利妥昔单抗说明书完整版.doc
- 格式:doc
- 大小:29.00 KB
- 文档页数:5



一文详解利妥昔单抗自1997年第一代抗CD20抗体利妥昔单抗应用于临床治疗B细胞非霍奇金淋巴瘤(B- NHL)以来,抗CD20单抗经历了嵌合鼠源单抗、人源化单抗、糖基化修饰Fe片段单抗三代更迭。
利妥昔单抗(R)联合CHOP、CVP等化疗方案目前已成为DLBCL、滤泡细胞淋巴瘤等B- NHLs的标准治疗方案。
今天医伴旅小编就带大家了解一下利妥昔单抗这个药物。
关于淋巴瘤B细胞非霍奇金淋巴瘤(B-NHLs)代表了一组异质性的来源于血液系统的恶性肿瘤,世界卫生组织(WHO)的淋巴恶性肿瘤分类确定了大约50种具有不同临床、病理和遗传特征的B细胞来源的恶性淋巴增生性疾病。
其中常见的有弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤(DLBCL)、滤泡性淋巴瘤、黏膜相关淋巴组织淋巴瘤(MALT),小淋巴细胞淋巴瘤/慢性淋巴细胞白血病(CLL)、套细胞淋巴瘤(MCL)等。
关于利妥昔单抗利妥昔单抗为一种治疗癌症的单克隆抗体,自2000年进口到国内后,成为治疗非霍奇金淋巴瘤的首选药物,其治疗效果确切,但其价格较为昂贵,给患者的家庭带来了沉重的经济负担。
国产利妥昔单抗2019年经国家药品监管局批准在国内上市,已经应用于临床治疗弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤等疾病,且治疗效果良好。
利妥昔单抗的作用利妥昔单抗属于一种人鼠嵌合型单克隆抗体,可以特异性的与跨膜抗原CD20有效结合,进而促进肿瘤细胞凋亡,并且和抗体进行结合之后,CD20存在的形式作为非游离抗原,比较难以从细胞膜中脱落,因此能够在提升治疗效果的同时刺激产生B细胞溶解免疫反应,提升肿瘤细胞对于所用药物的敏感性。
利妥昔单抗的治疗效果选取66例CD20阳性弥漫大B细胞性非霍奇金淋巴瘤患者作为研究对象,将患者随机分为观察组与对照组,每组33例。
给予对照组患者标准CHOP 化疗治疗,给予观察组患者利妥昔单抗联合标准CHOP化疗治疗,对比两组患者治疗效果,1年、2年、3年的生存率与局部复发率以及不良反应情况。
结果:观察组患者客观缓解率48.48% 、疾病控制率87.88%,高于对照组客观缓解率21.21%、疾病控制率57.58%(P<0.05);对比两组患者的生存率发现,观察组和对照组患者1年生存率对比无明显差异(P >0.05),观察组患者的2年3年生存率明显高于对照组(P<0.05)对比两组患者的局部复发率发现,观察组和对照组患者1年局部复发率对比无明显差异(P>0.05);观察组患者的2年、3年局部复发率明显低于对照组(P<0.05);两组患者等级及不良反应发生率对比无明显差异(P>0.05)。


利妥昔单抗注射液(美罗华)在儿科的临床应用【摘要】目的探讨利妥昔单抗注射液(美罗华)治疗非霍奇金淋巴瘤(NHL)时的观察及护理。
方法使用美罗华前予非那根针肌肉注射、地塞米松针静脉注射,配制美罗华时严防泡沫产生,现配现用;使用智能输液泵,严格控制输液速度,先快后慢,使用过程中用监护仪严密监测生命体征的变化。
结果通过用药前的处理及控制输液速度的方法,药物不良反应明显减少,副作用及时得到控制。
结论有效的措施可明显减少不良反应的发生。
【关键词】利妥昔单抗注射液;SLE;药物疗法;护理利妥昔单抗注射液(美罗华)是一种嵌合型鼠/人单克隆抗体,与细胞表面CD20抗原特异性结合后能很快地清除肿瘤性CD20细胞,属于蛋白制品生物制剂。
SLE,多数起源于B淋巴细胞。
95%以上的B淋巴细胞表达CD20抗体,CD20抗原的表达出现在前B淋巴细胞的晚期和成熟B淋巴细胞,在造血干细胞、祖细胞和其他正常组织中无CD20抗原的表达。
当B淋巴细胞分化为浆细胞时,CD20抗原的表达也随之消失。
因此,CD20抗原是免疫治疗SLE的理想作用点。
美罗华属于蛋白制品的生物制剂,可能发生过敏性或高敏感性反应,在使用前后采取一系列措施,减少不良反应的发生。
1临床资料1.1一般资料:病例1:王小语女岁确诊SLE4年余病例2:王璇女岁确诊SLE2年10月利妥昔单抗注射液(美罗华)(化学名:RituximabInjection,生产厂家:F.Hoffmann-LaRocheLtd.批号:100mg/10ml,J20040110 ;500mg/50mlJ20040111)治疗,美罗华使用剂量均为375mg/m2.1.2方法(1)在输注美罗华前,床边备好氧气,并予心电监护。
停用今日泼尼松片口服,静脉注射美罗华前30min予西替利嗪滴剂10滴口服,异丙嗪25mg静推,地塞米松10mg静脉入壶,以减少过敏反应的发生。
(2)建立两路静脉通路,静脉输注美罗华必须是独立的静脉通路,另一路为碱化水化以维持水、电解质平衡。

美罗华(利妥昔单抗)
Roche top2美罗华(利妥昔单抗)2018年前半年销售额3454CHFm,美国地区2127CHFm,欧洲地区505CHFm,1997年上市,全球第一个抗肿瘤单抗,2016年美国专利到期,2018年前半年仍维持2%的增长率,2017年医保价格8289.87/500mg,支付8个疗程,非医保价格17100/500mg,主要适应症CD20阳性的NHL的各种亚型(淋巴瘤多发于淋巴结,几乎可以侵犯到全身各个组织和器官,其中高发病率的是非霍奇金淋巴瘤NHL)、CD20阳性的慢性淋巴瘤(CLL)、类风湿性关节炎等自身免疫疾病。
95%以上的B细胞性NHL细胞表达CD20,免疫状态下的Pre-B 细胞到成熟B细胞表面均表达CD20,所以这个靶点同时对自身免疫疾病有效,pro-B细胞和浆细胞表面没有,这使得健康B细胞可以在治疗后再生。
CD20是B细胞表面磷酸化的糖基蛋白,无自然的配体,其功能可能与钙离子通道有关。
非滤泡性NHL无进展生存期可增加一年,弥漫型大B淋巴瘤DLBCL 无进展生存期可增加一年半,RA治疗24周ACR20多33%,ACR50多21%,ACR70多11%。
加上DLBCL是NHL中比例比较大的,复星先做了DLBCL的临床试验。
国内队列,复宏汉霖(国产罗氏)HLX01已报生产CXSS1700026,2018年CDE纳入优先审评。
生物类似物上报第一名。

利妥昔单抗治疗类风湿关节炎、狼疮肾炎、膜性肾病疾病超说明用药注意事项
类风湿关节炎。
推荐 RTX 联合甲氨蝶呤(MTX),用于对一种或多种 TNF 抑制剂治疗效果欠佳的成人中重度类风湿关节炎。
抗中性粒细胞胞浆抗体相关血管炎。
推荐 RTX 联合糖皮质激素,用于≥2 岁患者肉芽肿性多血管炎(GPA)和显微镜下多血管炎(MPA)。
寻常型天疱疮。
推荐 RTX 用于成人中重度寻常型天疱疮。
视神经脊髓炎谱系障碍。
推荐 RTX 用于血清 AQP4-IgG 阳性的视神经脊髓炎谱系障碍。
SLE。
推荐 RTX 用于中重度活动性 SLE。
狼疮肾炎。
推荐 RTX 用于顽固性狼疮肾炎。
膜性肾病。
推荐 RTX 用于至少有 1 个疾病进展危险因素的膜性肾病。
FSGS 和 MCD。
推荐 RTX 用于成人频繁复发的或激素依赖的局灶性节段性肾小球硬化(FSGS)。
推荐 RTX 用于成人频繁复发的或激素依赖的微小病变肾病(MCD)。
难治性肾病综合征。
推荐 RTX 用于儿童频繁复发(FRNS)或激素依赖性肾病综合征(SDNS)。

利妥昔单抗特殊不良反应的处理原则与高危人群预防措施利妥昔单抗(rituximab)是一种常用于治疗恶性和非恶性淋巴瘤、类风湿性关节炎等疾病的生物制剂。
尽管它具有显著的疗效,但在应用过程中也存在一些特殊不良反应,特别是与免疫抑制相关的不良反应。
因此,在使用利妥昔单抗时,需要注意以下处理原则和高危人群的预防措施。
处理原则:1.提前评估患者的风险因素:在给患者应用利妥昔单抗之前,应该对患者进行详细评估,了解其患病情况、病史和既往不良反应情况,并评估其潜在的高危因素。
2.监测患者的免疫相关指标:利妥昔单抗可能导致患者的免疫功能受损,因此,在给患者应用药物前和用药期间,应及时监测患者的免疫相关指标,包括血细胞计数、免疫球蛋白水平等。
3.及时处理不良反应:利妥昔单抗可能引发多种不良反应,包括过敏反应、疼痛反应、感染、肺部反应等。
一旦出现不良反应,应及时停止药物的给予,并针对不同的不良反应进行相应的处理措施。
4.个体化药物治疗:针对患者的具体情况,需要个体化的调整利妥昔单抗的剂量和给药方案,以最大限度地减少不良反应的发生。
在给予药物时还要遵循逐渐增加剂量的原则。
高危人群预防措施:1.具有免疫功能受损的患者:对于免疫功能受损的患者如艾滋病病毒感染者、器官移植患者等,应慎重使用利妥昔单抗,并加强感染防控措施,包括使用消毒剂、多次筛查患者的感染症状等。
2.预防感染:利妥昔单抗可能导致患者的免疫功能受损,增加感染的风险。
因此,在给予药物前,应对患者进行相应的感染检查,并给予充分的预防治疗,如抗感染药物的应用等。
3.合理药物组合:利妥昔单抗往往与其他化疗药物或免疫调节剂联合使用,为了减少不良反应的发生,应该合理选择药物组合,并控制药物的剂量和给药时间。
4.并发症的预防和处理:利妥昔单抗可能引发一些特殊的并发症,如心脏衰竭、肺部疾病等。
因此,在应用药物过程中,应定期进行心脏和肺功能的评估,并根据具体情况采取相应的预防和处理措施。


利妥昔单抗 (Rituxan)治疗的疾病及其副作用利妥昔单抗(Rituxan)治疗的疾病及其副作用利妥昔单抗(Rituxan)是一种用于治疗多种疾病的生物制剂,它是一种单克隆抗体药物,具有抗体依赖性的细胞毒性(ADCC)和补体依赖性细胞毒性(CDC)。
本文将介绍利妥昔单抗治疗的主要疾病,并探讨其副作用。
一、利妥昔单抗治疗的主要疾病1. 非霍奇金淋巴瘤(NHL)利妥昔单抗是FDA批准的一线治疗非霍奇金淋巴瘤的药物。
它可与化疗药物联合使用,提高患者的生存率和缓解病情。
利妥昔单抗通过结合并抑制CD20阳性B细胞的生长,阻断其繁殖和扩散。
2. 风湿性关节炎(RA)利妥昔单抗也被应用于风湿性关节炎的治疗。
它能减少炎症因子的释放,改善关节炎患者的症状和生活质量。
与传统的疾病修饰抗风湿药物(DMARDs)相比,利妥昔单抗治疗RA的效果更为显著。
3. 自身免疫性溶血性贫血(AIHA)自身免疫性溶血性贫血是一种自身免疫性疾病,患者的免疫系统攻击自己的红细胞,导致溶血和贫血。
利妥昔单抗通过减少自身抗体的产生,从而改善AIHA患者的贫血症状。
4. 多发性骨髓瘤(MM)多发性骨髓瘤是一种恶性肿瘤,主要发生在骨髓。
利妥昔单抗可以与其他化疗药物联合使用,帮助控制病情和延长患者的生存期。
它通过靶向CD20阳性浆细胞,阻断其生长和扩散。
二、利妥昔单抗治疗的副作用1. 过敏反应部分患者在接受利妥昔单抗治疗后可能出现过敏反应,表现为皮肤红肿、呼吸急促、荨麻疹等。
医生会在给患者注射前进行过敏测试,以减少过敏反应的发生。
2. 感染利妥昔单抗会抑制免疫系统的功能,增加感染的风险。
患者在接受治疗期间需要注意个人卫生,并避免接触有传染性的疾病。
3. 心血管副作用少数病人可能在接受利妥昔单抗治疗后出现心脏问题,如心肌梗死、心律失常等。
在治疗期间,医生会进行定期的心脏监测并咨询患者有关任何心脏症状的变化。
4. 血液系统副作用利妥昔单抗可能会导致血小板减少和贫血等血液系统副作用。
NMOSD患友须知:利妥昔单抗怎么用本期主播:商熵先生审稿专家:周红雨教授点击►即可收听本文音频文字版朋友们好,欢迎收听本期主题,我是主播商熵,本人也是一名视神经脊髓炎患者,愿意与您一道共抗疾病,享受人生。
视神经脊髓炎患者住院治疗期间,医生会给患者使用利妥昔单抗治疗。
有的患者对药物比较陌生,会去网络搜索查看。
结果一看会吓一跳,因为这个药是普遍用来治疗淋巴瘤的。
这个时候有的患者可能会犯嘀咕,觉得为什么自己要用这种药。
实际上这是个误会。
利妥昔单抗是一款什么药利妥昔单抗在国内医保的适应症是淋巴瘤化疗治疗。
利妥昔单抗的药物作用机制是消减产生抗体的免疫细胞,因此这个药物也可以应用于视神经脊髓炎患者,可以起到减少AQP4抗体的生成的目的,因此是视神经脊髓炎谱系疾病缓解期临床中常用的预防复发的药物。
利妥昔单抗的临床应用那么,利妥昔单抗怎么使用呢?利妥昔单抗是一种静脉使用的药物,药物的剂量是根据患者的体表面积计算出来的,使用剂量为375mg/m2。
按照国际的应用惯例,一般是每周一次,连续使用4周;或者是1000mg静脉滴注,共用两次,每次间隔2周。
我们国内应用的治疗经验表明,小剂量的应用利妥昔单抗对预防视神经脊髓炎复发仍有效果,并且这样副作用较少。
目前我们国内常用的方法主要有两种:一种是单次500mg静脉点滴,6-12个月后重复应用;另一种是100mg静脉点滴,每周一次,连用4周,6-12个月后重复应用。
当然,由于利妥昔单抗为超适应症用药,目前没有明确的使用剂量说明,临床医生会根据患者的病情,与患者共同协商制定诊疗方案。
由于利妥昔单抗属于B细胞耗竭治疗,临床中需要监测B细胞水平,因此患友们一定要做好定期随访,跟医生一起成为疾病的管理者。
一般来说,服用了利妥昔单抗以后,大概要2-6周的时间才会起效,所以服用的朋友不要心急。
使用利妥昔单抗的注意事项最后,使用利妥昔单抗需要注意些什么呢?主要有5点:1、利妥昔单抗在静脉滴注的过程中可能发生输液反应,主要变现为寒战、高热,一般是发生在输注2小时内,其他症状可能还有瘙痒、荨麻疹、皮疹、头痛、支气管痉挛等,一般这些不良反应随着慢慢滴注会减轻,所以不用担心。
Published on USP Medicines Compendium (https:// )RituximabFinal Authorized Version 1.0RITUXIMAB HEAVY CHAINQVQLQQPGAE LVKPGASVKM SCKASGYTFT SYNMHWVKQT PGRGLEWIGA IYPGNGDTSY NQKFKGKATL TADKSSSTAY MQLSSLTSED SAVYYCARST YYGGDWYFNV WGAGTTVTVS AASTKGPSVF PLAPSSKSTS GGTAALGCLV KDYFPEPVTV SWNSGALTSG VHTFPAVLQSSGLYSLSSVV TVPSSSLGTQ TYICNVNHKP SNTKVDKKAE PKSCDKTHTC PPCPAPELLG GPSVFLFPPK PKDTLMISRT PEVTCVVVDV SHEDPEVKFN WYVDGVEVHN AKTKPREEQY NSTYRVVSVL TVLHQDWLNG KEYKCKVSNK ALPAPIEKTI SKAKGQPREP QVYTLPPSRD ELTKNQVSLT CLVKGFYPSD IAVEWESNGQ PENNYKTTPP VLDSDGSFFL YSKLTVDKSR WQQGNVFSCS VMHEALHNHY TQKSLSLSPG KRITUXIMAB LIGHT CHAINQIVLSQSPAI LSASPGEKVT MTCRASSSVS YIHWFQQKPG SSPKPWIYAT SNLASGVPVR FSGSGSGTSY SLTISRVEAE DAATYYCQQW TSNPPTFGGG TKLEIKRTVA APSVFIFPPS DEQLKSGTAS VVCLLNNFYP REAKVQWKVD NALQSGNSQE SVTEQDSKDS TYSLSSTLTL SKADYEKHKV YACEVTHQGL SSPVTKSFNR GECC 6416H 9874N 1688O 1987S 44 Molecular weight, approx. 144,187 DaImmunoglobulin G 1 (human-mouse monoclonal IDEC-C2B8 γ1-chain anti-human antigen CD 20), disulfide with human-mouse monoclonal IDEC-C2B8 κ-chain, dimer;Immunoglobulin G 1 (human-mouse monoclonal IDEC-C2B8 γ1-chain anti-human antigen CD 20), disulfide with human-mouse monoclonal IDEC-C2B8 κ-chain, dimer [174722-31-7].Rituximab is a genetically engineered chimeric murine/human monoclonal antibody directed against the CD20 antigen found on the surface of normal and malignant B lymphocytes. This IgG1 kappa antibody contains murine light and heavy chain variable regions, and human gamma 1 heavy chain and kappa light chain constant regions. Rituximab is composed of two heavy chains each having 451amino acids and two light chains each having 213 amino acids.Rituximab is a clear colorless liquid.Performance-Based Monograph(Contains tests, procedures, and acceptance criteria for the material under test. It also includes the criteria-based procedures to demonstrate that an Acceptable Procedure is equivalent to the Reference Procedures .)DEFINITIONRituximab contains recombinant chimeric murine/human monoclonal antibody directed against the CD20 antigen in a sterile solution having measured potency of NLT 80.0% and NMT 125.0% of the stated potency.IDENTIFICATION • A. B IOASSAYStandard solution: USP Rituximab RS in an appropriate diluentSample solution: Rituximab diluted in an appropriate diluent similar to that of the Standard solution .System performance requirements and Analysis: Proceed as directed in the Assay for Potency .Acceptance criteriaMeasured potency: 80.0%–125.0% of the stated potency • B. P EPTIDE M APPINGUse a chromatographic system. (Proceed as directed in Biotechnology Derived Articles—Peptide Mapping <1055>.)Analyze the material to be tested by a chromatographic technique capable of resolving peptides generated from a Trypsin digest. The digest is carried out under reducing conditions which provides NLT 80% digestion. The test procedure used provides a minimum of 90% coverage of the protein sequence.Standard solution: Digest and dilute a portion of USP Rituximab RS in an appropriate diluent.Sample solution: Digest and dilute a quantity of Rituximab in an appropriate diluent to obtain a nominal concentration ofRituximab similar to that of the Standard solution.Control solution: Digest and dilute a portion of an appropriate control (non-Rituximab monoclonal antibody) in an appropriate diluent to obtain a nominal concentration of the control that is similar to that of Standard solution. [N OTE—The digests described in the Standard solution, Sample solution, and Control solution are conducted at the same time, using the same stock andconcentration of reagents.]Analytical system: Use a procedure validated as described in MC general chapter Assessing Validation Parameters for Reference and Acceptable Procedures <10>.System performance requirementsSpecificity: The profile obtained from the Standard solution, CDR regions should be identified using a suitable procedure. The peptide profile obtained from the Control solution is distinctly different from that obtained from the Standard solution.AnalysisSamples:Standard solution and Sample solutionThe peptide profiles obtained from the Standard solution are visually compared to the Sample solution.Acceptance criteria: The profile obtained from the Standard solution is similar to the profile obtained from the Sample solution.The retention times of the peaks from the Sample solution differ from retention times of the corresponding peaks in the Standard solution by NMT ± 0.2 min.• C. C APILLARY I SOELECTRIC F OCUSINGAnalyze Rituximab using a capillary isoelectrophoretic focusing procedure using a broad range ampholyte (isoelectric point range of 3.0–10.0).Standard solution: USP Rituximab RS in an appropriate diluentSample solution: Dilute a quantity of Rituximab in an appropriate diluent to obtain a nominal concentration similar to that of the Standard solution.Control solution: Dilute a quantity of a non-Rituximab protein (such as Trastuzumab) in an appropriate diluent to obtain a nominal concentration similar to that of the Standard solution.Analytical system: Use a validated procedure. (See Biotechnology-Derived Articles—Capillary Electrophoresis <1053>.)System performance requirementsSpecificity: The isoelectric point obtained from the Standard solution is between 9.1 and 9.5. The isoelectric point obtained from the Control solution should be different from the isoelectric point obtained from the Standard solution.AnalysisSamples:Standard solution and Sample solutionCompare the isoelectric point from the Sample solution and the Standard solution.Acceptance criteria: The isoelectric point (pI) of the main peak obtained from the Sample solution differs by NMT ± 0.2 pI units from the corresponding peak from the Standard solution.ASSAY• P OTENCY [C OMPLEMENT D EPENDENT C YTOTOXICITY (CDC) A SSAY]Determine the potency using a suitable CD20 positive cell line (similar to WIL2-S) in a CDC assay with a suitable read out. Perform a comparison of a dilution series of the Sample solution with a dilution series of the Standard solution.Standard solution: USP Rituximab RS in an appropriate diluentSample solution: Rituximab in an appropriate diluent to obtain a nominal concentration similar to that of the Standard solution Control solution: Dilute a quantity of an appropriate protein (such as non-specific monoclonal antibody) in an appropriate diluent to obtain a nominal concentration similar to that of the Standard solution.Analytical system: Use a validated procedure. (See Biotechnology-Derived Articles—Biological Assay Validation <1033>.)System performance requirementsSpecificity: The Standard solution provides a significant dose response and the Control solution shows no response.PrecisionRepeatability: NMT 10.0% RSDIntermediate precision: NMT 15.0% RSDLinearity: Plot the measured potency versus expected potency. The R2 is NLT 0.95. [N OTE—The slope should be NLT 0.80.] Accuracy: Spike recovery 85.0%–115.0%Range: Should be wider than 80.0% and above 125.0%.AnalysisSamples: Standard solution and Sample solutionThe potency of the Sample solution is calculated relative to the Standard solution using a suitable parallel line method.(Proceed as directed in Analysis of Biological Assays <1034>.)Calculate 95.0% confidence limits for each independent determination of the measured potency.Acceptance criteria95.0% Confidence limits for independent determination: 74.0%–136.0%Mean measured potency: 80.0%–125.0% of the stated potency obtained as a mean of a minimum of three independent determinations.95% Confidence limits of the mean measured potency: 85.0%–115.0%. [N OTE—Measure as many independent Sample solutions as necessary to achieve the 95.0% confidence limits.]• G LYCAN P ROFILINGUse a procedure that is capable of separating all glycans.Standard solution: USP Rituximab RS in an appropriate diluentSample solution: Rituximab in an appropriate diluentResolution solution: Use Standard solutionControl solution: Use a non-glycosylated protein in an appropriate diluent.Analytical system: Use a procedure validated as described in MC general chapter Assessing Validation Parameters for Reference and Acceptable Procedures <10>. (See Glycoprotein and Glycan Analysis—General Considerations <1084>.)System performance requirements[N OTE—Identify the peaks using commercial glycan standards of G0, G0F, G1, G1F, G1F', G2, and G2F, or any other suitable procedure.]SpecificityPeak profile: The profile obtained from the Resolution solution shows prominent peaks for G0, G0F, G1, G1F, G1F', G2, and G2F.Resolution: NLT 1.0 between G0–G0F and G2–G2F glycan peaks from the Resolution solution.Negative control: The Control solution shows no glycan peaks.[N OTE—The following criteria are with respect to the G0F peak in the Standard solution.]PrecisionRepeatability: NMT 4.0% RSDIntermediate precision: NMT 5.0% RSDAccuracy: Probability NLT 0.95 for 90.0%–110.0%Linearity: R2 NLT 0.99Range: 80.0%–120.0% of the Acceptance criteria set for oligosaccharides with galactoseAnalysisSamples: Standard solution and Sample solutionCalculate the percentage of oligosaccharides with galactose in the Sample solution.Acceptance criteriaSum of all oligosaccharides with galactose: NLT 35.0%• C ATION E XCHANGE C HROMATOGRAPHY(AFTER C ARBOXYPEPTIDASE T REATMENT)Use the normalization procedure. (See Chromatography <621>.)Standard solution: USP Rituximab RS in an appropriate diluentSample solution: Rituximab in an appropriate diluent to obtain a nominal concentration similar to that of the Standard solution. Resolution solution: USP Rituximab RS in an appropriate diluent without carboxypeptidase treatmentAnalytical system: Use a procedure validated as described in MC general chapter Assessing Validation Parameters for Reference and Acceptable Procedures <10>.System performance requirementsSpecificityPeak profile: The chromatogram obtained from the Resolution solution shows presence of lysine (K1) variant when compared to the Standard solution.Resolution: NLT 1.5 between the main peak (K0) and lysine variant peak (K1)[N OTE—The following criteria are with respect to the main peak (K0).]PrecisionRepeatability: NMT 2.0% RSDIntermediate precision: NMT 4.0% RSDAccuracy: Probability NLT 0.95 at 95.0%–105.0%Linearity: R2 NLT 0.99Range: 80.0%–120.0% of the Acceptance criteriaAnalysisSamples: Standard solution and Sample solutionCalculate the percentage of acidic and basic variants in the Sample solution.Acceptance criteriaAcidic variants: NMT 20.0%Basic variants: NMT 20.0%IMPURITIES• CE-SDS (UNDER R EDUCING C ONDITION)Analyze Rituximab using an electrophoretic method capable of giving separation in the range 10–250 kDa followed by UV detection by normalization procedure.Standard solution: USP Rituximab RS in an appropriate diluent.Sample solution: Rituximab in an appropriate diluent to obtain a nominal concentration similar to that of the Standard solution. Non-glycosylated heavy chain (NGHC) solution: Combine a portion of the Standard solution with PNGase enzyme under suitable conditions to achieve at least 95% deglycosylation.Resolution solution: 2.0% NGHC spiked in Standard solutionAnalytical system: Use a validated procedure carried out under reducing conditions. (See Biotechnology-Derived Articles—Capillary Electrophoresis <1053>.)Use a procedure validated as described in MC general chapter Assessing Validation Parameters for Reference and Acceptable Procedures <10>. (Although general chapter <10> is directed to chromatographic methods, concepts in the guideline are general.) System performance requirementsSpecificity: The electropherogram obtained from the Standard solution includes a peak corresponding to light chain and heavy chain.Resolution: NLT 1.5 between the NGHC and heavy chain peaks from the Resolution solution[N OTE—The following criteria are with respect to the NGHC peak in the Standard solution.]PrecisionRepeatability: NMT 2.0% RSDIntermediate precision: NMT 4.0% RSDAccuracy: Probability NLT 0.95 at 90.0%–110.0%Linearity: R2 NLT 0.99Range: 50.0%–200.0% of the Acceptance criteriaAnalysisSamples: Standard solution and Sample solutionCalculate the percentage of NGHC in the Sample solution.Acceptance criteriaNGHC impurity: NMT 2.0%• CE-SDS (UNDER N ON-R EDUCING C ONDITION)Analyze Rituximab using an electrophoretic method capable of giving separation in the range 10–250 kDa followed by UV detection by normalization procedure.Standard solution: USP Rituximab RS in an appropriate diluentSample solution: Rituximab in an appropriate diluent to obtain a nominal concentration similar to that of the Standard solution. NGHC solution: Combine a portion of the Standard solution with PNGase enzyme under suitable conditions to achieve at least 95% deglycosylation.Resolution solution: 2.0% NGHC spiked in S tandard solution under reducing conditionAnalytical system: Use a validated procedure carried out under non-reducing conditions. (See Biotechnology-Derived Articles—Capillary Electrophoresis <1053>.)Use a procedure validated as described in MC general chapter Assessing Validation Parameters for Reference and Acceptable Procedures <10>. (Although MC general chapter <10> is directed to chromatographic methods, concepts in the guideline are general.)System performance requirementsSpecificity: The Standard solution contains a principal peak corresponding to Rituximab.Resolution: NLT 1.5 between the NGHC and heavy chain peaks from the Resolution solution[N OTE—The following criteria is with respect to the light chain peak.]PrecisionRepeatability: NMT 2.0% RSDIntermediate precision: NMT 4.0% RSDAccuracy: Probability NLT 0.95 at 90.0%–110.0%Linearity: R2 NLT 0.99Range: 50.0%–200.0% of the Acceptance criteriaAnalysisSamples: Standard solution and Sample solutionCalculate the percentage of impurities in the Sample solution.Acceptance criteriaSum of low molecular weight impurities: NMT 8.0%• S IZE E XCLUSION C HROMATOGRAPHYUse the normalization procedure. (See Chromatography <621>.)Standard solution: USP Rituximab RS in an appropriate diluentSample solution: Rituximab in an appropriate diluent to obtain a nominal concentration similar to that of the Standard solution. Resolution solution: Dilute USP Rituximab RS in water to obtain a 1.0 mg/mL solution, incubate under UV light (at 254 nm) for 2 h. Analytical system: Use a procedure validated as described in MC general chapter Assessing Validation Parameters for Reference and Acceptable Procedures <10>.System performance requirementsSpecificityPeak profile: The chromatogram obtained from the Resolution solution shows a high molecular weight (HMW) peak eluting before the main peak.Resolution: NLT 1.5 between the HMW peak and the main peak from the Resolution solution[N OTE—The following criteria is with respect to the main peak.]PrecisionRepeatability: NMT 4.0% RSDIntermediate precision: NMT 4.0% RSDAccuracy: Probability NLT 0.95 for 90.0%–110.0%Linearity: R2 NLT 0.99Range: 50.0%–200.0% of the Acceptance criteriaAnalysisSamples: Standard solution and Sample solutionCalculate the percentage of HMW impurities in the Sample solution.Acceptance criteriaTotal impurities: NMT 2.0%• P ROCESS R ELATED I MPURITIESProtein A: NMT 10 ppmHost cell proteins: NMT 100 ppmHost cell DNA: NMT 10 ng/doseSPECIFIC TESTS• M ICROBIAL E NUMERATION T ESTS <61> and T ESTS FOR S PECIFIED M ICROORGANISMS <62>: Total aerobic count does not exceed 1 cfu/mL.• B ACTERIAL E NDOTOXINS T EST <85>: NMT 0.1 EU/mg of RituximabADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS• S TORAGE: Store at 2°–8° C in an airtight container.• L ABELING: The label states the name, content in mg/mL, and potency of the drug substance.• R EFERENCE S TANDARDS <11>USP Rituximab RSREFERENCE PROCEDURES(This section provides detailed descriptions of procedures that may be used for the evaluation of the material under test. These procedures have been fully validated, and the data is available on the MC website.)IDENTIFICATION• A. P EPTIDE M APPINGSolution A: 0.1% Trifluoroacetic acid in waterSolution B: 0.1% Trifluoroacetic acid in acetonitrileSolution C: 0.5 M dithiothreitol in waterSolution D: 0.5 M iodoacetamide in waterSolution E: 0.25 M tris buffer in water. Adjust with dilute hydrochloric acid to a pH of 7.5.Solution F: 6 M guanidine hydrochloride and 1 mM EDTA in Solution E (denaturing buffer)Solution G: 0.1 M tris buffer in water. Adjust with dilute hydrochloric acid to a pH of 7.8.Solution H: 2 M urea in Solution G (digest buffer)Solution I: 0.05 M acetic acid in waterSolution J: 1 mg/mL of trypsin in Solution ISolution K: 10 mg/mL of USP Rituximab RS in waterStandard stock solution 1: Mix 100 µL of Solution K, 400 µL of Solution F, and 10 µL of Solution C, and incubate at 37° for 30 min. Add 24 µL of Solution D and incubate at room temperature for an additional 30 min in dark. Add 10 µL of Solution C and mix well. Standard stock solution 2: Wash the PD-10 Sephadex G-25 column with 20 mL of water and equilibrate with 35–40 mL of Solution H. Load Standard stock solution 1 on the column, and elute using Solution H in volumes of 700 μL each. Collect 6 independent fractions. Measure the absorbance of each fraction at 280 nm against Solution H. The fraction having an absorbance between 1.3 and 2.0 is used for digestion. [N OTE—If the absorbance of the fraction is more than 2.0, dilute it using Solution H to get an absorbance of 2.0.]Standard solution: Mix well 50 μL of Standard stock solution 2 and 2 μL of Solution J and incubate for 18–20 h at room temperature. Add 1 μL of trifluoroacetic acid and store the mixture at 4°.Sample solution: Prepare Rituximab similar to that of the Standard solution. [N OTE—Prepare the Standard solution and the Sample solution at the same time, using the same stock of reagents and concentrations.]Mobile phase: See Table 1.Table 1Time (min)Solution A(%)Solution B(%)09825982120554512501001300100131982135982Chromatographic system(See Chromatography <621>.)Mode: UPLCDetector: UV 215 nmColumn: 2.1-mm × 10-cm; 130Å, 1.7-μm, packing L1 (similar to Waters BEH C18)Flow rate: 0.3 mL/minTemperaturesColumn oven: 60°Autosampler: 5°Injection volume: 10 μLSystem suitabilitySample: Standard solutionSuitability requirementsRelative retention time of peaks corresponding to CDR regionsHeavy chain CDR regions 1 and 2 should be seen at an RRT (with respect to reference peak around 89 min) of 0.61 and 0.71 respectively within ± 0.02 RRT.Light chain CDR regions 1, 2 (single peak), and 3 should be seen at an RRT (with respect to reference peak around 89 min) of0.81 and 0.58 respectively within ± 0.02 RRT.AnalysisSamples: Standard solution and Sample solutionThe peptide profiles obtained from the Sample solution are visually compared to those from the Standard solution.• B. C APILLARY I SOELECTRIC F OCUSING (CIEF)Solution A: 0.2 M phosphoric acid in water (anolyte)Solution B: 0.3 M sodium hydroxide in water (catholyte)Solution C: 0.35 M acetic acid in water (chemical mobilizer)Solution D: 0.2 M iminodiacetic acid in water (anodic stabilizer)Solution E: 0.5 M arginine in water (cathodic stabilizer)Solution F: 4.3 M urea in waterSolution G: 3.0 M urea in cIEF gelSolution H: 5 mg/mL of USP Rituximab RS in waterSystem suitability solution: Mix 200 µL of Solution G, 12 µL of Pharmalyte 3-10, 20 µL of Solution E, 2 µL of Solution D, and 2 µL of each of the pI markers (10.0, 9.5, 7.0, 5.5, and 4.1). Vortex the solution for 15 s and mix well. Transfer 200 µL to a micro vial for analysis.Standard solution: Mix well 10 µL of Solution H, 200 µL of Solution G, 12 µL of Pharmalyte 3-10, 20 µL of Solution E, 2 µL of Solution D, and 2 µL of each of the pI markers (10, 5.5, and 4.1). Vortex the solution for 15 s and mix well. Transfer 200 µL to a micro vial for analysis.Sample solution: Prepare Rituximab similar to that of the Standard solution. [N OTE—Prepare the Standard solution and the Sample solution at the same time, using the same stock reagents and concentrations.]Capillary electrophoresis systemMode: Capillary isoelectric focusingDetector: UV 280 nmCapillary: 30.2-cm × 50-μm (similar to Beckman coulter, Neutral coated)Effective length: 20 cmTemperaturesCapillary: 20 ± 2°Sample: 10 ± 2°Polarity: Anode at the inlet and cathode at the outletInjection time: 25 psi for 99.0 sFocusing voltage: 25.0 kV for 15.0 minChemical mobilization: 30.0 kV for 30.0 minSystem suitabilitySamples: System suitability solution and Standard solutionSuitability requirementsR2: NLT 0.99 from the System suitability solutionpI: Should be between 9.1–9.5 from the Standard solutionAnalysisSamples: System suitability solution, Standard solution, and Sample solutionPlot a curve using the migration time and pI of the markers spiked in the Sample solution. Calculate the pI of Rituximab main peak in the Sample solution.ASSAY• P OTENCYDetermination of the biological activity of Rituximab solution based on the cytotoxicity activity (similar to lysis of WIL2-S cells, ATCC No. CRL-8885) in presence of human serum complement using Resazurin sodium staining method.Medium A: Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640 (RPMI 1640) with 2 mM glutamine, 2 g/L of sodium bicarbonate, 4.5 g/L of glucose, 10 mM HEPES, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS)Medium B: RPMI 1640 with 2 mM glutamine, 2 g/L of sodium bicarbonate, 4.5 g/L of glucose, 10 mM HEPES, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, and 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA)Complement source: Pooled normal human serum. [N OTE—Fold dilution should be estimated by titrating each new lot with the old lot.]Cell line: WIL2-S, grow cells in Medium A. [N OTE—Cells can be directly thawed and used in the Assay without further sub-culturing.] Cell suspension: 0.7–0.8 ×106 WIL2-S cells/mL in Medium B. [N OTE—Maintain the cells in a uniform suspension during addition.] Standard solution 1: 10 µg/mL of USP Rituximab RS in Medium BStandard solution 2: 5.0 µg/mL of USP Rituximab RS from Standard solution 1, in Medium BStandard solution 3: 2.5 µg/mL of USP Rituximab RS from Standard solution 2, in Medium BStandard solution 4: 1.25 µg/mL of USP Rituximab RS from Standard solution 3, in Medium BStandard solution 5: 0.625 µg/mL of USP Rituximab RS from Standard solution 4, in Medium BStandard solution 6: 0.313 µg/mL of USP Rituximab RS from Standard solution 5, in Medium BStandard solution 7: 0.156 µg/mL of USP Rituximab RS from Standard solution 6, in Medium BStandard solution 8: 0.078 µg/mL of USP Rituximab RS from Standard solution 7, in Medium BSample solution 1: 10 µg/mL of Rituximab in Medium BSample solution 2: 5.0 µg/mL of Rituximab from Sample solution 1, in Medium BSample solution 3: 2.5 µg/mL of Rituximab from Sample solution 2, in Medium BSample solution 4:1.25 µg/mL of Rituximab from Sample solution 3, in Medium BSample solution 5: 0.625 µg/mL of Rituximab from Sample solution 4, in Medium BSample solution 6: 0.313 µg/mL of Rituximab from Sample solution 5, in Medium BSample solution 7: 0.156 µg/mL of Rituximab from Sample solution 6, in Medium BSample solution 8: 0.078 µg/mL of Rituximab from Sample solution 7, in Medium BAnalysisTo a suitable 96 well microtitre plate, transfer 50 µL each of Standard solutions1–8 and Sample solutions 1–8 to designated wells for the standard and sample controls (see Design and Development of Biological Assays <1032>). Transfer 150 µL of Medium B to the wells designated as medium control. Transfer 100 µL of Medium B to the wells designated as cell control. Transfer 50 µL of Medium B to the wells designated as complement control. Add 50 µL of Cell suspension to each standard, sample, cell, and complement control wells. Add 50 µL of 5 fold diluted pooled normal human serum to all wells except medium control and cell control. Mix and incubate the plate at 37 ± 1° for a period of 2 h in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. Remove the plate from the incubator and add 20 µL of pre-warmed Resazurin (Sodium) to each well. Gently agitate the plate and incubate for an additional 20± 4 h. Remove the plates from the incubator and allow them to cool to room temperature by placing on a plate shaker for 10–15 min. Determine the potency by measuring the fluorescence (relative fluorescence units, RFU) using a suitable 96 well plate reader using an excitation wavelength of 530 nm and emission wavelength of 590 nm. Generate dose response curves for Standard solutions and Sample solutions using the final concentrations of Rituximab before the addition of alamar blue, i.e., concentrations before the addition of alarm blue. Calculate the relative potency, 95% confidence limits for each sample relative to the standard.(See Analysis of Biological Assays <1034>.)System suitabilityThe ratio between the RFU of highest concentration of the Standard solutions and RFU of the cell control should be ≥ 3.5.The ratio between the RFU of highest and lowest concentrations in the linear range of the Standard solutions should be ≥ 3.0. [N OTE —Medium control and complement control are included for Assay monitoring purpose only and have no acceptance criteria.]• G LYCAN P ROFILING—N ORMAL P HASE C HROMATOGRAPHYSolution A: 0.05 M ammonium formate solution in water. Adjust with dilute ammonia solution to a pH of 4.4.Solution B: AcetonitrileSolution C: 10X Glycoprotein denaturing buffer (5% SDS and 0.4 M dithiothretol), Make: New England BiolabsSolution D: 10X G7 reaction buffer (0.5 M sodium phosphate at pH 7.5), Make: New England BiolabsSolution E: 10% NP40, Make: New England BiolabsSolution F (2 AB glycan labeling reagent): Transfer 150 µL of glacial acetic acid to the vial of DMSO and mix well. Transfer 100 µL of DMSO-acetic acid mixture to a vial of tag 2-AB dye (Make: Ludger) and mix gently until dye is dissolved. Add dissolved dye to a vial of sodium cyanoborohydride (Make: Ludger) and mix gently until the solution is completely dissolved. To aid in proper dissolution, heat the final mixture at 65° for 30 s. [N OTE—Use within 60 min.]Solution G: 30% Acetic acid in waterSolution H: 96% Acetonitrile in waterSolution I: 80% Acetonitrile in waterSolution J: 3 mg/mL of USP Rituximab RS in waterSolution K: 500,000 units/mL of PNGase enzyme, Make: New England BiolabsStandard solution: Mix 6.7 µL of Solution J, 1 µL of Solution C, and make up to 10 µL with water. Denature the solution for 10 min at 96 ± 2°. Add 2 µL of Solution D, 2 µL of Solution E, and 2 µL of Solution K to the denatured solution, and make up the final volume to 20 µL with water. Gently mix the solution and incubate for 1 h at 37 ± 2°. Vacuum dry the solution, add 5 µL of Solution F, and mix well.Incubate the solution for 2.5 h at 65 ± 2°. Wash the clean S cartridge (Make: Ludger) with 1 mL of water, 5 mL of Solution G, and 1 mL of Solution B, sequentially. Load the sample onto clean S cartridge. [N OTE—Ensure the disc is in wet condition with Solution B before loading.] Allow the sample to adsorb onto membrane for 15 min. Wash the disc with 1 mL of Solution B followed by 1 mL of Solution H five times. Elute the glycans with three individual aliquots of 0.5 mL of water in individual micro centrifuge tubes. Vacuum dry the eluted glycans. Reconstitute the aliquots in a total volume of 200 µL with Solution I.Sample solution: Prepare Rituximab similar to that of the Standard solution. [N OTE—Prepare the Standard solution and the Sample solution at the same time, using the same reagents and concentrations.]Mobile phase: See Table 2.Table 2Time (min)Flow rate(mL/min)Solution A(%)Solution B(%)。
利妥昔单抗说明书【商品名称】美罗华【拼音名】Lituoxidankang Zhusheye【英文名】Rituximab Injection【成份】主要组成成份:本品主要活性成分为重组利妥昔单抗,组成成分还包括枸橼酸钠,聚山梨醇酯80,氯化钠和注射用水。
【性状】为无色或淡黄色澄明液体,无异物、絮状物及沉淀。
【适应症】本品适用于:复发或耐药的滤泡性中央型淋巴瘤(国际工作分类B、C和D亚型的B细胞非霍奇金淋巴瘤)的治疗。
CD20阳性弥漫大B细胞性非霍奇金淋巴瘤(DLBCL)应与标准CHOP化疗(环磷酰胺、阿霉素、长春新碱、强的松)8个周期联合治疗。
【用法用量】在无菌条件下抽取所需剂量的利妥昔单抗,置于无菌无致热源的含0.9%生理盐水或5%葡萄糖溶液的输液袋中,稀释到利妥昔单抗的浓度为1mg/ml。
轻柔的颠倒注射袋使溶液混合并避免产生泡沫。
由于本品不含抗微生物的防腐剂或抑菌制剂,必须检查无菌技术。
静脉使用前应观察注射液有无微粒或变色。
利妥昔单抗稀释后通过一种专用输液管静脉滴注,适用于不卧床患者的治疗。
利妥昔单抗的治疗应在具有完备复苏设备的病区内进行,并在有经验的肿瘤医师或血液科医师的直接监督下进行。
对出现呼吸系统症状或低血压的患者至少监护24小时。
每次滴注利妥昔单抗前应预先使用止痛剂(例如扑热息痛)和抗组胺药(例如苯海拉明)(开始滴注前30到60分钟)。
如果所使用的治疗方案不包括皮质激素,那么还应该预先使用皮质激素。
每名患者均应被严密监护,监测是否发生细胞因子释放综合征。
对出现严重反应的患者,特别是有严重呼吸困难,支气管痉挛和低氧血症的患者应立即停止滴注。
还应该评估患者是否出现肿瘤溶解综合征,例如可以进行适当的实验室检查。
预先存在肺功能不全或肿瘤肺浸润的患者必须进行胸部X线检查。
所有的症状消失和实验室检查恢复正常后才能继续滴注,此时滴注速度不能超过原滴注速度的一半。
如再次发生相同的严重不良反应,应考虑停药。
利妥昔单抗绝不能未稀释就静脉滴注,制备好的注射液也不能用于静脉推注。
滤泡性非霍奇金淋巴瘤,成年患者利妥昔单抗单药治疗的推荐剂量为375mg/㎡体表面积,每周静脉滴注1次,在22天内使用4次。
弥漫大B细胞性非霍奇金淋巴瘤,利妥昔单抗应与CHOP化疗联合使用。
推荐剂量为375mg/㎡体表面积,每个化疗周期的第一天使用。
化疗的其它组分应在利妥昔单抗应用后使用。
初次滴注,推荐起始滴注速度为50mg/h;最初60分钟过后,可每30分钟增加50mg/h,直至最大速度400mg/h。
以后的滴注,利妥昔单抗滴注的开始速度可为100mg/h,每30分钟增加100mg/h,直至最大速度400mg/h。
治疗期间的剂量调整.不推荐利妥昔单抗减量使用。
利妥昔单抗与标准化疗合用时,标准化疗药剂量可以减少。
【不良反应】1、全身症状:腹痛、背痛、胸痛、颈痛、不适、腹胀、输液部位疼痛。
2、心血管系统:高血压、心动过缓、心动过速、体位性低血压、心律失常。
3、消化系统:腹泻、消化不良、厌食症。
4、血液和淋巴系统:淋巴结病。
5、代谢和营养疾病:高血糖、外周水肿、LDH增高、低血钙。
6、骨骼肌肉系统:关节痛、肌痛、疼痛、肌张力增高。
7、神经系统:头昏、焦虑、感觉异常、感觉过敏、易激惹、失眠、神经质。
8、呼吸系统:咳嗽增加、鼻窦炎、支气管炎、呼吸道疾病、阻塞性细支气管炎。
9、皮肤和附属物:盗汗、出汗、单纯疱疹、带状疱疹。
10、感觉器官:泪液分泌疾病、结膜炎、味觉障碍。
【禁忌】已知对本药的任何组份和鼠蛋白过敏的患者禁用利妥昔单抗。
【注意事项】1、循环中有大量恶性肿瘤细胞(>25,000/ml)或高肿瘤负荷(病灶>10cm)者,发生严重的细胞因子释放综合征或肿瘤溶解综合征的风险较高,使用利妥昔单抗应极其慎重,可给予其他治疗选择。
应该考虑降低肿瘤负荷的预备治疗。
这类患者在第1次滴注利妥昔单抗时应考虑减慢滴注速度。
肺功能不全或高肿瘤负荷者出现严重的细胞因子释放综合征或肿瘤溶解综合征的风险增加。
这些反应在临床上可能与超敏反应无法区别。
严重的细胞因子释放综合征以严重的呼吸困难(常伴支气管痉挛和低氧血症),发热(可能出现高热惊厥),寒战,荨麻疹和血管性水肿为特征。
还可伴随出现一些肿瘤溶解综合征的特征,例如高尿酸血症,高钾血症,低钙血症,LDH升高,急性肾功能衰竭以及危及生命的呼吸衰竭。
2、急性呼吸衰竭可伴有胸部X线可见的肺间质浸润和水肿。
出现严重细胞因子释放综合症的患者应立即停止滴注,并给予积极的对症治疗。
少数患者在临床症状开始好转后再次出现恶化,所以应严密监护这些患者,直至症状和体征完全消失。
在症状和体征完全消退后对患者继续进行治疗,很少导致严重的输液相关反应。
预先存在肺功能不全或肿瘤肺浸润的患者用利妥昔单抗治疗必须极其谨慎,尤其是万一出现上述严重症状和体征时。
静脉滴注蛋白可导致患者发生过敏样反应或其它超敏反应。
与细胞因子释放综合征不同,典型的超敏反应常于开始滴注的几分钟内发生。
过敏反应临床上可与细胞因子释放综合征表现相似。
在滴注利妥昔单抗的过程中发生过敏反应,应立即使用抗变态反应的药物,如肾上腺素,抗组胺药和皮质激素。
约50%接受利妥昔单抗治疗的患者会出现输液相关不良反应。
这些反应通常是轻微的,类似流感,但大约10%的患者较严重,出现低血压、呼吸困难和支气管痉挛。
这些症状是可逆的,通常在停止静滴利妥昔单抗,并给予退热药和抗组胺药后好转。
偶尔需要吸氧,静滴生理盐水,甚至可能给予支气管扩张药和皮质激素。
由于滴注利妥昔单抗期间可能出现一过性低血压,所以滴注利妥昔单抗前12小时以及滴注期间应该考虑停用抗高血压药。
3、有心脏病史的患者(例如心绞痛、房扑和心房纤颤等心律失常或心衰)在利妥昔单抗滴注过程中应严密监护。
虽然利妥昔单抗单药治疗不会导致骨髓抑制,但在中性粒细胞计数<1.5×10E9/l和/或血小板计数<75×10E9/l的患者接受治疗时,仍应谨慎,因为在这类患者中使用利妥昔单抗的临床经验有限。
利妥昔单抗曾应用于21例接受过自体骨髓移植及骨髓功能可能减低的其他风险组患者,并没有引起骨髓抑制。
与其他肿瘤治疗一样,利妥昔单抗单药治疗过程中应定期监测全血细胞计数,包括血小板计数。
当利妥昔单抗与CHOP化疗联合使用时,根据通常的医疗实践应定期检查全血细胞计数。
在单独利妥昔单抗治疗的患者中已有严重的皮肤粘膜反应的报道,有些甚至导致致命后果。
这些反应出现在开始治疗后1和13周之间。
出现这种情况的患者应停止滴注利妥昔单抗,并且必须立即接受医疗检查。
皮肤活检有利于区别不同的皮肤反应并决定随后的治疗。
报道的皮肤粘膜反应包括副肿瘤性天疱疮和中毒性表皮融解坏死。
在这些病例中再次使用利妥昔单抗治疗的安全性尚不清楚。
4、特别说明:对疫苗和基于抗原抗体反应的诊断性试验的可能反应尚未研究。
不相容性:未观察到利妥昔单抗与聚氯乙烯或聚乙烯袋或输液器之间的不相容性。
对驾驶和操作机器能力的影响:未知利妥昔单抗是否损害驾驶和操作机器的能力,尽管药理学特性和迄今为止报告的不良反应中没有显示上述的不良影响。
【进口药品】是【孕妇及哺乳期妇女用药】妊娠:利妥昔单抗尚未进行动物生殖毒性研究。
也不知妊娠妇女使用利妥昔单抗是否引起胎儿损害或利妥昔单抗是否影响生育能力。
但已知免疫球蛋白IgG可通过胎盘屏障,所以除非可能给患者带来的益处大于潜在的危险,利妥昔单抗不应用于妊娠妇女。
育龄妇女在使用利妥昔单抗的过程中及治疗后的12个月,应采取有效的避孕措施。
哺乳:尚不清楚利妥昔单抗是否分泌入乳汁。
已知母体的IgG可进入乳汁,那么利妥昔单抗就不能用于哺乳的母亲。
【儿童用药】利妥昔单抗应用于儿童的有效性和安全性尚未确定。
【老年用药】国外和国内临床研究中均纳入了老年患者,结果提示本品可用于老年患者,无特殊禁忌。
【药物相互作用】目前,尚无关于利妥昔单抗的可能药物相互作用的资料。
特别是利妥昔单抗与化疗(例如CHOP)合用的相互作用尚未研究。
人抗鼠抗体(HAMA)或人抗嵌合抗体(HACA)滴定阳性的患者,在接受其他诊断性或治疗性单克隆抗体时可发生过敏反应。
同时或序贯使用利妥昔单抗和其他倾向于引起正常B细胞耗竭的药物的耐受性尚未得到足够的研究。
[查看]【药代动力学】对滤泡性非霍奇金淋巴瘤的患者,以125、250或375mg/㎡体表面积的利妥昔单抗治疗,每周静脉滴注一次,共4次,血清抗体浓度随着剂量的增加而增加。
对于接受375mg/㎡剂量的患者,第一次滴注后利妥昔单抗的平均血清半衰期是68.1小时,Cmax是238.7μg/ml,而平均血浆清除率是0.0459L/小时;第四次滴注后的血清半衰期、Cmax和血浆清除率的平均值分别为189.9小时、480.7μg/ml和0.0145L/小时,但血清水平的变异性较大。
其次,反应患者的利妥昔单抗血清浓度明显较高。
一般来说,3~6个月时利妥昔单抗仍能在血清中被检出。
在弥漫大B细胞性非霍奇金淋巴瘤患者中,利妥昔单抗与CHOP合用时的清除和分布尚未进行研究。
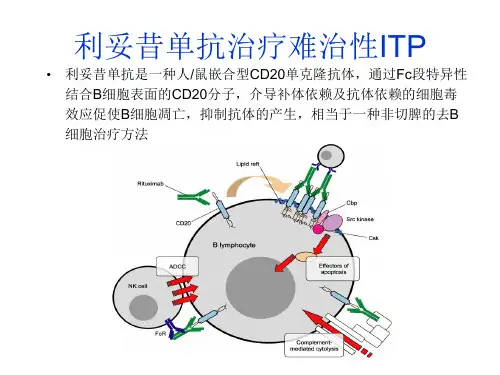
[隐藏]【药理毒理】利妥昔单抗是一种人鼠嵌合性单克隆抗体,能特异性地与跨膜抗原CD20结合。
CD20抗原位于前B和成熟B淋巴细胞的表面,而造血干细胞、前前B细胞、正常浆细胞或其它正常组织不表达CD20。
95%以上的B细胞性非霍奇金淋巴瘤瘤细胞表达CD20。
抗原抗体结合后,CD20不会发生内在化,或从细胞膜上脱落进入周围的环境。
CD20不以游离抗原的形式在血浆中循环,因此不可能与抗体竞争性结合。
利妥昔单抗与B细胞上的CD20抗原结合后,启动介导B细胞溶解的免疫反应。
B细胞溶解的可能机制包括:补体依赖的细胞毒作用(CDC),抗体依赖细胞的细胞毒作用(ADCC)。
第一次输注利妥昔单抗后,外周B淋巴细胞计数明显下降,低于正常水平,6个月后开始恢复,治疗完成后9~12个月之间恢复正常。
体外实验显示,利妥昔单抗可以使耐药的人B淋巴瘤细胞株对某些化疗药物细胞毒作用的敏感性增强。
[隐藏]【贮藏】瓶装制剂保存在2~8℃。
【包装】152支/箱【产地】瑞士。