1化学专业英语介绍
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:5.01 MB
- 文档页数:17

unite 1. Inorganic chemistry1.1 what is chemistry(1). 重点专业词汇讲解:Chemical: adj . 化学的、化学药品Transformation: 变化,化学转变,转化Dye: n. 染料染色,或者vt. 染Charcoal: ['tʃɑkəʊl] 木炭Cellulose :纤维素细胞的['seljʊləʊz; ]Fat:n. 脂肪肥肉adj . 肥大的alkalis:碱adj . 碱性的glycerin: 甘油丙三醇alkalis: n. 碱金属alloy: 合金使成合金bronze:青铜色的n. 青铜(铜和锡的合金)brass:[brɑs] n. 黄铜(铜和锌)要求学生会区别黄铜及青铜的不同翻译Poison:毒物毒药t. 毒害放毒下毒Proton:n. 质子Nulei: n. 核(nucleus的复数形式)['njuklɪəs]Identical : adj . 同一的Chirality n. 手性手征和Handeness的区别Amino acid :n. 氨基酸Alanine: n.丙氨酸2. 课文中重点词组(phrase)Chemical change: 化学变化physical change:物理变化Explore: 探险研究research investigate studyIsolate: 分离chemical bonds 化学键chemical reaction:化学反应Natural substance 天然物质Coke :焦炭carbon monoxide 一氧化碳Carbon Dioxide 二氧化碳Chemical bond 化学键fundamental principle 基本原理The periodic table of elements :元素周期表numbers of protons 质子数atomic number 原子序数covalent bonds 共价键positive 正阳性negative 负阴性3. 课文中重点句子The first and most important principle is that chemical substances are made up of molecules in which atoms of various elements are linked in well-defined ways. 需要着重给学生讲解第一条也是最重要的原理是化学物质是有分子组成的,分子中的不同元素的原子是以一定的方式连接在一起的。






一、写出简称:乙酰基,Ac三甲基硅基,TMS对映体过量,ee氢化锂铝,LAH 四氢呋喃,THF N, N-二甲基甲酰氨,DMF对甲苯磺酰基,Ts 叔丁氧羰基,Boc咪唑(基),Im间氯过氧苯甲酸m-CPBA二、写出全称:BSA,N,O-双(三甲基硅基)乙酰胺DABCO 1,4-二氮杂双环[2.2.2]辛烷,EWG,吸电子基NBS,N-溴化丁酰亚胺DCC,1.3-二环己基碳化二亚胺NMR,核磁共振PPA,多聚磷酸DMAP,4-二甲基氨基吡啶PDC,重铬酸吡啶EDA重氮乙酸乙脂CDI N,N’-酰基二咪唑三、翻译:1、The teacher may be asked questions.可以向老师提一些问题。
2、Salts may also be found by the replacement置换of hydrogenfrom an acid with a metal.3、In the reaction both the acid and the base are neutralized(中和)forming water and salt.4、Organic compounds were once thought to be produced onlyby living organism.有机化合物一度被认为是只能由生物体产生5、It was reported that scientist had worked at the problem ofstoring the sun’s heat for many years.据报道,科学家曾在储存太阳热量的问题上研究了许多年。
6、The principles of absorption(吸收) and desorption解吸arebasically the same.7、Total determination of molecular structure is possible bymeans of X-ray diffraction.分子结构的完全确定有可能用X射线衍射方法。

化学专业英语1、化学专业英语:一、无机化学术语1、periodic table 元素周期表2、electronic structure电子构型3、wavelength波长4、frequency频率5、wave number波数6、diffraction衍射7、quantum量子8、quantized量子化9、quantum theory量子理论10、photoelectric effect光电效应11、photon光子12、quantum mechanics量子力学13、Heisenberg uncertainty principle海森堡测不准原理14、momentum动量15、angular momentum角动量16、ground state基态17、excited states激发态18、quantum number量子数19、atomic orbital原子轨道20、the four quantum numbers四个量子数21、electron configuration电子构型22、Pauli exclusion principle泡利不相容原理23、Hund’s principle洪特规则24、paramagnetism顺磁性25、diamagnetism反磁性26、period周期27、noble gas惰性气体28、Representative elements代表性元素29、Transition elements过渡元素30、Metals金属31、nonmetals非金属32、semiconducting elements半导体元素33、chemical bond化学键34、valence electrons价电子35、Lewis symbol路易斯符号36、Chemical stability化学稳定性37、octet rule八隅体规则38、chemical reactivity化学反应性39、metallic bonding金属键40、ionic bonding 离子键41、Lewis structures路易斯结构42、nonbonding electron pairs(lone pairs)非成键电子对43、covalent bonding共价键44、single单键45、multiple(double,triple) and coordinate(donor atom and acceptor atom) covalent bond配位键46、resonance共振47、resonance hybrid共振杂化48、nonpolar and polar covalent bond非极性和极性共价键49、dipole偶极50、network covalent substances51、bond dissociation energy键解离能52、lattice energy点阵能,晶格能53、atomic radii原子半径54、effective nuclear charge有效核电荷55、screening effect屏蔽效应56、Scanning 扫描57、Lanthanide contraction镧系收缩58、isoelectronic ions等电子离子59、ionization energy电离能60、noble gas configuration惰性气体构型61、electron affinity电子亲和能62、pseudo-noble gas configuration稀有气体原子实63、polarization of an ion离子极化64、electronegativity电负性65、electronegative atom电正性原子66、electropositive atom电负性原子67、Oxidation numbers氧化值68、Oxidation state氧化态69、molecular geometry分子几何70、bond axis键轴71、valence bond theory价键理论72、hybridization杂化73、isomers异构体74、structural isomers结构异构75、delocalized electrons离域电子76、dipole moment偶极矩77、London bond色散力78、nuclide核素79、nucleons核子80、mass defect质量缺陷81、nuclear binding energy核结合能82、nuclear fusion核聚变83、nuclear fission核裂变84、radioactivity放射性85、radionuclides放射性核素86、magic number幻数87、bombardment reaction轰击反应88、antineutrino反中微子89、neutrino中微子90、positron正电子(阳电子)91、electron capture电子捕获92、chain reaction链式反应93、crtical mass临界质量94、nuclear reaction 核反应95、thermonuclear reactions热核反应96、breeder reactor增殖反应97、hydration水合98、solvation溶剂化99、chemical equilibrium化学平衡100、hydrolysis水解101、hydrates水合物102、efflorescence风化物103、hygroscopic 吸湿104、deliquescence潮解105、electrolytes电解质106、strong(weak)electrolytes强电解质107、nonelectrolytes非电解质108、acidic(alkaline)aqueous solution109、polyprotic acids多元酸110、neutralization中和反应111、complex ion络合离子112、ligands配体113、hard water 硬水114、carbonate hardness碳酸盐硬度115、water softening水软化116、permanent hardness永久硬度117、ion exchange离子交换118、fossil fuels化石燃料119、oxidation氧化120、reduction还原121、oxidation-reduction(redox)reactions氧化还原反应122、oxidizing agent氧化剂123、heavy water重水124、absorption吸附125、acidic anhydride(oxide)酸性酸酐126、basic anhydride(oxide)碱性酸酐127、amphoteric两性128、allotropes同素异形体129、acid salt酸式盐130、oxidizing anion氧化性阴离子131、disproportionation reaction歧化反应132、oxidizing acids氧化性酸。

1、Beginning in the late seventeenth century with the work of Robert Boyle, who proposed the presently accepted concept of an element, numerous investigations produced a considerable knowledge of the properties of elements and their compounds.早在17义耳就开始了这项工作,他提出了现在公认的元素概念,大量的研究使我们对元素极其化合物的性质有了相当的了解。
In modern form, the law states that the properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. In other words, when the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number, elements having closely similar properties will fall at definite intervals along the list.用现代的话说,这个规律叙述了元素的性质是它们的原子序数的周期性函数。
换句话说,当元素按照原子序数逐渐递增的顺序列表(排列时),性质非常接近的元素将占据表格中具有一定间隔的位置.Thus it is possible to arrange the list of elements in tabular form with elements having similar properties placed in vertical columns.于是,将具有类似性质的元素排成纵列,从而把元素排成表格形式是可能的。
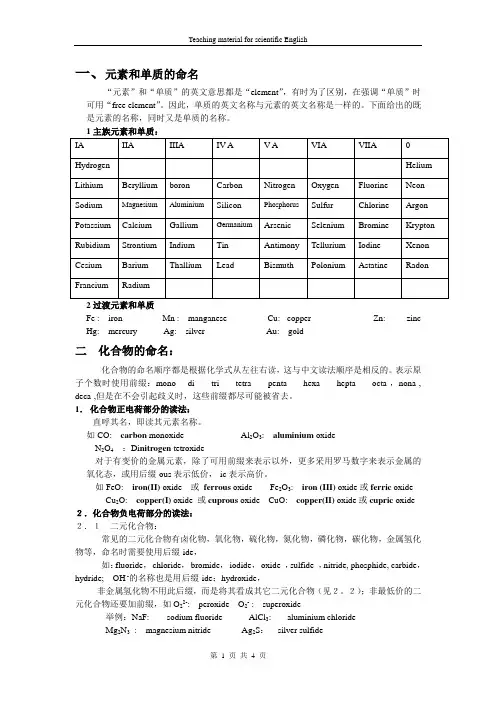
一、元素和单质的命名“元素”和“单质”的英文意思都是“element”,有时为了区别,在强调“单质”时可用“free element”。
因此,单质的英文名称与元素的英文名称是一样的。
下面给出的既是元素的名称,同时又是单质的名称。
2过渡元素和单质Fe : iron Mn : manganese Cu: copper Zn: zinc Hg: mercury Ag: silver Au: gold二化合物的命名:化合物的命名顺序都是根据化学式从左往右读,这与中文读法顺序是相反的。
表示原子个数时使用前缀:mono-di -tri- tetra -penta- hexa-hepta- octa-,nona-, deca-,但是在不会引起歧义时,这些前缀都尽可能被省去。
1.化合物正电荷部分的读法:直呼其名,即读其元素名称。
如CO: carbon monoxide Al2O3: aluminium oxideN2O4:Di nitrogen tetroxide对于有变价的金属元素,除了可用前缀来表示以外,更多采用罗马数字来表示金属的氧化态,或用后缀-ous表示低价,-ic表示高价。
如FeO: iron(II) oxide 或ferrous oxide Fe2O3: iron (III) oxide或ferric oxide Cu2O: copper(I) oxide 或cuprous oxide CuO: copper(II) oxide或cupric oxide 2.化合物负电荷部分的读法:2.1二元化合物:常见的二元化合物有卤化物,氧化物,硫化物,氮化物,磷化物,碳化物,金属氢化物等,命名时需要使用后缀-ide,如:fluoride,chloride,bromide,iodide,oxide ,sulfide ,nitride, phosphide, carbide,hydride; OH -的名称也是用后缀-ide:hydroxide,非金属氢化物不用此后缀,而是将其看成其它二元化合物(见2。

(完整版)化学专业英语一、基础词汇篇1. 原子与分子Atom(原子):物质的基本单位,由质子、中子和电子组成。
2. 化学反应Reactant(反应物):参与化学反应的物质。
Product(物):化学反应后的物质。
Catalyst(催化剂):能改变化学反应速率而本身不发生永久变化的物质。
3. 物质状态Solid(固体):具有一定形状和体积的物质。
Liquid(液体):具有一定体积,无固定形状的物质。
Gas(气体):无固定形状和体积的物质。
4. 酸碱盐Acid(酸):在水溶液中能电离出氢离子的物质。
Base(碱):在水溶液中能电离出氢氧根离子的物质。
Salt(盐):由酸的阴离子和碱的阳离子组成的化合物。
5. 溶液与浓度Solution(溶液):由溶剂和溶质组成的均匀混合物。
Solvent(溶剂):能溶解其他物质的物质。
Solute(溶质):被溶解的物质。
Concentration(浓度):溶液中溶质含量的度量。
二、专业术语篇1. 有机化学Organic Chemistry(有机化学):研究碳化合物及其衍生物的化学分支。
Functional Group(官能团):决定有机化合物化学性质的原子或原子团。
Polymer(聚合物):由许多重复单元组成的大分子化合物。
2. 无机化学Inorganic Chemistry(无机化学):研究不含碳的化合物及其性质的化学分支。
Crystal(晶体):具有规则排列的原子、离子或分子的固体。
OxidationReduction Reaction(氧化还原反应):涉及电子转移的化学反应。
3. 物理化学Physical Chemistry(物理化学):研究化学现象与物理现象之间关系的化学分支。
Chemical Bond(化学键):原子间相互作用力,使原子结合成分子。
Thermodynamics(热力学):研究能量转换和物质性质的科学。
4. 分析化学Analytical Chemistry(分析化学):研究物质的组成、结构和性质的科学。
完整版)化学专业英语Teaching Material for Scientific EnglishI。
Naming of XXX1.Naming of XXXThe English word for both "元素" and "单质" is "element"。
To distinguish een the two。
"free element" may be used when emphasizing "单质"。
Therefore。
the English names for XXX are the same。
The following are the names of elements that are also names of free elements:Group IA:XXXXXXSodiumGroup IIA:XXXMagnesiumGroup IIIA: Boron AluminumGroup IVA: Carbon Silicon GermaniumGroup VA: Nitrogen PhosphorusGroup VIA: Oxygen Sulfur XXXXXXPoloniumGroup VIIA: Fluorine Chlorine Bromine IodineXXXGroup 0: XXXNeon ArgonXXX Xenon RadonGroup IA: Potassium CalciumGroup IIA:RubidiumCesiumFranciumGroup IIIA:GalliumIndiumXXXGroup IVA:ArsenicXXXXXXXXXLead2.Naming of CompoundsCompounds are named from left to right according to their chemical formula。