拼音:Zhusheyong Toubaotading【成份】本品活性成份为头孢他啶,化学名称:(6R , 7R )-7-[[(2-氨基-4-噻唑基)-[(1-羧基-1-甲基乙氧基)亚氨基]乙酰基]氨基]-2-羧基-8-氧代-5-硫杂-1-氮杂双环[4.2.0]辛-2-烯-3-甲基吡啶鎓内盐五水合物。
化学结构式:分子式:C 22H 22N 6O 7S 2·5H 2O分子量:辅 料:碳酸钠。
【性状】本品为白色或类白色结晶性粉末。
【适应症】用于敏感革兰氏阴性杆菌所致的败血症、下呼吸道感染、腹腔和胆道感染、复杂性尿路感染和严重皮肤软组织感染等。
对于由多种耐药革兰氏阴性杆菌引起的免疫缺陷者感染、医院内感染以及革兰氏阴性杆菌或铜绿假单胞菌所致中枢神经系统感染尤为适用。
【规格】1.0g(按头孢他啶计)【用法用量】静脉注射或静脉滴注。
剂量依感染的严重程度、微生物敏感性及患者机体状态而定。
成人:1. 败血症、下呼吸道感染、胆道感染等,一日4~6g ,分2~3次静脉滴注或静脉注射,疗程10~14日。
2. 泌尿系统感染和重度皮肤软组织感染等,一日2~4g ,分2次静脉滴注或静脉注射,疗程7~14日。
对于轻度尿路感染,每12小时~1g即已足够。
3. 对于某些危及生命的感染、严重铜绿假单胞菌感染和中枢神经系统感染,可酌情增量至一日~0.2g/kg,分3次静脉滴注或静脉注射。
儿童:2个月以上婴幼儿常用剂量为一日30~100mg/kg,分2~3次静脉滴注。
对新生儿至2个月婴儿临床经验有限。
肾功能损害患者:因头孢他啶主要经肾脏排泄,对肾功能损害患者应减量使用。
可根据肌酐清除率来计算合适的给药剂量。
透析后患者应重复适当维持剂量。
配制方法:5ml注射用水加入0.5g装瓶中或10ml注射用水加入1g或2g装瓶中,使完全溶解后,于3~5分钟静脉缓慢推注。
注射用头孢他啶说明书核准日期: 年 月 日注射用头孢她啶说明书请仔细阅读说明书并在医师指导下使用【药品名称】通用名称:注射用头孢她啶英文名称:Ceftazidime for Injection汉语拼音:Zhusheyong Toubaotading【成份】本品活性成份为头孢她啶,化学名称:(6R , 7R )-7-[[(2-氨基-4-噻唑基)-[(1-羧基-1-甲基乙氧基)亚氨基]乙酰基]氨基]-2-羧基-8-氧代-5-硫杂-1-氮杂双环[4.2.0]辛-2-烯-3-甲基吡啶鎓内盐五水合物。
化学结构式:H 3CH 3C OH O,5H 2O S N N +N-NH 2O分子式:C 22H 22N 6O 7S 2·5H 2O分子量:636.65辅 料:碳酸钠。
【性状】本品为白色或类白色结晶性粉末。
【适应症】用于敏感革兰氏阴性杆菌所致的败血症、下呼吸道感染、腹腔和胆道感染、复杂性尿路感染和严重皮肤软组织感染等。
对于由多种耐药革兰氏阴性杆菌引起的免疫缺陷者感染、医院内感染以及革兰氏阴性杆菌或铜绿假单胞菌所致中枢神经系统感染尤为适用。
【规格】1.0g(按头孢她啶计)【用法用量】静脉注射或静脉滴注。
剂量依感染的严重程度、微生物敏感性及患者机体状态而定。
成人:1. 败血症、下呼吸道感染、胆道感染等,一日4~6g,分2~3次静脉滴注或静脉注射,疗程10~14日。
2. 泌尿系统感染和重度皮肤软组织感染等,一日2~4g,分2次静脉滴注或静脉注射,疗程7~14日。
对于轻度尿路感染,每12小时0.5~1g即已足够。
3. 对于某些危及生命的感染、严重铜绿假单胞菌感染和中枢神经系统感染,可酌情增量至一日0.15~0.2g/kg,分3次静脉滴注或静脉注射。
儿童:2个月以上婴幼儿常见剂量为一日30~100mg/kg,分2~3次静脉滴注。
对新生儿至2个月婴儿临床经验有限。
肾功能损害患者:因头孢她啶主要经肾脏排泄,对肾功能损害患者应减量使用。
核准日期:2006年12月29日修改日期:2011年9月5日2013年9月7日2014年10月18日注射用头孢他啶使用说明书请仔细阅读说明书并在医师指导下使用。
【药品名称】通用名称:注射用头孢他啶商品名称:复达欣®英文名称:Ceftazidime for Injection汉语拼音:Zhusheyong Toubaotading【成份】化学名称:(6R,7R)-7(〔(2-氨基-4-噻唑基)-〔(1-羧基-1-甲基乙氧基)亚氨基〕乙酰基〕氨基〕-2-羧基-8-氧代-5-硫杂-1-氮杂双环[4.2.0]辛-2-烯-3-甲基吡啶鎓内盐五水合物化学结构式:分子式:C22H22N6O7S2·5 H2O分子量:636.65辅料:无水碳酸钠【性状】白色或类白色结晶性无菌粉末,供配制成注射液。
【适应症】头孢他啶适用于由敏感细菌所引起的单一感染及由二种或二种以上的敏感菌引起的混合感染。
全身性的严重感染;呼吸道感染;耳、鼻和喉感染;尿路感染;皮肤及软组织感染;胃肠、胆及腹部感染;骨骼及关节感染;与血液透析和腹膜透析及持续腹膜透析(CAPD)有关的感染。
对于脑膜炎,仅在得到敏感试验结果后,才能应用单一的头孢他啶治疗。
头孢他啶可用于耐其它抗生素包括氨基糖苷类和多数头孢菌素的感染。
如果合适,可联同氨基糖苷类或其它β-内酰胺类抗生素使用,例如在严重中性粒细胞减少时,或在怀疑是脆弱拟杆菌感染时,与另一种抗厌氧菌抗生素合用。
另外,头孢他啶还可用于经尿道前列腺切除手术的预防治疗。
头孢他啶的敏感性存在差异,应该咨询可适用的地理、时间和当地敏感性数据(见【药理毒理】部分)。
【规格】每瓶含1g头孢他啶(五水合物形式),及118mg碳酸钠。
【用法用量】头孢他啶是肠道外给药,剂量依感染的严重程度、敏感性、感染种类及病人的年龄、体重和肾功能而定。
成人:头孢他啶的成人剂量范围是每天1g至6g,分每8小时或每12小时作静脉注射或肌肉注射给药。
头孢他啶
【用法用量】静脉注射或静脉滴注。
1.败血症、下呼吸道感染、胆道感染等,一日4~6g,分2~3次静脉滴注或静脉注射,疗程10~14日。
2.泌尿系统感染和重度皮肤软组织感染等,一日2~4g,分2次静脉滴注或静脉注射,疗程7~14日。
3.对于某些危及生命的感染、严重铜绿假单胞菌感染和中枢神经系统感染,可酌情增量至一日
0.15~0.2g/kg,分3次静脉滴注或静脉注射。
4.婴幼儿常用剂量为
一日30~100mg/kg,分2~3次静脉滴注。
【注意事项】1.交叉过敏反应:对一种头孢菌素或头霉素(cephamycin)过敏者对其他头孢菌素或头霉素也可能过敏。
对青霉素类﹑青霉素衍生物或青霉胺过敏者也可能对头孢菌素或头霉素过敏。
对青霉素过敏病人应用头孢菌素时发生过敏反应者达5%~10%,如作过敏试验,则对青霉素过敏病人对头孢菌素过敏者达20%。
应用本品发生过敏性休克时,须予以肾上腺素,保持呼吸道通畅,吸氧﹑糖皮质激素及抗组胺等紧急措施。
2.对青霉素过敏病人应用本品时,应根据病人情况充分权衡利弊后决定。
有青霉素过敏性休克或即刻反应者,不宜再选用头孢菌素类。
3.有胃肠道疾病史者,特别是溃疡性结肠炎﹑局限性肠炎或抗生素相关性结肠炎(头孢菌素类很少产生伪膜性结肠炎)者应慎用。
4.肾功能明显减退者应用本品时,需根据肾功能损害程度减量。
5.对重症革兰阳性球菌感染,本品为非首选品种。
6.
在不同存放条件下,本品粉末的颜色可变暗,但不影响其活性。
7.
对诊断的干扰:应用本品的病人直接抗球蛋白(Coombs)试验可出现阳性;本品可使硫酸铜尿糖试验呈假阳性;血清丙氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT)﹑门冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)﹑碱性磷酸酶﹑血尿素氮和血清肌酐皆可升高。
8.以生理盐水﹑5%葡萄糖注射液或乳酸钠稀释成的静脉注射液(20mg/ml)在室温存放不宜超过24小时。
9.长期应用本品可能导致不敏感或耐药菌的过度繁殖,需要严密观察,一旦治程中发生二重感染,需要采取相应措施。
10.本品可诱导肠杆菌属﹑假单胞菌属和沙雷菌属产生I型β内酰胺酶,治疗过程中病原菌可产生耐药性,导致治疗失败。
【不良反应】本品的少见而轻微。
少数患者可发生皮疹﹑皮肤瘙痒﹑药物热,恶心﹑腹泻﹑腹痛,注射部位轻度静脉炎,偶可发生一过性血清氨基转移酶酶﹑血尿素氮﹑血肌酐值的轻度升高,白细胞﹑血小板减少及嗜酸性粒细胞增多等。
【禁忌】对头孢菌素类抗生素过敏者禁用。
【适应症】1.本品用于敏感革兰氏阴性杆菌所致的败血症﹑下呼吸道感染﹑腹腔和胆道感染﹑复杂性尿路感染和严重皮肤软组织感染等。
2.对于由多种耐药革兰氏阴性杆菌引起的免疫缺陷者感染﹑医院内感染以及革兰氏阴性杆菌或铜绿假单胞菌所致感染尤为适用。
【药物相互作用】1.本品与下列药物有配伍禁忌:硫酸阿米卡星﹑庆大霉素﹑卡那霉素﹑妥布霉素﹑新霉素﹑盐酸金霉素﹑盐酸四环素﹑盐酸土霉素﹑粘菌素甲磺酸钠﹑硫酸多粘菌素B﹑葡萄糖酸红
霉素﹑乳糖酸红霉素﹑林可霉素﹑磺胺异?f唑﹑氨茶碱﹑可溶性巴比妥类﹑氯化钙﹑葡萄糖酸钙﹑盐酸苯海拉明和其他抗组胺药﹑利
多卡因﹑去甲肾上腺素﹑间羟胺﹑哌甲酯﹑琥珀胆碱等。
偶亦可能与下列药物发生配伍禁忌:青霉素﹑甲氧西林﹑琥珀酸氢化可的松﹑苯妥英钠﹑丙氯拉嗪﹑维生素B族和维生素C﹑水解蛋白。
2.在碳酸氢钠溶液中的稳定性较在其他溶液中为差。
3.本品不可与氨基糖苷类抗生素在同一容器中给药。
与万古霉素混合可发生沉淀。
4.本品与氨基糖苷类抗生素或速尿等强利尿剂合用时需严密观察肾功能情况,以避免肾损害的发生。
【药理毒理】1.本品为第三代头孢菌素类抗生素。
对大肠埃希菌、肺炎杆菌等肠杆菌科细菌和流感嗜血杆菌、铜绿假单孢菌等有高度抗菌活性。
2.对硝酸盐阴性杆菌、产碱杆菌等亦有良好抗菌作用。
3.
对于细菌产生的大多数β内酰胺酶高度稳定,故其对上述革兰阴性杆菌中多重耐药菌株仍可具抗菌活性。
肺炎球菌、溶血性链球菌等革兰阳性球菌对本品高度敏感,但本品对葡萄球菌仅具中度活性,肠球菌和耐甲氧西林葡萄球菌则往往对本品耐药。
4.本品对消化球菌和消化链球菌等厌氧菌具一定抗菌活性,但对脆弱拟杆菌抗菌作用差。
5.其作用机制为与细菌细胞膜上的青霉素结合蛋白(PBPS)结合,使转肽酶酰化,抑制细菌中隔和细胞壁的合成,影响细胞壁粘肽成分的交叉连结,使细胞分裂和生长受到抑制,细菌形态变长,最后溶解和死亡。
【儿童用药】小儿一日最高剂量不超过6g。
【老人用药】65岁以上老年患者剂量可减至正常剂量的2/3~
1/2,一日最高剂量不超过3g。
【药物过量】未进行该项实验且无可靠参考文献。
【国家/地区】国产
【剂型】原料药
【药代动力学】1.成人单次静脉滴注和静脉注射头孢他啶1g后,血药峰浓度(Cmax)分别可达70~72mg/L和120~146mg/L。
血消除半衰期(t1/2β)约为1.5~2.3小时。
给药后在多种组织和体液中分布良好,也可透过血-脑脊液屏障,脑膜有炎症时,脑脊液内药物浓度可达同期血浓度到17%~30%.血浆蛋白结合率为5%~23%。
2.本品主要自肾小球滤过排出,静脉给药后24小时内以原形自尿中排出给药量的84%~87%,胆汁中排出量少于给药量的1%。
中、重度肾功能损害者本品的消除半衰期延长,当内生肌酐清除率≤2ml/分钟时,消除半衰期可延长至14~30小时。
在新生儿中的半衰期稍延长(平均4~5小时)。
本品可通过血液透析清除。
【成份】本品为头孢他啶。
说明:以上信息仅供参考,具体请以商品说明书为准。