lesson13 Placing an Order 国际商务英语函电教学课件
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.27 MB
- 文档页数:1


Unit1BasicKnowledgeofBusinessLetterWriting????第1单元商务书信写作的基础知识●Purpose:让学生掌握商务英语书信的格式及构成。
●Outline:ⅠFormandStructureofBusinessletter商务书信的格式及构成?ⅡThewaysofwritingparts各部分的写作要领Ⅲaddressingenvelopes信封的写法ⅣWritingPrinciplesoftheBusinessletter写信的原则●MainPoints1、FormandStructureofBusinessletter2、英美书信的不同写法●Methods●TimeAllotment●CourseⅠFormandStructureofBusinessletter商务书信的格式及构成?Form格式:(1)、FullBlockForm齐头式(2)、ModifiedBlock?FormwithIndentedStyle混合式(3)、ModifiedBlock?Form改良式(4)、Simplifiedform简化式?Structure构成:a、Letterhead信头b、Referenceanddate编号和日期????c、 Insidenameandaddress封内地址d、Attentionline注意事项?e、salutation?称呼??f、S ubjectline事由????g、Body信文h、ComplimentaryClose结尾礼词i、S ignature签署j、E nclosure附件k、 Carboncopynotation抄送?L、Postscripts?附言ⅡThewaysofwritingparts各部分的写作要领Ⅲaddressingenvelopes信封的写法ⅣWritingPrinciplesoftheBusinessletter写信的原则Ⅴ英美书信的不同写法(1)、英式的书信格式是缩行式或混合式,而美式则是绝对平头式或改良平头。



One of the major differences between domestic trade and foreign trade is documentation (单据的使用). Every shipment must be accompanied by a number of correct documents. If they are not the correct ones, the importer will have difficulties in taking delivery of 提货the goods, and delays caused by incorrect documentation may affect future business relations between the trading partners. In the case of documentary letter of credit, any discrepancy不同, even in minordetails, between the documents presented and those specified in the credit may lead to refusal by the bank to make payment. Different documents are required for different transactions, depending on the nature of the deal, the term of delivery, the type of commodity, stipulations of credit, regulations and practices in different countries, etc. However, most transactions require the following major documents.The commercial invoice:Generally called “the invoice” forshort, this document is the general description of the quality and quantity of the goods and the unit and total price. It constitutes the basis on which other documents are to be prepared制作, and the banks check the conformity between credit terms and documents 单证一致and the conformity between the documents单单一致. A commercial invoice normally include the following contents: Invoice number and the date; name and address of the buyer and the seller; contractnumber and credit number; description of the goods including name of the commodity, quantity, specifications, etc.; unit price, total price, price terms, and commission and discount if any; terms of delivery and terms of payment; packing, shipping marks唛头, etc.; and seal or signature of the exporter. It should be noted that the description of the goods in the invoice must comply with the credit while in other documents the goods can be described in general terms,and that the total invoice value should not exceed the total amount of the covering(适用的)L/C.The packing list (is a document that)gives information such as the number, date, name and description of the goods, shipping marks, packing, number of packages, specific contents of each package and its net weight and gross weight etc. Sometimes the credit stipulates for specification list规格清单which is similar to the packing list but emphasizes the description of thespecifications of the goods.The weight list, weight note, or weight memo are also similar to the packing list in content and function but emphasis on the weight of the goods and are generally used for goods which are based on the weight for price calculation.The Bill of lading is one of the most important documents and has three major functions: 1. It serves as a cargo receipt signed by the carrier and issued to the shipper or consignor; 2. It constitutes acontract of carriage(transport)between the carrier and the consignor; 3. It is a document of title 所有权to the goods,and the legal holder 合法持有人of the bill of lading is the owner of the goods it covers.The major contents of the bill of lading include: 1. the carrier, i. e. the shipping company; 2. the shipper or consignor, it is normally the exporter; 3. the consignee收货人. It is generally either the importer or made out “to order”; 4.the notifyparty, i. e. the party to be advised通知after arrival of the goods at the port of destination. It is often the agent of the consignee or the consignee himself. 5. a general description of the goods including the name, number of packages, weight,measurement 尺寸etc. 6. shipping marks; 7. the port of shipment and the port of destination;8. the freight运费, for CIF and CFR it should be “freight prepaid”, or “freight paid”, for FOB it should be “freight to collect”, or “freight to bepaid”, or “freight payable at destination”. 9. the place where the bill of lading is issued; 10. the date when the bill of lading is issued which is regarded as the time of shipment交货时间(time of delivery) and can by no means (never) be later than that stipulated in the credit.There are quite a few types of bills of lading classified in several ways. However, most letters of creditlading”.one which states (indicate) that the goods have been shipped in apparent (表面上) good order and condition. It is meant that the document is devoid of没有any qualifying remarks 批注性话语concerning the packing and the outer appearance of the goods. And the carrier admits full liability承担全部责任for the goods described in the bill of lading and is bound to有责任carry the goods and deliver them in like (similar) condition in which he hasreceived them.Traditionally, this has been the only acceptable type to be presented by the seller under the term CFR and CIF.The document similar to the ocean bill of lading海运提单is called airway bill for air transportation and railway bill, cargo receipt etc. for railway transportation.The insurance policy and the insurance certificate are similar in function, the only difference being that the latter is a bit simpler than the former. The main contents of such insurance documents include: 1. the insured. Under CIF terms, the insured is generally the beneficiary of the credit unless otherwise specified, while under CFR and FOB terms,the insured is usually the importer. 2. cargo description including name, quantity, weight, shipping marks etc . 3. the amountinsured and the risks covered 险别. It should be noted that the currency of the amount insured should be the same as that of the credit. 4. contents concerning transportation including the carrying vessel, the port of shipment and the port of destination, the sailing date起航日期etc. 5. the place where claims are to be settled (settle a claim索赔地点). Unless otherwise specified in the credit, the port of destination is taken as the place for settling claims. 6. the date on which the document is issued. Itcan be made earlier but by no means later than the date of the bill of lading.Various certificates may be required depending on the nature of the commodity and the stipulations of the specific countries. The major types are certificate of quality; certificate of weight; certificate of quantity; certificate of health; certificate of disinfection; veterinary certificate; certificate of origin(原)产地证明; etc.Other documents that may berequired are customs invoice, consular invoice, consular visa, shipping advice装船通知etc.。


商务英语函电专业课教案Unit一、课程概述本单元主要介绍商务英语函电的基本概念、格式和写作技巧。
通过本单元的学习,学生将能够理解商务英语函电的重要性,掌握商务英语函电的基本格式,提高商务英语函电的写作能力。
二、教学目标1. 了解商务英语函电的概念和作用。
2. 掌握商务英语函电的基本格式。
3. 学会使用商务英语函电的常用表达和写作技巧。
三、教学内容1. 商务英语函电的概念和作用2. 商务英语函电的基本格式3. 商务英语函电的常用表达和写作技巧四、教学方法1. 讲授法:讲解商务英语函电的概念、格式和写作技巧。
2. 案例分析法:分析商务英语函电的实例,让学生更好地理解和掌握知识点。
五、教学评估1. 课堂参与度:观察学生在课堂上的发言和讨论情况,评估学生的学习兴趣和积极性。
2. 练习完成情况:检查学生完成的商务英语函电练习,评估学生的写作能力和掌握程度。
3. 课后作业:布置相关的课后作业,要求学生独立完成,以巩固所学知识。
教案一、课程概述商务英语函电是商务沟通的重要手段,具有正式、规范和准确的特点。
通过本单元的学习,学生将能够理解商务英语函电的重要性,掌握商务英语函电的基本格式,提高商务英语函电的写作能力。
二、教学目标1. 了解商务英语函电的概念和作用。
2. 掌握商务英语函电的基本格式。
3. 学会使用商务英语函电的常用表达和写作技巧。
三、教学内容1. 商务英语函电的概念和作用讲解商务英语函电的定义、特点和作用,让学生了解其在商务沟通中的重要性。
2. 商务英语函电的基本格式介绍商务英语函电的组成部分,包括信头、称呼、、结尾、签名等,并讲解各部分的要求和注意事项。
3. 商务英语函电的常用表达和写作技巧讲解商务英语函电中常用的表达方式和写作技巧,如问候语、结束语、商议表达、礼貌用语等。
四、教学方法1. 讲授法:讲解商务英语函电的概念、格式和写作技巧。
2. 案例分析法:分析商务英语函电的实例,让学生更好地理解和掌握知识点。
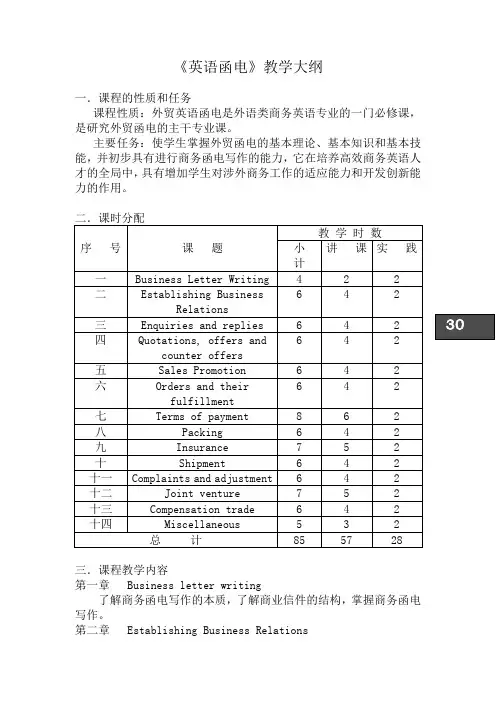
《英语函电》教学大纲一.课程的性质和任务课程性质:外贸英语函电是外语类商务英语专业的一门必修课,是研究外贸函电的主干专业课。
主要任务:使学生掌握外贸函电的基本理论、基本知识和基本技能,并初步具有进行商务函电写作的能力,它在培养高效商务英语人才的全局中,具有增加学生对涉外商务工作的适应能力和开发创新能力的作用。
三.课程教学内容第一章Business letter writing了解商务函电写作的本质,了解商业信件的结构,掌握商务函电写作。
第二章Establishing Business Relations了解建立商业关系的途径、方式,能进行有关建立商业关系的函电的写作。
重点:关于建立商业关系的函电的写作难点:关于建立商业关系的函电的写作第三章 Enquiries and replies了解询盘和回复的概念,掌握询盘和回复中的注意事项,能进行有关询盘和回复的写作。
重点:有关询盘与回复的写作难点:询盘与回复中应注意的事项第四章 Quotations, offers and counter offers了解报价、发盘、还盘的定义和类型,掌握报价、发盘、还盘中的注意事项,能进行有关报价、发盘和还盘的写作。
重点:有关报价、发盘、还盘的写作难点:报价、发盘、还盘的定义及类型、报价、发盘、还盘中的注意事项。
第五章 Sales Promotion了解促销的定义、策略,掌握促销中应注意的事项,能进行有关Array促销的函件的写作。
重点:有关促销的函件的写作难点:促销中应注意的事项第六章 Orders and their fulfillment了解定单的定义及其意义,熟悉定单的格式,能进行有关定单及其履行的函件的写作重点:有关定单及其函件的写作难点:定单的意义第七章 Terms of Payment掌握付款的三种方式:汇款、托收、信用证,熟悉催证、开证、改证等过程,能进行有关信用证的函件的写作。
重点:有关写信用证的函件的写作难点:催证、开证、改证等过程第八章包装了解包装的定义、功能及其种类,能进行有关包装的函件的写作。



国际商务英语函电课程教学大纲必备学习美式论文、报告写作技巧编者按:美式教育的特点即是课程内容强调学生参与及创新运用,因此,报告便成了常见的考核学生学习成果的方式,比如实验报告、学期报告、专题报告、研究报告及论文(含毕业论文)等。
研究生presentation 及seminar 的机会更是占很大的比重,有些甚至占学期成绩很大比例。
如何完成报告、论文同时得到良好的成绩,是本文提供给有志留学的有心人参考的目的。
美国大学生由於自小已养成自动寻找答案习惯,在启发式的教育环境下,写报告、论文对他们来说比较不陌生,虽然专业知识上美国学生不见得比外籍学生强,但是表达能力由於自小培养,加上英语能力的优势,常比外籍学生在报告、论文方面有较隹的利基。
反之中国学生比较缺乏报告写作的训练,因此如果在留学过程中无法适应美式教育会比较辛苦,其实论文、报告的写作要领其实不难,只要把握技巧就可水到渠成。
通常论文由篇首(Preliminaries),本文(Texts)以及参考资料(References)三部分构成;而这三大部分各自内容如下:(一) 篇首:封面(Title)序言(Preface)谢词(Acknowledge)提要(Summary)目录(Tables and Appendixes)(二) 本文:引言(Introduction)主体,含篇(Part)、章(Chapter)、节(Section) 、以及注释(Footnotes)(三)参考资料:参考书目(References or Bibliography)附录资料(Appendix)。
进行论文或报告写作之前,先要确定想要表达的主题,主题确定后,将其具体表达,即为题目。
题目可以提供研究者:一.研究的方向二.研究的范围三.资料搜集的范围四.预期研究成果通常在确定题目之後就开始找资料从事研究,建议在找资料之前最好去问教授有哪些参考资料来源可供参考引用。
构思为确定写作大纲或Proposal 的先前步骤,大纲是论文、报告的骨干,Proposal 是研究的架构、流程及范围的说明书。
外贸英文函电教案Captivating the global market with the art of communication, mastering the nuances of foreign trade correspondence is essential for any business looking to expand its horizons. In this lesson, we delve into the intricacies of crafting compelling and effective English correspondence for international trade.Begin with a strong opening that grabs the attention of your international clients. Use phrases like "We are delighted to explore the possibility of a mutually beneficial partnership" or "It is with great enthusiasm that we reach out to discuss potential collaboration opportunities." This sets the tone for a professional and engaging dialogue.Next, introduce your company and its offerings with precision and clarity. Highlight your strengths, such as "Our company prides itself on delivering top-tier products with unparalleled quality and service," or "We have a proven track record of innovation and excellence in our industry."When it comes to making inquiries or placing orders, be specific and concise. Use statements like "We are interested in your product line, particularly the XYZ model, and would like to request a detailed quotation," or "We are ready to proceed with an order for 500 units of the ABC product, as previously discussed."Always maintain a professional and courteous tone throughout your correspondence. Phrases such as "We appreciate your prompt attention to this matter" or "We look forward to your favorable reply" are polite and encourage a positive response.Closing your correspondence with a strong and memorable sign-off is crucial. Use phrases like "We eagerly anticipate the opportunity to work with you" or "Thank you for your consideration, and we hope to hear from you soon."Remember, the key to successful foreign trade correspondence is to be clear, professional, and courteous. By following these guidelines, you can establish strong business relationships and pave the way for prosperous international trade.。