高分子复合材料的英语介绍
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:2.70 MB
- 文档页数:89

复合材料英语复合材料专业术语高性能的长纤维增强热塑性复合材料:(LF(R)T)Long Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastics 玻璃纤维毡增强热塑性复合材料:(GMT)Glass Mat Reinforced Thermoplastics短玻纤热塑性颗粒材料:(LFT-G)Long-Fiber Reinforce Thermoplastic Granules长纤维增强热塑性复合材料:(LFT-D)Long-Fiber Reinforce Thermoplastic Direct玻纤:Glass Fiber 玄武岩纤维:Basalt Fibre (BF)碳纤维:CFRP 芳纶纤维:AFRP ( Aramid Fiber)添加剂:Additive 树脂传递模塑成型:(RTM)Resin Transfer Molding热压罐:autoclave 热压罐成型:autoclave moulding热塑性复合材料缠绕成型:filament winding of thermoplastic composite热塑性复合材料滚压成型:roll forming of thermoplastic composite热塑性复合材料拉挤成型:pultrusion of thermoplastic composite热塑性复合材料热压罐/真空成型:thermoforming of thermoplastic composite热塑性复合材料液压成型:hydroforming of thermoplastic composite热塑性复合材料隔膜成型:diaphragm forming of thermoplastic composite离心浇注成型:centrifugal casting moulding泡沫贮树脂成型:foam reserve resin moulding环氧树脂基复合材料:epoxy resin matrix composite聚氨酯树脂基复合材料:polyurethane resin matrix composite热塑性树脂基复合材料:thermoplastic resin matrix composite玻璃纤维增强树脂基复合材料:glass fiber reinforced resin matrix composite 碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料:carbon fiber reinforced resin matrix composite 芳纶增强树脂基复合材料:aramid fiber reinforced resin matrix composite混杂纤维增强树脂基复合材料:hybrid fiber reinforced resin matrix composite 树脂基复合材料层压板:resin matrix composite laminate树脂基纤维层压板:resin matrix fiber laminate树脂基纸层压板:resin matrix paper laminate树脂基布层压板:resin matrix cloth laminate树脂基木质层压板:resin matrix wood laminate纤维增强金属层压板:fiber reinforced metallaminate吸胶材料:bleeding materials;bleeder 脱模布:release cloth喷射成型:spray-up moulding 纤维缠绕成型:filament winding压机模压成型:press moulding 拉挤成型:pultrusion process预压时间:dwelling time 预吸胶:debulking 固化:curing加压时机:pressure applying opportunity 固化周期:curing cycle固化温度:curing temperature 脱模剂:mold release agent一、玻璃纤维:GFRP空心纤维:hollow fiber 非织造物:nonwovens, nonwoven fabric毡:mat 连续原丝毡:continuous strand mat, continuous filament mat短切原丝毡:chopped strand mat 干切原丝:dry chopped strands湿切原丝:wet chopped strands 复合毡:combination mat薄毡:veil,tissue 织物:fabric机织物:woven fabric 电子布:electronic fabric, PCB cloth无捻粗纱布/方格布:roving cloth, woven rovings 机织带:woven tape编织物:braided fabric 单向布:unidirectional fabric, UD网布:mesh fabric, scrim 非织造网布:nonwoven scrim, laid scrim陶瓷加工:ceramic processing 表格:tabulation 氧化铝陶瓷管:alumina tube 有机物:organics 化学品安全说明书:material safety data sheets (MSDS)天然橡胶:nature rubber 碳黑:carbon black 颗粒:particle中大颗粒增强复合材料:large-particle reinforced composites弥散强化复合材料:dispersion-strengthened composites原子或分子水平:atomic or molecular level增强机理:mechanism of reinforcement 直径:diameter晶须:whiskers 单晶:single crystals 硼:boron多晶或非晶体材料:polycrystalline or amorphous material片状结构:laminar composites 夹层结构:sandwich panels低密度:less-dense 硬度:stiffness 强度:strength 延展性:ductility冲击强度:impact resistance 断裂韧性:fracture toughness拉伸:tension 压缩:compression 脆性材料:brittle material延性材料:ductile material 弹性材料:elastic material拉伸试验:tensile test 树脂:resin 增强体:reinforcement耐磨性:abrasion resistance陶瓷加工:ceramic processing 表格:tabulation 氧化铝陶瓷管:alumina tube 有机物:organics 化学品安全说明书:material safety data sheets (MSDS)天然橡胶:nature rubber 碳黑:carbon black 颗粒:particle中大颗粒增强复合材料:large-particle reinforced composites弥散强化复合材料:dispersion-strengthened composites原子或分子水平:atomic or molecular level增强机理:mechanism of reinforcement 直径:diameter晶须:whiskers 单晶:single crystals 硼:boron多晶或非晶体材料:polycrystalline or amorphous material片状结构:laminar composites 夹层结构:sandwich panels低密度:less-dense 硬度:stiffness 强度:strength 延展性:ductility冲击强度:impact resistance 断裂韧性:fracture toughness拉伸:tension 压缩:compression 脆性材料:brittle material延性材料:ductile material 弹性材料:elastic material拉伸试验:tensile test 树脂:resin 增强体:reinforcement耐磨性:abrasion resistanceAcetyl||乙酰Acid-proof paint||耐酸涂料, 耐酸油漆Acrylic fiber||丙烯酸纤维Acrylic resin||丙烯酸树脂Active filler||活性填料Adapter assembly||接头组件Addition polyimide||加成型聚酰亚胺Addition polymer||加聚物Adjusting valve||调整阀,调节阀Adhersion assembly||粘合装配Adhersion bond||胶结Adjustable-bed press||工作台可调式压力机Adjuster shim||调整垫片Adjusting accuracy||调整精度,调校精度Admissible error||容许误差Admissible load||容许载荷Adsorbed layer||吸附层Advanced composite material||先进复合材料,高级复合材料Advanced development vehicle||试制车,预研样车AE(Automobile Engineering)||汽车工程技术Aeolotropic material||各向异性材料Aerated plastics||泡沫塑料, 多孔塑料Aerodynamic body||流线型车身Aft cross member||底盘/车架后横梁Air bleeder||排气孔Air clamp||气动夹具Air deflector||导流板;导风板,气流偏转板Air intake manifold||进气歧管Air servo||伺服气泵Air-tight joint||气密接头All-plastic molded||全塑模注的All polyster seat||全聚酯座椅Alligatoring||龟裂,涂膜皱皮,表面裂痕Amino resin||氨基树脂Angular test||挠曲试验Anti-chipping primer||抗破裂底漆(底层涂料)Apron||防护挡板Aramid fibre composites||芳胺纤维复合材料Assembly drawing||装配图Assembly jig||装配夹具Assembly part||装配件,组合件Autoclave forming||热压罐成型Autocorrection||自动校正Automatic compensation||自动补偿Automatic feed||自动进料Automobile instrument||汽车仪表板Automotive transmission||汽车传动装置,汽车变速器Auxiliary fasia console||副仪表板Axial strain||轴向应变Axle bushing||轴衬Axle fairing||底盘车桥整流罩A Stage||A 阶段(某些热固性树脂聚合作用的初期阶段)AAC(Auxiliary Air Control)||辅助空气控制ABC(Active Body Control)||主动式车身控制装置Abherent||阻粘剂Ability meter||测力计,性能测试仪ABL (Ablative)||烧蚀剂Ablation||烧蚀Ablative composite material||烧蚀复合材料Ablative insulative material||烧蚀绝热材料Ablative polymer||烧蚀聚合物Ablative prepreg||烧蚀性预浸料Ablative resistance||耐烧蚀性ABR(Acrylate Butadience Rubber)||丙烯酸丁二烯橡胶Abradant material||研磨材料,磨料Abrade||研磨;用喷砂清理Abrasion||磨耗Abrasion coefficient||磨耗系数Abrasion loss||磨耗量,磨损量Abrasion performance||磨耗性Abrasion-proof material||耐磨材料Abrasion resistant paint||耐磨涂料Abrasion test||磨损试验Abrasive blast system||喷砂清理系统Abrasive cloth||砂布Abrasive disc||砂轮盘,砂轮片Abrasive finishing||抛光Abrasive paper||砂纸Abrasive resistance||耐磨性ABS(Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)resin||ABS 树脂,丙烯腈-丁二烯-苯乙烯(热塑性)树脂ABSM(American Bureau of Standard Materials)||美国标准材料局Absolute dynamic modulus||绝对动态模量Absolute error||绝对误差Absorbent material||吸收性材料,吸收性物质,吸声材料,吸收剂Absorber||减振器,阻尼器,缓冲器ACA(Automotive Composite Alliance)||汽车复合材料协会ACC(Automatic Clutch Control)||自动离合器操纵控制Accelerant||促进剂,加速剂Accelerated aging test||加速老化试验,人工老化试验Accelerator pedal shaft||加速踏板轴Accelerator pump nozzle||加速泵喷嘴Acceptable life||有效使用寿命Acceptance test specification||验收测试规范Access panel||罩板,盖板Accessory||配件,附属品Accessory equipment||辅助设备Accessory kit||附件包,成套附件Accumulator can||储电池外壳Accumulator package||蓄压器组件,蓄压器单元Accuracy in calibration||校准精度Accuracy of finish||最终加工精度Accuracy of manufacture||制造精度Accuracy of positioning||定位精度Accuracy of repetition||重现精度,复制精度Acetal matrix composites||缩醛树脂基复合材料Acetal plastic||缩醛塑料,聚甲醛塑料Acetal resin||缩醛树脂Acetamide||乙酰胺Acetate fiber||醋酸纤维,乙酸纤维Acetone||丙酮Back corner panel||后围角板Back panel||后围板Back side panel||后侧板Back wall pillar||后围立柱Backer||衬料Baffler||挡板,阻尼器;导流叶片Bag Molding||气囊施压成型(袋模法)Baggage holder||行李架Barrier coat||阻挡层;防渗涂层Batch mixing||分批混合,批混Batching unit||分批加料装置Bearing assembly||轴承组合件Biaxial winding||双角缠绕, 双轴缠绕Binder fiber||粘合纤维Bipolymer||二元共聚物Bismaleimide composites||双马来酰亚胺复合材料Blank placement||坯料的放置Blanket||玻璃纤维毡;坯料Blanking press||冲压机, 冲割压力机Blending resin||掺合树脂BMC(Bulk Moulding Compound)||团状膜塑料BMI (Bismaleimide)||双马来酰亚胺Body back panel||车身后板Body back wall||车身驾驶室后围Body bracket||车身支架Body control module||车身控制模块Body frame (Body skeleton)||车身骨架Body front panel||车身驾驶室前围板Body monocoque||单壳体车身,单壳式结构车身Body outer panel||驾驶室覆盖件;驾驶室覆盖件Body structural member||车身结构件Body trim||车身装饰件Bonded riveted structure||胶铆结构Bonnet||发动机罩Brake||制动器Brake arrangement||制动装置Brinell hardness test||布氏硬度试验Brittle coating||脆性涂层Bulk coat||整体涂层Bulk heat treatment||整体热处理Bulk moulding compound||(增强塑料)预制整体模塑料Bumper bracket(holder)||保险杠托架Bus brake system||客车制动系Butt flange||对接法兰Butt joint||对接接头;对接Butterfly valve||节流阀,节气门BWI (Body In White)||白车身Cab deflector shield||驾驶室导流板Cab fairing||驾驶室整流罩Cab floor||驾驶室地板Cab mounting||驾驶室悬置CAD(Computer Aided Design)||计算机辅助设计CAE (Computer Aided Engineering)||计算机辅助工程设计Calibration tolerance||校准公差Calibrating instrument||校准仪表Camouflage paint||覆面漆, 盖面涂料, 伪假漆Cantilever beam impact test||悬臂梁冲击试验Carbon-felt reinforced carbon composites||碳毡增强碳复合材料Carbon fiber clutch||碳纤维离合器Carbon filament cloth||碳丝织物Case extension||外壳的伸出部分,延伸外壳Casing gasket||外壳密封垫Catalyst manifold||固化剂总成Catalyst pump||固化剂泵Catalyst ratio||固化剂比率Cavity||模槽,型腔;凹模Cavity block||阴模Cavity depth||模槽深度Cellular board||蜂窝状板,多孔板Cellular plastics||泡沫塑料,多孔塑料Centre boss||轮毂Centre pin||销轴,枢轴,主销Centrifugal casting moulding||离心浇铸成型Centrosymmetry||中心对称层板Ceramic matrix composites||陶瓷基复合材料Charge||填充气体,填充料Chasis||底盘;机壳,车架Chlorinated polyethlene||聚氯乙烯Chopped fiber||短切纤维Chopped random mat||短切无序毡Chopped strand||短切原丝CIRTM(Co-Injection RTM)||共注射RTM Clamping fixture||夹具,夹紧装置Clamping force||夹持力,合模力Class A surface||A级表面Clear coat||透明涂层,透明罩漆,清漆层Clear coat finish||清漆涂层Clicker die||冲模Climb milling||同向铣削, 顺铣Clipping press||切边压力机Closure pressing speed||合模速度CMM(Closed Mould Moulding)||闭合模塑CMT(Compression Molding||挤压成型工艺CNC(Computerized Numerical Control)||电脑数值控制Coarse grinding||粗磨,用砂轮初加工Coating defect||涂层缺陷Collision test||碰撞试验,撞车试验Combination property||综合性能Concept design||概念设计Convection modulus||对流模量Convergence test||收敛试验Cooling fixture||冷却夹具Cooling tower||冷却塔Crazing||龟裂,细裂纹Cresol resin||甲酚树脂Cutting felt||毡的剪切Cutting-off bushing||环形下料模; 下料环Damped structure||阻尼缓冲结构Damper bracket||件振器支架Dashboard illumination||仪表板照明Dash trimming||前围板衬板Deburring||去毛刺,倒角,除飞边Deepdrawing forming||深拉成型Deflection test||挠曲试验Dent resistance||耐冲击性Design freedom||设计自由度Detail drawing||祥图,零件图Die assembly||压模装置Die casting||压模铸件,压模铸法Dimethyl fomamide||二甲基甲酰胺Dimethyl ketone||二甲基甲酮; 丙酮Dip pretreatment||浸渍预处理Die prime coat||浸渍打底漆Dimensional stability||尺寸稳定性Dip coating||浸涂Dip forming||浸渍成型Durability testing||耐久性试验,寿命试验Dwell||保压,暂停加压;滞留时间Dynamometer||测力计Edge effect||边缘效应,边界效应Edge feed||边缘进料Edge gate||侧浇口Ejection force||脱模力Ejector||起模杆Ejector guide pillar||推板导套Ejector housing||支架Elasticizer||增塑剂Elastomeric composites||高弹体复合材料Elongation at break||断裂延伸率Energy absorbing foam||吸能泡沫塑料Epoxy resin||环氧树脂Ether ketone||酮醚Explosion proof||防爆Exterior body panelling||车身外板部蒙皮Exterior trim||外饰,外饰件Fabric composites||织物复合材料Fabric impregnation||织物浸渍Fabric preform||织物预成型Fabric prereg||织物预浸料Fabrication parameter||制造参数Fabrication procedure||制造工序Fabricating machinery||加工设备Face plate coupling||法兰式连接Factory primer||工厂底漆,工厂防锈漆Fairing||整流罩,整流装置Fairing panel||前裙板Fascia bracket||仪表板支架Fascia mask||仪表板罩板Fastening clamp||夹紧装置,紧固夹子Fatigue tension test||拉伸疲劳性试验FCM(Fibrous Composite material)||纤维复合材料FEA(Finite Element Anlysis)||有限元分析Feed system||供料系统Feeding pump||供给泵Feeding speed||进给速度Female groove||凹模Female mould(tooling)||阴模Fender||翼子板;护板Fender apron||挡泥板Fender inner panel||翼子板内衬护板Fiber composite laminate||纤维复合材料层板Fiber mat layer||纤维毡层Finisher(Finishing component)||装饰件Flange||法兰, 凸缘Flange fitting||法兰式管接头Flash||毛边Flash mold||毛边模具Front sheet metal||车前板制件Fuselage fairing||机身整流装置Gage kit||仪表组,仪表套件Gas cavity||气泡,砂眼Gauge panel||仪表板Gear assembly||齿轮传动装置, 减速器Gearbox cover||变速器壳盖Gear bracket support||齿轮托支架Gel coat||胶衣,凝胶涂层Gel coat drum||胶衣圆桶Gel coat flow monitor||胶衣流量监控器Gel time||凝胶时间Glass fiber winding machine||玻璃纤维缠绕机Glass wool||玻璃棉Glass yarn||玻璃丝Guiding device||导向装置Gunk||预混料Gusset||角撑件Gutter channel||流水槽Hand lay-up ||手工铺叠,手工铺贴Hardness testing machine||硬度测试仪Hauling truck||拖车Header board outside panel||前板外板Headrest||靠枕Heat barrier material||隔热材料Heat forming||热成型High molecular material||高分子材料High pressure bag molding||高压袋成型工艺High pressure injection moulding||高压注射成型,高压注射模塑High-strength structural adhesives||高强度结构粘合剂此资源来自:如需转载,请注明出处,谢谢合作!~High temperature coating||高温涂层Hose support||软管支架Hub assembly||毂组件Hub bearing||车轮轮毂轴承Hydraulic device||液压装置Hydraulic engine||液压发动机Hydrostatic strength||流体静力强度IMC(In-Mold Coating)||模具内部涂层Immersion paint||浸漆Immersion test||浸渍试验,浸泡试验Immovable support||固定刀架Impact analysis||碰撞试验撞击分析Impact bending||冲击挠曲Impact specimen||冲击试样Impegnate||浸渍Impelling strength||冲击韧性Injection head||注射头Injection-moulded composites||注射模塑复合材料Injection moulded part||注塑制件Injection nozzle||注射喷口,压注喷口Intermittent entry||间歇供给,不连续供给Intermittent failure||间接性故障Izod test||悬臂冲击试验Jack||千斤顶,起重器;传动装置Jack engine||辅助发动机Jackbit insert||切刀,刀具,刃口Jacket||护套,套管,保护罩,蒙皮Jar-proof||防震的Jaw||钳口;定位销Jell||胶凝,凝固,固结Jet milling||喷射研磨Jig||夹具,定位模具Jig-adjusted||粗调的Job program||工作程序Joining nipple||接合螺管Joining on butt||对头接合Joint face of a pattern||分模面Joint gate||分型面内浇口Joint packing||填充垫圈,接合填密Joint sealing material||填缝料Joint-shaped support||铰接支架Joint strenght||连接强度Jump welded tube||对缝焊管,焊接管Junction bolt||接合螺栓Junction point||接点Keeping life||保存期,产品有效期Kenel||型芯Ketene||乙烯酮, 烯酮Ketene dimethyl||二甲酮Ketimide||酰基酮亚胺Ketimine||酮亚胺Ketoamine||酮胺,氨基酮Ketol||乙酮醇Ketone||甲酮Keying strength||咬合强度Knife holder||刀具,刀架Knockout||脱模Knockout pin||脱模销Knockout plate||脱模板Knoop scale||努氏硬度标度Knuckle joint||铰链连接Koplon||高湿模量粘胶纤维Koroseal||氯乙烯树脂Lacquer||挥发性漆;涂漆Lacquer finish||喷漆,上漆,罩光Lacquer formation||漆膜形成,成漆Lacquer putty||腻子,整面用油灰Lacquering ||上清漆Laminate construction thickness||结构层厚度Laminated panel||薄层状板Laminated plastics||层压塑料制品, 塑料层板Laminated thermosetting plastics||层压热固塑料Latex paints ||清漆Lay-up||(塑料,夹板的)铺叠成型Light-alloy body part||轻合金车身零件Lining ||衬里,衬垫Loaded haul cycle||载货行程Location bearing||定位轴承Location guide||固定导杆,定位导杆Location hole||定位孔Location tolerance||位置公差, 安装公差Locatin pin||定位销Lock bolt||锁紧螺钉Low pressure injection moulding||低压模塑成型Low shrink resin||低收缩树脂Luggage rack||行李架Machining accuracy||加工精度Machining center||加工中心Main shaft gear bushing||主轴齿轮衬套Mandrel ||卷芯,模芯;芯轴Manifold hood||歧管外罩Manual Lay-Up||人工手糊Manual spray-up||手工喷射Manual truck||手推车Manufacturing drawing||制造图纸Matched molds||合模Matrix ||基体,基质Mechanical properties||机械性能Metal bonding||金属粘结Metal-working machine||金属加工机床Methanol||甲醇Mismachining tolerance||加工误差Modular||组装式的Mofulus of elasticity||弹性模量Mould operation||模具操作Moulded plastics||模压塑料Moulding||嵌条;成型;装饰件Mount support||装配支架Multi-axial stress||多轴向应力Multi-tool machining||多刀切削加工||Needled mat||针刺毡,针织毡Non-ductile fracture||无塑性破坏Nontwisting fiber||不加捻纤维Notched izod test||带缺口悬臂梁式冲击试验Nozzle||管嘴,喷嘴Numerically controlled engine lathe||数控普通车床Nylon resin||尼龙树脂OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) ||原始设备生产商Offset cab||侧置驾驶室On-site forming||现场发泡On-site winding||现场缠绕成型Open molding||敞开式模塑法Opening mould||开模Optimized design||优化设计Orifice||注孔Orthophenyl tolyl ketone||邻苯基甲苯基酮Orthophthalic resin ortho||邻苯二甲酸树脂Osmotic pressure||渗透压力Outboard wing||外翼Outer panel skin||蒙皮Oven heating||烘箱加热,加热固化Over-engineering||过份设计的Over flow||溢流Over-spray||过喷Overhead traveling crane||高空移动行车Overhead-valve engine||顶置气门发动机Overhung trailer||外伸式拖车Oxide paint||氧化物涂料Package power||动力装置总成Packed ||紧密的,密实的;有密封的,有填料的Packing||衬垫;填料,密封填料;包装PAD(Paint As Required)||按需涂漆Paint base coat||上底漆Paint blemish||涂漆缺陷Paint blower||喷漆用压力机,喷漆枪Paint brush||涂漆刷Paint dilution||油漆稀释PE(Polyethlene)||聚乙烯Pedestal mounted||落地安装的Phenolic plastic||酚醛塑料Phenyl ketone||苯基甲酮Pit mounted||嵌入式安装Pivotal arm||枢轴Platic structural component||塑料结构零部件Plastic upholstery||(座椅)塑料蒙面Play compensation||间隙补偿PLC(Programmable Logical Controller) ||可编程序逻辑控制器Polycarbonate plastics||聚碳酸脂塑料Polyester resin||聚脂树脂Polyimide||聚酰亚胺Polymer||聚合物,高分子,多聚体Polyurethane foam||聚氨酯泡沫塑料Polyvinyl||聚乙烯的, 聚乙烯Polyvinyl fluoride||聚氟乙烯Prefabricated parts||成品零部件,制造好的零部件Propylene resin||丙烯类树脂Protecting lacquer||防护漆PSF(Polystyrene Foam)||聚苯乙烯泡沫塑料PTFE(Polytetrafluoroethylene)||聚四氟乙烯Pultrusion||拉挤成型Putty knife||油灰(腻子)刮铲QC(Quality Control)||质量控制QCS(Quality Control Standard)||质量管理控制标准QR(Quality Requirements)||质量规格(要求) Quality certification||质量认证Quantity production||大量(成批)生产,大规模生产Quantity production||大量(成批)生产,大规模生产Quarter panel brace||后侧围板支撑件Quarter panel lower extension||后侧围板下延伸部Quarter trim cap||后侧围装饰板盖Quarte wheel house||后侧围轮滚罩,后侧围车轮室Quasi-isotropic laminate||准各向同性层板Quench||淬火Rack truck||架子车, 移动架Radial dispersion||径向位移Radial loading||径向力(载荷)Radial pump||径向离心泵Radiation protective paint||防辐射涂料Radiator||散热器Rag||毛刺RARTM(Rubber-assisted RTM)||橡胶辅助RTM(用橡胶取代芯材的热膨胀RTM)Reactive resin||活性树脂, 反应型树脂Rear skirt rail||后围裙边梁Reciprocating engine||活塞式发动机, 往复式发动机Reinforcement||车身加强件,增强材料;构架Repeat accuracy||重复精确度Repeatability||设备重复定位精度Resin formulation||树脂配方Retaining nest||定位槽Return trip||回程,返回行程Rib||筋,加强筋RIFT(Resin Infusion Under Flexible Tooling)||挠性上模具树脂浸渍工艺RIM(Reaction Injection Molding)||反应注射模塑Safety hood||安全罩Sample testing||样品试验Sand wet||(车身/涂装)湿砂打磨Sandwich body||夹层结构车身Sandwich construction||夹层结构Sandwich panel||多层板,复合板Shaft assembly||轴组件Skin coat||表层;罩面层Solvent reclaim||溶剂的回收Stiffener||加强件Storage modulus||储能模量Stress at definite elongation||定伸应力Stretched actylic plastic||拉伸丙烯酸塑料String milling||连续铣削Stroke||(悬架)减振器,冲程Structural instrument panel||结构仪表板Structural layer||结构层Styrene||苯乙烯Styrofoam||聚苯乙烯泡沫塑料Surface mat||表面薄毡Synthetic resin paint||合成树脂涂料T ack strength||粘着强度T ail gate||(卡车等的)后挡板Teflon||聚四氟乙烯(塑料, 绝缘材料)TERTM(Thermal-Expansion Resin Transfer Molding)||热膨胀树脂传递模塑Thermoplastic plastics||热塑性塑料Thermoset resin||热固性树脂Thickening agent||增粘剂Trim waste||内饰废料Trimming orientation||修边定位Turbulent heating||湍流加热Turndown ratio||衰减比率Twisting stress||扭胁强, 扭应力U bolt||U形螺栓U bolt plate||U 形螺栓垫板Ultimate mechanical strength||极限机械强度Ultraviolent sensitive coating||紫外线感光涂层Undercoat paint||头道漆Uniaxial drawing||单轴拉伸Unsaturated polyester resin||非饱和聚酯树脂Unyielding support||不可压缩支架, 刚性支架Upper yield stress||上屈服应力Urethane coating||氨基甲酸乙酯涂层UVRTM(Ultra-violet RTM)||紫外线固化RTM(利用紫外线进行固化)VA RTM (Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding) ||真空辅助RTMVacuum bag molding||真空袋模制法VARI(Vacuum Assisted Resin njection)||真空辅助树脂注射Variable speed||无级变速Ventilation duct||通风管Ventilator(Ventilating equipment)||通风装置Vibratory stress||振动应力VIMP (Variable Infusion Molding Process)||可变浸渍模塑Vinyl chloride resin||聚氯乙烯树脂VOC(Volatile Organic Compound)||挥发性有机化合物Volume modulus||体积模数Vortex generator||(车身)扰流器,导流板VRV(Vacuum Reducer Valve)||真空减压阀Warping stress||翘曲应力Waste utilization||废物利用,废物处理Water shield||防水罩,挡泥板;密封条Water tolerance||耐水性Wedge gripping||楔形夹具Wheel fender||翼子板Wing trussgrid||翼子(挡泥)板加强件Winding||缠绕Wingtip assembly||翼尖整流罩Wire drawing||拉丝Wiring press||卷边压力机, 嵌线卷边机Workpiece grippe||工件夹子(持器),机械手Woven roving fabric||(玻璃纤维)无捻粗纱布织物Xylenol Carboxylic Acid||二甲苯酚酸Xlylene||亚二甲苯基Xyster||刮刀X alloy||铜铝合金Xenidium||胶合板Xenidium||胶合板Xylene ||二甲苯Xylene resin||二甲苯树脂Yard-crane||移动吊车,场内移动起重机Yarn count||纱线支数,丝线支数Yarn strength||纱线强度,长丝强度Yield limit||屈服极限,屈服点Yield point under bending stress||弯曲应力下的屈服点Yield stress||屈服应力, 屈服点Yield stress controlled bonding||屈服应力粘结Zedeflon||四氟乙烯均聚物Zero checker||定零位装置, 零位校验Zero clearance||零间隙Zero compensation||零位补偿Zero initial condition||零初始条件Zero setting||(仪表)零位调整, 置零Zero shrinkage resin||零收缩树脂Zone control||区域控制。

如何介绍一个材料范文英语(2篇精选)如何介绍一个材料范文英语(篇1)1. Title and AuthorThe title of this essay is "Introducing the Revolutionary Polymer Material: A Breakthrough in Sustainable Technology." The author is John Doe, a materials scientist with a decade of experience in the field of polymer research.2. Background InfoPolymers have been a staple of the materials science world for decades, but recent advancements in technology have led to the development of a new type of polymer material that is revolutionizing the industry. This material, known as "EcoPoly," is made from renewable resources and boasts unparalleled durability and sustainability.3. Material OverviewEcoPoly is a polymer material that is derived from plant-based sources, such as corn starch and sugarcane. It is biodegradable, meaning it can be naturally broken down by microorganisms, reducing the environmental impact of waste. Additionally, EcoPoly has a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for use in a variety of applications.4. Key FeaturesEcoPoly's key features include its durability, sustainability, and biodegradability. Its strength-to-weight ratio is comparable to traditional petroleum-based polymers, but its environmental credentials are significantly better. It can be used in a wide range of applications, from packaging materials to automotive components.5. ApplicationsEcoPoly has a wide range of potential applications. It can be used in the packaging industry, replacing traditional plastic packaging materials with a more environmentally friendly option. Additionally, it can be used in the automotive industry to create lightweight and durable components that reduce fuel consumption and emissions. EcoPoly can also be used in the construction industry for sustainable building materials.6. Advantages & DisadvantagesThe main advantage of EcoPoly is its sustainability. It is derived from renewable resources and is biodegradable, reducing the environmental impact of waste. Additionally, it has a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it an effective material for a variety of applications. However, one disadvantage of EcoPoly is its production cost, which is currently higher than traditional petroleum-based polymers.As research and development continue, however, these costs are expected to decrease.7. ConclusionEcoPoly is a groundbreaking polymer material that offers a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional petroleum-based polymers. Its durability, sustainability, and biodegradability make it an ideal material for a wide range of applications, including packaging, automotive, and construction industries. Although its production cost is currently higher, with continued research and development, it has the potential to become a cost-effective and widely adopted material in the future.如何介绍一个材料范文英语(篇2)1. Material NameIn this article, we delve into the fascinating world of XYZ Alloy, a unique material that has captivated the attention of industries across the globe.2. OriginXYZ Alloy originates from the cutting-edge manufacturing facilities in the United States of America, where it is produced using state-of-the-art technology.3. PropertiesXYZ Alloy stands out for its exceptional properties. It is extremely lightweight, yet incredibly strong, making it an ideal material for applications where weight reduction is crucial. This alloy's high strength-to-weight ratio sets it apart from traditional materials.4. ApplicationsDue to its unique properties, XYZ Alloy finds widespread use in the automotive and aerospace industries. In the automotive sector, it is used to create lighter, more fuel-efficient vehicles. In the aerospace industry, itslightweight strength is essential for creating componentsthat can withstand the rigors of space travel.5. ManufacturingThe manufacturing of XYZ Alloy involves high-tech processes that ensure its consistency and quality. These processes are meticulously controlled to produce a material that meets the stringent requirements of various industries.6. AdvantagesXYZ Alloy offers several advantages. Its durability ensures long-lasting performance, making it a cost-effective choice in the long run. Additionally, its lightweight properties contribute to reduced energy consumption and a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions.7. DisadvantagesOne major disadvantage of XYZ Alloy is its limited availability. As it is produced using high-tech processes,its production capacity is currently constrained. This limits its widespread adoption and can sometimes lead to supplychain issues.8. Future ScopeDespite its current limitations, XYZ Alloy holds promise for a sustainable future. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that the manufacturing processes will becomemore efficient, increasing the availability of this alloy. Furthermore, its lightweight and durable properties make it a prime candidate for use in sustainable technologies, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.In conclusion, XYZ Alloy is a remarkable material that offers unique advantages in terms of strength, weight, and durability. While its limited availability presents challenges, the potential for future growth and applicationsin sustainable technologies make it a material worth watching.。

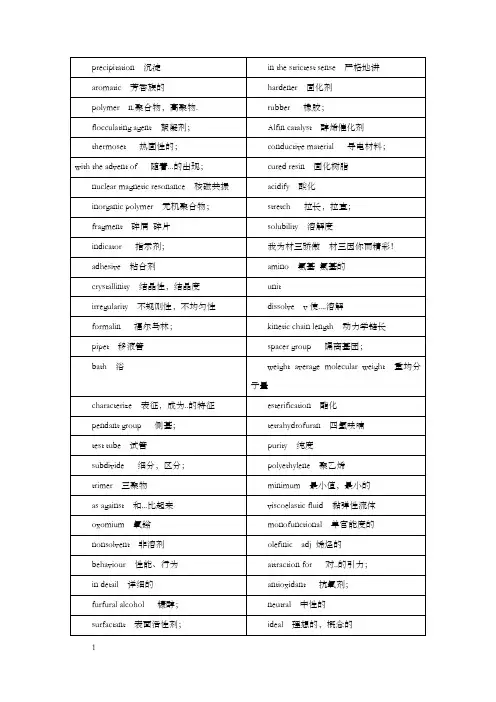
专业英语词汇accordion 手风琴activation 活化(作用)addition polymer 加成聚合物,加聚物aggravate 加重,恶化agitation 搅拌agrochemical 农药,化肥Alfin catalyst 醇(碱金属)烯催化剂align 排列成行aliphatic 脂肪(族)的alkali metal 碱金属allyl 烯丙基aluminum alkyl 烷基铝amidation 酰胺化(作用)amino 氨基,氨基的amorphous 无定型的,非晶体的anionic 阴(负)离子的antioxidant 抗氧剂antistatic agent 抗静电剂aromatic 芳香(族)的arrangement (空间)排布,排列atactic 无规立构的attraction 引力,吸引backbone 主链,骨干behavior 性能,行为biological 生物(学)的biomedical 生物医学的bond dissociation energy 键断裂能boundary 界限,范围brittle 脆的,易碎的butadiene 丁二烯butyllithium 丁基锂calendering 压延成型calendering 压延carboxyl 羧基carrier 载体catalyst 催化剂,触媒categorization 分类(法)category 种类,类型cation 正[阳]离子cationic 阳(正)离子的centrifuge 离心chain reaction 连锁反应chain termination 链终止char 炭characterize 表征成为…的特征chilled water 冷冻水chlorine 氯(气)coating 涂覆cocatalyst 助催化剂coil 线团coiling 线团状的colligative 依数性colloid 胶体commence 开始,着手common salt 食盐complex 络合物compliance 柔量condensation polymer 缩合聚合物,缩聚物conductive material 导电材料conformation 构象consistency 稠度,粘稠度contaminant 污物contour 外形,轮廓controlled release 控制释放controversy 争论,争议conversion 转化率conversion 转化copolymer 共聚物copolymerization 共聚(合)corrosion inhibitor 缓释剂countercurrent 逆流crosslinking 交联crystal 基体,结晶crystalline 晶体,晶态,结晶的,晶态的crystalline 结晶的crystallinity 结晶性,结晶度crystallite 微晶decomposition 分解defect 缺陷deformability 变形性,变形能力deformation 形变deformation 变形degree of polymerization 聚合度dehydrogenate 使脱氢density 密度depolymerization 解聚deposit 堆积物,沉积depropagation 降解dewater 脱水diacid 二(元)酸diamine 二(元)胺dibasic 二元的dieforming 口模成型diffraction 衍射diffuse 扩散dimension 尺寸dimensional stability 尺寸稳定性dimer 二聚物(体)diol 二(元)醇diolefin 二烯烃disintegrate 分解,分散,分离dislocation 错位,位错dispersant 分散剂dissociate 离解dissolution 溶解dissolve 使…溶解distort 使…变形,扭曲double bond 双键dough (生)面团,揉好的面drug 药品,药物elastic modulus 弹性模量elastomer 弹性体eliminate 消除,打开,除去elongation 伸长率,延伸率entanglement 缠结,纠缠entropy 熵equilibrium 平衡esterification 酯化(作用)evacuate 撤出extrusion 注射成型extrusion 挤出fiber 纤维flame retardant 阻燃剂flexible 柔软的flocculating agent 絮凝剂folded-chain lamella theory 折叠链片晶理论formulation 配方fractionation 分级fragment 碎屑,碎片fringed-micelle theory 缨状微束理论functional group 官能团functional polymer 功能聚合物functionalized polymer 功能聚合物gel 凝胶glass transition temperature 玻璃化温度glassy 玻璃(态)的glassy 玻璃态的glassy state 玻璃态globule 小球,液滴,颗粒growing chain 生长链,活性链gyration 旋转,回旋hardness 硬度heat transfer 热传递heterogeneous 不均匀的,非均匀的hydocy acid 羧基酸hydrogen 氢(气)hydrogen bonding 氢键hydrostatic 流体静力学hydroxyl 烃基hypothetical 假定的,理想的,有前提的ideal 理想的,概念的imagine 想象,推测imbed 嵌入,埋入,包埋imperfect 不完全的improve 增进,改善impurity 杂质indispensable 不了或缺的infrared spectroscopy 红外光谱法ingredient 成分initiation (链)引发initiator 引发剂inorganic polymer 无机聚合物interaction 相互作用interchain 链间的interlink 把…相互连接起来连接intermittent 间歇式的intermolecular (作用于)分子间的intrinsic 固有的ion 离子ion exchange resin 离子交换树脂ionic 离子的ionic polymerization 离子型聚合irradiation 照射,辐射irregularity 不规则性,不均匀的isobutylene 异丁烯isocyanate 异氰酸酯isopropylate 异丙醇金属,异丙氧化金属isotactic 等规立构的isotropic 各项同性的kinetic chain length 动力学链长kinetics 动力学latent 潜在的light scattering 光散射line 衬里,贴面liquid crystal 液晶macromelecule 大分子,高分子matrix 基体,母体,基质,矩阵mean-aquare end-to-end distance 均方末端距mechanical property 力学性能,机械性能mechanism 机理medium 介质中等的,中间的minimise 最小化minimum 最小值,最小的mo(u)lding 模型mobility 流动性mobilize 运动,流动model 模型modify 改性molecular weight 分子量molecular weight distribution 分子量分布molten 熔化的monofunctional 单官能度的monomer 单体morphology 形态(学)moulding 模塑成型neutral 中性的nonelastic 非弹性的nuclear magnetic resonance 核磁共振nuclear track detector 核径迹探测器number average molecular weight 数均分子量occluded 夹杂(带)的olefinic 烯烃的optimum 最佳的,最佳值[点,状态] orient 定向,取向orientation 定向oxonium 氧鎓羊packing 堆砌parameter 参数parison 型柸pattern 花纹,图样式样peculiarity 特性pendant group 侧基performance 性能,特征permeability 渗透性pharmaceutical 药品,药物,药物的,医药的phenyl sodium 苯基钠phenyllithium 苯基锂phosgene 光气,碳酰氯photosensitizer 光敏剂plastics 塑料platelet 片晶polyamide 聚酰胺polybutene 聚丁烯polycondensation 缩(合)聚(合)polydisperse 多分散的polydispersity 多分散性polyesterification 聚酯化(作用)polyethylene 聚乙烯polyfunctional 多官能度的polymer 聚合物【体】,高聚物polymeric 聚合(物)的polypropylene 聚苯烯polystyrene 聚苯乙烯polyvinyl alcohol 聚乙烯醇polyvinylchloride 聚氯乙烯porosity 多孔性,孔隙率positive 正的,阳(性)的powdery 粉状的processing 加工,成型purity 纯度pyrolysis 热解radical 自由基radical polymerization 自由基聚合radius 半径random coil 无规线团random decomposition 无规降解reactent 反应物,试剂reactive 反应性的,活性的reactivity 反应性,活性reactivity ratio 竞聚率real 真是的release 解除,松开repeating unit 重复单元retract 收缩rubber 橡胶rubbery 橡胶态的rupture 断裂saturation 饱和scalp 筛子,筛分seal 密封secondary shaping operation 二次成型sedimentation 沉降(法)segment 链段segment 链段semicrystalline 半晶settle 沉淀,澄清shaping 成型side reaction 副作用simultaneously 同时,同步single bond 单键slastic parameter 弹性指数slurry 淤浆solar energy 太阳能solubility 溶解度solvent 溶剂spacer group 隔离基团sprinkle 喷洒squeeze 挤压srereoregularity 立构规整性【度】stability 稳定性stabilizer 稳定剂statistical 统计的step-growth polymerization 逐步聚合stereoregular 有规立构的,立构规整性的stoichiometric 当量的,化学计算量的strength 强度stretch 拉直,拉长stripping tower 脱单塔subdivide 细分区分substitution 取代,代替surfactant 表面活性剂swell 溶胀swollen 溶胀的synthesis 合成synthesize 合成synthetic 合成的tacky (表面)发粘的,粘连性tanker 油轮,槽车tensile strength 抗张强度terminate (链)终止tertiary 三元的,叔(特)的tetrahydrofuran 四氢呋喃texture 结构,组织thermoforming 热成型thermondynamically 热力学地thermoplastic 热塑性的thermoset 热固性的three-dimensionally ordered 三维有序的titanium tetrachloride 四氯化钛titanium trichloride 三氯化铁torsion 转矩transfer (链)转移,(热)传递triethyloxonium-borofluoride 三乙基硼氟酸羊trimer 三聚物(体)triphenylenthyl potassium 三苯甲基钾ultracentrifugation 超速离心(分离)ultrasonic 超声波uncross-linked 非交联的uniaxial 单轴的unsaturated 不饱和的unzippering 开链urethane 氨基甲酸酯variation 变化,改变vinyl 乙烯基(的)vinyl chloride 氯乙烯vinyl ether 乙烯基醚viscoelastic 黏弹性的viscoelastic state 黏弹态viscofluid state 黏流态viscosity 黏度viscosity average molecular weight 黏均分子量viscous 粘稠的vulcanization 硫化weight average molecular weight 重均分子量X-ray x射线x光yield 产率Young's modulus 杨氏模量课文翻译第一单元什么是高聚物?什么是高聚物?首先,他们是合成物和大分子,而且不同于低分子化合物,譬如说普通的盐。

材料英语证书考试(PEC)-复合材料词汇Acetyl||乙酰Acid-proof paint||耐酸涂料, 耐酸油漆Acrylic fiber||丙烯酸纤维Acrylic resin||丙烯酸树脂Active filler||活性填料Adapter assembly||接头组件Addition polyimide||加成型聚酰亚胺Addition polymer||加聚物Adjusting valve||调整阀,调节阀Adhersion assembly||粘合装配Adhersion bond||胶结Adjustable-bed press||工作台可调式压力机Adjuster shim||调整垫片Adjusting accuracy||调整精度,调校精度Admissible error||容许误差Admissible load||容许载荷Adsorbed layer||吸附层Advanced composite material||先进复合材料,高级复合材料Advanced development vehicle||试制车,预研样车AE(Automobile Engineering)||汽车工程技术Aeolotropic material||各向异性材料Aerated plastics||泡沫塑料, 多孔塑料Aerodynamic body||流线型车身Aft cross member||底盘/车架后横梁Air bleeder||排气孔Air clamp||气动夹具Air deflector||导流板;导风板,气流偏转板Air intake manifold||进气歧管Air servo||伺服气泵Air-tight joint||气密接头All-plastic molded||全塑模注的All polyster seat||全聚酯座椅Alligatoring||龟裂,涂膜皱皮,表面裂痕Amino resin||氨基树脂Angular test||挠曲试验Anti-chipping primer||抗破裂底漆(底层涂料)Apron||防护挡板Aramid fibre composites||芳胺纤维复合材料Assembly drawing||装配图Assembly jig||装配夹具Assembly part||装配件,组合件Autoclave forming||热压罐成型Autocorrection||自动校正Automatic compensation||自动补偿Automatic feed||自动进料Automobile instrument||汽车仪表板Automotive transmission||汽车传动装置,汽车变速器Auxiliary fasia console||副仪表板Axial strain||轴向应变Axle bushing||轴衬Axle fairing||底盘车桥整流罩A Stage||A 阶段(某些热固性树脂聚合作用的初期阶段)AAC(Auxiliary Air Control)||辅助空气控制ABC(Active Body Control)||主动式车身控制装置Abherent||阻粘剂Ability meter||测力计,性能测试仪ABL (Ablative)||烧蚀剂Ablation||烧蚀Ablative composite material||烧蚀复合材料Ablative insulative material||烧蚀绝热材料Ablative polymer||烧蚀聚合物Ablative prepreg||烧蚀性预浸料Ablative resistance||耐烧蚀性ABR(Acrylate Butadience Rubber)||丙烯酸丁二烯橡胶Abradant material||研磨材料,磨料Abrade||研磨;用喷砂清理Abrasion||磨耗Abrasion coefficient||磨耗系数Abrasion loss||磨耗量,磨损量Abrasion performance||磨耗性Abrasion-proof material||耐磨材料Abrasion resistant paint||耐磨涂料Abrasion test||磨损试验Abrasive blast system||喷砂清理系统Abrasive cloth||砂布Abrasive disc||砂轮盘,砂轮片Abrasive finishing||抛光Abrasive paper||砂纸Abrasive resistance||耐磨性ABS(Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)resin||ABS树脂,丙烯腈-丁二烯-苯乙烯(热塑性)树脂ABSM(American Bureau of Standard Materials)||美国标准材料局Absolute dynamic modulus||绝对动态模量Absolute error||绝对误差Absorbent material||吸收性材料,吸收性物质,吸声材料,吸收剂Absorber||减振器,阻尼器,缓冲器ACA(Automotive Composite Alliance)||汽车复合材料协会ACC(Automatic Clutch Control)||自动离合器操纵控制Accelerant||促进剂,加速剂Accelerated aging test||加速老化试验,人工老化试验Accelerator pedal shaft||加速踏板轴Accelerator pump nozzle||加速泵喷嘴Acceptable life||有效使用寿命Acceptance test specification||验收测试规范Access panel||罩板,盖板Accessory||配件,附属品Accessory equipment||辅助设备Accessory kit||附件包,成套附件Accumulator can||储电池外壳Accumulator package||蓄压器组件,蓄压器单元Accuracy in calibration||校准精度Accuracy of finish||最终加工精度Accuracy of manufacture||制造精度Accuracy of positioning||定位精度Accuracy of repetition||重现精度,复制精度此资源来自:由FanE『翻译中国』 http;//整理。

复合材料英语Acetyl||乙酰Acid-proof paint||耐酸涂料, 耐酸油漆Acrylic fiber||丙烯酸纤维Acrylic resin||丙烯酸树脂Active filler||活性填料Adapter assembly||接头组件Addition polyimide||加成型聚酰亚胺Addition polymer||加聚物Adjusting valve||调整阀,调节阀Adhersion assembly||粘合装配Adhersion bond||胶结Adjustable-bed press||工作台可调式压力机Adjuster shim||调整垫片Adjusting accuracy||调整精度,调校精度Admissible error||容许误差Admissible load||容许载荷Adsorbed layer||吸附层Advanced composite material||先进复合材料,高级复合材料Advanced development vehicle||试制车,预研样车AE(Automobile Engineering)||汽车工程技术Aeolotropic material||各向异性材料Aerated plastics||泡沫塑料, 多孔塑料Aerodynamic body||流线型车身Aft cross member||底盘/车架后横梁Air bleeder||排气孔Air clamp||气动夹具Air deflector||导流板;导风板,气流偏转板Air intake manifold||进气歧管Air servo||伺服气泵Air-tight joint||气密接头All-plastic molded||全塑模注的All polyster seat||全聚酯座椅Alligatoring||龟裂,涂膜皱皮,表面裂痕Amino resin||氨基树脂Angular test||挠曲试验Anti-chipping primer||抗破裂底漆(底层涂料)Apron||防护挡板Aramid fibre composites||芳胺纤维复合材料Assembly drawing||装配图Assembly jig||装配夹具Assembly part||装配件,组合件Autoclave forming||热压罐成型Autocorrection||自动校正Automatic compensation||自动补偿Automatic feed||自动进料Automobile instrument||汽车仪表板Automotive transmission||汽车传动装置,汽车变速器Auxiliary fasia console||副仪表板Axial strain||轴向应变Axle bushing||轴衬Axle fairing||底盘车桥整流罩A Stage||A 阶段(某些热固性树脂聚合作用的初期阶段)AAC(Auxiliary Air Control)||辅助空气控制ABC(Active Body Control)||主动式车身控制装置Abherent||阻粘剂Ability meter||测力计,性能测试仪ABL (Ablative)||烧蚀剂Ablation||烧蚀Ablative composite material||烧蚀复合材料Ablative insulative material||烧蚀绝热材料Ablative polymer||烧蚀聚合物Ablative prepreg||烧蚀性预浸料Ablative resistance||耐烧蚀性ABR(Acrylate Butadience Rubber)||丙烯酸丁二烯橡胶Abradant material||研磨材料,磨料Abrade||研磨;用喷砂清理Abrasion||磨耗Abrasion coefficient||磨耗系数Abrasion loss||磨耗量,磨损量Abrasion performance||磨耗性Abrasion-proof material||耐磨材料Abrasion resistant paint||耐磨涂料Abrasion test||磨损试验Abrasive blast system||喷砂清理系统Abrasive cloth||砂布Abrasive disc||砂轮盘,砂轮片Abrasive finishing||抛光Abrasive paper||砂纸Abrasive resistance||耐磨性ABS(Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styr ene)resin||ABS树脂,丙烯腈-丁二烯-苯乙烯(热塑性)树脂ABSM(American Bureau of Standard Materials)||美国标准材料局Absolute dynamic modulus||绝对动态模量Absolute error||绝对误差Absorbent material||吸收性材料,吸收性物质,吸声材料,吸收剂Absorber||减振器,阻尼器,缓冲器ACA(Automotive Composite Alliance)||汽车复合材料协会ACC(Automatic Clutch Control)||自动离合器操纵控制Accelerant||促进剂,加速剂Accelerated aging test||加速老化试验,人工老化试验Accelerator pedal shaft||加速踏板轴Accelerator pump nozzle||加速泵喷嘴Acceptable life||有效使用寿命Acceptance test specification||验收测试规范Access panel||罩板,盖板Accessory||配件,附属品Accessory equipment||辅助设备Accessory kit||附件包,成套附件Accumulator can||储电池外壳Accumulator package||蓄压器组件,蓄压器单元Accuracy in calibration||校准精度Accuracy of finish||最终加工精度Accuracy of manufacture||制造精度Accuracy of positioning||定位精度Accuracy of repetition||重现精度,复制精度Acetal matrix composites||缩醛树脂基复合材料Acetal plastic||缩醛塑料,聚甲醛塑料Acetal resin||缩醛树脂Acetamide||乙酰胺Acetate fiber||醋酸纤维,乙酸纤维Acetone||丙酮Back corner panel||后围角板Back panel||后围板Back side panel||后侧板Back wall pillar||后围立柱Backer||衬料Baffler||挡板,阻尼器;导流叶片Bag Molding||气囊施压成型(袋模法) Baggage holder||行李架Barrier coat||阻挡层;防渗涂层Batch mixing||分批混合,批混Batching unit||分批加料装置Bearing assembly||轴承组合件Biaxial winding||双角缠绕, 双轴缠绕Binder fiber||粘合纤维Bipolymer||二元共聚物Bismaleimide composites||双马来酰亚胺复合材料Blank placement||坯料的放置Blanket||玻璃纤维毡;坯料Blanking press||冲压机, 冲割压力机Blending resin||掺合树脂BMC(Bulk Moulding Compound)||团状膜塑料BMI (Bismaleimide)||双马来酰亚胺Body back panel||车身后板Body back wall||车身驾驶室后围Body bracket||车身支架Body control module||车身控制模块Body frame (Body skeleton)||车身骨架Body front panel||车身驾驶室前围板Body monocoque||单壳体车身,单壳式结构车身Body outer panel||驾驶室覆盖件;驾驶室覆盖件Body structural member||车身结构件Body trim||车身装饰件Bonded riveted structure||胶铆结构Bonnet||发动机罩Brake||制动器Brake arrangement||制动装置Brinell hardness test||布氏硬度试验Brittle coating||脆性涂层Bulk coat||整体涂层Bulk heat treatment||整体热处理Bulk moulding compound||(增强塑料)预制整体模塑料Bumper bracket(holder)||保险杠托架Bus brake system||客车制动系Butt flange||对接法兰Butt joint||对接接头;对接Butterfly valve||节流阀,节气门BWI (Body In White)||白车身Cab deflector shield||驾驶室导流板Cab fairing||驾驶室整流罩Cab floor||驾驶室地板Cab mounting||驾驶室悬置CAD(Computer Aided Design)||计算机辅助设计CAE (Computer Aided Engineering)||计算机辅助工程设计Calibration tolerance||校准公差Calibrating instrument||校准仪表Camouflage paint||覆面漆, 盖面涂料, 伪假漆Cantilever beam impact test||悬臂梁冲击试验Carbon-felt reinforced carbon composites||碳毡增强碳复合材料Carbon fiber clutch||碳纤维离合器Carbon filament cloth||碳丝织物Case extension||外壳的伸出部分,延伸外壳Casing gasket||外壳密封垫Catalyst manifold||固化剂总成Catalyst pump||固化剂泵Catalyst ratio||固化剂比率Cavity||模槽,型腔;凹模Cavity block||阴模Cavity depth||模槽深度Cellular board||蜂窝状板,多孔板Cellular plastics||泡沫塑料,多孔塑料Centre boss||轮毂Centre pin||销轴,枢轴,主销Centrifugal casting moulding||离心浇铸成型Centrosymmetry||中心对称层板Ceramic matrix composites||陶瓷基复合材料Charge||填充气体,填充料Chasis||底盘;机壳,车架Chlorinated polyethlene||聚氯乙烯Chopped fiber||短切纤维Chopped random mat||短切无序毡Chopped strand||短切原丝CIRTM(Co-Injection RTM)||共注射RTMClamping fixture||夹具,夹紧装置Clamping force||夹持力,合模力Class A surface||A级表面Clear coat||透明涂层,透明罩漆,清漆层Clear coat finish||清漆涂层Clicker die||冲模Climb milling||同向铣削, 顺铣Clipping press||切边压力机Closure pressing speed||合模速度CMM(Closed Mould Moulding)||闭合模塑CMT(Compression Molding||挤压成型工艺CNC(Computerized Numerical Control)||电脑数值控制Coarse grinding||粗磨,用砂轮初加工Coating defect||涂层缺陷Collision test||碰撞试验,撞车试验Combination property||综合性能Concept design||概念设计Convection modulus||对流模量Convergence test||收敛试验Cooling fixture||冷却夹具Cooling tower||冷却塔Crazing||龟裂,细裂纹Cresol resin||甲酚树脂Cutting felt||毡的剪切Cutting-off bushing||环形下料模; 下料环Damped structure||阻尼缓冲结构Damper bracket||件振器支架Dashboard illumination||仪表板照明Dash trimming||前围板衬板Deburring||去毛刺,倒角,除飞边Deepdrawing forming||深拉成型Deflection test||挠曲试验Dent resistance||耐冲击性Design freedom||设计自由度Detail drawing||祥图,零件图Die assembly||压模装置Die casting||压模铸件,压模铸法Dimethyl fomamide||二甲基甲酰胺Dimethyl ketone||二甲基甲酮; 丙酮Dip pretreatment||浸渍预处理Die prime coat||浸渍打底漆Dimensional stability||尺寸稳定性Dip coating||浸涂Dip forming||浸渍成型Durability testing||耐久性试验,寿命试验Dwell||保压,暂停加压;滞留时间Dynamometer||测力计Edge effect||边缘效应,边界效应Edge feed||边缘进料Edge gate||侧浇口Ejection force||脱模力Ejector||起模杆Ejector guide pillar||推板导套Ejector housing||支架Elasticizer||增塑剂Elastomeric composites||高弹体复合材料Elongation at break||断裂延伸率Energy absorbing foam||吸能泡沫塑料Epoxy resin||环氧树脂Ether ketone||酮醚Explosion proof||防爆Exterior body panelling||车身外板部蒙皮Exterior trim||外饰,外饰件Fabric composites||织物复合材料Fabric impregnation||织物浸渍Fabric preform||织物预成型Fabric prereg||织物预浸料Fabrication parameter||制造参数Fabrication procedure||制造工序Fabricating machinery||加工设备Face plate coupling||法兰式连接Factory primer||工厂底漆,工厂防锈漆Fairing||整流罩,整流装置Fairing panel||前裙板Fascia bracket||仪表板支架Fascia mask||仪表板罩板Fastening clamp||夹紧装置,紧固夹子Fatigue tension test||拉伸疲劳性试验FCM(Fibrous Composite material)||纤维复合材料FEA(Finite Element Anlysis)||有限元分析Feed system||供料系统Feeding pump||供给泵Feeding speed||进给速度Female groove||凹模Female mould(tooling)||阴模Fender||翼子板;护板Fender apron||挡泥板Fender inner panel||翼子板内衬护板Fiber composite laminate||纤维复合材料层板Fiber mat layer||纤维毡层Finisher(Finishing component)||装饰件Flange||法兰, 凸缘Flange fitting||法兰式管接头Flash||毛边Flash mold||毛边模具Front sheet metal||车前板制件Fuselage fairing||机身整流装置Gage kit||仪表组,仪表套件Gas cavity||气泡,砂眼Gauge panel||仪表板Gear assembly||齿轮传动装置, 减速器Gearbox cover||变速器壳盖Gear bracket support||齿轮托支架Gel coat||胶衣,凝胶涂层Gel coat drum||胶衣圆桶Gel coat flow monitor||胶衣流量监控器Gel time||凝胶时间Glass fiber winding machine||玻璃纤维缠绕机Glass wool||玻璃棉Glass yarn||玻璃丝Guiding device||导向装置Gunk||预混料Gusset||角撑件Gutter channel||流水槽Hand lay-up ||手工铺叠,手工铺贴Hardness testing machine||硬度测试仪Hauling truck||拖车Header board outside panel||前板外板Headrest||靠枕Heat barrier material||隔热材料Heat forming||热成型High molecular material||高分子材料High pressure bag molding||高压袋成型工艺High pressure injection moulding||高压注射成型,高压注射模塑High-strength structural adhesives||高强度结构粘合剂此资源来自:由FanE『翻译中国』http;//整理。

A 高分子化学和高分子物理UNIT 1 What are Polymer?第一单元什么是高聚物?What are polymers? For one thing, they are complex and giant molecules and are different from low molecular weight compounds like, say, common salt. To contrast the difference, the molecular weight of common salt is only 58.5, while that of a polymer can be as high as several hundred thousand, even more than thousand thousands. These big molecules or ‘macro-molecules’ are made up of much smaller molecules, can be of one or more chemical compounds. To illustrate, imagine that a set of rings has the same size and is made of the same material. When these things are interlinked, the chain formed can be considered as representing a polymer from molecules of the same compound. Alternatively, individual rings could be of different sizes and materials, and interlinked to represent a polymer from molecules of different compounds.什么是高聚物?首先,他们是合成物和大分子,而且不同于低分子化合物,譬如说普通的盐。

生产实习(Advanced Practicum)本课程是材料科学与工程本科专业的必修课。
课程内容包括带生到工厂和科研院所了解和实践专业知识在实际生产中的应用。
同时配合仿真实习软件掌握化工生产工艺的操作,为学生进社会工作打好基础。
材料学院开课;预修:PSE3840T,PSE3620T。
橡胶工程高等实验(Rubber Engineering Advanced Experiment)本课程开设研制弹性体高分子材料的综合实验,以完成小型科题的训练为教学目标,培养学生的基本科研素质和创新能力。
教师给出科研课题,学生自行设计方案,完成材料选用、配合点、测试表征方案、结果与讨论等步骤。
最后撰写实验和研究报告。
材料学院开课;预修:PSE3620T,PSE3840PSE3421T。
文献查阅(Literature Searching)本课程的特点:是一门实践课;掌握文献检索的基本知识;工具书的使用方法;熟悉图书馆的检索方法;记住必要的专业术语;掌握相关检索工具的网络检索方法。
材料学院秋季开课预修:MSE2022T,MSE2140T,MSE3440T。
聚合物表征(Techniques for Characterization of Polymers)本课程是材料学专业的核心基础课程系统讲授聚合物结构与性能表征的分析方法,主要内容包括:波谱分析,聚合物分子质量及分子质量分布表征,聚合物微结构分析,聚合物热分析,聚合物流变性能分析,聚合物动态力学分析。
材料学院秋季开课;预修:PSE2150PSE2250T,PSE3620T。
橡胶制品及模具设计(Rubber Products and Mold Design)介绍国内外橡胶工业制品种类及生产,讲述橡胶模压制品设计一般要求和规律,讲述橡胶压模类型对制品的影响、结构设计、模具导向与定位、模具的尺寸与强关系、模具材料、热处理及表面处理的要求及模具的尺寸公差与配合、整体设计。
材料学院秋季开课;预修:M1120T,MEE2250T,MEE1640T。

高分子专业英语词汇必备250个1 高分子 macromolecule, polymer 又称"大分子"。
2 超高分子 supra polymer3 天然高分子 natural polymer4 无机高分子 inorganic polymer5 有机高分子 organic polymer6 无机-有机高分子 inorganic organic polymer7 金属有机聚合物 organometallic polymer8 元素高分子 element polymer9 高聚物 high polymer10 聚合物 polymer11 低聚物 oligomer 曾用名"齐聚物"。
12 二聚体 dimer13 三聚体 trimer14 调聚物 telomer15 预聚物 prepolymer16 均聚物 homopolymer17 无规聚合物 random polymer18 无规卷曲聚合物 random coiling polymer 419 头-头聚合物 head-to-head polymer20 头-尾聚合物 head-to-tail polymer21 尾-尾聚合物 tail-to-tail polymer22 反式有规聚合物 transtactic polymer23 顺式有规聚合物 cistactic polymer24 规整聚合物 regular polymer25 非规整聚合物 irregular polymer26 无规立构聚合物 atactic polymer27 全同立构聚合物 isotactic polymer 又称"等规聚合物"。
28 间同立构聚合物 syndiotactic polymer 又称"间规聚合物"。
29 杂同立构聚合物 heterotactic polymer 又称"异规聚合物"。

brush polymercoiling type polymer电荷转移复合物,电荷转移络合物热引发转移终止剂封端[反应]e value17三单元组triad18四单元组tetrad19五单元组pentad20无规线团random coil21自由连接链freely-jointed chain22自由旋转链freely-rotating chain23蠕虫状链worm-like chain24柔性链flexible chain25链柔性chain flexibility26刚性链rigid chain27棒状链rodlike chain28链刚性chain rigidity29聚集aggregation30聚集体aggregate31凝聚、聚集coalescence32链缠结chain entanglement33凝聚缠结cohesional entanglement34物理缠结physical entanglement35拓扑缠结topological entanglement36凝聚相condensed phase37凝聚态condensed state38凝聚过程condensing process39临界聚集浓度critical aggregation concentration 40线团-球粒转换coil-globule transition41受限链confined chain42受限态confined state43物理交联physical crosslinking44统计线团statistical coil45等效链equivalent chain46统计链段statistical segment47链段chain segment48链构象chain conformation49无规线团模型random coil model50无规行走模型random walk model51自避随机行走模型self avoiding walk model52卷曲构象coiled conformation53高斯链Gaussian chain54无扰尺寸unperturbed dimension55扰动尺寸perturbed dimension56热力学等效球thermodynamically equivalent sphere 57近程分子内相互作用short-range intramolecular interaction 58远程分子内相互作用long-range intramolecular interaction 59链间相互作用interchain interaction60链间距interchain spacing61长程有序long range order62近程有序short range order63回转半径radius of gyration64末端间矢量end-to-end vector65链末端chain end66末端距end-to-end distance67无扰末端距unperturbed end-to-end distance68均方根末端距root-mean-square end-to-end distance 69伸直长度contour length70相关长度persistence length71主链;链骨架chain backbone72支链branch chain73链支化chain branching74短支链short-chain branch75长支链long-chain branch76支化系数branching index77支化密度branching density78支化度degree of branching79交联度degree of crosslinking80网络network81网络密度network density82溶胀swelling83平衡溶胀equilibrium swelling84分子组装,分子组合molecular assembly85自组装self assembly86微凝胶microgel87凝胶点gel point88可逆[性]凝胶reversible gel89溶胶-凝胶转化sol-gel transformation90临界胶束浓度critical micelle concentration,CMC91组成非均一性constitutional heterogenity, compositionalheterogenity92摩尔质量平均molar mass average 又称“分子量平均”93数均分子量number-average molecular weight,number-average molar mass94重均分子量weight-average molecular weight,weight-average molar mass95Z均分子量Z(Zaverage)-average molecular weight,Z-molar mass96黏均分子量viscosity-average molecular weight,viscosity-average molar mass97表观摩尔质量apparent molar mass98表观分子量apparent molecular weight99聚合度degree of polymerization100动力学链长kinetic chain length101单分散性monodispersity102临界分子量critical molecular weight103分子量分布molecular weight distribution,MWD104多分散性指数polydispersity index,PID105平均聚合度average degree of polymerization106质量分布函数mass distribution function107数量分布函数number distribution function108重量分布函数weight distribution function109舒尔茨-齐姆分布Schulz-Zimm distribution110最概然分布most probable distribution 曾用名“最可几分布”111对数正态分布logarithmic normal distribution 又称“对数正则分布”112聚合物溶液polymer solution113聚合物-溶剂相互作用polymer-solvent interaction114溶剂热力学性质thermodynamic quality of solvent115均方末端距mean square end to end distance116均方旋转半径mean square radius of gyration117θ温度theta temperature118θ态theta state119θ溶剂theta solvent120良溶剂good solvent121不良溶剂poor solvent122位力系数Virial coefficient 曾用名“维里系数”123排除体积excluded volume124溶胀因子expansion factor125溶胀度degree of swelling126弗洛里-哈金斯理论Flory-Huggins theory127哈金斯公式Huggins equation128哈金斯系数Huggins coefficient129χ(相互作用)参数χ-parameter130溶度参数solubility parameter131摩擦系数frictional coefficient132流体力学等效球hydrodynamically equivalent sphere133流体力学体积hydrodynamic volume134珠-棒模型bead-rod model135球-簧链模型ball-spring [chain] model136流动双折射flow birefringence, streaming birefringence 137动态光散射dynamic light scattering138小角激光光散射low angle laser light scattering139沉降平衡sedimentation equilibrium140沉降系数sedimentation coefficient141沉降速度法sedimentation velocity method142沉降平衡法sedimentation equilibrium method143相对黏度relative viscosity144相对黏度增量relative viscosity increment145黏度比viscosity ratio146黏数viscosity number147[乌氏]稀释黏度计[Ubbelohde] dilution viscometer148毛细管黏度计capillary viscometer149落球黏度计ball viscometer150落球黏度ball viscosity151本体黏度bulk viscosity152比浓黏度reduced viscosity153比浓对数黏度inherent viscosity, logarithmic viscositynumber154特性黏数intrinsic viscosity, limiting viscosity number 155黏度函数viscosity function156零切变速率黏度zero shear viscosity157端基分析analysis of end group158蒸气压渗透法vapor pressure osmometry, VPO159辐射的相干弹性散射coherent elastic scattering of radiation160折光指数增量refractive index increment161瑞利比Rayleigh ratio162超瑞利比excess Rayleigh ratio163粒子散射函数particle scattering function164粒子散射因子particle scattering factor165齐姆图Zimm plot166散射的非对称性dissymmetry of scattering167解偏振作用depolarization168分级fractionation169沉淀分级precipitation fractionation170萃取分级extraction fractionation171色谱分级chromatographic fractionation172柱分级column fractionation173洗脱分级,淋洗分级elution fractionation174热分级thermal fractionation175凝胶色谱法gel chromatography176摩尔质量排除极限molar mass exclusion limit177溶剂梯度洗脱色谱法solvent gradient [elution] chromatography 178分子量排除极限molecular weight exclusion limit179洗脱体积elution volume180普适标定universal calibration181加宽函数spreading function182链轴chain axis183等同周期identity period184链重复距离chain repeating distance185晶体折叠周期crystalline fold period186构象重复单元conformational repeating unit187几何等效geometrical equivalence188螺旋链helix chain189构型无序configurational disorder190链取向无序chain orientational disorder191构象无序conformational disorder192锯齿链zigzag chain193双[股]螺旋double stranded helix194[分子]链大尺度取向global chain orientation195结晶聚合物crystalline polymer196半结晶聚合物semi-crystalline polymer197高分子晶体polymer crystal198高分子微晶polymer crystallite199结晶度degree of crystallinity, crystallinity200高分子[异质]同晶现象macromolecular isomorphism201聚合物形态学morphology of polymer202片晶lamella, lamellar crystal203轴晶axialite204树枝[状]晶体dendrite205纤维晶fibrous crystal206串晶结构shish-kebab structure 207球晶spherulite208折叠链folded chain209链折叠chain folding210折叠表面fold surface211折叠面fold plane212折叠微区fold domain213相邻再入模型adjacent re-entry model 214接线板模型switchboard model215缨状微束模型fringed-micelle model 216折叠链晶体folded-chain crystal 217平行链晶体parallel-chain crystal 218伸展链晶体extended-chain crystal 219球状链晶体globular-chain crystal 220长周期long period221近程结构short-range structure 222远程结构long-range structure 223成核作用nucleation224分子成核作用molecular nucleation 225阿夫拉米方程Avrami equation226主结晶primary crystallization 227后期结晶secondary crystallization 228外延结晶,附生结晶epitaxial crystallizationepitaxial growth229外延晶体生长,附生晶体生长230织构texture231液晶态liquid crystal state232溶致性液晶lyotopic liquid crystal233热致性液晶thermotropic liquid crystal234热致性介晶thermotropic mesomorphism235近晶相液晶smectic liquid crystal236近晶中介相smectic mesophase237近晶相smectic phase238条带织构banded texture239环带球晶ringed spherulite240向列相nematic phase241盘状相discotic phase242解取向disorientation243分聚segregation244非晶相amorphous phase 曾用名“无定形相”245非晶区amorphous region246非晶态amorphous state247非晶取向amorphous orientation248链段运动segmental motion249亚稳态metastable state250相分离phase separation251亚稳相分离spinodal decomposition252bimodal decomposition253微相microphase254界面相boundary phase255相容性compatibility256混容性miscibility257不相容性incompatibility258不混容性immiscibility259增容作用compatiibilizationlower critical solution temperature, LCST 260最低临界共溶(溶解)温度upper critical solution temperature , UCST 261最高临界共溶(溶解)温度262浓度猝灭concentration quenching263激基缔合物荧光excimer fluorescence264激基复合物荧光exciplex fluorescence265激光共聚焦荧光显微镜laser confocal fluorescence microscopy 266单轴取向uniaxial orientation267双轴取向biaxial orientation, biorientation268取向度degree of orientation269橡胶态rubber state270玻璃态glassy state271高弹态elastomeric state272黏流态viscous flow state273伸长elongation274高弹形变high elastic deformation275回缩性,弹性复原nerviness276拉伸比draw ratio, extension ratio277泊松比Poisson's ratio278杨氏模量Young's modulus279本体模量bulk modulus280剪切模量shear modulus281法向应力normal stress282剪切应力shear stress283剪切应变shear strain284屈服yielding285颈缩现象necking 又称“细颈现象”286屈服应力yield stress287屈服应变yield strain288脆性断裂brittle fracture289脆性开裂brittle cracking290脆-韧转变brittle ductile transition291脆化温度brittleness(brittle) temperature292延性破裂ductile fracture293冲击强度impact strength294拉伸强度tensile strength 又称“断裂强度,breaking strength”295极限拉伸强度ultimate tensile strength296抗撕强度tearing strength 又称“抗扯强度”297弯曲强度flexural strength, bending strength298弯曲模量bending modulus299弯曲应变bending strain300弯曲应力bending stress301收缩开裂shrinkage crack302剪切强度shear strength303剥离强度peeling strength304疲劳强度fatigue strength, fatigue resistance305挠曲deflection306压缩强度compressive strength307压缩永久变形compression set308压缩变形compressive deformation309压痕硬度indentation hardness310洛氏硬度Rockwell hardness311布氏硬度Brinell hardness312抗刮性scrath resistance313断裂力学fracture mechanics314力学破坏mechanical failure315应力强度因子stress intensity factor316断裂伸长elongation at break317屈服强度yield strength318断裂韧性fracture toughness319弹性形变elastic deformation320弹性滞后elastic hysteresis321弹性elasticity322弹性模量modulus of elasticity323弹性回复elastic recovery324不可回复形变irrecoverable deformation325裂缝crack 俗称“龟裂”326银纹craze327形变;变形deformation328永久变形deformation set329剩余变形residual deformation330剩余伸长residual stretch331回弹,回弹性resilience332延迟形变retarded deformation333延迟弹性retarded elasticity334可逆形变reversible deformation335应力开裂stress cracking336应力-应变曲线stress strain curve337拉伸应变stretching strain338拉伸应力弛豫tensile stress relaxation339热历史thermal history340热收缩thermoshrinking341扭辫分析torsional braid analysis,TBA 342应力致白stress whitening343应变能strain energy344应变张量strain tensor345剩余应力residual stress346应变硬化strain hardening347应变软化strain softening348电流变液electrorheological fluid349假塑性pseudoplastic350拉胀性auxiticity351牛顿流体Newtonian fluid352非牛顿流体non-Newtonian fluid353宾汉姆流体Bingham fluid354冷流cold flow355牛顿剪切黏度Newtonian shear viscosity 356剪切黏度shear viscosity357表观剪切黏度apparent shear viscosity358剪切变稀shear thinning359触变性thixotropy360塑性形变plastic deformation361塑性流动plastic flow362体积弛豫volume relaxation363拉伸黏度extensional viscosity364黏弹性viscoelasticity365线性黏弹性linear viscoelasticity366非线性黏弹性non-linear viscoelasticity367蠕变creep368弛豫[作用] relaxation 又称“松弛”369弛豫模量relaxation modulus370蠕变柔量creep compliance371热畸变温度heat distortion temperature372弛豫谱relaxation spectrum373推迟[时间]谱retardation [time] spectrum374弛豫时间relaxation time375推迟时间retardation time376动态力学行为dynamic mechanical behavior377动态黏弹性dynamic viscoelasticity378热-机械曲线thermo-mechanical curve379动态转变dynamic transition380储能模量storage modulus381损耗模量loss modulus382复数模量complex modulus383复数柔量complex compliance384动态黏度dynamic viscosity385复数黏度complex viscosity386复数介电常数complex dielectric permittivity387介电损耗因子dielectric dissipation factor388介电损耗常数dielectric loss constant389介电弛豫时间dielectric relaxation time390玻璃化转变glass transition391玻璃化转变温度glass-transition temperature。

复合材料英语词汇复合材料是由两种或多种不同的材料组成的新型材料,具有优异的力学性能和功能性能。
复合材料在航空航天、汽车、建筑、医疗等领域有广泛的应用。
为了更好地了解和学习复合材料,我们需要掌握一些与之相关的英语词汇。
本文将介绍一些常用的复合材料英语词汇,并给出中英文对照表和例句。
一、复合材料的分类复合材料可以根据不同的标准进行分类,例如根据基体材料的类型、增强材料的形态、界面结构等。
下面是一些常见的复合材料分类的英语词汇:中文英文例句金属基复合材料Metal matrixcomposites (MMCs)金属基复合材料是由金属或合金作为基体,与陶瓷、金属或碳纤维等作为增强相组成的复合材料。
Metalmatrix composites are composites consisting of a metal or alloy as the matrix and ceramics, metals orcarbon fibers as the reinforcement phase.陶瓷基复合材料Ceramic matrixcomposites (CMCs)陶瓷基复合材料是由陶瓷或碳作为基体,与陶瓷、金属或碳纤维等作为增强相组成的复合材料。
Ceramicmatrix composites are composites consisting of ceramics or carbon as the matrix and ceramics, metals orcarbon fibers as the reinforcement phase.树脂基复合材料Resin matrixcomposites (RMCs)树脂基复合材料是由树脂(如环氧树脂、聚酯树脂等)作为基体,与玻璃纤维、碳纤维、芳纶纤维等作为增强相组成的复合材料。
Resin matrix composites are composites consisting of resin (such as epoxy resin,polyester resin, etc.) as the matrix and glass fiber, carbon fiber, aramid fiber, etc. as the reinforcementphase.碳-碳复合材料Carbon-carboncomposites (C/C)碳-碳复合材料是由碳素纤维作为增强相,经过高温处理后与碳素基体结合而成的复合材料。
Family of Materials 材料家族Today, we are introducing the Family of Materials。
We are living in a world of materials. With so many materials, how can we understand them? The method used here is to consider all materials as members of a big family. The family is composed of four basic groups, which are metals, ceramics, polymers and composites. Each of the groups posses common characteristics.译文:今天我们来介绍材料家族。
我们生活在材料的世界里。
对于身边这么多的材料,我们如何了解它们呢?今天我们这里介绍的是把所有材料看成一个大家庭。
这个大家庭包括四类材料,它们是金属材料,陶瓷材料,聚合物材料和复合材料。
每一类材料都有他们的共性,我们将在下面逐一介绍.Metals金属材料Metals comprise about three-fourths of the elements that we use, they are the earliest materials used by man. Simply, metallic are broken into subgroups of ferrous and nonferrous metals. Ferrous is a Latin-based word meaning “iron”,including iron, steel, stainless steel. Metal elements other than iron are called non-ferrous metal, include aluminum, copper, magnesium, nickel, titanium,and precious metals, such as gold, silver, palladium,platinium,etc. In nature, few metals find service in their pure form, but in alloy form. So,the word “Metal Alloys” consist of one or more metallic elements, and nonmetallic elements in relatively small amounts, such as carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. We will introduce the metallic materials in chapter 4.译文:金属元素在元素周期表里占了四分之三,是最早被人类制造和利用的材料。
Acetyl||乙酰Acid-proof paint||耐酸涂料, 耐酸油漆Acrylic fiber||丙烯酸纤维Acrylic resin||丙烯酸树脂Active filler||活性填料Adapter assembly||接头组件Addition polyimide||加成型聚酰亚胺Addition polymer||加聚物Adjusting valve||调整阀,调节阀Adhersion assembly||粘合装配Adhersion bond||胶结Adjustable-bed press||工作台可调式压力机Adjuster shim||调整垫片Adjusting accuracy||调整精度,调校精度Admissible error||容许误差Admissible load||容许载荷Adsorbed layer||吸附层Advanced composite material||先进复合材料,高级复合材料Advanced development vehicle||试制车,预研样车AE(Automobile Engineering)||汽车工程技术Aeolotropic material||各向异性材料Aerated plastics||泡沫塑料, 多孔塑料Aerodynamic body||流线型车身Aft cross member||底盘/车架后横梁Air bleeder||排气孔Air clamp||气动夹具Air deflector||导流板;导风板,气流偏转板Air intake manifold||进气歧管Air servo||伺服气泵Air-tight joint||气密接头All-plastic molded||全塑模注的All polyster seat||全聚酯座椅Alligatoring||龟裂,涂膜皱皮,表面裂痕Amino resin||氨基树脂Angular test||挠曲试验Anti-chipping primer||抗破裂底漆(底层涂料)Apron||防护挡板Aramid fibre composites||芳胺纤维复合材料Assembly drawing||装配图Assembly jig||装配夹具Assembly part||装配件,组合件Autoclave forming||热压罐成型Autocorrection||自动校正Automatic compensation||自动补偿Automatic feed||自动进料Automobile instrument||汽车仪表板Automotive transmission||汽车传动装置,汽车变速器Auxiliary fasia console||副仪表板Axial strain||轴向应变Axle bushing||轴衬Axle fairing||底盘车桥整流罩A Stage||A 阶段(某些热固性树脂聚合作用的初期阶段)AAC(Auxiliary Air Control)||辅助空气控制ABC(Active Body Control)||主动式车身控制装置Abherent||阻粘剂Ability meter||测力计,性能测试仪ABL (Ablative)||烧蚀剂Ablation||烧蚀Ablative composite material||烧蚀复合材料Ablative insulative material||烧蚀绝热材料Ablative polymer||烧蚀聚合物Ablative prepreg||烧蚀性预浸料Ablative resistance||耐烧蚀性ABR(Acrylate Butadience Rubber)||丙烯酸丁二烯橡胶Abradant material||研磨材料,磨料Abrade||研磨;用喷砂清理Abrasion||磨耗Abrasion coefficient||磨耗系数Abrasion loss||磨耗量,磨损量Abrasion performance||磨耗性Abrasion-proof material||耐磨材料Abrasion resistant paint||耐磨涂料Abrasion test||磨损试验Abrasive blast system||喷砂清理系统Abrasive cloth||砂布Abrasive disc||砂轮盘,砂轮片Abrasive finishing||抛光Abrasive paper||砂纸Abrasive resistance||耐磨性ABS(Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)resin||ABS树脂,丙烯腈-丁二烯-苯乙烯(热塑性)树脂ABSM(American Bureau of Standard Materials)||美国标准材料局Absolute dynamic modulus||绝对动态模量Absolute error||绝对误差Absorbent material||吸收性材料,吸收性物质,吸声材料,吸收剂Absorber||减振器,阻尼器,缓冲器ACA(Automotive Composite Alliance)||汽车复合材料协会ACC(Automatic Clutch Control)||自动离合器操纵控制Accelerant||促进剂,加速剂Accelerated aging test||加速老化试验,人工老化试验Accelerator pedal shaft||加速踏板轴Accelerator pump nozzle||加速泵喷嘴Acceptable life||有效使用寿命Acceptance test specification||验收测试规范Access panel||罩板,盖板Accessory||配件,附属品Accessory equipment||辅助设备Accessory kit||附件包,成套附件Accumulator can||储电池外壳Accumulator package||蓄压器组件,蓄压器单元Accuracy in calibration||校准精度Accuracy of finish||最终加工精度Accuracy of manufacture||制造精度Accuracy of positioning||定位精度Accuracy of repetition||重现精度,复制精度此资源来自:由FanE『翻译中国』http;//整理。
unit1all polymers are built up from bonding together a single kind of repeating unit. At the other extreme ,protein molecules are polyamides in which n amino acide repeat units are bonded together. Although we might still call n the degree of polymerization in this case, it is less usefull,since an amino acid unit might be any one of some 20-odd molecules that are found in proteins. In this case the molecular weight itself,rather than the degree of the polymerization ,is generally used to describe the molecule. When the actual content of individual amino acids is known,it is their sequence that is of special interest to biochemists and molecular biologists.并不是所有的聚合物都是由一个重复单元链接在一起而形成的;在另一个极端的情形中,蛋白质分子是由n个氨基酸重复单元链接在一起形成的聚酰胺;尽管在这个例子中,我们也许仍然把n称为聚合度,但是没有意义,因为一个氨基酸单元也许是在蛋白质中找到的20多个分子中的任意一个;在这种情况下,一般是分子量本身而不是聚合度被用来描述这个分子;当知道了特定的氨基酸分子的实际含量,它们的序列正是生物化学家和分子生物学家特别感兴趣的地方;1,题目:Another striking ...答案:.that quantity low saturation bottom much absorb 2. 乙烯分子带有一个双键,为一种烯烃,它可以通过连锁聚合大量地制造聚乙烯,目前,聚乙烯已经广泛应用于许多技术领域和人们的日常生活中,成为一种不可缺少的材料;Ethylene molecule with a double bond, as a kind of olefins, it can make chain polymerization polyethylene, at present, polyethylene has been widely used in many fields of technology and People's Daily life, become a kind of indispensable materials.Unit31 The polymerization rate may be experimentally followed by measuring the changes in any of several properties of the system such as density,refractive index,viscosity, or light absorption. Density measurements are among the most accurate and sensitive of the techniques. The density increases by 20-25 percent on polymerization for many monomers. In actual practice the volume of the polymerizing system is measured by carrying out the reaction in a dilatometer. This is specially constructed vessel with a capillary tube which allows a highly accurate measurement of small volume changes. It is not uncommon to be able to detect a few hundredths of a percent polymerization by the dilatometer technique. 聚合速率在实验上可以通过测定体系的任一性质的变化而确定,如密度、折射率、黏度、或者吸光性能;密度的测量是这些技术中最准确最敏感的;对许多单体的聚合来说,密度增加了20%-25%;在实际操作中,聚合体系的体积是通过在膨胀计中进行反应测定的;它被专门设计构造了毛细导管,在里面可以对微小体积变化进行高精确度测量;通过膨胀计技术探测聚合过程中万分之几的变化是很常见的;Unti42 合成聚合物在各个领域中起着与日俱增的重要作用,聚合物通常是由单体通过加成聚合与缩合聚合制成的;就世界上的消耗量而论,聚烯烃和乙烯基聚合物居领先地位,聚乙烯、聚丙烯等属聚烯烃,而聚氯乙烯、聚苯乙烯等则为乙烯基聚合物;聚合物可广泛地用作塑料、橡胶、纤维、涂料、粘合剂等The synthetic polymers play an increasingly important role on a range of domains, which are synthesized by monomers through addition polymerization or condensation polymerization. Polyolefin and vinyl polymer have taken the lead in terms of the world consumption. PE, PP, etc. belong to the polyolefin, while PS, PVC etc. belong to the vinyl polymer. Polymers can be widely applied in plastics, rubbers, fibers, coatings, glues and so on.Unit7Ring-opening polymerizations proceed only by ionic mechanisms, the polymerization of cyclic ethers mainly by cationic mechanisms, and the polymerization of lactones andlactones by either a cationic or anionic mechanism. Important initiators for cyclic ethers and lactone polymerization are those derived from aluminum alkyl and zinc alkyl/water systems. It should be pointed out that substitution near the reactive group of the monomer is essential for the individual mechanism that operates effectively in specific cases; for example, epoxides polymerize readily with cationic and anionic initiators, while fluorocarbon epoxides polymerize exclusively by anionic mechanisms.开环聚合反应只能通过离子机理进行,环醚的开环聚合主要通过阳离子机理,而内酯和内酰胺的聚合物是通过阳离子或阴离子机理;对于环醚和内酯型聚合物很重要的引发剂是那些来自于烷基铝和烷基锌/水的体系;应该指出的是对于在活性基团附近有取代的单体,只能由单一机理,这一机理是在特定条件下的有效;1 Polymers can be classified into two main groups, addition polymers and ___condensation__ polymers. This classification is based on whether or not the repeating unit of the polymer contains the same atoms __as____ the monomer. The repeating unit of an addition polymer is identical _with/to____ the monomer, while condensation polymers contain __different/less___ because of formation of __compound/byproduct___ during the polymerization process. The corresponding polymerization processed would then be called addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. As was mentioned earlier, this classification can result ___in__ confusion, since it has been shown in later years that many important types of polymers can be _prepared by both addition and condensation processes. For example, polyesters, polyamides and polyurethanes are usually considered to be _condensation____ polymers, but they can be prepared by addition as well as by condensation reaction. Similarly, polyethylene normally considered an _addition_ polymer, can also be prepared by _condensation_ reaction.2. Answer the following questions in English1 What is chain polymerization Manyolefinicandvinylunsaturatedcompoundsareabletoformchain-likemacromoleculesthrougheliminationofdoublebond.2 Which kinds of monomers can carry out step-growth polymerization processThere are two kinds of monomers could carry out step-growth polymerization process. One ispolyfunctionalmonomers and the other isasinglemonomercontainingbothtypesoffunctional groups.3 What properties of polymers can be based on for measuring the molecular weightThe molecular weight of polymer could be measured based on colligativeproperties, lightscattering, viscosity, ultracentrifugation sedimentation.3. Please write out at least 10 kinds of polymers both in English and in Chinesethe corresponging chemical structure5 In general,head-to-tail addition is considered to be the predominant mode of propagation in all polymerizations;However,when the substitutes on the monomer are small and do not offer appreciable steric hindrance to the approaching radical or do not have a large resonance stabilizing effect,as in the case of fluorine atoms,sizable amounts of head-to-head propagation may occur. The effect of increasing polymerization temperature is to increase the amount of head-to-head placement;Increased temperature leads to less selective more random propagation but the effect is not large. Thus,the head-to-head content in poly vinyl acetate only increases from to percent when the polymerization temperature in increased from 30 to 90 ℃.通常在所有聚合物的链增长中,头-尾加成是主要方式;然而,当单体中的取代基很小对接近的自由基没有空间阻碍或没有较大的共振稳定作用,如氟原子,则有相当量的头头增长发生;提高聚合温度的影响是提高头-头排列的量;温度的提高导致较少的选择更多的无规增长,但影响不大;因而,在聚乙酸乙烯酯中,当聚合温度由30C提高到90C,头-头含量仅由%提高到%;2.Write out an abstract in English for the text in this unitPolymers with different structures present various properties. Usually, polymers are divided into three categories, . plastic, elastomer, fiber with different initial modulus range respectively. Polymers show quite different behaviors due to the different interchain forces in elastomer and fiber. However, with the advent of new techniques and mechanisms to improve the structure of polymers, polymers may be classified and named according to the mechanism, and their properties will largely depend on the structure. 3.Put the following words into Chineseentanglement 纠缠 irregularity 无规 sodium isopropylate异丙醇钠 permeability渗透性crystallite 微晶stoichiomertric balance 当量平衡fractionation分馏法light scattering光散射 matrix 基体 diffraction衍射4.Put the following words into English形态 morphology 酯化 esterification 异氰酸酯isocyanate杂质impurity 二元胺 diamine 转化率change ratio 多分散性polydispersity 力学性能mechanical property 构象conformation 红外光谱法infrared spectroscopy常见聚合物命名1常见杂链和元素有机聚合物类型Polyamide ----聚酰胺. Polyester----聚酯 Poly‘urethane ------聚氨酯 Polysiloxane -------聚硅氧烷Phenol-formaldehyde----酚醛.Urea-formaldehyde-----脲醛Polyureas------聚脲 Polysulfide -----聚硫Polyacetal-------聚缩醛 Polysulfone polysulphone------聚砜 Polyether---------聚醚第五单元Traditional methods of living polymerization are based on ionic, coordination or group transfer mechanisms.活性聚合的传统方法是基于离子,配位或基团转移机理;Ideally, the mechanism of living polymerization involves only initiation and propagation steps.理论上活性聚合的机理只包括引发和增长反应步骤;All chains are initiated at the commencement of polymerization and propagation continues until all monomer is consumed.在聚合反应初期所有的链都被引发,然后增长反应继续下去直到所有的单体都被消耗殆尽;A type of novel techniques for living polymerization, known as living possibly use “controlled” or “mediated” radical polymerization, is developed recently. 最近开发了一种叫做活性自由基聚合的活性聚合新技术;The first demonstration of living radical polymerization and the current definition of the processes can be attributed to Szwarc.第一个活性自由基聚合的证实及目前对这一过程的解释或定义,应该归功于Szwarc;Up to now, several living radical polymerization processes, including atom transfer radical polymerization ATRP, reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization RAFT, nitroxide-mediated polymerization NMP, etc., have been reported one after another.到目前为止,一些活性自由基聚合过程,包括原子转移自由基聚合,可逆加成-断裂链转移聚合,硝基氧介导聚合等聚合过程一个接一个被报道;The mechanism of living radical polymerization is quite different not only from that of common radical polymerization but also from that of traditional living polymerization. 活性自由基聚合的机理不仅完全不同于普通自由基聚合机理,也不同于传统的活性聚合机理;It relies on the introduction of a reagent that undergoes reversible termination with the propagating radicals thereby converting them to a following dormant form:活性自由基聚合依赖于向体系中引入一种可以和增长自由基进行可逆终止的试剂,形成休眠种:The specificity in the reversible initiation-termination step is of critical importance in achieving living characteristics.这种特殊的可逆引发-终止反应对于获得分子链活性来说具有决定性的重要意义;This enables the active species concentration to be controlled and thus allows such a condition to be chosen that all chains are able to grow at a similar rate if not simultaneously throughout the polymrization.可逆引发终止使活性中心的浓度能够得以控制;这样就可以来选择适宜的反应条件,使得在整个聚合反应过程中只要没有平行反应所有的分子链都能够以相同的速度增长;This has, in turn, enabled the synthesis of polymers with controlled composition, architecture and molecular weight distribution.这样就可以合成具有可控组成,结构和分子量分布的聚合物;They also provide routes to narrow dispersity end-functional polymers, to high purity block copolymers, and to stars and other more complex architecture.这些还可以提供获得狭窄分布末端功能化聚合物,高纯嵌段共聚物,星型及更复杂结构高分子的合成方法;The first step towards living radical polymerization was taken by Ostu and his colleagues in 1982.活性自由基聚合是Ostu和他的同事于1982年率先开展的;In 1985, this was taken one step further with the development by Solomon et al. of nitroxide-mediated polymerization NMP.1985年,Solomon等对氮氧化物稳定自由基聚合的研究使活性自由基聚合进一步发展;This work was first reported in the patent literature and in conference papers but was not widely recognized until 1993 when Georges et al. applied the method in the synthesis of narrow polydispersity polystyrene.这种方法首先在专利文献和会议论文中报道,但是直到1993年Georges等把这种方法应用在窄分子量分布聚苯乙烯之后,才得以广泛认知;The scope of NMP has been greatly expended and new, more versatile, methods have appeared. NMP的领域已经得到很大的延展,出现了新的更多样化的方法;The most notable methods are atom transfer radical polymerization ATRP and polymerization with reversible addition fragmentation RAFT.最引人注目的方法是原子转移自由基聚合和可逆加成断裂聚合;到2000年,这个领域的论文已经占所有自由基聚合领域论文的三分之一;如图所示;Naturally, the rapid growth of the number of the papers in the field since 1995 ought to be almost totally attributable to development in this area. 、自然地,纸的数量的迅速增长在领域,因为1995在这个区域应该是几乎完全可归属的到发展;UNIT9 Structure and Properties of Polymers 聚合物的结构和性质Most conveniently, polymers are generally subdivided in three categories, namelyviz., plastics, rubbers and fibers. 很方便地,聚合物一般细分为三种类型,就是塑料,橡胶和纤维; In terms of initial elastic modules, rubbers ranging generally between 106 to 107dynes/cm2, represent the lower end of the scale, while fibers with high initial modjulai, of 1010 to 1011dynes/cm2 are situated on the upper end of the scale; plastics, having generally an initial elastic modulus of 108 to 109dynes/cm2, lie in-between. 就初始弹性模量而言,橡胶一般在 6到107达因平方厘米,在尺度的低端, 10到1011达因平方厘米,尺度的高端,而纤维具有高的初始模量, 达到10到1011达因平方厘米,尺度的高端,塑料的弹性模量一般在 8到109达因平方厘米,在尺度的中间As is found in all phases of polymer chemistry, there are many exceptions to this categorization. 正如高分子化学的各个部分都可以看到的那样,在高分子化学的所有阶段,我们都可以发现,这种分类方法有许多例外的情况;An elastomer or rubber results from a polymer having relatively weak interchain forces and high molecular weights. 弹性体是具有相对弱的链之间作用力和高分子量的聚合物; When the molecular chains are “straightened out” or stretched by a process of extension, they do not have sufficient attraction for each other to maintain the oriented state and will retract once the force is released. This is the basis of elastic behavior. 当通过一个拉伸过程将分子链拉直的时候,分子链彼此之间没有足够的相互吸引力来保持其取向状态,作用力一旦解除,将发生收缩;这是弹性行为的基础;However, if the interchain forces are very great, a polymer will make a good fiber. 然而,如果分子链之间的力非常大,聚合物可以用做纤维;Therefore, when the polymer is highly stretched, the oriented chain will come under the influence of the powerful attractive forces and will “crystallize” permanently in a more or less oriented matrix. 因此,当聚合物被高度拉直的时候,取向分子链在不同程度取向的母体中将受强引力的影响而“永久地结晶;These crystallization forces will then act virtually as crosslinks, resulting in a material of high tensile strength and high initial modulus, ., a fiber. 而后,这些结晶力实际上以交联方式作用,产生高拉伸强度和高初始模量的材料,如纤维;Therefore, a potential fiber polymer will not become a fiber unless subjected to a “drawing” process, ., a process resulting in a high degree of intermolecular orientation. 因此,一个可能的潜在的纤维高分子不会变成纤维,除非经历一个拉伸过程, 即, 这导致分子间高度取向的拉伸过程;Crosslinked species are found in all three categories and the process of crosslinking may change the cited characteristics of the categories. 交联的种类在所有三种类型塑料,橡胶,纤维中找到,而交联过程可以改变分类的引用特征;Thus, plastics are known to possesspzes a marked range of deformability in the order of 100 to 200%; they do not exhibit this property when crosslinked, however. 因此,我们熟知塑料具有的形变能力大约在100-200%范围内,然而当交联发生时塑料不能展示这个性能; Rubber, on vulcanization, changes its properties from low modulus, low tensile strength, low hardness, and high elongation to high modulus, high tensile strength, high hardness, and low elongation. 对橡胶而言,硫化可以改变其性质,从低模量,低拉伸强度,低硬度及高拉伸率到高模量,高拉伸强度,高硬度及低拉伸率;Thus, polymers may be classified as noncrosslinked and crosslinked, and this definition agrees generally with the subclassification in thermoplastic and thermoset polymers. 这样,聚合物可以分为非交联和交联的,这个定义与把聚合物细分为热塑性和热固性聚合物相一致; From the mechanistic point of view, however, polymers are properly divided into addition polymers and condensation polymers. Both of these species are found in rubbers, plastics, and fibers. 然而,从反应机理的观点看,聚合物可以分成加聚物和缩聚物;这些种类聚合物在塑料,橡胶和纤维中都可以找得到;In many cases polymers are considered from the mechanistic point of view. Also, the polymer will be named according to its source whenever it is derived from a specific hypothetical monomer, or when it is derived from two or more components which are built randomly into the polymer. 在许多情况下,聚合物可以从反应机理的角度考虑分类; 每当聚合物来自于一个假象单体,或来自于两个或两个以上组成物无规则构建聚合物时,也可以根据聚合物的来源来命名; This classification agrees well with the presently used general practice. 这种分类方法与目前实际情况相符合;When the repeating unit is composed of several monomeric components following each other in a regular fashion, the polymer is commonly named according to its structure. 当重复单元由几个单体组成物规则排布,聚合物通常根据它的结构来命名;It must be borne in mind that, with the advent of Ziegler-Natta mechanisms and new techniques to improve and extend crystallinity, and the closeness of packing of chains, many older data given should be critically considered in relation to the stereoregular and crystalline structure. 必须记住,随着Ziegler-Natta机理,以及提高结晶度和链堆砌紧密度新技术的出现,对许多过去已经得到的关于空间结构和晶体结构旧的资料,应当批判地接受;The properties of polymers are largely dependent on the type and extent of both stereoregularity and crystallinity. As an example, the densities and melting points of atactic and isotactic species are presented in Table . 聚合物的性质主要依靠立体规整性和结晶度的类型和程度;如,无规立构和全同立构物质的密度和熔点展示在表中 ;UNIT11 Functional PolymersFunctional polymers are macromolecules to which chemically functional groups are attached; they have the potential advantages of small molecules with the same functional groups. 功能聚合物是具有化学功能基团的大分子,这些聚合物与具有功能聚合物是具有化学功能基团的大分子, 相同功能基团的小分子一样具有潜在的优点;Their usefulness is related both to the functional groups and to the nature of the polymers whose characteristic properties depend mainly on the extraordinarily large size of the molecules.它们的实用性不仅与功能基团有关,而且与巨大分子尺寸带来的聚合物特性有关;The attachment of functional groups to a polymer is frequently the first step towards the preparation of a functional polymer for a specific use. 把功能基团连接到聚合物上常常是制备特殊用途功能高分子的第一步;However, the proper choice of the polymer is an important factor for successful application. 然而,对成功应用而言,选择适当的聚合物是的一个重要因素;In addition to the synthetic aliphatic and aromatic polymers, a wide range of natural polymers have also been functionalized and used as reactive materials. 除了合成的脂肪组和芳香组聚合物之外,许多天然高分子也被功能化,被用做反应性材料;Inorganic polymers have also been modified with reactive functional groups and used in processes requiring severesi’vi service conditions. 无机聚合物也已经用反应功能基团改性,被用于要求耐用条件的场合;In principle, the active groups may be part of the polymer backbone or linked to a side chain as a pendant group either directly or viavai a space rs’peis group. 理论上讲,活性基团可以是聚合物主链上的一部分,或者直接连接到侧链或通过一个中间基团的侧基;A required active functional group can be introduced onto a polymeric support chain 1 by incorporation during the synthesis of the support itself through polymerization or copolymerization of monomers containing the desired functional groups, 2 by chemical modification of a nonfunctionalized performed support matrix and 3 by a combination of 1 and 2. 所需的活性功能基团可以通过几种方法引入到聚合物主链上, 1在主链的合成过程中,通过聚合或共聚合含有理想功能基团的单体来获得,2通过对已有的非功能化主链进行化学改性的方法,3通过结合1和2来获得;Each of the two approaches has its own advantages and disadvantages, and one approach may be preferred for the preparation of a particular functional polymer when the other would be totally impractical.两种途径中的每一种都有自身的优点和缺点,对特殊功能聚合物的制备而言,当其他方法都无法实现时,所选的方法或许是更合适的;The choice between the two ways to the synthesis of functionalized polymers depends mainly on the required chemical and physical properties of the support for a specific application. 功能聚合物合成的两种方法中,如何选择主要取决于特殊应用要求的主链聚合物的化学和物理性质;Usually the requirements of the individual system must be thoroughly examined in order to take full advantage of each of the preparative techniques. 为了充分利用每种制备方法,必须全面地考察独立体系的要求;Rapid progress in the utilization of functionalized polymeric materials has been noted in the recent past. 近年来,功能化聚合物材料的使用方面有了飞速的发展;Interest in the field is being enhanced due to the possibility of creating systems that combine the unique properties of conventional active moieties and those of high molecular weight polymers. 由于能够制造出来兼有活性官能团特性和高分子量聚合物性能的功能聚合物,所以,人们对功能聚合物这个领域的兴趣与日俱增;The successful utilization of these polymers are based on the physical form, solution behavior, porosity, chemical reactivity and stability of the polymers. 这些聚合物的成功利用,基于功能聚合物的物理形态,溶液行为,空隙率,化学活性及稳定性;The various types of functionalized polymers cover a broad range of chemical applications, including the polymeric reactants, catalysts, carriers, surfactants, stabilizers,ionexchange resins, etc.各种功能化聚合物类型覆盖化学应用的宽广领域,包括聚合物试剂,催化剂, 载体,表面活性剂,稳定剂,离子交换树脂等;In a variety of biological and biomedical fields, such as the pharmaceutical, agriculture, food industry and the like, they have become indispensable materials, especially in controlled release formulation of drugs and agrochemicals. 在生物学及生物医学领域中,如药物,农业,食品工业等, 在生物学及生物医学领域中,如药物,农业,食品工业等,功能聚合物是不可缺少的材料,尤其在药物和农药的控制释放配方上;Besides, these polymers are extensively used as the antioxidants, flame retardants, corrosion inhibitors, flocculating agents, antistatic agents and the other technological applications. 此外,这些聚合物被广泛地用做抗氧化剂,阻燃剂,缓蚀剂, 絮凝剂,抗静电剂及其他技术应用;In addition, the functional polymers possessp’zes broad application prospects in the high technology area as conductive materials, photosensitizers, nuclear track detectors, liquid crystals, the working substances for storage and conversion of solar energy, etc. 另外,功能化聚合物在高科技领域具有广阔的应用前景; 如导电材料,光敏剂,核径迹探测器,液晶,用于太阳能等的转化与储存的工作物质;第十二单元实验室制备氨基树脂氨基树脂是由氨基衍生物和醛在酸性或碱性条件下反应生产得到的其中最重要最具代表性的物质是脲醛树脂和蜜胺树脂; 药品:尿素,福尔马林37%,乙醇,2N NaOH, NaOH溶液,1N标准NaOH溶液,1N标准HCl溶液,冰醋酸,糠醇,三乙醇胺,木粉,磷酸钙,氯化铵, H2SO4溶液,Na 2SO3,1%乙醇百里酚酞指示剂溶液,三聚氰胺,甘油和单羟甲基脲; 装置:烧瓶和烧杯,500ml的三口烧瓶,加热套,机械搅拌器,冷凝器,迪安—斯达克塔分水器,烘箱,广泛试纸,试管,250mL的容量烧瓶,冰浴,10ml 的移液管,滴管,油浴和广口瓶; 酸性条件下制备脲醛树脂:为了证明尿素和甲醛在酸性条件下的迅速反应,将5 g尿素和6 mL福尔马林在试管中混合,振荡试管直到尿素全部溶解;滴加4滴 N H2SO4以调节溶液pH到4,观察析出沉淀所需要的时间,取出部分沉淀并比较此沉淀以及单羟甲基脲样品在水中的溶解性;制备脲醛树脂粘合剂:将600g1mole尿素和137g福尔马林放入500ml三口烧瓶中,并安装好机械搅拌器和回流冷凝器,通过用广泛试纸测定用2NNaOH溶液把混合物PH值调至7~~8,然后将混合物回流2小时;1每隔半小时用下面的方法测定一次混合物中的自由甲醛含量,直到水完全脱除为止;2 当混合物回流2小时后,将迪安—斯达克塔分水器安装在烧瓶和回流冷凝器之间 ;大约有40ml水被蒸馏,用5滴冰醋酸将溶液酸化;将44g糠醇和的三乙醇胺加入到反应混合液中,加热此溶液到90℃并恒温15分钟;将混合物冷却到室温;取出15g的树脂样品和由1g木粉,磷酸钙和氯化铵组成的硬化剂混合 ;将混合物进行室温固化;3将剩下的没有加工硬化剂的树脂放入广口瓶中并提交给实验导师;自由甲醛含量的测定:自由甲醛含量的测定:准备250mL 1N Na2SO3溶液,并中和该溶液,从而使其产生淡蓝色的百里酚酞指示剂溶液;在250ml锥形瓶中加入重为2到3克的树脂样品到100mL的水中,摇晃锥形瓶使锥形瓶内的溶液充分溶解;如果树脂不能溶解,加入乙醇可以帮助溶解;在冰浴中使溶液的温度下降到4℃,加25mL的1M Na2SO3溶液在100mL的烧瓶中,用移液管移取10ml标准的1N HCl溶液到烧瓶中,降温至4℃;加10-15滴百里酚酞指示剂溶剂到样品烧瓶中,调整溶液的颜色至淡蓝色;用冷水冷却以后迅速地转移酸式亚硫酸盐溶液到样品烧瓶中;4滴定溶液到百里酚酞的终点标准1N NaOH 溶液;CH2O+Na2SO3+H2O →CH2OHSO3-Na++NaOH通过中和树脂溶液的HCl溶液的量来测定自由甲醛的百分含量;三聚氰胺甲醛树脂的制备:在一个500ml的配置有机械搅拌器和一个冷凝器的反应器中加入63g 的三聚氰胺和122g的福尔马林37%;混合物回流40分钟;%自由甲醛需要每隔十分钟测定一次;自由甲醛的测定步骤如上所述;样品经过20分钟加热后,在烧瓶和冷凝器间插入一个迪安—斯达克分水器,从而有10mL的水被蒸馏掉;把未固化的样品放入螺丝帽的坛子中,连同固化的树脂一起交给实验指导老师;15单元到目前为止大多数的PVC生产通过悬浮聚合;在这个过程中,氯乙烯单体悬浮液体滴,在连续水相剧烈的搅拌和保护胶体的悬浮剂;使用单体溶自由基引发剂polymeri等自下而上发生在悬浮液滴内,通过一个机制,已被证明相当于本体聚合;商业植物是基于批量反应堆,这增加了支持的大小,多年来;原来的工厂建于1940年代通常由IOOO 加仑反应堆;在1960年代和1950年代这t0 3000一5000加仑和增加随后,在1970年代初,29000加仑反应堆系统开发的胫完全②,t0 44000加仑200立方米的德国公司Huls;目前一些新的工厂正在建造的反应堆由不到isooo加仑容量,有一个批处理大小约25吨单体;小型反应堆通常衬玻璃给光洁度,抵制存款的搁置在墙上;~大反应堆通常的抛光不锈钢;氯乙烯的聚合反应是一个放热反应的能力,移走热量通常试图减少反应时间的限制因素;随着规模的反应堆已经增加了表面积体积比,因此加重这一问题;内部冷却线圈通常不用作吸引存款和很难清洁,从而对产品性能有不利影响;问题通常是克服使用冷冻水或回流冷凝器的装置,通过氯乙烯单体的连续回流;利用其潜热冷却的目的;一个简单的悬浮聚合配方可能包含以下成分:冷水通常是首先向反应堆虽然有时预热;然后添加pH值调节剂紧随其后的是分散剂的形式解决方案;发起者年代立即撒到水相的表面密封反应堆然后撤离前去除氧,因为这可以增加聚合时间,影响产品性能;当引发反应完成乙烯氯化物被指控和加热反应堆的内容开始;反应但真正的,产品分子量的主要控制因素;通常是在50——70 'c导致反应堆压力范围100 - 165 psi;趋势是朝着大的操作只打开关闭反应堆维护或可能偶尔打扫道;”:在这种情况下所有的原料都是负责解决方案或分散体,一般不需要疏散的一步;当达到所需的转换了,通常75%一95%,反应可以如果需要化学short-stopped和剩余的大部分单体恢复;他产品泥浆然后剥下来非常低的残留氯乙烯治疗-水平表示“状态”姆温度升高,在反应堆或类似容器,或接触蒸汽在逆流多平台汽提塔;然后脱水离心法和由此产生的泥浆湿饼乾,多级闪蒸干燥机一般,虽然各种不同的干燥类型使用不同的生产;干燥后,产品是通过某种剥皮屏幕去除无关的大颗粒装袋之前或装载散装油轮;—T 16 Styrene-Butadiene Copolymer第十六单元丁二烯-苯乙烯共聚物合成橡胶工业,以自由基乳液过程为基础,在第二次世界大战期间几乎很快地形成;那时,丁苯橡胶制造的轮胎性能相当优越,使天然橡胶在市场黯然失色;丁苯橡胶的标准制法是组分重量分数组分重量分数丁二烯72 过硫酸钾苯乙烯25 肥皂片十二烷基硫醇水180 混合物在搅拌下50℃加热,每小时转化5%~6%,在转化率达70%~75%时通过加入“终止剂”聚合反应终止,例如对苯二酚大约的重量百分含量,抑制自由基并避免过量支化和微凝胶形成;未反应的丁二烯通过闪蒸去除,苯乙烯在萃取塔中通过蒸汽萃取剥离;在加入抗氧剂后,例如N-甲基-β-萘胺的重量百分含量,加入盐水,其次加入稀释的硫酸或硫酸铝后乳液凝胶;凝胶碎片被洗涤、干燥。
Graft copolymerization is an efficient method to modify polymers .Various vinyl monomers have been investigated to graft onto starch ,and the starch graft copolymers have been used as flocculating agents , superabsorbents,ion exchanges and matrix or filler of thermo plastics. In this paper,mo dified starch paste by grafting with butylacrylate(BA) is firstly investigated as rubber-reinforcing filler. Three types of natural rubber(NR)/starch composites are prepared . Properties and morphology of these composites and corresponding starch powders are examined .The observed reinforcement effect of modified starch powder on NR/starch composites is interpreted.NO20this exploratory investigation examined the structural mechanism accounting for the enhanced compressive properties of heat-treated Kevlar-29 fibers . A novel theory was set forth that hydrogen-bond disruption and concurrent misorientation of crystallites may account for the observed augmentation of compressive properties. To examine the said theory ,as-received Kevlar-29 fibers were characterized by themogravimetric analysis and differential scanning calorimetry in an effort to determine if crosslinking and/or hydrogen disruption was responsible for the improved behavior in compression.NO21to prevent the loss of fiber strength , ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fibers were treated with an ultraviolet radiation technique combined with a corana-discharge treatment .the physical and chemical changes in the fiber surface were examined with scanning electron microscopy and Fourier transform infrared/attenuated total reflectance .the gel contents of the fibers were measured by a standard device .the mechanical properties of the treated fibers and the interfacial adhesion properties of UHMWPE-fiber-reinforced vinyl ester resin composites were investigated with tensile testing .NO22bicomponent fiber were wet-spun from soybean protein and poly(vinyl alcohol). the protein core of spun bicomponent fiber was brittle .our effort was then to study the soybean protein solution ,with the aim of trying to understand the cause for fiber brittleness and to determine the optimum solution conditions for fiber spinning . the effectsof alkali ,urea ,and sodium sulfite on the viscosity of the soybean protein solution were examined. the hydrolytic stability of the soybean protein solution was examined at various pH values at two temperatures .NO13a novel natural polymer blend ,namely ,a semi-interpenetrating polymer network (semi-IPN)composed of crosslinked chitosan with glutaraldehyde and silk fibroin was prepared .the FTIR spectra of the semi-IPN manifested that the chitosan and silk fibroin had a strong hydrogen-bond interaction and formed an interpolymer complex . the semi-IPN showed good pH sensitivity and ion sensitivity, and could also act as an "artificial muscle" because its swelling-shrinking behavior exhibited a fine reversibility.a number of papers have been published on the structure of PAN using X-ray diffraction ,infrared spectroscopy ,nuclear resonance ,and molecular simulations .based on the scattering pattern ,PAN is considered either orthorhombic with 3D,or hexagonal with 2D order . it has been proposed that hexagonal packing ,of PAN chains in dry samples becomes orthorhombic due to co-crystallization of PAN with polar solvent molecules .in this study ,we use in still XRD measurements, and draw upon these earlier publication ,to understand the deformation process on microscopic scale in PAN and its nanocompositeNO15new organic-inorganic hybrids based on PS/TiO2 hybrid membranes were prepared by sol-gel and phase inversion process. the membranes were characterized in terms of morphology, structure ,hydrophlicity, UF ,performance and thermal stability .the results showed that macrovoids were nearly suppressed with formation of sponge like membrane structure .the TiO2 particles were uniformly dispersed in membrane . the nanodispersed morganic network formed after sol-gel process and the strong interaction between inorganic network and polymeric chains led to the improvement of porosity and thermal stability.NO16polymers carrying a hydrolyzable ester function and bactericidal quaternary ammonium salts were successfully synthesized in two steps . the first one was the modification of hydroxyl functions of poly(vinyl alcohol) by chloroacetic anhydride . the structure of synthesized polymers was confirmed by infrared ,1H-,and 13C- nuclear magnetic resonance .the kinetic results were consistent with a 1-order reaction ,and the activation energy in the case of total modification was found to be 16.8(J/Mol) . the second step was the quaternization of the pendant chlorine atom with a long alkyl chain or aromatic tertiary amines.NO17blending homopolymers with block copolymers has been proved to be another interesting approach to modify the morphology of the block copolymer self-assembly. by blending homopolymer of identical chemical structure with one block in the copolymer , the dimension of the domains in the final phase separation has been adjusted , by changing either the volume fraction or the molecular weight of the homopolymer .at low volume fraction of the block copolymers , the structure formation is analogous to micelle formation of surfactant molecules in solutions, and the interfacial tension between the copolymer and the homopolymer is a critical factor.NO18differential scanning calorimetry and dynamic mechanical zhermal analysis techniques have been used to characterize different Kevlar/epoxy composites. tetra-functional aliphatic amine and anhydride/diglycidyl epoxy have been used as matrix and different quantities of continuous Kevlar fibers as reinforcement .Kevlar fibers had different effects on curing kinetics and final thermal properties depending on epoxy matrix type . a significant decrease in the glass transition temperature(Tg)was observed as Kevlar content increased when anhydride matrix was used .NO10the electrostatic spinning technique was used to produce ultrafine polyamide-6 fibers. the effects of solution conditions on the morphological appearance and the average diameter of as-spun fibers were investigated by optical scanning and scanning electron ,microscopy techniques . it was shown that the solution properties (i.e. viscosity , surface tension and conductivity) were important factors characterizing the morphology of the fibers obtained .among these three properties ,solution viscosity was found to have the greatest effect . solutions with high enough viscosities were necessary to produce fibers without beads.NO11ternary blend fibers (TBFs) ,based on melt blends of poly(ethylene 2,6-naphthalate) , poly(ethylene terephthalate ), and a thermotropic liquid-crystal polymer (TLCP), were prepared by a process of melt blending and spinning to achieve high performance fibers . the reinforcement effect of the polymer matrix by the TLCP component the fibrillar structure with TLCP fibrils of high aspect ratios and the development of more ordered and perfect crystalline structures by an annealing process resulted in the improvement of the tensile strength and modulus for the TBFs .NO12an amphiphilic AB block copolymer composed of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) as a hydrophilic segment and poly (10-undecenoic acid) as a hydrophobic segment was synthesized . the lower critical solution temperature (LCST) of the copolymer was 30.8 ..,as determined by the turbidity method . the block copolymer forms micells in an aqueous medium. transmission electron microscopy images showed that these nanoparticles were regularly spherical in shap . the micelle size determined by size analysis was around 160 nm .NO7this work examines the PBT/PET sheath/core conjugated fiber with reference to melt spinning, fiber properties and thermal bonding . regarding the rheological behaviors in the conjugated spinning , PET and PBT show the smallest difference between their melt -viscosity at temperatures of 290 and 260 respectively , which has been thought to represent optimal spinning conditions . the effect of processing parameters on the crystallinity of core material-PET was observed and listed . in order of importance , these factors are the draw ratio, the heat-set temperature , and the drawing temperature.NO8thermoresponsive shape memory fibers were prepared by melt spinning form a polyester polyol-based polyurethane shape memory polymer and were subjected to different postspinning operations to modify their structure . the effect of drawing and heatsetting operations on the shape memory behavior , mechanical properties , and structure of the fibers was studied . in contrast to the as-spun fibers , which were found to show permanent shape , the drawn and heat-set fibers showed significantly higher stresses and complete recovery.NO9the dry-jet-wet spinning process was employed to spin poly(lactic acid) fiber by the phase inversion technique using chloroform and methanol as solvent and nonsolvent ,respectively , for PLA . the as-spun fiber was subjected to two-stage hot drawing to study the effect of various process parameters , such as take-up speed ,drawing temperature , and heat-setting temperature on the fiber structural propertics . the take-up speed speed had a pronounced influence on the maximum draw ratio of the fiber . the optimum drawing temperature was observed to be 90 to get a fiber with the tenacity of 0.6 GPa for the draw ratio of 8 .NO1the purpose of this work is to examine zhe changes in thermal properties and zhe crystallization behavior of polyamide 6(PA6) when filled with multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT). the composites were produced by melt mixing starting from an industrial available masterbatch containing as produced MWCNT . the focus of this article is a detailed discussion of results obtained by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) ,X-ray ,diffraction (XRD) dynamic mechanical thermal analysis (DMTA), and water sorption . the influence of CNT on zhe thermal transitions (glass transition temperature ,melting ,and crystallization) of PA6 is investigated .NO2the effects of nucleating agents (NAs) on fracture toughness of injection-molded isotactic poly(propylene)/ethylene-diene terpolymer (PP/EPDM) were studied in this work . compared with PP/EPDM blends without any NA,EP/EPDM/NA blends show very small and homo geneous PP sphernlites . as we expected ,PP/EPDM blends nucleated with B-phase NA(TMB-5) present not only a significant enhancement in toughness but also a promotion of brittle-ductile transition . however ,the addition of A-phase NA(DMDBS) has no apparent affect on the toughness of the blends . the impact-fractured surface morphologies of such samples were analyzed via scanning electronic microscope(SEM).NO3solutions of poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) or EVOH ,ranging in composition from 56 to 71 wt% vinyl alcohol ,can be readily electrospun at room temperature from solutions in 70% 2-propanol/water . the solutions are prepared at 80 and allowed to cool to room temperature .interestingly, the solutions are not stable at room temperature and eventually the polymer precipitates after several hours . however prior to precipitation , electrospinning is extensive and rapid ,allowing coverage of fibers on various substrates . fiber diameters of ca. 0.2-8.0 um were obtained depending upon the solution concentration .NO4the use of macromonomers is a convenient method for preparing branched polymers . however graft copolymers obtained by conventional radical copolymerization of macromonomers often exhibit poorly controlled molecular weights and high polydispersities as well as large compositional heterogeneities from chain-to-chain . in contrast , the development of "living"/controlled radical polymerization has facilitated the precise synthesis of well-defined polymers with lowpolydispersities in addition to enabling synthetic chemists to prepare polymers with novel and complex architectures .NO5the thermal and electrical conductivities in nanocomposites of single ,walled carbon nanotubes (SWNT) and polyethylene (PE) are investigated in terms of SWNT loading the degree of PE crystallinity , and the PE alignment . isotropic SWNT/PE nanocomposites show a significant increase in thermal conductivity with increasing SWNT loading , having 1.8 and 3.5 W/m K at a SWNT volume fraction of ———0.2 in low-density PE(LDPE) and high-density PE (HDPE), respectively . this increase suggests a reduction of the interfacial thermal resistance . oriented SWNT/HDPE nanocomposites exhibit higher thermal conductivities , which are attributed primarily to the aligned PE matrix .NO6we previously discovered that isotropic monomer solution show birefringence due to its anisotropic structure after gelation in the presence of a small amount of rod-like polyelectrolyte. here ,we focus on what mechanism is responsible for the formation of anisotropic structure during gelation .various optical measurements are perfected to elucidate the structure change during gelation . it is found that the existence of a large-size structure in monomer solution with the rod-like polyelectrolyte is essentially important to induce birefringence during gelation .。
单词engineeringmaterials 工程材料ductile 延展metallic materials 金属材料durable 耐久的ferrous alloys 黑色金属合金合金quote 引用援引non-ferrous metals 有色金属eminently 杰出地organic polymer materials 有机高分子材料rust 生锈plastic 塑料precipitation 沉淀沉积rubber 橡胶dislocation 位错synthetic fibers 合成纤维arbitrary 独断的,任意的inorganic non-metallic materials 无机非金属材料smelt 熔炼,精炼composite materials 复合材料Intricate 复杂的,精巧的wrought iron 熟铁combination 结合,化合物pig iron 生铁ductile 易延展的four general types of cast iron 铸铁的四种类型low ductility 低延展性ductile iron 球墨铸铁tough 艰难的gray iron 灰铸铁toughness 韧性white iron 白口铸铁porosity 孔隙度,气孔,气泡malleable iron 可锻铸铁insulating 绝缘alloying elements 合金元素flexible 灵活的chromium 铬corrosion resistance 抗腐蚀性nickel 镍lightweight 轻impurity 杂质reduce 还原,减少majority 多数weight reduction of vehicle 汽车轻量化wool fibres 毛纤维automobile bodies 汽车车身the sheep 羊cutlery 餐具silk fibres 丝纤维springs 弹簧silkworms 蚕slip systems 滑移性cementite 渗碳体oxide 氧化物proteins 蛋白质spheroidal graphite 球状石墨varnish 清漆ballbearing 滚珠轴承pigment 颜料dislocation motion 位错的运动solvent 溶剂precipitation hardening 沉积硬化additives 添加剂balance 平衡paint 油漆cultivate 培养drying oils 干燥油shatterproof 碎cure 固化against 反对cured or dried 固化或干燥compared to 相比ancient times 古代aesthetic appeal 艺术感染力millennia 千年more dense 更密集的arbitrary boundary 任意边界判断1.The name “cast iron”derives from the fact that there is only iron in cast irons2.There are a lot of alloys in which there is no iron.3.3.Tungsten can bear the temperature of 2000℃in air.4.There are more than one step in the process to make a plstic product。