天津理工大学计算机网络实验三
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:1014.04 KB
- 文档页数:5
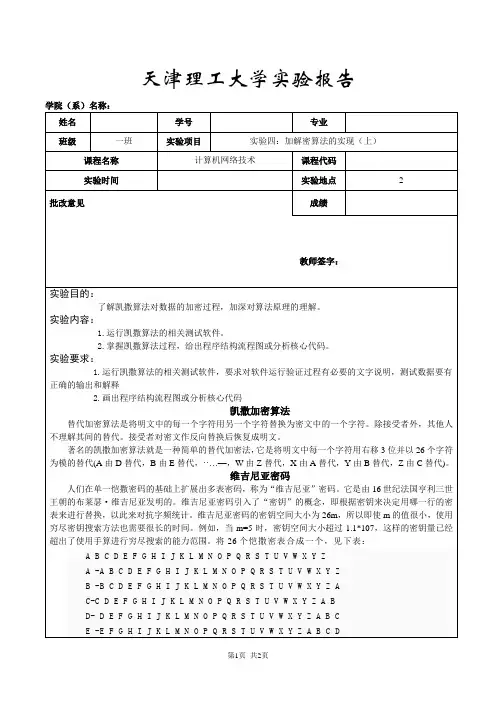
天津理工大学实验报告学院(系)名称:F -FGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ A B C D EG- G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z A B C D E FH -H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z A B C D E F GI- I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z A B C D E F G HJ -J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z A B C D E F G H IK -K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z A B C D E F G H I JL -L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z A B C D E F G H I J KM -M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z A B C D E F G H I J K LN -N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z A B C D E F G H I J K L MO -O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z A B C D E F G H I J K L M NP -P Q R S T U V W X Y Z A B C D E F G H I J K L M N OQ -Q R S T U V W X Y Z A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O PR -R S T U V W X Y Z A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P QS -S T U V W X Y Z A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q RT -T U V W X Y Z A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R SU -U V W X Y Z A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S TV -V W X Y Z A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T UW -W X Y Z A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U VX -X Y Z A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V WY -Y Z A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W XZ -Z A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y加密方法:维吉尼亚密码引入了“密钥”的概念,即根据密钥来决定用哪一行的密表来进行替换,以此来对抗字频统计。

实验报告学院(系)名称:计算机与通信工程学院输入查找内容:查找结果:人员编辑新增界面:判断信息输入是否合法:2)整理上机步骤,总结经验和体会。
人员添加页面主要代码:(ashx)context.Response.ContentType = "text/html";string sno = context.Request["Sno"];string dept = context.Request["Dept"];DataTable dt;if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(sno)&&string.IsNullOrEmpty(dept)){dt =SqlHelper.ExecuteDataTable("select * from Student");}else if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(sno)){dt =SqlHelper.ExecuteDataTable("select * from Student where Sno=@Sno", new SqlParameter("@Sno", sno));}else{dt =SqlHelper.ExecuteDataTable("select * from Student where Sdept=@Sdept", new SqlParameter("@Sdept", dept));}string html = CommonHelper.RenderHtml("PersonList.htm", dt.Rows);【实验过程记录(源程序、测试用例、测试结果及心得体会等)】实验心得:不会写老师教的aspx下外链css和js,再加上老师鼓励把界面做的漂亮一点,就用了ashx,和html分开,觉得比aspx容易一些。

大工春计算机网络实验实验报告Document serial number【NL89WT-NY98YT-NC8CB-NNUUT-NUT108】姓名:报名编号:学习中心:层次:专升本(高起专或专升本)专业:网络工程实验一:交换机的登录与配置实验目的:1、掌握Console口登录交换机和使用Telnet方式登录交换机的方法;2、Comware平台的基本使用。
实验问题讨论:1.使用Telnet方式登录交换机:(1)在交换机上做出必须的预先配置,例如配置交换机的IP地址和子网掩码,配置登录交换机的用户密码,配置登录用户的权限级别等。
请把你为完成这些预先配置所执行的配置命令写到实验报告中。
答:配备IP:<Quidway>sytem→<Quidway>interfaceVLAN-interfacel→配置权限:<Quidway>user-inerfacevty04→[QW-vi-vty0-4]authentication?→[QW-vi-vtu0-4]setauthenticationsample123456→[QW]userprivilege3(2)配置PCA的IP地址和子网掩码,注意要把PCA的IP地址与交换机的IP地址设在同一网段。
请把你所做的配置写到实验报告中。
答:将PC机IP实验二:交换机VLAN间路由配置实验实验目的:1、掌握交换机VLAN间路由的配置方法;2、掌握VLAN间路由配置命令。
实验问题讨论:1.“resetsaved-configuration”命令和“reboot”命令的功能是什么?答:“reset?saved-configuration”命令的功能是擦除旧的配置文件。
“reboot”命令的功能是用来复位单板。
2.SwitchA中VLAN1的端口都包括哪几个端口VLAN2的端口包括哪几个端口VLAN3的端口都包括哪几个端口答:VLAN1:Fa0/1-6和Fa0/9-24VLAN2:Fa0/7?VLAN3:Fa0/8实验三:路由器的登录与基础配置实验目的:1、掌握路由器两种登录方式;2、掌握路由器基础命令功能。
天津理工大学实验报告学院(系)名称:计算机与通信工程学院
【实验过程记录(源程序、测试用例、测试结果及心得体会等)】用户用传真机发送文件的成功情况顺序图:
用户用传真机发送文件的失败情况顺序图:
测试结果及心得体会:
通过画交互模型顺序图,更能清晰的理解一个事件发生的全过程,中的各种细节,可能发生的问题,并进行实时处理,更好的掌握事件的脉络。
大学啊不错啊,好好学习,不要耽误了青春,但是是这个专业坑爹啊,,找好自己的方向,不要被这个专业误导了啊,,
理工的学妹,学弟们,你说呢,,哈哈哈哈,嘿嘿联系/。

2022年天津理工大学网络工程专业《计算机网络》科目期末试卷A(有答案)一、选择题1、TCP/IP模型中的网络接口层对应OSI参考模型的()。
I.物理层Ⅱ.数据链路层Ⅲ.网络层Ⅳ.传输层A. I、IIB. II、III.C. I、ⅢD.Ⅱ、Ⅳ2、()是计算机网络中的OSI参考模型的3个主要概念。
A.服务、接口、协议B.结构、模型、交换C.子网、层次、端口D.广域网、城域网、局域网3、下面有关BGP4的描述中,不正确的是()。
A.BGP4是自治系统之间的路由协议B.BGP4不支持CIDR技术C.BGP4加入路由表的路由并不一定是最佳路由D.BGP4封装在TCP段中传送4、在IP首部的字段中,与分片和重组无关的是()。
注:假设现在已经分片完成。
A.总长度B.标识C.标志D.片偏移5、信道速率为4kbit/s,采用停止-等待协议。
传播时延t=20ms,确认帧长度和处理时间均可忽略。
问帧长()才能使信道的利用率达到至少50%。
A.40bitB.80bitC.160bitD.320bit6、下列关于交换机的叙述中,正确的是()A.以太网交换机本质上是一种多端口网桥B.通过交换机互连的一组工作站构成一个冲突域C.交换机每个端口所连网络构成一个独立的广播域D.以太网交换机可实现采用不同网络层协议的网络互连7、一个UDP用户数据报的数据字段为8192B。
在链路层要使用以太网来传输,那么应该分成()IP数据片。
A.3个B.4个C.5个D.6个8、假设某时刻接收端收到有差错的UDP用户数据报,其动作为()。
A.将其丢弃B.请求重传C.纠错D.忽略差错9、如果用户程序使用UDP进行数据传输,那么()协议必须承担可靠性方面的全部工作。
A.数据链路层B.网络层C.传输层D.应用层10、当客户端请求域名解析时,如果本地DNS服务器不能完成解析,就把请求发送给其他服务器,当某个服务器知道了需要解析的IP地址,把域名解析结果按原路返回给本地DNS服务器,本地DNS服务器再告诉客户端,这种方式称为()。

实验报告
学院(系)名称:计算机与通信工程学院
姓名学号专业
班级实验名称实验三:路由器配置
课程名称计算机网络课程代码
实验时间实验地点7#219批改意见成绩
教师签字:
1.实验目的
理解路由器工作原理和配置方法,掌握路由器的接线方法,登录方式,静态路由和动态路由的配置。
2.实验环境
Windows
3.实验要求
进行网络地址规划,配置路由器;检查路由器配置。
掌握路由协议的种类和特点。
掌握静态路由、默认路由的配置方法。
掌握查看路由条目的方法。
并验证路由的作用。
4.实验过程记录(源程序、测试用例、测试结果及心得体会等)
(1)静态路由:
配置路由器 1 和各个端口 ip:
验证:
(2)Rip 路由配置路由器 1:
验证:
(3)Ospf 路由验证:
心得体会:
通过此次实验,我不仅学会了配置静态、动态路由的方法,还掌握了查看路由条目的方法、验证路由的作用,收获颇多。
【本文档内容可以自由复制内容或自由编辑修改内容期待
你的好评和关注,我们将会做得更好】。


天津理工大学计算机科学与技术学院《编译原理》上机指导《编译原理》课程组实验一词法分析器一实验目的1掌握手工生成词法分析器的方法,了解词法分析器的内部工作原理。
2通过设计编制调试一个具体的词法分析程序,加深对词法分析原理的理解。
并掌握在对程序设计语言源程序进行扫描过程中将其分解为各类单词的词法分析方法。
3掌握根据程序的伪代码来编写程序模块程序源代码。
二实验涉及到的知识要点词法分析器的功能输入是源程序,输出单词符号。
词法分析可以采用如下两种处理结构:(1)把词法分析程序作为主程序;(2)把词法分析程序作为语法分析程序调用的子程序。
三实验预习(以把词法分析程序作为主程序为例)程序语言的单词符号通常可以分以下五种:保留字、标识符、常数、运算符、界符。
语法分析程序输出的单词符号通常以二元式的形式表示:(单词种别,单词自身的值)四实验程序流程(仅供参考)五程序结构(仅供参考)Token=‘’; /*对token数组初始化*/S=getch( ); /*读入一个字符*/Getbc( ); /*滤除空白*/Switch(s){case ‘a’:case ‘b’:…case ‘z’:while (letter( ) || digit( )){concat(); /*将当前读入的字符送token数组*/getch();}retract(); /*非字母或数字则扫描指针回退一个字符*/c=reserve(); /*判断token是否为关键字,把返回值给c*/ if(c==0) /*若token是标识符*/{buildlist(); /*将标识符登录到符号表中*/return(id,指向符号表入口指针);}else /*若token不是标识符*/return(保留字,null);break;case ‘0’:case ‘1’:…case ‘9’:while (digit()) /*若当前读入的字符是数字*/ {concat(); /*将当前读入的数字送token数组*/getch();}retract(); /*非数字则扫描指针回退一个字符*/buildlist(); /*将常数登录到常数表*/return(num,num的常数表入口指针);break;case ‘+’:return(‘+’,null);break;case ‘-’:return(‘-’,null);break;case ‘*’:return(‘*’,null);break;case ‘<’:getch();if(ch==‘=’)return(relop,LE);else{retract(); /*扫描指针回退一个字符*/return(relop,LT)} break;case ‘;’:return(‘;’,null);break;default:error();}六实验内容题目:用以下语言词法构造规则,来构造词法分析器。
天津理工大学实验报告学院(系)名称:管理学院
ping -l +数值:所发送缓冲区大小。
ping -t :继续执行ping命令,直到用户按ctrl+c终止。
①ping命令
②ping -t :继续执行ping命令,直到用户按ctrl+c终止。
③ping -n +(数据包个数):发出的测试包个数。
二、使用ipconfig命令:
三、使用netstat命令:
①netstat 用于显示与IP 、TCP 、UDP 和ICMP 协议相关的统计数据,一般用于检验本机各端口的网络连接情况。
②netstat -a 本选项显示一个所有的有效连接信息列表,包括已建立的连接,也包括监听连接请求,断开连接或者处于联机等待状态等
③netstat -e ——本选项用于显示关于以太网的统计数据。
四、使用route,tracert,arp命令:①route命令
②route print 打印路由表
③tracert+网址
arp -a显示所有接口的 ARP 缓存表
⑥其他相关命令arp -s、arp -d、arp -g。
一、教学目标1. 知识目标:使学生掌握计算机网络的基本概念、组成、工作原理和应用。
2. 能力目标:培养学生分析问题和解决问题的能力,提高学生的动手操作能力。
3. 情感目标:激发学生对计算机网络的兴趣,培养学生严谨、求实的科学态度。
二、教学重难点1. 教学重点:计算机网络的基本概念、组成、工作原理。
2. 教学难点:计算机网络的工作原理和应用。
三、教学过程1. 导入新课教师简要介绍计算机网络的发展历程,激发学生的学习兴趣。
2. 讲授新课(1)计算机网络的基本概念讲解计算机网络的定义、分类、拓扑结构等基本概念。
(2)计算机网络的组成介绍计算机网络的硬件设备(如路由器、交换机、网卡等)和软件系统(如操作系统、网络协议等)。
(3)计算机网络的工作原理讲解计算机网络的数据传输、路由选择、网络通信协议等基本原理。
3. 课堂练习教师布置相关练习题,让学生巩固所学知识。
4. 案例分析选取一个实际案例,分析计算机网络在实际应用中的问题和解决方案。
5. 总结归纳教师总结本节课的重点内容,强调计算机网络在实际生活中的应用。
6. 布置作业布置课后作业,巩固所学知识。
四、教学反思1. 教学方法:本节课采用讲授法、案例分析法等多种教学方法,提高学生的学习兴趣。
2. 教学效果:通过本节课的学习,学生对计算机网络的基本概念、组成、工作原理有了较为全面的认识。
3. 改进措施:在今后的教学中,将更加注重理论与实践相结合,提高学生的动手操作能力。
五、教学评价1. 学生评价:学生对本节课的学习效果表示满意,认为教学内容丰富,易于理解。
2. 教师评价:教师对本节课的教学效果表示肯定,认为学生能够积极参与课堂活动,掌握所学知识。
总之,本节课的教学目标达成,教学效果良好。
在今后的教学中,将继续优化教学方法,提高教学质量。
PART Ⅰ: ChoiceB 1. Which of the following services does not the transport layer provide for the application layer?A.In-order delivery of data segments between processesB.Best effort delivery of data segments between communicating hostsC.Multiplexing and demultiplexing of transport layer segmentsD.Congestion controlA 2. What are the two of the most important protocols in the Internet?A. TCP and IPB. TCP and UDPC. TCP and SMTPD. ARP and DNSC 3. The Internet provides two services to its distributed applications: a connection oriented reliable service and a ( ).A. connection oriented unreliable serviceB. connectionless reliable serviceC. connectionless unreliable serviceD. In order data transport serviceD 4. Processes on two different end systems communicate with each other by exchanging ( ) across the computer network.A. packetsB. datagramC. framesD. messagesA 5. The job of delivering the data in a transport-layer segment to the correct socket is called ( ).A. demultiplexingB. multiplexingC. TDMD. FDMC 6. Two important reasons that the Internet is organized as a hierarchy of networks for the purposes of routing are:A.Least cost and maximum free circuit availabilityB.Message complexity and speed of convergenceC.Scale and administrative autonomyD.Link cost changes and link failureB 7. Which of characters is not distance-vector algorithm’s characters?()A. iterativeB. globalC. asynchronousD. distributedD 8. The length of IPV6 address is ()bits.A. 32B. 48C. 64D. 128C 9. The host component of a CIDR address of the form a.b.c.d/25 can contain addresses for:A.225 hosts (minus “special” hosts)B.512 hosts (minus “special” hosts)C.2(32-25) hosts (minus “special” hosts)D.25 hosts (minus “special” hosts)C 10. The primary function of the address resolution protocol (ARP) that resides in Internet hosts androuters is:A.To provide LAN router functionsB.To translate between LAN addresses and physical interface addressesC.To translate IP addresses to LAN addressesD.To calculate the shortest path between two nodes on a LANA 11. The POP3 protocol runs over ____ and uses port ____.A. TCP 110B. UDP 110C. UDP 25D. TCP 25D 12.When a destination host transport layer receives data from the network layer, it unambiguouslyidentifies the appropriate process to pass the data to by using a triplet consisting of:A. Source port #, destination IP address, and source IP addressB. Destination port #, source port #, process ID#C. Destination port #, source port #, destination IP addressD. Destination port #, source port #, source IP addressD 13. From the list below, select the items found in the TCP segment structure that are not found in theUDP segment structure:A. Application Generated DataB. Destination Port #C. Source Port #D. Sequence #A 14. The RIP routing protocol is based on an algorithm that is:A. Based on information received only from link “neighbors”B. A link state algorithmC. An OSPF algorithmD. A centralized routing algorithmB 15. With an exterior routing protocol, which of the following issues generally dominates the routing decisions?A. Geographical distance between AS’sB. PolicyC. Number of AS’s traversedD. Current congestion levels in the AS’sA 1. End system are connected together by ____.A. communication linksB. application layerC. transport layerD. the network layerC 2. Which application’s NOT using TCP?A. SMTPB. HTTPC. DNSD. All of themB 3. In the polling protocols, the master node polls each of the nodes in a/an ____ fashion.A. randomB. appointedC. round-robinD. uncirculatedC 4. The DNS protocol runs over ____ and uses port ____.A. UDP 36B. TCP 36C. UDP 53D. TCP 53A 5. TCP provides a ____ service to its applications to eliminate the possibility of the sender over-flowingthe receiver’s buffer.A. flow-controlB. congestion controlC. reliability controlD. data connectionD 6. We can classify just about any multiple access protocol as belonging to one of three categories: channel partitioning protocols, random access protocols, and ____.A. address resolution protocolsB. Dynamic host configuration protocolsC. link-control protocolsD. taking-turns protocolsB 8. The maximum transfer unit(MTU) in Ethernet frame structure is ()byte .A. 1000B. 1500C. 800D. 2000B 9. The socket of UDP is identified by _____ and _______.A. source IP address and source port numberB. destination IP address and destination port number.C. source IP address and destination port number.D. destination IP address and source IP address.C 10. Which is not plug and play in the following four items?A. DHCPB. HubsC. RoutersD. SwitchesD 11.Which of routers is not default routers ?A. first-hop routerB. source routerC. destination routerD. second-hop routerB 13. ICMP is_____.A. the protocol of Application layerB. the protocol of network layerC. the protocol of transport layerD. not a part of TCP/IP protocolsB 14. As general, we has following channel partitioning protocols except ____.A. TDMB. CSMAC. FDMD.CDMAD 15. ____ is most used for error reporting.A. UDPB. SMTPC. FTPD. ICMPB 16. The header of IPV6 is ____byte.A. 20B. 40C. 60D. 80B 17. In the network layer these service are host-to-host service provided by ____. (B)A. the transport layer to the network layerB. the network layer to the transport layerC. the network layer to the network layerD. the transport layer to the transport layerA 18. If there is not enough memory to buffer an incoming packet , a policy that drop the arriving packet called ____.A. drop-tailB. packet lossC. protocolD. encapsulationC 19. In either case, a ____ receives routing protocol messages, which are used to configure its forwarding table.A. serverB. hostC. routerD. ModemD 20. Which of the following functions does not belong to PPP___.A. framingB. link-control protocolsC. network-control protocolsD. error correctionB 1. Which of the following services does the Internet network layer provide for the Internet transport layer?A.In-order delivery of data segments between processesB.Best effort delivery of data segments between communicating hostsC.Multiplexing and demultiplexing of transport layer segmentsD.Congestion controlD 2. The main task of the Internet’s Domain Name System (DNS) is to:A.Translate port numbers to IP addressesB.Specify the standards for Internet domain namesC.Provide an authority for registering domain namesD.Translate mnemonic(记忆的)names to IP addressesA 10. The FTP protocol runs over ____ and uses port ____.A. TCP 21B. TCP 80C. UDP 20D. TCP 110C 3.RDT3.0’s receiver FSM is same to:a) RDT1.0 b) RDT2.1 c) RDT2.2 d) RDT2.0B 4.The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) provides which of the following services?a)End-to-end station addressingb)Application multiplexingc)Inter network routingd)Medium access control (MAC)D 6.Given that the requested information is not available at any intermediate databases, a non-iterated DNS query from a requesting host would follow the path:a)Root name server, local name server, authoritative name serverb)Authoritative name server, root name server, host name serverc)Local name server, root name server, local name server, authoritative name servere)Local name server, root name server, authoritative name serverA 8.lect the four essential steps, briefly described, for terminating a TCP connection between a client and a server, assuming that the initiating host is the client:(1)Client sends TCP segment with ACK0 and final sequence number(2)Client sends TCP segment with FIN =1 and goes into FIN_WAIT state(3)Server sends TCP segment to ACK the client’s FIN request and enters CLOSE_WAIT state(4)Server sends TCP segment with FIN=0(5)Server sends TCP segment with FIN=1(6)Client sends TCP segment with to ACK server’s FIN and enters second FIN_WAIT state(7)Client sends TCP segment with FIN=0a) 2,3,5,6 b) 5,1,2,3 c) 1,3,5,7 d) 2,3,4,6B 10.When compensating for link cost changes in the distance vector algorithm, it can generally be said that:a)Increased costs are propagated quickly, i.e., “bad news” travels fastb)Decreased costs are propagated rapidly, i.e., “good news” travels fastc)Decreased costs do not converged)None of the aboveB 14.As an IP datagram travels from its source to its destination:a)the source IP address is changed at each router to identify the sending routerb)the router uses the destination IP address to consult its routing tablec)the router does not use the IP addresses in the datagramd)the destination IP address is changed at each router to reflect the next hopC 15.From the list below, choose the bit pattern which could be a valid generator value for the CRC code (R) 11010:a)1110b)011010c)100101d)10011A 16.Consider sending a 1300 byte IPv4 datagram into a link that has an MTU of 500 bytes:a)Three fragments are created.b)Four fragments are created.c)Three fragments are created with offsets 0, 500 1000d)The last fragment consists of exactly 300 bytes of data from the original datagramC 17.Suppose one IPv6 router wants to send a datagram to another IPv6 router, but the two are connected together via an intervening IPv4 router. If the two routers use tunneling, then:a)The sending IPv6 router creates an IPv4 datagram and puts it in the data field of an IPv6datagram.b)The sending IPv6 router creates one or more IPv6 fragments, none of which is larger than themaximum size of an IPv4 datagram.c)The sending IPv6 router creates an IPv6 datagram and puts it in the data field of an IPv4datagram.d)The sending IPv6 router creates an IPv6 datagram and intervening IPv4 router will reject theIPv6 datagramD 18.Which of the following was an important consideration in the design of IPv6a)fixed length 40-byte header and specified options to decrease processing time at IPv6 nodesb)128-bit addresses to extend the address spacec)different types of service (flows) definedd)all of the aboveD 19.A network bridge table is used to perform the following:a)Mapping MAC addresses to bridge port numbersb)Forwarding frames directly to outbound ports for MAC addresses it handlesc)Filtering (discarding) frames that are not destined for MAC addresses it handlesd)All of the abovePART Ⅱ: True / False (1 points per question – total:20 points)1. The DNS server can update the records. (T)2. The TCP connection is a direct virtual pipe between the client’s socket and the server’s connection socket. (T)3. SMTP protocol connect the sender’s mail server and receiver’s mail server (T)4. Whereas a transport-layer protocol provides logical communication between processes running on different hosts, a network-layer protocol provides logical communication between hosts. (T)5. UDP and TCP also provide integrity checking by including right-detection fields in their headers. (F)6. If the application developer chooses UDP instead of TCP, then the application is not directly talking with IP. ( F )7. When we develop a new application, we must assign the application a port number. ( T )8. Real-tine applications, like Internet phone and video conferencing, react very poorly to TCP’s congestion control. ( T )9. The sender knows that a received ACK or NAK packet was generated in response to its most recently transmitted data packet. (T)10. To simplify terminology, when in an Internet context, we refer to the 4-PDU as a unit. (F)11. DV algorithm is essentially the only routing algorithm used in practice today in the Internet。
《计算机网络原理》实验指导书课程代码:0660086天津理工大学计算机计算机科学与工程学院2007年9月目录一、实验指导书的选用范围............................ 错误!未定义书签。
二、计算机网络技术课程简介.......................... 错误!未定义书签。
三、实验的地位、作用和目的及学生能力标准............ 错误!未定义书签。
四、实验方式与基本要求.............................. 错误!未定义书签。
五、考核方式与实验报告要求.......................... 错误!未定义书签。
六、实验项目........................................ 错误!未定义书签。
实验一:验证常用网络命令........................ 错误!未定义书签。
实验验证常用的网络命令...................... 错误!未定义书签。
实验用telnet方式收发邮件................... 错误!未定义书签。
实验二:基于TCP/UDP的Socket编程............... 错误!未定义书签。
实验:基于TCP and UDP的socket编程.......... 错误!未定义书签。
实验:基于TCP的Web Server .................. 错误!未定义书签。
实验:基于TCP/UDP的Daytime的客户端和服务器端错误!未定义书签。
实验:基于TCP/UDP的Echo的客户端和服务器端.. 错误!未定义书签。
实验 SOCKET编程实现聊天程序................ 错误!未定义书签。
实验 SOCKET编程实现mini FTP Client/ Server程序错误!未定义书签。
附录1 参考程序............................ 错误!未定义书签。
计算机与信息学院实验报告实验名称:计算机网络实验,网络传输速率的测试与探究一、实验目的:1.了解计算机网络中的传输速率概念及其原理;2.学习如何测试网络传输速率;3.探究不同网络环境对传输速率的影响。
二、实验器材:1.若干台联网计算机;2.网络测试软件(如iperf);3.计时器;4.实验用数据传输网络。
三、实验步骤:1.计划网络拓扑,确定测试机器和网络环境。
2.安装并配置iperf软件。
3.根据实际情况,选择合适的测试模式(客户端或服务器端)。
4.使用iperf测量网络传输速率,记录结果。
5.在不同网络环境下进行测试,包括有线网络和无线网络。
6.比较不同网络环境下的传输速率,分析原因。
四、实验数据及结果:1.根据实验步骤测量得出不同网络环境下的传输速率数据,并整理成表格或图表。
2.根据实验数据,计算平均传输速率,并进行比较。
五、实验分析与讨论:1.分析不同网络环境下的传输速率数据,比较其差异性。
2.分析导致传输速率差异的原因,如网络带宽限制、网络拥塞等。
3.讨论影响传输速率的其他因素,如数据包大小、网络延迟等。
4.讨论如何优化网络传输速率,提高网络效率。
六、实验结论:1.总结实验结果,对不同网络环境下的传输速率进行归纳和总结。
2.得出结论并提出相关建议,如选择合适的网络环境、避免网络拥塞等。
七、实验心得:1.总结实验过程中的体会和收获;2.评价实验设计和实施的合理性,提出改进建议;3.总结实验对个人学习的影响,并展望未来进一步的研究方向。
以上是一个计算机与信息学院实验报告的模板,根据实际情况可以进行适当修改和完善。
实验报告的重点是对实验结果进行详细分析和合理讨论,以展示实验的目的、结果与结论。
实验报告
学院(系)名称:计算机与通信工程学院
姓名学号专业
班级实验名称实验三:路由器配置
课程名称计算机网络课程代码
实验时间实验地点7#219
批改意见成绩
教师签字:
1.实验目的
理解路由器工作原理和配置方法,掌握路由器的接线方法,登录方式,静态路由和动态路由的配置。
2.实验环境
Windows
3.实验要求
进行网络地址规划,配置路由器;检查路由器配置。
掌握路由协议的种类和特点。
掌握静态路由、默认路由的配置方法。
掌握查看路由条目的方法。
并验证路由的作用。
4.实验过程记录(源程序、测试用例、测试结果及心得体会等)
(1)静态路由:
配置路由器1和各个端口ip:
验证:
配置路由器1:
验证:
(3)Ospf路由
验证:
心得体会:
通过此次实验,我不仅学会了配置静态、动态路由的方法,还掌握了
查看路由条目的方法、验证路由的作用,收获颇多。