Verilog硬件描述语言(7)设计实例
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:193.50 KB
- 文档页数:2

verilog的移位运算Verilog 编程语言是专门用于数字电路设计的硬件描述语言之一,它可以描述电子电路的行为。
其中,移位运算是 Verilog 中的一种重要运算,它可以让我们对数字信号进行位的移动操作,并且还可以进行逻辑移位或算术移位运算。
在 Verilog 中,移位运算符是 ">>" 和 "<<",它们可以分别实现右移和左移运算。
在移位运算中,所移动的位数可以作为操作符的参数进行定义。
移位运算符的操作数可以是以下任意一种:1. 一个位向量或一个寄存器。
2. 一个常量或一个表达式。
例如,下面的代码实现了一个移位器,将一个 8 位的输入向右移动 n 位,并在输出上输出结果:```module shift_register(input [7:0] D, input [2:0] n, output [7:0] Q);assign Q = D >> n;endmodule```上面的代码中,我们定义了一个shift_register 模块,它有三个输入和一个输出。
其中,输入D 表示要移动的数据,n 表示要移动的位数,而Q 则表示输出的结果。
移位运算还可以实现不同类型的位移动:逻辑移位 (_logic shift)逻辑移位运算将移动后的结果填充0 或者1,可以分为两种类型:左移和右移。
左移操作符: "<<",它将将一个数据左移指定位数,并用 0 填充。
右移操作符: ">>",它将将一个数据右移指定位数,并用 0 填充。
例如,下面的代码实现了一个逻辑移位器,用于将一个 8 位的输入向左移动 n 位,并在输出上输出结果:```module logic_shift_register(input [7:0] D, input [2:0] n, output [7:0] Q);assign Q = D << n;endmodule```算术移位 (arithmetic shift)算术移位运算比逻辑移位运算更为复杂,它是通过重复移动最高位的数值来完成的。


用Verilog语言实现奇数倍分频电路3分频5分频7分频Verilog是一种硬件描述语言(HDL),用于描述数字电路的行为和结构。
使用Verilog语言实现奇数倍分频电路可以分为以下几个步骤:1.定义输入和输出端口通过module关键字定义一个模块,并指定输入和输出端口的信号。
```verilogmodule OddDividerinput clk,output reg out_3x,output reg out_5x,output reg out_7x```2.定义局部变量和计数器定义一个局部变量和一个计数器,用于跟踪时钟周期并确定何时输出。
```verilogreg [2:0] count;```3.实现分频逻辑使用always块,根据计数器的值判断何时输出,并在输出端口上更新信号。
```verilogif (count == 3'b000) beginout_3x <= !out_3x;endif (count == 3'b001) beginout_5x <= !out_5x;endif (count == 3'b010) beginout_7x <= !out_7x;endcount <= count + 1;end```4.结束模块使用endmodule关键字结束模块定义。
```verilogendmodule完整的Verilog代码如下:```verilogmodule OddDividerinput clk,output reg out_3x,output reg out_5x,output reg out_7xreg [2:0] count;if (count == 3'b000) begin out_3x <= !out_3x;endif (count == 3'b001) begin out_5x <= !out_5x;endif (count == 3'b010) begin out_7x <= !out_7x;endcount <= count + 1;endmodule```以上代码实现了一个奇数倍分频电路,其中输入时钟信号为`clk`,输出分别是3倍分频的信号`out_3x`,5倍分频的信号`out_5x`和7倍分频的信号`out_7x`。

eda 7分频代码
在 EDA(电子设计自动化)中,可以使用 Verilog 或 VHDL 等硬件描述语言来实现 7 分频电路。
以下是一个使用 Verilog 实现 7 分频的简单示例代码:
```verilog
module七分频( input clk, output clk_out );
reg [6:0] count;
reg clk_out;
always @(posedge clk) begin
if (count == 6'd6) begin
count <= 6'd0;
clk_out <= ~clk_out;
end else begin
count <= count + 1'd1;
end
end
endmodule
```
上述代码中,我们使用了一个计数器`count`来对输入时钟`clk`进行计数。
当计数器的值达到 6 时,我们将输出时钟`clk_out`取反,并将计数器重置为 0。
这样就实现了 7 分频的功能。
在实际应用中,可能需要根据具体的需求对代码进行修改。
例如,如果需要使用异步复位信号来重置计数器,可以添加一个复位信号`rst`,并在代码中添加相应的复位逻辑。
请注意,上述代码只是一个简单的示例,实际的 7 分频电路可能需要考虑更多的细节和优化。
在设计实际电路时,建议使用专业的 EDA 工具进行综合、仿真和验证,以确保电路的正确性和可靠性。

verilog hdl语言100例详解Verilog HDL语言是一种硬件描述语言,用于描述数字电路和系统的行为和结构。
它是硬件设计工程师在数字电路设计中的重要工具。
本文将介绍100个例子,详细解释Verilog HDL语言的应用。
1. 基本门电路:Verilog HDL可以用于描述基本门电路,如与门、或门、非门等。
例如,下面是一个描述与门电路的Verilog HDL代码:```verilogmodule and_gate(input a, input b, output y);assign y = a & b;endmodule```2. 多路选择器:Verilog HDL也可以用于描述多路选择器。
例如,下面是一个描述2:1多路选择器的Verilog HDL代码:```verilogmodule mux_2to1(input a, input b, input sel, output y);assign y = sel ? b : a;endmodule```3. 寄存器:Verilog HDL可以用于描述寄存器。
例如,下面是一个描述8位寄存器的Verilog HDL代码:```verilogmodule register_8bit(input [7:0] d, input clk, input reset, output reg [7:0] q);always @(posedge clk or posedge reset)if (reset)q <= 0;elseq <= d;endmodule```4. 计数器:Verilog HDL可以用于描述计数器。
例如,下面是一个描述8位计数器的Verilog HDL代码:```verilogmodule counter_8bit(input clk, input reset, output reg [7:0] count);always @(posedge clk or posedge reset)if (reset)count <= 0;elsecount <= count + 1;endmodule```5. 加法器:Verilog HDL可以用于描述加法器。

Verilog的135个经典设计实例王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》【例3.1】4位全加器module adder4(cout,sum,ina,inb,cin);output[3:0] sum;output cout;input[3:0] ina,inb;input cin;assign {cout,sum}=ina+inb+cin;endmodule【例3.2】4位计数器module count4(out,reset,clk);output[3:0] out;input reset,clk;reg[3:0] out;always @(posedge clk)beginif (reset) out<=0; //同步复位else out<=out+1; //计数endendmodule【例3.3】4位全加器的仿真程序`timescale 1ns/1ns`include "adder4.v"module adder_tp; //测试模块的名字reg[3:0] a,b; //测试输入信号定义为reg型reg cin;wire[3:0] sum; //测试输出信号定义为wire型wire cout;integer i,j;adder4 adder(sum,cout,a,b,cin); //调用测试对象always #5 cin=~cin; //设定cin的取值initialbegina=0;b=0;cin=0;for(i=1;i<16;i=i+1)#10 a=i; //设定a的取值end- 1 - 程序文本initialbeginfor(j=1;j<16;j=j+1)#10 b=j; //设定b的取值endinitial //定义结果显示格式begin$monitor($time,,,"%d + %d + %b={%b,%d}",a,b,cin,cout,sum);#160 $finish;endendmodule【例3.4】4位计数器的仿真程序`timescale 1ns/1ns`include "count4.v"module coun4_tp;reg clk,reset; //测试输入信号定义为reg型wire[3:0] out; //测试输出信号定义为wire型parameter DELY=100;count4 mycount(out,reset,clk); //调用测试对象always #(DELY/2) clk = ~clk; //产生时钟波形initialbegin //激励信号定义clk =0; reset=0;#DELY reset=1;#DELY reset=0;#(DELY*20) $finish;end//定义结果显示格式initial $monitor($time,,,"clk=%d reset=%d out=%d", clk, reset,out);endmodule【例3.5】“与-或-非”门电路module AOI(A,B,C,D,F); //模块名为AOI(端口列表A,B,C,D,F)input A,B,C,D; //模块的输入端口为A,B,C,Doutput F; //模块的输出端口为F- 2 -王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》wire A,B,C,D,F; //定义信号的数据类型assign F= ~((A&B)|(C&D)); //逻辑功能描述endmodule【例5.1】用case语句描述的4选1数据选择器module mux4_1(out,in0,in1,in2,in3,sel);output out;input in0,in1,in2,in3;input[1:0] sel;reg out;always @(in0 or in1 or in2 or in3 or sel) //敏感信号列表case(sel)2'b00: out=in0;2'b01: out=in1;2'b10: out=in2;2'b11: out=in3;default: out=2'bx;endcaseendmodule【例5.2】同步置数、同步清零的计数器module count(out,data,load,reset,clk);output[7:0] out;input[7:0] data;input load,clk,reset;reg[7:0] out;always @(posedge clk) //clk上升沿触发beginif (!reset) out = 8'h00; //同步清0,低电平有效else if (load) out = data; //同步预置else out = out + 1; //计数endendmodule【例5.3】用always过程语句描述的简单算术逻辑单元`define add 3'd0`define minus 3'd1`define band 3'd2`define bor 3'd3`define bnot 3'd4- 3 - 程序文本module alu(out,opcode,a,b);output[7:0] out;reg[7:0] out;input[2:0] opcode; //操作码input[7:0] a,b; //操作数always@(opcode or a or b) //电平敏感的always块begincase(opcode)`add: out = a+b; //加操作`minus: out = a-b; //减操作`band: out = a&b; //求与`bor: out = a|b; //求或`bnot: out=~a; //求反default: out=8'hx; //未收到指令时,输出任意态endcaseendendmodule【例5.4】用initial过程语句对测试变量A、B、C赋值`timescale 1ns/1nsmodule test;reg A,B,C;initialbeginA = 0;B = 1;C = 0;#50 A = 1; B = 0;#50 A = 0; C = 1;#50 B = 1;#50 B = 0; C = 0;#50 $finish ;endendmodule【例5.5】用begin-end串行块产生信号波形`timescale 10ns/1nsmodule wave1;reg wave;parameter cycle=10;initialbegin- 4 -王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》wave=0;#(cycle/2) wave=1;#(cycle/2) wave=0;#(cycle/2) wave=1;#(cycle/2) wave=0;#(cycle/2) wave=1;#(cycle/2) $finish ;endinitial $monitor($time,,,"wave=%b",wave); endmodule【例5.6】用fork-join并行块产生信号波形`timescale 10ns/1nsmodule wave2;reg wave;parameter cycle=5;initialforkwave=0;#(cycle) wave=1;#(2*cycle) wave=0;#(3*cycle) wave=1;#(4*cycle) wave=0;#(5*cycle) wave=1;#(6*cycle) $finish;initial $monitor($time,,,"wave=%b",wave); endmodule【例5.7】持续赋值方式定义的2选1多路选择器module MUX21_1(out,a,b,sel);input a,b,sel;output out;assign out=(sel==0)?a:b;//持续赋值,如果sel为0,则out=a ;否则out=b endmodule【例5.8】阻塞赋值方式定义的2选1多路选择器module MUX21_2(out,a,b,sel);input a,b,sel;- 5 - 程序文本output out;reg out;always@(a or b or sel)beginif(sel==0) out=a; //阻塞赋值else out=b;endendmodule【例5.9】非阻塞赋值module non_block(c,b,a,clk);output c,b;input clk,a;reg c,b;always @(posedge clk)beginb<=a;endendmodule【例5.10】阻塞赋值module block(c,b,a,clk);output c,b;input clk,a;reg c,b;always @(posedge clk)beginb=a;c=b;endendmodule【例5.11】模为60的BCD码加法计数器module count60(qout,cout,data,load,cin,reset,clk); output[7:0] qout;output cout;input[7:0] data;input load,cin,clk,reset;reg[7:0] qout;always @(posedge clk) //clk上升沿时刻计数- 6 - 王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》beginif (reset) qout<=0; //同步复位else if(load) qout<=data; //同步置数else if(cin)beginif(qout[3:0]==9) //低位是否为9,是则beginqout[3:0]<=0; //回0,并判断高位是否为5if (qout[7:4]==5) qout[7:4]<=0;elseqout[7:4]<=qout[7:4]+1; //高位不为5,则加1endelse //低位不为9,则加1qout[3:0]<=qout[3:0]+1;endendassign cout=((qout==8'h59)&cin)?1:0; //产生进位输出信号endmodule【例5.12】BCD码—七段数码管显示译码器module decode4_7(decodeout,indec);output[6:0] decodeout;input[3:0] indec;reg[6:0] decodeout;always @(indec)begincase(indec) //用case语句进行译码4'd0:decodeout=7'b1111110;4'd1:decodeout=7'b0110000;4'd2:decodeout=7'b1101101;4'd3:decodeout=7'b1111001;4'd4:decodeout=7'b0110011;4'd5:decodeout=7'b1011011;4'd6:decodeout=7'b1011111;4'd7:decodeout=7'b1110000;4'd8:decodeout=7'b1111111;4'd9:decodeout=7'b1111011;default: decodeout=7'bx;endcaseend- 7 - 程序文本endmodule【例5.13】用casez描述的数据选择器module mux_casez(out,a,b,c,d,select); output out;input a,b,c,d;input[3:0] select;reg out;always @(select or a or b or c or d) begincasez(select)4'b1: out = a;4'b??1?: out = b;4'b?1??: out = c;4'b1: out = d;endcaseendendmodule【例5.14】隐含锁存器举例module buried_ff(c,b,a);output c;input b,a;reg c;always @(a or b)beginif((b==1)&&(a==1)) c=a&b;endendmodule【例5.15】用for语句描述的七人投票表决器module voter7(pass,vote);output pass;input[6:0] vote;reg[2:0] sum;integer i;reg pass;always @(vote)beginsum=0;- 8 -王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》for(i=0;i<=6;i=i+1) //for语句if(vote[i]) sum=sum+1;if(sum[2]) pass=1; //若超过4人赞成,则pass=1 else pass=0;endendmodule【例5.16】用for语句实现2个8位数相乘module mult_for(outcome,a,b);parameter size=8;input[size:1] a,b; //两个操作数output[2*size:1] outcome; //结果reg[2*size:1] outcome;integer i;always @(a or b)beginoutcome=0;for(i=1; i<=size; i=i+1) //for语句if(b[i]) outcome=outcome +(a << (i-1));endendmodule【例5.17】用repeat实现8位二进制数的乘法module mult_repeat(outcome,a,b);parameter size=8;input[size:1] a,b;output[2*size:1] outcome;reg[2*size:1] temp_a,outcome;reg[size:1] temp_b;always @(a or b)beginoutcome=0;temp_a=a;temp_b=b;repeat(size) //repeat语句,size为循环次数beginif(temp_b[1]) //如果temp_b的最低位为1,就执行下面的加法outcome=outcome+temp_a;temp_a=temp_a<<1; //操作数a左移一位- 9 - 程序文本temp_b=temp_b>>1; //操作数b右移一位endendendmodule【例5.18】同一循环的不同实现方式module loop1; //方式1integer i;initialfor(i=0;i<4;i=i+1) //for语句begin$display(“i=%h”,i);endendmodulemodule loop2; //方式2integer i;initial begini=0;while(i<4) //while语句begin$display ("i=%h",i);i=i+1;endendendmodulemodule loop3; //方式3integer i;initial begini=0;repeat(4) //repeat语句begin$display ("i=%h",i);i=i+1;endendendmodule【例5.19】使用了`include语句的16位加法器- 10 -王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》`include "adder.v" module adder16(cout,sum,a,b,cin);output cout;parameter my_size=16;output[my_size-1:0] sum;input[my_size-1:0] a,b;input cin;adder my_adder(cout,sum,a,b,cin); //调用adder模块endmodule//下面是adder模块代码module adder(cout,sum,a,b,cin);parameter size=16;output cout;output[size-1:0] sum;input cin;input[size-1:0] a,b;assign {cout,sum}=a+b+cin;endmodule【例5.20】条件编译举例module compile(out,A,B);output out;input A,B;`ifdef add //宏名为addassign out=A+B;`elseassign out=A-B;`endifendmodule【例6.1】加法计数器中的进程module count(data,clk,reset,load,cout,qout);output cout;output[3:0] qout;reg[3:0] qout;input[3:0] data;input clk,reset,load;- 11 - 程序文本always @(posedge clk) //进程1,always过程块beginif (!reset) qout= 4'h00; //同步清0,低电平有效else if (load) qout= data; //同步预置else qout=qout + 1; //加法计数endassign cout=(qout==4'hf)?1:0; //进程2,用持续赋值产生进位信号endmodule【例6.2】任务举例module alutask(code,a,b,c);input[1:0] code;input[3:0] a,b;output[4:0] c;reg[4:0] c;task my_and; //任务定义,注意无端口列表input[3:0] a,b; //a,b,out名称的作用域范围为task任务内部output[4:0] out;integer i;beginfor(i=3;i>=0;i=i-1)out[i]=a[i]&b[i]; //按位与endendtaskalways@(code or a or b)begincase(code)2'b00: my_and(a,b,c);/* 用任务my_and,需注意端口列表的顺序应与任务定义中的一致,这里的a,b,c分别对应任务定义中的a,b,out */2'b01: c=a|b; //或2'b10: c=a-b; //相减2'b11: c=a+b; //相加endcaseendendmodule- 12 -王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》【例6.3】测试程序`include "alutask.v"module alu_tp;reg[3:0] a,b;reg[1:0] code;wire[4:0] c;parameter DELY = 100;alutask ADD(code,a,b,c); //调用被测试模块initial begincode=4'd0; a= 4'b0000; b= 4'b1111;#DELY code=4'd0; a= 4'b0111; b= 4'b1101;#DELY code=4'd1; a= 4'b0001; b= 4'b0011;#DELY code=4'd2; a= 4'b1001; b= 4'b0011;#DELY code=4'd3; a= 4'b0011; b= 4'b0001;#DELY code=4'd3; a= 4'b0111; b= 4'b1001;#DELY $finish;endinitial $monitor($time,,,"code=%b a=%b b=%b c=%b", code,a,b,c);endmodule【例6.4】函数function[7:0] get0;input[7:0] x;reg[7:0] count;integer i;begincount=0;for (i=0;i<=7;i=i+1)if (x[i]=1'b0) count=count+1;get0=count;endendfunction【例6.5】用函数和case语句描述的编码器(不含优先顺序)module code_83(din,dout);input[7:0] din;output[2:0] dout;- 13 - 程序文本function[2:0] code; //函数定义input[7:0] din; //函数只有输入,输出为函数名本身casex (din)8'b1xxx_xxxx : code = 3'h7;8'b01xx_xxxx : code = 3'h6;8'b001x_xxxx : code = 3'h5;8'b0001_xxxx : code = 3'h4;8'b0000_1xxx : code = 3'h3;8'b0000_01xx : code = 3'h2;8'b0000_001x : code = 3'h1;8'b0000_000x : code = 3'h0;default: code = 3'hx;endcaseendfunctionassign dout = code(din) ; //函数调用endmodule【例6.6】阶乘运算函数module funct(clk,n,result,reset);output[31:0] result;input[3:0] n;input reset,clk;reg[31:0] result;always @(posedge clk) //在clk的上升沿时执行运算beginif(!reset) result<=0; //复位else beginresult <= 2 * factorial(n); //调用factorial函数endendfunction[31:0] factorial; //阶乘运算函数定义(注意无端口列表)input[3:0] opa; //函数只能定义输入端,输出端口为函数名本身reg[3:0] i;beginfactorial = opa ? 1 : 0;for(i= 2; i <= opa; i = i+1) //该句若要综合通过,opa应赋具体的数值factorial = i* factorial; //阶乘运算end- 14 -王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》endfunction【例6.7】测试程序`define clk_cycle 50`include "funct.v"module funct_tp;reg[3:0] n;reg reset,clk;wire[31:0] result;initial //定义激励向量beginn=0; reset=1; clk=0;for(n=0;n<=15;n=n+1)#100 n=n;endinitial $monitor($time,,,"n=%d result=%d",n,result);//定义输出显示格式always # `clk_cycle clk=~clk; //产生时钟信号funct funct_try(.clk(clk),.n(n),.result(result),.reset(reset)); //调用被测试模块endmodule【例6.8】顺序执行模块1module serial1(q,a,clk);output q,a;input clk;reg q,a;always @(posedge clk)beginq=~q;a=~q;end【例6.9】顺序执行模块2 module serial2(q,a,clk); output q,a;- 15 - 程序文本input clk;reg q,a;always @(posedge clk) begina=~q;q=~q;endendmodule【例6.10】并行执行模块1 module paral1(q,a,clk); output q,a;input clk;reg q,a;always @(posedge clk) beginq=~q;endalways @(posedge clk) begina=~q;endendmodule【例6.11】并行执行模块2 module paral2(q,a,clk); output q,a;input clk;reg q,a;always @(posedge clk)begina=~q;endalways @(posedge clk)beginq=~q;endendmodule【例7.1】调用门元件实现的4选1 MUX- 16 -王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》module mux4_1a(out,in1,in2,in3,in4,cntrl1,cntrl2);output out;input in1,in2,in3,in4,cntrl1,cntrl2;wire notcntrl1,notcntrl2,w,x,y,z;not notcntrl1,cntrl2),(notcntrl2,cntrl2);and (w,in1,notcntrl1,notcntrl2),(x,in2,notcntrl1,cntrl2),(y,in3,cntrl1,notcntrl2),(z,in4,cntrl1,cntrl2);or (out,w,x,y,z);endmodule【例7.2】用case语句描述的4选1 MUXmodule mux4_1b(out,in1,in2,in3,in4,cntrl1,cntrl2);output out;input in1,in2,in3,in4,cntrl1,cntrl2;reg out;always@(in1 or in2 or in3 or in4 or cntrl1 or cntrl2)case({cntrl1,cntrl2})2'b00:out=in1;2'b01:out=in2;2'b10:out=in3;2'b11:out=in4;default:out=2'bx;endcaseendmodule【例7.3】行为描述方式实现的4位计数器module count4(clk,clr,out);input clk,clr;output[3:0] out;reg[3:0] out;always @(posedge clk or posedge clr)beginif (clr) out<=0;else out<=out+1;endendmodule- 17 - 程序文本【例7.4】数据流方式描述的4选1 MUXmodule mux4_1c(out,in1,in2,in3,in4,cntrl1,cntrl2);output out;input in1,in2,in3,in4,cntrl1,cntrl2;assign out=(in1 & ~cntrl1 & ~cntrl2)|(in2 & ~cntrl1 & cntrl2)|(in3 & cntrl1 & ~cntrl2)|(in4 & cntrl1 & cntrl2);endmodule【例7.5】用条件运算符描述的4选1 MUXmodule mux4_1d(out,in1,in2,in3,in4,cntrl1,cntrl2); output out;input in1,in2,in3,in4,cntrl1,cntrl2;assign out=cntrl1 ? (cntrl2 ? in4:in3):(cntrl2 ? in2:in1); endmodule【例7.6】门级结构描述的2选1MUXmodule mux2_1a(out,a,b,sel);output out;input a,b,sel;not (sel_,sel);and a1,a,sel_),(a2,b,sel);or (out,a1,a2);endmodule【例7.7】行为描述的2选1MUXmodule mux2_1b(out,a,b,sel);output out;input a,b,sel;reg out;always @(a or b or sel)beginif(sel) out = b;else out = a;endendmodule【例7.8】数据流描述的2选1MUXmodule MUX2_1c(out,a,b,sel);output out;- 18 -王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》input a,b,sel;assign out = sel ? b : a; endmodule【例7.9】调用门元件实现的1位半加器module half_add1(a,b,sum,cout); input a,b;output sum,cout;and cout,a,b);xor sum,a,b);endmodule【例7.10】数据流方式描述的1位半加器module half_add2(a,b,sum,cout); input a,b;output sum,cout;assign sum=a^b;assign cout=a&b;endmodule【例7.11】采用行为描述的1位半加器module half_add3(a,b,sum,cout); input a,b;output sum,cout;reg sum,cout;always @(a or b)begincase ({a,b}) //真值表描述2'b00: begin sum=0; cout=0; end2'b01: begin sum=1; cout=0; end2'b10: begin sum=1; cout=0; end2'b11: begin sum=0; cout=1; end endcaseendendmodule【例7.12】采用行为描述的1位半加器module half_add4(a,b,sum,cout); input a,b;output sum,cout;- 19 - 程序文本reg sum,cout;always @(a or b)beginsum= a^b;cout=a&b;endendmodule【例7.13】调用门元件实现的1位全加器module full_add1(a,b,cin,sum,cout); input a,b,cin;output sum,cout;wire s1,m1,m2,m3;and m1,a,b),(m2,b,cin),(m3,a,cin);xor s1,a,b),(sum,s1,cin);or (cout,m1,m2,m3);endmodule【例7.14】数据流描述的1位全加器module full_add2(a,b,cin,sum,cout); input a,b,cin;output sum,cout;assign sum = a ^ b ^ cin;assign cout = (a & b)|(b & cin)|(cin & a);endmodule【例7.15】1位全加器module full_add3(a,b,cin,sum,cout);input a,b,cin;output sum,cout;assign {cout,sum}=a+b+cin;endmodule【例7.16】行为描述的1位全加器module full_add4(a,b,cin,sum,cout);input a,b,cin;output sum,cout;- 20 -王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》reg sum,cout; //在always块中被赋值的变量应定义为reg型reg m1,m2,m3;always @(a or b or cin)beginsum = (a ^ b) ^ cin;m1 = a & b;m2 = b & cin;m3 = a & cin;cout = (m1|m2)|m3;endendmodule【例7.17】混合描述的1位全加器module full_add5(a,b,cin,sum,cout);input a,b,cin;output sum,cout;reg cout,m1,m2,m3; //在always块中被赋值的变量应定义为reg型wire s1;xor x1(s1,a,b); //调用门元件always @(a or b or cin) //always块语句beginm1 = a & b;m2 = b & cin;m3 = a & cin;cout = (m1| m2) | m3;endassign sum = s1 ^ cin; //assign持续赋值语句endmodule【例7.18】结构描述的4位级连全加器`include "full_add1.v"module add4_1(sum,cout,a,b,cin);output[3:0] sum;output cout;input[3:0] a,b;input cin;full_add1 f0(a[0],b[0],cin,sum[0],cin1); //级连描述full_add1 f1(a[1],b[1],cin1,sum[1],cin2);full_add1 f2(a[2],b[2],cin2,sum[2],cin3);- 21 - 程序文本full_add1 f3(a[3],b[3],cin3,sum[3],cout); endmodule【例7.19】数据流描述的4位全加器module add4_2(cout,sum,a,b,cin);output[3:0] sum;output cout;input[3:0] a,b;input cin;assign {cout,sum}=a+b+cin;endmodule【例7.20】行为描述的4位全加器module add4_3(cout,sum,a,b,cin);output[3:0] sum;output cout;input[3:0] a,b;input cin;reg[3:0] sum;reg cout;always @(a or b or cin)begin{cout,sum}=a+b+cin;endendmodule【例8.1】$time与$realtime的区别`timescale 10ns/1nsmodule time_dif;reg ts;parameter delay=2.6;initialbegin#delay ts=1;#delay ts=0;#delay ts=1;#delay ts=0;endinitial $monitor($time,,,"ts=%b",ts); //使用函数$time- 22 - 王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》endmodule【例8.2】$random函数的使用`timescale 10ns/1nsmodule random_tp;integer data;integer i;parameter delay=10;initial $monitor($time,,,"data=%b",data);initial beginfor(i=0; i<=100; i=i+1)#delay data=$random; //每次产生一个随机数endendmodule【例8.3】1位全加器进位输出UDP元件primitive carry_udp(cout,cin,a,b);input cin,a,b;output cout;table//cin a b : cout //真值表0 0 0 : 0;0 1 0 : 0;0 0 1 : 0;0 1 1 : 1;1 0 0 : 0;1 0 1 : 1;1 1 0 : 1;1 1 1 : 1;endtableendprimitive【例8.4】包含x态输入的1位全加器进位输出UDP元件primitive carry_udpx1(cout,cin,a,b);input cin,a,b;output cout;table// cin a b : cout //真值表0 0 0 : 0;- 23 - 程序文本0 1 0 : 0;0 0 1 : 0;0 1 1 : 1;1 0 0 : 0;1 0 1 : 1;1 1 0 : 1;1 1 1 : 1;0 0 x : 0; //只要有两个输入为0,则进位输出肯定为0 0 x 0 : 0;x 0 0 : 0;1 1 x : 1; //只要有两个输入为1,则进位输出肯定为1 1 x 1 : 1;x 1 1 : 1;endtableendprimitive【例8.5】用简缩符“?”表述的1位全加器进位输出UDP元件primitive carry_udpx2(cout,cin,a,b);input cin,a,b;output cout;table// cin a b : cout //真值表0 0 : 0; //只要有两个输入为0,则进位输出肯定为00 ? 0 : 0;0 0 ? : 0;1 1 : 1; //只要有两个输入为1,则进位输出肯定为11 ? 1 : 1;1 1 ? : 1;endtableendprimitive【例8.6】3选1多路选择器UDP元件primitive mux31(Y,in0,in1,in2,s2,s1);input in0,in1,in2,s2,s1;output Y;table//in0 in1 in2 s2 s1 : Y0 ? ? 0 0 : 0; //当s2s1=00时,Y=in01 ? ? 0 0 : 1;0 ? 0 1 : 0; //当s2s1=01时,Y=in1 - 24 -王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》1 ? 0 1 : 1;0 1 ? : 0; //当s2s1=1?时,Y=in21 1 ? : 1;0 0 ? 0 ? : 0;1 1 ? 0 ? : 1;0 ? 0 ? 0 : 0;1 ? 1 ? 0 : 1;0 0 ? 1 : 0;1 1 ? 1 : 1;endtableendprimitive【例8.7】电平敏感的1位数据锁存器UDP元件primitive latch(Q,clk,reset,D);input clk,reset,D;output Q;reg Q;initial Q = 1'b1; //初始化table// clk reset D : state : Q1 ? : ? : 0 ; //reset=1,则不管其他端口为什么值,输出都为00 0 0 : ? : 0 ; //clk=0,锁存器把D端的输入值输出0 0 1 : ? : 1 ;1 0 ? : ? : - ; //clk=1,锁存器的输出保持原值,用符号“-”表示endtableendprimitive【例8.8】上升沿触发的D触发器UDP元件primitive DFF(Q,D,clk);output Q;input D,clk;reg Q;table//clk D : state : Q(01) 0 : ? : 0; //上升沿到来,输出Q=D(01) 1 : ? : 1;(0x) 1 : 1 : 1;(0x) 0 : 0 : 0;(?0) ? : ? : -; //没有上升沿到来,输出Q保持原值(??) : ? : - ; //时钟不变,输出也不变- 25 - 程序文本endtableendprimitive【例8.9】带异步置1和异步清零的上升沿触发的D触发器UDP 元件primitive DFF_UDP(Q,D,clk,clr,set);output Q;input D,clk,clr,set;reg Q;table// clk D clr et state : Q (01) 1 0 0 : ? : 0; (01) 1 0 x : ? : 0;0 x : 0 : 0;(01) 0 0 0 : ? : 1; (01) 0 x 0 : ? : 1;x 0 : 1 : 1;(x1) 1 0 0 : 0 : 0;(x1) 0 0 0 : 1 : 1;(0x) 1 0 0 : 0 : 0;(0x) 0 0 0 : 1 : 1;1 ? : ? : 1; //异步复位0 1 : ? : 0; //异步置1 n ? 0 0 : ? : -;* ? ? : ? : -;(?0) ? : ? : -;(?0): ? : -;: ? : x;endtableendprimitive【例8.12】延迟定义块举例module delay(out,a,b,c); output out;input a,b,c;and a1(n1,a,b);or o1(out,c,n1);specify(a=>out)=2;(b=>out)=3;(c=>out)=1;- 26 -王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》endspecifyendmodule【例8.13】激励波形的描述'timescale 1ns/1nsmodule test1;reg A,B,C;initialbegin //激励波形描述A = 0;B = 1;C = 0;#100 C = 1;#100 A = 1; B = 0;#100 A = 0;#100 C = 0;#100 $finish;endinitial $monitor($time,,,"A=%d B=%d C=%d",A,B,C); //显示endmodule【例8.15】用always过程块产生两个时钟信号module test2;reg clk1,clk2;parameter CYCLE = 100;alwaysbegin{clk1,clk2} = 2'b10;#(CYCLE/4) {clk1,clk2} = 2'b01;#(CYCLE/4) {clk1,clk2} = 2'b11;#(CYCLE/4) {clk1,clk2} = 2'b00;#(CYCLE/4) {clk1,clk2} = 2'b10;endinitial $monitor($time,,,"clk1=%b clk2=%b",clk1,clk2); endmodule【例8.17】存储器在仿真程序中的应用module ROM(addr,data,oe);output[7:0] data; //数据信号input[14:0] addr; //地址信号input oe; //读使能信号,低电平有效- 27 - 程序文本reg[7:0] mem[0:255]; //存储器定义parameter DELAY = 100;assign #DELAY data=(oe==0) ? mem[addr] : 8'hzz; initial $readmemh("rom.hex",mem); //从文件中读入数据endmodule【例8.18】8位乘法器的仿真程序`timescale 10ns/1nsmodule mult_tp; //测试模块的名字reg[7:0] a,b; //测试输入信号定义为reg型wire [15:0] out; //测试输出信号定义为wire型integer i,j;mult8 m1(out,a,b); //调用测试对象//激励波形设定initialbegina=0;b=0;for(i=1;i<255;i=i+1)#10 a=i;endinitialbeginfor(j=1;j<255;j=j+1)#10 b=j;endinitial //定义结果显示格式begin$monitor($time,,,"%d * %d= %d",a,b,out);#2560 $finish;endendmodulemodule mult8(out, a, b); //8位乘法器源代码parameter size=8;input[size:1] a,b; //两个操作数output[2*size:1] out; //结果assign out=a*b; //乘法运算符- 28 -王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》endmodule 【例8.19】8位加法器的仿真程序`timescale 1ns/1nsmodule add8_tp; //仿真模块无端口列表reg[7:0] A,B; //输入激励信号定义为reg型reg cin;wire[7:0] SUM; //输出信号定义为wire型wire cout;parameter DELY = 100;add8 AD1(SUM,cout,A,B,cin); //调用测试对象initial begin //激励波形设定A= 8'd0; B= 8'd0; cin=1'b0;#DELY A= 8'd100; B= 8'd200; cin=1'b1;#DELY A= 8'd200; B= 8'd88;#DELY A= 8'd210; B= 8'd18; cin=1'b0;#DELY A= 8'd12; B= 8'd12;#DELY A= 8'd100; B= 8'd154;#DELY A= 8'd255; B= 8'd255; cin=1'b1;#DELY $finish;end//输出格式定义initial $monitor($time,,,"%d + %d + %b = {%b, %d}",A,B,cin,cout,SUM);endmodulemodule add8(SUM,cout,A,B,cin); //待测试的8位加法器模块output[7:0] SUM;output cout;input[7:0] A,B;input cin;assign {cout,SUM}=A+B+cin;endmodule【例8.20】2选1多路选择器的仿真`timescale 1ns/1nsmodule mux_tp;reg a,b,sel;wire out;- 29 - 程序文本MUX2_1 m1(out,a,b,sel); //调用待测试模块initialbegina=1'b0; b=1'b0; sel=1'b0;#5 sel=1'b1;#5 a=1'b1; el=1'b0;#5 sel=1'b1;#5 a=1'b0; b=1'b1; el=1'b0;#5 sel=1'b1;#5 a=1'b1; b=1'b1; sel=1'b0;#5 sel=1'b1;endinitial $monitor($time,,,"a=%b b=%b sel=%b out=%b",a,b,sel,out);endmodulemodule MUX2_1(out,a,b,sel); //待测试的2选1MUX模块input a,b,sel;output out;not #(0.4,0.3) (sel_,sel); //#(0.4,0.3)为门延时and #(0.7,0.6) (a1,a,sel_);and #(0.7,0.6) (a2,b,sel);or #(0.7,0.6) (out,a1,a2);endmodule【例8.21】8位计数器的仿真`timescale 10ns/1nsmodule count8_tp;reg clk,reset; //输入激励信号定义为reg型wire[7:0] qout; //输出信号定义为wire型parameter DELY=100;counter C1(qout,reset,clk); //调用测试对象always #(DELY/2) clk = ~clk; //产生时钟波形initialbegin //激励波形定义clk =0; reset=0;- 30 -王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》#DELY reset=1;#DELY reset=0;#(DELY*300) $finish;end//结果显示initial $monitor($time,,,"clk=%d reset=%d qout=%d",clk,reset,qout);endmodulemodule counter(qout,reset,clk); //待测试的8位计数器模块output[7:0] qout;input clk,reset;reg[7:0] qout;always @(posedge clk)begin if (reset) qout<=0;else qout<=qout+1;endendmodule【例9.1】基本门电路的几种描述方法(1)门级结构描述module gate1(F,A,B,C,D);input A,B,C,D;output F;nand(F1,A,B); //调用门元件and(F2,B,C,D);or(F,F1,F2);endmodule(2)数据流描述module gate2(F,A,B,C,D);input A,B,C,D;output F;assign F=(A&B)|(B&C&D); //assign持续赋值endmodule(3)行为描述module gate3(F,A,B,C,D);input A,B,C,D;output F;- 31 - 程序文本reg F;always @(A or B or C or D) //过程赋值beginF=(A&B)|(B&C&D);endendmodule【例9.2】用bufif1关键字描述的三态门module tri_1(in,en,out);input in,en;output out;tri out;bufif1 b1(out,in,en); //注意三态门端口的排列顺序endmodule【例9.3】用assign语句描述的三态门module tri_2(out,in,en);output out;input in,en;assign out = en ? in : 'bz;//若en=1,则out=in;若en=0,则out为高阻态endmodule【例9.4】三态双向驱动器module bidir(tri_inout,out,in,en,b);inout tri_inout;output out;input in,en,b;assign tri_inout = en ? in : 'bz;assign out = tri_inout ^ b; endmodule【例9.5】三态双向驱动器module bidir2(bidir,en,clk);inout[7:0] bidir;input en,clk;reg[7:0] temp;assign bidir= en ? temp : 8'bz; always @(posedge clk)begin- 32 -王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》if(en) temp=bidir;else temp=temp+1;endendmodule【例9.6】3-8译码器module decoder_38(out,in);output[7:0] out;input[2:0] in;reg[7:0] out;always @(in)begincase(in)3'd0: out=8'b11111110;3'd1: out=8'b11111101;3'd2: out=8'b11111011;3'd3: out=8'b11110111;3'd4: out=8'b11101111;3'd5: out=8'b11011111;3'd6: out=8'b10111111;3'd7: out=8'b01111111;endcaseendendmodule【例9.7】8-3优先编码器module encoder8_3(none_on,outcode,a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h); output none_on;output[2:0] outcode;input a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h;reg[3:0] outtemp;assign {none_on,outcode}=outtemp;always @(a or b or c or d or e or f or g or h)beginif(h) outtemp=4'b0111;else if(g) outtemp=4'b0110;else if(f) outtemp=4'b0101;else if(e) outtemp=4'b0100;else if(d) outtemp=4'b0011;else if(c) outtemp=4'b0010;- 33 - 程序文本else if(b) outtemp=4'b0001;else if(a) outtemp=4'b0000;else outtemp=4'b1000;endendmodule【例9.8】用函数定义的8-3优先编码器module code_83(din, dout);input[7:0] din;output[2:0] dout;function[2:0] code; //函数定义input[7:0] din; //函数只有输入端口,输出为函数名本身if (din[7]) code = 3'd7;else if (din[6]) code = 3'd6;else if (din[5]) code = 3'd5;else if (din[4]) code = 3'd4;else if (din[3]) code = 3'd3;else if (din[2]) code = 3'd2;else if (din[1]) code = 3'd1;else code = 3'd0;endfunctionassign dout = code(din); //函数调用endmodule【例9.9】七段数码管译码器module decode47(a,b,c,d,e,f,g,D3,D2,D1,D0);output a,b,c,d,e,f,g;input D3,D2,D1,D0; //输入的4位BCD码reg a,b,c,d,e,f,g;always @(D3 or D2 or D1 or D0)begincase({D3,D2,D1,D0}) //用case语句进行译码4'd0: {a,b,c,d,e,f,g}=7'b1111110;4'd1: {a,b,c,d,e,f,g}=7'b0110000;4'd2: {a,b,c,d,e,f,g}=7'b1101101;4'd3: {a,b,c,d,e,f,g}=7'b1111001;4'd4: {a,b,c,d,e,f,g}=7'b0110011;4'd5: {a,b,c,d,e,f,g}=7'b1011011;- 34 -王金明:《Verilog HDL程序设计教程》4'd6: {a,b,c,d,e,f,g}=7'b1011111;。

verilog hdl应用程序设计实例精讲网上现在有很多关于verilog hdl应用程序设计的资料,但是并没有一个很系统和全面的教程来帮助初学者快速入门。
本文就verilog hdl应用程序设计实例进行了精讲,从基本概念到应用实例一步一步地回答了初学者的问题,帮助大家理解verilog hdl的设计和应用。
一、verilog hdl的基本概念Verilog HDL是一种硬件描述语言,用于描述数字系统,包括逻辑电路、集成电路等等。
它既可以进行仿真验证,也可以直接生成硬件电路。
简单来说,verilog hdl就是一种用来描述数字系统的语言。
1.1 模块与实例化在verilog hdl中,模块是最基本的设计单元,每个模块包含一个或多个端口和内部逻辑电路。
模块可以包含其他模块,这被称为实例化。
实例化可以理解为创建一个模块的实例,并根据实例进行连接。
1.2 端口和内部信号模块的端口是与其他模块或外部电路连接的接口,可以是输入、输出或双向。
内部信号是模块内部产生和使用的信号,只在模块内部可见。
1.3 组合逻辑与时序逻辑组合逻辑是指只有输入信号改变时才会改变输出信号的逻辑电路,而时序逻辑是指输出信号的改变还受到时钟信号的控制。
在verilog hdl中,可以使用逻辑门、逻辑运算符和条件语句来实现组合逻辑和时序逻辑。
二、verilog hdl应用程序设计实例接下来,我们通过一些实例来展示verilog hdl的应用程序设计。
2.1 4位全加器我们首先来实现一个4位全加器。
全加器是用来实现两个二进制数的加法的电路,它能够实现两个输入和一个进位的相加操作,输出结果和进位。
在verilog hdl 中,可以使用逻辑运算符和条件语句来实现全加器。
2.2 4位加法器我们可以使用四个全加器来实现一个4位加法器。
加法器是用来实现两个二进制数的加法的电路,它能够实现多位的相加操作,输出结果和进位。
2.3 4位计数器计数器是一种能够实现计数功能的电路,它能够根据时钟信号进行计数,并在达到一定数值时输出特定信号。


verilog编程实例我们需要明确这个电路的功能和设计要求。
假设我们需要实现一个4位二进制加法器,即输入两个4位的二进制数,输出它们的和。
为了简化问题,我们先考虑只有无符号整数的加法,即只需要实现两个正整数的相加。
接下来,我们可以使用Verilog语言来描述这个电路的结构和行为。
我们首先声明输入端口和输出端口的位宽,即4位。
然后,我们定义一个module,命名为"binary_adder"。
在这个module中,我们定义了两个4位的输入信号a和b,以及一个4位的输出信号sum。
同时,我们还定义了一个内部信号carry,用于记录进位信息。
在module的主体部分,我们使用assign语句来实现信号之间的逻辑关系。
具体地,我们可以通过逐位相加的方式,将输入信号a和b的每一位与进位carry相加,并将结果存储在输出信号sum的对应位上。
同时,我们还需要更新进位carry的值,以确保加法运算的正确性。
为了实现这个逻辑,我们可以使用Verilog中的加法运算符"+"和逻辑与运算符"&"。
通过对输入信号的每一位进行逐位运算,我们可以得到输出信号sum的每一位的值。
同时,我们还需要根据输入信号和进位carry的值,计算出新的进位carry的值。
在实际的Verilog编程中,我们需要注意信号的声明和赋值的顺序。
一般而言,我们需要先声明信号,然后再通过assign语句对信号进行赋值。
这样可以确保信号的值能够正确传递和计算。
完成Verilog代码的编写后,我们需要使用相应的仿真工具来验证电路的功能。
常用的仿真工具有ModelSim和Xilinx ISE等。
通过仿真工具,我们可以为输入信号a和b设置不同的值,并观察输出信号sum的变化。
通过比较输出信号sum和预期的结果,我们可以验证电路的正确性。
除了验证电路的正确性外,我们还可以通过综合工具将Verilog代码转换成对应的门级电路。
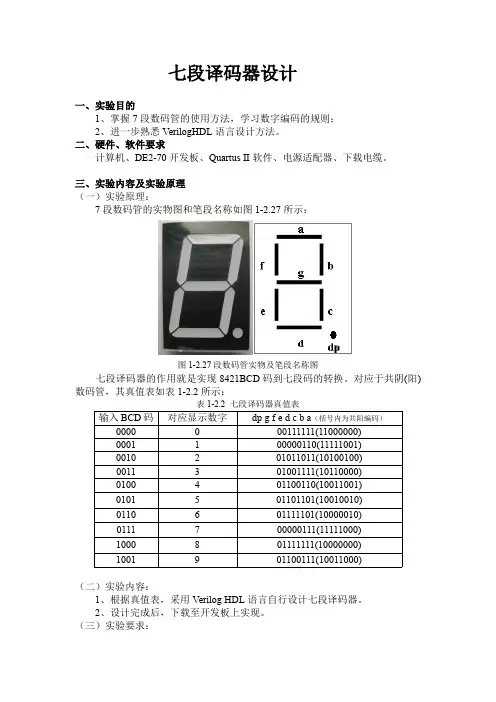
七段译码器设计一、实验目的1、掌握7段数码管的使用方法,学习数字编码的规则;2、进一步熟悉VerilogHDL语言设计方法。
二、硬件、软件要求计算机、DE2-70开发板、Quartus II软件、电源适配器、下载电缆。
三、实验内容及实验原理(一)实验原理:7段数码管的实物图和笔段名称如图1-2.27所示:图1-2.27段数码管实物及笔段名称图七段译码器的作用就是实现8421BCD码到七段码的转换。
对应于共阴(阳)数码管,其真值表如表1-2.2所示:表1-2.2七段译码器真值表输入BCD码对应显示数字dp g f e d c b a(括号内为共阳编码)0000000111111(11000000)0001100000110(11111001)0010201011011(10100100)0011301001111(10110000)0100401100110(10011001)0101501101101(10010010)0110601111101(10000010)0111700000111(11111000)1000801111111(10000000)1001901100111(10011000)(二)实验内容:1、根据真值表,采用Verilog HDL语言自行设计七段译码器。
2、设计完成后,下载至开发板上实现。
(三)实验要求:1、采用Verilog HDL语言设计方法完成七段译码器设计,写出Verilog程序;2、对程序进行功能仿真,仿真无误后进行管脚分配(输入8421BCD码:SW0-SW3,输出七段码:HEX0_D[0]-HEX0_D[6]),编译后将编程文件下载到DE2-70开发板,进行功能验证,并观察实验结果。
程序设计如下:module decoder7(data_in,data_out);input[3:0]data_in;output[7:0]data_out;reg[7:0]data_out;always@(data_in)begincase(data_in)4'b0000:data_out=8'b01000000;4'b0001:data_out=8'b01111001;4'b0010:data_out=8'b00100100;4'b0011:data_out=8'b00110000;4'b0100:data_out=8'b00011001;4'b0101:data_out=8'b00010010;4'b0110:data_out=8'b00000011;4'b0111:data_out=8'b01111000;4'b1000:data_out=8'b00000000;4'b1001:data_out=8'b00011000;default:data_out=8'b01111111;endcaseend endmodule。
Verilog HDL硬件描述语言2.1 Verilog HDL概述2.1.1 Verilog HDL的特点Verilog HDL和VHDL一样,是目前大规模集成电路设计中最具代表性、使用最广泛的硬件描述语言之一。
作为硬件描述语言,Verilog HDL具有如下特点:1. 能够在不同的抽象层次上,如系统级、行为级、RTL(Register Transfer Level)级、门级和开关级,对设计系统进行精确而简练的描述;2. 能够在每个抽象层次的描述上对设计进行仿真验证,及时发现可能存在的设计错误,缩短设计周期,并保证整个设计过程的正确性;3. 由于代码描述与具体工艺实现无关,便于设计标准化,提高设计的可重用性。
如果有C语言的编程经验,只需很短的时间内就能学会和掌握Verilog HDL,因此,Verilog HDL可以作为学习HDL设计方法的入门和基础。
2.1.2 Verilog HDL的基本结构Verilog HDL描述是由模块(module)构成的,每个模块对应的是硬件电路中的逻辑实体。
因此,每个模块都有自己独立的功能或结构,以及用于与其它模块之间相互通信的端口。
例如,一个模块可以代表一个简单的门,一个计数器,一个存储器,甚至是计算机系统等。
例2-1-1 加法器的verilog描述module adder (in1, in2, sum);input in1,in2;output [1:0] sum;wire in1,in2;reg [1:0] sum;always @ (in1 or in2)beginsum=in1+in2;endendmodule从这个例子中可以看出,一段完整的代码主要由以下几部分组成:可以了解到一些基本信息,如代码中加法器的主要功能、设计工程师、完成的日期及版本。
例2-1-1的模块名是adder,有两个输入端口in1,in2和一个输出端口sum。
其中,输入信号是一位的,其数据类型声明为连线型(wire);输出是两位的寄存器类型。
verilog硬件描述语言上机《硬件描述语言》上机作业西电微电子\第一题:用Verilog语言的结构描述和行为描述分别设计下面的电路。
A[0] Array B[0]A[1]B[1]A[2]B[2]结构描述:电路设计:module hw1(A,B,Y); input[2:0] A,B;output Y;wire w1,w2,w3;xor U1(w1,A[0],B[0]);xor U2(w2,A[1],B[1]);xor U3(w3,A[2],B[2]);nor U4(Y,w1,w2,w3);endmodule仿真测试:module test_hw1;reg[2:0] A,B;wire Y;hw1 U1(A,B,Y);initialbeginA=3'b000;B=3'b000;#50 A=3'b000;B=3'b000;#50 A=3'b111;B=3'b111;#50 A=3'b000;B=3'b110;#50 A=3'b111;B=3'b000;#50 A=3'b110;B=3'b110;#50 A=3'b011;B=3'b010;#50 A=3'b001;B=3'b011;#50 A=3'b111;B=3'b010;#50 $stop;endinitial $monitor($time,"\tA=%d\tB=%d\tY=%d",A,B,Y); Endmodule行为描述:电路设计:module hw2(A,B,Y);input[2:0] A,B;output Y;wire Y;assign Y=~((A[0]^B[0])||(A[1]^B[1])||(A[2]^B[2])); endmodule 仿真测试:module test_hw2;reg[2:0] A,B;wire Y;hw2 U1(A,B,Y);initialbeginA=3'b000;B=3'b000;#50 A=3'b000;B=3'b000;#50 A=3'b111;B=3'b111;#50 A=3'b000;B=3'b110;#50 A=3'b111;B=3'b000;#50 A=3'b110;B=3'b110;#50 A=3'b011;B=3'b010;#50 A=3'b001;B=3'b011;#50 A=3'b111;B=3'b010;#50 $stop;endinitial $monitor($time,"\tA=%b\tB=%b\tY=%b",A,B,Y); endmodule第二题:参数化电路设计1. 用行为描述方式实现下图所示的具有“one -hot”(独热)状态的环形计数器。
verilog signed用法Verilog 是一种硬件描述语言,主要用于设计和描述数字电路。
在Verilog 中,signed 是一种数据类型修饰符,用于表示有符号整数。
在 Verilog 中,整数类型数据默认为有符号数。
使用 signed 修饰符可以明确地表示一个整数是有符号数,而不是无符号数。
有符号数表示一个数可以是正的,零或负的。
通常使用有符号数来表示现实中的量,如温度、压力、速度等。
相对地,无符号数只能表示非负整数,如计数器、地址等。
使用 signed 修饰符可以确保数据在计算或逻辑操作中使用正确的数值范围和运算符号。
当使用 signed 修饰符时,Verilog 将对该变量进行符号扩展,以确保正确的数值范围。
以下是一些 signed 修饰符的用法示例:1.定义有符号变量```verilogreg signed [7:0] value;```上述代码定义了一个 8 位有符号变量 value。
方括号中的 [7:0] 表示最高位(MSB)和最低位(LSB)的位置,这里表示数据的位宽为 8。
2.赋值有符号常量```verilogvalue = -5;```以上代码将 -5 赋值给变量 value。
由于 value 是有符号类型,在赋值操作中,Verilog 会自动对 -5 进行符号扩展,以适应该变量的位宽。
3.运算符使用```verilogreg signed [7:0] a, b, result;assign result = a + b;```上述代码将两个有符号变量 a 和 b 相加,并将结果赋值给变量result。
在这种情况下,加法操作会根据 a 和 b 的符号进行有符号运算。
4.扩展至更大的位宽```verilogreg signed [7:0] a;reg signed [15:0] b;assign b = {{8{a[7]}}, a};```上述代码将一个8位有符号变量a扩展为一个16位有符号变量b。
verilog的位宽
Verilog是一种硬件描述语言,用于描述数字电路的行为和结构。
在Verilog中,位宽指的是信号或寄存器的位数。
位宽的选择取决于设计的需求和硬件的限制。
例如,在设计一个32位的整数加法器时,输入和输出信号应该都是32位,这样才能确保正确的运算结果。
但是,在设计一个简单的计数器时,位宽可能只需要8位或16位。
在Verilog中,位宽可以用参数或常量来定义。
例如,下面是一个宽度为8位的寄存器的定义:
reg [7:0] my_reg;
在这个定义中,[7:0]表示该寄存器的位宽为8位,即从7号位到0号位。
这个定义可以在模块中使用,例如:
module my_module(input clk, input reset, output reg [7:0] output_reg);
在这个模块中,输出信号output_reg的位宽也是8位。
在Verilog中,还可以使用符号$bits来获取信号或寄存器的位宽。
例如,下面是一个使用$bits的例子:
reg [7:0] my_reg;
integer width;
initial begin
width = $bits(my_reg);
$display('my_reg的位宽是 %d', width);
end
这个例子中,$bits被用来获取my_reg的位宽,并打印出来。
总的来说,Verilog中的位宽是非常重要的,它决定了信号或寄存器能够表示的数据范围和精度。
正确选择位宽可以让设计更高效和正确。