ISO14001:2015内审检查表-英文版
- 格式:doc
- 大小:274.00 KB
- 文档页数:11

GuidanceScoring CriteriaThe following audit scoring criteria have been used to identify the level of compliance with each requirement that is set out in the standard. In the 'Opportunities for Improvement' field, note down any situation or condition of the management system that may be weak, cumbersome, redundant, overly complex, or in some other manner, may, in the opinion of the auditor, offer an opportunity for the organization to improve its current status. In the 'Audit Evidence' field, fill in the evidence that you saw and your thoughts about the implementation and documentation. If any of the requirements are not applicable, please type 'N/A' to denote that the particular requirement is not applicable to the organization.Compliant: Yes, requirement fully documented and implemented. Adherence with the requirements of the standard or specification. No major or minor non-conformances found.Opportunity for Improvement (OFI): Minor gap, mostly documented and implemented The management system that may be weak, cumbersome, redundant, overly complex, or in some other manner, may, in the opinion of the auditor, offer an opportunity for an organization to improve its currentstatus.Minor Non-conformance: Requirement partially implemented but no documentation or partially documented but not implemented. A non-conformity that, based on the judgment and experience of the auditor, is not likely to result in the failure of the management system or reduce itsability to assure controlled processes or products. It may be either a failure in some part of the supplier's management systemrelative to a specified requirement or a single observed lapse in following one item of a company's management system.Major Non-conformance: No provision, requirement not documented or implemented. The absence (omission, not addressed) or total breakdown (commission, failure, not implemented) of a system to meet a specified requirement. A number of minor non-conformities againstone requirement can represent a total breakdown of the system and thus be considered a major non-conformity. Any non-compliance that would result in the probable shipment of a non-conforming product. Conditions that may result in the failure of ormaterially reduce the usability of the products or services for their intended purpose. A non-compliance that, in the judgment andexperience of the auditor, is likely to either to result in the failure of the management system or to materially reduce its ability toassure controlled processes and products.RequirementsAn audit of customer related processes should be conducted at planned intervals in order to determine whether the process conforms to planned arrangements in order to determine whether the process is properly implemented and maintained and to provide process performance information to top management. Effective auditing requires theauditor to identify and record audit trails that will make a difference to the organization. The audit should begin with the process owner in order to understand how the process interacts with the other process inputs, outputs, suppliers and/or customers. The auditor should be able to determine whether the outputs are complete and that process measurements demonstrate whether all of the outputs are consistently fit for purpose and are efficiently managed. Do the customers agree with the outputs and the measures?An audit of customer related processes is conducted at planned intervals to:•Determine whether the process conforms to planned arrangements•Determine whether the process is properly implemented and maintained•Provide information on process performance to Top ManagementConsider these points during the audit:•Is there continuity between the various support processes?•Is the task done consistently on a person-to-person or day-to-day basis?•Do the interfaces between the departments operate smoothly?•Does product information flow freely?•Is the procedure right?•Does it meet the requirements of the standard or specification?•Is it helping the organization effectively?Process Audit Turtle DiagramPROCESS NAME/DESCRIPTION:What steps are involved in the process? What happens at each step in the process? What documents and records are generated? Is the process implemented in accordance with procedures, instructions or plans? Are controls applied as described?PROCESS INPUTS:What triggers the process? What inputs are required?Where do the inputs come from? Are they received in a timely manner? Are they fit for purpose?PROCESS OUPUTS:What is the product produced by this process? Are product measures in place to ensure that product meets requirements? How are processes measured?Are product and process measures achieved? What feedback is received from customers?EQUIPMENT & FACILITIES:What equipment and resources are required? Is equipment suitable and properly maintained? Is the work environment maintained?Is there evidence of appropriate maintenance of all equipment used by this process?INSTRUCTIONS & PROCEDURES:Review the documents that describe and control the process. Review all the important steps and activities of the process being audited. This info must be documented within the QMS. Evaluate how effectively the process flows through the steps. Do you see roadblocks or issues?SUPPORT PROCESSES:As you audit, you will see how it connects and interacts with other processes. Interactions with other processes are always important . As you audit the, you will see how it connects and interacts with other processes. Audit the relevant links to related processes and support processes.KEY PERFORMANCE INDICATORS:Review metrics and performance with Managers, Supervisors and operators. They should know how things are running, objectives, customer issues, problem areas. If they do not, the requirements were not met. Is there evidence that quality objectives and targets affected by this process are being achieved?PERSONNEL:Review employee skill lists for the process. Are there lists of skills for each position? Do they show enough detail? This is often a finding, where lists are generic with inadequate detail. Training is a key process of any system. Are there particular skills you want to evaluate?CONTROL PROCESSES:How is the process defined and who is responsible? How are customer requirements defined? What specifications apply defined?What objectives and targets apply process? What controls/check points are there? What acceptance criteria exist?Supplier Audit Questions Quality ManagementContinuous Improvement。

1.0 PurposeThe purpose of this procedure is to define the process for executing periodic audits of the environmental management system. The procedure describes the process for planning, executing and reporting the environmental audits.This procedure covers all internal audits which are carried out within ourcompany.The scope of the internal audits includes all activities and processes of theenvironmental management system or some of its elements.2.0 ScopeThe entire environmental management system.3.0 Forms to useEF-921 Internal auditorsEF-922 Audit planningEF-923 Audit questionnaireEF-924 Audit findings4.0 ReferencesISO 14001:2015, Element 9.2.5.0 DefinitionsNone6.0 ExclusionsNone7.0 General rulesInternal environmental audits help to ensure the right implementation andmaintenance of the environmental management system by verifying that the activities are in accordance with the documented procedures and thatcorrective measures are effectuated and that they are efficacious.All audits are performed by trained auditors. The training of auditors is inaccordance with procedure EP-721. Records of the auditor training areretained in accordance with procedure EP-753.When a candidate is designated as auditor and becomes part of the audit team, the lead auditor will evaluate the performance of the candidate after the audit. The environmental manager is responsible for retaining audit records,including a list of trained auditors, auditor training records, audit schedulesand audit reports.The environmental audits are planned in such a way that all elements of theenvironmental management system are audited at least annually.The environmental manager is responsible for informing the auditors ofupcoming audits a reasonable time before the planned audit date. Thedepartments and functions which are audited, will also be informed areasonable time before the planned audit date.The lead auditor is responsible for fulfilling the audit, the audit report and the feedback to the audited departments and/or functions.In consultation with the lead auditor, the environmental manager ensures that non-conformity-reports with the audit findings are set up.8.0 Method8.1. Selection of the audit team:An audit team can consist of one or several auditors. When the audit teamconsists of more than one auditor, a lead auditor is designated. The lead auditor is responsible for the work allocation, the coordination and the preparation of the audit report. The auditors are independent of the domain to be audited and adopt impartiality and objectivity.8.2. Orientation of the audit team:The lead auditor ensures that the team is properly prepared to begin the audit. Relevant standards, regulations, policy elements and previous audit reports are available for audit team to be consulted. Each auditor took a suitableauditor training as specified in procedure EP-721.8.3. Written audit plan:The lead auditor is responsible for preparing a written audit plan. The checklist for internal audits can serve as guidance for this audit plan.。
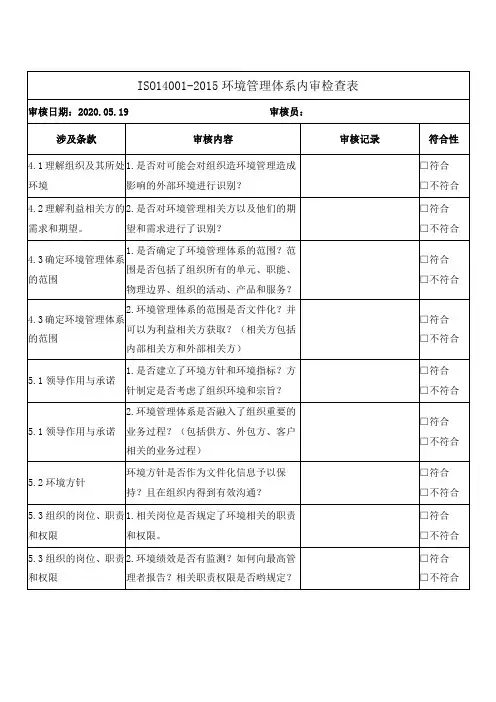
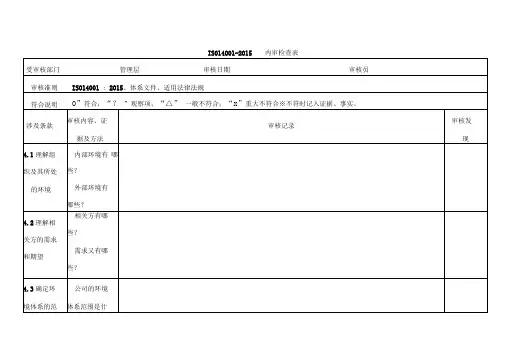
ISO14001内审检查表:2015(按部门(bùmén)审核)记录(jìlù)编号(biān hào):编号(biān hào)ISO14001内审检查表(按部门(bùmén)审核)记录(jìlù)编号:编号ISO14001内审检查表(按部门(bùmén)审核)记录(jìlù)编号:编号ISO14001内审检查表(按部门(bùmén)审核)记录(jìlù)编号:编号ISO14001内审检查表(按部门(bùmén)审核)记录(jìlù)编号:编号ISO14001内审检查表(按部门(bùmén)审核)记录(jìlù)编号:编号ISO14001内审检查表(按部门(bùmén)审核)记录(jìlù)编号:编号ISO14001内审检查表(按部门(bùmén)审核)记录(jìlù)编号:编号ISO14001内审检查表(按部门(bùmén)审核)记录(jìlù)编号:编号ISO14001内审检查表(按部门(bùmén)审核)记录(jìlù)编号:编号ISO14001内审检查表(按部门(bùmén)审核)记录(jìlù)编号:编号ISO14001内审检查表(按部门(bùmén)审核)记录(jìlù)编号:编号ISO14001内审检查表(按部门(bùmén)审核)记录(jìlù)编号:编号内容总结。

4Context of the organization4.1Understanding the organization and its contextThe organization shall determine external and internal issues that are relevant to its purpose and that affect its ability to achieve the intended outcome(s) of its environmental management system. Those issues include environmental conditions capable of affecting or being affected by the organization.4.2 Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties The organization shall determine:‐the interested parties that are relevant to the environmental management system;‐the relevant needs and expectations (i.e. requirements) of these interested parties;‐which of these needs and expectations become compliance obligations.4.3Determining the scope of the environmental management systemThe organization shall determine the boundaries and applicability of the environmental management system to establish its scope.When determining this scope, the organization shall consider:‐the external and internal issues referred to in 4.1;‐the compliance obligation referred to in 4.2;‐its organizational unit(s), function(s), and physical boundaries;‐its activities, products and services;‐its authority and ability to exercise control and influence.Once the scope is defined, activities, products and services that can have significant environmental aspects (see 6.1.2) shall be included within the scope of the environmental management system.The scope shall be maintained as documented information and be available to interested parties.4.4 Environmental management systemThe organization shall establish, implement, maintain and continually improve an environmental management system, including the processes needed and their interactions, in accordance with the requirements of this International Standard, to ensure its environmental performance.The organization shall consider the knowledge of its context when establishing and maintaining the environmental management system. 4 组织环境4.1 理解组织及其环境组织应确定外部和内部那些与组织的宗旨、影响环境管理体系实现预期结果的能力的事项。
MRF Name / LogoMP10 – Control of equipmentApproved:Management RepresentativeNote:Within this manual template, red italic text should be replaced by MRF specific information and any guidance in ‘text boxes’ should be implemented.1 PurposeThe purpose of this procedure is to provide appropriate methods relating to the control of monitoring and measuring devices and associated MRF equipment.The procedure ensures that all monitoring and measuring equipment is identified, registered and maintained so that monitoring and measuring can be carried out in a manner consistent with inspection and test requirements.The procedure also ensures that records of calibration and verification are maintained and that appropriate actions are taken if equipment is found to be out of calibration.2ScopeThis procedure contains the following sections: Array 4.1 Control of monitoring and measuring devices4.2 Equipment maintenance5 Related documents3 Definitions and glossaryECR Equipment Calibration RecordsMR Management RepresentativeOM Operations ManagerVOSA Vehicle and Operator Services AgencyPAT Portable Appliance Testing4 ProcedureThe Operations Manager (OM) is responsible for the overall implementation of this procedure. It is the responsibility of the Management Representative (MR) to ensure the implementation of this procedure and the maintenance of appropriate records. Records are maintained in accordance with MP02 Control of Records.4.1 Control of monitoring and measuring devicesAll items of inspection, measuring and test equipment are passed to the OM for inclusion in the Equipment Calibration Records as required.All items of inspection, measuring and test equipment are permanently marked with a unique reference number. Monitoring and measuring that equipment used within the manufacturing processes but not requiring calibration are labelled as such. Calibration certificates are obtained for new measuring equipment and equipment calibrated or serviced by approved suppliers or sub-contractors. The certificates are filed by the OM. Where appropriate, the calibration of equipment is traceable to National and International Standards. Monitoring equipment that is calibrated in house will be recorded as such on the ECR.The frequency of calibration is determined from the rate of usage of equipment and its required accuracy. Calibration records are evaluated periodically to ascertain the adequacy of calibration frequencies presently in use.Equipment that falls due for calibration is identified from the ECR and calibration carried out.The results of the calibration are recorded on the ECR and, where possible, a calibration status indicator is attached to the calibrated equipment.Equipment which, based on defined parameters, fails calibration is either repaired and re-calibrated or replaced. If equipment is replaced, a new equipment reference number is issued and added to the ECR.Where equipment is found to be out of calibration, the results of previous inspections and tests are assessed, documented and where necessary appropriate action taken. The ECR is also used to record any maintenance activity that may have an effect on service delivery.All equipment is stored, handled and used with care. All damaged or suspect monitoring or measuring equipment is promptly passed on to the OM for review / re-calibration. Obsolete or unserviceable equipment as identified fromequipment records is scrapped.4.2 Equipment maintenanceGeneral maintenance requirements are fulfilled either by in-house resource or by approved/preferred suppliers as identified on the Approved Suppliers List. This activity includes general infrastructure maintenance as well as unplanned office maintenance.Manufacturer’s guidance and legislative requirements are observed and maintenance schedules determined for plant and equipment.Maintenance schedule managed through identification of current status for each significant piece of equipment and a full description of work done and outstanding work is maintained.Vehicle maintenance is carried out in accordance with VOSA requirements.All electrical equipment is PAT tested for safety and the test recorded on the ECR.5 Related documents•Approved Suppliers List.•MP02 Control of Records.•Equipment Calibration Register.。
ISO 9001:2015Compa ny: Clie nt- no.:DateLead Auditor(s)Note:1 Objective audit evide nee shall be docume nted and uploaded to iCert.2This Audit questi on list is reeomme nded as the primary source of docume ntatio n of objective audit evide nces. Alter natively, audit no tes, process sheets, etc. could be used.3As a rule, documented audit evidence (audit question list, audit notes or process sheets) should be completed separately for each audit and for each site (if applicable), for the pert inent process eleme nts.4The evaluatio n can be en tered in the audit evaluati on colu mn (E): 1 = Con formity (in cludi ng pote ntial for improveme nt, where applicable). 2 = Minor noncon formity (lower-level non-con formity). 3= Noncon formity (major noncon formity)n.a. = not applicable5The final result of the evaluati on shall always be docume nted in the action list (Ann ex1)Compa ny:Clie nt- no.:Requireme nts (Audit notes identified withAudit no tes“ * ” are to be reported in the Audit Report)(Implementation / Documented Information / reviewed evidence ...)Order- no.:4 Con text of the orga ni zati on4.1Understanding the org. and its contextdetermine external and internal issues monitor and reviewinfo.4.2Understanding the needs and expectations ofinterested partiesdetermine:a)the interested parties relevant to the QMSb)the req. of these interested parties monitor and review info. about interested parties and their relevant req.4.3Determining the scope of theQMSdetermine the boundaries and applicabilityof the its scope.consider:a)the external and internal issuesb)the req. of relevant interested partiesc)the prods & servs of the org.apply all the req. of this Standard if they are applicable within the scope of its QMS. The scope shall be docu. info . state the types of prods and servs covered, and provide justification for any req. not applicable. *Min. of 1 ex.: context of the org.*Min. of 1 ex.: interested parties*Min. of 1 ex.:statutory/regulatory req.*Appropriateness of scope:4.4 QMS and its processes *Min. of 1 ex.:Order- no.:Order- no.:Order- no.:Compa ny:Clie nt- no.:Requireme nts (Audit notes identified withAudit no tes“ * ” are to be reported in the Audit Repoit)(Implementation / Documented Information / reviewed evidence ...)Order- no.:resources:a)are suitable for the specific type of monitoring andmeasurementb)are maintained to ensure their fitness retain docu. Info. of fitness for purpose of monitoring and measurement resources.measuring equipment shall be:a)calibrated or verified, or both, at specified intervals, to measurement standards; when no standards exist, the basis for calibration shall be retained as docu. Info.b)identified to determine thestatusc)safeguarded from adjustments, damage or deteriorationdetermine if the validity of previous measurement results has been adversely affected when measuring equipment is found unfit for its intended purpose, and take action .7.1・6 Organizational knowledgedetermine knowledge for the operation of its processes and conformity of prods & servs.knowledge shall be maintained and made available.When addressing changing needs and trends, consider current knowledge and determine how to acquire additional knowledge and required updates.7.2 Competencea)determine the competence of person(s)b)ensure that persons are competentc)actions to acquire the necessary competence, evaluate the effectiveness of the actionsd)retain docu. Info. of competence7.3Awarenessensure that persons are aware of:a)Q-policyb)Q-objectivesc)their contribution to the QMS, including the benefits of improved performanced)implications of not conforming with the QMS req.7.4Communicationdetermine the communications relevant to the QMS:a)whatb)whenc)with whomd)how *Evidence of fitness for purpose of monitoring and measurement resources:*Evidence of basis used for calibration or verification (if applicable):*Min. of 1 ex.:Order- no.:Order- no.:Order- no.:Order- no.:。
1. Contents0. Survey of Changes1. Contents2. Scope and Application3. Introduction4. Definitions and Abbreviations5. Responsibilities6. Procedures7. Interacting Procedures8. Supporting Forms9. Flow Chart of Procedures2. Scope and ApplicationThis procedure is written for Philips LCD Cells & Modules Shenzhen Factory, which is called ‘Philips’ in the following texts of this document. This procedure stated the generalenvironmental concerns to all Philips‘ subcontractors.3. IntroductionAs a customer, Philips shall determine the general environmental concerns for itssubcontractors. The aim of the concerns shall be enable Philips’ subcontractors to initiate their continual improvement and prevention of pollution and to formulate processes formutual communication between Philips and its subcontractors.The environmental concerns are reflected by the following three points;I)Philips shall acknowledge the up-to-date Philips’ Environmental Policy tosubcontractors.II)Philips shall encourage subcontractors to conduct and review the identification andevaluation of environmental aspects and impacts in their factories on a half yearlybasis and make it presentable to Philips.III)Philips shall conduct an annual survey on subcontractor environmentalperformance.As part of the responsibility and procedure is taken up by subcontractors, Chinese translation is prepared as appendix in which are the contents should be understood by subcontractors.4. Definitions and AbbreviationsIEEAI – Identification and Evaluation of Environmental Aspects and ImpactsEMS – Environmental Management SystemSubcontractor – Product related subcontractor such as cell manufacturing processes, PCBA bonding processes.5.ResponsibilitiesSubcontracting DepartmentAct as a bridge of communication between subcontractors and Philips in all aspect ofenvironmental protection issues.EMS OfficerReceive and review the IEEAI reports from subcontractors; Conduct survey of subcontractor environmental protection performance.SubcontractorsUnderstand the Philips’ environmental Policy; Initiate the IEEAI for its factory; Reply the survey to Philips EMS officer.6. Procedure6.1 EMS officer shall issue an copy of up-to-date Philips Environmental Policy to allsubcontractors. Subcontractors shall also formally sign on receipt of the Policy and the receipt shall be kept by EMS officer.6.2 Subcontractors shall conduct and review their IEEAI on a half yearly basis and keepPhilips EMS officer informed for any changes. The form refers IEEAI procedureQKW-666-EMS0006, form 1.6.3 Philips EMS officer shall conduct an annual survey of subcontractor environmentalperformance.6.4In case a corrective action on the aspect of environmental protection, Philips shallhandle according to the Environmental Incident Registration Procedure procedureQKW-666-EMS0006 and Corrective and Preventive Action Procedure – Environmental Management System (QKW-666-EMS0003).6.5The environmental measures in subcontractors shall be audited during subcontractoraudit. The procedures refer to QKW-666-SUB0005.7. Interacting ProceduresIdentification and evaluation of environmental aspects and impacts,QKW-666-EMS0006 Environmental Incident Registration Procedure, QKW-666-EMS0003Corrective and Preventive Action Procedure – Environmental Management System, QKW-666-EMS0004.Cell subcontractor quality system elements and assessment, QKW-666-EMS0005.8. Supporting FormsSubcontractor Environmental Performance Questionnaire加工商環境保護表現問卷調查QKW-666-EMS0015 Form 1 AA 9. Flow Chart of ProcedureN/A。
ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management System Assessment ChecklistRP-2Table of ContentsIntroduction (2)Assessment Summary Sheet - Sample (7)Assessment Summary Sheet (10)4 –Context of the Organization (13)5 –Leadership (14)6 –Planning for the Quality Management System (16)7—Support (17)8 –Operation (22)9 –Performance Evaluation (33)10 –Improvement (36)The Quality System Checklist is intended to help you gain a better understanding of the requirements of ISO 9001:2015. ISO9001:2015 requires the adoption of the process approach which extends to internal quality audits. This checklist follows the structure of the standard, thus it is not process based. For this reason it is not intended to be used as the only tool for internal quality audits.You can gain a better understanding of ISO 9001:2015 Standard as it applies to your company by reviewing these questions. You may wish to discuss them with your auditors to enhance everyone’s understanding of the ISO 9001:2015 requirements and the assessment process.You should be aware that although the following questions include most of the requirements of the ISO 9001:2015 standard, they do not necessarily cover all aspects of the Standard. So, the use of this checklist will give you only a sample of your organization’sconformance to the ISO 9001:2015 standard.Assessment Summary SheetThe Assessment Summary Sheet may be used for visualizing the big picture: wha t areas were checked and where discrepancies were found. You’ll see from the sample Assessment Summary Sheet that assessment of thePurchasing Process uncovered discrepancies for clauses 4.1, 5.3, 7.1.5, 8.1,8.2, 8.3.1 and 8.5.3. This may be a sign of problems in that process, whichwarrant planning and close monitoring of corrective actions. The Processes Assessed column reveals that for clause 7.1.2 for Resource Requirements or8.2 for Determination of requirements for products and services,discrepancies were uncovered in all applicable areas. This may giveevidence of a system breakdown.On the sample Assessment Summary Sheet, the circled numberscorrespond to the following:① The ISO 9001:2015 Assessment Standard correspond to theISO9001:2015 International Standard which your company has selected for assessment.② The column Process Assessed lists the areas (i.e. process) wherecompliance to given clauses will be evaluated.③ These columns contain the list of clauses for the applicable ISO Standardto which compliance is being sought. NOTE: All clauses of the ISO 9001Standard must be addressed. See section 0.1. “Forward”, for furtherinformation.④Use this grid to indicate where discrepancies are found by entering a “D”into the corresponding boxes. Where no discrepancies are uncovered,enter an “X” in the appropriate boxes.0.2 Process ApproachISO9001:2015 promotes the adoption of a process approach. As a first step, all processes of the organization need to be identified and theirinterrelation defined. A process is a set of activities that transform inputsinto outputs. The outputs of one process may be the input of anotherprocess, or the finished product. Although a process map is not required,it is an effective method for demonstrating process interrelation. Any other method will equally meet the requirements of the standard as long as theprocess interaction is somehow shown.An example of a typical process map is noted on the next page. Please note that a process map is not a process flow diagram, but merely highlights the main processes of the organization that are needed to be effectivelymonitored to ensure “consistent and predictable results”. Also, theprocesses noted are not the names of the functions within the organization, but value added activities within the organization that may involve sub-processes that will have to be further defined.Assessment Summary Sheet – SAMPLE* Use an “X” to indicate that the cl ause was assessed in the area described. Use a “D” to indicate that a discrepancy was found.Assessment Summary Sheet* Use an “X” to indicate that the clause was assessed in the area described. Use a “D” to indicate that a discrepancy was found.。
1. Contents1. Contents2. Scope and application3. Introduction4. Definitions and abbreviations5. Responsibilities6. Procedures7. Interacting Procedure – N.A.8. Supporting form9. Flow chart of procedure- N.A.2. Scope and applicationThis Procedure serves as a guideline to identify and register local legislation and other environmental regulations for ShenZhen Factory.3. IntroductionWith reference to ISO 14001 standard, the Factory should identify and have access to legal and other environmental requirements to which our organization subscribes to that are applicable to the environmental aspects of the Factory activities, products or services.The aims of this document are:a). Make us in full compliance with all local legislation and other Philips environmentalrequirements.b). Guarantee, with all possible endeavors, the human and property safety within the factory,and if needed, to vicinity as also a kind of goodwill to the environment.4. Definitions and abbreviationsCEEO - Philips Corporate Environmental & Energy OfficeEMS - Environmental Management SystemMain Engg - Manufacturing EngineeringCAR - Corrective Action Request for EMS5. ResponsibilitiesMR - For overall managementEMS officer - To judge which material, facility, and operation need to comply withlegislation and other environmental requirements.M.E. - License application and maintenancePMC - To provide in house chemical storage information to EMS Officer.Purchasing - To provide updated information on in-house chemicals anddangerous goods to EMS Officer.6. Procedures6.1 EMS officer looks into material, facility and operation from time to time to maintainregulatory compliance of the process and supportive functions for environmentalissues in ShenZhen Factory .6.2 Regulations / requirements can exist in several forms:●International standards for ISO 14000●Local environmental laws & regulations●Authorizations, licenses and permits●Philips Corporate Environmental Documents6.3 Several sources can be used to identify environmental regulations & requirements andongoing changes, including:●Government bodies responsible for drafting and establishing environmentalregulations.●Industrial associations or groups●Commercial databases from public internet and Philips internet.●Professional consultant services●Philips Corporate Environmental & Energy Office●Environmental Interested Parties, such as Green Peace6.4 Maintenance Manager shall apply and maintains the licenses and permits accordingly.6.5 EMS officer keeps the contents updated in licensing form QKW-666-EMS0001 form1.6.6 EMS officer keeps track of legal requirements and maintains a list of allenvironmental laws and regulations pertaining to the Factory’s. The list(QKW-666-EMS0001 form 2) shall be approved by the MR.6.7 The list of environmental laws and regulations shall be reviewed and updated yearlyby the EMS Officer. A log of environmental laws and regulations will be maintainedand updated by the EMS Officer.6.8 EMS Officer complies and summarizes local environmental laws and Philipsenvironmental requirements by using Register of Regulation A (LegislativeRegulations ) QKW-666-EMS0001 form 3 and Register of Regulation B (OtherCompany Regulations) form 4.6.9 EMS Officer should check and evaluate compliance with relevant environmentallegislation and regulations by using Register of Regulation A (LegislativeRegulations) QKW-666-EMS0001 form 3 and Register of Regulation B (OtherCompany Regulations) form 4.6.10 The evaluation of compliance with relevant environmental legislation and regulationsenvironmental laws and regulations shall be done and updated every three months byEMS Officer. The latest version of Register of Regulation A (Legislative Regulations)QKW-666-EMS0001 form 3 and Register of Regulation B (Other CompanyRegulations) form 4 shall be approved by MR and filed in EMS Office.6.11 Any new/regulatory changes in local environmental legislation/ regulations andcompany environmental requirements are communicated with concerned departmentthrough e-mail, memo and training. An implementation plan/ procedure shall beestablished by the concerned department. The review of compliance shall be onemonth from the start of implementation. Such checking and reviews shall besubjected to internal audit.6.12 Any non-conformance related to environmental legislation is identified, CAR shouldbe issued to the concerned department according to Corrective and Preventive Actionfor Environmental Management (QKW-666-EMS0004).7. Interacting ProcedureCorrective and Preventive Action for Environmental Management SystemQKW-666-EMS0004.8. Supporting formQKW-666-EMS0001 Form 1 License or Certification of Plant FacilitiesQKW-666-EMS0001 Form 2 Logs of Environmental Laws and RegulationsQKW-666-EMS0001 Form 3 Register of Regulation A (Legislative Regulations)QKW-666-EMS0001 Form 4 Register of Regulation B (Other Company Regulations)9. Flow chart of procedureN/AAppendixQKW-666-EMS0001 Form 1LICENSE OR CERTIFICATION OF PLANT FACILITIESQKW-666-EMS0001 Form 1 AAQKW-666-EMS0001 Form 2Logs of environmental laws and regulationsQKW-666-EMS0001 Form 2 AAQKW-666-EMS0001 Form 3Register of Regulation A (Legislative Regulations)QKW-666-EMS0001 Form 4Register of Regulation B (Other Company Regulations)。
-Maintenance Service1. Contents1.Contents2.Scope and application3.Introduction4.Definitions and abbreviations5.Responsibilities6.Procedures7.Interacting Procedure8.Supporting form9.Flow chart of Procedure10.Appendix2. Scope and applicationThis procedure outlines the control and monitor for the subcontractor for their works and service ensure that they are all comply with the local environments requirement. This procedureis applicable to the Shenzhen Factory.2.1 All subcontractor activities in Shenzhen Factory relating toa). Plant Facility/Building Maintenanceb). Waste Collection Servicesc). Factory Internal/External Construction Work3. IntroductionTo define a procedure to control/monitor the subcontractor services to ensure compliance with environmental requirement and minimize potential pollution risks.4. Definitions and AbbreviationsPTE Plant Engineering Section of Maintenance Engineering departmentME Dept. Manager Maintenance Engineering ManagerEMS Environmental Management SystemSubcontractor Subcontractors to provide maintenance or waste collecting service to Philips (Shenzhen)EMS officer EMS officer (Shenzhen)-Maintenance Service5. ResponsibilitiesPTE Mechanic/Engineer Monitor the subcontractor’s work and make sure they complyto the environmental concerns Record the information detailswith the Subcontractor and inform EMS requirement to thembefore the works started Communicate and review theenvironmental concerns with the EMS OfficerME Dept. Manager Monitor & review the performance of the subcontractors fortheir overall management on yearly basisEMS Officer Overall review the environmental concerns with PTE Engineerand Subcontractor. Receive/review the EIA from thesubcontractor.Subcontractor Make sure the all work & activity comply with theenvironmental protection concerns & reply the survey to EMSofficer.6. Procedures6.1 Plant Facility Maintenance Service/Factory Construction Work6.1.1 All work and activity must comply to Philips in-house EMS requirement.PTE group should monitor all the activity during the process and also thecondition of the facility/equipment will not cause any environment impact or pollution.6.1.2If there is any waste generated, they should be handled according tothe General Waste Management Procedure QKW-666-EMS0018.6.1.3 In case the situation is out of control the General Emergency ResponsePlan QKW-666-EMS0012 should be followed and inform theEMS Officer to registrate the incident according to EnvironmentalRegistration Procedure QKW-666-EMS0003.6.1.4 Before the Subcontractor starts to work, make sure that they understandour EMS requirement and fill in the QKW-666-EMS0014 form 2. The recordshould be kept for one year by PTE for follow up and review use.-Maintenance Service6.2 Waste Collection Service6.2.1Collect and re-build the waste according to the General Waste ManagementProcedure QKW-666-EMS0018 and they shall be handled separately.6.2.2All disposed re-usable waste should be recorded on the record formQKW-666-EMS0018 Form 1.6.3The ME Dept. Manager should be responsible for maintaining a list of approvedwaste collector/contractor with appropriate waste disposal licenses.7. Interacting ProcedureQKW-666-EMS0002 Fire Precaution and Fire Escape ProcedureQKW-666-EMS0003 Environmental Incident Registration ProcedureQKW-666-EMS0004 Corrective and Preventive Action for EMSQKW-666-EMS0005 Spill Control/Cleanup ProcedureQKW-666-EMS0012 General Emergency Response PlanQKW-666-EMS0018 General Waste ManagementQKW-666-EMS0017 Instruction of Handling of Chemical-Maintenance Service8.Supporting FormSubcontractor Environmental Performance Questionnaire加工商環境保護表現問卷調查From發文者:Company name: 公司名稱: Address:地址:Tel電話:Fax傳真:Ref.參考:To受文者:Company name: 公司名稱: Address:地址:Tel電話:Fax傳真:Ref.參考:Completed by: 填寫人: Position:職位:Date:日期:Signature:簽名:1) Description of product / service supplied:所供應產品/服務:2) Please answer the following questions. If you would like to expand on any of your answers, please supply separatedetails.請回答以下問題, 如需要詳細回答, 請另用紙張詳細說明.3) Do you have a written environmental policy? If yes, please enclose a copy.貴公司有沒有制訂環境保護政策? 若有,請附送一份資料給我們.Y/N 是/否4) Do you carry out environmental review or auditing?貴公司有沒有執行一些環境保護檢討及自我審核?Y/N 是/否-Maintenance Service5) Do you have / Are you in the process of setting up environmental management system?貴公司有沒有或巳正在建立有關的環境管理系統?Y/N是/否5.1) If yes, do you comply / intend to comply with ISO14001 or the Eco-Management and AuditScheme?若有, 貴公司會/計划將會跟從ISO14001.Y/N 是/否6) Do you conform to ISO9000?貴公司有沒有跟從ISO9000系統標准.Y/N 是/否7) Do you offer facilities for customers to return your used products / packaging for recycling orsafe disposal?貴公司有沒有提供一些設備來收回顧客所用過的產品或包裝物料, 將之循環再用或作安全處理.Y/N 是/否8) Do you check the environmental performance of your supplier?貴公司有沒有檢查本公司的供應商的環境保護工作表現?Y/N 是/否9) Has there been any civil action against you in respect of the environment in last five years?貴公司在過去五年內有沒有因違反有關環境保護條例而受到當地政府檢控?Y/N是/否10) Do you have managers / directors with specific responsibilities for environment?If yes, please state name and position.貴公司有沒有專門負責環保工作的職員?若有, 請寫出其姓名及職位.Y/N 是/否11) Are there any environmental initiatives you are carrying out / have carried out?If yes, please supply details separately.貴公司有沒有正在進行或巳完成直些与環保有關的工作? 若有, 請詳細說明.Y/N是/否QKW-666-EMS0014 Form 1 AA-Maintenance ServiceSERVICE SUBCONTRACTOR WORKING RECORD加工商工作記錄Company Name:公司名稱:Description of Service Provided:所提供服務:Period:日期及時間:Working location:工作地點:Number of working:工作人數:EMS Concerns:環保注意事項:Waste generated:-Maintenance Service廢物:Remarks備注:Follow up by PTE:厂房維修:_______________________ Approved by PTE Engineer工程師核准_______________________QKW-666-EMS0014 Form 2 AA9. Flow chart of procedureN/A10. Appendix I Chinese translation of section 5 and 65. 責任厂房技術員/工程師監察加工商的工作确保沒有污染環境.報告環境污染事件及通知EMS主任.制造工程部經理監察及檢討加工商的工作表現,作為加工商的全面管理及每年檢討.EMS主任管理及存檔有關環境之文件及檔案,存檔加工商之E1A,和厂房工程師檢討檢討環境事情.加工商确保工作沒有污染環境及回覆EMS主任發出之E1A.6. 工作程序SUBCONTRACTOR EMS CONTROLPROCEDURE-Maintenance Service QKW-666-EMS0014/AA Page: 8of 8Date: 99-10-066.1 厂房維修及工作6.1.1厂房維修工程部确保所有工程及工作附合內部環保要求.6.1.2所有工程后之廢物必須根据 QKW-666-EMS0018的廢物程序處理.6.1.3如果污染情況發生,根据 QKW-666-EMS0003的環境污染報告處理.6.1.4在開始工作前填寫工作記錄及講解Philips環保及緊急應變要求給加工商知道.6.2廢物收集商工作6.2.1根据QJV-PTE-0056收集廢物及分類.6.2.2所有回收廢物必須記錄在 QKW-666-EMS0018 Form1.6.3 維修工程部經理負責記錄廢物收集商的名單及資料.。
Process Audit ChecklistSystem & Process Compliance AuditingSystem & Process Compliance AuditingGuidanceAbout this ChecklistThe audit checklist is just one of the many tools which are available from the auditor’s toolbox that help ensure your audits address the necessary requirements. It stands as a reference point before, during and after the audit process and if developed for a specific audit and used correctly will provide the following benefits:∙Ensures the audit is conducted systematically;∙Promotes audit planning;∙Ensures a consistent audit approach;∙Actively supports your organization’s audit process (ISO 9001:2015, Clause 9.2.1);∙Provides a repository for notes collected during the audit;∙Ensures uniformity in the performance of different auditors;∙Provides reference to objective evidence.This audit checklist comprises tables of the certifiable (‘shall’) requirements, from Section 4.0 to Section 10.0 of ISO 9001:2015, each required is phrased as a question. This audit checklist may be used for element compliance audits and for process audits. If you wish to create separate process audit checklists, select the clauses from the tables below that are relevant to the process and copy and paste the audit questions into a new audit checklist. We suggest that you retain this audit checklist as your ‘master copy’.System & Process Compliance AuditingAudit Scoring CriteriaA risk-based internal audit approach allows the internal audit to concentrate on reviewing the major risks to your organization. The audit’s role is to provi de assurance that key risks to your organization’s objectives are being well controlled.The audit findings ‘traffic lights’ are intended to visually communicate the risk posed by the audit finding of any system or processes being audited. The rating system is stratified from ‘compliant’ to ‘major non-conformance’ to convey a concise and consistent method for scoring each audit finding. At the end of the audit, you can transfer the findings into an Excel spreadsheet to create charts, summary tables and trend data to paste into your audit report or management review documentation.This methodology should be uniformly applied to all types of internal audit (gap analysis, system audits and process audits) that your organization will likely undertake.System & Process Compliance Auditing Process Activity MapSystem & Process Compliance AuditingProcess Audit ChecklistProcess DefinitionSystem & Process Compliance AuditingSystem & Process Compliance Auditing Process ResourcesSystem & Process Compliance AuditingSystem & Process Compliance AuditingSystem & Process Compliance Auditing Process Execution。