集成电路封装和可靠性Chapter2-1-芯片互连技术
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:4.11 MB
- 文档页数:81


UESTC-Ning Ning1Chapter 2Chip Level Interconnection宁宁芯片互连技术集成电路封装测试与可靠性UESTC-Ning Ning2Wafer InWafer Grinding (WG 研磨)Wafer Saw (WS 切割)Die Attach (DA 黏晶)Epoxy Curing (EC 银胶烘烤)Wire Bond (WB 引线键合)Die Coating (DC 晶粒封胶/涂覆)Molding (MD 塑封)Post Mold Cure (PMC 模塑后烘烤)Dejunk/Trim (DT 去胶去纬)Solder Plating (SP 锡铅电镀)Top Mark (TM 正面印码)Forming/Singular (FS 去框/成型)Lead Scan (LS 检测)Packing (PK 包装)典型的IC 封装工艺流程集成电路封装测试与可靠性UESTC-Ning Ning3⏹电子级硅所含的硅的纯度很高,可达99.9999 99999 %⏹中德电子材料公司制作的晶棒(长度达一公尺,重量超过一百公斤)UESTC-Ning Ning4Wafer Back Grinding⏹PurposeThe wafer backgrind process reduces the thickness of the wafer produced by silicon fabrication (FAB) plant. The wash station integrated into the same machine is used to wash away debris left over from the grinding process.⏹Process Methods:1) Coarse grinding by mechanical.(粗磨)2) Fine polishing by mechanical or plasma etching. (细磨抛光)UESTC-Ning Ning5旋转及振荡轴在旋转平盘上之晶圆下压力工作台仅在指示有晶圆期间才旋转Method:The wafer is first mounted on a backgrind tape and is then loaded to the backgrind machine coarse wheel . As the coarse grinding is completed, the wafer is transferred to a fine wheel for polishing .。

集成电路封装技术一、概述集成电路封装技术是指将芯片封装成实际可用的器件的过程,其重要性不言而喻。
封装技术不仅仅是保护芯片,还可以通过封装形式的不同来满足不同应用领域的需求。
本文将介绍集成电路封装技术的基本概念、发展历程、主要封装类型以及未来发展趋势等内容。
二、发展历程集成电路封装技术随着集成电路行业的发展逐渐成熟。
最早的集成电路封装形式是引脚直插式封装,随着技术的不断进步,出现了芯片级、无尘室级封装技术。
如今,随着3D封装、CSP、SiP等新技术的出现,集成电路封装技术正朝着更加高密度、高性能、多功能的方向发展。
三、主要封装类型1.BGA封装:球栅阵列封装,是一种常见的封装形式,具有焊接可靠性高、散热性好等优点。
2.QFN封装:裸露焊盘封装,具有体积小、重量轻、成本低等优点,适用于尺寸要求严格的应用场合。
3.CSP封装:芯片级封装,在尺寸更小、功耗更低的应用场合有着广泛的应用。
4.3D封装:通过将多个芯片垂直堆叠,实现更高的集成度和性能。
5.SiP封装:系统级封装,将多个不同功能的芯片封装在一起,实现更复杂的功能。
四、未来发展趋势随着物联网、人工智能等领域的兴起,集成电路封装技术也将迎来新的挑战和机遇。
未来,集成电路封装技术将朝着更高密度、更低功耗、更可靠、更环保的方向发展。
同时,新材料、新工艺和新技术的应用将为集成电路封装技术带来更多可能性。
五、结语集成电路封装技术是集成电路产业链中至关重要的一环,其发展水平直接关系到整个集成电路的性能和应用范围。
随着技术的不断进步,集成电路封装技术也在不断演进,为各个领域的技术发展提供了强有力的支撑。
希望本文能够帮助读者更好地了解集成电路封装技术的基本概念和发展趋势,为相关领域的研究和应用提供一定的参考价值。


一、填空题1、将芯片及其他要素在框架或基板上布置,粘贴固定以及连接,引出接线端子并且通过可塑性绝缘介质灌封固定的过程为狭义封装;在次根基之上,将封装体与装配成完整的系统或者设备,这个过程称之为广义封装。
2、芯片封装所实现的功能有传递电能;传递电路信号;提供散热途径;构造保护与支持。
3、芯片封装工艺的流程为硅片减薄与切割、芯片贴装、芯片互连、成型技术、去飞边毛刺、切筋成形、上焊锡、打码。
4、芯片贴装的主要方法有共晶粘贴法、焊接粘贴法、导电胶粘贴发、玻璃胶粘贴法。
5、金属凸点制作工艺中,多金属分层为黏着层、扩散阻挡层、表层金保护层。
6、成型技术有多种,包括了转移成型技术、喷射成型技术、预成型技术、其中最主要的是转移成型技术。
7、在焊接材料中,形成焊点完成电路电气连接的物质叫做煤斜;;用于去除焊盘外表氧化物,提高可焊性的物质叫做助焊剂;在SMT中常用的可印刷焊接材料叫做锡直。
8、气密性封装主要包括了金属气密性封装、陶瓷气密性封装、玻璃气密性封装。
9、薄膜工艺主要有遮射工艺、蒸发工艺、电镀工艺、光刻工艺。
10、集成电路封装的层次分为四级分别为模块元件(MOdUIe)、⅛路卡工艺(Card)、主电路板(Board)、完整电子产品。
11、在芯片的减薄过程中,主要方法有磨削、研磨、干式抛光、化学机械平坦工艺、电化学腐蚀、湿法腐蚀、等离子增强化学腐蚀等。
12、芯片的互连技术可以分为打线键合技术、载带自动键合技术、倒装芯片键合技术。
13、DBG切割方法进展芯片处理时,首先进展在硅片正面切割一定深度切口再进展反面磨削。
14、膜技术包括了薄膜技术和厚膜技术,制作较厚薄膜时常采用丝网印刷和浆料枯燥烧结的方法O15、芯片的外表组装过程中,焊料的涂覆方法有点涂、丝网印刷、钢模板印刷三种。
16、涂封技术一般包括了顺形涂封和封胶涂封。
二、名词解释1、芯片的引线键合技术(3种)是将细金属线或金属带按顺序打在芯片与引脚架或封装基板的焊垫上而形成电路互连,包括超声波键合、热压键合、热超声波键合。


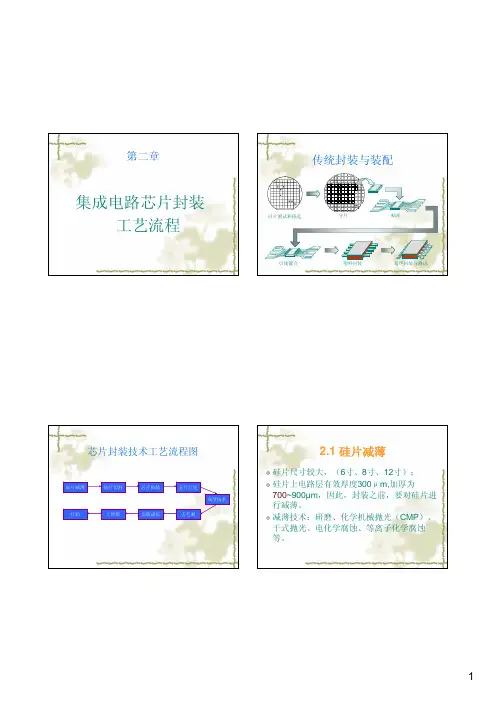
第二章集成电路芯片封装工艺流程传统封装与装配硅片测试和拣选引线键合分片塑料封装最终封装与测试贴片芯片封装技术工艺流程图硅片减薄硅片切割芯片贴装芯片互连打码上焊锡切筋成形去毛刺成型技术2.1 硅片减薄硅片尺寸较大,(6寸、8寸、12寸);硅片上电路层有效厚度300μm,加厚为700~900µm,因此,封装之前,要对硅片进行减薄。
减薄技术:研磨、化学机械抛光(CMP)、干式抛光、电化学腐蚀、等离子化学腐蚀等。
硅片减薄转动和摆动秆转动卡盘上的硅片向下施加力Figure 20.42.2 芯片切割(分片)减薄后的芯片贴在一个带有金属环的薄膜(蓝膜)上,送到划片机进行划片。
方式:手动操作(老式划片机);自动划片机(配备脉冲激光束或金刚石划片刀)。
划片工艺:采用DBG 、DBT技术。
分片硅片台锯刃Figure 20.52.3 芯片粘贴共晶粘贴法(Au-Si合金)焊接粘贴法(Pb-Sn合金焊接)环氧树脂粘结(重点)玻璃胶粘贴法贴装方式4种:装架芯片引线引线框架塑料DIPFigure 20.62.3.1 共晶粘贴法金—硅共晶(Au-Si)粘贴,在陶瓷封装中广泛应用。
利用金—硅合金,在高温时共晶熔合反应使IC芯片粘贴固定。
工艺方法—看下页图缺点:工艺温度高,生产效率低,不适应高速自动化生产。
只应用于大功率元件。
芯片粘结-Au-Si共晶贴片Silicon Gold film 金/硅共晶合金Al2O3 Figure 20.82.3.2 焊接粘贴法另一种利用合金反应进行芯片粘贴的方法。
优点:热传导性好,适合高功率器件的封装。
2.3.3 导电胶粘贴法也称环氧树脂粘结;优点:操作简单、成本低、大量用于塑料封装;缺点:热稳定性较差、易在高温下劣化、可靠性差。
芯片粘结-环氧树脂粘贴芯片环氧树脂引线框架Figure 20.7导电胶粘贴法工艺过程和导电胶材料涂布粘贴剂放芯片到粘贴剂上固化处理。
固化条件:150℃,1h 或(186℃,0.5h)三种导电胶材料配方:①各向同性②导电硅橡胶③各向异性导电聚合物导电胶功能:(形成化学结合、具有导电功能)2.3.4 玻璃胶粘贴法为低成本芯片粘贴材料,适用于低成本的陶瓷封装。

第一章集成电路芯片封装技术1. (P1)封装概念:狭义:集成电路芯片封装是利用膜技术及微细加工技术,将芯片及其他要素在框架或基板上布置、粘贴固定及连接,引出接线端子并通过可塑性绝缘介质灌封固定,构成整体结构的工艺。
广义:将封装体与基板连接固定,装配成完整的系统或电子设备,并确保整个系统综合性能的工程。
2. 芯片封装实现的功能:1 传递电能,主要是指电源电压的分配和导通。
2 传递电路信号,主要是将电信号的延迟尽可能减小,在布线时应尽可能使信号线与芯片的互连路径以及通过封装的IO接口引出的路径达到最短。
3 提供散热途径,主要是指各种芯片封装都要考虑元器件、部件长期工作时如何将聚集的热量散出的问题。
4 结构保护与支持,主要是指芯片封装可为芯片和其他连接部件提供牢固可靠的机械支撑,并能适应各种工作环境和条件的变化。
3.在确定集成电路的封装要求时应注意以下儿个因素:1 成本2 外形与结构3 可靠性4 性能4.在选择具体的封装形式时,主要需要考虑4种设计参数:性能、尺寸、重量、可靠性和成本目标。
5.封装工程的技术层次:第一层次(Level1或First Level):该层次又称为芯片层次的封装(Chip Level Packaging),是指把集成电路芯片与封装基板或引脚架(Lead Frame)之间的粘贴固定、电路连线与封装保护的工艺,使之成为易于取放输送,并可与下一层次组装进行连接的模块(组件Module)元件。
第二层次(Level2或Second Level:将数个第一层次完成的封装与其他电子元器件组成个电路卡(Card〉的工艺.第三层次(Level3或Third Level):将数个第二层次完成的封装组装成的电路卡组合成在一个主电路板(Board)上使之成为一个部件或子系(Subsystem)的工艺。
第四层次(Level4或Fourth Level)将数个子系统组装成为一个完整电子产品的工艺过程。
在芯片上的集成电路元器件间的连线工艺也称为零级层次(Level 0)的封装,6.封装的分类:按照封装中组合集成电路芯片的数目,芯片封装可分为:单芯片封装与多芯片封装两大类。

引线键合应用范围:低本钱、高靠得住、高产量等特点使得它成为芯片互连的主要工艺方式,用于下列封装::一、陶瓷和塑料BGA、单芯片或多芯片二、陶瓷和塑料(CerQuads and PQFPs)3、芯片尺寸封装(CSPs)4、板上芯片(COB)硅片的磨削与研磨:硅片的磨削与研磨是利用研磨膏和水等介质,在研磨轮的作用下进行的一种减薄工艺,在这种工艺中硅片的减薄是一种物理的进程。
硅片的应力消除:为了堆叠裸片,芯片的最终厚度必需要减少到了30μm乃至以下。
用于3D互连的铜制层需要进行无金属污染的自由接触处置。
应力消除加工方式,主要有以下4种。
硅片的抛光与等离子体侵蚀:研磨减薄工艺中,硅片的表面会在应力作用下产生细微的破坏,这些不完全平整的地方会大大降低硅片的机械强度,故在进行减薄以后一般需要提高硅片的抗折强度,降低外力对硅片的破坏作用。
在这个进程中,一般会用到干式抛光或等离子侵蚀。
干式抛光是指不利用水和研磨膏等介质,只利用干式抛光磨轮进行干式抛光的去除应力加工工艺。
等离子侵蚀方式是指利用氟类气体的等离子对工件进行侵蚀加工的去除应力加工工艺。
TAIKO工艺:在实际的工程应用中,TAIKO工艺也是用于增加硅片研磨后抗应力作用机械强度的一种方式。
在此工艺中对晶片进行研削时,将保留晶片外围的边缘部份(约3mm左右),只对圆内进行研削薄型化,通过导入这项技术,可实现降低薄型晶片的搬运风险和减少翘曲的作用,如图所示。
激光开槽加工:在高速电子元器件上慢慢被采用的低介电常数(Low-k)膜及铜质材料,由于难以利用普通的金刚石磨轮刀片进行切割加工,所以有时无法达到电子元件厂家所要求的加工标准。
为此,迪思科公司的工程师开发了可解决这种问题的加工应用技术。
减少应力对硅片的破坏作用先在切割道内切开2条细槽(开槽),然后再利用磨轮刀片在2条细槽的中间区域实施全切割加工。
通过采用该项加工工艺,能够提高生产效率,减少乃至解决因崩裂、分层(薄膜剥离)等不良因素造成的加工质量问题。
UESTC-Ning Ning1Chapter 2Chip Level Interconnection宁宁芯片互连技术集成电路封装测试与可靠性UESTC-Ning Ning2Wafer InWafer Grinding (WG 研磨)Wafer Saw (WS 切割)Die Attach (DA 黏晶)Epoxy Curing (EC 银胶烘烤)Wire Bond (WB 引线键合)Die Coating (DC 晶粒封胶/涂覆)Molding (MD 塑封)Post Mold Cure (PMC 模塑后烘烤)Dejunk/Trim (DT 去胶去纬)Solder Plating (SP 锡铅电镀)Top Mark (TM 正面印码)Forming/Singular (FS 去框/成型)Lead Scan (LS 检测)Packing (PK 包装)典型的IC 封装工艺流程集成电路封装测试与可靠性UESTC-Ning Ning3⏹电子级硅所含的硅的纯度很高,可达99.9999 99999 %⏹中德电子材料公司制作的晶棒(长度达一公尺,重量超过一百公斤)UESTC-Ning Ning4Wafer Back Grinding⏹PurposeThe wafer backgrind process reduces the thickness of the wafer produced by silicon fabrication (FAB) plant. The wash station integrated into the same machine is used to wash away debris left over from the grinding process.⏹Process Methods:1) Coarse grinding by mechanical.(粗磨)2) Fine polishing by mechanical or plasma etching. (细磨抛光)UESTC-Ning Ning5旋转及振荡轴在旋转平盘上之晶圆下压力工作台仅在指示有晶圆期间才旋转Method:The wafer is first mounted on a backgrind tape and is then loaded to the backgrind machine coarse wheel . As the coarse grinding is completed, the wafer is transferred to a fine wheel for polishing .UESTC-Ning Ning6 Wafer Back Grinding processObjective:To reduce thethicknesswith a coarse grindingwheel.Objective:To load and alignthe wafer into thewafer cleaning andtape laminationmachine.Objective:To clean the waferfor the nextlamination step.Objective:To laminate a protectivelayer of film on thecircuitry surface of thewafer .2. Wafer cleaning1. Load and Align 3. Back grind Tape lamination4. Coarse grindingUESTC-Ning Ning7Wafer Back Grinding process (Cont.)Objective:To unload the wafer from back grinding machine.5. Fine polishing6. UnloadObjective:To load the wafer to wafer mounter.Objective:To remove the back grind tape afterwafer mounted on the frame.8. Tape removal7. LoadUESTC-Ning Ning8Wafer Back Grinding Issues and Challenges⏹Issues☐Ease of process–Thin wafer handling from one step to another –Back grinding tape removal–Excessive stresses removal or reduction from the wafer.(应力)☐Yield–Wafer breakage due to stress built up during thinning process. –Scratches .(划痕)–Die metallization smearing.(污点,模糊)☐Equipment stability and capability⏹Challenges☐Market requirements drive for very thin wafer (<3 mils)☐Flip chip wafer back grindingUESTC-Ning Ning9Wafer sawing⏹Wafer Separation Process►Purpose:The wafer separation process is to divide the wafer into individual dice or chips.Process Methods:1)Sawing (with diamond-impregnated saw blade) 锯切☐Single or dual cut ☐Step cut or bevel cut2) Partial scribing (with laser beam, diamond-tipped scribing tool, or diamond-impregnated saw blade) 局部划片器UESTC-Ning Ning10Wafer sawingUESTC-Ning Ning11►Wafer Sawing is a Front-of-Line (FOL) operation that cuts the wafer along the streets separating the individual die. Streets, also called scribe lines , are lines on the wafer that separate each individual die from the surrounding dice. Kerf width is the saw width. After the wafer is sawn, the wash station, using a detergent, removes residual cut material fromthe wafer.Wafer sawingDicing Blade晶圆工作台刀刃NingUESTC-Ning Ning13The SAWING process is broken down into four steps:Objective:To rinse slurry (silicon dust)before it dries with de-ionized water and CO2. Also to drywafer by pinning and with clean air , and unload wafer .1. Load and Align2. Pattern Recognition System (PRS)3. Cut4. Wash, Rinse, Dry and UnloadObjective:To separate dice from a wafer with resin-bonded diamond wheel . (First blade is used to remove metal structures and stresses on street for second blade.)Wafer sawingUESTC-Ning Ning14Wafer Sawing Issues and Challenges⏹Issues:☐Ease of process--Die chipping control (碎屑)--Multiple die types and sizes processing☐Yield--Saw on die--Scratches (划痕)--Chipping --Die crack☐Equipment stability and capability⏹Challenges:☐Smaller kerf width for more die per wafer☐Larger wafer size (300mm)with multiple die types and sizesUESTC-Ning Ning15--Die Attach Process☐Purpose:The die attach process is to attach the sawed die in the right orientation accurately onto the substrate with a bonding medium in between to enable the next wire bond first level interconnection operation .☐Process Methods1)Semi-automated eutectic die attach .低共熔物芯片粘接2)Fully automated adhesive die attach.胶粘剂粘接--Die Attach Process 晶粒--Die Attach Process☐Au-Si 低共熔合金粘接法金膜◆低共融合金粘接法主要用在芯片产品需要非常低的背部接触电阻。
1Chapter 2Chip Level Interconnection芯片互连技术集成电路封装测试与可靠性UESTC-Ning Ning2Wafer InWafer Grinding (WG 研磨)Wafer Saw (WS 切割)Die Attach (DA 黏晶)Epoxy Curing (EC 银胶烘烤)Wire Bond (WB 引线键合)Die Coating (DC 晶粒封胶/涂覆)Molding (MD 塑封)Post Mold Cure (PMC 模塑后烘烤)Dejunk/Trim (DT 去胶去纬)Solder Plating (SP 锡铅电镀)Top Mark (TM 正面印码)Forming/Singular (FS 去框/成型)Lead Scan (LS 检测)Packing (PK 包装)典型的IC 封装工艺流程集成电路封装测试与可靠性UESTC-Ning Ning3⏹电子级硅所含的硅的纯度很高,可达99.9999 99999 %⏹中德电子材料公司制作的晶棒(长度达一公尺,重量超过一百公斤)UESTC-Ning Ning4Wafer Back Grinding⏹PurposeThe wafer backgrind process reduces the thickness of the wafer produced by silicon fabrication (FAB) plant. The wash station integrated into the same machine is used to wash away debris left over from the grinding process.⏹Process Methods:1) Coarse grinding by mechanical.(粗磨)2) Fine polishing by mechanical or plasma etching. (细磨抛光)UESTC-Ning Ning5旋转及振荡轴在旋转平盘上之晶圆下压力工作台仅在指示有晶圆期间才旋转Method:The wafer is first mounted on a backgrind tape and is then loaded to the backgrind machine coarse wheel . As the coarse grinding is completed, the wafer is transferred to a fine wheel for polishing .UESTC-Ning Ning6 Wafer Back Grinding processObjective:To reduce thethicknesswith a coarse grindingwheel.Objective:To load and alignthe wafer into thewafer cleaning andtape laminationmachine.Objective:To clean the waferfor the nextlamination step.Objective:To laminate a protectivelayer of film on thecircuitry surface of thewafer .2. Wafer cleaning1. Load and Align 3. Back grind Tape lamination4. Coarse grindingUESTC-Ning Ning7Wafer Back Grinding process (Cont.)Objective:To unload the wafer from back grinding machine.5. Fine polishing6. UnloadObjective:To load the wafer to wafer mounter.Objective:To remove the back grind tape afterwafer mounted on the frame.8. Tape removal7. LoadUESTC-Ning Ning8Wafer Back Grinding Issues and Challenges⏹Issues☐Ease of process–Thin wafer handling from one step to another –Back grinding tape removal–Excessive stresses removal or reduction from the wafer.(应力)☐Yield–Wafer breakage due to stress built up during thinning process. –Scratches .(划痕)–Die metallization smearing.(污点,模糊)☐Equipment stability and capability⏹Challenges☐Market requirements drive for very thin wafer (<3 mils)☐Flip chip wafer back grindingUESTC-Ning Ning9Wafer sawing⏹Wafer Separation Process►Purpose:The wafer separation process is to divide the wafer into individual dice or chips.Process Methods:1)Sawing (with diamond-impregnated saw blade) 锯切☐Single or dual cut ☐Step cut or bevel cut2) Partial scribing (with laser beam, diamond-tipped scribing tool, or diamond-impregnated saw blade) 局部划片器UESTC-Ning Ning10Wafer sawingUESTC-Ning Ning11►Wafer Sawing is a Front-of-Line (FOL) operation that cuts the wafer along the streets separating the individual die. Streets, also called scribe lines , are lines on the wafer that separate each individual die from the surrounding dice. Kerf width is the saw width. After the wafer is sawn, the wash station, using a detergent, removes residual cut material fromthe wafer.Wafer sawingDicing Blade晶圆工作台刀刃NingUESTC-Ning Ning13The SAWING process is broken down into four steps:Objective:To rinse slurry (silicon dust)before it dries with de-ionized water and CO2. Also to drywafer by pinning and with clean air , and unload wafer .1. Load and Align2. Pattern Recognition System (PRS)3. Cut4. Wash, Rinse, Dry and UnloadObjective:To separate dice from a wafer with resin-bonded diamond wheel . (First blade is used to remove metal structures and stresses on street for second blade.)Wafer sawingUESTC-Ning Ning14Wafer Sawing Issues and Challenges⏹Issues:☐Ease of process--Die chipping control (碎屑)--Multiple die types and sizes processing☐Yield--Saw on die--Scratches (划痕)--Chipping --Die crack☐Equipment stability and capability⏹Challenges:☐Smaller kerf width for more die per wafer☐Larger wafer size (300mm)with multiple die types and sizesUESTC-Ning Ning15--Die Attach Process☐Purpose:The die attach process is to attach the sawed die in the right orientation accurately onto the substrate with a bonding medium in between to enable the next wire bond first level interconnection operation .☐Process Methods1)Semi-automated eutectic die attach .低共熔物芯片粘接2)Fully automated adhesive die attach.胶粘剂粘接--Die Attach Process 晶粒--Die Attach Process☐Au-Si 低共熔合金粘接法金膜◆低共融合金粘接法主要用在芯片产品需要非常低的背部接触电阻。
--Die Attach ProcessUESTC-Ning Ning19--Die Attach ProcessUESTC-Ning Ning20 1. Units and Dice/ wafer LoadObjective:To load the carrierswith the units placedon them. To loadthe dice/wafer intothe machine.2. Bonding Medium DispenseObjective:To dispense thebonding mediumonto the substratedie attach paddle.3. Pattern Recognition System(PRS) & AlignObjective:To align the theta(rotation) position ofthe wafer. To align thedie (X-Y)with respectto the package PRSeye points.4. Die AttachObjective:To attach the dieprecisely and form agood adhesion withdesired bond linethickness (BLT).--Die Attach Process--Die Attach Process 5. Unload (Die Attach)UESTC-Ning Ning22Wire Bonding Technology Die Attach ProcessIssues and Challenges☐Issues:◆Ease of process–Delamination control –Void control ◆Yield–Adhesive on die–Incomplete wet out/fillet –Die crack–Die placement◆Equipment stability and capability☐Challenges:◆Market requirements drive for very thin die (<3 mils).◆Material selection (e.g. lead free compatible, thermal Materialselection and electrical requirements).UESTC-Ning Ning23--Wire Bonding ProcessUESTC-Ning Ning245. UnloadObjective:To unload the carriers after wire bond.To unload the wire spool when the wireis used upThe Wire Bonding Process --Wire Bonding ProcessUESTC-Ning Ning25Wire Bonding Issues and Challenges◆Challenges:☐Market requirements drive for tighter bond pitch . (<37/75um staggered , <60um non-staggered).☐Smaller wire diameter (<1.0mils).☐Brittle Intermetallic composition (IMC) on lead free.◆Issues:☐Ease of process-Looping profile control.-Process optimization for bond ability and bond reliability.☐Yield-Lifted bond (non stick on pad or lead).-Sagging and swayed wire. 引线塌陷或歪斜-Tight loop.☐Equipment stability and capability.交错排列无铅工艺中易脆的金属间化合物UESTC-Ning Ning26 MD(封塑)(Molding)BM(背印)(Back Mark)D/T(去胶/去纬)(Dejunk/Trim)SP(电镀)(Solder Panting)F/S(成型/去框)(Form/Singulation)F/T(功能测试)(Function/Test)PK(包装)(Packing)PMC(烘烤)(Post Mold Cure)MC(烘烤)(Mark Cure)TM(正印)(Top Mark)LS(检测)(lead Scan)Molding塑封成型UESTC-Ning Ning27按封装材料分类:陶瓷封裝常用于特殊用途和专业领域IC芯片例如:高频和军事通讯加盖式气密性封装UESTC-Ning NingUESTC-Ning Ning29☐Hermetic lid Sealing在第一级互连完成后,将周围印刷有焊料的盖子(或陶瓷,金属或塑料盖)放置在封装基板腔体上(芯片已键合在腔体内)。