生物工程专业英语1
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:527.50 KB
- 文档页数:52


Abstract:Biological engineering, a relatively young yet rapidly growing field, combines principles from biology, engineering, and computer science to solve complex problems in healthcare, agriculture, and the environment. This interdisciplinary field is at the forefront of technological advancements, offering innovative solutions to some of the most pressing challenges faced by humanity. This paper provides an overview of the field of biological engineering, its history, key areas of research, applications, and future prospects.1. IntroductionThe field of biological engineering emerged in the late 20th century as a response to the increasing need for interdisciplinary approaches to address complex problems in various sectors. By integrating knowledge from biology, engineering, and computer science, biological engineers strive to develop innovative solutions that can improve human health, enhance agricultural productivity, and protect the environment. This field has gained significant attention in recent years, thanks to advancements in biotechnology, genetics, and computational tools.2. History of Biological EngineeringThe roots of biological engineering can be traced back to the early 20th century when scientists began to explore the application of engineering principles to biological systems. The field gained momentum in the 1950s and 1960s with the development of recombinant DNA technology and the establishment of biotechnology companies. Over the years, the field has evolved to encompass a wide range of applications, including medical devices, biofuels, and environmental remediation.3. Key Areas of Research in Biological Engineering3.1 Biomedical EngineeringBiomedical engineering is a major subfield of biological engineeringthat focuses on the application of engineering principles to improve human health. This includes the development of medical devices,diagnostic tools, and therapeutic agents. Some key areas of research in biomedical engineering include:- Tissue engineering: Developing bioartificial tissues and organs for transplantation.- Nanomedicine: Using nanotechnology to deliver drugs and imaging agents directly to diseased cells.- Biocompatibility: Ensuring that medical devices and implants are compatible with the human body.3.2 Biochemical EngineeringBiochemical engineering involves the design and optimization of processes that use biological systems to produce valuable products. This includes the development of industrial fermentation processes, enzyme engineering, and bioreactors. Some key areas of research in biochemical engineering include:- Bioprocessing: Developing efficient and sustainable methods for producing biofuels, pharmaceuticals, and other chemicals.- Enzyme engineering: Improving the properties of enzymes for industrial applications.- Bioreactor design: Optimizing the design of reactors to maximize the production of desired products.3.3 Environmental EngineeringEnvironmental engineering in biological engineering focuses on the development of technologies to protect and restore the environment. This includes the treatment of wastewater, air pollution control, and bioremediation. Some key areas of research in environmental engineering include:- Bioremediation: Using biological agents to clean up contaminated sites.- Wastewater treatment: Developing efficient methods for treating and recycling wastewater.- Air pollution control: Using biological systems to remove pollutants from industrial emissions.4. Applications of Biological Engineering4.1 HealthcareBiological engineering has revolutionized healthcare by developing new treatments, diagnostics, and medical devices. Some notable applications include:- Gene therapy: Using genetic engineering to treat genetic disorders.- Artificial organs: Developing bioartificial organs for transplantation.- Drug delivery systems: Using nanotechnology to deliver drugs directly to diseased cells.4.2 AgricultureBiological engineering has contributed to the development of sustainable agricultural practices that enhance crop yield and reduce environmental impact. Some key applications include:- Genetically modified organisms (GMOs): Developing crops with improved resistance to pests and diseases.- Precision agriculture: Using sensors and data analytics to optimize crop management.- Biopesticides: Developing environmentally friendly alternatives to chemical pesticides.4.3 Environmental ProtectionBiological engineering plays a crucial role in protecting the environment by developing technologies to remediate pollution and reduce waste. Some applications include:- Bioremediation: Using biological agents to clean up oil spills and contaminated sites.- Wastewater treatment: Developing sustainable methods for treating and recycling wastewater.- Air pollution control: Using biological systems to remove pollutants from industrial emissions.5. Future ProspectsThe field of biological engineering is expected to continue growing rapidly in the coming years, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for sustainable solutions. Some future prospects include:- Development of personalized medicine: Tailoring treatments to individual patients based on their genetic makeup.- Advancements in biofuels: Developing more efficient and sustainable methods for producing biofuels.- Addressing global challenges: Using biological engineering to address issues such as climate change, food security, and water scarcity.6. ConclusionBiological engineering is a dynamic and rapidly evolving field that offers immense potential for solving complex problems in healthcare, agriculture, and the environment. By integrating knowledge from various disciplines, biological engineers are at the forefront of technological innovation, developing innovative solutions that can improve the quality of life for people around the world. As the field continues to grow, it is poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of humanity.。

acid酸acidify酸性actinomycete放线菌adapability适应性adjunct辅助剂adjunctive therapy辅助治疗adsorbeacid酸acidify酸性actinomycete放线菌adapability适应性adjunct辅助剂adjunctive therapy辅助治疗adsorbent吸附剂adsorption吸附aeration通气,通风agar琼脂agarose gel琼脂糖凝胶agitation搅动alcohol醇,乙醇alga海藻algae(复)藻类alkalinity碱性amio氨基的ammonium铵amply扩增amylase淀粉酶anaerobe厌氧的analog类似物analogue类似物antibiotic抗生素antibiotic resistance抗生素抗性antibody抗体antifoam消泡剂antigen抗原apparatus仪器,器械archeologist考古学家aseptic无菌的bacterial细菌的bacteriophage噬菌体base pair碱基对batch一次生产量biodegredable可降解的bioinformatics生物信息学biomolecule生物分子biosensor生物传感器botany植物学brew酿造broth肉汤,发酵液bubble column bioreacter鼓泡塔式反应器buffer缓冲液,缓冲calcium钙carbohydrate碳水化合物carbonate碳酸盐catabolic分解代谢的cellulase纤维素酶cellulose纤维素centrfugal离心的,离心机centrifugation离心法,离心centrifuge离心机chemostat恒化器chitin几丁质chloroplast叶绿体chromatography色谱chromosome染色体citric acid柠檬酸clarification澄清clone克隆clone library克隆文库cloning vector克隆载体coefficient系数colony菌落colorimeter比色计comparison比较,对照complementrary互补的component成分,组分composition组成compound化合物concentration浓缩,浓度conformation构象contamination污染,污染物crystallisation结晶化decomposition分解,腐烂decontaminate净化deficient缺乏的degrade降解,降级deplete使衰竭,耗尽deposite沉淀物,沉淀detoxification解毒devoid缺乏的dextran葡萄糖diameter直径digest消化,酶切diluent稀释的,稀释液dilute稀释dilution稀释disintegrant崩解剂disintegration瓦解dissociate解里,游离dissolve溶解double helix双螺旋double stranded双链的downcomer下流管,溢流管,液降duplicate使重复,复制electrophoresis电泳enzyme酶eradication根除eukaryote真核细胞exaggerate使增大,使夸大exceed超过,胜过expertise专门技术expression vector表达载体extracellular细胞外的fabricate虚构,制作,伪造feedback反馈fermentation发酵fermenter发酵罐filter过滤,过滤器filtration过滤flask烧瓶。

生物工程(生物技术)专业英语翻译Lesson One(4学时)Inside the Living Cell: Structure andFunction of Internal Cell Parts教学目的:使学生掌握细胞的组成结构(各种细胞器以及它们在细胞中的位置),Cytoplasm: The Dynamic, Mobile Factory细胞质:动力工厂Most of the properties we associate with life are properties of the cytoplasm. Much of the mass of a cell consists of this semifluid substance, which is bounded on the outside by the plasma membrane. Organelles are suspended within it, supported by the filamentous network of the cytoskeleton. Dissolved in the cytoplasmic fluid are nutrients, ions, soluble proteins, and other materials needed for cell functioning.生命的大部分特征表现在细胞质的特征上。
细胞质大部分由半流体物质组成,并由细胞膜(原生质膜)包被。
细胞器悬浮在其中,并由丝状的细胞骨架支撑。
细胞质中溶解了大量的营养物质,离子,可溶蛋白以及维持细胞生理需求的其它物质。
2The Nucleus: Information Central(细胞核:信息中心)The eukaryotic cell nucleus is the largest organelle and houses the genetic material (DNA) on chromosomes. (In prokaryotes the hereditary material is found in the nucleoid.) The nucleus also contains one or two organelles-the nucleoli-that play a role in cell division. A pore-perforated sac called the nuclear envelope separates the nucleus and its contents from the cytoplasm. Small molecules can pass through the nuclear envelope, but larger molecules such as mRNA and ribosomes must enter and exit via the pores.真核细胞的细胞核是最大的细胞器,细胞核对染色体组有保护作用(原核细胞的遗传物质存在于拟核中)。

生物医学工程专业英语English:Biomedical engineering is a multidisciplinary field that applies principles and techniques of engineering to solve problems in biology and medicine. It involves the design and development of medical devices, diagnostic equipment, prosthetics, pharmaceuticals, and other healthcare technologies. Biomedical engineers work at the intersection of engineering, biology, and healthcare to improve the quality of patient care, enhance the efficiency of medical procedures, and advance medical research. They collaborate with healthcare professionals, scientists, and industry experts to innovate new solutions for diagnosing, treating, and preventing diseases and injuries. Biomedical engineering encompasses various subfields such as biomaterials, biomechanics, bioinformatics, medical imaging, tissue engineering, and rehabilitation engineering. This diverse range of specialties allows biomedical engineers to address a wide array of health-related challenges, from creating artificial organs to developing advanced medical imaging techniques. The field also plays a crucial role in addressing global health issues by designing affordable and accessible healthcare technologies for underservedpopulations. Overall, biomedical engineering is a dynamic and rapidly evolving field that combines cutting-edge technology with a deep understanding of biological systems to improve human health and well-being.中文翻译:生物医学工程是一个跨学科领域,应用工程学原理和技术解决生物学和医学中的问题。


probe 探针atrium 中庭,心房(atria )heart values 心脏瓣膜ventricle 室,心室Doppler shift 多普勒频移artery 动脉blood flow 血流,血流量trace 踪迹carotid 颈动脉physiological 生理的misdiagnosis 误诊echo sounding 回声探测gallstones 胆结石breast masses 乳房包块tumors 肿瘤gray scale 灰度,灰阶spectral 光谱的hand-held 手提式,便携式scanner 扫描仪clinical 临床的,诊断的Sonography 超声波扫描术platform 平台chemotherapy 化学疗法Ultrasonic waves 超声波disruptive 破坏的malignant 恶性的,有害的transducer 传感器pulse 脉冲Disk Storage 磁盘储存器Piezoelectric Effect 压电效应electric currents 电流crystals 晶体propagate 传播,传送Receipt 接extensively 广阔地non-invasive 非侵入性的,非侵入的congenital 先天性的malformations 畸形Down syndrome 唐氏症polydactyl 多指畸形dysmorphia 畸形cleft lipn. [口腔] 唇裂;[胚][口腔] 兔唇amplitude 振幅duration 持续Amplification 放大Scan Converter 扫描变换器Vibrate 振动anatomical 解剖的,结构上的conventional 常见的vibrations 振动共鸣amplifier 放大器compensation 补偿sequence 序列,顺序format 格式,版式matrix 矩阵matrix 格式修改storage 存储therapeutic 治疗的blood clots 血栓kidney stones 肾结石Portability 可移植的Joint 关节rotating anode 旋转阳极fluoroscopic 荧光的image intensifier 图像增强器fluoroscopy 荧光镜检查radiography 放射线照相术electromagnetic [i,lektrəumæɡ‘netik] adj. 电磁的radiation [reidi'eiʃən] n. 辐射;发光;放射物Emitted v. 排放(emit的过去分词);发散charged particles带电粒子photons ['fəu,təns] n. 光子;光量. penetrate ['penitreit] vt.洞察;穿透charge [tʃɑ:dʒ] n. 费用;电荷;掌管decelerate 减速collision 冲突target 目标,靶子braking radiation 制动辐射bombarding 急袭的,爆炸的vacancy 空缺,空位electron [i'lektrɔn] n. 电子material [mə'tiəriəl] adj. 重要的;物质的accelerated 加速的Bremsstrahlung 轫致辐射electromagnetic radiation 电磁辐射region 地区electromagnetic spectrum 电磁谱elastically [i'læstikli] adv. 有弹性地;伸缩自如地Rebounding 弹回Photoelectric 光电的Compton Scattering 康普顿散射Pair Production 电子偶的产生Rayleigh scattering 瑞利散射coherent [kəu'hiərənt] adj. 连贯的,一致的dominant ['dɔminənt] adj. 显性的;占优势的;支配的,统治的interaction processes 互动过程relevant 有关的cross-sections 横截面Photoelectric absorption 光电吸收linear attenuation coefficient 线性衰减系数probability of ···的概率Avogadro [avɔ'gadrɔ] n. 阿佛加德罗radiation intensity 辐射强度traversing 穿过,通过thickness 厚度molecule 分子Ionisation 电离作用release 释放free radicals 自由基,游离基hydrogen ['haidrədʒən] n. [化学] 氢peroxide [pə'rɔksaid] n. 过氧化氢;过氧化物excited molecules 受激分子Barium meal钡餐Flat Panel 扁平面板Formation 形成,构造incident 附带的Subject contrast 受照者对比度Sharpness 清晰度shortened form 简称signal to noise ratio 信噪比Penumbra 半影Focal spot 电子焦点,焦斑Quantum noise 量子噪声Grainy 粒状的exposure factors 曝光系数emulsion [i'mʌlʃən] n. [药] 乳剂;[物化] 乳状液;感光乳剂halide ['hælaid] adj. 卤化物的receptors n. 受体;接受器;神经末梢(receptor的复数)pixel n. (显示器或电视机图象的)象素(等于picture elementelectrode n. 电极;电焊条storage capacitor储存电容;[电] 储能电容器;存储电容器class substrate 玻璃基片flat panel detector 扁平面板探测器radiography 射线照相术fluoroscopy room 透视室ancillary equipment 辅助设备image intensifier tower 图像增强器control console 控制台energize the console. 激励控制台electric circuits 电路possibility of shock 振动的可能性Line Compensation 线性补偿ionization chamber 电离室,电离箱Anatomically Programmed Radiography ( APR)结构结构程控放射线照射术x-ray circuity x线间接性electromagnetic induction 电磁感应from cathode to anode 从阴极到阳极milliampere 毫安thermionic emission 热电子发射tube current 管电流Made radiolucent 使射线可透过的Photomultiplier detector assembly 光电倍增管检测装备fluorescent screen 荧光屏photodiode 光电二极管filament transformer 丝级变压器rectifier 整流器step up transformer 升压变压器V oltage Rectification 电压整流single phase 单相Half-Wave Rectification 半波整流voltage ripple 电压波纹quality and quantity 质量和数量constant positive voltage 正电压恒定Radiographic Rating Chart 影像评级图Angiogram 血管照影片Digital Subtraction Angiography 数字减影血管照影Coronary Arteries 冠状动脉thin fan beam 扇状束Serologic 血清学研究immunodeficiency 免疫缺陷phosphorylation 磷酸化作用kinase 激酶esophageal mucosa 食道粘膜endoscope 内窥镜cell carcinoma 细胞癌spinal cord 脊柱差别:gaps between, differentiate between, discrepancies存在,出现:occurred, occurrence ,existed, existence, presence, present多数,少数:the overwhelming majority of, in the majority of cases ,a marked majority, handful(一把,少数)方法:approaches, avenues, methods, techniques, means, tools发生率:Incidence, frequency, prevalence发现,阐明,报道,证实:verify, confirm, identify, define, characterize, clarify, establish, ascertain, explain, observe, illuminate, illustrate,demonstrate, show, indicate, exhibit, presented, reveal, display, manifest,suggest, propose, estimate, prove, imply, disclose,report, describe,facilitate the identification of ,screening ,isolation改变:change, alteration,高,增加:high, enhanced, elevated, increased, forced各种,多种:in multiple types of, in various types of, in a variety of关系,相关,参与:closely involved in, associated广泛的:in an extensive survey执行:perform, carry out降,少,缺:decrease, reduction, reduced, diminish, loss, suppression, deficient, low, weak, faint, light, absence, absent, undetectable, lack ,defective,negative,poor,impaired, greatly reduced or completely absent, frequently lost or down-expressed角色,起作用:role, part (limited, potential, early, possible role)可能性:feasibility密切地:intimately难理解的,似谜的:enigmatic (x remains enigmatic)潜在假定的:potential, candidate, putative,缩写:abbreviations识别,辨别:discernment提供,帮助:provide, supply, help (to), contribute to, offer, allow, dedicate, devote, assist in调节(失调,上调,下调):dis-regulation, dys-regulation, up-regulation, up-expression, over-expression, down-expression, down-regulation,推测:presume,speculate ,confer, conjecture ,guess, deduce,deduction显著,优先的:prominent, pronounced, obvious, marked, predominant, strong, striking ,notable, Conspicuously, remarkably,significant, preferential, prevalence, prevalent,相同,同等并列:with a similar pattern to协同,加强:synergize with研究:analysis, survey, study, research, investigation, experiments, trial, observations, assessment, inquiry, examinations ,pursue investigation into, analyze, detect, determinate, be focused on, measure, examine, test, assess, evaluate, explore,一致:which is in accord with the results,which corroborated the resultswhich supported the results优缺点:merits and drawbacks,beneficial and detrimental异常:aberration, abnormality重要:crucial, key, important, major, be of critical importance相反:On the contrary, In contrary,but quite on the contrary,in sharp contrast, contrary to what would be expected,Contrary to the expectation that,与一起:in combination with, coupled with由于、鉴于:In light of,In view that。

1 Unit 1 Biomedical Engineering Lesson 1A History of Biomedical EngineeringIn its broadest sense, biomedical engineering has been with us for centuries, perhaps even thousands of years. In 2000, German archeologists uncover a 3,000-year-old mummy from Thebes with a wooden prosthetic tied to its foot to serve as a big toe. Researchers said the wear on the bottom surface suggests that it could be the oldest known limb prosthesis. Egyptians also used hollow reeds to look and listen to the internal goings on of the human anatomy. In 1816, modesty prevented French physician Rene Laennec from placing his ear next to a young woman’s bare chest, so he rolled up a newspaper and listened through it, triggering the idea for his invention that led to today’s ubiquitous stethoscope.广义上来说,生物医学工程与我们已经几个世纪以来,甚至数千年。
2000年,德国考古学家发现一个3000岁高龄的木乃伊从底比斯木制假肢与作为大脚趾的脚。
生物工程专业英语单词内生孢子Endospore 无菌的aseptic 氧oxygen 耐高渗Halotolerant 毒力virulence 氯chlorine 病原微生物pathogen 稀释attenuation 钠sodium 肠道的entero 消毒sterilization 分裂fission Deoxyribonucleic acid RNA Ribonucleic acidSulfuric acid TCA Tricarboxylic acid Polymerase chain reaction cfu Colony forming unit 黑曲霉Aspergillus niger 沙门氏菌Salmonella typhi大肠杆菌Escherichia coli 巴氏杀菌pesteurization human immunodeficiency virus 革兰氏阳/阴性Gram positive/negativeTube 烧杯Beaker 鞭毛flagellaFunnel 属genus 纤毛pili 培养皿Petri dishes 命名法nomenclature 荚膜capsule 移液枪Pipette 球菌coccus 细胞膜plasma membrane胰岛素insulin 制造业manufacture 益生元prebiotic 糖尿病diabete(s) 促进facilitate 抗生素antibiotic 极性共价键polar bond 共价键covalent bond 离子键ionic bond 氢键hydrogen bondatom 底物substrate 色素(photo)pigment electron 延长、拉长elongate 染色stainidentical 瘫痪paralysis 原子核nucleus 完全相同的复制、折叠replicate 外显子exon 杂交hybridization algae 内含子intron 合成synthetic流行病学epidemiology 终止子terminator synthesis生物降解bioremediation 启动子promoter 同时地simultaneously 防腐剂preservative 转录transcription 噬菌体bacteriophage 洗涤剂detergent 翻译translation 颗粒particleAdenine 氨基酸amino acid 杂种muleThymine 简并性degenerate 小麦wheatGuanine 调控regulate 大麦barleyCytocine 神经元neuron 玉米maze/cornUracil 成纤维细fibroblast 大豆soybean胞strand 肌肉细胞muscle cell 高粱sorghum orientation 源于;得自derive 谷物cereal primer 表明;指出indicate 豆类legume complementary 分离isolate 穗panicle sequence 扩增amplification 生理盐水saline单倍体hyploid 载体vector 胆固醇chloesterol 双倍体diploid 质粒plasmid 白灵药panacea 常染色体autosomal chromosomes 性染色体sex chromosome作业。
单词整理a- 不,非aseptic 无菌的;apolar 非极性的;asymmetercal 不对称的ab- 去,离开,脱离abnormal 反常的;abuse 滥用;abduct 外展神经aceto- 乙酰acetolactate 乙酰乳酸;acetyl 乙酰(基);acetyl phosphate 乙酰磷酸actino- 光线,射线,放线菌acrinomycin 放线菌;actinometer 化学光度计acyl- 酰基acyltransferase 转酰基酶aden(o)- 腺adenovirus 腺病毒aer(o)- 空气的aerobic 需氧的;aeration 通气agro- 土壤;农业agrochemical 农用化学品;agronomical 农艺学的amidino- 脒基amidinotransferase 转脒基酶amylo- 淀粉amylopectin 支链淀粉;amylose 直链淀粉;amyloplastid 造粉粒an- 不,非anaerobic 厌氧的;analgesic 止痛的;anapepsia 胃蛋白酶缺乏ane- 烷methane 甲烷anti- 反对,对抗,取消,抑制,解除antagonistic 对抗的;antibody 抗体;antigen 抗原angio- 血管angiogenin 血管生成素;angioma 血管瘤aut(o)- 自己的,自动的autotroptic 自养的;autonomous 自发的;autosensitization 自身致敏bio- 生物的biochemistry 生物化学;bioamine 生物胺;biocatalyst 生物催化剂bromo- 溴的5-bromouracil 5-溴尿嘧啶bis- 双,二bisexualism 雌雄异体;bisphenols 双酚类brady- 缓慢hradycardia 心动过缓;bradykinin 缓激肽carb(o)- 碳的carbodiimide 碳二亚胺;carbohydrate 碳水化合物carboxy(l) 羧基carboxy methylcellulose 羧甲基纤维素carcin(o)- 癌carcinogen 致癌物cardio- 心脏cardiotonic 强心的cent(i)- 一百的,百分之一的,厘century 世纪;centimeter 厘米;centimorgan 厘摩chemo- 化学chemoautotrophy 化能自养;chemosynthesis 化能合成;chemoattractant 化学引诱物chlor- 氯,绿chloramphenicol 氯霉素;chlorobenzene 氯苯;chloroplast 叶绿体chrom(o)- (chromat(o)-) 颜色chromatid 染色单体;chromosome 染色体;chromatography 色谱法cis- 顺cistrion 顺反子;cis regulation 顺式调节;cis-isomer 顺式异构体co- 一起,共同cooperate 合作;coincide 重合;cognate 同源的con- (col-,com-,cor-)连同,一起complexant 络合剂;concentrate 集中;combine 结合contra- 反对,相反contrast 对照;contrary 相反的;contrasuppression 反抑制counter- 反,逆couner-circulation 逆向循环;counter-ecolution 逆进化;counter receptor 反受体cryo- 寒冷,冷冻cryopreservation 冷冻保藏;cryogen 冷冻剂;cryophile 适寒性cyano- 青,蓝,氰cyanobacteria 蓝细菌;cyanocobalamin 氰钴胺素;cyanogen bromide 溴化氰de- 否定,除去,离开,降低,脱debug 排除故障;deceleration 降速;degeneration 退化deca- 十,葵decahedron 十面体;decane 葵烷;decamer 十聚体deoxy- 脱氧deoxycytosine 脱氧胞嘧啶di- 二,二倍,二重diploid 二倍体;dimer 二聚体;divinylbenzene 二乙烯苯dia- 横穿diameter 直径;dialysis 透析;diaphragm 隔膜dis- 否定,分离disintegration 破碎;disagree 不同意;dissemination 散播dodeca- 十二dodecahedron十二面体;dodecane 十二烷;dodecamer 十二聚体eco- 生态,居处,宿主ecogentics 生态遗传学;ecology 生态学;ecomone 生态信息素ectoblast 外胚层;ectohormone 外激素;ectodomain 胞外结构electr(o)- 电electrodialysis 电渗析en-(em-) 使成为,置于……中enable 能够;encode 编码;embed 包埋end(o)- 内endergonic 吸能的;endospore 内生孢子enol 烯醇phosphoenolpyruvate 磷酸烯醇丙酮酸enter(o)- 肠enteroacteria 肠细菌;enterobactin 肠杆菌素;enterocyte 肠细胞epi- 表;变化epichlorohydrin 表氯醇;epimerase 差向异构体酶;epithelial cell 上皮细胞erythr(o)- 红,赤erythrose 赤藓糖;erythromycin 红霉素;erythrocyte 红细胞eu- 真正eukaryote 真核生物;eukaryocyte 真核细胞;eubacteria 真细菌e(x)- 向外,超出,完全,彻底explant 外植体;elongate 拉长;evaluate 评价ex(o)- 外,在外,产生exothermic 放热的;exergonic 放能的;exogenous gene 外源基因extra- 超出extracellular 胞外的;extract 抽提物;extracellular virus 胞外病毒ferri- 高铁ferricytochrome 高铁细胞色素;ferritin 铁蛋白;ferridoxin 铁氧还原蛋白ferro- 亚铁ferrocytochrome 亚铁细胞色素;ferroheme 血红素;ferrochelatase 亚铁螯合酶flavanol 黄烷酮;flavin 黄素;flavone 黄酮fluoro- 氟基,氟代,荧光fluorochrome 荧光染料;fluoroacetate 氟乙酸;fluorometer 荧光剂formyl- 甲酰formyltetrahydrofolate 甲酰四氢叶酸;formyl 甲酰基;formylation 甲酰化geo 土地geographical barrier 地理障碍;geographical isolation 地理隔离;geosmin 土腥味素glyc(o)- 糖glycoprotein 糖蛋白hem(o,a)-,haem(o,a)-,haemat(o)-血的hemoglobin 血红蛋白;haemagglutinin 血凝素;haem 血红素hemi- 半hemicellulase 半纤维素;hemizygote 半合子;hemiacetal 半缩醛heter(o)- 异,杂,异种heterogeneous 异质的,不均一的;heterotrophic 异养的;heteroantigen 异种抗原hepato- 肝hepatocarcinoma 肝癌;hepatocyte 肝细胞;hepatotoxin 肝脏毒素homeo- 同源,同祖homeotic gene 同源异形基因hom(o)- 相同homogeneous 同质的,均一的;homologous 同源的;homoeosis 同源异形hydr(o)- 水,液体,氢hydrocarbon 烃;hydrocolloid 水胶体;hydrobios 水生生物hydroxy(l) 羟基hydroxyapatite 羟磷灰石;hydroxylase 羟化酶hyper- 超出,过度hyperfiltration 反渗透;hypertension 高血压hypo- 低,(过)少sodium hypochlorite 次氯酸钠;hypoblast 下胚层;hypoimmunity 低免疫性imino- 亚胺基iminodiacetic acid 亚胺基二乙酸immuno- 免疫immunogenic 致免疫的;immunoassay 免疫分析in-(il-,im-,ir-)不,无;在内,入内insoluble 不能溶解的;insuperable 不能克服的;impermeable 不能渗透的infra- 下面,内部infrastructure 基础结构;infrared 红外线的inter- 相互,在……之间interact 相互作用;intergeneric 属间的;inter-particle 颗粒间的intra- 在内,向内intraspecific 种内的;intra-particle 颗粒内的;intravenous 进入静脉的iodo- 碘基,碘代iodometry 碘量法;iodouracil 碘尿嘧啶;iodoacetic acid 碘乙酸iso- 同,等,异isomer 同分异构体;isomerase 异构酶;isobutyl 异丁基kary(o)- 核,细胞核karyology 胞核学keto- 酮基ketohexulose 酮己酮糖;keto acid 酮酸;ketoamin 酮胺lacto- 乳lactobacillus 乳杆菌属;lactogen 催乳素;lactoglobulin 乳球蛋白leuco- 白,无色的leucocyte 白细胞lipo- 脂lipoprotein 脂蛋白;lipoxygenase 脂氧合酶lympho- 淋巴lymphocyte 淋巴细胞macro- 大的,宏观的macromolecule 大分子;macroporous 大孔的mal- 不当,不良malabsorption 吸收不良;malassimulation 同化不全;malnutrition 营养不良megal(o)- 巨大cytomegalovirus 巨细胞病毒mercapto- 巯基β-mercaptoethylamine β-巯基乙胺meso- 内消旋;中(间)meso inositol 内消旋肌醇;mesophilic 嗜温的meth- 甲基methacrylate 甲基丙烯酸methyl 甲基methyltroph 甲基营养菌micro- 微,微小的microscope 显微镜;microcarrier 微载体;microbe 微生物mono- 一,单,单一monoclonal 单克隆的;monolayer 单层multi- 多,多方面multistage 多级;multicellularity 多细胞性;myco- 真菌mycolytic 溶真菌的;mycotoxin 真菌毒素;mycoprotein 真菌蛋白myelo- 髓鞘,髓myeloblast 成髓细胞;myelocyte 髓细胞;myeloma 骨髓瘤myo- 肌myoalbumin 肌白蛋白;myoblast 成肌细胞;myocyte 肌细胞nano- 纳nanobacteria 微小细菌;nanosecond 纳秒;nanotechnology 纳米技术neo- 新neocarcinostatin 新制癌菌素;neocerebellum 新小脑;neomycin 新霉素neur(o)- 神经neural 神经的;neurotoxin 神经毒素nitro- 硝基nitrofuran 硝基呋喃;nitroalkane 硝基烷;nitrobacteria 硝化细菌nucle(o)- 核nucleoside 核苷;nucleophilic 亲核的non- 非,无,不non-newtonian fluid 非牛顿型流体;non-aqueous solution 非水溶液nor- 去甲,正noradrenalin 去甲肾上腺素;normal 正常,正交;normocyte 正红细胞over- 在上面,超过,过overshooting 过调节;overview 简明概述;overcooled 过冷的oligo- 寡oligosaccharide 寡糖,低聚糖onco- 肿瘤oncogene 致癌基因ovo- 卵ovocenter 卵中心体;ovorubin 卵红蛋白;ovum 卵细胞oxalo- 草酰,乙二酸-酰基oxalo acetate 草酰乙酸oxy- 氧;羟基deoxyguanosine 脱氧鸟苷;oxytetracycline 土霉素;oxyproline 羟脯氨酸path(o)- 病pathogen 病原菌para- 旁(位),对(位),副parabronchus 复支气管;parathyroid gland 甲状旁腺;paraoxon 对氧磷peri- 周,周围perimeter 周长;periplasmic space 周质间隙;periblast 胚周区per- 过peroxisome 过氧化质体phenyl 苯基phenylalanine 苯丙氨酸phospho- 磷酸基phosphofructokinase 磷酸果糖激酶phosphoryl- 磷酰基phosphorylation 磷酸化作用phyto- 植物phytoalexin 植物抗毒素;phytology 植物学;phytoplankton 浮游植物plasm(o)- 原生质,血浆plasmolemma 质膜pleio- 多pleiotropic 多效的;pleioxeny 多主寄生;pleiotropy 多效性poly- 多,聚polysaccharide 多糖;polystyrene 聚苯乙烯;polyacid 多酸post- 后post-transcriptional modification 转录后修饰作用;post-exponential growth phase 后对数生长期pre- 前,在前premature 过早的;precursor 前体;premise 前提pro- 原,前prokaryote 原核生物;prostate 前列腺proteo- 蛋白proteolipid 蛋白脂质;proteome 蛋白质组;proteolysis 蛋白酶解proto- 原始,初prototype 原型;protoplast 原生质体pseud(o)- 假的pseudo-plastic fluid 假塑性流体;psudodominance 假显性;pseudohypha 假菌丝pyro- 焦,火,热pyrophosphorylase 焦磷酸化酶;pyrogen 热源;progenic exotoxin 热源性外毒素quasi- 类似,准quasi-homogeneous 准均匀的radio- 辐射,放射autoradiography 放射自显影;radiotracer 放射性示踪物;radiology 放射学re- 再,重新,反复recirculation 循环;reversion 回复;reactivity 反应性retro- 后,向后,回复retrovirus 逆转录病毒ribo- 核糖riboflavin 核黄素;ribonucleic acid 核糖核酸;ribonucleotide 核糖核苷酸self- 自身的self-fertilization 自体受精semi- 半,部分semi-permeable membrane 半透膜;semi-synthetic 半合成的;semiconservative replication 半保留复制sero- 血清serological 血清学;seroconversion 血清转变soma- 体soma 体质,胞体;somatic cell 体细胞;somatization 体部分化somato- 生长somatocrinin 生长素释放肽;somatotroph 促生长素细胞;somatotropin 促生长素,生长激素sub- 下面,次于,近于subcellular 亚细胞的;subunit 亚基;subdivide 再分super- 上,上面,超,超级superior 上面的;supernatant 上清液的syn-(sym-) 共同,合synchronize 同步;symbiosis 共生现象;synergistic 协同作用的techn(o)- 技术,工艺technology 技术(学),工艺学;technique 技术therm(o)- 热thermistor 热敏电阻;themometer 温度计thi(o)- 硫,硫代thiamine 硫胺素;thioacylation 硫代酰化;thiokinase 硫激酶thym(o)- 胸腺thymosin 胸腺素toti- 全,全部,整个totipotency 全能性trans- 横穿,通过,转移transformation 转化;transcribe 转录;transposen 转位子tri- 三,三次,三级triplet 三联体;triangle 三角形;triacylglycerol 三酰甘油ultra- 超,极端,过分ultrasonic 超声波;ultracentrifugation 超离心un- 不,相反,出去unfold 展开under- 下面,低于,不足undergraduate 大学本科生;underpin 加固……的基础uni- 单,一,同一uninucleate 单核的;unique 独一无二的up- 向上,在上upstream 上游;upright 直立的uro- 尿urokinase 尿激酶vinyl- 乙烯基polyvinylchloride 聚氯乙烯后缀:-able(-ible) 可能的practicable 可行的;responsible 负责的-ability 能力acceptability 可接受性;permeability 渗透性-age 表示动作过程、量spillage 溢出;percentage 百分比-al 接在名词后形成形容词,接在动词后形成名词personal 个人的;exceptional 例外的;refusal 拒绝-aldehyde 醛glutaraldehyde 戊二醛-amin 胺methylamine 甲胺-ane 烷methane 甲烷-ant 动作者inactivant 失活剂;bioprotectant 生物保护剂-ase 酶protease 蛋白酶;polymerase 聚合酶-ate 盐,酯phosphate 磷酸盐;sebacate 奎二酸酯-cide 杀害,消灭suicide 自杀;bactericide 杀菌剂;amoebicide 抗阿米巴药-cyte 细胞leucocyte 白细胞-derm 皮,皮层blastoderm 胚层;dermadrone 内病性皮疹-ene 烯ethylene 乙烯-(e)ry 场所;一类事物bakery 面包房;circuitry 电路系统;poultry 家禽-fold 倍twofold 两倍-(i)fy 接名词或形容词后构成动词solidify 固化;simplify 简化-gen 原,剂antigen 抗原;mutagen 诱变剂;carcinogenic 致癌的-gram 图形;记录的东西chromatogram 色谱图;polarograph 极谱图-graphy 描绘、记录的方式、学科chromatography 色层分离法;autoradiography 放射自显影术-ic anhydride 酸酐sodium chloride 氯化钠-imine 亚胺iminodiacetic acid 亚胺基二乙胺-ish 略带一点的greyish 浅灰色的-ist ……的实行者,……专业人员(专家)scientist 科学家;geneticist 遗传学家-itis 炎,发炎hepatitis 肝炎;encephalitis 脑炎-ize(-ise) 使成为atomize 雾化;oxidize 使氧化-lactone 内酯β-propiolactone β-丙醇酸内酯-lemma 皮,壳,鞘膜basilemma 基底膜;lemmatoxin 鞘毒素-less 无,不,不能stainless 不锈的-like 如……样的sponge-like 海绵状的-(o)logy(-ological,形容词)学科biology 生物学;technology 技术学,工艺学;toxicology 毒理学的-lysis 分解作用,过程glycolysis 糖酵解作用;hydrolysis 水解作用;analysis 分析-lytic(形容词,分解的)-lyze(-lise)(动词,分解)-lysate(名词,分解液)hydrolytic 水解的;hydrolyze 水解;hydro-lysate 水解液-ment 在动词后构成名词development 发展;entrainment 夹带-meter 计,表spectormeter 发光剂;viscometer 粘度计-metric 测量的gravimetric (测定)重量的;volumetric (测定)体积的;potentiometric (测量)电位的-mycete 霉菌streptomycete 链霉菌-mycin 霉素,菌素mitomycin 丝裂霉素;actinomycin 放线菌素-nema 丝,线amphinema 偶线;chromonema 染色体;nemacicide 杀线虫剂-oid 类,似,……样、状的acidoid 似酸的;amyloid 淀粉样的;carotenoid 类胡萝卜素-ol 醇butanol 丁醇;inositol 肌醇-oma 瘤myeloma 骨髓瘤;hybridoma 杂交瘤-one 酮phenoxazinone 吩噁嗪酮-ory 构成形容词transitory 短暂的;respiratory 呼吸的;构成名词,表场所depository 储藏所-ose 糖heptose 庚糖;lactose 乳糖-oside 糖苷galactoside 半乳糖苷;cardiac glycoside 强心苷-osis 病,症;acalcicosis 缺钙症;hepatitis 肝炎-ous 构成形容词extraneous 外来的;rigorous 严格的-philic 亲……的lipophilic 亲脂性的;hydrophilic 亲水的-phobic 疏……的hydrophobic 疏水的-phoresis 移动electrophoresis 电泳-phil 亲,嗜,喜acidopil 嗜酸的;aerophil 好气的-plasm 血浆,原生质protoplasm 原生质-plast 原始细胞,(质)体,血浆centroplast 中心质体;hematoplast 成血细胞;plasmolemma 质膜-proof 耐……的flame-proof 耐火的;explosion-proof 防爆的-side 苷nucleside 核苷;glycoside 糖苷-sis 构成名词,表示作用,过程mutagenesis 诱变作用;mitosis 有丝分裂;meiosis 减速分裂-some 体,粒chromosome 染色体;idiosome 核旁体;ribosome 核糖体-stat 稳定装置chemostat 恒化器-taxis,tropism 趋向性aerotaxis 趋氧性;chemiotaxis 趋化性;lipotropism 亲脂性-tion(-ation,-ition,-sion) 构成名词instrumentation 仪表化;trypsinization 胰蛋白消化酶;adhesion 粘着-tide 甘酸,肽deoxyribotide 脱氧核苷酸;propeptide 前肽-troph ……营养生物,……营养型(-trophic 构成形容词)methanotroph 甲烷营养型;autotroph 自养生物;autotrophic 自养的-wise 接名词或形容词后构成副词batchwise 分批的;likewise 同样的。
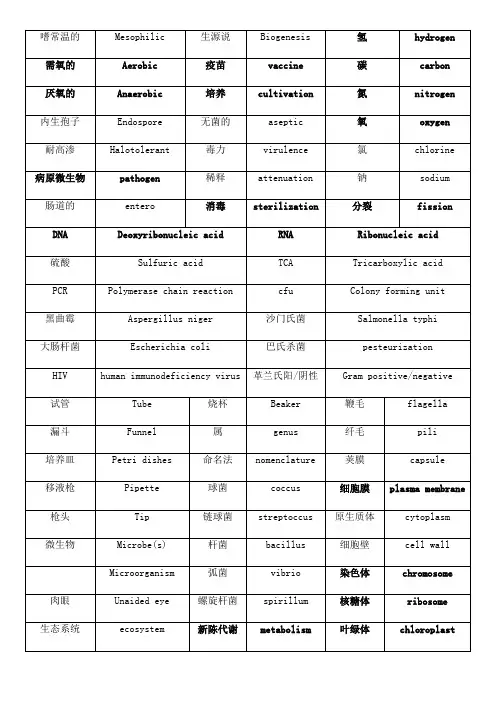
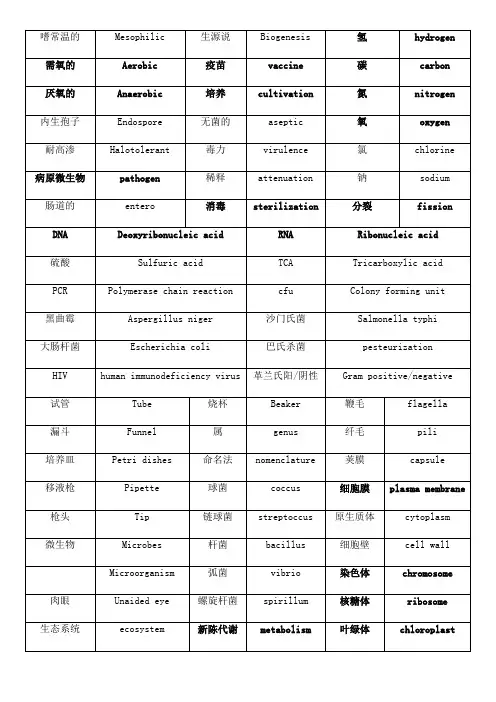
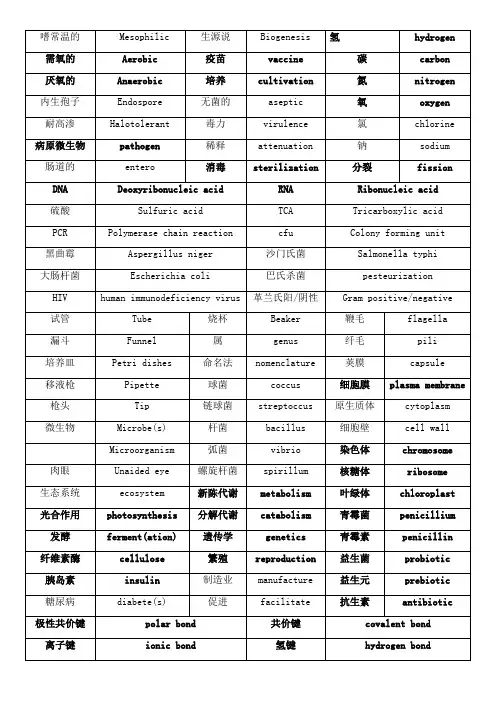
生物工程专业英语单词嗜常温的Mesophilic 生源说Biogenesis 氢hydrogen 需氧的Aerobic 疫苗vaccine 碳carbon 厌氧的Anaerobic 培养cultivation 氮nitrogen 内生孢子Endospore 无菌的aseptic 氧oxygen 耐高渗Halotolerant 毒力virulence 氯chlorine 病原微生物pathogen 稀释attenuation 钠sodium 肠道的entero 消毒sterilization 分裂fission DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid RNA Ribonucleic acid 硫酸Sulfuric acid TCA Tricarboxylic acid PCR Polymerase chain reaction cfu Colony forming unit 黑曲霉Aspergillus niger 沙门氏菌Salmonella typhi大肠杆菌Escherichia coli 巴氏杀菌pesteurization HIV human immunodeficiency virus 革兰氏阳/阴性Gram positive/negative 试管Tube 烧杯Beaker 鞭毛flagella 漏斗Funnel 属genus 纤毛pili 培养皿Petri dishes 命名法nomenclature 荚膜capsule 移液枪Pipette 球菌coccus 细胞膜plasma membrane 枪头Tip 链球菌streptoccus 原生质体cytoplasm 微生物Microbe(s) 杆菌bacillus 细胞壁cell wall Microorganism 弧菌vibrio 染色体chromosome 肉眼Unaided eye 螺旋杆菌spirillum 核糖体ribosome生态系统ecosystem 新陈代谢metabolism 叶绿体chloroplast相互作用interaction 三联密码triplet 酿brewing子核苷酸碱基nucleotide bases 内质网endoplasmic reticulumA Adenine 氨基酸amino acid 杂种muleT Thymine 简并性degenerate 小麦wheatG Guanine 调控regulate 大麦barleyC Cytocine 神经元neuron 玉米maze/cornU Uracil 成纤维细fibroblast 大豆soybean胞链strand 肌肉细胞muscle cell 高粱sorghum 定位orientation 源于;得自derive 谷物cereal 引物primer 表明;指出indicate 豆类legume 互补complementary 分离isolate 穗panicle 序列sequence 扩增amplification 生理盐水saline 单倍体hyploid 载体vector 胆固醇chloesterol 双倍体diploid 质粒plasmid 白灵药panacea 常染色体autosomal chromosomes 性染色体sex chromosome 红细胞red blood cell 生殖细胞germ cell端粒telomere 转化transformatio插入addingn精子sperm 提取extract 敲除removing 卵子egg 组织tissue 克隆clone 基因组genome 器官organ 花粉pollencDNA complementary DNA 探针probe 干预intervention 生物技术biotechnology 纯化purify 症状indication 生物学的biological 重组recombinant 前体物precursor 裂解性噬菌体lytic cycle 机制,机理mechanism 膳食纤维dietary fiberbiodiversity 溶源性噬菌体lysogenic cycle 传统的conventional 生物多样性衣壳capsid 合成,混合compound 耕种tillage 成熟maturation 标识,标签label 造假adulteration 基因差异表达differential gene expression 副作用adverse/side effect 计划生育birth control 水土流失soil erosion 胚胎embryo 改善,改良amelioration 过敏原allergen非天然添加剂artificial ingredient 液态深层发酵罐submerged fermentor 饮料beverage 接种inoculation 麦汁wort 啤酒花hop 不足的deficient 探针probe 酸acid 碱alkali 糖化mashing液态发酵LSF liquid-state fermentation 固态发酵SSF solid-state fermentation 生物反应器fermentorbioreactor作业甘油三酯triglycerides 乳糖lactose 希拉细胞Hela cellmRNA messengerRNA 蔗糖sucrose 蛋白质protein rRNA ribosomal RNA 核糖ribose 糖sugar tRNA transferRNA 酶enzyme 溶酶体lysosome R基R-Group 细胞核nucleus 生物体organism 胰腺pancreas 小分子micromolecule 专业的;特化specialized 有机物organic 大分子macromolecule 细胞器organelle 细胞cell 细胞学cytology 合成synthesis 组织tissue 亲水的hydrophilic 子单位subunit 器官organ 疏水的hydrophobic 基团group 多糖polysaccharide 聚合物polymer 羧基carboxyl 缠绕intertwine 分子molecule 调节,控制regulate 细胞的cellular 功能function 细胞系cell line 脂质lipid 二糖disaccharide 由...组成compose of 葡萄糖glucose 半乳糖galactose 果糖fructose分泌secrete 碳水化合物carbohydrate 消化液digestivefluids上皮的epithelial 转换conversion 指令instruction 折叠fold 多肽polypeptide 催化catalyze 核苷,核苷酸nucleotide 围绕enclose。