轮胎基础知识(普利司通)资料
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:403.50 KB
- 文档页数:17


1.轮胎的商标brand 在轮胎的两侧有,一般字体很大的。
2.轮胎一般规定是寿命在3年或者里程在50000(6W)以上。
一般,轮胎没有长深裂纹,胎侧没有裂口,冠部没有严重偏磨,花纹残沟还在磨耗标志(TWI)之上,是可以使用。
以下是名牌轮胎商标的中英文希望对你有帮助1、普利司通/日本、BRIDGESTONE2、米其林/法国、MECHELIN (胎侧有轮胎堆砌的小人)3、固特异/美国、GOODYEAR4、大陆/德国\continental (马牌,有马的图案)5、倍耐力/意大利、PIRELLI6、住友橡胶/日本、SUMITOMO7、横滨橡胶/日本、YOKOHAMA8、韩泰轮胎/韩国、HANKOOK9、库珀轮胎橡胶/美国\COOPER10、锦湖/韩国\KUMHO11、东洋轮胎橡胶/日本\TOYO12、正新橡胶工业/中国台湾Maxxis13、佳通轮胎/新加坡GITI14、三角集团/中国Triangle (三角形)15、邓禄普DUNLOP (飞鱼标识)16、诺基亚轮胎/芬兰Nokian百路驰/美国BFGoodrich19、上海回力轮胎橡胶/中国Warriorshoes20、山东玲珑橡胶/中国LINGLONG23、杭州中策橡胶/中国WESTLAKE24、山东成山/中国Chengshan32、青岛双星轮胎/中国Double Star33、贵州轮胎/中国38、华南轮胎橡胶/中国58、广州珠江橡胶/中国62、北京首创轮胎/中国BCT63、青岛黄海橡胶/中国64、山东中策轮胎/中国66、双钱轮胎/中国Double coin (2个古代的钱币67、辽宁轮胎集团/中国68、徐州轮胎集团/中国W是生产国家,德国,P是生产厂商,也就是PORSCHE的首字母,代表保时捷1是生产车的类型,1代表卡宴,0是跑车.ZZZ是美规车,中规车的话是AA(卡宴3.6),AB(卡宴4.8)AC(卡宴TURBO),AD(卡宴GTS)LA前的那个3是生产年份,3就是2003年的,LA是生产地,代表莱比锡,最后5位是生产序列号,每辆车都是不一样的第1位:生产国家代码1 美国J 日本S 英国2 加拿大K 韩国T 瑞士3 墨西哥L 中国V 法国4 美国R 台湾W 德国6 澳大利亚Y 瑞典9 巴西Z 意大利第2位:汽车制造商代码1 Chevrolet B BMW M Hyundai2 Pontiac B Dodge M Mitsubishi3 Oldsmobile C Chrysler M Mercury4 Buick D Mercedes Benz N Infiniti5 Pontiac E Eagle N Nissan6 Cadillac F Ford P Plymouth7 GM Canada G General Motors S Subaru8 Saturn G Suzuki T Lexus8 Isuzu H Acura T ToyotaA Alfa Romeo H Honda V V olkswagenA Audi J Jeep V VolvoA Jaguar L Daewoo Y MazdaL Lincoln Z FordZ MazdaG = 所有属于通用汽车的品牌:Buick, Cadillac, Chevrolet, Oldsmobile, Pontiac, Saturn第3位:汽车类型代码(不同的厂商有不同的解释)有些厂商可能使用前3位组合代码表示特定的品牌:TRU/W AU Audi 1YV/JM1 Mazda4US/WBA/WBS BMW WDB Mercedes Benz2HM/KMH Hyundai VF3 PeugeotSAJ Jaguar WP0 PorscheSAL Land Rover YK1/YS3 SaabYV1 V olvo第4-8位(VDS)是车辆特征代码(不同的厂商有不同的解释)第9位:校验位0-9或X(罗马数字10)第10位:车型年份B 1981 K 1989 V 1997 5 2005C 1982 L 1990 W 1998 6 2006D 1983 M 1991 X 1999 7 2007E 1984 N 1992 Y 2000 8 2008F 1985 P 1993 1 2001 9 2009G 1986 R 1994 2 2002H 1987 S 1995 3 2003J 1988 T 1996 4 2004第11位:装配厂(不同的厂商有不同的解释)第12-17位:汽车出厂序列号注意:VIN中不会包含I、O、Q 三个英文字母。

IncludingTires with Run-Flat TechnologyREPLACEMENT MARKET PASSENGER and LIGHT TRUCK TIRESTIRE MAINTENANCE, SAFETY and WARRANTY MANUAL Associated BrandsEffective December 20162Congratulations! You have just purchased quality tires from a BRIDGESTONE dealer.To ensure optimum tire performance and reduce the risk of a tire failure, Bridgestone Americas Tire Operations, LLC strongly recommends you read and follow all maintenance and safety information contained in this manual. In addi-tion, we recommend periodic inspection and maintenance, if necessary, by a qualified tire service professional.CONTENTSTire Care Basics: Infl ate. Rotate. Evaluate. ......................... 3Tire Maintenance and Safety Information ............................. 8Tire Failure While Driving ...................................................... 8Tire Infl ation Pressure .. (8)Tips For Safe Tire Infl ation (10)Tips For Safe Loading (11)Tire Damage, Inspection and Service Life ........................... 11Tire Manufacture Date .. (13)Tire Repairs (13)Tire Mounting and Other Servicing ...................................... 15High Performance, Low Aspect Ratio Tires .. (16)Winter Tires (16)High Speed Driving ............................................................. 17Tire Speed Ratings . (17)Tire Spinning (19)Radial Tire Rotation (19)Tire Replacement and Tire Mixing ....................................... 20Your Spare Tire . (21)Tire Storage (22)Tire Service Customer Satisfaction (22)Tire Registration ................................................................. 22RFT Tires with Run-Flat Technology .................................... 23RFT Infl ation Pressure (23)Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) (23)Run-Flat or Low Tire Pressure Operation (24)Distance—How Far You Can Drive (25)Special Service and Repair Issues ...................................... 25Reference Information .......................................................... 27Tire Sidewall Labeling (27)Uniform Tire Quality Grading ............................................... 29Limited Warranty (30)Customer, Vehicle, and Tire Identification .......................... 31Recommended Inflation Pressure ......................... Back Cover Tire Maintenance Record ...................................... Back Cover 4C E R T30psi20psi 4This chart shows you how underinfl ation can create an overload on tires.Check your tire pressure every month to make sure it’s up to specifi cation, especially before long trips or carrying extra weight.Serious personal injury or death may result from a tire fail-ure. Many tire failures are preceded by vibration, bumps, bulges or irregular wear. If a vibration occurs while driving your vehicle or you notice a bump, bulge or irregular wear,It is not often that a properly maintained tire will “blow out” while you are driving. More commonly, if in pressure is lost, it will be gradual. If you do experience a blowout or sudden tire failure, the following informationDriving on tires with improper in•Under-ininternal structural damage.•Over-inFigure 1: EXAMPLE—Tire and Loading Information Placard9Figure 2: EXAMPLE—Tire Information Placard Maximum Pressure Indicated on the Tire Sidewall: This is the maximum permissible in ation pressure for the tire only. The vehicle manufacturer’s recommended tire pressures may be lower than, or the same as, the maxi-mum pressure indicated on the tire sidewall. The vehicle manufacturer’s speci cation of tire pressure is limitedto your particular vehicle and takes into account your vehicle’s load, ride, and handling characteristics, among other criteria. Since there may be several possible vehicle applications for a given tire size, a vehicle manufacturer may choose a different in ation pressure speci cation for that same size tire on a different vehicle. Therefore, always refer to the in ation pressure speci cations on the vehicle tire information placard and/or in your vehicle owner’s manual.Different Tire Pressures for the Front and Rear Tires: For some vehicles, the recommended front and rear in a-tion pressures may be different (such as in the example shown in Figure 2). Make sure you take this into account during in ation pressure checks and when rotating tires. Pressure Loss: Tires can lose 1 psi (7 kPa) per month un-In ating an unsecured tire is dangerous. If it bursts, it could be hurled into the air with explosive force resulting in serious personal injury or death. Never init is secured to the vehicle or a tire mounting machine.Driving your vehicle in an overloaded condition is danger-ous. Overloading causes excessive tire heat build-up and internal structural damage. This can cause a tire failure - (even after the load is reduced) - which could lead to seriousDriving on damaged tires is dangerous. A damaged tire can suddenly fail causing serious personal injury or death. Have your tires regularly inspected by a qualiservice professional.Tires Produced Prior to 2000: The last three (3) digits of the serial code identify the week and year of production. For example, a tire with a code ending in “329” would likely have been produced in the 32nd week of 1999, but possibly produced in 1989. If in doubt, consult a quali ed tire service professional.TIRE REPAIRSSAFETY WARNINGDriving on an improperly repaired tire is dangerous. An improper repair can be unreliable or permit further damage to the tire. The tire may suddenly fail, causing serious personal injury or death. A complete inspection and repairof the tire and the puncture hole is lled with aThis helps ensure that the in-terior of the tire is adequately sealed to prevent in ation pressure loss and prevents contamination of the steel belts and other plies from the elements (such as water)Tell the tire service professional if you have used an aerosol xer to ina highly volatile gas. Always remove the valve core outdoors, away from sources of excessive heat,Removing and replacing tires on wheels can be dangerous. Attempting to mount tires with improper tools or proce-dures may result in a tire explosion causing serious per-sonal injury or death. This is only a job for a qualiWinter driving presents special challenges for vehicle mobility. The use of winter tires (including studs and chains)—while improving traction performance in snow and ice—requires special care with regard to acceleration,Driving at high speed is dangerous and can cause an ac-cident, resulting in serious personal injury or death.•Regardless of the speed and handling capabilities of your18•The tire’s speed rating is void if the tire is repaired,retreaded, damaged, abused, or otherwise altered from its original condition. Thereafter, it should be treated as a non-speed rated tire.•Non-speed rated tires are usually for ordinary passenger car or light truck service and not for high speed driving.•For winter tires used in cold weather conditions, it is generally acceptable to apply a tire with a lower speed rating than your original tires; however, speed should be reduced accordingly. All winter tires should be the same speed rating. Some vehicles have speci c recommen-dations regarding winter tire use; consult your vehicle owner’s manual and tire information placard. See “Win-ter Tires” in this manual.These speed ratings are based on standardized laboratory tests under speci c, controlled conditions. While these tests may relate to performance on the road, real-world driving is rarely identical to any test conditions. Your tire’s actual speed capability may be less than its rated speed since it is affected by factors such as in ation pressure, load, tire condition (including damage), wear, vehicle condition (including alignment), driving conditions, and duration at which the speed is sustained. Use the following chart to compare the speed ratings of tires. Remember: reg-erdless of the tire’s speed rating, drivers should obey speed limits and adjust their speed based on traf c, weather,vehicle and road conditions.The tire’s speed rating designation appears on the tire side-wall with the tire size. Examples:P275/40ZR17 max > 149 mph (240 km/h) ****P275/40R17 93W max = 168 mph (270 km/h)P275/40ZR17 93W max = 168 mph (270 km/h)P275/40ZR17 93Y max = 186 mph (300 km/h)P275/40ZR17 93(Y) max > 186 mph (300 km/h) *****In standardized laboratory tests that relate to highway speeds. Actual tire speed and performance capability Speed Speed Category*Symbol mph km/hM 81 130Q 99 160R 106 170S 112 180T 118 190U 124 200H 130 210V 149 240Z** >149>240W 168 270Y 186 300(Y)*** >186>300dit om ,Spinning a tire to extract a vehicle stuck in mud, ice, snow, or wet grass can be dangerous. A tire spinning at a speed-ometer reading above 35 mph (55 km/h) can in a matter of seconds reach a rotation speed capable of disintegrat-Driving your vehicle with an improper mix of tires is dangerous. Your vehicle’s handling characteristics may be seriously affected. You could have an accident resulting in serious personal injury or death. Consult your vehicleCheck inin ation pressure when using your spare tire can result in serious personal injury or death. See “Tire Insure” in this manual.Mounting a “temporary use” tire on a wheel which is not speci cally designed for it, or placing another type tire on a wheel designated for temporary use can be dangerous. Your vehicle’s handling characteristics can be seriously af-Improper storage can damage your tires in ways that may not be visible and can lead to a failure resulting in serious personal injury or death.TIRES with RUN-FLAT TECHNOLOGY If your vehicle is equipped with Bridgestone or Firestone brand RFT tires, this chapter presents speci c maintenanceSerious personal injury or death may result from a tire fail-ure or accident due to improper run-operation. Read and follow the instructions below, and the other maintenance and safety recommendations elsewhere25DISTANCE—HOW FAR YOU CAN DRIVERFT tires are capable of operating up to the distance of 50 miles (80km) at a maximum speed of 50 mph (80 km/h) in run-flat or low pressure operation. However, the distance capability may be less (or more) depending upon the actual vehicle application and specific operating conditions.Factors affecting run-flat or low tire pressure operating distance include vehicle speed, load, and maneuvering; the amount of inflation pressure loss; the extent of any tire damage; and ambient temperature. To maximize the dis-tance capability in a run-flat or low pressure condition:•Reduce vehicle speed as much as safely and reasonablypossible. Do not exceed 50 mph (80 km/h).• Avoid abrupt or aggressive acceleration, braking, or cornering maneuvers as much as safely and reasonably possible. Avoid pot holes and other road hazards.Higher vehicle loads (such as with more passengers or cargo) and higher ambient temperatures decrease the dis-tance capability of an RFT tire in run-flat or low pressure operation.Note:•If the sidewall of the RFT tire specifies a run-flat or low pressure distance limitation, do not exceed the specified distance.•The distance capability of the vehicle is limited to the distance capability of the specific RFT tire that is operat-ing in a run-flat or low pressure condition.•For original equipment specification RTF tires applied to vehicles originally equipped with these tires, see the vehicle owner’s manual for distance limitations during run-flat or low pressure operation.If in doubt about the distance capability of an RFT tire, do not exceed 50 miles (80 km) in run-low or low pressure operation. Seek tire service as soon as possible to minimize tire damage.SPECIAL SERVICE and REPAIR ISSUESAuthorized RFT Service Centers Because of the advanced technology and design of RFT tires and the required tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS), only qualified tire service professionals with the proper equipment and training should service RFT tires. For instance, the use of tire mounting equipment that is unsuitable for an RFT tire may damage the tire beyond repair. Therefore, it is recommended to go to an authorized Bridgestone or Firestone brand tire retailer for service and replacement.Call toll-free 1-800-847-3272 or visit to locate the nearest Bridgestone or Firestone brand retailer.. r-il-he e n -r d r- w yhe d yInspection after Run-Flat or Low Pressure Operation Following run-flat or low tire pressure operation, or in the event of any other tire damage or unusual condition, it is very important to obtain a proper and complete tire evaluation as soon as possible.RotationFollow the vehicle manufacturer’s recommenda-tions, or rotate every 5,000 miles (8,000 km) per the recommendations in this manual (see “Radial Tire Rota-tion”). In some cases, TPMS devices require reprogram-ming with each tire rotation.RFT Tire ReplacementDo not replace or mix RFT tires with conventional tires, unless on an emergency/temporary basis. Conventional tires do not have run-flat capability and the handling characteristics of the vehicle with these tires may be different. If a conventional tire is used on an emergency/ temporary basis, verify that its size, load capacity, inflation pressure, and speed rating specifications meet the require-ments of the vehicle. Replace any conventional tire with the proper RFT tire as soon as possible.RFT Tire Damage and RepairNo tire, regardless of its design or quality is indestructible. RFT tires can be ultimately rendered unusable due to a puncture or other road hazard as well as from improper low tire pressure operation. Some punctures may be repaired under certain restrictions and prescribed procedures. An im-proper repair is unsafe and will void the Limited Warranty. When driven fl at or with low pressure, factors affecting reparability include vehicle speed, load, and maneuvering; the amount of inflation pressure loss; and ambient tem-perature. In any situation, the extent and location of direct damage from a puncturing object or other road hazard are also critical factors.RFT tires are not repairable in any of the following situations:•If the tire was operated with infl ation pressure less than 15 psi (100 kPa).• Abrasion or other damage is present on the exterior tread, sidewall or bead areas.• Abrasion, wrinkling, or separation is present on the tire interior.• Any condition or damage is present that disqualifies repair of a conventional tire.A qualifi ed tire service professional should fully inspect your tire, inside and out, to determine if the tire can be repaired. Tire damage is not always visible from the outside and the tire must be removed from the wheel for a complete inspection. For more information, see “Tire Repairs” in this manual.l low26Figure 3: Typical Passenger Tire MarkingsFigure 4: Typical Light Truck Tire Markings2728Tire Size, Load Range, Load Index, and Speed Symbol:DOT Symbol and Tire Identi cation Number: The “DOT” symbol constitutes a certi cation that the tire conforms to applicable U.S. Department of Transportation motor vehicle safety standards (for tires). Following the “DOT” symbol is the tire identi cation number, also knownas the DOT serial number or code. For example:(a)DOT Symbol(b)Plant of Manufacture Code(c)Tire Size Code(d)Tire Manufacturer’s Code(e)Week of Production (01-53)(f)Year of Production (last two digits of year)**For tires produced from 2000-on. In the example above,the tire was produced in the 18th week of 2000. For tires produced prior to 2000, there is one digit in group (f) which identi es the last digit of the year of production, i.e. “329”would likely signify the 32nd week of 1999, but could pos-sibly signify the 32nd week of 1989. If in doubt, consult a quali ed tire service professional.The DOT symbol and tire identi cation number can be found on at least one sidewall near the wheel. The other sidewall may have a partial serial code that excludes (e) and (f) above.Maximum Load and Ination: The maximum load and maximum in ation pressure is marked on each sidewall in metric and English units. For example:MAX LOAD 685 kg (1510 lbs) AT 240 kPa (35 psi) MAX PRESSNote: The load and in ation values marked on the tiresidewall are maximum permissible values for the tire only. Never assume that these values are the actual recommended load capacity or tire pressure values for your vehicle. See “Tire In ation Pressure,” “Tips for Safe Tire In ation,” and “Tips for Safe Loading” in this manual.Ply Composition and Materials: The actual number of plies in the sidewall and tread area and the generic name(s) Examples: Tire Size Load Speed Load Index Symbol Range Figure 3 P215/65R15 95 H --Figure 4 LT235/85R16 114/111 Q D DOT EL CB DKE 1800(a)(b) (c) (d) (e) (f)*wa u les per r r a e29ol:n e, 9” os- a d n X y e s) eof their cord material(s) are marked on at least one side-wall. For example:TREAD 2 PLY POLYESTER + 2 STEEL SIDEWALL 2 PLY POLYESTERRadial: Radial ply tires will have the word “radial” on at least one sidewall. An “R” in the tire size designation also indicates radial ply construction.Tubeless or Tube Type: Tires are marked as either “tube-less” or “tube type,” whichever is applicable, on at least one sidewall.UNIFORM TIRE QUALITY GRADINGThe Uniform Tire Quality Grading (“UTQG”) standards are intended to assist you in making an informed choice in your purchase of passenger car tires by providing information indicating relative performance of these tires in the areas of tread wear, wet braking traction (straight-ahead), and tem-perature resistance. All passenger car tires must conform to federal safety requirements in addition to these grades.Treadwear The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on thewear rate of the tire when tested under controlled condi-tions on a speci ed government test course. For example, a tire graded 150 would wear one and one half (1½ ) times as well on the government course as a tire graded 100. The relative performance of tires depends upon the actual conditions of their use, however, and may depart signi -cantly from the norm due to variation in driving habits, service practices and differences in road characteristics and climate.Traction The traction grades, from highest to lowest, are AA, A, B, and C. Those grades represent the tire’s ability to stop onwet pavement as measured under controlled conditions on speci ed government test surfaces of asphalt and concrete.Warning: The traction grade assigned to a tire is based onstraight-ahead braking traction tests, and does not include acceleration, cornering, hydroplaning, or peak traction characteristics.TemperatureThe temperature grades are A (the highest), B, and C, representing the tire’s resistance to the generation of heat and its ability to dissipate heat when tested under con-trolled conditions on a speci ed indoor laboratory testwheel. Sustained high temperature can cause the material of the tire to degenerate and reduce tire life, and excessivetemperature can lead to sudden tire failure. The grade C corresponds to a level of performance which all passenger car tires must meet under the Federal Motor Vehicle SafetyTires with Run-Flat TechnologyMAINTENANCE RECORDI n s p e c ti o n R o t a ti o n B a la n c eMileage Date Retailer。


汽车轮胎知识大全提起轮胎的种类,其实有很多种分法:有按车种分类的,有按用途分类的,有按大小分类的,有按花纹分类的,有按构造分类的。
按汽车种类分类轮胎按车种分类,大概可分为8种。
即:PC——轿车轮胎;LT——轻型载货汽车轮胎;TB——载货汽车及大客车胎;AG——农用车轮胎;OTR——工程车轮胎;ID——工业用车轮胎;AC——飞机轮胎;MC——摩托车轮胎。
按轮胎用途分类轮胎按用途分类,包括载重轮胎、客车用轮胎及矿山用轮胎等种类。
按轮胎大小分类轮胎按大小分类,一般是指外胎的断面宽度在17in(英寸,1in=25.4mm)以上的轮胎,这种轮胎属于巨型轮胎;外胎断面宽度在17in以下、10in以上的轮胎属于大型轮胎;外胎断面宽度在10in以下的轮胎属于中小型轮胎。
按轮胎花纹分类轮胎按花纹分类有很多种,但大体上可以分为五种:直沟花纹,也叫普通花纹、横沟花纹、泥雪地花纹、越野花纹按轮胎结构分类轮胎按照构造分类,以目前广泛使用的情况来分,可分为斜交轮胎和子午线轮胎两大类。
轮胎的作用一部汽车由上万种零部件组成,而每一个部件,一般只能起到一种作用。
轮胎,也是汽车的零部件之一,但是,它和其他零部件所起到的作用却不同,它在汽车行驶当中要起到以下四种作用。
承受载荷一部汽车不论是它的自重,还是乘人或载物,其重量都要通过车体传到轮胎,最后由轮胎肩负起全部的重担,所以,轮胎在承载方面起着十分重要的作用。
产生驱动力与制动力因为轮胎是汽车上唯一与路面接触的部位,因此,不论是汽车的起动、行驶、还是制动、停车都要通过轮胎与路面"沟通",并通过轮胎来完成汽车或汽车驾驶人员的意愿。
缓冲和吸震未经铺设的路面,大多是凸凹不平的石子路,路面上会有很多碎石或坑、包,即使是铺设的路面,也经常有一些障碍物,影响汽车的正常行驶。
在这种情况下,轮胎就会发挥它的卓越的缓冲和吸震功能,使汽车能在较为舒适的情况下前行。
这是因为,轮胎本身就是由具有弹性的50%左右的橡胶制成,加之轮胎内的空气的绝妙的吸震功能,所以才能使汽车在恶劣的路面也能轻松自如地前行。

轮胎知识大全及各品牌轮胎型号轮胎知识大全及各品牌轮胎型号和报价1,轮胎知识:有许多有用的信息被模制到轮胎的胎侧上,例如轮胎种类、花纹、规格、有无内胎、速度级别、载重指数、扁平比以及重要的安全标示等等。
例: P215/65R15 89H“P” 是指轿车轮胎。
(用以区别卡车或其他车型适用的轮胎)“215”指的是轮胎断面的宽度,是两个胎侧之间的宽度(以毫米为单位)。
此宽度随轮胎所匹配轮辋宽度的不同而不同:宽轮辋配宽轮胎,窄轮辋配窄轮胎。
一般在胎侧上所标示的胎宽,是指当轮胎安装到所建议宽度的轮辋时的宽度。
“65”是轮胎的扁平比,是胎宽与胎高的比例,这里指胎高占胎宽的65%,数值越小,越显扁平。
“R”是指轮胎的结构,表示此轮胎为子午线结构,也就是说它的帘布层是呈辅射状排布在胎体内的。
“B”表示轮胎为斜交结构,目前斜交结构的轿车轮胎已不复存在。
“15”表示轮辋直径(以英寸为单位),此轮胎必须匹配15英寸的轮辋,否则无法安装。
“89”表示载重指数:此轮胎最高载重为1,279磅。
不同的载重指数代表不同的最高载重(通常以磅或公斤为单位)。
“H”表示速度级别:此轮胎最高时速为每小时130英里。
旧式欧洲胎边标示系统中以215/65HR15表示。
不同的英文字母表示不同的速度级别。
“DOT”则表示此轮胎符合美国交通部(U.S. Department of Transportation, DOT)规定的安全标准。
“DOT”后面紧挨着的11位数字及字母则表示此轮胎的识别号码或序列号。
胎侧通常也显示帘线种类、胎侧和胎面帘布层数。
轮胎分级:统一轮胎品质分级系统(Uniform Tire Quality Grading System, UTQG) 除雪地胎外,DOT要求制造厂依据“胎面磨耗” “抓地力” 及“耐高温”三个性能要素将轿车轮胎分级。
胎面磨耗率超过100-较优100-标准低于100-较差。
磨耗等级是根据在美国**指定的试验场地,按标准条件测试的磨耗率换算得出的。


十大汽车轮胎品牌介绍(jièshào)及几大品牌评点十大汽车轮胎品牌(pǐn pái)米其林在1898年里昂的第一次展览会上,米其林兄弟发现墙角的一堆直径大小不同的轮胎很像人的形状。
不久后画家欧家洛就根据那堆轮胎的样子创造出一个由许多轮胎组成的特别人物造型,于是(yúshì),米其林轮胎人——“必比登(Bibendum)”诞生了。
由可拆换轮胎发展至最新的“胎唇垂直锚泊”轮胎(PAX系统),米其林的产品已经遍及许多领域,无论是汽车,或是工程、农业机械、悬挂系统,甚至是航天领域,米其林的技术无所不在。
全球每一个国度的汽车,包括古董车、轻型客车、豪华轿车、四轮驱动越野车、各种级别(jíbié)的卡车……都装备了其全天候轮胎或是雪地轮胎,米其林的足迹遍及全球。
如果(rúguǒ)对这品牌认可,可以小推荐一下。
在国内你可以买到以下系列偏向于经济型与操控型:EnergyXM1+、EnergyXM1偏向舒适型与操控型:EnergyMXV8、CERTIS舒适型:VIVACY运动型+操控型:PilotPrecedaPP2、PilotSportCup、PilotSportPS2、PilotSportPS2、PilotPrecedaPP1、PilotPrimacy邓禄普英国人J.B.邓禄普1888年首创充气轮胎,建立了邓禄普品牌。
大约100年后,邓禄普品牌归入日本住友橡胶工业集团旗下。
上个世纪90年代初期,住友将邓禄普轮胎推向中国市场。
2002年6月,住友在江苏常熟建立了独资的住友橡胶(常熟)有限公司。
邓禄普在中国制造的轮胎为中高档轮胎,全部采用其独有的“数码配方”技术,被称之为“数码轮胎”。
“数码配方”技术是利用超级计算机将轮胎转动中发生的各种现象的模拟试验变为可能的数字旋转技术与由此产生的固有技术的总称。
国产邓禄普轮胎最大的特点是没特点(和普利司通类似,下面会提到),静音舒适性不如米其林和马牌,抓地力不如倍耐力,属于比较中性的轮胎。
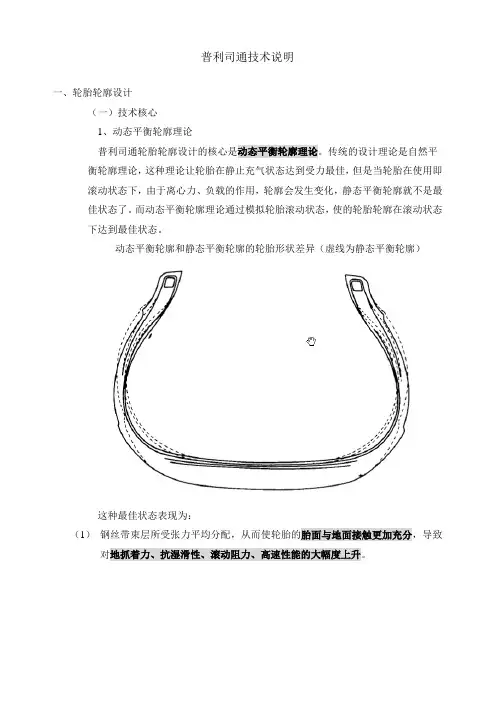
普利司通技术说明一、轮胎轮廓设计(一)技术核心1、动态平衡轮廓理论普利司通轮胎轮廓设计的核心是动态平衡轮廓理论。
传统的设计理论是自然平衡轮廓理论,这种理论让轮胎在静止充气状态达到受力最佳,但是当轮胎在使用即滚动状态下,由于离心力、负载的作用,轮廓会发生变化,静态平衡轮廓就不是最佳状态了。
而动态平衡轮廓理论通过模拟轮胎滚动状态,使的轮胎轮廓在滚动状态下达到最佳状态。
动态平衡轮廓和静态平衡轮廓的轮胎形状差异(虚线为静态平衡轮廓)这种最佳状态表现为:(1)钢丝带束层所受张力平均分配,从而使轮胎的胎面与地面接触更加充分,导致对地抓着力、抗湿滑性、滚动阻力、高速性能的大幅度上升。
传统理论设计的轮胎接地状态,胎面与地面接触不充分动态平衡理论设计的轮胎接地状态,胎面与地面接触比较充分(2)动态平衡轮廓的轮胎因为轮廓形状设计的合理,轮胎子口部位在充气压力的作用下向上抬起,减少了子口部位和轮辋的应力作用,耐久性能更好;传统设计理论的轮廓子口部位往往被充气压力压向轮辋,当子口部位不断曲挠变形的时候很容易损坏,耐久性能不佳。
2、BBB设计理论BBB设计理论是在动态平衡轮廓理论基础上发展起来的,它的目的是在保持轮胎总体良好性能的基础上把轮廓缩小,从而达到有效降低轮胎成本、提升轮胎性价比的效果。
一般轮胎的直径和宽度都是按照国际标准值设计,如果小于标准值就会造成轮胎体积偏小,负载能力和刚性不足,影响安全性和操作性能。
但是BBB设计技术的应用可以使轮胎的直径和宽度都小于标准值(仍然在标准值的下限范围之内),它的原理就是通过特定程序的计算,得出轮胎轮廓的几个关键点,然后依据这几个点按照特定的方法绘制出轮廓,使的整个轮胎的胎肩和子口这两个轮胎最关键的部位处于最佳平衡状态,并且在轮胎的体积缩小的情况下仍然保证足够的刚性,满足车辆操纵的需求。
BBB设计使的轮胎比普通轮胎具有明显的成本优势,并且性能也犹有过之。
(二)技术优势普利司通轮胎轮廓设计的两大支柱就是动态平衡轮廓理论和BBB设计理论,这两种理论综合运用,用最小的资源消耗达到最佳的性能,具有巨大的竞争优势:1、在使用相同的骨架材料和胶料的情况下,普利司通技术的轮胎具有更好操纵性、安全性、低滚阻、抗湿滑性。

汽车轮胎知识大全轮胎的种类提起轮胎的种类,其实有很多种分法:有按车种分类的,有按用途分类的,有按大小分类的,有按花纹分类的,有按构造分类的。
●按汽车种类分类轮胎按车种分类,大概可分为8种。
即:PC——轿车轮胎;LT——轻型载货汽车轮胎;TB——载货汽车及大客车胎;AG——农用车轮胎;OTR——工程车轮胎;ID——工业用车轮胎;AC——飞机轮胎;MC——摩托车轮胎。
●按轮胎用途分类轮胎按用途分类,包括载重轮胎、客车用轮胎及矿山用轮胎等种类。
载重轮胎除了在胎壁上标有规格尺寸以外,还必须标明层级数。
但在这里需要告诉大家的是,载重轮胎的层级数并不是指它的实际层数,而是指用高强度材料帘线制作胎体的轮胎,其负荷性能相当于用棉帘线制作胎体的轮胎帘布层数。
这是因为棉帘线是最早用于制作胎体帘线的,因此,国际惯例即以棉帘线层为表示轮胎层数的基准。
不同层级,轮胎的负荷能力不同。
即使相同规格的轮胎,因为它的层级数不同,它的负荷能力也不相同,所以,不同层级的轮胎,不能在同一轴上使用,否则,在高速行驶并负载的情况下就会发生危险。
比如:解放车用的900—20轮胎(16层级) 就不能和900—20轮胎(14层级)同用在一轴上,因为它们的层级不同,负荷不同,混用以后就容易发生危险。
轻型货车或面包车用的轻型子午线载重轮胎都要在轮胎型号的后面加一个字母"C",以便和轿车用的子午线轮胎加以区分。
如:金杯面包车用的轮胎185SR14C,其中的"C"即指此轮胎为轻型载重轮胎。
而美国标准则规定:客车用的轮胎,要在轮胎规格前面用字母"P"加以表示。
如:切诺基用的 P215/75R15轮胎,其中的"P"即指此轮胎为客车用轮胎。
有很多驾驶员不懂得这个"P"字的含义,一味迷信它,认为美国车上就必须使用带"P"的轮胎,因此,在换轮胎时没有"P"字的轮胎不敢使用,经常闹出一些笑话。

轮胎基本知识培训教材第一章轮胎基础知识一、轮胎发展简史:• 1493-1495年哥伦布发现橡胶• 1839年美国固特异轮胎公司发明硫化方法• 1888年英国邓录普公司开发充气自行车胎• 1900年使用棉帘线• 1905年在胎圈部位使用钢丝• 1912年使用碳黑• 1931年美国DUPONT公司成功地将合成橡胶用于工业化生产• 1938年使用人造丝帘子布 (RAYON CORD)• 1942年使用尼龙帘子布 (NYLON CORD)• 1948年法国米其林公司开发子午线轮胎• 1948年 B.F. GOOD RICH 开发无内胎轮胎• 1963年使用涤纶帘子布(POLYESTER)• 1971年皮列里公司开发VR轿车胎 (V-240Km/Hr)• 1979年费尔斯通公司开发微型备用胎• 1983年法国米其林公司开发飞机子午线轮胎• 1984年普利司通轿车轮胎的新断面设计理论RCOT发表二、轮胎用原材料轮胎制造的早期,采用基本的原料是天然橡胶,棉纱帘子线和钢丝。
未经加工的天然橡胶是塑胶形态,只有将其变为弹性状态,才能使它有足够的强度来抵抗运行中遇到的各种情况。
人造合成橡胶是以天然橡胶为基楚加配各种化学物品进行改良以达到硬度,耐磨,及抗热等特性。
在制造轮胎过程需要利用热和特定的化学品,作为引发变化的启动剂和加快变化的催化剂。
硫磺作为交叉连结的媒介(硫化)。
1( 橡胶:天然橡胶存在于橡树中的奶状树汁中。
割开橡胶树的树皮时,奶状树汁(胶乳)便会流出来。
这种橡树主要生长于东南亚、非洲和南美洲。
在胶乳加入醋酸和甲酸三至四小时后,一块白色的海棉状凝结块便形成了。
凝结物被传送到压片机组,在这里它同时被压平和清洗,再被切割成1/8英寸厚的长片段,放在架上烘干,然后在工厂里进行混合或加工。
橡胶需要加入化学品变成人工合成橡胶具备一些截然不同的特性,以适应各种产品所需要的特性。
轮胎对橡胶有很多样化的要求,其中有:抗热,抗磨,抗油,抓地力,防渗透,及有弹性(全橡胶)。
轮胎的知识——天热了,请重视- -近年来,车辆的爆胎事故骤然增多。
据统计,高速公路上的交通事故中爆胎占70%以上。
频频发生的爆胎事故造成的车祸引起了人们的警觉和困惑。
为什么以前的车况路况都不怎么好时爆胎不多见,现在车况路况都提高了,爆胎反而这么多?这主要是因为人们没有意识到高速行驶的车辆对轮胎和轮胎的保护提出了更高的要求。
爆胎的原因是多方面的,是一种复杂的轮胎破坏现象。
爆胎事故危险大,车毁人亡慨率高,保险公司不理赔。
致使有些人谈虎色变,认为爆胎防不胜防。
其实只要弄清楚爆胎的根本原因,找到祸根,问题是不难解决的。
轮胎缺气行驶是爆胎的祸根。
车辆在缺气(轮胎胎压低于标准胎压)行驶时,随着胎压的下降,轮胎与地面的摩擦成倍增加,胎温急剧升高,轮胎变软,强度急剧下降。
这种情况下,如果车辆在低速行驶,也会伤胎,而且潜伏期长,隐蔽性大,更有危害性,为以后高速行车时埋下爆胎的重大隐患。
现以无内胎轮胎(即子午线轮胎)为例说明轮胎缺气行驶是爆胎的祸根。
剖析如下:为了提高轮胎的强度,在其帘布层外围加有一层钢丝。
这种结构的轮胎强度高,散热条件好,适应高速行驶。
但它也有一个极大的弱点,最怕缺气行驶。
当轮胎缺气行驶时,除了轮胎与地面摩擦生热外,胎体内的钢丝与轮胎之间也会摩擦生热,过热状态会加速钢丝与橡胶的老化、变形,甚至内部断裂以致断层,致使轮胎强度遭到破坏,种下爆胎的祸根。
所谓重视平时对轮胎的保护,其中重要的一条,就是一定要做到防止车辆轮胎缺气行驶。
一定要定期检查胎压,保持标准胎压(车辆出厂对胎压都有严格的规定)。
简而言之,哪怕是发生一次缺气行驶,也会破坏轮胎结构和强度,种下爆胎的祸根!而只要防止了缺气行驶,就能保护轮胎的结构和强度,避免爆胎事故的发生。
看来预防爆胎的问题转变成了防止轮胎缺气行驶的问题,进而又转变成克服慢撒气的问题。
也就是说,只要克服了轮胎的慢撒气就可以克服缺气行驶,从而防止爆胎;而对受过伤的轮胎不要再使用,也能有效地防止爆胎。
轮胎基础知识Establish standards and manage them well. January 26, 2023汽车知识轮胎基础知识总集轮胎基本知识一轮胎原料"轮胎原料宏观:"1橡胶丁苯橡胶SBR顺丁橡胶PBD异戊橡胶PI"2帘子布1)棉纱——强度低,易吸水2)人造丝——强度高,用于带束层3)尼龙——强度高,耐疲劳,用于胎体4)聚酯——强度高,用于胎体5)玻璃纤维——用于轿车胎6)钢丝——强度高,与胶料之粘着性佳,用于带束层与胎体"3化学添加物1)炭黑:增加橡胶强度耐磨性降低成本2)氧化锌:白胶之补强填充剂,加硫活化剂3)硫磺粉:硫化剂4)油料:使胶料易于加工5)硬脂酸:是各种成分均匀分散剂加硫活化剂6)树脂:增加胶料与帘布间的粘着强度7)促进剂:减少硫化时间8)抗氧化剂:防止龟裂及耐天候"4钢丝用于胎圈及胎体,带束层等"轮胎原料料微观:"14%天然橡胶"27%人造聚合物"28%炭黑"10%石油"4%其他石油产品"4%纤维"10%钢丝"3%其他成分"100%=+/-8.5公斤轮胎分类a)"轮胎常见得分类方式是按照结构划分为斜交线轮胎、子午线轮胎;b)"主要区别是胎体帘线角度和胎体骨架材料不同,同时带束层也采用了不同的材料;c)"子午线轮胎与斜交线轮胎的根本区别在于胎体;斜交线轮胎的胎体是斜线交叉的帘布层,采用尼龙帘线,其帘线与轮胎圆周有一定的角度30—45°;d)"而子午线轮胎的胎体是聚合物多层交叉材质,帘线角度如地球子午线状排列,其顶层是数层由几乎不能伸张的、沿周向小角度钢丝帘线编成的钢丝带束层,其作用如同坦克履带在路面上延展可减少轮胎被异物刺破的几率子午线轮胎中的钢丝带则具有较好的柔韧性以适应路面的不规则冲击,又经久耐用,它的帘布层还意味着在汽车行驶中有比斜交线小的多的摩擦,从而获得了较长的胎纹使用寿命和较好的燃油经济性;e)"从设计上讲,斜交线轮胎的适用路面范围更广,在高负载情况下的下沉量小,能满足一般速度下的使用要求,斜交线轮胎有许多局限性,如由于交叉的帘线强烈摩擦,使胎体易生热,因此加速了胎纹的磨损,且其帘线布局也不能很好地提供优良的操控性和舒适性;另外,和斜交线轮胎相比,子午线轮胎还有更好的抓地性;f)"由于子午线轮胎胎侧较薄,容易被割破损坏,不适合长期在差路面上行驶;g)"子午线轮胎本身具有的特点使轮胎无内胎成为可能;无内胎轮胎有一个公认优点,即当轮胎被扎破以后,不象有内胎斜交线轮胎那样爆裂这是非常危险的,而是使轮胎能在一段时间内保持气压,提高了汽车的行驶安全性;目前轿车普遍使用子午线轮胎,俗称真空胎或钢丝胎;轮胎基本知识二子午线轮胎的基本结构1)"胎面:是轮胎直接与地面接触的部位,胎面具有不同种类或形式的花纹以适应不同的路面条件;胎面花纹提供驱动、牵引、制动、排水、防滑、转向等功能;它包括接地的中央部分和胎肩部分;2)"胎侧:胎侧与地面并不直接接触,但是它能起到一个“柔性弹簧”的作用,吸收震动和冲击,减轻车辆的颠簸,有利于提高舒适性能;同时轮胎的各种标记及必要的使用说明也都集中于此;3)"胎体帘线:通俗的说法就是轮胎的骨架;它主要能形成包容轮胎内部的气腔,承受轮胎的载荷;4)"胎圈:是与轮辋配合的部分它的主要作用是使轮胎能够紧紧固定在轮辋上;它是由高张力的钢丝组组成的;5)"内衬层:对于无内胎轮胎来说,其胎里内部有一层密封性能良好的胶料,称为内衬层;它可以起到防止空气泄露的作用;6)"带束层:钢丝带束层是子午线轮胎特有结构,它位于胎面和胎体之间,宽度覆盖整个轮胎行驶面;它由钢丝组成,能承受相当的负荷,增强整个胎面区域的强度缓和路面的冲击,使轮胎具有高速、耐穿刺等优异性能;轮胎基础知识三轮胎花纹"在轮胎表面刻有各式各样的花纹,这些花纹是配合轮胎、车辆的使用性能及路面情况而设计的; "主要作用是:增加轮胎与地面的摩擦力,减少车辆的滑动,增强车辆的牵引性能,从而保证安全行驶;花纹还能够帮助轮胎排水,减轻或杜绝水膜现象的发生;合理调整花纹排列及大小可降低轮胎在行驶过程中产生的噪音,有利于驾驶者舒适驾驶;同时,好的花纹设计对于车辆来说可以增加整体的美感,也是一种时尚;1)"从安装的角度:可分为普通花纹、单导向花纹、非对称花纹;2)"从使用的角度:可分为铺装路面花纹、非铺装路面花纹、两用花纹;3)"从气候的角度:可分为四季花纹、夏季花纹、冬季花纹;在花纹的深处,有一个“小平台”或“小突起”,它表示的是花纹的磨耗标记,即花纹如果一旦磨损到这个位置,那么这条轮胎就必须换下,否则在使用中就会发生打滑等危险;在花纹接近胎侧的侧面均标有“TWI””或“△”的标记,指明磨耗标记所在的位置;轮胎基础知识四轮胎胎侧标示"轮胎是汽车的重要部件,在汽车轮胎上的标记有十余种,正确识别这些标记对轮胎的选配、使用、保养十分重要,对于保障行车安全,延长轮胎使用寿命具有重要意义;""轮胎规格:规格是轮胎几何参数与物理性能的标志数据;轮胎规格常用一组数字表示,如185/60R14 82H"185 胎面宽单位:毫米"60 扁平比胎高/胎宽"R子午线结构"14 轮辋直径单位:毫米"82 载重指数单胎所能承受最大载荷,单位:kg 475kg"H 速度级别最高安全时速,210km/h1)"层级:指轮胎橡胶层内帘布的公称层数,与实际帘布层数不完全一致,是轮胎强度的重要指示;中文标示12层级英文标示12PR2)"帘线材料:尼龙NYLON聚脂POLYESTER钢丝STEEL3)"负荷及气压:一般标示最大负荷及相称气压,负荷以“kg”为单位,气压既轮胎胎压,单位为“kpa”,MAXLOAD475kg1047ibs300kpa44psiMAXPRESS4)"平衡标志:用彩色橡胶制成标记形状,印在轮胎胎侧,表示轮胎此处最轻,组装时应正对气门嘴,以保证整个轮胎的平衡性;轮胎基础知识五(一)"滚动方向:轮胎上的花纹对行驶中的排水防滑特别关键,所以运动款“v”字型花纹的轮胎常用箭头标志装配滚动方向,不对称花纹常在一面胎侧标示“SIDEFACINGOUTWARDS”意思此面冲外;以保证设计的附着力、防滑等性能,如装反则适得其反;(二)"磨耗指示点:在轮胎胎肩对应六个“△”型标记,在标记处花纹沟槽中有橡胶棱台标示轮胎磨损极限,一旦轮胎磨损到这一位置时,应及时更换;(三)"这时花纹剩余沟深不足10%1.6毫米,轮胎大部分故障发生在这一阶段,轮胎对正常路面已不能提供足够大的抓地力,在潮湿积水路面行驶时,则会出现打滑现象,亦会因强度不够中途爆胎;(四)"生产批号:DOT美国标准美国联邦交通委员会的英文缩写意为符合美国联邦交通委员会强制认证标准;如DOT7LF82YMR3706前面两组是技术代号,后面四位为生产日期2006年第37周生产;(五)"商标:是轮胎生产厂家的标志,包括商标文字及图案,一般比较突出和醒目,易于识别;(六)"花纹代号:常用英文、数字或英文加数字表示;如固特异DUCAROGA、韩泰866、普利司通SF-350轮胎基础知识六"其他标记:"ALLSTEELRADIAL或RADIA 全钢子午线轮胎"TREADPLESSTEELCORD 胎面/层钢丝"SIDEWALLPLYSTEELCORD胎侧/层钢丝"EECE证号欧盟强制认证标准"DUCAROGA 花纹代号"TUBELESSTYPE或TUBELESS 无内胎"MADEIN生产国别"Treadwear240磨耗系数"TemperatureB温度指数温度级数是B级,级别由好到差A,B,C三种;""TractionA抓地级别抓地等级是A级,级别由好到差A,B,C三种;"注意:“CCC”三C强制认证,没有有问题;" 轮胎标记一般都标志得比较规范,识别清楚后就可以放心选配装;轮胎基础知识七主要轮胎品牌英文对照固特异轮胎GOODYEAR""米其林MICHELIN""普利司通BRIDGESTONE""倍耐力PIRELLI登录普DONLUP""韩泰HANKOOK横滨YOKOHAMA""马牌CONTINENTAL""锦湖KUMHO""常用名词英文对照""胎面tread胎侧sidewall""带束层belt帘布层ply""世界轮胎三大品牌是""固特异米其林普利司通轮胎花纹的作用轮胎花纹的主要作用就是增加胎面与路面间的磨擦力,以防止车轮打滑,这与鞋底花纹的作用如出一辙;轮胎花纹提高了胎面接地弹性,在胎面和路面间切向力如驱动力、制动力和横向力的作用下,花纹块能产生较大的切向弹性变形;切向力增加,切向变形随之增大,接触面的“磨擦作用”也就随之增强,进而抑制了胎面与路面打滑或打滑趋势;这在很大程度上消除了无花纹光胎面轮胎易打滑的弊病,使得与轮胎和路面间磨擦性能有关的汽车性能——动力性、制动性、转向操纵性和行驶安全性的正常发挥有了可靠的保障;有研究表明,产生胎面和路面间磨擦力的因素还包括有这两面间的粘着作用,分子引力作用以及路面小尺雨微凸体对胎面貌一新微切削作用等,但是,起主要作用的仍是花纹块的弹性变形;花纹都分哪几种纵沟胎纹=操纵安定性优良/转动抵抗小抵噪音/排水性佳/不易横向滑动;横沟胎纹=驱动力、制动力、牵引力优/耐磨性佳;纵横胎纹=兼具纵沟及横沟胎纹的优点;块状胎纹=驱动力及制动力都很好;越野花纹=越野花纹是专门为适应干、湿、崎岖山路和泥泞、沙路而设计的花纹;轮胎基础知识七轮胎各部分的功能胎面:抓地力耐磨性带束层:加强胎体稳固胎面防止刺穿帘布层:构成胎体承受重力传导外力胎侧:保护胎体耐屈挠及耐天候内衬胶:在无内胎型轮胎中扮演内胎包住空气三角胶:天充下胎边,为耐屈挠胎侧及坚硬钢丝圈之过度物防擦胶:保护钢丝圈,高耐摩擦之硬橡胶GG线:轮胎与轮毂同心之指示线钢丝圈:高强度钢丝束,维持轮胎和轮毂在同一转动面,并固定在轮毂上子午线轮胎的有点较大里程较低的滚动阻力省油防刺阻力增加钢丝带束层噪音小胎体冷却较快不易故障抓地力强安全车子零件磨损少货物不易受损无内胎型轮胎的有点减少路上的耽误装胎简易安全减轻重量散热快阻力小影响轮胎磨耗的因素不可控因素天侯气温路面构造弯路或直路可控制的因素充气压力载重速度定位驾驶习惯机械维护轮胎选择悬吊系统米其林MICHELIN1889法国邓禄普DUNLOP1888日本普利司通BRIGDESTONE1931日本横滨YOKOHAMA1917日本固特异GOODYEAR1898美国固铂COOPER1914美国马牌CONTINANTAL1871德国东洋TOYO1945日本倍耐力PIRELLI1872意大利玛吉斯MAXXIS1967台湾。