精益看板制作
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:2.21 MB
- 文档页数:11


精益生产如何实现生产过程可视化管理在当今竞争激烈的市场环境中,企业都在寻求提高生产效率、降低成本、提升产品质量的方法。
精益生产作为一种先进的生产管理理念,已经被越来越多的企业所采用。
而实现生产过程的可视化管理,是精益生产中的一个重要环节,它能够帮助企业更直观地了解生产状况,及时发现问题,从而做出准确的决策,优化生产流程。
一、什么是精益生产与可视化管理精益生产,是一种通过消除浪费、优化流程和持续改进,以最小的投入获得最大产出的生产方式。
其核心思想是追求完美,即在满足客户需求的前提下,尽可能减少不必要的环节和资源浪费。
可视化管理,则是指通过直观的方式,将生产过程中的各种信息展示出来,让管理者和员工能够一目了然地了解生产的状况。
这些信息可以包括生产进度、质量数据、设备状态、库存水平等。
二、为什么要实现生产过程可视化管理1、提高生产效率通过可视化管理,员工能够快速了解自己的工作任务和目标,以及整个生产流程的进展情况。
这有助于减少等待时间和不必要的协调沟通,从而提高工作效率。
2、及时发现问题生产过程中的问题如果不能及时发现,往往会导致延误和成本增加。
可视化管理能够将问题直观地呈现出来,使管理者和员工能够在第一时间察觉到异常,从而迅速采取措施解决问题。
3、促进团队协作当生产过程的信息清晰可见时,不同部门和岗位的员工能够更好地理解彼此的工作,加强协作和配合,共同为实现生产目标而努力。
4、便于决策制定管理者能够基于可视化的生产数据,做出更准确、更及时的决策,优化生产资源的配置,提高企业的竞争力。
三、如何实现生产过程可视化管理1、确定需要可视化的关键信息首先,企业需要明确在生产过程中哪些信息是最重要的,需要进行可视化展示。
这可能因企业的行业、产品特点和生产流程的不同而有所差异。
一般来说,生产进度、质量指标、设备运行状况、人员出勤情况等都是常见的关键信息。
2、选择合适的可视化工具(1)看板看板是一种常见的可视化工具,它可以是物理看板,也可以是电子看板。
XX浩迪服饰XX现场环境管理控制看板
编制:李玉霞审核:批准:生效日期:2011年05月06日
XX浩迪服饰XX过程检验管理控制看板
2 / 21
3 / 21
编制:李玉霞审核:批准:生效日期:2011年05月06日
XX浩迪服饰XX产前样管理控制看板
编制:李玉霞审核:批准:生效日期:2011年05月06日
5 / 21
编制:李玉霞审核:批准:生效日期:2011年05月06日
XX浩迪服饰织造XX
6 / 21
审核:填表:填表日期:年月日
XX浩迪服饰织造XX
审核:填表:填表日期:年月日
7 / 21
XX浩迪服饰XX过程检验控制看板
8 / 21
9 / 21
编制:李玉霞审核:批准:生效日期:2011年05月06日
XX浩迪服饰织造XX
过程质量检验记录表
10 / 21
品管部主管: 检验员:检验日期: 年月日
XX浩迪服饰织造XX
缝制质量巡检验记录表
11 / 21
巡检人: 巡检日期: 年月日
12 / 21
13 / 21
14 / 21
编制:李玉霞审核:批准:生效日期:2011年05月06日
15 / 21
16 / 21
XX浩迪服饰XX
月份生产计划表
编号:HD-QR-14-04
17 / 21
XX浩迪服饰XX
18 / 21
编制:李玉霞审核:批准:生效日期:2011年05月06日
XX浩迪服饰XX
审核:填表人:填表日期:年月日
XX浩迪服饰XX
20 / 21
21 / 21。

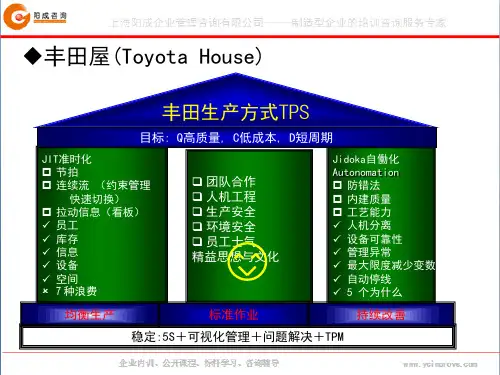
JIT看板管理及精益生产模式JIT看板管理及精益生产模式是一种以减少浪费和提高生产效率为目标的生产管理方法。
它通过使用看板进行信息传递和控制流程,使生产过程更加高效,并在生产过程中实现精益化管理。
JIT看板管理是“Just-in-Time”(及时生产)的缩写,它强调在必要时及时生产产品,以避免过度生产和库存积压。
看板是一种可视化工具,用于传达信息和控制物料的流动。
通过设置看板,例如生产看板和配送看板,可以实现按需生产和物料供应的精确控制。
当一个看板被触发时,它表示有一个特定数量的产品或物料需要生产或补充。
JIT看板管理的核心理念是“拉动式生产”,即根据最终客户需求来组织生产。
相比之下,传统的生产管理方式是“推动式生产”,即根据计划和预测进行生产。
通过使用JIT看板管理,可以减少生产过程中的浪费,例如过度生产、过度运输和库存积压,从而提高生产效率。
JIT看板管理与精益生产模式密切相关。
精益生产是一种基于“精益思维”的生产管理方法。
精益思维强调实现最大价值和最小浪费。
在精益生产模式中,通过消除无价值的活动和浪费,提高生产效率和质量。
JIT看板管理以及其他精益工具和方法,例如价值流图和5S,都是精益生产模式的重要组成部分。
使用JIT看板管理及精益生产模式的好处是显而易见的。
它可以帮助企业减少库存和运营成本,提高效率和客户满意度。
通过实时反馈和可视化管理,问题可以更快地被发现和解决。
此外,JIT看板管理还可以促进团队合作和沟通,以快速响应和适应市场需求。
总的来说,JIT看板管理及精益生产模式是一种强调高效生产和精益化管理的生产管理方法。
它通过使用看板和其他精益工具,实现按需生产和物料供应的精确控制。
通过减少浪费和提高效率,企业可以实现更高的生产质量和利润。
因此,JIT看板管理及精益生产模式已成为许多企业追求卓越和竞争优势的重要工具。
JIT看板管理及精益生产模式是一种以减少浪费和提高生产效率为目标的生产管理方法。

精益班组管理看板运营规则1. 简介精益班组管理看板是一种可视化管理工具,用于协调和监控班组工作进展。
本文档将为班组管理看板的运营提供一套规则和准则,以确保看板的有效使用和运作。
2. 看板设置2.1 看板命名每个班组看板应有一个唯一的、简明扼要的名称,以便成员能够轻松识别。
2.2 看板列班组看板应包含以下基本列: - 待办事项:列出需要完成的工作任务。
- 进行中:列出当前正在进行的工作任务。
- 完成:列出已完成的工作任务。
根据具体需求,班组也可以自行添加其他列,以支持更细粒度的任务分类和跟踪。
2.3 看板卡片每个工作任务应以卡片的形式表示,并包含以下信息: - 标题:简明扼要地描述工作任务。
- 负责人:指定工作任务的负责人。
- 截止日期:设定工作任务的最后期限。
- 描述:描述工作任务的详细内容。
2.4 看板标签为了更好地分类和过滤工作任务,可以使用标签来标示卡片。
可以根据需求自行定义标签,例如优先级、任务类型等。
3. 看板操作3.1 卡片移动根据任务的进度,将卡片从一列移动到另一列,以反映任务的状态变化。
例如,当一个任务从待办事项开始进行时,将其移动到进行中列;当任务完成时,将其移动到完成列。
3.2 卡片排序按照任务的重要性、紧急性或其他标准,可以在同一列中对卡片进行排序,以优先处理重要的任务。
3.3 标签使用在卡片上添加适当的标签,以帮助对任务进行分类和过滤。
请确保标签的准确性和一致性,以使标签的使用更加有效和有意义。
3.4 协作与沟通通过评论功能,在卡片中进行协作和讨论。
可以使用评论来提醒负责人或其他成员注意特定任务或问题。
3.5 更新与维护保持看板的更新和维护是关键。
负责人应定期检查并更新卡片的状态、进度和相关信息。
过期或无效的卡片应及时进行清理。
4. 角色和权限管理4.1 管理员角色每个班组看板应有一个或多个管理员,负责看板的设置、维护和权限管理。
管理员可以添加和删除成员,并设定他们的权限。

HUASHENG MACHINERY COMPANY(5年专业机加工公司)KANBAN PROCEDURESHUASHENG Kanban Procedure .Objective:To maintain optimal inventory for serving customers, balancing the need to provide good service with best possible inventory turns. This is especially necessary with our overseas suppliers where the transportation time is long.Overview:The HS 2 Bin Kanban SystemThe basic approach will be to utilize a kanban “pull” process, as initially developed by Toyota. The customer and the overseas supplier will each carry a predetermined amount of inventory. The basic unit of inventory will be the kanban quantity, also called a bin quantity. This will be calculated by the customer, and agreed upon by the supplier.HS will operate a 2 kanban system for sourcing . The supplier and the customer will each maintain 2 kanbans. The supplier 2 kanbans bins of inventory will be finished goods that have been inspected, packed and are ready to ship. The customer in the HS will maintain 2 kanbans.The Blanket Purchase OrderThe customer and supplier will negotiate a yearly blanket purchase order for the parts that will operate on the kanban system. Contained within the purchase order will be a yearly forecasted quantity of units. This quantity is merely a forecast or estimate and does not represent a commitment by HS to purchase this quantity. HS Company is only financially responsible for a maximum of 2 kanbans of material.The number of units in each kanban is fixed across all kanbans. The customer may at times change the quantity of units in each kanban. The following information will be defined in the blanket purchase order for each part number: unit cost, surcharges, quantity in each kanban, number of containers per kanban, quantity in each container, size of container (length, width and height in inches and centimeters) and weight of container. Warning! The yearly forecasted quantity specified by the blanket purchase order is a forecasted quantity. The supplier is not authorization to produce the entire yearly forecasted amount nor is it a commitment to purchase the entire amount.Operation of the 2 Bin Kanban SystemFigure 1 represents the operation of the two bin kanban system. When the customer consumes a kanban, a kanban shipping release instruction will be sent to the supplier. Upon receipt of the kanban release, the supplier will have a maximum of 2 weeks (14 calendar days) from the date of receipt of the kanban release instruction to deliver the kanban to the departure seaport of the ship (see table 1). The supplier is responsible for ensuring that the kanban is boarded on the ship and the ship departs the seaport within this two week period.Then upon shipment of the kanban, the supplier should immediately begin production to refill the kanban. The Supplier normally has the “total replenishment time” indicated in Table 1 to fill the kanban. In the case of a China supplier and a HS customer the supplier has seven weeks.Figure 1Operation of the 2 Bin Kanban System.Standard Replenishment Lead TimesTable 1 defines the standard replenishment time from the supplier’s location to the customer’s location. As an example, the China to HS kanban system is designed to deliver material in seven weeks to the HS located customer from a China based supplier. This seven weeks is broken down as follows:∙ A two week supplier response time represents:o The time for the China or India based supplier to process the order,o To arrange for transportation,o To deliver the order to the port,o To ensure the order is properly boarded,o To ensure the ship departs the port.∙ A seven week transit time represents:o The time for the ship to sail to the arrival port,o To clear customs in the HS,o To be loaded on the truck,o To arrive at the customer site.Standard Transit Times from Supplier Location to Customer LocationThe Use of Visual Management to Maintain Kanban SystemVisual management is key to the successful management of a kanban system. The two weaknesses of the kanban system are lost cards and containers. Both items must be displayed such that the human eye can identify lost or missing kanban or their cards. Remember the saying “ one picture is worth a tho HS nd words”.The Use of Green/Red Scheduling Boards By the Customer and the SupplierThe Green/Red scheduling board will be set up as shown below. It is used to visually manage the kanban cards. It is made of pegboard or plywood, painted green on the left, red on the right, and has hooks arranged to hold the cards. The board will be placed in the area where the parts are produced, as a tool for visual scheduling. The use of the board is required in both customer and supplier manufacturing plants.Figure 2.Green (Left)/Red (Right) Traffic BoardWhen the first kanban is shipped or consumed, it’s kanban card will be detached from the bin and hung on the left (green) hand side of the board. When the second kanban is consumed or shipped the first card on the green side along with the second kanban card is moved to the red side.As the kanbans are emptied in the warehouse, the kanbans are sent to purchasing so that shipping release instructions can be given to the supplier. The purchasing department then annotates the due date on the back of the card and the card is returned to the traffic board. Then the cards are placed on the board to quickly and easily reveal what the inventory position is.Rules for the order in which to produce parts for the kanban:∙First priority to produce parts –o The first kanban card of the double out kanban that is hung on the red side.Two kanban cards of the same part number that are hung on the board indicatethat we are entirely out of material.o If there are no other two card sets of kanbans on the red side of the board then both cards can be produced at the same time.o If there is another pair of kanban cards on the red side then the second card is moved back to the green side after production is begun on the first card.∙Second priority to produce parts - Any kanban card on the green side. The operator or supplier can produce a kanban card on the green side in any order. He may consider such things as common set-up, tool availability or other such things to make his decision on what to make first.∙For kanbans that consist of multiple containers as shown in figure 7, the kanban container cards are collected until all the cards are consumed in the first kanban,before the kanban is ordered or replenished. Normally it does not matter whichkanban is consumed first. In the case of a multiple container kanban, all of thecontainers must be consumed, before beginning on the next set of kanbancontainers.Examples of Green Only (Normal) Replenishment.Figure 3 represents the normal state of operation of the two bin kanban system. The manufacturing cell can produce any green cardGreen (Left) Only Traffic Board OperationExamples of Red (Emergency) Replenishment.Figure 4 represents an emergency replenishment of the two bin kanban system. In this situation both kanbans are empty. This is an emergency situation and the manufacturing cell or the supplier must immediately produce a single kanban container of the part number. This must be produced immediately. The organization must work 24 hours per day and expedite all material necessary to produce the product.Emergency ReplenishmentUnexpected Customer DemandThe kanban system is based on forecasted demand. When demand exceeds the forecast, the supplier must still meet the requirements of the order regardless of the lead-time given. When the supplier has two kanban cards unfilled he is in an emergency situation and needs to ship the first kanban immediately. Before shipping in this scenario he should contact the customer to determine whether to transport via ship or plane.When Suppliers’ Cumulative Manufacturers Lead Time Exceeds Total Replenishment Time.When the manufacturing time of the part exceeds the total replenishment time specified by table 1, the supplier must take steps to reduce his response time to the customer order. In the case of China, the replenishment time is seven weeks, this means the supplier must be able to manufacture the part in less that seven weeks. If the supplier cannot, he musteither keep extra containers of material in each kanban beyond the two required or locate raw material kanbans within his manufacturing process to bring his cumulative manufacturing lead time below 7 weeks. As an example, if the supplier of a machined casting has a cumulative manufacturing leadtime of 12 weeks (four weeks required to machine the raw casting and eight weeks for the foundry to pour the raw casting). The supplier must establish raw casting kanbans to support the machine shop. This buffer of raw material will enable the supplier to replenish the finish goods kanban in less than seven weeks.Management of the Kanban Card within the Customer’s CompanyAs the kanbans are emptied in the warehouse, the kanban cards are sent to purchasing so that shipping release instructions can be given to the supplier. The purchasing department then annotates the due date on the back of the kanban card and the card is returned to the traffic board.Movement of the Kanban Card with the Supplier’s CompanyAs the kanbans are emptied in the warehouse, the kanban cards are sent to the production cell to produce more of the product. When the production kanban is complete, inspected and packaged The kanban card is removed from the kanban board, the back of the kanban card is annotated with the in and out date and the kanban card in attached to the container. The kanban of finish goods is then forwarded to the warehouse and stored until the next customer demand is received.The Kanban Card and the Multiple Container KanbansFigure 6a- 6d represents an examples of a kanban cards for a two bin multiple containers kanban system. Multiple containers are required when the quantity of parts cannot be kept in one kanban container. In this situation the kanban is made up of multiple containers. In the ocean freight 2 bin kanban system we may have multiple container within a single kanban. Such a system will be required to ship heavy large castings. The bin quantity is divided equally between the containers. Below is an example of such a system.Figure 6a The Kanban CardFigure 6b Examples of Kanban CardsTop Production Kanban Middle: SuperMarket KanbanBotton: Supplier KanbanBack of Production Kanban CardBack of Purchasing KanbanFigure 7Example of Labeling of a 2 bin, 4 Container Kanban System.Movement of the Kanban CardKanban cards must be treated carefully and not lost. They are attached to the rack or to the container in the warehouse location where the kanban is kept. The card is detached and sent to the traffic board for replenishment when the kanban is shipped. When the kanban is filled, the card travels with the finished items to the storage location where the kanban will be kept until it is released for shipment. The picture below (Figure 8)shows kanban cards attached to racks. It also shows an actual, physical “bin” or kanban. It too has a kanban card permanently attached to it in order to identify the part number that would normally be present in the container.Each kanban has a permanently assigned home location and this home is f identified by a label on the storage rack. When the kanban is empty, the container will be gone, the detachable kanban card will be gone, and the space will be empty. The shelf label will indicate that this location is reserved for this. In this type of arrangement, the second kanban is placed behind the first one. You can see that the bin on the left does not have another behind it. You can see some empty Velcro to the left of the shelf label where the cards from the first kanban have been removed. On the right you can see two bins, one behind the other, with both cards in place.Figure 8Kanban Storage RackIt is an absolute requirement that the supplier must keep kanban in stock, and ship immediately upon receipt of release instructions. The supplier manufacturing replenishment lead time must be fast, so that the empty kanban can be replenished quickly, so if business is strong, the supplier will never be out of kanban. If the supplier cannot do this, then they must improve their manufacturing process. It may also be necessary for the supplier to work with their suppliers on kanban, if supply of raw materials is a limiting factor.Suppliers’ Responsibilities:∙Always maintain two kanbans of material of each part number in the program, ina finished goods state, inspected, packed and ready to be shipped immediatelyafter receiving notification.∙Immediately replenish the empty kanban, in order to be prepared in case another shipment release is received quickly.∙Only part number will be packaged in any single shipping crate/box/package.Boxes should not be packed with multiple different items.∙Only the kanban quantity should be shipped. Overages/underages will not beacceptable.∙The supplier will immediately (next business day) confirm receipt of kanban release instructions to customer.∙The supplier will take immediate steps to arrange ocean freight for the kanban item. The supplier will confirm shipping details within five days of notification, and will ship from their location in a timely manner.。


Topics主题Section1:What is Kanban?什么是看板?Section2:Two-card Kanban Systems2张看板卡系统Section3:Kanban Calculation看板的计算Section4:Managing the Kanban System管理看板系统Section5:Kanban System Implementation看板系统的实施Jargon Buster专业术语Kanban看板Supermarket超市Production Instruction Kanban生产指示看板Withdrawal Kanban取料看板Supplier供应商Signal Kanban信号看板Safety stock安全库存Buffer stock缓冲库存Section1Topics第1章主题What is Kanban?什么是看板?A tool of the pull system拉动系统的工具A signal that authorizes production or movement(withdrawal)of items授权生产或移动物料的信号The actual card,container or physical signal itself实物卡,周转箱或者实际的信号A visual method of controlling workflow,invented in the days before IT一个目视化的控制生产流的方法,在IT之前发明The system that uses kanban这个系统使用看板Kanban is a simple and effective method for visually controlling material flow看板是一个针对目视化管理物料流的简单高效的方法The kanban system itself is full of waste such as handling,inventory and processing看板体系本身也是充满了浪费,例如物料搬运,库存及操作Kanban is the acknowledgement of the failure to implement one piece flow看板承认不能实现单件流的表现Definitions is kanban看板的定义Functions of kanban看板的功能Sets limits设定限制Kanban is like currency–you cannot buy parts without paying for them!看板就像货币—你不能在没有付钱的情况下买东西Nothing is made or moved without a kanban在没有看板的情况不生产或者移动物料Makes problems visible让问题可视化Kanban=inventory=waste看板=库存=浪费Instruct processes to produce指示工序进行生产Limits overproduction限制过量生产Instruct material handlers to move product指示物料员运送产品Withdrawal from upstream by downstream process下工序从上工序取料Forms of kanban看板的形式Classic“two card”system(uses production and withdrawal cards)经典的“2种卡”系统(使用生产及取料看板)“One card”system uses one of the following“看板”系统使用以下的方式Card卡片Triangular plates三角板Containers周转箱Carts推车Colored balls不用颜色的球Electronic signal电子信号Or anything that conveys only the necessary information.或者其他人能能够转换必要信息的工具Forms of Kanban看板的形式Forms of Kanban看板的形式Section2:Two-card Kanban Systems2张看板卡系统Types of kanban看板的类型Production instruction kanban生产指示看板Signal kanban信号看板Lot making board批量生产板Withdrawal kanban取料看板Supplier kanban供应商看板Kanban cycles看板循环Types of Kanban看板的类型Section2:Two-card Kanban Systems2张看板卡系统Types of kanban看板的类型Basic Card Design基本的卡片设计Information on a Kanban Card看板卡上的信息The action(make,move,etc.)行动(制造,移动)Part number物料名称Part description物料描述The supplier(or process)name供应商(工序)名称Quantity数量Container quantity周转箱数量The source location物料存储的地址The delivery location物料运送地址The timing of the action(kanban cycle)行动的时间(看板循环时间)Etc.等等。

生产车间常见的七种类型管理看板6S管理咨询公司语看板是精益工具里较为高端的一个工具,这里的看板KANBAN不是指工作场地的显示和记录状况的白板,看板在这里是一种触发信号,而且尤其是指拉动方式里的触发信号。
较为复杂,却意义重大。
看板作为拉动的实施工具,作为准时生产JIT的实现方式,起的是个触发的作用。
5S管理看板管理作为精益生产的核心手段之一,无疑对提高工作效率及降低生产成本方面发挥了重要的作用。
看板管理模块主要有:A.生产看板:生产看板是将计划部门的排程计划以生产指示的形式分发到各个车间,明确各车间的生产任务及生产进度等。
电子看板:将生产看板的生产任务以电子牌(电子看板)形式显示到各个生产线下,加工人员根据电子看板内容明确加工任务,从而使得各个生产人员职责更加清晰,避免生产人员凭感觉判断先做什么任务,后做什么任务,实现车间生产现场管理透明化。
C.生产异常看板:当车间生产现场发生异常状况,如缺料,未按计划开工或完工时,通过电子看板或PC机屏幕显示生产异常,协助车间生产管理人员及时处理,确保生产稳定进行。
物料管理看板:物料管理模块通过精确计算每种物料(原材料、半成品及成品)的出入库时间、数量变化,清楚记录每种物料的过去与未来的库存变化,了解每个物品的库存是否过剩?是否够用?从而更好控制和管理物料,有效消减库存并防止缺货。
E.设备管理:设备是车间生产加工的基础和必要保证,也是车间生产管理的重点。
设备故障将直接影响车间的生产能力,进而影响企业的接单能力。
华商永续精益生产管理咨询培训导师认为,设备管理可满足车间对设备的日常所有管理,提高设备的使用寿命,减少设备故障,从而提高车间生产管理水平。
F.质量管理:质量管理涉及到产品良率、产品质量信息记录等。
通过看板管理系统,可以直观的了解产品实时质量信息并对不良品进行追踪与管控,并及时做出改正措施以预防不良品的产生。
G.绩效考核:华商永续精益生产管理咨询培训导师认为,通过对交货期达成率、每日计划达成率、资源(计划与实际)负荷率、物品平均生产周期、工序平均生产工时、平均生产准备时间等进行有效统计与考核分析,对各层级计划的合理性及现场执行情况进行有效考核,进一步加强生产管控,方便企业作出正确决策。