随机变量、矢量和序列
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:413.50 KB
- 文档页数:44

数学专业词汇及翻译一、字母顺序表 (1)二、常用的数学英语表述 (7)三、代数英语(高端) (13)一、字母顺序表1、数学专业词汇Aabsolute value 绝对值 accept 接受 acceptable region 接受域additivity 可加性 adjusted 调整的 alternative hypothesis 对立假设analysis 分析analysis of covariance 协方差分析analysis of variance 方差分析 arithmetic mean 算术平均值 association 相关性assumption 假设 assumption checking 假设检验availability 有效度average 均值Bbalanced 平衡的 band 带宽 bar chart 条形图beta-distribution 贝塔分布 between groups 组间的 bias 偏倚 binomial distribution 二项分布 binomial test 二项检验Ccalculate 计算 case 个案 category 类别 center of gravity 重心central tendency 中心趋势chi-square distribution 卡方分布chi-square test 卡方检验classify 分类cluster analysis 聚类分析coefficient 系数 coefficient of correlation 相关系数collinearity 共线性 column 列 compare 比较 comparison 对照 components 构成,分量compound 复合的 confidence interval 置信区间 consistency 一致性 constant 常数continuous variable 连续变量 control charts 控制图 correlation 相关 covariance 协方差 covariance matrix 协方差矩阵critical point 临界点critical value 临界值crosstab 列联表cubic 三次的,立方的cubic term 三次项cumulative distribution function 累加分布函数 curve estimation 曲线估计Ddata 数据default 默认的definition 定义deleted residual 剔除残差density function 密度函数dependent variable 因变量description 描述design of experiment 试验设计deviations 差异df.(degree of freedom) 自由度diagnostic 诊断dimension 维discrete variable 离散变量discriminant function 判别函数discriminatory analysis 判别分析distance 距离distribution 分布D-optimal design D-优化设计Eeaqual 相等 effects of interaction 交互效应 efficiency 有效性eigenvalue 特征值equal size 等含量equation 方程error 误差estimate 估计estimation of parameters 参数估计estimations 估计量evaluate 衡量exact value 精确值expectation 期望expected value 期望值exponential 指数的exponential distributon 指数分布extreme value 极值F factor 因素,因子 factor analysis 因子分析 factor score 因子得分 factorial designs 析因设计factorial experiment 析因试验fit 拟合fitted line 拟合线fitted value 拟合值 fixed model 固定模型 fixed variable 固定变量fractional factorial design 部分析因设计frequency 频数F-test F检验full factorial design 完全析因设计function 函数Ggamma distribution 伽玛分布geometric mean 几何均值group 组Hharmomic mean 调和均值 heterogeneity 不齐性histogram 直方图homogeneity 齐性homogeneity of variance 方差齐性hypothesis 假设 hypothesis test 假设检验Iindependence 独立independent variable 自变量independent-samples 独立样本 index 指数 index of correlation 相关指数 interaction 交互作用 interclass correlation 组内相关 interval estimate 区间估计intraclass correlation 组间相关inverse 倒数的iterate 迭代Kkernal 核 Kolmogorov-Smirnov test柯尔莫哥洛夫-斯米诺夫检验 kurtosis 峰度Llarge sample problem 大样本问题layer 层least-significant difference 最小显著差数least-square estimation 最小二乘估计least-square method 最小二乘法 level 水平 level of significance 显著性水平leverage value 中心化杠杆值life 寿命life test 寿命试验likelihood function 似然函数 likelihood ratio test 似然比检验linear 线性的linear estimator 线性估计linear model 线性模型linear regression 线性回归linear relation 线性关系linear term 线性项logarithmic 对数的logarithms 对数 logistic 逻辑的 lost function 损失函数Mmain effect 主效应matrix 矩阵maximum 最大值maximum likelihood estimation 极大似然估计 mean squared deviation(MSD) 均方差 mean sum of square 均方和 measure 衡量 media 中位数 M-estimator M估计minimum 最小值missing values 缺失值mixed model 混合模型 mode 众数model 模型Monte Carle method 蒙特卡罗法moving average 移动平均值multicollinearity 多元共线性multiple comparison 多重比较multiple correlation 多重相关multiple correlation coefficient 复相关系数multiple correlation coefficient 多元相关系数multiple regression analysis 多元回归分析multiple regression equation 多元回归方程 multiple response 多响应 multivariate analysis 多元分析Nnegative relationship 负相关nonadditively 不可加性nonlinear 非线性nonlinear regression 非线性回归noparametric tests 非参数检验 normal distribution 正态分布null hypothesis 零假设 number of cases 个案数Oone-sample 单样本 one-tailed test 单侧检验 one-way ANOVA 单向方差分析one-way classification 单向分类optimal 优化的optimum allocation 最优配制 order 排序order statistics 次序统计量 origin 原点orthogonal 正交的 outliers 异常值Ppaired observations 成对观测数据paired-sample 成对样本parameter 参数parameter estimation 参数估计 partial correlation 偏相关partial correlation coefficient 偏相关系数 partial regression coefficient 偏回归系数percent 百分数percentiles 百分位数pie chart 饼图point estimate 点估计poisson distribution 泊松分布polynomial curve 多项式曲线polynomial regression 多项式回归polynomials 多项式positive relationship 正相关 power 幂P-P plot P-P概率图predict 预测predicted value 预测值prediction intervals 预测区间principal component analysis 主成分分析 proability 概率probability density function 概率密度函数 probit analysis 概率分析proportion 比例Qqadratic 二次的 Q-Q plot Q-Q概率图 quadratic term 二次项quality control 质量控制 quantitative 数量的,度量的 quartiles 四分位数Rrandom 随机的 random number 随机数 random number 随机数random sampling 随机取样random seed 随机数种子random variable 随机变量 randomization 随机化 range 极差rank 秩 rank correlation 秩相关 rank statistic 秩统计量 regression analysis 回归分析regression coefficient 回归系数regression line 回归线reject 拒绝rejection region 拒绝域relationship 关系reliability 可*性repeated 重复的report 报告,报表 residual 残差 residual sum of squares 剩余平方和response 响应risk function 风险函数robustness 稳健性 root mean square 标准差 row 行 run 游程run test 游程检验Sample 样本sample size 样本容量sample space 样本空间sampling 取样 sampling inspection 抽样检验 scatter chart 散点图S-curve S形曲线separately 单独地sets 集合sign test 符号检验significance 显著性significance level 显著性水平significance testing 显著性检验 significant 显著的,有效的 significant digits 有效数字 skewed distribution 偏态分布 skewness 偏度 small sample problem 小样本问题 smooth 平滑 sort 排序 soruces of variation 方差来源 space 空间 spread 扩展square 平方 standard deviation 标准离差 standard error of mean 均值的标准误差standardization 标准化 standardize 标准化 statistic 统计量 statistical quality control 统计质量控制 std. residual 标准残差 stepwise regression analysis 逐步回归stimulus 刺激strong assumption 强假设stud. deleted residual 学生化剔除残差stud. residual 学生化残差 subsamples 次级样本 sufficient statistic 充分统计量sum 和 sum of squares 平方和 summary 概括,综述Ttable 表t-distribution t分布test 检验test criterion 检验判据test for linearity 线性检验 test of goodness of fit 拟合优度检验 test of homogeneity 齐性检验test of independence 独立性检验test rules 检验法则 test statistics 检验统计量 testing function 检验函数time series 时间序列tolerance limits 容许限total 总共,和transformation 转换 treatment 处理 trimmed mean 截尾均值 true value 真值 t-test t检验 two-tailed test 双侧检验unbalanced 不平衡的unbiased estimation 无偏估计unbiasedness 无偏性 uniform distribution 均匀分布Vvalue of estimator 估计值 variable 变量 variance 方差 variance components 方差分量 variance ratio 方差比 various 不同的 vector 向量Wweight 加权,权重weighted average 加权平均值within groups 组内的ZZ score Z分数2. 最优化方法词汇英汉对照表Aactive constraint 活动约束 active set method 活动集法 analytic gradient 解析梯度approximate 近似 arbitrary 强制性的 argument 变量 attainment factor 达到因子Bbandwidth 带宽be equivalent to 等价于best-fit 最佳拟合bound 边界Ccoefficient 系数complex-value 复数值component 分量constant 常数constrained 有约束的constraint 约束constraint function 约束函数continuous 连续的converge 收敛cubic polynomial interpolation method三次多项式插值法 curve-fitting 曲线拟合Ddata-fitting 数据拟合default 默认的,默认的define 定义diagonal 对角的direct search method 直接搜索法direction of search 搜索方向 discontinuous 不连续eigenvalue 特征值empty matrix 空矩阵equality 等式exceeded 溢出的Ffeasible 可行的 feasible solution 可行解 finite-difference 有限差分 first-order 一阶GGauss-Newton method 高斯-牛顿法 goal attainment problem 目标达到问题 gradient 梯度 gradient method 梯度法Hhandle 句柄 Hessian matrix 海色矩阵Independent variables 独立变量inequality 不等式infeasibility 不可行性infeasible 不可行的initial feasible solution 初始可行解initialize 初始化inverse 逆 invoke 激活 iteration 迭代 iteration 迭代JJacobian 雅可比矩阵LLagrange multiplier 拉格朗日乘子large-scale 大型的least square 最小二乘 least squares sense 最小二乘意义上的 Levenberg-Marquardt method 列文伯格-马夸尔特法line search 一维搜索linear 线性的linear equality constraints 线性等式约束linear programming problem 线性规划问题 local solution 局部解M medium-scale 中型的minimize 最小化mixed quadratic and cubic polynomialinterpolation and extrapolation method 混合二次、三次多项式内插、外插法multiobjective 多目标的Nnonlinear 非线性的 norm 范数Oobjective function 目标函数observed data 测量数据optimization routine 优化过程optimize 优化optimizer 求解器over-determined system 超定系统Pparameter 参数partial derivatives 偏导数polynomial interpolation method 多项式插值法Qquadratic 二次的 quadratic interpolation method 二次内插法quadratic programming 二次规划Rreal-value 实数值 residuals 残差 robust 稳健的 robustness 稳健性,鲁棒性S scalar 标量semi-infinitely problem 半无限问题Sequential Quadratic Programming method 序列二次规划法 simplex search method 单纯形法solution 解sparse matrix 稀疏矩阵sparsity pattern 稀疏模式 sparsity structure 稀疏结构 starting point 初始点step length 步长subspace trust region method 子空间置信域法sum-of-squares 平方和 symmetric matrix 对称矩阵Ttermination message 终止信息 termination tolerance 终止容限 the exit condition 退出条件 the method of steepest descent 最速下降法 transpose 转置Uunconstrained 无约束的 under-determined system 负定系统Vvariable 变量 vector 矢量Wweighting matrix 加权矩阵3 样条词汇英汉对照表Aapproximation 逼近 array 数组 a spline in b-form/b-spline b 样条 a spline of polynomial piece /ppform spline 分段多项式样条Bbivariate spline function 二元样条函数 break/breaks 断点Ccoefficient/coefficients 系数cubic interpolation 三次插值/三次内插cubic polynomial 三次多项式 cubic smoothing spline 三次平滑样条 cubic spline 三次样条cubic spline interpolation 三次样条插值/三次样条内插 curve 曲线Ddegree of freedom 自由度 dimension 维数Eend conditions 约束条件input argument 输入参数interpolation 插值/内插 interval取值区间Kknot/knots 节点Lleast-squares approximation 最小二乘拟合Mmultiplicity 重次 multivariate function 多元函数Ooptional argument 可选参数 order 阶次 output argument 输出参数P point/points 数据点Rrational spline 有理样条 rounding error 舍入误差(相对误差)Sscalar 标量sequence 数列(数组)spline 样条spline approximation 样条逼近/样条拟合spline function 样条函数 spline curve 样条曲线spline interpolation 样条插值/样条内插spline surface 样条曲面 smoothing spline 平滑样条Ttolerance 允许精度Uunivariate function 一元函数Vvector 向量Wweight/weights 权重4 偏微分方程数值解词汇英汉对照表Aabsolute error 绝对误差 absolute tolerance 绝对容限 adaptive mesh 适应性网格Bboundary condition 边界条件Ccontour plot 等值线图 converge 收敛 coordinate 坐标系Ddecomposed 分解的 decomposed geometry matrix 分解几何矩阵diagonal matrix 对角矩阵Dirichlet boundary conditions Dirichlet边界条件Eeigenvalue 特征值elliptic 椭圆形的error estimate 误差估计exact solution 精确解Ggeneralized Neumann boundary condition 推广的Neumann 边界条件 geometry 几何形状geometry description matrix 几何描述矩阵 geometry matrix 几何矩阵 graphical user interface(GUI)图形用户界面Hhyperbolic 双曲线的Iinitial mesh 初始网格Jjiggle 微调LLagrange multipliers 拉格朗日乘子Laplace equation 拉普拉斯方程linear interpolation 线性插值 loop 循环Mmachine precision 机器精度 mixed boundary condition 混合边界条件NNeuman boundary condition Neuman边界条件 node point 节点 nonlinear solver 非线性求解器 normal vector 法向量PParabolic 抛物线型的 partial differential equation 偏微分方程plane strain 平面应变 plane stress 平面应力 Poisson's equation 泊松方程 polygon 多边形 positive definite 正定Qquality 质量Rrefined triangular mesh 加密的三角形网格relative tolerance 相对容限 relative tolerance 相对容限 residual 残差 residual norm 残差范数Ssingular 奇异的二、常用的数学英语表述1.Logicthere existfor allp?q p implies q / if p, then qp?q p if and only if q /p is equivalent to q / p and q are equivalent2.Setsx∈A x belongs to A / x is an element (or a member) of Ax?A x does not belong to A / x is not an element (or a member) of AA?B A is contained in B / A is a subset of BA?B A contains B / B is a subset of AA∩B A cap B / A meet B / A intersection BA∪B A cup B / A join B / A union BA\B A minus B / the diference between A and BA×B A cross B / the cartesian product of A and B3. Real numbersx+1 x plus onex-1 x minus onex±1 x plus or minus onexy xy / x multiplied by y(x - y)(x + y) x minus y, x plus yx y x over y= the equals signx = 5 x equals 5 / x is equal to 5x≠5x (is) not equal to 5x≡y x is equivalent to (or identical with) yx ≡ y x is not equivalent to (or identical wit h) yx > y x is greater than yx≥y x is greater than or equal to yx < y x is less than yx≤y x is less than or equal to y0 < x < 1 zero is less than x is less than 10≤x≤1zero is less than or equal to x is less than or equal to 1 | x | mod x / modulus xx 2 x squared / x (raised) to the power 2x 3 x cubedx 4 x to the fourth / x to the power fourx n x to the nth / x to the power nx ?n x to the (power) minus nx (square) root x / the square root of xx 3 cube root (of) xx 4 fourth root (of) xx n nth root (of) x( x+y ) 2 x plus y all squared( x y ) 2 x over y all squaredn! n factorialx ^ x hatx ˉ x barx ?x tildex i xi / x subscript i / x suffix i / x sub i∑ i=1 n a i the sum from i equals one to n a i / the sum as i runs from 1 to n of the a i4. Linear algebra‖ x ‖the norm (or modulus) of xOA →OA / vector OAOA ˉ OA / the length of the segment OAA T A transpose / the transpose of AA ?1 A inverse / the inverse of A5. Functionsf( x ) fx / f of x / the function f of xf:S→T a function f from S to Tx→y x maps to y / x is sent (or mapped) to yf'( x ) f prime x / f dash x / the (first) derivative of f with respect to xf''( x ) f double-prime x / f double-dash x / the second derivative of f with r espect to xf'''( x ) triple-prime x / f triple-dash x / the third derivative of f with respect to xf (4) ( x ) f four x / the fourth derivative of f with respect to xf ? x 1the partial (derivative) of f with respect to x12 f ? x 1 2the second partial (derivative) of f with respect to x1∫ 0 ∞the i ntegral from zero to infinitylim?x→0 the limit as x approaches zerolim?x→0 + the limit as x approaches zero from abovelim?x→0 ?the limit as x approaches zero from belowlog e y log y to the base e / log to the base e of y / natural log (of) yln?y log y to the base e / log to the base e of y / natural log (of) y一般词汇数学mathematics, maths(BrE), math(AmE)公理axiom定理theorem计算calculation运算operation证明prove假设hypothesis, hypotheses(pl.)命题proposition算术arithmetic加plus(prep.), add(v.), addition(n.)被加数augend, summand加数addend和sum减minus(prep.), subtract(v.), subtraction(n.)被减数minuend减数subtrahend差remainder乘times(prep.), multiply(v.), multiplication(n.)被乘数multiplicand, faciend乘数multiplicator积product除divided by(prep.), divide(v.), division(n.)被除数dividend除数divisor商quotient等于equals, is equal to, is equivalent to 大于is greater than 小于is lesser than大于等于is equal or greater than小于等于is equal or lesser than运算符operator数字digit数number自然数natural number整数integer小数decimal小数点decimal point分数fraction分子numerator分母denominator比ratio正positive负negative零null, zero, nought, nil十进制decimal system二进制binary system十六进制hexadecimal system权weight, significance进位carry截尾truncation四舍五入round下舍入round down上舍入round up有效数字significant digit无效数字insignificant digit代数algebra公式formula, formulae(pl.)单项式monomial多项式polynomial, multinomial系数coefficient未知数unknown, x-factor, y-factor, z-factor 等式,方程式equation一次方程simple equation二次方程quadratic equation三次方程cubic equation四次方程quartic equation不等式inequation阶乘factorial对数logarithm指数,幂exponent乘方power二次方,平方square三次方,立方cube四次方the power of four, the fourth power n次方the power of n, the nth power开方evolution, extraction二次方根,平方根square root三次方根,立方根cube root四次方根the root of four, the fourth root n次方根the root of n, the nth root集合aggregate元素element空集void子集subset交集intersection并集union补集complement映射mapping函数function定义域domain, field of definition值域range常量constant变量variable单调性monotonicity奇偶性parity周期性periodicity图象image数列,级数series微积分calculus微分differential导数derivative极限limit无穷大infinite(a.) infinity(n.) 无穷小infinitesimal积分integral定积分definite integral不定积分indefinite integral 有理数rational number无理数irrational number实数real number虚数imaginary number复数complex number矩阵matrix行列式determinant几何geometry点point线line面plane体solid线段segment射线radial平行parallel相交intersect角angle角度degree弧度radian锐角acute angle直角right angle钝角obtuse angle平角straight angle周角perigon底base边side高height三角形triangle锐角三角形acute triangle直角三角形right triangle直角边leg斜边hypotenuse勾股定理Pythagorean theorem钝角三角形obtuse triangle不等边三角形scalene triangle等腰三角形isosceles triangle等边三角形equilateral triangle四边形quadrilateral平行四边形parallelogram矩形rectangle长length宽width附:在一个分数里,分子或分母或两者均含有分数。


矢量的概念与运算法则矢量是物理学中一个重要的概念,它不仅在力学、电磁学等领域中有着广泛的应用,而且在计算机图形学、数据分析等领域中也扮演着重要的角色。
本文将介绍矢量的概念以及常见的运算法则。
一、矢量的概念矢量是一个有大小和方向的量,用箭头表示。
在二维空间中,矢量可以表示为一个有序的数对(x, y),其中x和y分别表示矢量在x轴和y轴上的分量。
在三维空间中,矢量可以表示为一个有序的数组(x, y, z),其中x、y和z分别表示矢量在x 轴、y轴和z轴上的分量。
矢量的大小可以用长度来表示,即矢量的模。
在二维空间中,矢量的模可以通过勾股定理计算:|v| = √(x^2 + y^2)。
在三维空间中,矢量的模可以通过类似的方法计算:|v| = √(x^2 + y^2 + z^2)。
矢量的方向可以用角度来表示。
在二维空间中,矢量的方向可以通过与x轴的夹角来确定。
在三维空间中,矢量的方向可以通过与x、y和z轴的夹角来确定。
二、矢量的运算法则1. 矢量的加法矢量的加法是指将两个矢量相加得到一个新的矢量。
在二维空间中,矢量的加法可以通过将两个矢量的分量相加来进行:v1 + v2 = (x1 + x2, y1 + y2)。
在三维空间中,矢量的加法可以通过类似的方法进行:v1 + v2 = (x1 + x2, y1 + y2, z1 + z2)。
2. 矢量的减法矢量的减法是指将一个矢量减去另一个矢量得到一个新的矢量。
在二维空间中,矢量的减法可以通过将两个矢量的分量相减来进行:v1 - v2 = (x1 - x2, y1 - y2)。
在三维空间中,矢量的减法可以通过类似的方法进行:v1 - v2 = (x1 - x2, y1 - y2, z1 -z2)。
3. 矢量的数量积矢量的数量积又称为点积,表示为v1 · v2。
在二维空间中,矢量的数量积可以通过将两个矢量的对应分量相乘再相加来计算:v1 · v2 = x1 * x2 + y1 * y2。


简述随机变量
随机变量 (random variable) 是概率论中的一个重要概念,表示一个未知量在某种条件下的一个取值。
通常用大写字母 X、Y、Z 等表示,其中 X 表示随机变量,表示某个未知量在某种条件下的取值。
随机变量是随机过程的组成部分,表示随机过程中某个未知量的取值。
例如,在投掷一枚骰子的过程中,掷出 1 点是一个随机变量,表示骰子掷出 1 点的取值。
随机变量具有两个基本性质:不确定性和可重复性。
不确定性是指某个未知量的取值是不确定的,需要通过随机过程来获得;可重复性是指某个未知量的取值可以重复出现,即每次投掷骰子掷出 1 点的概率都是相等的。
随机变量可以进行变量变换,即根据变量之间的关系进行变量转换。
例如,在投掷一枚骰子的过程中,如果已知掷出 1 点的随机变量为 X,那么掷出 2 点的概率可以用 X 的相反数表示,即 P(X=-1)=1-P(X=1)。
随机变量在概率论中有广泛的应用,例如在概率分布、期望、方差、协方差等概念中都需要用到随机变量。
其中,概率分布是随机变量最重要的应用之一,表示随机变量取某个值的概率。
例如,在投掷一枚骰子的过程中,掷出 1 点的概率是 1/6,掷出 2 点的概率是 1/6,以此类推。
拓展:
随机变量在生活中有广泛的应用,例如在赌博、投掷骰子、抽奖等活动中都是用到随机变量来描述未知量的取值。
在金融领域中,随机变量的应用也非常广泛,例如在投资决策、风险评估、收益率计算等活动中都需要应用随机变量的概念。

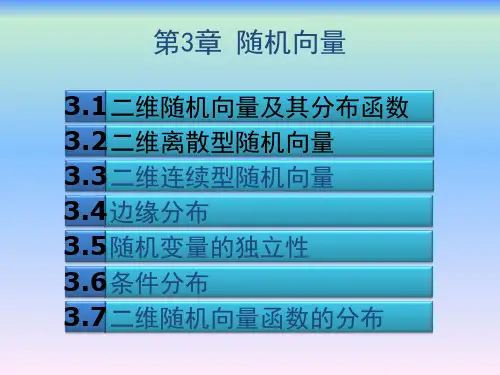
大学概率论第三章----随机向量第三章 随机向量第一节 二维随机向量及其分布1、二维随机向量及其分布函数定义1:设E 是一个随机试验,它的样本空间是{}e Ω=.设X(e)与Y(e)是定义在同一样本空间Ω上的两个随机变量,则称(X(e),Y(e))为Ω上的二维随机向量或二维随机变量。
简记为(X,Y).定义2:设(X,Y)是二维随机向量,对于任意实数x,y ,称二元函数 F(x,y)=P{X ≦x ,Y ≦y}为二维随机向量(X,Y)的分布函数或联合分布函数。
(X,Y)的分布函数满足如下基本性质: (1)F(x,y)是变量x,y 的不减函数. (2)0≦F(x,y)≦1,(,)0y F y -∞=对于任意的 ,(,)0x F x -∞=对于任意的(,)0(,)1F F -∞-∞=+∞+∞=,(3)(,), (,)(0,)(,)(,0)F x y x y F x y F x y F x y F x y =+=+关于是右连续的,即, 1122121222211211(4)(,)(,),, (,)(,)(,)(,)0x y x y x x y y F x y F x y F x y F x y <<--+≥对于任意和,有2、二维离散型随机变量定义3:若二维随机向量(X,Y)的所有可能取值是有限对或无限可列多对,则称(X,Y) 为二维离散型随机向量。
设(X,Y)的一切可能值为(,) , ,1,2,i j X Y i j =L ,且(X,Y)取各对可能值的概率为,(,), ,1,2,i j i j P X Y P i j ==L(1) 非负性:,0, ,1,2,i j P i j ≥=L ;,(2)1ij i jp =∑规范性:, (,){,}i i ijx x y yX Y F x y P X x Y Y p ≤≤=≤≤=∑∑离散型随机变量的联合分布函数为定义4:{,}(,1,2,...)(,)ij P X x Y Y p i j X Y X Y ≤≤==称为二维离散型随机变量的概率分布或分布律,或随机变量和的联合分布律。


矢量分析的知识点总结一、矢量的定义和表示1.1 矢量的定义矢量是指在空间中具有大小和方向的量,它可以用来表示物理量的大小和方向,如力、速度等。
矢量通常用箭头表示,箭头的长度表示矢量的大小,箭头的方向表示矢量的方向。
1.2 矢量的表示矢量可以用不同的方式表示,常见的表示方法有坐标表示和分量表示。
坐标表示是指用矢量所在空间的坐标系来表示矢量,分量表示是指将矢量在坐标系中的投影表示为一组数值。
1.3 矢量的运算矢量的运算包括加法、减法、数量乘法和点乘等。
加法和减法的运算结果是一个新的矢量,数量乘法是指将矢量的长度进行缩放,点乘是指将两个矢量的长度和夹角进行运算得到一个标量。
二、矢量的微积分2.1 矢量的导数矢量的导数是指对矢量的每个分量分别求导,得到的是一个新的矢量。
矢量的导数在物理学中有着广泛的应用,如速度、加速度等物理量都可以用矢量的导数来表示。
2.2 矢量场矢量场是指在空间中的每个点都有一个矢量与之对应的场,它可以用来描述流体的速度场、电场、磁场等。
矢量场的微积分可以用来研究矢量场的性质和行为。
2.3 曲线积分曲线积分是指对沿着曲线的矢量场进行积分,得到的是一个标量。
曲线积分在物理学中有着重要的应用,如对力沿着曲线的功的计算等。
2.4 曲面积分曲面积分是指对矢量场在曲面上的投影进行积分,得到的是一个标量。
曲面积分在物理学中也有着广泛的应用,如对电场在闭合曲面上的通量计算等。
三、矢量分析的应用3.1 物理学中的应用矢量分析在物理学中有着广泛的应用,如在力学中用于描述力、速度、加速度等物理量;在电磁学中用于描述电场、磁场等物理量。
3.2 工程学中的应用矢量分析在工程学中也有很多应用,如在流体力学中用于描述流体的速度场、压力场等;在航空航天工程中用于描述飞行器的运动状态、姿态等。
3.3 计算机科学中的应用矢量分析在计算机科学中也有着重要的应用,如在图形学中用于描述图像的旋转、平移等运动;在机器学习中用于描述数据的特征、相似度等。


关于矢量的总结矢量,即向量,是物理学与数学中常用的概念。
它具有方向和大小,并可以用箭头来表示。
矢量在各个学科中都有广泛的应用,例如力学、物理学、工程学、计算机图形学等。
下面将对矢量的定义、性质、运算法则以及应用进行详细的总结。
一、矢量的定义与性质1. 定义:矢量是一个有向线段,它具有大小和方向。
用加粗的小写字母表示,例如 a、b。
2. 大小:矢量的大小是指矢量的长度,用绝对值表示,例如|a|。
3. 方向:矢量的方向由与其平行的无数直线所组成的集合表示。
4. 自由矢量与固定矢量:自由矢量表示一个具有大小和方向的箭头,可以平行移动而不改变其性质;固定矢量表示一个固定在空间中的点,它具有大小和方向,但不能平行移动。
5. 等于矢量:如果两个矢量的大小及方向都相等,则称它们是等于矢量,用等号表示,例如 a = b。
6. 相反矢量:如果两个矢量的大小相等,方向相反,则称它们是相反矢量,用负号表示,例如 -a。
7. 单位矢量:大小为1的矢量称为单位矢量,用小写的带一个“^”的字母表示,例如 a^。
二、矢量的运算法则1. 矢量的加法:矢量的加法满足交换律和结合律,即 a + b = b + a,(a + b) + c = a + (b + c)。
2. 矢量的减法:矢量的减法可以看作是加上相反矢量,即 a - b = a + (-b)。
3. 数量积(点积):数量积是指两个矢量的乘积与它们夹角的余弦值的乘积,记作a·b,其结果是一个标量。
4. 向量积(叉积):向量积是指两个矢量的乘积与它们夹角的正弦值的乘积,记作a×b,其结果是一个矢量。
5. 数量积和向量积的运算法则:数量积满足分配律和交换律,a·(b + c) = a·b + a·c,a·b = b·a;向量积不满足交换律,a×b = -b×a。
6. 混合积:混合积是指三个矢量的乘积的结果,记作(a×b)·c,其结果是一个标量,它表示一个平行六面体的体积。
随机变量的基本概念与性质随机变量是概率论中的重要概念,它用于描述一个随机试验中可能出现的各种结果与其对应的数值。
在统计学和概率论中,研究随机变量及其性质对了解和分析随机事件具有重要意义。
本文将介绍随机变量的基本概念和性质。
一、随机变量的定义随机变量通常用大写拉丁字母表示,如X、Y。
它可以是离散的,也可以是连续的。
离散随机变量只取有限个或可列个值,而连续随机变量则可取任意实数值。
离散随机变量的概率函数可以通过概率质量函数(probability mass function,简称PMF)来描述。
对于任意一个取值x,概率质量函数P(X=x)表示该随机变量取值为x的概率。
连续随机变量的概率可以通过概率密度函数(probability density function,简称PDF)来描述。
对于一个连续随机变量X,其概率密度函数f(x)表示在某个区间[a, b]内X取值的概率。
二、随机变量的性质1. 期望值(均值)期望值是随机变量的平均数,用E(X)表示。
对于离散随机变量,其期望值计算方式为E(X) = ΣxP(X=x),即每个取值乘以相应的概率,再求和。
对于连续随机变量,期望值计算方式为E(X) = ∫xf(x)dx,即概率密度函数的加权平均。
2. 方差方差衡量了随机变量取值与其期望值之间的离散程度。
方差用Var(X)表示。
对于离散随机变量,方差的计算方式为Var(X) = Σ(x-E(X))^2P(X=x),即每个取值与期望值的差的平方乘以相应的概率,再求和。
对于连续随机变量,方差的计算方式为Var(X) = ∫(x-E(X))^2f(x)dx。
3. 标准差标准差是方差的平方根,用σ表示。
标准差和方差都可以用来度量随机变量的离散程度,但标准差更容易理解和比较。
4. 协方差协方差度量了两个随机变量之间的相关程度。
如果协方差为正,说明两个随机变量正相关;如果协方差为负,说明两个随机变量负相关;如果协方差为零,说明两个随机变量不相关。