机械原理--速度瞬心习题讲解学习
- 格式:doc
- 大小:241.50 KB
- 文档页数:5

机械原理中的速度瞬心讲解速度瞬心是机械原理中的一个重要概念,它在机械传动、运动学和动力学问题的研究中扮演着至关重要的角色。
本文将从定义、原理、应用以及相关公式等多个角度对速度瞬心进行详细讲解。
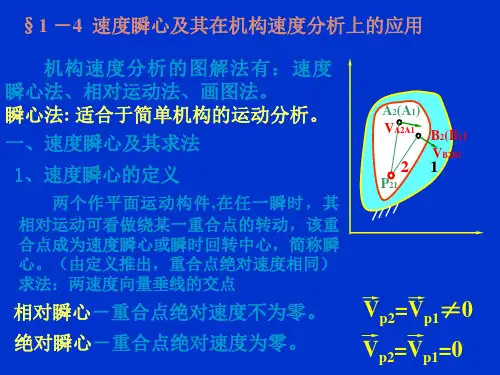
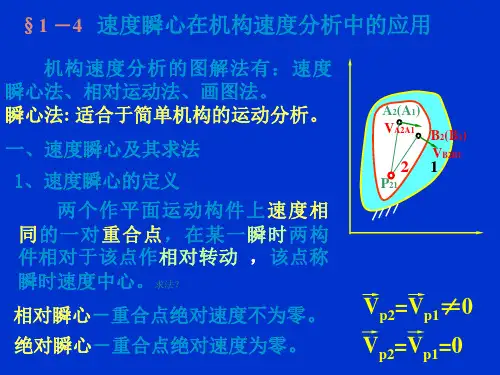
一、定义和原理速度瞬心是指在机械运动过程中,质点速度矢量的方向和瞬心所在直线方向相重合的点。
简单来说,速度瞬心就是质点瞬时速度的方向与它所在直线方向的交点。
在机械运动过程中,瞬时速度是质点在某一瞬间的瞬时速度,它的大小是瞬时速度的矢量,方向是切线方向。
而速度瞬心则是质点的速度矢量方向与瞬心所在直线方向相重合的点。
速度瞬心的计算方法有很多,其中最常用的方法是使用切线的性质。
在曲线运动中,我们可以通过将切线向后延长,找到两条切线的交点,这个交点就是速度瞬心。
二、速度瞬心的应用速度瞬心在机械工程中有广泛的应用,尤其在运动学和动力学的问题分析中起到了重要作用。
下面以几个具体的例子来说明速度瞬心的应用。
1. 齿轮传动齿轮传动中,速度瞬心常用来确定传动比和齿轮的尺寸。
在两个齿轮相互啮合时,它们的速度瞬心位于齿轮啮合线上,通过计算速度瞬心的位置,可以确定齿轮的啮合情况、传动比和齿轮的尺寸。
2. 曲柄连杆机构曲柄连杆机构中,速度瞬心可用于分析和计算连杆的运动规律。
通过计算连杆各个位置的速度瞬心,可以得到连杆的位移、速度和加速度等参数,从而研究连杆运动的特性和工作原理。
3. 自行车前叉自行车前叉是一种常见的悬挂系统,其原理基于速度瞬心。
在自行车行驶过程中,前叉通过改变前轮的速度瞬心位置来调整悬挂系统的刚度。
通过调整速度瞬心的位置,可以使得前叉对不同路面的冲击吸收能力更好,提高骑行的舒适性和稳定性。
三、速度瞬心的计算方法计算速度瞬心的方法有多种,下面介绍几种常见的计算方法。
1. 直接法直接法是速度瞬心计算的最基本方法,它适用于已知点的速度矢量和所在直线方向的情况。
根据已知点的速度矢量和所在直线的方向,我们可以直接求解速度瞬心。


机械原理瞬心法求速度习题引言机械原理是工程力学的一部分,研究物体的运动及力学效应。
在机械原理中,瞬心法是一种常用的分析方法,用于求解物体的速度和加速度。
本文将通过解答一些瞬心法求速度的习题,加深对机械原理的理解。
问题一有一个直径为1m的转盘,上面有一个固定在轴上的活动滑块。
滑块到轴的距离为0.5m。
转盘以5 rad/s的角速度逆时针旋转。
求滑块上某点P的速度。
首先,我们需要确定滑块上的点P的位置。
由于滑块到轴的距离为0.5m,而转盘的直径为1m,因此点P的位置位于滑块上与轴对称的位置,距离轴0.5m。
我们可以使用瞬心法来求解滑块上点P的速度。
瞬心法的基本原理是,在运动过程中,物体的速度等于通过瞬时转动中心与物体上的某一点所作的相对速度。
在本题中,我们可以选择转盘的轴作为瞬时转动中心。
因此,我们需要确定点P相对于转动中心的位置向量和其相对于转动中心的速度向量。
点P相对于转动中心的位置向量为[0.5, 0],即P的横坐标为0.5m,纵坐标为0,代表距离转动中心0.5m。
点P相对于转动中心的速度向量为[0, R * ω],其中R 为转盘的半径,即0.5m,ω为转盘的角速度,即5 rad/s。
代入数值计算,得到速度向量为[0, 2.5],即P点的速度大小为2.5 m/s,方向为垂直于转盘的切线方向。
问题二一个直径为0.8m的小车以2 rad/s的角速度逆时针旋转。
小车上有一根长1.2m的杆,杆上距离小车中心0.6m处有一个质量为1kg的小球。
求小球的速度大小和方向。
我们可以使用瞬心法来求解小球的速度。
同样地,选择小车的中心作为瞬时转动中心。
首先,我们需要确定小球相对于转动中心的位置向量和其相对于转动中心的速度向量。
小球相对于转动中心的位置向量为[0.6, 0],即小球距离转动中心0.6m。
小球相对于转动中心的速度向量为[0, R * ω],其中R为小车直径的一半,即0.4m,ω为小车的角速度,即2 rad/s。





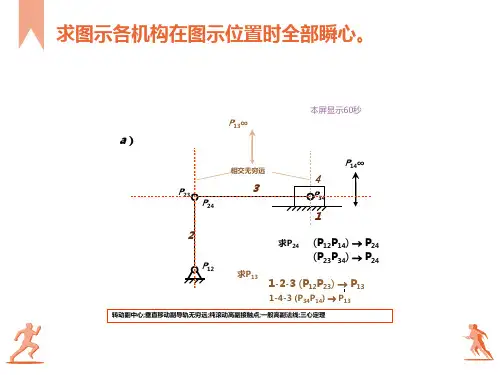
习题 > 答案一.概念1.当两构件组成转动副时,其相对速度瞬心在转动副的圆心处;组成移动副时,其瞬心在垂直于移动导路的无穷远处;组成滑动兼滚动的高副时,其瞬心在接触点两轮廓线的公法线上.2.相对瞬心与绝对瞬心相同点是都是两构件上相对速度为零,绝对速度相等的点 ,而不同点是相对瞬心的绝对速度不为零,而绝对瞬心的绝对速度为零 .3.速度影像的相似原理只能用于同一构件上的两点,而不能用于机构不同构件上的各点.4.速度瞬心可以定义为互相作平面相对运动的两构件上,相对速度为零,绝对速度相等的点.5.3个彼此作平面平行运动的构件共有 3 个速度瞬心,这几个瞬心必位于同一条直线上 .含有6个构件的平面机构,其速度瞬心共有 15 个,其中 5 个是绝对瞬心,有 9 个相对瞬心.二.计算题1、2.关键:找到瞬心P366 Solution:The coordinates of joint B arey B=ABsinφ=0.20sin45°=0.141mx B=ABsinφ=0.20sin45°=0.141mThe vector diagram of the right Fig is drawn by representing the RTR (BBD) dyad.The vector equation, corresponding to this loop, is written asrB+r -rD =0 orr =r D-rBWherer =BD and r=γ.When the above vectorial equation is projected on the x and y axes, two scalar equations are obtained: r*cos(φ3+π)=x D -xB=-0.141mr*sin(φ3+π)=y D -y B =-0.541mAngle φ3 is obtained by solving the system of the two previous scalar equations:tgφ3=141.0541.0 ⇒φ3=75.36°The distance r isr=)cos(3πϕ+-B D x x =0.56mThe coordinates of joint C arex C =CDcosφ3=0.17m y C =CDsinφ3-AD=0.27mFor the next dyad RRT (CEE), the right Fig, one can write Cecos(π- φ4)=x E - x C Cesin(π- φ4)= y E - y CVector diagram represent the RRT (CEE) dyad.When the system of equations is solved, the unknowns φ4 and x E are obtained: φ4=165.9° x E =-0.114m7. Solution: The origin of the system is at A, A≡0; that is,x A =y A =0.The coordinates of the R joints at B are x B =l 1cosφ y B = l 1sinφFor the dyad DBB (RTR), the following equations can be written with respect to the sliding line CD:mx B - y B +n=0 y D =mx D +nWith x D =d 1, y D =0 from the above system, slope m of link CD and intercept n can be calculated:m=111cos sin d l l -ϕϕ n=ϕϕcos sin 1111l d l d -The coordinates x C and y C of the center of the R joint C result from the system of two equations:y C =mx C +n=ϕϕϕϕcos sin cos sin 1111111l d l d x d l l C -+-,(x C- xD )2+(y C- y D )2=l 23Because of the quadratic equation, two solutions are abstained for x C and y C.For continuous motion of the mechanism, there are constraint relations for the Choice of the correct solution; that is x C< x B< x D and y C>0For the last dyad CEE (RRT), a position function can be written for joint E:(x C-x E)2+(y C-h)2=l24The equation produces values for x1E and x2E, and the solution x E >x C is selected for continuous motion of the mechanism.枣元中心幼儿园教学活动评课记录。
机械原理--速度瞬心
习题
习题 > 答案
一.概念
1.当两构件组成转动副时,其相对速度瞬心在转动副的圆心处;组成移动副时,其瞬心在垂直于移动导路的无穷远处;组成滑动兼滚动的高副时,其瞬心在接触点两轮廓线的公法线上.
2.相对瞬心与绝对瞬心相同点是都是两构件上相对速度为零,绝对速度相等的点 ,而不同点是相对瞬心的绝对速度不为零,而绝对瞬心的绝对速度为零 .
3.速度影像的相似原理只能用于同一构件上的两点,而不能用于机构不同构件上的各点.
4.速度瞬心可以定义为互相作平面相对运动的两构件上,相对速度为零,绝对速度相等的点.
5.3个彼此作平面平行运动的构件共有 3 个速度瞬心,这几个瞬心必位于同一条直线上 .含有6个构件的平面机构,其速度瞬心共有 15 个,其中 5 个是绝对瞬心,有 9 个相对瞬心.
二.计算题
1、
2.关键:找到瞬心P36
6 Solution:
The coordinates of joint B are
y B=ABsinφ=0.20sin45°=0.141m
x B=ABsinφ=0.20sin45°=0.141m
The vector diagram of the right Fig is drawn by representing the RTR (BBD) dyad. The vector equation, corresponding to this loop, is written as
r B+ r-r D=0 or r=D-B
r= and r=γ.
Where
When the above vectorial equation is projected on the x and y axes, two scalar equations are obtained:
r*cos(φ3+π)=x D -x B =-0.141m
r*sin(φ3+π)=y D -y B =-0.541m
Angle φ3 is obtained by solving the system of the two previous scalar equations:
tgφ3=141.0541
.0 ⇒φ3=75.36°
The distance r is
r=)cos(3πϕ+-B
D x x =0.56m
The coordinates of joint C are x C =CDcosφ3=0.17m y C =CDsinφ3-AD=0.27m
For the next dyad RRT (CEE), the right Fig, one can write
Cecos(π- φ4)=x E - x C Cesin(π- φ4)= y E - y C
Vector diagram represent the RRT (CEE) dyad.
When the system of equations is solved, the unknowns φ4 and x E are obtained: φ4=165.9° x E =-0.114m
7. Solution: The origin of the system is at A, A≡0; that is,
x A =y A =0.
The coordinates of the R joints at B are x B =l 1cosφ y B = l 1sinφ
For the dyad DBB (RTR), the following equations can be written with respect to the sliding line CD:
mx B - y B +n=0 y D =mx D +n
With x D =d 1, y D =0 from the above system, slope m of link CD and intercept n can be calculated:
m=111cos sin d l l -ϕϕ n=ϕϕ
cos sin 1111l d l d - The coordinates x C and y C of the center of the R joint C result from the system of two equations:
y C =mx C +n=ϕϕϕϕcos sin cos sin 111
1111l d l d x d l l C -+-,
(x C - x D )2+(y C - y D )2=l 2
3
Because of the quadratic equation, two solutions are abstained for x C and y C .For continuous motion of the mechanism, there are constraint relations for the Choice of the correct solution; that is x C < x B < x D and y C >0
For the last dyad CEE (RRT), a position function can be written for joint E:
(x C -x E )2+(y C -h)2=l 2
4
The equation produces values for x 1E and x 2E , and the solution x E >x C is selected for continuous motion of the mechanism.。