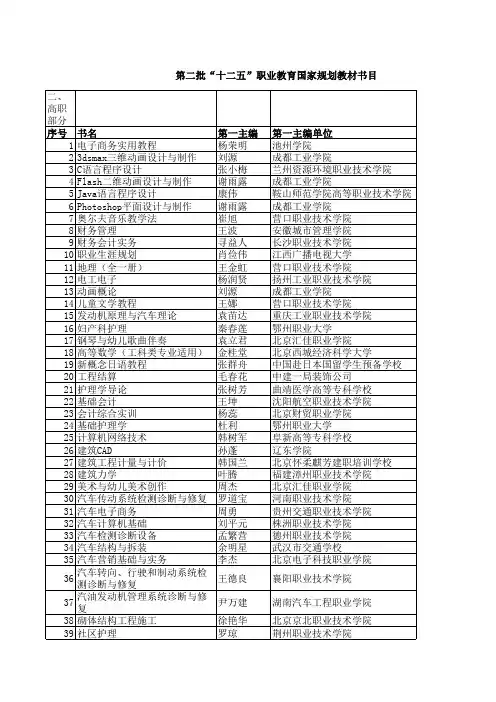
20财经专业英语教程 (5)
- 格式:pptx
- 大小:198.42 KB
- 文档页数:20


财经专业英语词汇(G)财经专业英语词汇(G)财经专业英语词汇(G)gain 收益;增益garnishee order 债权扣押令ge capital finance ltd. 通用金融财务有限公司gearing ratio 资本与负债比率;杠杆比率〔认股权证〕general acceptance 一般承兑general account 一般帐目;总帐general administrator 一般遗产管理人general agreement on tariffs and trade [gatt] 《关税及贸易总协议》〔《关贸总协议》〕general agreement on trade in services [gats] 《服务贸易总协议》general apportionment 一般分摊general arrangements to borrow [gab] 《借款总安排》general body of shareholders 全体股东general business 一般业务general capital increase 总增资general clearing member 一般结算会员general consumer price index [gcpi] 一般消费物价指数general crossed cheque 普通划线支票general crossing 普通划线general expenses 一般开支general fund 普通基金general household survey 综合住户统计调查general insurance council [hong kong federation of insurers] 一般保险总会〔香港保险业联会〕general ledger 总分类帐general levy 一般征款general offer 公开要约;全面收购建议general partner 普通合伙人general partnership 普通合伙general policy 一般保单general proxy 一般委托书general rates 一般差饷general reserve 一般储备金general revaluation [rates] 全面重估应课差饷租值general revenue 一般收入;政府一般收入general revenue account [gra] 政府一般收入帐目general revenue account expenditure 政府一般收入帐目开支general revenue account revenue 政府一般收入帐目收入general revenue balance 政府一般收入余额general support grant 一般经费补助金general warrant 普通拨款令generale belgian bank (also known as belgian bank) 华比银行generalized system of preference [gsp] 普及特惠制〔普惠制〕gilt-edged investment 稳当投资gilt-edged market 金边证券市场gilt-edged securities 金边证券gini coefficient 基尼系数global allocation 总拨款;拨款总额global costing 整体成本计算法go private 私有化;私营化go public 上市godown warrant 仓单going concern 经营中的机构;持续经营gold 黄金gold bullion 金条;黄金gold bullion held on an allocated basis 特别划分方式持有的黄金gold bullion market 黄金市场gold coin 金币gold coin certificate 金币证明书;金币证gold coin coupon 金币配给券gold exchange standard 黄金汇兑本位制gold futures 黄金期货;期金gold identity marks registry 黄金标记注册处gold market 黄金市场gold on paper 黄金券;纸黄金gold, silver and platinum held in physical form 实金、实银及实白金gold standard 金本位;金本位制good book debt 可收回的账面债项good delivery 合格交货;合格交割good year 丰年goods and services 商品及服务;货物与服务goodwill 商誉;信誉government bond 政府债券government consumption expenditure 政府消费开支government conveyancing 政府产权转易government economist 政府经济顾问government expenditure 政府开支government lotteries 政府奖券government lotteries management committee 政府奖券管理委员会government mortgage institution 政府按揭贷款机构government property 政府财产government property assets 政府物业资产government regulations 《政府规例》government rent 地税;地租government reserve 政府储备government revenue 政府收入government securities consultant 政府证券业顾问government trading department 参与商业活动的政府部门government utility 政府公用事业graduated rate 渐进税率grant 补助金;拨款grantor 授予人gratuitous payment 赏金gratuity 酬金gratuity benefit 酬金福利grey market 暗盘市场;灰市;暗市grey market trading 暗盘交易gross amount 毛额gross capital formation 资本形成总额gross claim 申索毛额gross claim paid 已偿付申索毛额gross commission payable 须付的佣金毛额gross contract value 合约总值gross domestic capital formation 本地资本形成总额gross domestic fixed capital formation 本地固定资本形成总额gross domestic price capital formation 本地价格资本形成总额gross domestic product [gdp] 本地生产总值;国内生产总值gross domestic product at constant (1980) market price 按固定(一九八零年)市价计算的本地生产总值gross domestic product at factor cost 按生产要素成本计算的本地生产总值gross domestic product at market price 按市价计算的本地生产总值gross domestic product by industrial sector 按工业类别计算的本地生产总值gross domestic product component 本地生产总值的组成部分gross domestic product deflator 本地生产总值平减物价指数gross domestic product estimate 估计本地生产总值;本地生产总值的估计数字gross domestic product per capita 按人口平均计算的本地生产总值gross expenditure 开支总额;总支出gross expenses 开支总额;总开支gross income 收入总额;总收益gross insurance liabilities 毛保险负债gross liabilities 总负债gross loss 毛损;亏损总额gross margin 毛利gross margining 总额保证金制度gross national product [gnp] 本地居民生产总值;国民生产总值gross output 总产出;总产值;总产量gross premium 毛保费;保费总额gross premium income 毛保费收入;保费收入总额gross principal value 基本价值总额gross proceeds 总收益gross proceeds from sales 销售总收入gross profit 毛利;溢利总额gross receipt 总收入gross return 总收益gross trading income 营业总收入group account 集团帐目group consolidated balance sheet 集团综合资产负债表group loss relief 对集团的亏损给予税项宽免group of seven [g7] 七大工业国group of seven leaders 七大工业国元首group of ten [g10] 十国集团;十国财团组织group tax relief 集团税项宽减group trading system 集体贸易制度grow at a respectable pace 有可观的增长;有不俗的增长率growth enterprise market department [stock exchange of hong kong limited] 创业板部〔香港联合交易所有限公司〕growth momentum 增长劲力growth movement 增长趋势growth path 增长线;增长途径growth rate of domestic export 本地产品出口增长率growth with stability 稳步增长guarantee 担保;保证guarantee company 担保公司;保证公司guarantee corporation 保证法团guarantee deposit and margin paid 缴付的保证按金guarantee deposit and margin received 存入的保证按金guarantee fund 保证基金;担保基金guarantee law 《担保法》guarantee of bank loan 银行贷款保证guarantee of due payment 付款保证书guarantee scheme [stock exchange of hong kong limited] 担保计划〔香港联合交易所有限公司〕guaranteed benefit 保证利益guaranteed debenture 保付债权证guaranteed line of credit 保证贷款限额guaranteed note 保证票据;保证单;担保债券guaranteed surrender value 保证退保现金价值guarantor 保证人;担保人guardian 监护人guide for directors of listed companies 《上市公司董事指引》guide to applicants [hong kong monetary authority] 《认可机构开业与经营指引》〔香港金融管理局〕guideline figure 准则数字guideline on leveraged foreign exchange trading  《杠杆式外汇买卖指引》guideline on minimum criteria for authorization 《认可的最低准则的指引》guideline on recognition of interest [hong kong monetary authority] 《确认利息收入指引》〔香港金融管理局〕guideline ratio 准则比率guidelines for the exemption of listed companies from the securities (disclosure of interests) ordinance 《豁免上市公司遵守〈证券(披露权益)条例〉的指引》guidelines for the exemption of listed companies from the share repurchase requirements of s.49ba of the companies ordinance 《豁免上市公司遵守〈公司条例〉第49ba条股份购回规定的指引》guiding exchange rate 指导性汇率gulf cooperation council 海湾合作委员会gunma finance (hong kong) limited 群马财务(香港)有限公司财经专业英语词汇(G) 相关内容:11。

财经专业英语句子翻译题一、将下列句子翻译为中文。
1. China is projecting a deficit of 1.2 trillion yuan, 400 billion more than the budgeted figure last year.今年拟安排财政赤字1.2万亿元人民币,比去年预算增加4000亿元人民币。
2. Our housing market is healing, our stock market is rebounding, and consumers, patients, and homeowners enjoy stronger protections than ever before.我们的住宅市场正在复苏,我们的股票市场正在反弹。
消费者、病人、房产所有者也享受比之前更有力的保护。
3. Zhangping , director of NDRC, said Wednesday the country is studying a new fuel pricing scheme to make it reflect the global markets' oil price fluctuations more swiftly.国家发改委主任张平本周三表示,我国正研究制定新的成品油定价机制,使油价定价机制更加适应国际市场的变动。
4. China's top 10 lenders' outstanding overdue loans, an indicator of future non-performing loans, or NPLs, reached 489 billion yuan ($77.6 billion) by the end of June, up 112.9 billion yuan from six months earlier.6月底,中国十大银行未清的逾期贷款,已达4890亿元(合776亿美元),比去年底增加了1129亿元。

新世纪会计学专业精品教材国家级双语教学示范课程会计专业英语教程(第三版)章后习题答案马建威编著东北财经大学出版社大连ContentsChapter 1 (3)Chapter 2 (5)Chapter 3 (7)Chapter 4 (10)Chapter 5 (12)Chapter 6 (14)Chapter 7 (17)Chapter 8 (19)Chapter 9 (22)Chapter 10 (25)Chapter 11 (26)Chapter 12 (28)Chapter 13 (29)Chapter 14 (30)Chapter 15 (32)Chapter 16 (34)Chapter 11. True or false1.1 T1.2 T1.3 T1.4 T1.5 F1.6 F1.7 F1.8 F1.9 F2. Short answer questions2.1 Accounting may be described as the process of identifying, measuring, recording, and communicating economic information to permit informed judgments and decisions by users of that information.2.2 The simplest answer to this question is that financial accounting provides information for managers to use in operating the business. In addition, financial accounting provides information to other stakeholders to use in assessing the economic performance and the condition of the business.2.3 A set of financial statements consists of four related accounting reports that summarize in a few pages the financial resources, obligations, profitability, and cash transactions of a business. A complete set of financial statements includes: A balance sheet, an income statement, a statement of owner s’ equity and a statement of cash flow.2.4 There are several objectives of financial reporting. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) concluded that the objectives of the financial reporting are to provide information that:is useful to those making investment and credit decisions;is helpful in assessing future cash flows; andidentifies the economic resources (assets), the claims to those resources(liabilities), and the changes in those resources and claims.2.5 Using cash-basis accounting, income and expenses are recognized only when cash is received or paid out. Using accrual-basis accounting, receivables and payables are recognized when a sale is agreed to, even though no cash has been received or paid out as yet.3. Problem solvingA L OE(a) + +(b) + +(c) - -(d) + +(e) - -(f) +,-(g) - -(h) + +(i) - -(j) +,-(k) - -(l) - -(m) + -(n) - -(o) +,-4. Case studyOmitted.Chapter 21. True or false1.1 T1.2 F1.3 F1.4 T1.5 F1.6 F1.7 F1.8 T1.9 T1.10 T2. Short answer questions2.1 An internal control system refers to the policies and procedures designed to protect the firm's assets and to ensure reliable accounting. It also should promote efficient operations and urge employees to comply with company policies. Internal control systems can help prevent losses, help mangers plan operations, and monitor company and employer performance.2.2 A bank reconciliation is a report explaining any differences between the balance according to a depositor's records and the balance on the company's bank statement. The reconciliation procedure examines the differences based on the information available to the company and adjusts for the differences. It also serves as a format for the discovery and correction of errors.2.3 The net method assumes that a firm will take all cash discounts offered for prompt payment. Any discounts missed are recorded in a discounts lost account. Discounts lost is considered to be an operating expense, and to be a record of presumed inefficiencies in managing cash (of course, further analysis may reveal that the discounts lost reflect purchase discounts at unfavorable terms). The net method of accounting for purchases is used to assist in the internal control function.2.4 Accounts receivable arise from credit sales to customers. Accounts receivable are reported at their realizable value, which is their total amount less an estimate for the amount of uncollectible accounts. Accounts receivable are also recorded into an accounts receivable subsidiary ledger that separately lists amounts owed by individual customers.2.5 A company’s receivables are normally converted to cash as the customers pay off their accounts. However, there are at least three options available to a company that wishes to convert its receivables before they are at least due. First a company can sell the receivables to a factor. Second, a company can use its receivables as collateral for a loan. Third, a company can discount the receivables to a bank in return for cash.3. Problem solvingYear 1: ($49,000/$285,000) ×365 = 63 daysYear 2: ($85,000/$575,000) ×365 = 54 daysThe decrease of 9 days means that this company has improved its management of receivables and its liquidity position.4. Case studyOn December 31, of the current year, a company's unadjusted trial balance revealed the following: Accounts receivable of $185,600; Sales Revenue of $1,280,000; (75% were on credit), and Allowance for Doubtful Accounts of $1,600 (credit balance).Chapter 31. True or false1.1 F1.2 T1.3 T1.4 T1.5 F1.6 F1.7 F1.8 T1.9 T1.10 T2. Short answer questions2.1 Merchandise inventory consists of goods owned by a company and held for resale. Three special cases involving ownership decisions are goods in transit, consigned goods, and damaged goods. Goods in transit are included in the inventory of the company that owns the goods. Consigned goods are included in the inventory of the consignor. Damaged goods are valued at net realizable value.2.2 The specific identification method exactly identifies the costs of the inventory items sold. The weighted average method smoothes out changes in costs by ―averaging‖ inventory costs. However, LIFO and FIFO provide different amounts in periods of rising or falling costs. For example, in periods of rising costs, LIFO provides a lower income and thus lower taxes. In periods of falling costs, LIFO provides a higher income and thus higher taxes. FIFO calculations provide both higher income and taxes in periods of rising costs and lower income and taxes in periods of declining costs.2.3 An inventory error causes misstatements in cost of good sold, gross profit, net income, current assets, and equity. It also causes misstatements in the next period's cost of goods sold and net income. However, the inventory error is said to be self-correcting because the error in the first period is offset by the error in the second period.2.4 A merchandiser's ability to pay its short term obligations depends, among other factors, on how quickly it sells its merchandise inventory. The inventory turnover ratio reveals how many times a company turns over (sells) its inventory during a period. A low ratio compared to competitors suggests the company may be holding more inventory than necessary to support its sales volume. On the other hand, a ratio that is too high compared to competitors may suggest that the inventory level is too low and customers may have to back order merchandise.The days' sales in inventory ratio helps to better interpret inventory turnover. It can be interpreted as the number of days one can sell from inventory if no new items are purchased, and can be viewed as a measure of the buffer against out-of-stock inventory.2.5 The retail method is generally used to prepare interim statements. It uses the cost to retail ratio to give an estimated ending inventory at cost. The gross profit method is typically used to reconstruct the value of lost, stolen, or destroyed inventory. It uses the (historical) gross profit ratio to estimate cost of goods sold and the value of ending inventory.3. Problem solving(1)(2)4. Case study(2) LCM, applied separately to each product = $3,470Chapter 41. True or false1.1 F1.2 F1.3 T1.4 F1.5 F1.6 T1.7 F1.8 T1.9 T1.10 T2. Short answer questions2.1 The cost of plant and equipment includes all expenditures reasonable and necessary in acquiring an asset and placing it in a position and condition for use in the operation of the business. Only reasonable and necessary expenditures should be included.2.2 Depreciation, as the term is used in accounting, is the allocation of the cost of a tangible plant asset to expense in the periods in which services are received from the asset. In short, the basic purpose of depreciation is to achieve the matching principle — that is, to offset the revenue of an accounting period with the costs of the goods and services being consumed in the effort to generate that revenue.2.3 The term accelerated depreciation means recognition of relatively large amounts of depreciation in the early years of use and reduced amounts in the later years. This is consistent with the basic accounting concept of matching costs with related revenue. Accelerated depreciation methods have been widely used in income tax returns because they reduce the current year’s tax burden by recognizing a relatively large amount of depreciation expense.2.4 (1) the expected life of the asset; (2) the expected useful life of another asset that is related to the life of the intangible asset, such as the mineral rights that relate to adepleting asset; (3) any legal, regulatory, or contractual provisions that enable renewal or extension of the asset’s legal or contractual life w ithout substantial economic cost;(4) the effects of obsolescence, demand, competition, and other economic factors; and(5) the level of maintenance costs required to obtain the expected future cash flows from the asset.2.5 Intangible assets are separated into three categories to determine whether or not they are amortized, and how they are reviewed for impairment. The three categories are: (1) intangible assets with a finite (limited) life, (2) intangible assets with an indefinite life, and (3) goodwill.3. Problem solving2014 July 1Computer Equipment 2,700Cash 2,700Nov.3 Repairs Expense 140Cash 140Dec.31 Depreciation Expense 275Accumulated Depreciation 275[($2,700 – $500) ÷ 4 × 1/2]2015 Dec.31 Depreciation Expense 550Accumulated Depreciation ($2,200 ÷ 4) 5502016 Jan.1 Computer Equipment 500Cash 5004. Case studyOmitted.Chapter 51. True or false1.1 T1.2 F1.3 F1.4 T1.5 T1.6 T1.7 F1.8 T1.9 F1.10 T2. Short answer questions2.1 For purposes of valuation and reporting at a financial statement date, debt and stock investments are classified into three categories of securities:(1)Trading securities are securities bought and held primarily for sale in the near term to generate income on short-term price differences.(2)Available-for-sale securities are securities that may be sold in the future.(3)Held-to-maturity securities are debt securities that the investor has the intent and ability to hold to maturity.2.2 Corporations purchase investments in debt or stock securities generally for one of three reasons. First, a corporation may have excess cash that it does not need for the immediate purchase of operation assets. Second, some companies such as banks, purchase investments to generate earnings from investment income. Third, some companies invest for strategic purposes.2.3 Reporting the unrealized gain or loss in the stockholders’ equity sections serves two important purposes: (1) it reduces the volatility of net income due to fluctuations in fair value. (2) it informs the financial statement user of the gain or loss that would occur if the securities were sold at fair value.2.4 Short-term investments are securities held by a company that are (1) readilymarketable, and (2) intended to be converted into cash within the next year or operating cycle, whichever is longer. Investments that do not meet both criteria are classified as long-term investments.2.5 Consolidated financial statements present the total assets and liabilities controlled by the parent company. They also present the total revenues and expenses of the subsidiary companies. Consolidated statements are prepared in addition to the financial statements for the parent and individual subsidiary companies.3. Problem solving(1) Jan.1 Stock Investments ..................................................................9,720Cash ....................................................................... 9,720 June 1 Cash (900 × $.50) .. (450)Dividend Revenue (450)Sep.15 Cash ($4,300 – $100) ..........................................................4,200Loss on Sale of Stock Investments (120)Stock Investments .................................................. 4,320[400 × ($9,720 ÷ 900)]Dec.1 Cash (500 × $.50) (250)Dividend Revenue (250)(2) Dividend Revenue is reported under Other Revenues and Gains on the incomestatement. Loss on Sale of Stock Investments is reported under Other Expenses and Losses on the income statement.4. Case studyJan. 2 Debt Investments .................................................................................... 32,000Cash ................................................................................... 32,000July 1 Cash ($30,000 × 10% × 1/2) ................................................................... 1,500Interest Revenue ................................................................ 1,500Chapter 61. True or false1.1 T1.2 F1.3 T1.4 T1.5 T1.6 F1.7 T1.8 T1.9 F1.10 F2. Short answer questions2.1 Current liabilities are obligations that must be paid within one year or within the operating cycle, whichever is longer. Another requirement for classification as a current liability is the expectation that the debt will be paid from current assets (or through the rendering of service). Liabilities that do not meet these conditions are classified as long-term liabilities.2.2 Bonds usually are very long-term notes, maturing in perhaps 30 or 40 years. The bonds are transferable; however, so individual bond-holders may sell their bonds to other investors at any time. Most bonds call for semi-annual interest payments to the bond-holders, with interest computed at a specified contract rate throughout the life of the bond. Thus, investors often describe bonds as ―fixed income‖ investments.2.3 Bonds payable differ from capital stock in several ways. First, bonds payable are a liability; thus, bond-holders are creditors of the corporation, not owners. Bond-holders generally do not have voting rights and do not participate in the earnings of the corporation beyond receiving contractual interest payments. Next, bond interest payments are contractual obligations of the corporation. Dividends, on the other hand, do not become legal obligations of the corporation until they have been formally declared by the board of directors. Finally, bonds have a specific maturing date, upon which the corporation must redeem the bonds at their face amount. Capital stock, onthe other hand, does not have a maturing date and may remain outstanding indefinitely.2.4 A principal advantage of raising money by issuing bonds instead of stock is that interest payments are deductible in determining income subject to corporate income taxes. Dividends paid to stockholders, however, are not deductible in computing taxable income.2.5 Bonds are sometimes retired before the maturity date. The principal reason for retiring bonds early is to relieve the issuing corporation of the obligation to make future interest payments. If interest rates decline to the point that a corporation can borrow at an interest rate below that being paid on a particular bond issue, the corporation may benefit from retiring those bonds and issuing new bonds at a lower interest rate.3. Problem solving(1) June 30 Bonds Payable ......................................................400,000Loss on Bond Redemption ...................................40,800Discount on Bonds Payable ............................... 32,800Cash .................................................................... 408,000($400,000 – $367,200 = $32,800)($400,000 × 102% = $408,000)(2) June 30 Bonds Payable ........................................................600,000Discount on Bonds Payable ............................... 10,000Gain on Bond Redemption ................................. 14,000Cash .................................................................... 576,000($600,000 – $590,000 = $10,000)($600,000 × 96% = $576,000)(3) Dec. 31 Bonds Payable ........................................................50,000Common Stock ................................................... 20,000Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par ......................... 30,000($5 × 80 × 50 = $20,000)4. Case studyThe alternative effects on net income and earnings per share are as follows:Issue Stock Issue BondsIncome before interest and taxes $1,500,000 $1,500,000 Interest (10% × $2,500,000) —(250,000) Income before income taxes 1,500,000 1,250,000 Income tax expense (450,000) (375,000) Net income $1,050,000 $ 875,000Outstanding shares 250,000 200,000Earnings per share $4.20 $4.38Net income is higher if the equipment is financed through the issuance of stock. However, earnings per share is lower because of the additional number of shares of common stock that are outstanding.Chapter 71. True or false1.1 T1.2 F1.3 T1.4 F1.5 F1.6 T1.7 F1.8 T1.9 T1.10 F2. Short answer questions2.1 Common stockholders generally have the right to vote at stockholders' meetings, sell or otherwise dispose of their stock, receive the same dividend, if any on each common share, and share in any assets remaining after creditors are paid when and if the corporation is liquidated. Stockholders generally also have a preemptive right, which is the right to purchase their proportional share of any common stock later issued by the corporation.2.2 Stockholders' equity consists of two main parts, paid-in capital and retained earnings. Paid-in capital consists of funds raised by the issuance of stock, either common or preferred. Paid-in capital is the total amount of cash and other assets the corporation receives in exchange for stock. Paid-in capital in excess of par value represents the amount a corporation receives from issuing stock when the market value exceeds the par value of the stock. Retained earnings is the cumulative net income and loss retained by the corporation less any dividends declared.2.3 Stock options are the rights to purchase common stock at a fixed price over a specified period. As the stock's price rises above the fixed price, the option's value increases. As a general rule, stock options motivate managers and employees to (1) focus on company performance, (2) take a long-term perspective, and (3) remain with the company. A stock option is like having an investment with no risk.2.4 The price-earnings ratio of a common stock is computed by dividing the stock's market value per share by its earnings per share. The price-earnings ratio represents the stock market's expectations of a company's future performance. Some analysts view a high PE (greater than 20 to 25, for instance) ratio as an indication that a stock is overvalued. A low ratio (less than 5 to 8) may indicate that a stock is undervalued.2.5 Dividend yield is the ratio of annual cash dividends per share divided by the market value per share of stock. The resulting dividend yield represents the percent of cash return investors receive from an investment in a company's stock. Dividend yield can be used to identify whether a stock is an income stock or a growth stock. Companies that pay large dividends on a regular basis are income stocks. Companies that distribute little or no cash but use the cash to finance expansion are known as growth stocks.3. Problem solving(1)Book value per preferred share:$560,000/5,000 shares = $112 per preferred share(2)Book value per common share:$2,550,000/150,000 shares = $17 per common share4. Case studyChapter 81. True or false1.1 T1.2 F1.3 T1.4 F1.5 T1.6 T1.7 F1.8 F1.9 F1.10 T2. Short answer questions2.1 The basic components of income begin with net sales. Cost of goods sold is subtracted from net sales to get gross profit (also called gross margin). Operating expenses are then subtracted from gross margin to determine net income.2.2 The gross margin ratio is calculated by dividing gross margin (or net sales less cost of goods sold) by net sales. The gross margin ratio measures a firm's profitability in selling its inventory. The gross margin must be large enough to cover operating expenses and provide sufficient net income to the owner(s).2.3 Selling expenses include the expenses of promoting sales by displaying and advertising merchandise, making sales, and delivering goods to customers. General and administrative expenses support a company's overall operations and include expenses related to accounting, human resource management, and financial management. Some expenses can relate to both areas and are allocated between them.2.4 The three important guidelines for revenue recognition include: (1) Revenue is recognized when earned. (2) Assets received from selling products and services do not need to be in cash. (3) Revenue recognized is measured by cash received plus the cash equivalent of other assets received.2.5 Revenues are the gross increases in equity from a company's earnings activities.Expenses are the costs of assets or services used to earn revenues. Net income is the excess of revenues over expenses.3. Problem solving(1)(2) Trico had the more favorable ratio for each year.(3) Unico's gross margin ratio is increasing, while Trico's is decreasing. Moreover, these changes appear significant and warrant further analysis.4. Case studyChapter 91. True or false1.1 F1.2 F1.3 T1.4 F1.5 T1.6 T1.7 T1.8 F1.9 T1.10 T2. Short answer questions2.1 Both stockholders and creditors use financial statement analysis to (1) predict their expected returns and (2) assess the risks associated with those returns.2.2 The analysis of financial data employs various techniques to emphasize the comparative and relative significance of the data presented and to evaluate the position of the firm. Three commonly used tools are as following.Horizontal analysis evaluates a series of financial statement data over a period of time.Vertical analysis evaluates financial statement data by expressing each item in a financial statement as a percent of a base amount.Ratio analysis expresses the relationship among selected items of financial statement data.2.3 For users of financial statements t o determine ―earning power‖ or regular income, the ―irregular‖ items are separately identified on the income statement. Three types of ―irregular‖ items are reported:(1) Discontinued operations.(2) Extraordinary items.(3) Changes in accounting principle.2.4 When two conditions are met (1) management can show that the new principle is preferable to the old principle, and (2) the effects of the change are clearly disclosed in the income statement.2.5 (1) Financial statements contain numerous estimates.(2) Traditional financial statements are based on cost.(3) Companies vary in the generally accepted accounting principles they use.(4) Fiscal year-end data may not be typical off the financial condition during the year.(5) Diversification within a global environment also limits the usefulness of financial analysis.3. Problem solving(1) Current = 1.45:1 ($160,000 ÷ $110,000)(2) Acid-test = 0.77:1 ($85,000 ÷ $110,000)4. Case study(1) Credit salesReceivables turnover = —————————————Average accounts receivable= $5,110,000 ÷ $700,000= 7.3 times365 daysAverage collection period = ——————————Receivables turnover= 365 ÷ 7.3 times= 50 days(2) Inventory turnover = Cost of goods sold ÷ Average inventoryFirst calculate ending inventory.Beginning Inventory $ 482,000+ Purchases 4,146,000– Cost of Goods Sold (4,088,000)*Ending Inventory $ 540,000*Since the gross profit ratio is 20%, the cost of goods sold ratio is 80%.80% × $5,110,000 (net sales) = $4,088,000.Ending Inventory = $540,000 (per above)Average Inventory = ($482,000 + $540,000) ÷ 2 = $511,000Inventory Turnover = $4,088,000 ÷ $511,000 = 8 timesDays to Sell = 365 days ÷ 8 times = 45.6 days(3) Net incomeReturn on common stockholders' equity = —————————————————Average common stockholders' equity =$490,000 ÷ $3,500,000 = 14%Chapter 101. True or false1.1 T1.2 T1.3 T1.4 F1.5 T1.6 T1.7 F1.8 T1.9 F2. Short answer questionsOmitted.3. Problem solving(1) Direct-labor-hour basisOverhead recovery rate=£50,000/2000=£25 per machine-hour.A £25×1500=£37500B £25×500=£12500(2) Machine-hour basisOverhead recovery rate=£50,000/1200=£41.6667 per machine-hour.A £41.6667×800=£33333B £41.6667×400=£166674. Case studyThe relevant costs to be included in the minimum price are:Stock item: A1 £6×500=£3,000B2 £8×800=£6,400We are told that the stock of item A1 is in frequent use and so, if it is used on the contract, it will need to be replaced. We are told the stock of item B2 will never be used by the business unless the contract is undertaken. Thus, if the contract is not undertaken, the only reasonable thing for the business to do is sell the stock. This means that the opportunity cost is £8 a unit.Chapter 111. True or false1.1 T1.2 T1.3 F1.4 F1.5 F1.6 T1.7 T1.8 T1.9 F2. Short answer questionsOmitted.3. Problem solvingThe original budget, the flexed budget and the actual are as follows:Budget Actual Flexed budget Output (production and sales) 1,000 units 1050 units 1050 units£££Sale revenue 100,000 104,300 105,000 Raw materials 40,000 41,200 42,000 Labor 20,000 12,300 21,000 Fixed overheads 20,000 19,400 20,000 Operating profit 20,000 22,400 22,000 Reconciliation of the budgeted and actual operating profits for JulyBudgeted profit 20,000Add favorable variances:Sales volume (22,000-20,000) 2,000Direct materials usage {[(1050×40)-40,500]×£1} 1,500Direct labor efficiency{[(1050×2.5)-2,600]×£8} 200Fixed overhead spending (20,000-19,400) 60024,300Less Adverse variances:Sales price variance (105,000-104,300) 700Direct materials price[(40,500×£1)-41,200] 700Direct labor rate[(2,600×£8) -21,300] 500Actual profit 22,4004. Case studyPilot Ltd(1)and (2)BudgetActualOriginal FlexedOutput (units)(production and sales)5,000 5,400 5,400£££Sales revenue 25,000 27,000 26,460Raw materials (7,500) (8,100) (2,700 kg) (8,770) (2,830 kg) Labor (6,250) (6,750) (1,350 hr) 6,885 (1,300 hr) Fixed overheads (6,000) (6,000) (6,350)Operating profit 5,250 6,150 4,455£Manager accountableSales volume varianceSales price variance Materials usage variance Materials price variance Labor efficiency variance Labor rate variance Fixed overhead variance5250-615027000-26460[(5400×0.5)-2830]×£3(2830×3)-8770[(5400×0.25)-1300]×£5(1300×5)-68856000-6350900 (F)(540) (A)(280) (A)(390) (A)(385) (A)250(F)(350) (A)SalesSalesBuyerProductionPersonnelProductionDepends on the natureof the overheadsTotal net variances 795(A) Note: F—favorable; A—adverse.。

《财务专业英语》课程教学大纲课程代码:ABGS0519课程中文名称:财务专业英语课程英文名称:Financial English课程性质:选修课程学分数:2课程学时数:32授课对象:财务管理专业本课程的前导课程:财务管理基础、中级财务会计、财政与金融、金融市场学、财务报表分析一、课程简介《财经专业英语》是财务管理专业的一门专业选修课程。
通过本课程的学习,强化学生财务管理专业英语的综合运用能力,为学生营造一个在国际视野下用英语思考财务问题和解决财务问题的环境。
二、教学基本内容和要求1 Introduction to Financial Management (1)1.1 Financial Management and Financial Manager1.2 Financial Management Decision: Investment Decisions, Financing Decisions, Working Capital Management Decisions1.3 Risk-Return Tradeoff本章重点:Financial Management Decision.本章难点:Financial Management Decision.2 Introduction to Financial Management (2)2.1 Types of Business Organization: Sole Proprietorship, Partnership, Corporation2.2 Corporate Structure of the Company: Shareholders, Board of Directors, CEO, CFO2.3 Objectives of Financial Management: Stakeholder Theory, Value of Wealth Maximization2.4 Separation of Ownership and Control2.5 Agency Relationships: Agency Problem, Agency Costs, Practical Solutions to the Agency Problem本章重点:Objectives of Financial Management.本章难点:Objectives of Financial Management, Agency Problem and Solutions.3 Interpreting Financial Statement3.1 Basics of Annual Repots and Financial Statements: Corporate Annual Reports,Overview of Financial Statements3.2 Balance Sheet3.3 Income Statement3.4 Statement of Retained Earnings3.5 Statement of Cash Flow: Operating Cash Flows, Investing Cash Flows, Financing Cash Flows本章重点:Interpretation of Financial Statements.本章难点:Interpretation of Financial Statements.4 Financial Ratio Analysis4.1 Financial Ratio Analysis4.2 Liquidity Ratios: Current Ratio, Quick Ratio, Cash Ratio4.3 Debt Management Ratios: Debt Ratio, Long-term Debt Ratio, Cash Flow Coverage Ratio4.4 Asset Management Ratios: Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio, Inventory Turnover Ratio, Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio, Asset Turnover Ratios4.5 Profitability Ratios: Gross Profit Margin, Operating Profit Margin, Net Profit Margin, Return on Assets, Total Return on Assets, Return on Equity, Return on Common Equity, DuPont Analysis of ROE4.6 Market Value Ratios: Price/earnings Ratio, Market-to-book Value Ratio, Dividend Yield and Payout4.7 Uses and Limitations of Financial Ratio Analysis本章重点:Principle Financial Ratios.本章难点:Calculation and Signification of Principle Financial Ratios, DuPont Analysis.5 Time Value of Money and Valuation5.1 Central Concepts in Financial Management5.2 Simple vs. Compound Interest Rates and Future vs. Present Value: Simple Interest, Compound Interest, Future Value, Present Value5.3 Annuity: Ordinary Annuity, Annuity Due, Deferred Annuity, Perpetuity, Nominal and Effective Interest Rates5.4 Valuation Fundamentals: Going-concern Value, Liquidation Value, Book Value, Market Value, Intrinsic Value, Valuation Approaches, Discounted Cash Flow Valuation5.5 Bond Valuation: Contractual Provisions of a Typical Bond, the Bond Valuation Formula, Bond Prices and Returns5.6 Common Stock Valuation: Common Stock Characteristics and Features, Common Stock Valuation本章重点:Compound Interest Rates, Future Value, Present Value, Annuity, Valuation Approaches.本章难点:Present Value of Different Annuity.6 Risk and Return6.1 Introduction to Risk and Return: Return, Risk6.2 Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH): Introduction, Financial Market Efficiency, Anomalies in Finance6.3 Portfolio Theory: The Expected Return of a Portfolio, Risk in a Portfolio Context, Modern Portfolio Theory, Diversified Risk versus Market Risk6.4 Beta and Capital Asset Pricing Model: The Concept of Beta, CAPM6.5 Arbitrage Pricing Theory本章重点:CAPM.本章难点:CAPM.7 Capital Budgeting7.1 Capital Investment Decisions: Nature of Capital Budgeting, Project Classifications7.2 Guidelines for Estimating Project Cash Flows: Incremental Cash Flows, Focus on After-tax Cash Flows, Postpone Considering Financing Costs, Other Cash Flow Considerations7.3 Investment Rules: Payback Period, Net Present Value, Internal Rate of Return, Profitability Index7.4 Business Practice7.5 Analyzing Project Risk: Sensitivity Analysis, Break-even Analysis, Simulation7.6 Project Selection with Resource Constrains7.7 Qualitative Factors and the Selection of Projects7.8 The Post-Audit本章重点:Capital Investment Decision Indices.本章难点:Internal Rate of Return.8 Capital Market and Raising Funds8.1 Financial Markets: Role of Financial Markets, Types of Financial Markets, Recent Trend8.2 Investment Banks: Advising, Underwriting, Marketing8.3 The Decision to Go Public: Advantages of Going Public, Disadvantages of Going Public, Different Methods of Issuing New Securities8.4 Cost of Capital Concept: Use of the Cost of Capital, Capital Components, Weighted Average Cost of Capital本章重点:Cost of Capital.本章难点:Cost of Capital.9 Capital Structure9.1 The Choices: Types of Financing9.2 The Financing Mix9.3 Understanding Financial Risk9.4 Capital Structure and the Value of a Firm: The Modigliani-Miller Theorem, The M&M Theorem in the Real World, Tradeoff Theory of Optimal Capital Structure, Pecking Order Theory of Capital Structure9.5 Checklist for Capital Structure Decisions本章重点:Capital Structure Decisions.本章难点:Capital Structure Decisions.10 Dividend Policy10.1 Dividends and Dividend Policy: Dividend Payout Procedure, Types of Dividends10.2 The Dividend Puzzle: Dividend Irrelevance Theory, Dividend Relevance Theory10.3 Factors Influencing the Dividend Decision: Shareholder Factors, Firm Factors, Managerial Preferences and Constraints10.4 Dividend Policies: Residual Dividend Policy, Stable Dollar Dividend Policy, Constant Dividend Payout Ratio, Low Regular plus Specially Designated Dividends10.5 Stock Repurchases: Ways of Repurchases, Reasons for Stock Buybacks本章重点:Dividend Policies.本章难点:Stock Repurchases.11 Working Capital11.1 Introduction to Working Capital Management11.2 Cash Management: Three Motives for Holding Cash, Determining Appropriate Cash Balances, Investment Idle Cash, Types of Money Market Securities, Managing Collections and Disbursements11.3 Accounts Receivable Management: Credit Policy, Collection Policy11.4 Inventory Management: Successful Inventory Management, The Purchasing Plan, Inventory Management Techniques本章重点:Motives for Holding Cash, Determination of Appropriate Cash Balances.本章难点:Determination of Appropriate Cash Balances.12 International Financial Management12.1 Introduction: The Global Economy, Multinational Corporations12.2 Foreign Exchange Market: Exchange Rates, Currency Risk, Types of Transactions12.3 Exchange Rate Parity: Interest Rate Parity, Purchasing Power Parity, Unbiased Forward Rates, Inflation, Interest Rates and Exchange Rates12.4 Multinational Capital Budgeting12.5 International Financial Decision12.6 Working Capital Management12.7 Hedging Currency Risk: Currency Forward Contracts, Currency Futures Contracts, Currency Swaps, Currency Option Contracts本章重点:International Financial Decision.本章难点:Hedging Currency Risk.三、实验教学内容及基本要求无四、教学方法与手段教学方法:理论教学、案例教学、启发示教学、情境教学教学手段:板书教学、多媒体教学五、教学学时分配六、考核方式与成绩评定标准1、考核方法:集中考核(考核方式:考查)2、成绩评定:平时成绩(考勤、课堂表现及作业)占40%,期末考核成绩占60%。

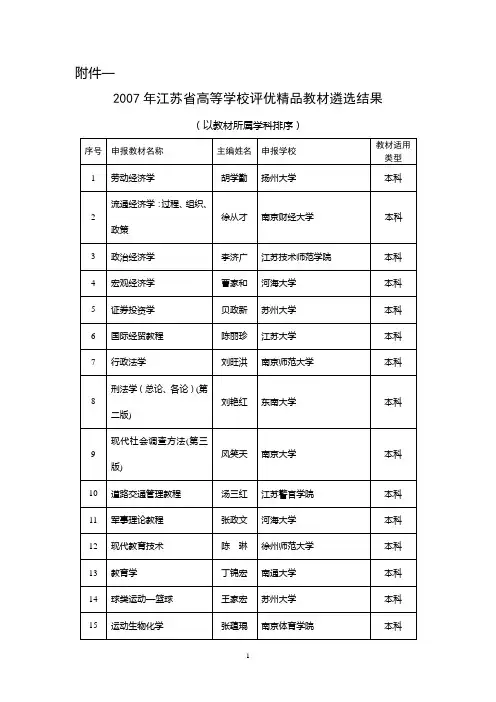
常见的金融词汇中英对照1. 金融市场 (Financial Markets)金融市场是指用于实现资金交易和资金融通的场所,包括股票市场、债券市场、外汇市场和商品市场等。
•股票市场 (Stock Market): the market for buying and selling shares of publicly traded companies.•债券市场 (Bond Market): the market for buying and selling bonds.•外汇市场 (Foreign Exchange Market): the market for trading foreign currencies.•商品市场 (Commodity Market): the market for trading commodities such as oil, gold, and agricultural products.2. 资本市场 (Capital Market)资本市场是指长期融资和投资的市场,包括股票市场和债券市场等。
•股票市场 (Stock Market): the market for buying and selling shares of publicly traded companies.•债券市场 (Bond Market): the market for buying and selling bonds.3. 证券 (Securities)证券是指可以转让和交易的金融工具,包括股票、债券、证券投资基金等。
•股票 (Stocks): shares of ownership in a company that can be bought and sold on a stock market.•债券 (Bonds): debt securities issued by governments, corporations, or other organizations to raise capital.•证券投资基金 (Mutual Funds): investment funds that pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, orother securities.4. 风险管理 (Risk Management)风险管理是指识别、评估和处理金融交易和投资中的各种风险,以减少损失和提高效益。

财经专业英语第五版张美兰课后答案1、It is reported()three people were badly injured in the traffic accident. [单选题] *A. whichB. that(正确答案)C.whileD.what2、--I can’t watch TV after school.--I can’t, _______. [单选题] *A. alsoB. tooC. either(正确答案)D. so3、You should stick to your()and tell him you won' t do the thing. [单选题] *A. principle(正确答案)B. qualityC. contactD. influence4、21 In a few years' time, there ________ thousands of trees on the hill. [单选题] * A.will haveB.will be(正确答案)C.are haveD.have5、Tom is ____ honest man, so we all like to work with him. [单选题] *A. aB. an(正确答案)C. /D. any6、I didn't hear _____ because there was too much noise where I was sitting. [单选题] *A. what did he sayB. what he had said(正确答案)C. what he was sayingD. what to say7、Which is _______ city, Shanghai, Beijing or Chengdu? [单选题] *A. largeB. largerC. largestD. the largest(正确答案)8、81.Some birds are flying ________ the lake. What a beautiful picture! [单选题] *A.forB.underC.inD.above(正确答案)9、72.I really don’t know how to thank you , but for your help, I ()my lost necklace.[单选题] *A.couldn’t have found(正确答案)B.mustn’t have foundC.couldn’t findD.wouldn’t find10、19.Students will have computers on their desks ________ . [单选题] *A.in the future(正确答案)B.on the futureC.at the momentD.in the past11、If it _______ tomorrow, I won’t go there. [单选题] *A. rains(正确答案)B. is rainingC. will rainD. would rain12、Her ()for writing was that she wished women to get the right to higher education. [单选题] *A. motivation(正确答案)B. motivateC. effectD. concentration13、They may not be very exciting, but you can expect ______ a lot from them.()[单选题] *A. to learn(正确答案)B. learnC. learningD. learned14、He kept walking up and down, which was a sure()that he was very worried. [单选题] *A. sign(正确答案)B. characterC. natureD. end15、_____ the plan carefully,he rejected it. [单选题] *A. To have consideredB.To considerC. Having considered(正确答案)D. Considering16、Mr. Bliss became the first person to die in a car accident. [单选题] *A. 事故(正确答案)B. 竞赛C. 检阅D. 交易17、Every means _____ but it's not so effective. [单选题] *A. have been triedB. has been tried(正确答案)C. have triedD. has tried18、_______! Jack,the floor is wet. [单选题] *A. Be careful(正确答案)B. Be careful toC. Be careful forD. Be careful with19、We should _______ a hotel before we travel. [单选题] *A. book(正确答案)B. liveC. stayD. have20、He was?very tired,so he stopped?_____ a rest. [单选题] *A. to have(正确答案)B. havingC. haveD. had21、Do not _______ me to help you unless you work harder. [单选题] *A. expect(正确答案)B. hopeC. dependD. think22、Seldom _____ in such a rude way. [单选题] *A.we have been treatedB. we have treatedC. have we been treated(正确答案)D. have treated23、Tony can _______ the guitar.Now he _______ the guitar. [单选题] *A. play; plays(正确答案)B. playing; playingC. plays; is playingD. play; is playing24、—Who came to your office today, Ms. Brown?—Sally came in. She hurt ______ in P. E. class. ()[单选题] *A. sheB. herC. hersD. herself(正确答案)25、He _______ walks to school, because he lives near school. [单选题] *A. sometimes(正确答案)B. neverC. doesn’tD. don’t26、Tom is very _______. He never cleans his room. [单选题] *A. lazy(正确答案)B. activeC. shyD. healthy27、—Is this Tony’s history book?—No, it isn’t ______.()[单选题] *A. himB. his(正确答案)C. heD. himself28、I’d?like _______ the English club. [单选题] *A. to join inB. joinC. to join(正确答案)D. join in29、If you do the same thing for a long time, you'll be tired of it. [单选题] *A. 试图B. 努力C. 厌倦(正确答案)D. 熟练30、A survey of the opinions of students()that they admit several hours of sitting in front of the computer harmful to health. [单选题] *A. show;areB. shows ;is(正确答案)C.show;isD.shows ;are。

财经专业英语词汇(S)财经专业英语词汇(S)财经专业英语词汇(S)safe custody business 保管业务safe custody fee 保管费safe deposit box rental received 保管箱租项收入safeguarding assets 保障资产safety factor 安全系数safety margin of profitability 盈利能力的安全界限sakura bank, limited 樱花银行salaried employee 受薪雇员salaried office 受薪职位salaries tax 薪俸税salaries tax assessment 薪俸税评税salaries tax borne by the employer 由雇主代付的薪俸税salaries tax payable 应缴的薪俸税salaries tax payer 缴交薪俸税人士salaries tax return 薪俸税报税表salaries tax threshold 薪俸税的免缴税入息额salary 薪金;薪俸salary adjustment 薪金调整salary earner 受薪人士salary rate index 薪金率指数salary statement 薪俸结算书sale and purchase agreement 买卖协议sale by auction 拍卖sale by private treaty 以私人协约形式售卖sale by public auction 公开拍卖sale by tender 招标出售sale of assets 售卖资产sale proceeds 售卖得益;销售收入sales account 销货帐sales commission 销售佣金sales counter 销售柜台sales price index 销售价格指数sales tax 销售税sampling frame 抽样范围sampling theory 抽样理论samurai bond 武士债券;外国日元债券sanction 认许;制裁sanwa bank, limited 三和银行sanwa international finance limited 三和国际财务有限公司satisfaction 清偿savings 储蓄;节省款项;节省开支额savings account 储蓄账户savings deposit 储蓄存款savings rate 储蓄率;储蓄存款利率scale of brokerages 经纪佣金收费表scale of fees 收费率;收费表schedule 清单;一览表;细目单;附表schedule of charges 费用表schedule of dealing 交易清单schedule of property 财产清单schedule of proportion 比例表schedule of rates 标准收费表scheme of arrangement 债务偿还安排scheme of control 管制计划scheme of control agreement [sca] 《管制计划协议》schengen agreement 《神根协议》schroders asia limited 宝源亚洲有限公司scrip 临时股票scrip dividend 以股代息scrip dividend scheme 以股代息计划scrip issue 红股发行scripless dealing of shares 无单股份交易seanza forum of bank supervisors 东南亚、新西兰与澳洲银行业监理组织search fee 查册费seasonal adjustment 季节性调整seasonal deficit 季节性赤字seasonal fluctuation 季节性波动seasoned securities 优质证券;价格稳定的证券second and third liner 二三线股second board 第二板市场second calculation 第二计算法second line stock 二线股票second mortgage 第二按揭;第二抵押权second participant 第二参与者second quarter economic report 19xx 《一九xx年第二季经济报告》secondary insider 次要的内幕人士secondary listing 第二上市secondary market 二级市场;次级市场;第二市场secondary mortgage market 第二按揭市场secondary production 第二级生产;第二产业secretary for economic services 经济局局长secretary for financial services 财经事务局局长secretary for the treasury 库务局局长sectional group 个别利益集团sector 界别;行业;机构sectorial index 分类指数secular trend 长期趋势secure 担保;抵押secured bond 有担保债券secured creditor 有抵押债权人secured loan 担保贷款;有抵押贷款securing debenture 担保债权证securities 证券securities advisory council 证券事务咨询委员会securities analyst 证券分析员securities and exchange commission [sec] [taiwan, united states] 证券管理委员会〔证管会〕〔台湾〕;证券交易委员会〔美国〕securities and futures appeals panel [securities and futures commission] 证券及期货事务上诉委员会〔证券及期货事务监察委员会〕securities and futures commission [sfc] 证券及期货事务监察委员会〔证监会〕securities and investment board [sib] [united kingdom] 证券及投资管理局〔英国〕securities borrowing 证券借用securities business 证券买卖业务securities commission [presently known as securities and futures commission] 证券事务监察委员会〔现称证券及期货事务监察委员会〕securities compensation fund 证券赔偿基金securities compensation fund committee [securities and futures commission] 证券赔偿基金委员会〔证券及期货事务监察委员会〕securities dealer 证券交易商securities dealers' deposit fund 证券交易商按金基金securities exchange of thailand 泰国证券交易所securities for money 贷款抵押物securities foundation 证券业培训基金securities institute of australia 澳大利亚证券学会securities introducing broker 证券介绍经纪securities investment adviser 证券投资顾问securities journal, the 《证券月刊》securities law 《证券法》securities lending 证券借贷securities market 证券市场securities officer 证券主任securities payable to bearer 须付款予持有人的证券securities register system 证券登记系统securities review committee 证券业检讨委员会securities review committee report 《证券业检讨委员会报告书》securities section [financial services bureau] 证券组〔财经事务局〕securities underwriter 证券包销商securitization of debt 债务证券化security 抵押品;保证金;保证security account 保付户口security by bond 担保契据形式的保证security features [bank notes] 防伪特色〔银行纸币〕security for note issue 发行纸币的保证物security instrument 保证文书security interest 担保权益security to the payment of money 付款保证seed capital 种子资本segregated account 独立账户;独立户口segregated trust account 独立信托账户sehk options clearing house limited [seoch] 联交所期权结算所有限公司sehk traded option 在联交所买卖的期权seizure 检取;扣押selective allowance 选择性免税额selective marketing basis 选择性销售方式selective tender 选择性投标;选择性招标self-assessment 自我评税self-clearing member [stock exchange of hong kong limited] 自行结算会员〔香港联合交易所有限公司〕self-correcting mechanism 自动调节机制self-financing 财政自给;自筹资金self-liquidating project 自动还本工程self-regulation 自律;自行规管;自行监管sell 卖出sell off 抛售;沽盘sell order 卖盘sell short 卖空;沽空;抛空seller's price 卖价;卖方价格selling dealer 卖方交易商selling hedge 沽空对冲selling pressure 沽售压力selling price 售价senior securities 优先证券seoulbank 汉城信托银行separate assessment 夫妇分别评税separate client account 独立客户帐目separate debt 独有的债项;各别的债项separate estate 各别产业separate estates account 各别产业的帐目separate instrument 独立文书separate listing 独立上市separate property 各别的财产separate share trading account 独立股票交易账户separate taxation for married couples 夫妇分开评税sequestration 暂押;扣押serial bond 分期还本债券series of transactions 连串交易service-led economy 以服务业为主导的经济set-off 抵销;对销set-off and transfer report 比对转帐报告set-off of the property tax 豁免物业税settled property 预先分配的财产settlement 交收;结算;交割;清偿;授产安排settlement backlog 积压交收settlement bank 结算银行settlement cap 交收限价settlement date 交收日期settlement of debts 清偿债务;偿还债务settlement of physical shares 股份实物交收settlement period 交收期限;结算期settlement price 结算价格;平仓价格settlement risk 结算风险;交收风险settlement system 交收制度;结算系统settlor 财产授予人seven-year exchange fund note 七年期外汇基金债券sewage services trading fund 污水处理服务营运基金shacom finance limited 上商财务有限公司shadow director 影子董事;幕后董事shanghai commercial bank ltd. 上海商业银行shanghai securities central clearing and registration corporation 上海证券中央登记结算公司shanghai stock exchange 上海证券交易所share 股份;股票;份额share beneficially owned 实益股份;实益拥有股份share capital 股本share certificate 股票share dealing 股票交易;股票买卖share in issue 已发行股份;已发行股票share investment 股份投资share margin lending “按仓”贷款share market 股票市场share of a business 生意股份share of mutual fund 互惠基金股份share of profit 利润份额share on local register 当地登记册所载的股份share option 股票期权;认股权;股份认购权share pending listing 等候上市股份share premium account 股份溢价账户share price 股票价格share registrar 股票过户登记处;过户处;股份登记员share repurchase 股份购回;股份回购share rights 股权share split 股份拆细;拆股share transfer 股票过户share warrant 认股权证share warrant to bearer 不记名认股权证shareholder 股东shareholders' fund 股东资金shareholding 持有股份sharp increase 急剧上升;暴升;飞涨shell company 空壳公司shell reactivation “借壳”上市;“买壳”上市;空壳公司重新活动shenzhen foreign exchange trading centre 深圳外汇交易中心shenzhen securities registration company limited 深圳证券登记公司shenzhen stock exchange 深圳证券交易所shinhan finance limited 新韩金融有限公司shizuoka bank, ltd. 静冈银行short 空头;空仓;淡仓;卖空;超卖short call 认购期权淡仓short covering 补仓;补空仓;空头补进short futures contract 淡仓期货合约short notice 短期通知书short notice and time deposit 短期通知及定期存款short of liquidity 资金紧绌short position 空仓;淡仓;空头;短盘short sell securities 卖空证券short selling 卖空;沽空;抛空short selling system 证券沽空制度short-dated securities 短期证券shortfall 差额;不足之数shortfall in expenditure 实际开支低于原来预算short-term deposit 短期存款short-term indicator of economic condition 短期经济指标short-term interest rate 短期利率short-term paper 短期票据short-term rating 短期评级shroff account number 收款账号siam commercial bank public company limited 汇商银行significant shareholder 持有大量股票的股东;重要股东silent partner 只拥有股权而不参与业务的合伙人;隐名合伙人silver 银silver currency 银制流通货币silver standard 银本位;银本位制simple guide to bankruptcy, a 《破产案简介》simple guide to compulsory winding-up of companies, a 《强制公司清盘案简介》simple interest 单利;以单息计算的利息simple portfolio 简单的投资组合simultaneous econometric model 联立计量经济模式simultaneous equation model 联立方程模式sin hua bank limited 新华银行sin hua finance company limited 新华财务有限公司singapore dollar [sgd] 新加坡元singapore international monetary exchange 新加坡国际金融交易所singapore stock exchange 新加坡证券交易所singapore strait times index 《新加坡海峡时报》指数single assessment 单一评税single entry system 单式簿记制度single equation model 单方程模式single fund 单一基金single market, the [europe] 单一市场〔欧洲〕single parent allowance 单亲免税额single premium 整付保费single premium policy 整付保费保单single tender 单一投标sinking fund 偿债基金size criterion [banking] 资产限额准则〔银行业〕size of issue 发行量size of the economy 经济规模slacken 放缓;呆滞slow down 减慢;放缓;退减slow trading 交投呆滞sluggish 市势疲弱;市况呆滞sluggish turnover 交投呆滞slump 急跌;下挫small and medium enterprise [sme] 中小型企业small and medium enterprises committee 中小型企业委员会small bankruptcy 小额破产案small business 小型企业small claims tribunal 小额钱债审裁处small claims tribunal suitors fund account 小额钱债审裁处诉讼人储存金账户small depositor 小额存户small economy 小规模经济体系small estate 小额遗产smart card 智能卡;聪明卡snake 蛇形浮动;蛇形浮动汇率制soaring market 旺市;好市;暴涨的市况social security assistance index of prices 社会保障援助价格指数social welfare expenditure 社会福利开支societe de compensation des marches conditionels  巴黎期权市场结算所societe generale 法国兴业银行societe generale asia limited 法国兴业亚洲有限公司society of actuaries of the united states of america  美国精算师公会society of chinese accountants and auditors 华人会计师公会society of worldwide interbank financial telecommunication [swift] 环球银行财务电讯协会socio-economic infrastructure 社会经济基础建设soft currency 软货币;弱势货币soft dollar practice 收取非金钱利益的做法soft market 市况疲软sole executor 唯一的遗嘱执行人sole proprietor 独资经营者sole proprietorship 独资经营sole trustee 单一受托人soliciting business 招揽生意solid growth 稳健增长solvency 偿债能力;偿付能力solvency fund 无偿付能力赔偿基金source of additional revenue 额外收入。

财经专业英语词汇(V财经专业英语词汇(V-W)财经专业英语词汇(V-W)valid and subsisting bill 有效及现存的汇票valid bilateral netting arrangement 有效双边净额结算协议valid branch registration certificate 有效分行登记证valid business registration certificate 有效商业登记证valid discharge 有效责任解除valid endorsement 有效背书valuable consideration 有值代价valuation 估值;估价valuation balance sheet 估值资产负债表valuation date 估值日期valuation effect 估值效果valuation list 估价册valuation of assets 资产估值valuation report 估值报告valuation strain 估值负担value 价值value at cost 成本值value index 价值指数value index for construction works 建筑工程价格指数value of cash-sweep chances 现金彩票活动的中彩机会的价值value of cash-sweep tickets sold 现金彩票活动售出的彩票价值value of construction works 建筑工程总值value of distribution 分派价值value of export 出口货值value of gross output 总产量的价值value of import 进口货值value of property 财产的价值value of re-export 转口货值value of sum assured 承保款项值value of the consideration 代价所值value-added product 附加值产品value-added tax [vat] 增值税value-at-risk model 风险数值模式value-for-money 衡工量值;合乎经济原则;合乎经济效益;物有所值value-for-money audit 衡工量值式审计;衡工量值式核数value-for-money criterion 衡工量值的准则value-for-money study 衡工量值式研究valuer 估价员;估价师;估值师value-weighted index 价值加权指数variable 变数;变动因素variable interest investment 浮息投资variable interest securities 浮息证券variation 波动variation of contract 更改合约的条款vendor 卖方;出售人;售卖人venture capital 创业资金;风险资本venture capital fund 创业资本基金venture capital market 创业资金市埸venture company 创业公司very substantial acquisition 非常重大的收购事项vested annuity 既得年金vested estate 既得产业权vested interest 既得权益;既得利益vested liabilities 既有负债vested reversionary bonus 既得的复归红利vesting date 归属日期vesting order 归属令viability 健全性;稳健性;财政上可行性vienna stock exchange 维也纳证券交易所vietnam finance company limited 越南财务有限公司virement 转帐visible trade 有形贸易visible trade account 有形贸易帐visible trade deficit 有形贸易逆差visible trade gap 有形贸易差额volatility 波动不定;股价波动volume index 物量指数volume of business 营业总额volume of trading 交投量;交易量volume of transaction 成交额;交易量voluntarily surrender 自愿交回voluntary agreement 无偿协议voluntary chargeable agreement for sale 可予征收印花税的无偿买卖协议voluntary code 自律守则voluntary disclosure of tax evasion 自动表白逃税情形voluntary disposition 无偿产权处置voluntary liquidation 自动清盘voluntary settlement 无偿授产安排voluntary winding-up 自动清盘vote 拨款vote on account 临时拨款vote on account warrant 临时拨款令;临时支款授权书vote on supplementary warrant 追加备付款项令;追加支款授权书voting of fund 拨款voting share 有表决权股份voucher 凭单;支款凭证;付款凭证;付款凭单wage 工资waiver 宽免;豁免;放弃waiver of fees 宽免费用waiver of loan 免除还款warehouse 仓库warrant 认股权证;拨款令;支款授权书warrant exercisable 可行使的认股权证warrant exercised [listing method] 行使认股权证〔上市方式〕warrant issue prospectus 认股权证发行章程warrant stock 认股权证;认购股权证书warrant to subscribe 认购权证wash sale 虚假销售;对销交易wayfoong credit limited wayfoong finance ltd. wayward and erratic movement 反复及不正常的变动weak 疲弱;偏软weak consumer spending 消费疲弱wealth effect 财富效应weight 权数weighted average 加权平均数weighted average of exchange rate 汇率的加权平均数weighted market capitalization 加权资本市值;加权市价总值weighted mean salary 加权平均薪金weighting system of the consumer price index 消费物价指数的权数模式well-capitalized 资本雄厚wellington stock exchange 惠灵顿证券交易所west germany's commerzbank index 西德商银指数westdeutsche landesbank girozentrale 西德意志州银行〔西德银行〕western european economies of greatest reference to hong kong 与本港经济最有关系的西欧国家western industrialized economy 西方工业国家westpac banking corporation 西太平洋银行whitewashed transaction 清洗交易wholesale bank 批发银行wholesale banking 批发银行业务wholesale tax 批发税wholly-owned subsidiary 全资附属公司w.i. carr indosuez capital asia limited 惠嘉融资亚洲有限公司wider margin of variation 较大幅度的偏差width of two tax bands 两个税阶的幅度wilful evasion 蓄意逃税will 遗嘱;意愿winding-up 清盘;结束winding-up order 清盘令winding-up petition 清盘呈请winding-up proceeding 清盘程序windsor declaration 《温莎声明》wing hang bank ltd. 永亨银行有限公司wing hang finance company limited 永亨财务有限公司wing lung bank limited 永隆银行有限公司wing lung finance limited 永隆财务有限公司winnipeg commodities exchange 温尼伯商品交易所winnipeg commodity clearing limited 温尼伯商品结算有限公司with recourse letter of credit 有追索权信用证withdrawal of offer 撤回要约withholding tax 预扣税;预扣税项without-profit business 不可分红业务with-profit business 可分红业务workforce 工作人口working balance 周转余额;营运结余working capital 营运资金;周转资金working group on corporate governance [stock exchange of hong kong limited] 公司管治工作小组〔香港联合交易所有限公司〕working group on financial facilities 财政设施工作小组working group on hong kong's economic relationship with china 香港与中国经济关系工作小组working group on new market development [stock exchange of hong kong limited] 新市场发展工作小组〔香港联合交易所有限公司〕working party on financial disclosure 财务资料披露工作小组working party on payment and settlement system  支付及交收系统工作小组working population 工作人口works account 工程帐world bank 世界银行world bank group 世界银行集团world bank/international monetary fund annual meeting 世界银行/国际货币基金组织年会world competitiveness report 19xx [published by the international institute for management development and the world economic forum] 《一九xx年世界竞争力报告书》〔由国际管理发展研究所与世界经济论坛出版〕world economic forum 世界经济论坛world gold council 世界黄金协会world trade organization [wto] 世界贸易组织〔世贸组织〕worldwide profit 来自世界各地的利润wound-up company 清盘公司write back 拨回;回记write down 减记write off 注销;撇帐write up 增记written commitment 书面承担written-down value 折余价值written-down value on disposal 变卖时折余价值财经专业英语词汇(V-W) 相关内容:。
财经专业英语教程第五版宋德富答案1、16.Lily is a lovely girl. We all want to ________ friends with her. [单选题] *A.haveB.make(正确答案)C.doD.take2、Just use this room for the time being ,and we’ll offer you a larger one _______it becomes available [单选题] *A. as soon as(正确答案)B unless .C as far asD until3、It’s usually windy in spring, ______ you can see lots of people flying kites.()[单选题] *A. so(正确答案)B. orC. butD. for4、Hurry up,?or we’ll _______ class. [单选题] *A. be late for(正确答案)B. late forC. late withD. be late with5、--Miss Li, could you please help me _______ math problem?--OK. Let me try. [单选题] *A. look upB. work out(正确答案)C. set upD. put up6、We can see ______ stars at night if it doesn’t rain. [单选题] *A. a thousand ofB. thousandsC. thousand ofD. thousands of(正确答案)7、A survey of the opinions of students()that they admit several hours of sitting in front of the computer harmful to health. [单选题] *A. show;areB. shows ;is(正确答案)C.show;isD.shows ;are8、Jim, it’s dark now. Please _______ the light in the room. [单选题] *A. turn on(正确答案)B. turn upC. turn offD. turn down9、I don't know the man _____ you are talking about. [单选题] *A. who'sB. whose(正确答案)C. whomD. which10、There are trees on both sides of the broad street. [单选题] *A. 干净的B. 狭窄的C. 宽阔的(正确答案)D. 宁静的11、My father can?_______ a little English. [单选题] *A. speak(正确答案)B. sayC. talkD. tell12、46.The pants look cool.You can ________. [单选题] *A.try it onB.try on itC.try them on(正确答案)D.try on them13、My mother’s birthday is coming. I want to buy a new shirt ______ her.()[单选题] *A. atB. for(正确答案)C. toD. with14、You can buy some pieces of bread from "_______". [单选题] *A. Bakery(正确答案)B. Travel AgencyC. LaundryD. Ticket Office15、Which is _______ city, Shanghai, Beijing or Chengdu? [单选题] *A. largeB. largerC. largestD. the largest(正确答案)16、The manager isn’t in at the moment. May I _______ a message? [单选题] *A. take(正确答案)B. makeC. haveD. keep17、6.Hi, boys and girls. How are you ________ your posters for the coming English Festival at school? [单选题] *A.getting onB.getting offC.getting with (正确答案)D.getting18、What surprised me ______ was that he succeeded. [单选题] *A. most(正确答案)B. mostlyC. almostD. at most19、It’s so nice to hear from her again. ______, we last met more than thirty year ago [单选题] *A. What ‘s wordB. That’s to sayC. Go aheadD. Believe it or not(正确答案)20、Is there going to ______ a football match in the stadium next month?()[单选题] *A. beingB. haveC. be(正确答案)D. having21、37.It’s fun _________ a horse with your best friends on the grass. [单选题] *A.to ride (正确答案)B.ridingC.ridesD.ride22、The carbon we produce when we breathe is much less than()produced by a car. [单选题] *A. oneB. itC. that(正确答案)D. those23、I saw the boy _______?the classroom. [单选题] *A. enter intoB. enter(正确答案)C. to enter intoD. to enter24、The paper gives a detailed()of how to create human embryos (胚胎)by cloning. [单选题] *A. intentionB. description(正确答案)C. affectionD. effort25、Mum is ill. I have to _______ her at home. [单选题] *A. look after(正确答案)B. look forC. look outD. look forward to26、The commander said that two _____ would be sent to the Iraqi front line the next day. [单选题] *A. women's doctorB. women doctorsC. women's doctorsD. women doctor(正确答案)27、Could you please ______ why you can’t come to attend the meeting? [单选题] *A. explain(正确答案)B. understandC. giveD. reach28、He does ______ in math.()[单选题] *A. goodB. betterC. well(正确答案)D. best29、( ) What _____ fine weather we have these days! [单选题] *A. aB. theC. /(正确答案)D. an30、If you do the same thing for a long time, you'll be tired of it. [单选题] *A. 试图B. 努力C. 厌倦(正确答案)D. 熟练。