企业所得税汇算清缴申报表A类 英文版
- 格式:xls
- 大小:51.00 KB
- 文档页数:3
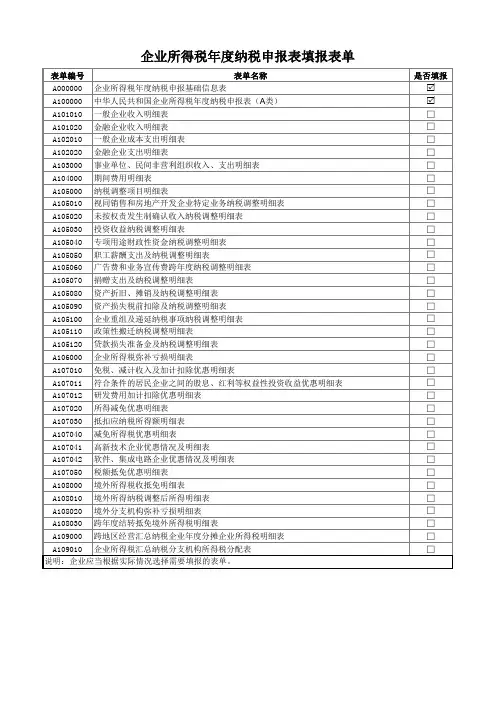

中华人民共和国企业所得税年度纳税申报表(A类,2017年版)国家税务总局2017年12月目录中华人民共和国企业所得税年度纳税申报表封面 (1)《中华人民共和国企业所得税年度纳税申报表(A类,2017年版)》封面填报说明 (2)企业所得税年度纳税申报表填报表单 (3)《企业所得税年度纳税申报表填报表单》填报说明 (4)A000000企业基础信息表 (9)A000000《企业基础信息表》填报说明 (10)A100000中华人民共和国企业所得税年度纳税申报表(A类) (13)A100000《中华人民共和国企业所得税年度纳税申报表(A类)》填报说明 (14)A101010一般企业收入明细表 (21)A101010《一般企业收入明细表》填报说明 (22)A101020金融企业收入明细表 (25)A101020《金融企业收入明细表》填报说明 (26)A102010一般企业成本支出明细表 (29)A102010《一般企业成本支出明细表》填报说明 (30)A102020金融企业支出明细表 (33)A102020《金融企业支出明细表》填报说明 (34)A103000事业单位、民间非营利组织收入、支出明细表 (37)A103000《事业单位、民间非营利组织收入、支出明细表》填报说明 (38)A104000期间费用明细表 (42)A104000《期间费用明细表》填报说明 (43)A105000纳税调整项目明细表 (45)A105000《纳税调整项目明细表》填报说明 (46)A105010视同销售和房地产开发企业特定业务纳税调整明细表 (55)A105010《视同销售和房地产开发企业特定业务纳税调整明细表》填报说明 (56)A105020未按权责发生制确认收入纳税调整明细表 (61)A105020《未按权责发生制确认收入纳税调整明细表》填报说明 (62)A105030投资收益纳税调整明细表 (64)A105030《投资收益纳税调整明细表》填报说明 (65)A105040专项用途财政性资金纳税调整明细表 (67)A105040《专项用途财政性资金纳税调整明细表》填报说明 (68)A105050职工薪酬支出及纳税调整明细表 (70)A105050《职工薪酬支出及纳税调整明细表》填报说明 (71)A105060广告费和业务宣传费跨年度纳税调整明细表 (76)A105060《广告费和业务宣传费跨年度纳税调整明细表》填报说明 (77)A105070捐赠支出及纳税调整明细表 (79)A105070《捐赠支出及纳税调整明细表》填报说明 (80)A105080资产折旧、摊销及纳税调整明细表 (83)A105080《资产折旧、摊销及纳税调整明细表》填报说明 (85)A105090资产损失税前扣除及纳税调整明细表 (89)A105090《资产损失税前扣除及纳税调整明细表》填报说明 (90)A105100企业重组及递延纳税事项纳税调整明细表 (93)A105100《企业重组及递延纳税事项纳税调整明细表》填报说明 (94)A105110政策性搬迁纳税调整明细表 (98)A105110《政策性搬迁纳税调整明细表》填报说明 (99)A105120特殊行业准备金及纳税调整明细表 (102)A105120《特殊行业准备金及纳税调整明细表》填报说明 (103)A106000企业所得税弥补亏损明细表 (107)A106000《企业所得税弥补亏损明细表》填报说明 (108)A107010免税、减计收入及加计扣除优惠明细表 (110)A107010《免税、减计收入及加计扣除优惠明细表》填报说明 (111)A107011符合条件的居民企业之间的股息、红利等权益性投资收益优惠明细表 (117)A107011《符合条件的居民企业之间的股息、红利等权益性投资收益优惠明细表》填报说明 (118)A107012研发费用加计扣除优惠明细表 (121)A107012《研发费用加计扣除优惠明细表》填报说明 (123)A107020所得减免优惠明细表 (129)A107020《所得减免优惠明细表》填报说明 (130)A107030抵扣应纳税所得额明细表 (136)A107030《抵扣应纳税所得额明细表》填报说明 (137)A107040减免所得税优惠明细表 (141)A107040《减免所得税优惠明细表》填报说明 (142)A107041高新技术企业优惠情况及明细表 (152)A107041《高新技术企业优惠情况及明细表》填报说明 (153)A107042软件、集成电路企业优惠情况及明细表 (157)A107042《软件、集成电路企业优惠情况及明细表》填报说明 (159)A107050税额抵免优惠明细表 (165)A107050《税额抵免优惠明细表》填报说明 (166)A108000境外所得税收抵免明细表 (169)A108000《境外所得税收抵免明细表》填报说明 (170)A108010境外所得纳税调整后所得明细表 (174)A108010《境外所得纳税调整后所得明细表》填报说明 (175)A108020境外分支机构弥补亏损明细表 (177)A108020《境外分支机构弥补亏损明细表》填报说明 (178)A108030跨年度结转抵免境外所得税明细表 (180)A108030《跨年度结转抵免境外所得税明细表》填报说明 (181)A109000跨地区经营汇总纳税企业年度分摊企业所得税明细表 (183)A109000《跨地区经营汇总纳税企业年度分摊企业所得税明细表》填报说明 (184)A109010企业所得税汇总纳税分支机构所得税分配表 (187)A109010《企业所得税汇总纳税分支机构所得税分配表》填报说明 (188)中华人民共和国企业所得税年度纳税申报表(A类 , 2017年版)税款所属期间:年月日至年月日纳税人统一社会信用代码:□□□□□□□□□□□□□□□□□□(纳税人识别号)纳税人名称:金额单位:人民币元(列至角分)谨声明:此纳税申报表是根据《中华人民共和国企业所得税法》《中华人民共和国企业所得税法实施条例》以及有关税收政策和国家统一会计制度的规定填报的,是真实的、可靠的、完整的。

汇算清缴英文版指南As a foreign individual or business operating in China, the process of "汇算清缴" (huì suàn qīng jiǎo) or "final settlement and clearance" of taxes can be a complex and daunting task. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the 汇算清缴 process in English, to help you navigate through the intricacies and ensure compliance with Chinese tax regulations.作为在中国经营的外国个人或企业,“汇算清缴”(huì suàn qīng jiǎo)即“最终结算和清算”税款的过程可能是一个复杂而艰巨的任务。
这份指南旨在全面介绍汇算清缴程序的英文版,帮助您在复杂的税收法规中航行,并确保您遵守中国的税收法规。
The first step in the "final settlement and clearance" process is to gather all relevant financial and tax documents from the previous year. This includes income statements, expense records, tax receipts, and any other documentation related to your financial activities in China.“最终结算和清算”过程的第一步是收集去年所有相关的财务和税务文件。

汇算清缴英文版指南English Response:Reconciliation and Clear Settlement.Reconciliation and clear settlement (RCS) is a process of reconciling and clearing transactions between two or more parties. It is typically used in financial transactions, such as banking, investments, and trade. The purpose of RCS is to ensure that both parties have a complete and accurate record of all transactions, and that all outstanding payments have been settled.The RCS process typically involves the following steps:1. The parties involved agree on the terms of the RCS, including the scope of the reconciliation, the frequency of reconciliation, and the method of settlement.2. The parties exchange data on all transactions thathave occurred during the reconciliation period.3. The data is reconciled to identify any discrepancies or errors.4. The discrepancies or errors are corrected and the data is re-reconciled.5. The parties agree on the final reconciled data and settle any outstanding payments.RCS can be a complex and time-consuming process, but it is essential for ensuring that both parties have a complete and accurate record of all transactions. It can also help to reduce errors and fraud, and improve the efficiency of financial transactions.Here are some of the benefits of RCS:Ensures that both parties have a complete and accurate record of all transactions.Reduces errors and fraud.Improves the efficiency of financial transactions.Helps to resolve disputes.Reconciliation and Clear Settlement in Different Industries.RCS is used in a variety of industries, including:Banking: RCS is used to reconcile and cleartransactions between banks and their customers. This includes transactions such as deposits, withdrawals, checks, and electronic payments.Investments: RCS is used to reconcile and clear transactions between investors and brokers. This includes transactions such as buying and selling stocks, bonds, and mutual funds.Trade: RCS is used to reconcile and clear transactionsbetween buyers and sellers of goods and services. This includes transactions such as purchase orders, invoices,and payments.The specific RCS process used in each industry may vary, but the overall goal is the same: to ensure that bothparties have a complete and accurate record of all transactions, and that all outstanding payments have been settled.中文回答:汇算清缴。

2020年修订版企业所得税年度纳税申报表(A类)填报详解(三十六)跨年度结转抵免境外所得税明细表(A108030)目录一、表样二、表单基本情况三、表单填报详解四、表内、表间关系五、填报案例一、表样二、表单基本情况本表适用于取得境外所得的纳税人填报。
纳税人应根据税法、《财政部国家税务总局关于企业境外所得税收抵免有关问题的通知》(财税〔2009〕125号)、《国家税务总局关于发布〈企业境外所得税收抵免操作指南〉的公告》(国家税务总局公告2010年第1号)、《财政部国家税务总局关于我国石油企业从事油(气)资源开采所得税收抵免有关问题的通知》(财税〔2011〕23号)、《财政部税务总局关于完善企业境外所得税收抵免政策问题的通知》(财税〔2017〕84号)规定,填报本年发生的来源于不同国家或地区的境外所得按照我国税收法律、法规的规定可以抵免的所得税额,并按国(地区)别逐行填报。
三、表单填报详解1.第2列至第7列“前五年境外所得已缴所得税未抵免余额”:填报纳税人前五年境外所得已缴纳的企业所得税尚未抵免的余额。
2.第8列至第13列“本年实际抵免以前年度未抵免的境外已缴所得税额”:填报纳税人用本年未超过境外所得税款抵免限额的余额抵免以前年度未抵免的境外已缴所得税额。
3.第14列至第19列“结转以后年度抵免的境外所得已缴所得税额”:填报纳税人以前年度和本年未能抵免并结转以后年度抵免的境外所得已缴所得税额。
四、表内、表间关系(一)表内关系1.第7列=第2+3+…+6列。
2.第13列=第8+9+…+12列。
3.第19列=第14+15+…+18列。
(二)表间关系1.若选择“分国(地区)不分项”的境外所得抵免方式,第13列各行=表A108000第14列相应行次;若选择“不分国(地区)不分项”的境外所得抵免方式,第13列合计=表A108000第1行第14列。
2.若选择“分国(地区)不分项”的境外所得抵免方式,第18列各行=表A108000第10列相应行次-第12列相应行次(当表A108000第10列相应行次大于第12列相应行次时填报);若选择“不分国(地区)不分项”的境外所得抵免方式,第18列合计=表A108000第1行第10列-第1行第12列(当表A108000第1行第10列次大于第1行第12列时填报)。
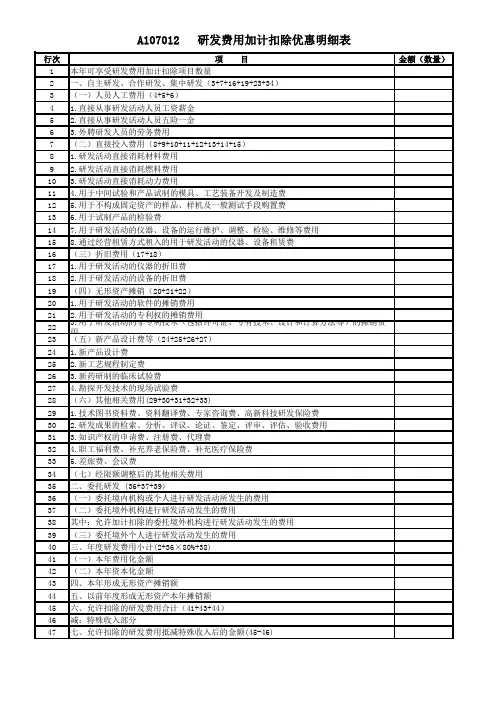
行次项 目金额(数量)1本年可享受研发费用加计扣除项目数量2一、自主研发、合作研发、集中研发(3+7+16+19+23+34)3(一)人员人工费用(4+5+6)41.直接从事研发活动人员工资薪金52.直接从事研发活动人员五险一金63.外聘研发人员的劳务费用7(二)直接投入费用(8+9+10+11+12+13+14+15)81.研发活动直接消耗材料费用92.研发活动直接消耗燃料费用103.研发活动直接消耗动力费用114.用于中间试验和产品试制的模具、工艺装备开发及制造费125.用于不构成固定资产的样品、样机及一般测试手段购置费136.用于试制产品的检验费147.用于研发活动的仪器、设备的运行维护、调整、检验、维修等费用158.通过经营租赁方式租入的用于研发活动的仪器、设备租赁费16(三)折旧费用(17+18)171.用于研发活动的仪器的折旧费182.用于研发活动的设备的折旧费19(四)无形资产摊销(20+21+22)201.用于研发活动的软件的摊销费用212.用于研发活动的专利权的摊销费用223.用于研发活动的非专利技术(包括许可证、专有技术、设计和计算方法等)的摊销费用23(五)新产品设计费等(24+25+26+27)241.新产品设计费252.新工艺规程制定费263.新药研制的临床试验费274.勘探开发技术的现场试验费28(六)其他相关费用(29+30+31+32+33)291.技术图书资料费、资料翻译费、专家咨询费、高新科技研发保险费302.研发成果的检索、分析、评议、论证、鉴定、评审、评估、验收费用313.知识产权的申请费、注册费、代理费324.职工福利费、补充养老保险费、补充医疗保险费335.差旅费、会议费34(七)经限额调整后的其他相关费用35二、委托研发 (36+37+39)36(一)委托境内机构或个人进行研发活动所发生的费用37(二)委托境外机构进行研发活动发生的费用38其中:允许加计扣除的委托境外机构进行研发活动发生的费用39(三)委托境外个人进行研发活动发生的费用40三、年度研发费用小计(2+36×80%+38)41(一)本年费用化金额42(二)本年资本化金额43四、本年形成无形资产摊销额44五、以前年度形成无形资产本年摊销额45六、允许扣除的研发费用合计(41+43+44)46减:特殊收入部分47七、允许扣除的研发费用抵减特殊收入后的金额(45-46)A107012 研发费用加计扣除优惠明细表48减:当年销售研发活动直接形成产品(包括组成部分)对应的材料部分49减:以前年度销售研发活动直接形成产品(包括组成部分)对应材料部分结转金额50八、加计扣除比例及计算方法L1本年允许加计扣除的研发费用总额(47-48-49)L1.1其中:第四季度允许加计扣除的研发费用金额L1.2前三季度允许加计扣除的研发费用金额(L1-L1.1)51九、本年研发费用加计扣除总额(47-48-49)×5052十、销售研发活动直接形成产品(包括组成部分)对应材料部分结转以后年度扣减金额(当47-48-49≥0,本行=0;当47-48-49<0,本行=47-48-49的绝对值)。


中华人民共和国企业所得税年度纳税申报表(A类 , 2014年版)税款所属期间:年月日至年月日纳税人识别号:□□□□□□□□□□□□□□□□□□纳税人名称:金额单位:人民币元(列至角分)谨声明:此纳税申报表是根据《中华人民共和国企业所得税法》、《中华人民共和国企业所得税法实施条例》、有关税收政策以及国家统一会计制度的规定填报的,是真实的、可靠的、完整的。
法定代表人(签章): 年月日企业所得税年度纳税申报表填报表单中华人民共和国企业所得税年度纳税申报表(A类)一般企业成本支出明细表金融企业支出明细表事业单位、民间非营利组织收入、支出明细表期间费用明细表纳税调整项目明细表视同销售和房地产开发企业特定业务纳税调整明细表未按权责发生制确认收入纳税调整明细表范文范例参考投资收益纳税调整明细表范文范例参考专项用途财政性资金纳税调整明细表范文范例参考职工薪酬纳税调整明细表范文范例参考WORD格式整理版A105060广告费和业务宣传费跨年度纳税调整明细表捐赠支出纳税调整明细表范文范例参考范文范例参考范文范例参考WORD格式整理版A105090资产损失税前扣除及纳税调整明细表资产损失(专项申报)税前扣除及纳税调整明细表范文范例参考范文范例参考政策性搬迁纳税调整明细表WORD格式整理版A106000企业所得税弥补亏损明细表范文范例参考WORD格式整理版A107010免税、减计收入及加计扣除优惠明细表符合条件的居民企业之间的股息、红利等权益性投资收益优惠明细表范文范例参考范文范例参考WORD格式整理版A107013金融、保险等机构取得的涉农利息、保费收入优惠明细表研发费用加计扣除优惠明细表范文范例参考所得减免优惠明细表范文范例参考范文范例参考抵扣应纳税所得额明细表范文范例参考减免所得税优惠明细表税额抵免优惠明细表范文范例参考境外所得税收抵免明细表范文范例参考境外所得纳税调整后所得明细表范文范例参考境外分支机构弥补亏损明细表范文范例参考跨年度结转抵免境外所得税明细表范文范例参考WORD格式整理版A109000跨地区经营汇总纳税企业年度分摊企业所得税明细表WORD格式整理版A109010企业所得税汇总纳税分支机构所得税分配表税款所属期间:年月日至年月日范文范例参考《中华人民共和国企业所得税年度纳税申报表(A类,2014年版)》封面填报说明《中华人民共和国企业所得税年度纳税申报表(A类,2014年版)》(以下简称申报表)适用于实行查账征收企业所得税的居民纳税人(以下简称纳税人)填报。
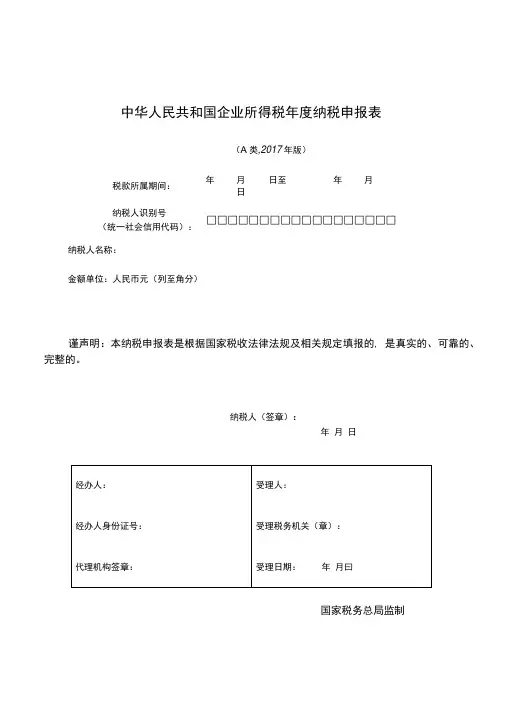
中华人民共和国企业所得税年度纳税申报表
(A类,2017年版)
税款所属期间:年月日至年月日
纳税人识别号
(统一社会信用代码):
□□□□□□□□□□□□□□□□□□纳税人名称:
金额单位:人民币元(列至角分)
谨声明:本纳税申报表是根据国家税收法律法规及相关规定填报的, 是真实的、可靠的、完整的。
纳税人(签章):
年月日
国家税务总局监制
企业所得税年度纳税申报表填报表单
AOOOOOO 企业所得税年度纳税申报基础信息表
A105050 职工薪酬支出及纳税调整明细表
A105090 资产损失税前扣除及纳税调整明细表
A106000 企业所得税弥补亏损明细表
A107012 研发费用加计扣除优惠明细表
A107012 研发费用加计扣除优惠明细表
A107020 所得减免优惠明细表
A107020 所得减免优惠明细表
A107040 减免所得税优惠明细表
A107041 高新技术企业优惠情况及明细表
A107041 高新技术企业优惠情况及明细表
A107042
软件、集成电路企业优惠情况及明细表
获利年度开始计算优惠期年度 1 获利年度开始计算优惠期年度 2
税收优惠有关情况
税收优惠基本信息
减免方式1 减免方式2
A108020 境外分支机构弥补亏损明细表。

2021年度企业所得税汇算清缴之《A100000企业所得税年度纳税申报表(A类)》填报详解目录一、表样二、企业所得税汇算清缴及年度纳税申报表基本知识三、表单基本情况四、表单填报详解五、表内、表间关系六、填报要点一、表样二、企业所得税汇算清缴及年度纳税申报表基本知识(一)企业所得税汇算清缴1、汇算清缴的概念及时限企业所得税汇算清缴是指纳税人自纳税年度终了之日起5个月内或实际经营终止之日起60日内、依照税收法律、法规、规章及其他有关企业所得税的规定、自行计算本纳税年度应纳税所得额和应纳所得税额、根据月度或季度预缴企业所得税的数额、确定该纳税年度应补或者应退税额、并填写企业所得税年度纳税申报表、向主管税务机关办理企业所得税年度纳税申报、提供税务机关要求提供的有关资料、结清全年企业所得税税款的行为。
企业所得税汇算清缴16字口诀:算准三额(利润总额、应纳税所得额、应纳所得税额)、备齐资料、准期申报、结清税款。
2、汇算清缴的范围和对象凡在纳税年度内从事生产、经营(包括试生产、试经营),或在纳税年度中间终止经营活动的纳税人,无论是否在减税、免税期间,也无论盈利或亏损,均应按照企业所得税法及其实施条例和企业所得税汇算清缴管理办法的有关规定进行企业所得税的汇算清缴。
企业所得税汇算清缴的具体对象包括:(1)查账征收纳税人;(2)核定征收纳税人(核定应税所得率);(3)按《公司法》、《企业破产法》等规定需要进行清算的企业;(4)企业重组中需要清算处理的企业。
注:实行核定定额征收企业所得税的纳税人,不进行汇算清缴。
3、汇算清缴填报申报表的选择(1)《中华人民共和国企业所得税年度纳税申报表(A类,2017年版)》(2021年修订版)及相关附表。
适用纳税人类型∶查账征收居民企业(含跨地区经营汇总纳税企业总机构)。
(2)《中华人民共和国企业所得税月(季)度预缴和年度纳税申报表(B类,2018年版)》及相关附表。
适用纳税人类型:核定征收居民企业。
The Law of the People’s Republic of China on Enterprise Income Tax Table of ContentChapter One General ProvisionsChapter Two Taxable IncomeChapter Three Payable TaxChapter Four Preferential Tax TreatmentChapter Five Tax Withheld at SourceChapter Six Special T ax Payment AdjustmentChapter Seven Administration of Tax Levying and CollectionChapter Eight Supplementary ProvisionsChapter One General ProvisionsArticle 1 Taxpayers of enterprise income tax shall be enterprises and other organizations that obtain income within the People’s Republic of China (hereinafter referred to as “Enterprises〞) and shall pay enterprise income tax in accordance with the provisions of this Law.This Law shall not apply to wholly individually-owned enterprises and partnership enterprises.Article 2 Enterprises are divided into resident enterprises and non-resident enterprises.For the purposes of this Law, the term “resident enterprises〞shall refer to Enterprises that are set up in China in accordance with the law, or that are set up in accordance with the law of the foreign country (region) whose actual administration institution is in China.For the purposes of this Law, the term “non-resident enterprises〞shall refer to Enterprises that are set up in accordance with the law of the foreign country (region) whose actual administration institution is outside China, but they have set up institutions or establishments in China or they have income originating from China without setting up institutions or establishments in China.Article 3 Resident enterprises shall pay enterprise income tax originating both within and outside China.Non-resident enterprises that have set up institutions or premises in China shall pay enterprise income tax in relation to the income originating from China obtained by their institutions or establishments, and the income incurred outside China but there is an actual relationship with the institutions or establishments set up by such enterprises.Where non-resident enterprises that have not set up institutions or establishments in China, or where institutions or establishments are set up but there is no actual relationship with the income obtained by the institutions or establishments set up by such enterprises, they shall pay enterprise income tax in relation to the income originating from China.Article 4 The rate of enterprise income tax shall be 25%.Non-resident enterprises that have obtained income in accordance with the provisions ofParagraph Three of Article 3 hereof, the applicable tax rate shall be 20%.Chapter Two Taxable IncomeArticle 5 The balance derived from the total income in each taxable year of Enterprises, after deduction of the non-taxable income, tax exempted income, other deductions and the making up of losses of previous years shall be the taxable income.Article 6 Income obtained by Enterprises from various sources in monetary and non-monetary terms shall be the total income, including1.income from sale of goods;2.income from provision of labour services;3.income from transfer of property;4.income from equity investment such as dividend and bonus;5.interest income;6.rental income;7.income from royalties;8.income from donations; and9.other income.Article 7 The following income from the total income shall not be taxable1.financial funding;2.administrative fees and government funds obtained and included in financial management in accordance with the law; and3.other non-taxable income prescribed by the State Council.Article 8 Reasonable expenses that are relevant to the income actually incurred and obtained by Enterprises, including costs, fees, tax payments, losses and other fees may be deducted from the taxable income.Article 9 In relation to the expenses from charitable donations incurred by Enterprises, the portion within 12% of the total annual profit may be deducted from the taxable income.Article 10 The following expenses may not be deducted from the taxable income1.income from equity investment paid to investors such as dividend and bonus;2.payment of enterprise income tax;te payment fines;4.penalties; fines and losses from confiscated property;5.expenses from donations other than those prescribed in Article 9 hereof;6.sponsorship fees;7.expenses for non-verified provisions; and8.other expenses irrelevant to the income obtained.Article 11 Where Enterprises compute the taxable income, the depreciation of fixed assets calculated in accordance with provisions may be deducted.No depreciation may be deducted for the following fixed assets1.fixed assets other than premises and buildings that have not yet been used;2.fixed assets leased from other parties by means of business lease;3.fixed assets leased to other parties by means of lease financing;4.fixed assets that have been depreciated in full but are still in use;5.fixed assets that are irrelevant to business activities;nd credited as fixed assets after independent price valuation;7.other fixed assets whose depreciation may not be calculated.Article 12 In Enterprises compute the taxable income, the amortization of intangible assets calculated in accordance with provisions may be deducted.The amortization of the following intangible assets may not be deducted1.the fees for self development of intangible assets that have been deducted from the taxable income;2.self-created goodwill;3.intangible assets that are irrelevant to business activities; and4.other intangible assets whose amortization fee may not be calculated.Article 13 Where Enterprises calculate taxable income, the following expenses incurred by Enterprises as long-term fees to be amortized and that are amortized in accordance with provisions may be deducted1.reconstruction expenses for fixed assets that have been depreciated in full;2.reconstruction expenses for fixed assets leased from other parties;3.heavy repair expenses of fixed assets; and4.other expenses that shall be treated as long-term amortization fees.Article 14 During the period when Enterprises invest outside the territory, the cost of investment in assets may not be deducted from the taxable income.Article 15 The inventory used or sold by Enterprises whose cost is calculated in accordance with provisions may be deducted from the taxable income.Article 16 Where Enterprises transfer assets, the net value thereof may be deducted from the taxable income.Article 17 Where Enterprises compute the consolidated enterprise income tax, the losses of business institutions outside the territory may not be offset by the profits of business institutions inside the territory.Article 18 Where there is a loss in a taxable year of Enterprises, it may be brought forward to the succeeding years and made up by the income of succeeding years, but the limit of bringing forward may not exceed five years.Article 19 Where non-resident enterprises obtain income provided in Paragraph Three of Article 3 hereof, the taxable income shall be calculated in accordance with the following methods1.income from equity investment such as dividend and bonus and interest income, rental income and royalties, the total income shall be the taxable income;2.income from property transfer, the balance derived from the deduction of net asset value from the total income shall be the taxable income;3.other income whose taxable income shall be calculated with reference to the previous two methods.Article 20 The income, specific scope and standard of deduction and the specific method of taxation treatment of assets prescribed in this Chapter shall be provided by the departments in charge of finance and taxation under the State Council.Article 21 In computing the taxable income, where financial and accounting treatment methods of Enterprises are inconsistent with tax laws and administrative regulations, suchtaxable income shall be computed in accordance with tax laws and administrative regulations.Chapter Three Payable TaxArticle 22 The taxable income of Enterprises shall be the balance derived from the taxable income of Enterprises multiplies the applicable rate and minus the tax amount of tax reduction and exemption pursuant to the preferential tax treatment hereof.Article 23 The income tax that has been paid outside the territory for the following income obtained by Enterprises may be offset from the payable tax of the current period. The offset limit is the payable tax calculated in accordance with provisions hereof in respect of the income of such item, the portion in excess of the offset limit may be made up by the balance of the offset amount of the current year out of the annual offset limit within the next five years1.The taxable income originating outside China by resident enterprises;2.The taxable income incurred outside China that is obtained by institutions or establishments of non-resident enterprises set up in China with an actual relationship with such institution or establishment.Article 24 Where income from equity investment such as dividend and bonus originating outside the territory of China is shared by foreign enterprises directly or indirectly controlled by resident enterprises, the portion undertaken by foreign enterprises in the actual income tax actually paid outside the territory by foreign enterprises may be offset in the offset limit prescribed in Article 23 hereof as the income tax that may be offset outside the territory by such resident enterprises.Chapter Four Preferential Tax TreatmentArticle 25 The industries and projects with key support and under encouraged development by the State may be given preferential enterprise income tax treatment.Article 26 The following income of Enterprises shall be tax-exempted income1.income from interests on government bonds;2.income from equity investment income such as dividend and bonus between qualified resident enterprises;3.income from equity investment such as dividend and bonus obtained from resident enterprises by non-resident enterprises that have set up institutions or establishments in China with an actual relationship with such institutions or establishments;4.income of qualified non-profit organizations.Article 27 The following income may be subject to exempted or reduced enterprise income tax1.income from engaging in projects of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fisheries by Enterprises;2.income from investment and operation of infrastructure projects with key state support such as habour, pier, airport, railway, highway, electricity and hydroelectricity by Enterprises;3.income from engaging in qualified projects of environmental protection and energy and water conservation;4.income from qualified transfer of technology by Enterprises; and5.income prescribed by Paragraph Three of Article 3 hereof.Article 28 Small-scale Enterprises with minimal profits that are qualified are subject to the applicable enterprise income tax rate with a reduction of 20%.High and new technology Enterprises that require key state support are subject to the applicable enterprise income tax rate with a reduction of 15%.Article 29 The autonomous authority of ethnic autonomous locality may decide on the reduction or exemption of the portion of enterprise income tax shared by the locality that shall be paid by Enterprises of the ethnic autonomous locality. Where an autonomous prefecture or autonomous county decides on the reduction or exemption, they must report to the people’s government of province, autonomous region or municipality directly under the central government for approval.Article 30 Weighted deduction may be computed in taxable income for the following expenses of Enterprises1.research and development fees incurred by Enterprises in the development of new technology, new products and new skills; and2.the wages paid by Enterprises for job placement of the disabled and of other personnel encouraged by the State.Article 31 Venture investment enterprises that engage in venture investment requiring key state support and encouragement may offset the taxable income at a certain ratio of the investment amount.Article 32 Where the fixed assets of Enterprises actually require accelerated depreciation due to technology advancement, the years of depreciation may be shortened or the accelerated depreciation method may be adopted.Article 33 The income obtained by Enterprises from the production of products in line with state industrial policies through comprehensive use of resources may be deducted from the taxable income.Article 34 The investment by Enterprises on procurement of special facilities for environmental protection, energy and water conservation and safe production may be subject to an offset tax amount at a certain ratio.Article 35 The specific measures of preferential tax treatment prescribed by this Law shall be formulated by the State Council.Article 36 Where there is a significant impact on the business activities of Enterprises pursuant to the needs of national economy and social development, or due to unexpected public incidents, the State Council may formulate the special preferential policy of enterprise income tax and report to the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress for the record.Chapter Five Tax Withheld at SourceArticle 37 The payable income tax from income obtained by non-resident enterprises in accordance with Paragraph Three of Article 3 hereof shall be subject to tax withheld atsource, with the payer as the withholding agent. The tax payment shall be withheld from the amount paid or the payable amount due from each tax payment and payable amount of the withholding agent.Article 38 In respect of the payable income tax from income obtained by non-resident enterprises from project works and labour services in China, the tax authority may designate the payer of project price or labour fee as withholding agent.Article 39 In respect of the income tax that shall be withheld in accordance with Articles 37 and 38 hereof, where the withholding agent has not withheld or fails to perform the withholding obligation in accordance with the law, the taxpayer shall pay in the place where the tax is incurred. Where the taxpayer does not pay in accordance with the law, the tax authority may pursue the payable tax amount of such taxpayer from the amount payable by the payer of other income projects in China of such taxpayer.Article 40 The withholding agent shall turn the tax payment withheld to the treasury within 7 days from the day of withholding, and submit a statement of withholding enterprise income tax to the tax authority of the place where it is located.Chapter Six Special Tax Payment AdjustmentArticle 41 The business transactions between Enterprises and their affiliates that reduce the taxable income or income of such Enterprises and their affiliates not in compliance with independent transaction principle, the taxation authority has the right to make an adjustment in accordance with reasonable methods.The cost incurred in joint development and transfer of intangible assets, or joint provision and acceptance of labour services by Enterprises and their affiliates shall be shared under the independent transaction principle in computing the taxable income.Article 42 Enterprises may report to the tax authority the pricing principle and calculation method of the transactions between their affiliates. Upon negotiation and confirmation with the Enterprises, the tax authority may reach the advance pricing arrangement.Article 43 Where Enterprises submit to the tax authority the annual enterprise income tax return, they shall enclose a statement of the annual business transactions between affiliates in respect of the business transactions of the Enterprises and their affiliates.Where the tax authority conducts affiliated business investigation, Enterprises and their affiliates, and other enterprises relevant to the affiliated business investigation shall provide the relevant information in accordance with provisions.Article 44 Where Enterprises fail to provide the information of business transactions of affiliates, or provide false and incomplete information that cannot faithfully reflect the actual affiliated business transaction, the tax authority has the right to verify its taxable income.Article 45 Where Enterprises controlled by resident enterprises or resident enterprises and Chinese residents in the country (region) where the actual tax burden is obviously lower than the tax rate prescribed by Paragraph One of Article 4 hereof, and profits are not distributed or distributed at a reduced rate due to reasons other than reasonable business needs, the portion of the above profits belonged to such residententerprises shall be included in the income of such resident enterprises of the current period.Article 46 The interest fee incurred in excess of the prescribed standard obtained by Enterprises from the loan investment and equity investment of their affiliates may not be deducted from the taxable income.Article 47 Where Enterprises implement other arrangement without reasonable business objectives to reduce the payable income or income, the tax authority has the right to adjust in accordance with reasonable methods.Article 48 Where tax payment requires to be levied additionally by tax authority in respect of the tax payment adjustment made in accordance with the provisions of this Chapter, such tax payment shall be levied additionally and interest shall be levied in accordance with the provisions of the State Council.Chapter Seven Administration of Tax Levying and CollectionArticle 49 The administration of levy and collection of enterprise income tax shall follow the provisions hereof in addition to the Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Administration of Levying and Collection of Tax.Article 50 Unless otherwise specified by tax laws and administrative regulations, resident enterprises whose place of tax payment is the place of registration of the Enterprise but the place of registration is outside the territory, the place of tax payment shall be the place where the actual administration institution is located.Where resident enterprises establish business institutions in China without legal person qualification, it shall consolidate the calculation and payment of enterprise income tax.Article 51 In respect of non-resident enterprises that obtain the income prescribed in Paragraph Two of Article 3 hereof, the place of tax payment shall be the place where the institution or the establishment is located. Non-resident enterprises that set up two or more institutions or establishments in China may, upon the examination and approval of the tax authority, select its main institution or establishment to pay the consolidated enterprise income tax.Where non-resident enterprises obtain the income prescribed in Paragraph Three of Article 3 hereof, the place of tax payment shall be the place where the withholding agent is located.Article 52 Enterprises may not pay consolidated enterprise income tax unless otherwise prescribed by the State Council.Article 53 Enterprise income tax shall be calculated in accordance with the taxable year which starts from 1 January to 31 December of a calendar year.If an Enterprise commences business or terminates its business activities during the taxable year and the actual business period of such taxable year is less than 12 months, the actual business period shall be treated as a taxable year.Where the Enterprise is liquidated in accordance with the law, the liquidation period shall be a taxable year.Article 54 Enterprise income tax shall be prepaid on a monthly or quarterly basis.Enterprises shall submit a prepaid enterprise income tax return to the tax authority within 15 days of the completion of the month or the quarter to make tax prepayment.Enterprises shall submit an annual enterprise income tax return to the tax authority within five months of the completion of the year and make the settlement of the payable and refundable tax payment.Enterprises that submit the enterprise income tax return shall enclose a financial report and other relevant information in accordance with provisions.Article 55 Where Enterprises terminate business activities in the interim of the year, they shall handle with the tax authority the settlement and payment of enterprise income tax of the current period within 60 days from the actual termination of business.Enterprises shall, prior to handling registration cancellation, file a return of the income settled and pay enterprise income tax in accordance with the law.Article 56 Enterprise income tax paid in accordance with this Law shall be calculated in Renminbi. Where the income is calculated in a currency other than Renminbi, it shall be converted into Renminbi for tax payment.Chapter Eight Supplementary ProvisionsArticle 57 Enterprises set up with approval prior to the promulgation of this Law that enjoy low preferential tax rate in accordance with the tax laws and administrative regulations at the current period may, pursuant to the provisions of the State Council, gradually transit to the tax rate provided herein within five years of the implementation of this Law. Where such enterprises enjoy regular tax exemption and reduction, the treatment continues to apply until expiry after the implementation of this Law. However, those that fail to be entitled to this treatment by reason of not making any profits, the preferential period shall be calculated from the year this Law is implemented.High and new technology enterprises that are set up in a specific zone in accordance with the law for the purpose of external economic cooperation and technology exchange and that are newly set up and require key state support in the region of special policy of such region specified by the State Council may eligible for transitional treatment and the specific measures shall be provided by the State Council.Other enterprises under the encouraged category confirmed by the state may eligible for tax exemption and reduction in accordance with the provisions of the State Council.Article 58 Where agreements on taxation concluded by the People’s Republic of China and foreign governments contain different provisions, such agreements shall prevail.Article 59 The implementing regulations shall be formulated by the State Council on the basis of this Law.Article 60 This Law shall come into effect as of 1 January 2021. The Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Enterprise Income Tax of Foreign-invested Enterprises and Foreign Enterprises adopted at the 4th sess ion of the 7th National People’s Congress on 9 April 1991 and the Tentative Regulations of the People’s Republic of China on Enterprise Income T ax promulgated by the State Council on 13 December 1993 shall be repealed simultaneously.。
中华人民共和国企业所得税年度纳税申报表(A类,2017年版)国家税务总局2017年12月中华人民共和国企业所得税年度纳税申报表(A类 , 2017年版)税款所属期间:年月日至年月日纳税人统一社会信用代□□□□□□□□□□□□□□□□□□码:(纳税人识别号)纳税人名称:金额单位:人民币元(列至角分)谨声明:此纳税申报表是根据《中华人民共和国企业所得税法》《中华人民共和国企业所得税法实施条例》以及有关税收政策和国家统一会计制度的规定填报的,是真实的、可靠的、完整的。
法定代表人(签章): 年月日国家税务总局监制企业所得税年度纳税申报表填报表单A000000 企业基础信息表A100000 中华人民共和国企业所得税年度纳税申报表(A类)A101010 一般企业收入明细表A101020 金融企业收入明细表A102010 一般企业成本支出明细表A102020 金融企业支出明细表A103000 事业单位、民间非营利组织收入、支出明细表A104000 期间费用明细表A105000 纳税调整项目明细表A105010 视同销售和房地产开发企业特定业务纳税调整明细表A105020 未按权责发生制确认收入纳税调整明细表A105030 投资收益纳税调整明细表A105040 专项用途财政性资金纳税调整明细表A105050 职工薪酬支出及纳税调整明细表A105060 广告费和业务宣传费跨年度纳税调整明细表A105070 捐赠支出及纳税调整明细表A105080 资产折旧、摊销及纳税调整明细表A105090 资产损失税前扣除及纳税调整明细表A105100 企业重组及递延纳税事项纳税调整明细表A105110 政策性搬迁纳税调整明细表A105120 特殊行业准备金及纳税调整明细表A106000 企业所得税弥补亏损明细表A107010 免税、减计收入及加计扣除优惠明细表A107011 符合条件的居民企业之间的股息、红利等权益性投资收益优惠明细表A107012 研发费用加计扣除优惠明细表A107020 所得减免优惠明细表A107030 抵扣应纳税所得额明细表A107040 减免所得税优惠明细表A107041 高新技术企业优惠情况及明细表A107042 软件、集成电路企业优惠情况及明细表A107050 税额抵免优惠明细表A108000 境外所得税收抵免明细表A108010 境外所得纳税调整后所得明细表A108020 境外分支机构弥补亏损明细表A108030 跨年度结转抵免境外所得税明细表A109000 跨地区经营汇总纳税企业年度分摊企业所得税明细表A109010 企业所得税汇总纳税分支机构所得税分配表税款所属期间:年月日至年月日总机构名称(盖章):总机构统一社会信用代码(纳税人识别号):金额单位: 元(列至角分)。
2020年修订版企业所得税年度纳税申报表(A类)填报详解(三十三)境外所得税收抵免明细表(A108000)目录一、表样二、表单基本情况三、政策要点四、表单填报详解五、表内、表间关系六、填报案例一、表样二、表单基本情况本表适用于取得境外所得的纳税人填报。
纳税人应根据税法、《财政部国家税务总局关于企业境外所得税收抵免有关问题的通知》(财税〔2009〕125号)、《国家税务总局关于发布〈企业境外所得税收抵免操作指南〉的公告》(2010年第1号)、《财政部国家税务总局关于我国石油企业从事油(气)资源开采所得税收抵免有关问题的通知》(财税〔2011〕23号)、《财政部税务总局关于完善企业境外所得税收抵免政策问题的通知》(财税〔2017〕84号)、《财政部税务总局关于海南自由贸易港企业所得税优惠政策的通知》(财税〔2020〕31号)等规定,填报本年来源于或发生于其他国家、地区的所得按照税收规定计算应缴纳和应抵免的企业所得税。
三、政策要点《财政部税务总局关于完善企业境外所得税收抵免政策问题的通知》(财税〔2017〕84号):企业可以选择按国(地区)别分别计算(即“分国(地区)不分项”),或者不按国(地区)别汇总计算(即“不分国(地区)不分项”)其来源于境外的应纳税所得额,并按照财税〔2009〕125号文件第八条规定的税率,分别计算其可抵免境外所得税税额和抵免限额。
上述方式一经选择,5年内不得改变。
抵免限额的计算1、计算公式。
某国(地区)所得税抵免限额=中国境内、境外所得依照企业所得税法及实施条例的规定计算的应纳税总额×来源于某国(地区)的应纳税所得额÷中国境内、境外应纳税所得总额。
2、注意事项。
(1)如果境外所得弥补了境内亏损,“来源于某国(地区)的应纳税所得额”应按弥补境内亏损后的应纳税所得额计算。
(2)“企业按照企业所得税法及其实施条例和本通知的有关规定计算的当期境内、境外应纳税所得总额”小于零的,应以零计算当期境内、境外应纳税所得总额,其当期境外所得税的抵免限额也为零。