低分子量的达肝素钠和依诺肝素钠在体积排阻色谱柱的分离
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:182.28 KB
- 文档页数:2

肝素类抗凝血药物摘要:肝素类药物是目前使用最广泛一类的抗凝血药物,并具有较好的抗血栓的疗效。
低分子肝素和合成肝素是现在最常用的一类肝素药物[1]。
但肝素类药物会有血小板减少症和出血的副作用。
如何减少副作用的发生是目前肝素类药物研发的一个重要方向。
Abstract:Heparin drugs is currently the most widely used class of anti-clotting drugs, and has good antithrombotic efficacy.Low molecular weight heparin, synthetic heparin is now the most commonly used type of heparin drugs.But heparin drugs has thrombocytopenia and bleeding side effects,How to reduce side effects is an important direction of research and development of the heparin drugs.关键词:肝素;抗凝血;抗血栓;血小板减少症;Keywords: heparin; anticoagulant; antithrombotic; thrombocytopenia;一.肝素的结构肝素是硫酸化的糖胺聚糖,由糖醛酸和葡萄糖胺以1→4 键连接起来的重复二糖单位组成的多糖链的混合物[2]。
含10—30 个二糖单位不等,分子量3000—30000, 平均分子量12000.整个结构变得异常复杂因其与硫酸和羧酸共价结合,故为强酸带有很强负电荷,每个糖单位之间可产生排斥力,使肝素分子链不易卷曲和交叉连接,因此呈线形结构,称为线形阴离子聚电解质体[3]。
[4]只有部分肝素分子(约三分之一)含核心五糖[5]。

肝素钠及低分子肝素钠生产工艺技术一、概况1,肝素钠(Heparin Sodium )系猪的肠黏膜中提取的硫酸氨基葡萄糖的钠盐,属粘多糖类物质,通过激活抗凝血酶Ⅲ(AT-Ⅲ)而发挥抗凝作用。
它对凝血过程的三个阶段均有影响,在体内外均有抗凝作用,可延长凝血时间、凝血酶原时间和凝血酶时间。
口服不吸收,皮下、肌肉或静脉给药均吸收良好。
医学统计显示,目前心脑血管疾病成为人类死亡的首要原因,作为临床应用最广泛和最有效的抗凝血、抗血栓药物之一,肝素类药物需求十分强劲。
而同时,受限于原料资源的有限增长,全球肝素原料药市场供给不能与需求同步增长,尤其是符合美国FDA认证或欧盟CEP认证标准的肝素原料药已呈现供不应求的局面。
少为人知的是,目前我国已是全球最大的肝素原料药出口国,肝素原料药已成为我国西药类产品出口重点品种之一。
不过,虽然生产企业众多,现阶段我国持有SFDA颁发的肝素原料药生产批准文号的企业有24家,而取得美国FDA认证或欧盟CEP认证的肝素原料药生产企业数量更少,其中仅4家同行业公司取得了欧盟CEP认证。
2,低分子肝素钠:低分子肝素(low-molecular-weight heparin,LMWH)是一类以未分级肝素为起始物料经过分级或降解而得到的具有较低分子量的低聚糖混合物。
它具有抗Xa 活性,可抑制体内、体外血栓和动静脉血栓的形成,但不影响血小板聚集和纤维蛋白原与血小板的结合。
EP7.0和BP2010收载了5种不同工艺的LMWH,达肝素钠(Dalteparin sodium)、依诺肝素钠(Enoxaparin sodium)、那曲肝素钙(Nadroparin calcium)、帕肝素钠(Parnaparin sodium)和汀肝素钠(Tinzaparin sodium,又名汀扎肝素)。
3,主要生产商:深圳市海普瑞药业有限公司,上海第一生化药业有限公司,南京健友生物化学制药有限公司,烟台东诚生化有限公司,常州千红生化制药有限公司,东营天东生化工业有限公司等。


22中国处方药 第18卷 第5期·医院药学·心血管疾病已成为危害人类健康和生命的主要疾病,冠心病、脑卒中等重大心血管疾病也带来严重的社会经济负担[1]。
随着人口老龄化、环境问题和不良的生活方式等因素,致使我国心血管病预防和管理形势更加严峻[2-3]。
血小板聚集性过高、血栓形成是诱发此类疾病的重要因素,目前临床常见的防治血栓的药物主要分为3类:抗血小板药物、抗凝药物和溶栓药物。
通过统计分析我院2017年~2019年抗血栓药物的使用情况,并结合相关指南对其临床使用进行评价,以期为临床合理用药提供参考。
1 资料与方法1.1 一般资料我院2017年~2019年(2019年包括1月~9月的数据)抗血栓药物的使用记录,包括抗血栓药物的种类、使用数量和销售金额等。
1.2 分析方法限定日剂量(DDD)主要来自www.whocc.no网站的数据,网站未公布的则根据《新编药物学》(第18版),《中华人民共和国药典》临床用药须知(2015年版)和药品说明书推荐的成人平均日剂量而定。
①DDDs=某药品年消耗量/该药品DDD值,它是药品管理和统计分析的重要参考数据,其大小可反映药品应用频率的高低。
②限定日费用(DDC)=该药品年度总销售金额/该药的DDDs,是药物价格的体现,克服了药品日剂量不同的缺点,使药品价格具有可比性。
③排序比值(RM)=某药品年总销售金额排序/DDDs排序,RM的大小表明药品的价位。
2结果2.1 抗血栓药物大类销售金额分析从表1结果可知:抗血小板药的销售量占总额的比例呈逐年下降趋势,但是构成比仍然占50%以上;抗凝药物的构成比逐年上升,并且年销售金额每年大约100万元趋势增长;溶栓药每年销售金额及构成比变化不大。
从三年总的销售情况看出,抗血栓药物的销售以抗血小板药为主,但是抗凝药物的销售比例每年上升,说明抗凝药物的应用越来越广泛。
各年度平均每个月的销售金额呈递增趋势,说明抗血栓药物的使用量不断增加。

体积排阻色谱法测定低分子量肝素抗凝血因子Xa的活性张倩倩;康经武【摘要】发展了一种基于体积排阻色谱测定低分子量肝素(LMWH)抗凝血活性的方法.利用肝素与抗凝血酶Ⅲ(ATⅢ)结合后可增强ATⅢ对凝血因子Xa (FXa)抑制作用的原理,通过测定加入LMWH后FXa水解其生色底物产生对硝基苯胺(pNA)这一反应的抑制程度确定LMWH的活性.首先将含有一定浓度LMWH的缓冲溶液与ATⅢ溶液混合,然后依次加入FXa和生色底物,分别孵育一段时间.底物被FXa水解,产生游离的pNA.体积排阻色谱可将小分子产物pNA与其他大分子分离开,因而可以在pNA的最大吸收波长下得到高灵敏度的测定,并且不再受其他成分的干扰.该方法重复性好,灵敏度高,极大地减少了样品的消耗量,降低了成本,并且还可进行各种复杂样品(如血浆)中LMWH抗FXa活性的监测.%The "gold standard" assay for monitoring low molecular weight heparins (LMWHs) activity is the chromogenic-based anti-factor Xa assay.The methodology of an anti-factor Xa assay is that LMWH is added to a known amount of excess factor Xa and excess antithrombin.It will bind to antithrombin and form a triplet complex with factor Xa,inhibiting the activity of factor Xa.However,the residual factor Xa can still hydrolyze chromogenic peptidesubstrate,releasing the chromophore for photometric detection.The absorbance is inversely proportional to the amount of heparin/LMWH.The results are given in anticoagulant concentration in units/ mL of anti-factor Xa,such that high values indicate high levels of anticoagulation and low values indicate low levels of anticoagulation.Herein,a novel assay method for anti-FXa activity of LMWHs using high performance liquid sizeexclusion chromatography (SEC) is reported,in which antithrombin m (AT m) was diluted by the buffer solution containedLMWHs.Subsequently,exogenous FXa and p-nitroaniline coupled peptide substrate were added and incubated for a period,separately.The resulting mixture was separated based on size by SEC,and the free chromophore p-nitroaniline can be detected at an absorption maximum of 385 nm without interference from the absorbance of p-nitroanilidesubstrates.Moreover,the measurements are not influenced by sample opacity or turbidity,so it is possible to test various complex samples,such as plasma.The assay is robust,sensitive,and cost effective.【期刊名称】《色谱》【年(卷),期】2013(031)007【总页数】7页(P684-690)【关键词】体积排阻色谱;抗凝血因子Xa;低分子量肝素【作者】张倩倩;康经武【作者单位】中国科学院上海有机化学研究所,上海200032;中国科学院上海有机化学研究所,上海200032【正文语种】中文【中图分类】O658低分子量肝素(LMWHs)是一类抗凝血药物,广泛用于血栓栓塞性疾病的预防及治疗[1]。


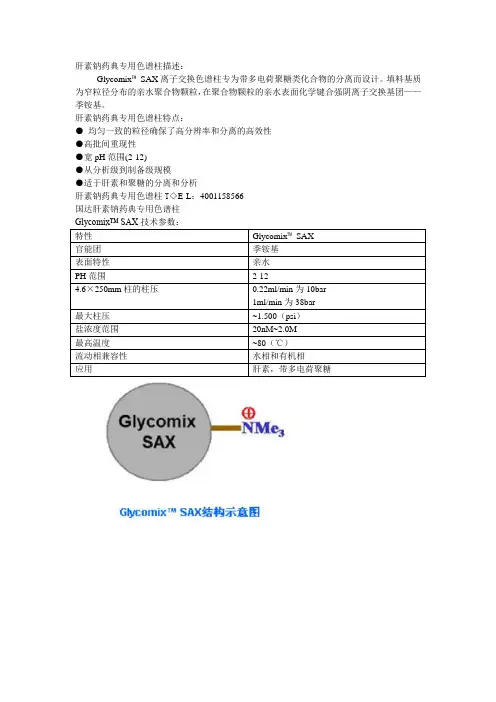
AuthorsXiaomi XuYuna LiAiyan CuiHaiying ChenSepax Technologies, Inc.5 Innovation Way Newark, DE 19711 USA High Resolution Analysis of Heparin and Heparin-like Impurities on Glycomix TM–an Anion Exchange ColumnGlycan SeparationAbstractAnalysis of heparin is challenging due to its heterogeneity, both in its size distribution and charge variance. Moreover, its impurities usually have properties that resemble heparin which makes it difficult to distinguish heparin and its impurities using analytical methods. To effectively separate heparin from its impurities, including naturally occurring impurities during manufacturing process (e.g., dermatan sulfate DS) and non-native contaminant from adulteration (e.g., oversulfated chondroitin sulfate OSCS), U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP) published a chromatographic method to identify heparin and heparin-like impurities using ion-exchange liquid chromatography. However, current commercially available ion-exchange column barely meets USP separation resolution criteria; the situation calls for a new stationary phase which can improve the resolution. Sepax has recently developed an ion-exchange column – Glycomix TM SAX. It grafts charged and a certain level of hydrophilic functional groups to polymer-based resin. Here we present the high efficiency separation of highly chargedglycans.IntroductionHeparin has been widely used as ananticoagulant or anti-thrombotic agent. It is a complex mixture of sulfated glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), which are highly negatively charged. During its extraction process from mammalian tissue (such as pig intestine), other polyanionic GAGs can co-purify with heparin since they share heparin-like properties [1]. Onerepresentative example of such impurities is dermatan sulfate (chondroitin sulfate B). Oversulfated chondroitin sulfate (OSCS) was identified as a non-native contaminant, which can induce severe side effects even death. The most recent heparin sodium monographpublished by U.S. Pharmacopeia [2] details the analytical method that heparin manufacturers must follow to ensure the quality of their heparin products. This application note reports the separation of heparin, DS and OSCS using Glycomix TM SAX with USP recommended method. The performance of Glycomix SAX is also discussed in comparison to competitor D’s column separation efficiency.ExperimentalHPLC systemAgilent 1200 HPLC with binary pumpIon-exchange columnsGlycomix TM -SAX (4.6 x 250 mm, P/N 901665-4625)Glycomix TM -SAX guard column (4.6 x 50 mm, P/N 901665-4605)Chemicals and ReagentsHeparin sodium salt and Dermatan sulfate (DS or chondroitin sulfate B) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Oversulfated chondroitin sulfate (part no. 1133580) was purchased from U.S. Pharmacopeia. Monobasic sodium phosphate and sodium perchlorate were purchased from EMD. All solutions were made with Milli-Q water.LC MethodMobile phase:A: 0.04% NaH 2PO 4, pH3.0;B: 0.04% NaH 2PO 4+ 14% NaClO 4, pH3.0Gradient: 20% B to 90% B in 60 minFlow rate: 0.22 mL/min Column temperature: 25 °C Detection: UV 202 nm Injection volume: 10 μL Pressure: 10 barResultsFollowing the conditions listed on USP heparin sodium monograph, Figure. 1 demonstrates the separation of heparin from its impurities, dermatan sulfate (DS) and oversulfatedchondroitin sulfate (OSCS). The three peaks, according to elution order, are identified as DS, heparin sodium salt and OSCS, the concentration of which are 0.2 mg/mL, 20 mg/mL and 0.2 mg/mL, respectively. The resolutions are 3.8 between DS and heparin and 5.8 between heparin and OSCS; both are well beyond the USP resolution requirements, which are 1.0 and 1.5, respectively. Glycomix TM column shows the separation resolution much higher than that of Competitor D column, which is 1.1 and 1.8[3]. It was also stated in competitor D’s literature [3] that dermatan sulfate may be unresolved from heparin at >20 mg/mL concentrations as the heparin peak starts eluting from the column within 2 min after the dermatan peak. Heparin loading is not a concern on Glycomix TM column.The high resolution between heparin and dermatan sulfate also enables identification of any unknown impurities that elutes between heparin and dermatan sulfate. As shown in Figure. 2, there is an impurity peak eluted after dermatan sulfate, which is marked by an arrow on the graph. Comparing it with each single standard, it is found that this unknown impurity peak, which may be chondroitin sulfate, is also present on heparin sodium salt (Sigma-Aldrich) sample. Figure 3 is another example of a real heparin injection product analysis, which shows the presence of OSCS.Glycomix ™ can be used i n the quantitative analysis of heparin and its impurities. Figure 4 shows the calibration curve with differentheparin and impurity loadings over concentration range from 0.5 mg/ml to 10 mg/ml for heparin and from 0.25 mg/ml to 4 mg/ml for OSCS. The R 2 values exceed 0.99 for both analytes (R 2heparin =0.9997; R 2OSCS =0.9972).Figure 1. Elution profile of standard solution, containing 0.2 mg/mL dermatan sulfate (DS), 20 mg/mL heparin sodium and 0.2 mg/mL oversulfated chondroitin sulfate (OSCS).Figure 2. Comparison of standard solution (1 mg/mL DS, 20 mg/mL heparin and 1 mg/mL OSCS) and one heparin injection product provided by an undisclosed drug company.Figure 3. Comparison of standard solution (0.2 mg/mL DS, 20 mg/mL heparin and 0.2 mg/mL OSCS) and another heparin injection product provided by an undisclosed drug company, a different source than that on Figure 2.Figure 4. Heparin calibration curve over the concentration range from 0.5 mg/ml to 10 mg/ml, OSCS from 0.25 mg/ml to 4 mg/ml.ConclusionIt has been demonstrated that with careful control of surface chemistry, high resolution separation of heparin and its impurities is successfully achieved on Sepax Glycomix TM column. Glycomix TM column is well suitable for quality control for heparin products, as well as quantitative analysis due to its high sensitivity.Reference1.Advances in the separation, sensitive detection, and characterization of heparin and heparinsulfate. Anal Bioanal Chem (2009) 393: 155-1692.Heparin Sodium, Pharmacopeia Forum2009, 35 (5), 1-4.3.Determination of oversulfated chondroitin sulfate and dermatan sulfate in heparin sodium usinganion-exchange chromatography with UV detection. Dionex Application Note 235. Ordering InformationFor more information on Glycomix TM products, please visit Sepax website: or contact us at 1-877-SEPAX-US。

肝素钠的提取技术一、肝素钠的提取技术介绍肝素钠是一种重要的生物活性物质,具有多种生物学功能,广泛应用于临床治疗血栓形成等病症。
肝素钠是有机硫醇化合物,也是一种嘌呤核苷酸衍生物,它主要来源于动物肝脏和胰腺。
肝素钠是一种重要的生物活性物质,具有抗凝血、抗血栓形成、促进细胞增殖、抑制血小板聚集等作用。
因此,肝素钠在临床上应用广泛,但传统的肝素钠提取技术低效且易受污染,因此,对其进行提取技术改进是十分必要的。
二、肝素钠的提取技术 1. 微生物提取技术:微生物提取技术是一种比较新的肝素钠提取方法,它通过利用发酵的微生物产生大量的肝素钠,从而获取肝素钠。
该技术将原料(如糖、果胶等)进行发酵,使用特定微生物(如酵母)产生肝素钠,再通过精制工艺进行提取和纯化,最终获得肝素钠。
该技术不仅可以获得高纯度的肝素钠,而且可以有效提高肝素钠的提取率,改善提取效率。
2. 水解酶技术:水解酶技术是一种常用的肝素钠提取技术,它通过利用特定的水解酶将原料中的肝素钠转化为水溶性的肝素钠,然后利用溶剂萃取或离子交换技术进行提取和纯化,最终获得肝素钠。
这种技术可以有效提高提取效率,改善肝素钠的质量,而且可以有效避免有机溶剂的污染。
3. 气相色谱技术:气相色谱技术是一种常用的肝素钠提取技术,它可以有效地将原料中的肝素钠分离出来,从而获取高纯度的肝素钠。
该技术将原料中的混合物通过气相色谱仪进行分离,然后根据肝素钠的特定物理性质进行提取和纯化,最终获得高纯度的肝素钠。
该技术可以有效地提高提取率,改善肝素钠的质量。
三、肝素钠的提取技术的优势 1. 提取率高:肝素钠的提取技术可以有效提高肝素钠的提取率,从而获取更高纯度的肝素钠。
2. 质量好:肝素钠提取技术可以有效改善肝素钠的质量,使其成为一种可靠的医疗产品,从而在临床上起到更好的作用。
3. 无污染:肝素钠提取技术可以避免有机溶剂的污染,从而保证肝素钠的质量,使其在临床上更安全有效。
四、总结肝素钠是一种重要的生物活性物质,具有抗凝血、抗血栓形成、促进细胞增殖、抑制血小板聚集等作用,在临床上应用广泛。

抗凝药物的种类及合理使用抗凝药物的分类及合理使用肝素是一种多功能的酸性黏多糖,可用于抗凝治疗。
临床上,肝素分为三类:第一代普通肝素,第二代低分子肝素和第三代合成的肝素戊糖。
肝素类抗凝药物的抗凝作用机制包括激活抗凝血酶Ⅲ(AT-Ⅲ)和激活肝素辅因子Ⅱ。
其中,肝素类药物能与AT-Ⅲ结合,催化灭活多种凝血因子。
肝素和AT结合后可以脱落参与再利用。
肝素-AT复合物能够灭活多种凝血因子,其中IIa和Ⅹa最易受抑制,但机制有所不同。
灭活凝血因子Ⅱa需要形成三联复合物,肝素分子链必须有足够的长度,至少要达到18个糖单位,相对分子质量要大于5400;而灭活凝血因子Ⅹa,则只需和AT结合,不需要形成三联复合物,对肝素相对分子质量大小没有要求。
因此,在使用肝素类抗凝药物时,应根据患者的具体情况和需要选择合适的药物,以达到最佳的抗凝效果。
肝素可以通过激活肝素辅因子Ⅱ来直接灭活凝血因子Ⅱa,这种作用是电荷依赖的,不需要戊糖结构,但需要较高的肝素浓度。
肝素辅因子Ⅱ介导的凝血因子Ⅱa灭活是相对分子质量依赖的,需要至少24个糖单位(相对分子质量7200以上)。
在严重AT缺乏时,肝素的这种机制可起作用。
TFPI是体内主要的生理抗凝物质,肝素能够促进与内皮结合的TFPI的释放。
TFPI与凝血因子Ⅹa结合并灭活Ⅹa,形成TFPI/凝血因子Ⅹa复合物,灭活与组织因子结合的凝血因子Ⅶa。
肝素通过这种途径可以抑制内皮损伤和粥样斑块破裂所导致的血栓形成。
肝素还可以与血小板结合,抑制血小板表面凝血酶的形成,抑制血小板聚集与释放,并且与血小板4因子(PF4)结合后可以抑制PF4依赖性血小板功能,引起出血。
此外,肝素还可以增加血管壁的通透性,抑制血管平滑肌细胞的增生,抑制成骨细胞的合成,激活破骨细胞促进骨质丢失。
此外,肝素还具有抗炎、调节细胞增殖作用、免疫调节、调节多肽生长因子、抗肿瘤转移等多种生物学活性和药理作用。
普通肝素是一种分子量不均一的混合物,相对分子质量范围3000-不等,绝大部分在5400以上,既可以灭活凝血因子Ⅹa又可以灭活凝血因子Ⅱa,抑制凝血因子Ⅹa和凝血因子Ⅱa的作用相似,且可抑制血小板聚集,与血小板4因子以及骨细胞结合力较强,易引起出血及骨钙流失。

达肝素钠分子量及分子量分布的测定与计算方法改进宋志新;丁建文;管惠娟;张超;王武萍【期刊名称】《食品与药品》【年(卷),期】2014(016)003【摘要】目的建立用高效分子排阻法测定达肝素钠分子量与分子量分布的方法,并与欧洲药典(EP) 7.0版低分子肝素专论中的方法比较.方法采用高效分子排阻法,示差检测器,色谱柱TSK G3000SWXL(300 mm×7.8 mm,5μm)和TSKG2000SWXL(300 mm×7.8 mm,5μm)串联,柱温30℃,流动相0.1 mol/L乙酸铵溶液,流速0.5 mL/min.结果方法专属性强,重复性试验中重均分子量(Mw)的RSD为0.6%,M<3000级分比例的RSD为2.1%,M3000~8000级分比例的RSD为0.9%,样品测定结果与EP7.0方法测定结果接近.结论本方法操作简便,重复性好,结果准确可靠,可用于测定达肝素钠分子量与分子量分布.【总页数】3页(P171-173)【作者】宋志新;丁建文;管惠娟;张超;王武萍【作者单位】常山生化药业(江苏)有限公司,江苏常州213149;常山生化药业(江苏)有限公司,江苏常州213149;常山生化药业(江苏)有限公司,江苏常州213149;常山生化药业(江苏)有限公司,江苏常州213149;常山生化药业(江苏)有限公司,江苏常州213149【正文语种】中文【中图分类】R917【相关文献】1.高效GPC测定聚甲基丙烯酸羟丙酯分子量和分子量分布测定的研究 [J], 陈昭国2.海藻多糖分子量及其分布测定Ⅱ——GPC/LALLS联机测定四种海藻多糖分子量分布 [J], 范慧红;管华诗;周如真3.依诺肝素钠注射液分子量与分子量分布比较研究 [J], 由鹏飞;薛维丽;杭宝健;李春焕;王玉团;陈晓;咸瑞卿4.依诺肝素钠注射液分子量与分子量分布比较研究 [J], 由鹏飞;薛维丽;杭宝健;李春焕;王玉团;陈晓;咸瑞卿5.水生腐殖酸分子量分布研究——Ⅰ.串联凝胶色谱法测定水生腐殖酸分子量分布[J], 陶澍;武会先;张宗敏因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。
“依诺肝素钠”vs“那屈肝素钙”“达肝素钠”大有不同低分子量肝素(Low-molecular-weight Heparin,LMWH)作为一个品类已经有30多年的使用历史,市场上有大约9种低分子量肝素:•阿地肝素•贝米肝素•舍脱肝素•达肝素•依诺肝素•那屈肝素•帕肝素•瑞肝素•亭扎肝素我国普遍应用的是“依诺肝素钠”“那屈肝素钙”“达肝素钠”;由于技术水平所限,2010年前所申报仿制的低分子量肝素并未进行分级管理。
在2015年~2016年面临技术水平提升的问题。
在这个大环境下,符合原研技术水平的新标准低分子量肝素将替换覆盖整个市场,预计2016年整体市场将超过50亿元。
依诺肝素钠将占据主导地位。
为何“依诺肝素钠”会一枝独秀占领大量市场?我们从以下几个方面来解析一下:生产工艺不同,带来疗效与杂质含量的差异依诺肝素钠的生产由于采用比较先进的苄醇裂解的方式,通过“β -消除降解法”将UFH(普通肝素)长链的多糖分子裂解成为短链的依诺肝素钠。
由于工艺的独特性:1.不会引入N-NO残留,对于产品的品质控制具有很大的优势2.患者使用的安全性更有保障。
3.生产成本较高,生产效率较低,价格稍高于其他产品。
药物分子结构差异,决定药品临床疗效大有不同同等国际单位剂量注射情况下,依诺肝素的抗血栓能力更强。
皮下注射血药浓度达到峰值时间最短,更快起效。
药物代谢的动力学数据,依诺肝素较其他低分子肝素更优*抗FXa/IIa 表现低分子肝素药物的抗血栓能力及出血风险的情况。
*iv 静脉注射,sc皮下注射•依诺肝素钠抗栓能力更强,具有更低的出血风险。
•半衰期更长,更适合作为血透时作为体外循环的抗凝剂;皮下注射每天1~2次给药即可满足临床使用的要求。
适应症,依诺肝素临床应用适应症范围更广:可用于内科预防DVT依诺肝素钠可用于预防非手术原因造成的DVT(深部静脉血栓形成)的预防,适用范围更宽。
质量标准,依诺肝素是唯一同时被列入:英国、美国和欧洲药典的低分子量肝素•美国药典: Enoxaparin Sodium Injection(USP38)•英国药典:Enoxaparin Sodium Injection (BP2015)•欧洲药典:依诺肝素钠(欧洲药典 8.0)………………越人医药………………· 致力于成为医药人身边的行业资讯推送专家· 及时传达药品政策信息· 专业传播实操营销智慧· 专注传颂前沿管理思想订阅账号。
临床依诺肝素、那屈肝素及达肝素药物区别低分子量肝素目前在抗凝治疗中使用非常广泛,临床常用低分子量肝素钠和低分子量肝素钙。
可使用低分子量肝素钠包括达肝素钠、依诺肝素钠和低分子肝素钠,低分子量肝素钙包括那屈肝素钙和低分子肝素钙。
低分子量肝素与普通肝素区别低分子量肝素是一种新型抗凝药,由普通肝素酶解或化学降解而得。
与普通肝素相比,低分子量肝素的抗凝血因子IIa 活性减弱,而抗凝血因子Xa 活性增强,且抗Xa/抗IIa 活性比值增加至(2~4): 1(普通肝素为1 : 1),使其具有更强的抗血栓形成作用,且具有半衰期长、副反应少,生物利用度高及不需要常规监测凝血功能等优点。
具体如下:不同低分子量肝素之间区别目前低分子量肝素有两类制剂,一类是分子量范围较宽的低分子量肝素钠和低分子量肝素钙,另一类是分子量较明确的制剂,如依诺肝素钠、那屈肝素钙和达肝素钠等。
不同低分子量肝素药动学特点低分子肝素平均分子量减少时,抗因子Xa/抗因子IIa 的比值增加,引起出血的风险可能会降低。
因此,由于依诺肝素钠抗Xa/IIa 比值较那屈肝素钙和达肝素钠大,其安全性较后二者更好,出血风险更小。
依诺肝素钠主要经肝脏代谢,因此在肾小球滤过率eGFR < 30 mL/(min·1.73 m2)的肾功能不全者中 [2],虽然大多数低分子量肝素禁用,但仍可通过调整剂量来选择使用依诺肝素,使用剂量为1 mg/kg、皮下注射,使用频率可以从12 小时1 次调整为24 小时1 次,但使用期间建议监测抗Xa 因子活性。
依诺肝素钠、那屈肝素钙和达肝素钠临床应用1、依诺肝素钠剂型:注射液0.4 mL : 4000AXaIU;0.6 mL : 6000AXaIU在特殊人群中使用时需注意:(1)肾损伤时:轻中度肾功能不全时,应严密监测不良反应;严重肾功能不全时,推荐预防剂量为2000 U/次、1 次/日,治疗剂量为100 U/(kg·次),1 次/日。
色谱技术在肝素结构分析中的研究进展欧阳艺兰;易琳;邱露允;张真庆【期刊名称】《色谱》【年(卷),期】2023(41)2【摘要】肝素(heparin,Hp)是目前临床应用最为广泛的抗凝剂,是由重复二糖单元组成的多硫酸化酸性直链多糖。
低分子量肝素(LMWHs)是以肝素为原料,经过化学或酶降解获得的相对分子质量相对较小的肝素衍生物,相对肝素,它们的出血副作用和免疫原性更小,皮下注射时生物利用度更高。
肝素及低分子量肝素具有一系列结构特点,如相对分子质量偏大且有一定分布,多种糖残基同时存在,硫酸酯位置和数量呈现多样化,以及不同工艺产生的特殊残基的种类和含量不一等。
该类药物结构的复杂性对分析方法提出了巨大的挑战,也限制了其质量控制提升、工艺优化、临床用药安全和新适应证拓展等。
该文以色谱分析方法为中心,从结构分析的不同角度,包括单糖、二糖、寡糖、多糖的识别、组成分析和不同层次,系统地梳理和阐述近年来肝素类药物在色谱分析方法上的进展,并对这些方法的应用范畴、创新性、局限性等进行总结。
该文将为肝素类药物的结构分析、质量控制提供较系统的方法学参考,为更多新方法开发提供思路,为更深入地研究肝素类药物结构、拓展其应用提供有力支撑。
【总页数】15页(P107-121)【作者】欧阳艺兰;易琳;邱露允;张真庆【作者单位】苏州大学医学院药学院【正文语种】中文【中图分类】O658【相关文献】1.气相色谱电子捕获技术分析检测葡萄酒及软木塞中TCA的研究进展2.胶束电动色谱技术在蛋白质分离分析中的应用研究进展3.气相色谱-嗅闻仪/质谱仪检测技术在食品香气物质分析中的研究进展4.固相萃取-色谱/质谱技术在油菜素内酯分析中的研究进展5.定量结构-色谱保留关系在分析化学中的研究进展因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。