BMJ最佳临床实践数据库介绍
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:3.72 MB
- 文档页数:24

•循证护理•糖尿病足发病风险筛查和评估的最佳证据总结谢晓冉!徐蓉摘要:目的总结糖尿病足发病风险筛查和评估的最佳证据"方法检索国内外相关数据库和专业团体网站中有关糖尿病足发病风险筛查和评估的证据,包括指南、证据总结、推荐实践和系统评价°检索时限为建库至2020年1月5日°应用临床指南研究与评价系统、系统评价评估工具、JBI证据预分级及证据推荐级别系统对文献进行质量评价和证据等级评定°结果共纳入9篇文献,包括5篇指南、1篇证据总结、1篇推荐实践和2篇系统评价°从全面采集健康史,周围神经病变的风险筛查和评估,末梢血管病变的风险筛查和评估,足部皮肤检查,足部压力的测量、足部畸形和鞋类的检查,风险分层系统的应用,风险筛查和评估的频率7个方面总结21条最佳证据°结论最佳证据总结为临床开展规范化的糖尿病足发病风险筛查和评估提供了循证依据,医护人员应结合临床环境与患者特点,合理地应用证据°关键词:糖尿病足;风险筛查;风险评估;证据总结;循证护理中图分类号.R473.5文献标识码:A DOI:10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2020.24.090Summary of best evidence on risk screening and assessment of diabetic foot Xie Xiaoran$Xu Long.Departmen4of Nursing$ Tongji Hospital$Tongji Medical College$Huazhong University of Science and Technology$Wuhan430030$China Abstract:Objective To summarize the best evidence on risk screening and assessment of diabetic foot.Methods We searched the related electronic databases and professional group's websites from inception to January5,2020,to collect guidelines$evidence summaries$best practice recommendation reports and systematic reviews on risk screening and assessment of diabetic foot.Then we used the such tools as Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation1(AGREE1),Assessment of Multiple Systematic Reviews(AMSTAR),JBI evidence pre-classification and evidence grading system to evaluate the quality of literatures and identify the level of evidence.Results A total of9publications were enrolled,including5guidelines,1evidence summary report,1best practice recommendation report,and2systematic reviews.Totally21pieces of best evidence were summarized from7aspects:ob-tainingacomp)ehensivehealthhisto)y)isksc)eeningandassessmentofpe)iphe)alneu)opathy)isksc)eeningandassessmentof pe)iphe)alvascula)disease footskininspection footp)essu)emeasu)ing examinationoffootdefo)mitiesandfootwea)theuseof )iskst)atificationsystems f)equencyof)isksc)eeningandassessment.Conclusion Thesumma)yofbestevidencep)ovidesanevi-dence-based reference for medical staff to carry out standardized risk screening and assessment of diabetic foot.The evidence shouldbeappliedreasonablyaccordingtoclinicalenvironmentandpatients'characteristics0Keywords:diabetes foot;risk screening;risk assessment;evidence summary;evidence-based nursing糖尿病足是糖尿病患者致畸致残的主要原因之一,给患者、家庭和社会带来了多方面的沉重负担(1)。

CDSS临床辅助决策支持系统介绍1.概述基于BMJ的BP开发了临床辅助决策支持系统,将BP深度结构化嵌入到医生的诊疗活动中,以此来提高医生的诊疗水平和服务质量,实现标准化治疗。
行心N HIS 的CDSS(临床辅助决策支持系统)解决了:●为临床医生、护士、医学生提供即时的诊疗知识,帮助他们优化诊断和治疗方案、保障患者安全、改善患者预后,并且终身学习。
●为医学研究者提供最新证据、总结和研究方向。
●帮助医疗机构和卫生主管部门改进医疗质量、降低费用。
系统分为两个版本:学校版和基层医疗机构版。
1.学校版:包含了临床辅助决策支持系统(Best Practice,以下简称BP)和Learning(在线学习)两大功能,以提升医学生的学习能力和临床思维;2.基层医疗机构版:则在上述两种功能的基础上,特别将BP进行深度结构化,并提供医疗质量评价系统、中国版QOF、云端专家在线指导等功能,并以此来提高医生的诊疗质量。
临床辅助决策支持系统是基于循证医学的临床诊疗决策支持工具,旨在为医务工作者在临床诊疗和学习过程中即时提供精准、可信并及时更新的诊疗知识,以帮助他们做出最佳诊断、优化治疗方案、改善患者预后。
2.系统介绍临床决策辅助系统建设采取集中部署一套平台,诊疗机构按各单位业务特点选取建设相对应的常用业务模块,特色业务模块也可定制开发集中部署,未来其他机构选用时开通站点即可。
2.1.BP系统知识库“BMJ最佳临床实践”,简称BP,是全球首个在循证医学基础上建立的临床决策支持系统。
BP国际版最早由英国医学杂志(BMJ)集团于2009年正式推出。
目前,将面向医疗机构推广已由中华医学会深度本地化的“最佳临床实践”,目的在于帮助医疗机构医生提高诊疗水平,规范诊疗标准,保障服务质量,降低医疗费用,最终达到帮助患者改善健康的目的。
1.以循证医学为基础,增强疾病诊治的科学性和有效性当前医疗机构普遍仍采用传统医学模式诊治疾病。
传统医学以个人经验为主,医生根据自己的实践、高年资师指导、教科书和医学期刊上零散的研究报告为依据来处理病人。
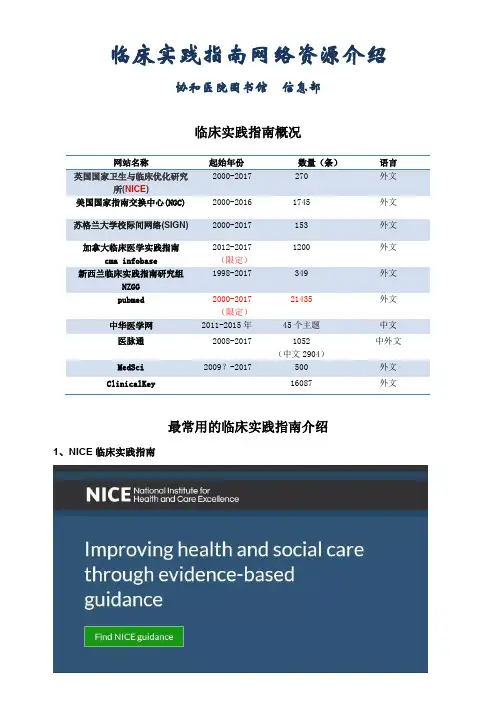
临床实践指南网络资源介绍协和医院图书馆 信息部临床实践指南概况1、NICE 临床实践指南网站名称起始年份 数量(条) 语言 英国国家卫生与临床优化研究所(NICE )2000-2017 270 外文 美国国家指南交换中心(NGC) 2000-2016 1745 外文 苏格兰大学校际间网络(SIGN) 2000-2017 153 外文 加拿大临床医学实践指南cma infobase2012-2017(限定) 1200 外文 新西兰临床实践指南研究组NZGG 1998-2017 349 外文 pubmed2000-2017(限定) 21435 外文 中华医学网 2011-2015年 45个主题 中文 医脉通 2008-2017 1052(中文2904)中外文 MedSci 2009?-2017500外文 ClinicalKey16087外文NICE是英国国家卫生和临床示范研究所(NationalInstitute forHealth and Clinical Excellence)的缩写,临床实践指南的网址是。
NICE总部设在伦敦和曼彻斯特,是一个为促进健康和防治疾病而提供国家性指导意见的独立研究机构,也是全球最大的国家级资助指南制定项目。
NICE成立于1999年4月,以评估卫生技术医疗市场的准入和提供临床诊治指南为宗旨。
NICE制定指南,设定质量标准,并定期更新,指南覆盖所有疾病领域,并在《英国医学杂志》(BMJ)刊出,每4年更新一次。
NICE收录了一定数量的涉及临床相关领域的指南,检索可选用主页上的直接检索,也可进入具有更多选择功能的检索页面;还可以针对指南的类型、主题或发表的时间等进行浏览或检索。
点击“NICE Guidance” →“Conditionsand diseases”→“Cardiovascularcondition”→“heart failure”,即可检索到关于心衰方面的指南,有多少篇及其分布的情况如何。



・84・JournalofNursingScience Jan2021Vol.36No.2•循证护理•维持性血液透析患者容量管理的最佳证据总结王爽】,黄海燕2,吕芳芳3,张玉曼4,祝筠1摘要:目的检索、评价并整合维持性血液透析患者容量管理的最佳证据,为完善维持性血液透析患者容量管理提供参考%方法系统检索循证资源及文献数据库、专业协会网站中有关维持性血液透析患者容量管理的证据,包括临床决策、指南、证据总结、最佳临床实践信息册、推荐实践、专家共识及系统评价%结果共纳入文献12篇,包括临床决策2篇、指南6篇、专家共识1篇、证据总结2篇、系统评价1篇,从评估与监测、钠水限制、容量超负荷处理、提高患者依从性4个方面汇总14条证据%结论医护人员可结合所在机构环境与患者意愿,选择性应用证据,为患者制定个性化容量管理方案,从而提高护理质量%关键词:终末期肾脏病;维持性血液透析;容量管理;证据总结中图分类号.R473.5文献标识码:A DOI:10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.202102.084Evidence summary on fluid management in maintenance hemodialysis patients Wang Shuang$Huang Haiyan$L d Fangfang$ Zhang Yu.an$Zhu Yun.Department of Nursing$Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University$Jinan250021$ChinaAbstract:Objective To retrieve,assess and summarize the existing evidence on fluid management in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Methods Systematic searches for evidence were performed across multiple sources as electronic databases and websites,to retrieve clinical decision,guideline,evidence summary,best practice information sheet,recommended practice,expert consensus and systematic review on fluid management in maintenance hemodialysis patients.Results Two best practice reports,6guidelines,1expert consensus statement,2evidence summaries and1systematic review were included.Four aspects with14pieces of evidence were summarized,including assessment and monitoring,sodium and fluid restriction,management of volume overload and enhancing patient compliance.Conclusion Medical staff could imple-menttheevidenceintoclinicalpracticebyconsideringsituationoftheinstitutionandpatient'spreference thustodeveloppatient-centeredfluid managementprotocolandimprovenursingqualityKey words:end stage renal disease;maintenance hemodialysis;维持性血液透析(Maintenance Hemodialysis, MHD)是终末期肾脏病患者最主要的肾脏替代治疗方式。

不孕女性体外受精⁃胚胎移植周期治疗不良心理应激评估与干预的最佳证据总结靳荣秀,赖文娟*,孙洪梅北京大学深圳医院,广东 518000with in vitro fertilization embryo transferJIN Rongxiu, LAI Wenjuan, SUN Hongmeipatients in infertile women with in vitro fertilization embryo transfer.Methods :Guidelines ,system evaluations ,and original were researched from guide library ,professional associations ,and databases.The retrieval time was from the establishment of the database to December 15,2022.Evidence extraction and integration were carried out after evaluating the quality of literature.Results :16 articles were analyzed ,including 2 guidelines ,1 expert consensus ,1 Meta‑integration ,6 systematic reviews and 6 randomized controlled trials ,the 29 pieces of best evidence were summarized into 6 categories ,including evaluation opportunity ,evaluation tools ,pre -treatment intervention measures ,intervention measures during treatment ,intervention measures after treatment failure ,successful pregnancy after treatment intervention measures.Conclusion :Medical staffs should actively monitor and accurately identify high ‑risk groups of psychological stress ,select the intervention factors ,determine the best time for intervention ,provide scientific evidence for making corresponding intervention measures ,and application of the best evidence in clinical practice according to the actual situation of the hospital.In order to reduce the psychological stress of patients ,improve their reproductive quality of life and improve the outcome of pregnancy.Keywords in vitro fertilization embryo transfer ; psychological stress ; evidence summary ; evidence‑based nursing摘要 目的:检索、评价并整合国内外关于不孕女性体外受精‑胚胎移植周期治疗不良心理应激评估与干预的最佳证据。

成人围术期肺康复管理的最佳证据总结刘天艺喻姣花2,李素云黄海燕3,柯卉4,张桃5,刘云访5,晏蓉6摘要:目的总结成人围术期肺康复管理的相关证据,为临床提供参考%方法从国内外循证资源和文献数据库中检索成人围手术期肺康复管理的证据%对各类型文献进行质量评价后提取并汇总证据%结果共纳入8篇文献%其中3篇临床决策!篇指南!篇证据总结!篇专家共识%从危险因素、评估方式、物理康复、患者教育、心理康复、围术期营养和术后镇痛7个方面综合22条最佳证据%结论在成人围术期肺康复临床护理标准尚未建立的背景下,可以通过循证证据总结,规范临床实践%在证据应用阶段,证据使用单位应充分考虑应用环境和患者的意愿选择证据%关键词:肺康复;呼吸康复;围术期;心理康复;营养;术后镇痛;循证护理;证据总结中图分类号.R473.6文献标识码:A DOI:10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.202102.088Evidence summary on perioperative pulmonary rehabilitation in adults Liu Tianyi$Yu Jiaohua$Li Suyun$Huang Haiyan,Ke Hui$Zhang Tao$Liu Yufang$Yan Rong.Union Hospital$Tongji Medical College$Huazhong University of Science and Technology$Wuhan430022$ChinaAbstract:Objective To summarize the existing evidence relating perioperative pulmonary rehabilitation in adults$and to provide referenceforclinicalpractice Methods Wesearchedelectronicdatabasesandsourcesofevidence-based medicinetoco l ectpapers relatingpulmonaryrehabilitation Qualityoftheliteraturewasevaluatedandthenevidencewasextractedandsummarized Results Tota l y8paperswereincluded$ofwhich3werebestpracticereports$1guideline$2evidencesummaries$and2expertconsensus statements Sevenaspectsinvolving22piecesofevidenceweresummarized$includingriskfactors$assessment$physicalrehabili-tation$patienteducation$psychologicalrehabilitation$perioperativenutritionandpostoperativepaincontrol Conclusion Underthe situationoflackofstandardsforclinicalnursingofperioperativepulmonaryrehabilitationinadults$evidence-basedsummarycould beformulatedtostandardizeclinicalpracticeInthephaseofevidenceapplication$theevidenceshouldbeimplementedbasedon clinical environment and the patient's preference.Key words:pulmonary rehabilitation;respiratory rehabilitation;perioperative period;psychological recovery;nutrition;postoperative pain control;evidence-based nursing;evidence summary术后肺部并发症是指患者术后出现临床症状和肺部异常表现$包括感染、肺不张、需要长期机械通气的呼吸衰竭及慢性肺部疾病恶化等[1](术后肺部并发症发生率1%〜23%,是术后病死率高、医疗费用增加和住院时间延长的主要原因因此,预防和控制术后肺部并发症尤为重要。


常见循证医学数据库对比循证医学被称为是“医学的圣经”、“震动21世纪的伟大思想”,循证医学的核心思想包括了医疗决策中将临床证据、个人经验与患者的实际状况和意愿三个要素组成的。
由此可见,寻找医疗决策的临床证据是循证医学的基础。
目前,能够帮助我们寻找证据的工具主要有:BMJ公司的Clinical Evidence、EBSCO公司的DynaMed、OVID公司的OVID EBM、美国的UpToDate、荷兰的First consult和北京康健公司推出的FEBM。
下面就针对这几个有代表性的数据库分别从每个库所含数据内容、系统功能、各自特点这几个角度进行总结与分析。
一、循证数据库产品的数据内容分析目前,市场上的循证产品的数据内容主要分为两大类:一种是知识型数据,另一种是二次文献型数据。
知识型数据库的内容并不是期刊文献,而是从这些证据文献中总结得到的某一具体临床问题的知识总结、摘要或结论。
像Clinical Evidence、DynaMed、UpT oDate、First Consult都属于这个类别的数据库。
二次文献型数据得到就是最基础的证据文献内容,例如OVID EBM、北京康健的FEBM。
因此,我们在谈EBM数据库的时候首先不可避免的要知道循证数据库的数据属于哪个类型。
知道了这些以后,我们还要对数据库的内容质量、容量、更新频率这些最基本的数据库情况做相应了解。
数据库的具体内容与特点对比详见附件1。
1.数据库的类型与数据量表数据库名称数据类型数据量Clinical Evidence 知识型470多种reviews DynaMed 知识型5500多主题UpToDate 知识型8500多主题First Consult 知识型1531多主题OVID EBM 文献型68万多篇FEBM 文献-知识型一千多万篇医学文献说明:FEBM之所以叫做文献-知识型数据库,就是因为FEBM不仅有循证文献检索的特点,同时经过数据标引等人工处理方式,而且拥有像对文献结论提取的TBL和即将推出的POEMS文献过滤等功能。
1美国国立临床诊疗指南数据库(NationalGuidelineClearinghouse,NGC)概况[1]NGC是由美国卫生健康研究与质量机构(A-gencyforHealthcareResearchandQuality,AHRQ)、美国医学会(AmericanMedicalAssociation,AMA)和美国卫生健康计划协会(AmericanAssociationofHealthPlans,AAHP)于1998年联合创立的一个提供临床实践指南和相关证据的免费数据库,目前收录有来自全世界310个机构发布的2400余篇指南。
1.1NGC的服务内容NGC为用户提供涵盖各种医学与健康主题的循证临床实践指南,另外还提供指南的专家点评意见以及相关医学信息。
NGC并不直接提供指南的原文,而是提供经过编辑人员对原指南进行分析、归纳后的指南摘要,以便于用户能够迅速、准确地了解指南内容。
NGC也提供指南原文的链接以供用户查阅。
1.2数据的更新该数据库每周进行1次更新,主要内容为新增的指南和对现有指南的修订,另外还包括最新的健康资讯、医学进展。
更新的信息将会发布在首页的“本周更新(NewThisWeek)”和“公告(Announcements)”上。
如果用户订阅了E-mail服务,更新的内容还会以邮件的形式发送到指定的邮箱,每一条信息都附有最近更新的日期。
美国国立临床诊疗指南数据库介绍汪宏包旭(四川大学华西药学院药理教研室,四川成都610041)【摘要】美国国立临床诊疗指南数据库是目前全球具有影响力的临床实践指南数据库之一。
本文通过对其数据库内容、服务方式以及功能特点等信息的介绍和分析,希望为国内广大医药专业人员了解和获取国际最新、最有效的临床实践指南提供参考。
【关键词】美国国立临床治疗指南数据库;临床实践指南;数据库doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-5433.2013.01.011An Introduction of the National Guideline Clearinghouse of the USAWangHong,BaoXu(PharmacologyDepartmentofWestChinaPharmacyCollegeofSichuanUniversity,SichuanChengdu610041,China)ABSTRACTTheNationalGuidelineClearinghouse(NGC)oftheUSAisoneoftheinfluentialandcomprehensivedatabasesoftheclinicalpracticeguidelines(CPGs)intheworld.Basedontheintroductionandanalysisofthecontents,thewayofservices,characteristicsandfunctionsofthisdatabase,thisarticleprovidedreferencesfordomesticmedicalandpharmaceuticalprofessionalswithtolearnandacquirethelatestandthemosteffectiveCPGs.KEY WORDSNationalGuidelineClearinghouse;ClinicalPracticeGuidelines;Database作者简介:汪宏,女,硕士,助教。