Fortran90第六章、第七章习题答案
- 格式:doc
- 大小:33.50 KB
- 文档页数:3
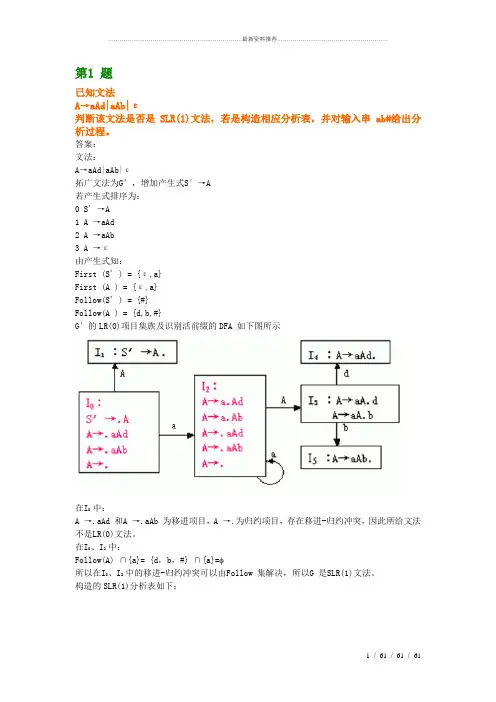
第1 题已知文法A→aAd|aAb|ε判断该文法是否是SLR(1)文法,若是构造相应分析表,并对输入串ab#给出分析过程。
答案:文法:A→aAd|aAb|ε拓广文法为G′,增加产生式S′→A若产生式排序为:0 S' →A1 A →aAd2 A →aAb3 A →ε由产生式知:First (S' ) = {ε,a}First (A ) = {ε,a}Follow(S' ) = {#}Follow(A ) = {d,b,#}G′的LR(0)项目集族及识别活前缀的DFA 如下图所示在I0 中:A →.aAd 和A →.aAb 为移进项目,A →.为归约项目,存在移进-归约冲突,因此所给文法不是LR(0)文法。
在I0、I2 中:Follow(A) ∩{a}= {d,b,#} ∩{a}=所以在I0、I2 中的移进-归约冲突可以由Follow 集解决,所以G 是SLR(1)文法。
构造的SLR(1)分析表如下:对输入串ab#的分析过程:第2 题若有定义二进制数的文法如下:S→L·L|LL→LB|BB→0|1(1) 试为该文法构造LR 分析表,并说明属哪类LR 分析表。
(2) 给出输入串101.110 的分析过程。
答案:文法:S→L.L|LL→LB|BB→0|1拓广文法为G′,增加产生式S′→S若产生式排序为:0 S' →S1 S →L.L2 S →L3 L →LB4 L →B5 B →06 B →1由产生式知:First (S' ) = {0,1}First (S ) = {0,1}First (L ) = {0,1}First (B ) = {0,1}Follow(S' ) = {#}Follow(S ) = {#}Follow(L ) = {.,0,1,#}Follow(B ) = {.,0,1,#}G′的LR(0)项目集族及识别活前缀的DFA 如下图所示:在I2 中:B →.0 和 B →.1 为移进项目,S →L.为归约项目,存在移进-归约冲突,因此所给文法不是LR(0)文法。

FORTRAN90 程序设计复习资料(2)一、选择题1.FORTRAN 90规定,变量类型声明的优先顺序是。
A.隐含约定(I-N规则)、IMPLICIT声明、类型声明B.类型声明、隐含约定(I-N规则)、IMPLICIT声明C.类型声明、IMPLICIT声明、隐含约定(I-N规则)D.IMPLICIT声明、类型声明、隐含约定(I-N规则)2.表达式15/4/2.0的值是。
A.整数2 B.实数1.5 C.实数2.25 D.实数1. 33.数组声明语句为:INTEGER,DIMENSION(-5:-1,-3:3,11:15) ::num ,数组共有个元素。
A.175 B.150 C.120 D.174.下列语句函数声明中,正确的是。
A.F1(I,I)=5*I-10*I**2 B. F2(MAT(5),A)=5*A+MAT(5)C. F3(X,Y,5.0)=X**2+Y**2+5.0**2D.F4(X,Y)=SQRT(X**2+Y**2+5.0**2)5.下列关于子程序的有关说法中,不正确的是。
A.对于无参子例行程序,调用时子例行程序名后的括号可取消B.对于无参函数子程序,调用时函数名后括号可取消C.对于有参子程序,形式参数可以是子程序名对于有参子程序,形式参数可以是星号“*”6.以下不是算法的特征。
(A) 灵活性(B)确定性(C)可行性(D)有穷性7.以下是FORTRAN 90源程序的扩展名。
(A)MDP (B)MAK (C)OBJ (D)F908.下列是正确的变量名。
(A)3SI (B)SI—3 (C)SI 3 (D)SI#39.若S为整型变量,且有S=1.25+11/4,则S的值为。
(A)3(B)3.25 (C)4 (D)4..2510.表达式MOD(5,6)+9/2**3/2的值为。
(A)37 (B)1 (C)5 (D)3211.已知a=3.0,b=9.0,c=5.0,d=7.0,逻辑表达式a+b/=c. and .a>=d的值为。

2
计数器的
增值为1
7
计数器的
增值为2
8
9
F77普遍使用
10
u Do 的语法结构
Ü③Do 循环的多层嵌套:
11
注:
内层先循环,外层后循环。
12
u Do 循环的编程技巧:
Ø①计数器的增值:可以是正整数(计数器的终止值>初值),也可以是负整数(计数器的终止值<初值)。
Ø②计数器的初值、终
止值和增值:可用已知变量指定。
Ø③计数器的变量i :在循环中,禁止改变其值
u固定执行次数的循环:do循环比do while循
环更简洁
14
u执行次数不确定的循环:
do while 循环能较好解决;
do循环用if和exit(goto)解决。
在大型数值计算模型
中,因循环众多,该
用法极少使用。
16
循环中执行cycle后,直接跳过4。
18
改写
20
ex0608.f90
21
24
【实例1】:ex0610.f90
ex0611.f90数值计算常用方法:计算完成后,变
量值更新,进行下一次循环。
解密
加密
取得字符串
实际长度
27
【实例4】
ex0614.f90
28。

FORTRAN 90 基础知识第三章基本知识,如:字符集、名称、关键字、程序单元、书写格式、数据类型。
名称:①名称只能由英文字母、数字、下划线符“_”和美元符号“$”组成。
②名称第一个字符必须是英文字母。
③名称不能超过31个字符。
合法名称: Number,Max, PrOgRaM, FIND_IT, read, x, a3b7, china, total, x$y$z 。
非法名称:X-Y-Z, 8q, a.5, _wrong,U.S.A., DR.WANG,$abcd,r a t e 。
书写格式:自由格式,固定格式3个通用标志符:注释标志符“!”、语句分隔标志符“;”和续行标志符“&”。
数据类型第四章 内部数据类型常量和变量:语法描述; 精度(kind 值)和取值范围 整型常量:整数(10进制)。
实型常量:实数。
复型常量:复数。
字符型常量:字符串。
逻辑型常量:逻辑值,布尔值。
.true. .false.变量的申明。
表达式算术表达式:算术运算符的优先级和结合规则;操作数的类型转换FORTRAN 90 数据类型内部数据类型派生类型(记录类型)数组类型指针类型 公用区类型类型整数类型 实数类型 复数类型字符类型 逻辑类型运算符 含义 结合顺序 优先级 运算速度 说明 ( ) 最高 ** 乘方 左←右 高 慢 两个**之间不能出现空格 * / 乘 除 左→右 ↑ ↑ 数学符号× ÷为非法字符,用*和/代替 + - 加(二元加) 减(二元减) 左→右 ↓ ↓ + - 正(一元加) 负(一元减) 低 快不同优先级运算符,“先高后低”结合先乘方、后乘除、再加减,括号最优先相同优先级运算符,“从左向右”结合,如9-4+12/3*2**3 = ?乘方算符,“从右向左”结合,如2**3**2 = ?尽量多地使用( ),以使意义明确,避免出现歧义和产生错误转换规则“由低级向高级转换”①数据类型和KIND相同的两个算术操作数,计算时不转换,运算结果的类型和KIND与原数据相同。

fortran考试题及答案分开1. 以下哪个选项是Fortran语言中正确的整型变量声明?A. INTEGER xB. REAL xC. COMPLEX xD. LOGICAL x答案:A2. Fortran程序中,哪个关键字用于定义数组?A. ARRAYB. LISTC. VECTORD. DIMENSION答案:D3. 在Fortran中,以下哪个选项是正确的条件语句?A. IF (x > 0) THENPRINT *, 'x is positive'B. IF x > 0 THENPRINT *, 'x is positive'C. IF (x > 0)PRINT *, 'x is positive'D. IF x > 0PRINT *, 'x is positive'答案:A4. Fortran中用于循环结构的关键字是什么?A. LOOPB. ITERATEC. DOD. FOR答案:C5. 如何在Fortran程序中包含另一个文件?A. 使用INCLUDE语句B. 使用IMPORT语句C. 使用INCLUDE关键字D. 使用IMPORT关键字答案:A6. Fortran中,哪个函数用于计算数组元素的总和?A. SUMB. TOTALC. AGGREGATED. ACCUMULATE答案:A7. 在Fortran中,如何声明一个具有默认值的变量?A. INTEGER :: x = 0B. INTEGER x = 0C. INTEGER x DEFAULT 0D. INTEGER x = DEFAULT 0答案:A8. Fortran程序中的主程序必须以哪个关键字开始?A. PROGRAMB. MAINC. PROCEDURED. FUNCTION答案:A9. 在Fortran中,如何声明一个二维数组?A. INTEGER :: matrix(10, 10)B. INTEGER :: matrix[10][10]C. INTEGER :: matrix(10)(10)D. INTEGER :: matrix(10,10)答案:A10. Fortran中用于计算数组元素平均值的函数是什么?A. AVGB. MEANC. AVERAGED. SUM答案:C。

Fortran90试题Fortran 复习题⽬类型:1、选择题2、填空题3、简答题4、编程题样题⼀、选择题1.下列名称中,符合FORTRAN 90命名规则的是。
A. a-b-cB. $123C. length_1D. date.year 2.关于FORTRAN 90程序单元,以下四种说法中正确的是。
A.⼀个FORTRAN 90程序由多个程序单元组成,其中有⼀个且只能有⼀个主程序单元B. ⼀个FORTRAN 90程序由多个程序单元组成,其中有⼀个且只能有⼀个模块单元C. ⼀个FORTRAN 90程序允许有多个程序单元,但每类程序单元只能有⼀个D. ⼀个FORTRAN 90程序允许有多个程序单元,但主程序单元和模块单元只能有⼀个3.关于FORTRAN 90的CASE结构,以下说法中正确的是。
A. CASE结构内必须取DEFAULT作为情况选择器的最终值B. CASE结构的情况表达式不能是字符类型C. CASE结构的情况表达式和情况选择器的取值类型必须相同D. CASE结构的不同情况选择器取值可以重复4.已知数组说明REAL A(20:22,0:9,-3:-1),数组A的数组元素个数是。
A.164 B.360 C.450 D.90 5.⼦程序的形式参数(虚拟变元或哑元)可以是。
A.变量名、数组名、过程名B.变量名、数组名、过程名和符号常量名C.变量名、数组名、数组⽚段、过程名D.任意符号名6. 语句OPEN(3,FILE=’ABC’,ACCESS=’DIRECT’,RECL=40)打开的是⽂件。
A.有格式顺序存取B.⽆格式顺序存取C.有格式直接存取D.⽆格式直接存取7、下列关于"SUBROUTINE MAP(X,Y)"语句⾏的叙述中,不正确的是( )A) 这是⼦程序的第⼀个语句 B) 字符串"MAP"是⼦程序名C) 变量X是⼦程序的形参D)⼦程序执⾏后,MAP将返回整型数据8、 FORTRAN表达式"2/4+0.5"的值是( )A) 0.5 B) 1 C) 1.0 D) 09、阅读下列FORTRAN程序:PI=3.14159265WRITE(*,'(F7.4) ')PIEND程序运⾏后输出结果是( )A) 3.142 B) 3.1415 C) 0.31416 D) 3.141610、圆的直径存放在整型变量K之中,下列计算圆⾯积的表达式中正确的是( )A) 3.1415926*K*K/4 B) 3.1415926*(K*K/4)C) 3.1415926*(K/2)**2 D) 3.1415926*(K/2)*(K/2)⼆、填空题1、下列FORTRAN函数⼦程序的功能是⽤以下公式计算⼀组数据Z1,Z2,…,Zn的标准差σ:σ2=(Z12 +Z22+…+Zn2)/n-[(Z1+Z2+…+Zn)/n]2请在程序中的下划线处填⼊合适的内容。
P
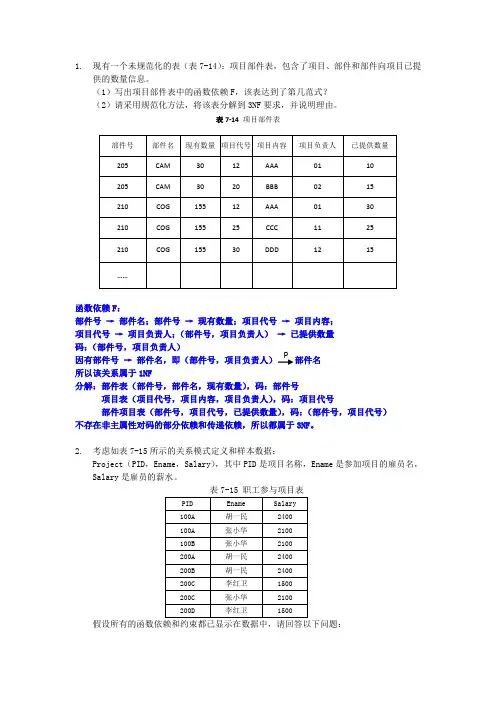
1. 现有一个未规范化的表(表7-14):项目部件表,包含了项目、部件和部件向项目已提
供的数量信息。
(1)写出项目部件表中的函数依赖F ,该表达到了第几范式? (2)请采用规范化方法,将该表分解到3NF 要求,并说明理由。
表7-14 项目部件表
函数依赖F :
部件号 → 部件名;部件号 → 现有数量;项目代号 → 项目内容; 项目代号 → 项目负责人;(部件号,项目负责人) → 已提供数量 码:(部件号,项目负责人)
因有部件号 → 部件名,即(部件号,项目负责人) 部件名 所以该关系属于1NF
分解:部件表(部件号,部件名,现有数量),码:部件号 项目表(项目代号,项目内容,项目负责人),码:项目代号 部件项目表(部件号,项目代号,已提供数量),码:(部件号,项目代号) 不存在非主属性对码的部分依赖和传递依赖,所以都属于3NF 。
2. 考虑如表7-15所示的关系模式定义和样本数据:
Project (PID ,Ename ,Salary ),其中PID 是项目名称,Ename 是参加项目的雇员名,Salary 是雇员的薪水。
(1)写出该关系的函数依赖集。
(2)该关系的码是什么?
(3)该关系属于第几范式?为什么?
函数依赖集:
Ename → Salary
码:(PID,Ename)
该关系属于1NF,因存在非主属性Salary部分依赖于码(PID,Ename)分解:P-E(PID,Ename),码:(PID,Ename)
E(Ename,Salary),码:Ename。

第一章课后习题参考答案一、填空题1.处理、处理2.黑盒、程序3.输入设备、运算器、存储器、控制器、输出设备4.运算器、控制器、中央处理器5.存储器、数据6.计算机硬件、软件7.电子管、晶体管、集成电路、超大规模集成电路8.处理器、存储器、输入/输出9.输入、输出、键盘、显示器10.更有效、更高速、更可靠11.过程、对象12.以图形用户接口技术13.程序、操作系统14.硬件、软件、数据/信息、过程(处理)、通信15.因特网、开放性16.Web、万维网、超文本置标17.音频、动画、图片18.资源19.抽象、自动化20.计算思维第二章课后习题参考答案一、填空题1.进位、进制2.十、八进制、十六进制3.补码、浮点数、小、整4.组合规则、ASCII、Unicode、特征5.位图、矢量图6.采样、量化7.逻辑非、逻辑与或,逻辑异或、门电路8.逻辑与、逻辑或、逻辑异或9.逻辑函数、二值函数(布尔函数)10.1、011.逻辑函数、逻辑变量12.低位、半加器13.触发器其中选择题6,7,8题中的数以8位长表示选择题10的结果是‘A’ –‘a’的值三.综合题(部分)4) 110110010001111010000000000 0.01111.00110.1017) 10 55 157 0.625 0.3125 0.8125 2.25 10.1259) (233.154)8 (1252.144)8 (9B.36)16 (2AA.32)1610) 111101.110001010 11001001010.11000011111112)设以一个字节来存储,最高位为符号位01100100 01100100 0110010011100100 10011011 1001110001111100 01111100 0111110011111100 10000011 1000010015)用十进制表示范围:-(1-2-8)*263至(1-2-8)*263第三章课后习题参考答案一、填空题1、输入/输出;总线2、处理器;端口3、CPU4、运算器;控制器;运算器;控制电路;数据5、运算器;与;或;非6、数据总线;地址总线;控制总线7、主频;字长;内部高速缓存器/协处理器8、复杂指令集计算机;精简指令集计算机9、存储单元;存储器地址10、存储单元;3276811、随机(访问)存储器;只读存储器;DRAM; EPROM; EEPROM12、电缆导线;扇区;SATA13、CD-R; CD-RW; DVD14、固态15、数据;外存;主存/内存;数据;外存16、高速缓存/Cache;虚拟内存17、键盘接口;鼠标接口;并行接口;串行接口;USB接口;音频接口;18、CRT; LCD; 分辨率;显卡;点密度/每英寸点数;激光打印机;针式打印机;RGB; CMYK19、笔记本电脑;通用串行总线;127第四章课后习题参考答案一、填空题1.接口硬件资源2.实时系统单用户单任务多用户多任务3.多多个4.iOS Windows Mobile Symbian OS Android5.内核 Shell6.进程管理器存储管理器设备管理器文件管理器7.程序作业进程8.外存内存9.块设备驱动10.硬件时钟软件时钟11.注册表应用程序 regedit 注册表编辑器12..exe 文本视频13.文件分配表 NTFS第五章课后习题参考答案第9题:Start:set p = 1;set i = n;while i<=m doif(i÷3的余数=0) p=p×i;i = i+1 ;end whileoutput p;End第18题:Startset i=1set sum=0while i<=n dosum=sum+1.0/ii=i+1end whileoutput sumEnd第六章课后习题参考答案一、填空题1.操作使用2.算法算法3.指令4.数据传输算术逻辑5.操作类型地址下一条指令的地址6.机器语言程序7.汇编语言源程序8.过程对象过程9. C语言 Pascal /Fortran C++ Java10.封装继承多态性11.属性行为12. HTML XML13.源程序目标程序14.逐句一次性整体15.算法错误16.运算对象变量常量17.整型实型字符型18.符号常量19.构造数据类型数组元素20.赋值语句复合语句返回语句21.算术运算22.一个变23.函数24. switch25. while for for26.do…while27.设计方案编码运行维护28.黑盒白盒29.瀑布螺旋30.使用第七章课后习题参考答案:第八章课后习题参考答案:第九章课后习题参考答案:第十章课后习题参考答案:。

fortran课后习题答案Fortran课后习题答案在学习Fortran编程语言时,课后习题是巩固知识、提高编程能力的重要途径。
通过解答课后习题,学生可以加深对Fortran语法和逻辑的理解,提高编程实践能力。
以下是一些Fortran课后习题答案,供大家参考。
1. 编写一个Fortran程序,计算并输出1到100的所有偶数的和。
程序代码如下:```fortranprogram sum_even_numbersimplicit noneinteger :: i, sumsum = 0do i = 2, 100, 2sum = sum + iend doprint *, 'The sum of even numbers from 1 to 100 is:', sumend program sum_even_numbers```2. 编写一个Fortran程序,找出一个整数数组中的最大值和最小值,并输出它们的位置。
程序代码如下:```fortranprogram find_max_minimplicit noneinteger :: i, n, max_val, min_val, max_pos, min_pos integer, dimension(10) :: arr! 初始化数组arr = (/3, 7, 2, 8, 5, 10, 1, 6, 4, 9/)! 初始化最大值和最小值max_val = arr(1)min_val = arr(1)max_pos = 1min_pos = 1! 找出最大值和最小值do i = 2, 10if (arr(i) > max_val) thenmax_val = arr(i)max_pos = iendifif (arr(i) < min_val) thenmin_val = arr(i)min_pos = iendifend doprint *, 'The maximum value is', max_val, 'at position', max_posprint *, 'The minimum value is', min_val, 'at position', min_posend program find_max_min```通过这些课后习题的答案,我们可以看到Fortran语言的一些基本特性和常用语法的运用。

第七章 习题解答1.设(X ,d )为一度量空间,令}),(,|{),(},),(,|{),(0000εεεε≤∈=<∈=x x d X x x x S x x d X x x x U问),(0εx U 的闭包是否等于),(0εx S ?解 不一定。
例如离散空间(X ,d )。
)1,(0x U ={0x },而)1,(0x S =X 。
因此当X 多于两点时,)1,(0x U 的闭包不等于)1,(0x S 。
2. 设 ],[b a C ∞是区间],[b a 上无限次可微函数的全体,定义)()(1)()(max 21),()()()()(0t g t f t g t f g f d r r r r b t a r r -+-=≤≤∞=∑证明],[b a C ∞按),(g f d 成度量空间。
证明 (1)若),(g f d =0,则)()(1)()(max)()()()(t g t ft g t f r r r r bt a -+-≤≤=0,即f=g(2))()(1)()(max 21),()()()()(0t g t f t g t f g f d r r r r b t a r r -+-=≤≤∞=∑ )()(1)()()()(1)()(max 21)()()()()()()()(0t g t h t g t h t g t f t g t f r r r r r r r r b t a r r -+-+-+-≤≤≤∞=∑ )()(1)()(max 21)()(1)()(max 21)()()()(0)()()()(0t g t h t g t h t g t f t g t f r r r r b t a r r r r r r b t a r r -+-+-+-≤≤≤∞=≤≤∞=∑∑=d (f ,g )+d (g ,h )因此],[b a C ∞按),(g f d 成度量空间。
3. 设B 是度量空间X 中的闭集,证明必有一列开集 n o o o 21,包含B ,而且B o n n =⋂∞=1。

第四章1.program main implicit none write(*,*) "Have a good time." write(*,*) "That's not bad." write(*,*) '"Mary" isn''t my name.' end program2.program main real, parameter :: PI=3 implicit none.14159 real radius write(*,*) "请输入半径长" read(*,*) radius write(*,"(' 面积='f8. 3)") radius*radius*PI end program3.program main implicit none real grades write(*,*) "请输入成绩" read(*,*) grades write(*,"(' 调整后成绩为 'f8.3)") SQRT(grades)*10.0 end program4.integer a,b real ra,rb a=2 b=3 ra=2.0 rb=3.0 write(*,*) b/a ! 输出1, 因为使用整数计算, 小数部分会无条件舍去 write(*,*) rb/ra ! 输出1.55.p rogram main implicit none type distance real meter, inch, cm end type type(distance) :: d write(*,*) "请输入长度:" read(*,*) d%meter d%cm =d%meter*100 d%inch = d%cm/2.54 write(*,"(f8.3'米 ='f8.3'厘米 ='f8.3'英寸')")d%meter, d%cm, d%inch end program第五章1.program main implicit none integer money real tax write(*,*) "请输入月收入" read(*,*) money if ( money<1000 ) then tax = 0.03 else if( money<5000) then tax = 0.1 else tax = 0.15 end if write(*,"(' 税金为 'I8)") nint(money*tax) end program2.program main implicit none integer day character(len=20) :: tv write(*,*) "请输入星期几" read(*,*) day select case(day) case(1,4) tv= "新闻" case(2,5) tv = "电视剧" case(3,6) tv = "卡通" case(7) tv = "电影" case default write(*,*) "错误的输入" stop end select write(*,*) tv end program3.program main implicit none integer age, money real tax write(*,*) "请输入年龄" read(*,*) age write(*,*) "请输入月收入" read(*,*) money if( age<50 ) then if ( money<1000 ) then tax = 0.03 else if ( money<5000 )then tax = 0.10 else tax = 0.15 end if else if ( money<1000 ) then tax =0.5 else if ( money<5000 )then tax = 0.7 else tax = 0.10 end if end if write(*,"(' 税金为 'I8)") nint(money*tax) end program4.program main implicit none integer year, days logical mod_4, mod_100,mod_400 write(*,*) "请输入年份" read(*,*) year mod_4 = ( MOD(year,4) ==0 ) mod_100 = ( MOD(year,100) == 0 ) mod_400 = ( MOD(year,400) == 0 ) if( (mod_4 .NEQV. mod_100) .or. mod_400 ) then days = 366 else days = 365end if write(*,"('这一年有'I3'天')") days stop end program第六章1.program main implicit none integer i do i=1,5 write(*,*) "Fortran" end do stop end program2.program main implicit none integer i,sum sum = 0 do i=1,99,2 sum =sum+i end do write(*,*) sum stop end program3.program main implicit none integer, parameter :: answer = 45 integer, parameter :: max = 5 integer weight, i do i=1,max write(*,*) "请输入体重" read(*,*) weight if ( weight==answer ) exit end do if ( i<=max ) thenwrite(*,*) "猜对了" else write(*,*) "猜错了" end if stop end program4.program main implicit none integer, parameter :: max=10 integer i realitem real ans ans = 1.0 item = 1.0 do i=2,max item = item/real(i)ans = ans+item end do write(*,*) ans stop end program5.program main implicit none integer, parameter :: length = 79 character(len=length) :: input, output integer i,j write(*,*) "请输入一个字串" read(*,"(A79)") input j=1 do i=1, len_trim(input) if ( input(i:i)/= ' ' ) then output(j:j)=input(i:i) j=j+1 end if end do write(*,"(A79)") output stop end program第七章1.program main implicit none integer, parameter :: max = 10 integer i integer :: a(max) = (/ (2*i, i=1,10) /) integer :: t ! sum()是fortran库函数write(*,*) real(sum(a))/real(max) stop end program2.integer a(5,5) ! 5*5=25 integer b(2,3,4) ! 2*3*4=24 integer c(3,4,5,6) !3*4*5*6=360 integer d(-5:5) ! 11 integer e(-3:3, -3:3) ! 7*7=493.program main implicit none integer, parameter :: max=10 integer f(max) integer i f(1)=0 f(2)=1 do i=3,max f(i)=f(i-1)+f(i-2) end do write(*,"(10I4)") f stop end program4.program main implicit none integer, parameter :: size=10 integer :: a(size)= (/ 5,3,6,4,8,7,1,9,2,10 /) integer :: i,j integer :: t do i=1, size-1do j=i+1, size if ( a(i) < a(j) ) then ! a(i)跟a(j)交换 t=a(i) a(i)=a(j) a(j)=t end if end do end do write(*,"(10I4)") a stop end5.a(2,2) ! 1+(2-1)+(2-1)*(5) = 7 a(3,3) ! 1+(3-1)+(3-1)*(5) = 13第八章1.program main implicit none real radius, area write(*,*) "请输入半径长"read(*,*) radius call CircleArea(radius, area) write(*,"(' 面积 = 'F8.3)")area stop end program subroutine CircleArea(radius, area) implicit nonereal, parameter :: PI=3.14159 real radius, area area = radius*radius*PIreturn end subroutine2.program main implicit none real radius real, external :: CircleAreawrite(*,*) "请输入半径长" read(*,*) radius write(*,"(' 面积= 'F8.3)") CircleArea(radius) stop end program real function CircleArea(radius) implicit none real, parameter :: PI=3.14159 real radius CircleArea =radius*radius*PI return end function3.program main implicit none call bar(3) call bar(10) stop end program subroutine bar(length) implicit none integer, intent(in) :: length integeri character(len=79) :: string string=" " do i=1,length string(i:i)='*'end do write(*,"(A79)") string return end subroutine4.p rogram main implicit none integer, external :: add write(*,*) add(100)end program recursive integer function add(n) result(sum) implicit none integer, intent(in) :: n if ( n<0 ) then sum=0 return else if ( n<=1 )then sum=n return end if sum = n + add(n-1) return end function5.program main implicit none integer, external :: gcd write(*,*) gcd(18,12)end program integer function gcd(A,B) implicit none integerA,B,BIG,SMALL,TEMP BIG=max(A,B) SMALL=min(A,B) do while( SMALL /= 1 ) TEMP=mod(BIG,SMALL) if ( TEMP==0 ) exit BIG=SMALL SMALL=TEMP end dogcd=SMALL return end function 6.program main use TextGraphLib implicit none integer, parameter :: maxx=60, maxy=20 real, parameter :: StartX=0.0,EndX=3.14159*2.0 real, parameter :: xinc = (EndX-StartX)/(maxx-1) real x integer i,px,py call SetScreen(60,20) call SetCurrentChar('*') x=StartXdo px=1,maxx py = (maxy/2)*sin(x)+maxy/2+1 call PutChar(px,py) x=x+xincend docall UpdateScreen() stop end program第九章1.program main implicit none character(len=79) :: filename character(len=79) :: buffer integer, parameter :: fileid = 10 integer count integer :: status = 0 logical alive write(*,*) "Filename:" read (*,"(A79)") filename inquire( file=filename, exist=alive) if ( alive ) then open(unit=fileid, file=filename, & access="sequential", status="old")count = 0 do while(.true.) read(unit=fileid, fmt="(A79)", iostat=status )buffer if ( status/=0 ) exit ! 没有资料就跳出循环 write(*,"(A79)")buffer count = count+1 if ( count==24 ) then pause count = 0 endif end do else write(*,*) TRIM(filename)," doesn't exist." end ifstop end2.p rogram main implicit none character(len=79) :: filename character(len=79) :: buffer integer, parameter :: fileid = 10 integer iinteger :: status = 0 logical alive write(*,*) "Filename:" read (*,"(A79)") filename inquire( file=filename, exist=alive) if ( alive ) then open(unit=fileid, file=filename, & access="sequential", status="old")do while(.true.) read(unit=fileid, fmt="(A79)", iostat=status ) bufferif ( status/=0 ) exit ! 没有资料就跳出循环do i=1, len_trim(buffer) buffer(i:i) = char( ichar(buffer(i:i))-3 ) end do write(*,"(A70)") bufferend do else write(*,*) TRIM(filename)," doesn't exist." end if stop end3.program main implicit none type student integer chinese, english, math, science, social, total end type type(student) :: s, total integer, parameter :: students=20, subjects=5 integer i open(10,file="grades.bin",access="direct",recl=1) write(*,"(7A10)") "座号","中文","英文","数学","自然","社会","总分" total = student(0,0,0,0,0,0) do i=1, students read(10,rec=(i-1)*subjects+1) s%chinese read(10,rec=(i-1)*subjects+2) s%english read(10,rec=(i-1)*subjects+3) s%math read(10,rec=(i-1)*subjects+4) s%science read(10,rec=(i-1)*subjects+5)s%social s%total = s%chinese+s%english+s%math+s%science+s%social total%chinese= total%chinese+s%chinese total%english = total%english+s%english total%math =total%math+s%math total%science = total%science+s%science total%social =total%social+s%social total%total = total%total+s%total write(*,"(7I10)") i,s end do write(*,"(A10,6F10.3)") "平均", & real(total%chinese)/real(students),&real(total%english)/real(students),& real(total%math)/real(students),& real(total%science)/real(students),&real(total%social)/real(students),& real(total%total)/real(students)stop end 4.program main implicit none character(len=79) :: filename character(len=79) :: buffer integer, parameter :: fileid = 10 integer i integer :: status = 0 logical alive write(*,*) "Filename:" read (*,"(A79)")filename inquire( file=filename, exist=alive) if ( alive ) then open(unit=fileid, file=filename, & access="sequential", status="old") do while(.true.) read(unit=fileid, fmt="(A79)", iostat=status ) buffer if ( status/=0 ) exit ! 没有数据就跳出循环do i=1, len_trim(buffer) buffer(i:i) = char( ichar(buffer(i:i))-(mod(i-1,3)+1) ) end do write(*,"(A70)") buffer end do else write(*,*) TRIM(filename)," doesn't exist." end if stop end5.module typedef type student integer :: num integer :: Chinese, English, Math, Natural, Social integer :: total integer :: rank end type end module program main use typedef implicit none integer, parameter :: fileid=10 integer, parameter :: students=20 character(len=80) :: tempstr type(student) :: s(students) ! 储存学生成绩 type(student) :: total ! 计算平均分数用integer i, num, error open(fileid,file="grades.txt",status="old", iostat=error) if ( error/=0 ) then write(*,*) "Open grades.txt fail." stop end if read(fileid, "(A80)") tempstr ! 读入第一行文字 total=student(0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0) ! 用循环读入每位学生的成绩do i=1,students read(fileid,*) s(i)%num, s(i)%Chinese,s(i)%English, & s(i)%Math, s(i)%Natural, s(i)%Social ! 计算总分 s(i)%Total = s(i)%Chinese + s(i)%English + & s(i)%Math +s(i)%Natural + s(i)%Social ! 累加上各科的分数, 计算各科平均时使用total%Chinese = total%Chinese + s(i)%Chinese total%English = total%English +s(i)%English total%Math = total%Math + s(i)%Math total%Natural = total%Natural + s(i)%Natural total%Social = total%Social + s(i)%Social total%Total = total%Total + s(i)%Total end do call sort(s,students) ! 重新输出每位学生成绩 write(*,"(8A7)") "座号","中文","英文","数学","自然","社会","总分","名次" do i=1,students write(*,"(8I7)") s(i) end do ! 计算并输出平圴分数write(*,"(A7,6F7.1)") "平均", &real(total%Chinese)/real(students),& real(total%English)/real(students),&real(total%Math) /real(students),& real(total%Natural)/real(students),&real(total%Social) /real(students),& real(total%Total) /real(students) stop end program subroutine sort(s,n) use typedef implicit none integer n type(student) :: s(n), t integer i,j do i=1,n-1 do j=i+1,n if( s(i)%total < s(j)%total ) then t = s(i) s(i)=s(j) s(j) = t end ifend do end do forall(i=1:n) s(i)%rank = i end forall end subroutine第十章1.integer(kind=4) :: a ! 4 bytes real(kind=4) :: b ! 4 bytes real(kind=8) :: c !8 bytes character(len=10) :: str ! 10 bytes integer(kind=4), pointer :: pa !4 bytes real(kind=4), pointer :: pb ! 4 bytes real(kind=8), pointer :: pc !4 bytes character(len=10), pointer :: pstr ! 4 bytes type student integer Chinese, English, Math end type type(student) :: s ! 12 bytes type(student), pointer ::ps ! 4 bytes2.integer, target :: a = 1 integer, target :: b = 2 integer, target :: c = 3 integer, pointer :: p p=>a write(*,*) p ! 1 p=>b write(*,*) p ! 2 p=>c p=5 write(*,*) c !53.module linklist type student integer :: num integer :: Chinese, English,Math, Science, Social end type type datalink type(student) :: item type(datalink), pointer :: next end type contains function SearchList(num, head) implicit none integer :: num type(datalink), pointer :: head, p type(datalink), pointer :: SearchList p=>head nullify(SearchList) do while( associated(p) ) if ( p%item%num==num ) then SearchList => p return end if p=>p%next end do return end function end module linklist programex1016 use linklist implicit none character(len=20) :: filename character(len=80) :: tempstr type(datalink), pointer :: head type(datalink), pointer :: p type(student), allocatable :: s(:) integer i,error,size write(*,*) "filename:" read(*,*) filename open(10, file=filename, status="old", iostat=error) if ( error/=0 ) then write(*,*) "Open file fail!" stop end if allocate(head) nullify(head%next) p=>head size=0 read(10, "(A80)") tempstr ! 读入第一行字符串, 不需要处理它 ! 读入每一位学生的成绩 do while(.true.) read(10,fmt=*, iostat=error) p%item if ( error/=0 )exit size=size+1 allocate(p%next, stat=error) ! 新增下一个数据 if ( error/=0 )then write(*,*) "Out of memory!" stop end if p=>p%next ! 移动到链表的下一个数据 nullify(p%next) end do write(*,"('总共有',I3,'位学生')") size allocate( s(size) ) p=>head do i=1,size s(i)=p%item p=>p%next end do do while(.true.) write(*,*) "要查询几号同学的成绩?" read (*,*) i if( i<1 .or. i>size ) exit ! 输入不合理的座号 write(*,"(5(A6,I3))") "中文",s(i)%Chinese,& "英文",s(i)%English,& "数学",s(i)%Math,& "自然",s(i)%Science,& "社会",s(i)%Social end do write(*,"('座号',I3,'不存在, 程序结束.')") i stopend program4.module typedef implicit none type :: datalink integer :: i type(datalink), pointer :: next end type datalink end module typedef programex1012 use typedef implicit none type(datalink) , pointer :: p, head, next integer :: i,n,err write(*,*) 'Input N:' read(*,*) n allocate( head ) head%i=1 nullify(head%next) p=>head do i=2,n allocate( p%next,stat=err ) if ( err /= 0 ) then write(*,*) 'Out of memory!' stop end if p=>p%next p%i=i end do nullify(p%next) p=>head do while(associated(p)) write(*, "(i5)" ) p%i p=>p%next end do ! 释放链表的存储空间p=>head do while(associated(p)) next => p%next deallocate(p) p=>next end do stop end program第十一章1.module utility implicit none interface area module procedure CircleArea module procedure RectArea end interface contains real function CircleArea(r) real, parameter :: PI=3.14159 real r CircleArea =r*r*PI return end function real function RectArea(a,b) real a,b RectArea = a*b return end function end module program main use UTILITY implicit none write(*,*) area(1.0) write(*,*) area(2.0,3.0) stop end program2.module time_utility implicit none type :: time integer :: hour,minute,second end type time interface operator(+) module procedureadd_time_time end interface contains function add_time_time( a, b ) implicit none type(time) :: add_time_time type(time), intent(in) :: a,binteger :: seconds,minutes,carry seconds=a%second+b%second carry=seconds/60 minutes=a%minute+b%minute+carry carry=minutes/60add_time_time%second=mod(seconds,60) add_time_time%minute=mod(minutes,60)add_time_time%hour=a%hour+b%hour+carry return end function add_time_time subroutine input( a ) implicit none type(time), intent(out) :: a write(*,*) " Input hours:" read (*,*) a%hour write(*,*) " Input minutes:"read (*,*) a%minute write(*,*) " Input seconds:" read (*,*) a%second return end subroutine input subroutine output( a ) implicit nonetype(time), intent(in) :: a write(*, "(I3,' hours',I3,' minutes',I3,'seconds')" ) a%hour,a%minute,a%second return end subroutine output endmodule time_utility program main use time_utility implicit nonetype(time) :: a,b,c call input(a) call input(b) c=a+b call output(c)stop end program main3.module rational_utility implicit none private public :: rational, & operator(+), operator(-), operator(*),& operator(/), assignment(=),operator(>),& operator(<), operator(==),operator(/=),& output, input type :: rational integer :: num,denom end type rational interface operator(+) module procedurerat__rat_plus_rat end interface interface operator(-) module procedurerat__rat_minus_rat end interface interface operator(*) module procedurerat__rat_times_rat end interface interface operator(/) module procedurerat__rat_div_rat end interface interface assignment(=) module procedurerat_eq_rat module procedure int_eq_rat module procedure real_eq_rat endinterface interface operator(>) module procedure rat_gt_rat endinterface interface operator(<) module procedure rat_lt_rat endinterface interface operator(==) module procedure rat_compare_rat endinterface interface operator(/=) module procedure rat_ne_rat endinterface contains function rat_gt_rat(a,b) implicit none logical ::rat_gt_rat type(rational), intent(in) :: a,b real :: fa,fbfa=real(a%num)/real(a%denom) fb=real(b%num)/real(b%denom) if ( fa > fb )then rat_gt_rat=.true. else rat_gt_rat=.false. end if return end function rat_gt_rat function rat_lt_rat(a,b) implicit none logical :: rat_lt_rat type(rational), intent(in) :: a,b real :: fa,fbfa=real(a%num)/real(a%denom) fb=real(b%num)/real(b%denom) if ( fb > fa )then rat_lt_rat=.true. else rat_lt_rat=.false. end if return end function rat_lt_rat function rat_compare_rat(a,b) implicitnone logical :: rat_compare_rat type(rational), intent(in) :: a,btype(rational) :: c c=a-b if ( c%num == 0 ) thenrat_compare_rat=.true. else rat_compare_rat=.false. end if return end function rat_compare_rat function rat_ne_rat(a,b) implicitnone logical :: rat_ne_rat type(rational), intent(in) :: a,btype(rational) :: c c=a-b if ( c%num==0 ) then rat_ne_rat=.false.else rat_ne_rat=.true. end if return end function rat_ne_rat subroutine rat_eq_rat( rat1, rat2 ) implicit none type(rational),intent(out):: rat1 type(rational), intent(in) :: rat2 rat1%num =rat2%num rat1%denom = rat2%denom return end subroutine rat_eq_ratsubroutine int_eq_rat( int, rat ) implicit none integer, intent(out):: inttype(rational), intent(in) :: rat int = rat%num / rat%denom return end subroutine int_eq_rat subroutine real_eq_rat( float, rat ) implicit none real, intent(out) :: float type(rational), intent(in) :: rat float =real(rat%num) / real(rat%denom) return end subroutine real_eq_rat function reduse( a ) implicit none type(rational), intent(in) :: a integer :: b type(rational) :: reduse b=gcv_interface(a%num,a%denom) reduse%num = a%num/b reduse%denom = a%denom/b return end function reduse function gcv_interface(a,b) implicit none integer, intent(in) ::a,b integer :: gcv_interface if ( min(a,b) .eq. 0 ) then gcv_interface=1 return end if if (a==b) then gcv_interface=a return else if ( a>b ) then gcv_interface=gcv(a,b) else if ( a<b ) then gcv_interface=gcv(b,a) end if return end function gcv_interface recursive function gcv(a,b) result(ans) implicitnone integer, intent(in) :: a,b integer :: m integer :: ans m=mod(a,b) select case(m) case(0) ans=b return case(1) ans=1 return case default ans=gcv(b,m) end select return end function gcv function rat__rat_plus_rat( rat1, rat2 ) implicitnone type(rational) :: rat__rat_plus_rat type(rational), intent(in) ::rat1,rat2 type(rational) :: act act%denom= rat1%denom * rat2%denom act%num = rat1%num*rat2%denom + rat2%num*rat1%denom rat__rat_plus_rat = reduse(act) return end function rat__rat_plus_rat functionrat__rat_minus_rat( rat1, rat2 ) implicit none type(rational) ::rat__rat_minus_rat type(rational), intent(in) :: rat1, rat2 type(rational) :: temp temp%denom = rat1%denom*rat2%denom temp%num =rat1%num*rat2%denom - rat2%num*rat1%denom rat__rat_minus_rat = reduse( temp ) return end function rat__rat_minus_rat function rat__rat_times_rat( rat1,rat2 ) implicit none type(rational) :: rat__rat_times_rat type(rational), intent(in) :: rat1, rat2 type(rational) :: temp temp%denom = rat1%denom* rat2%denom temp%num = rat1%num * rat2%num rat__rat_times_rat = reduse(temp) return end function rat__rat_times_rat function rat__rat_div_rat( rat1, rat2 ) implicit none type(rational) ::rat__rat_div_rat type(rational), intent(in) :: rat1, rat2 type(rational) :: temp temp%denom = rat1%denom* rat2%num temp%num =rat1%num * rat2%denom rat__rat_div_rat = reduse(temp) return end function rat__rat_div_rat subroutine input(a) implicit none type(rational), intent(out) :: a write(*,*) "分子:" read(*,*) a%num write(*,*) "分母:" read(*,*) a%denom return end subroutine input subroutine output(a) implicit none type(rational), intent(in) :: a if ( a%denom/=1 ) then write(*, "(' (',I3,'/',I3,')' )" ) a%num,a%denom else write(*, "(I3)" ) a%num end if return end subroutine outputend module rational_utility program main use rational_utility implicit none type(rational) :: a,b,c call input(a) call input(b) c=a+b write(*,*)"a+b=" call output(c) c=a-b write(*,*) "a-b=" call output(c) c=a*b write(*,*) "a*b=" call output(c) c=a/b write(*,*) "a/b=" call output(c)if (a>b) write(*,*) "a>b" if (a<b) write(*,*) "a<b" if (a==b) write(*,*) "a==b"if (a/=b) write(*,*) "a/=b" stop end program main4.module vector_utility implicit none type vector real x,y end type interface operator(+) module procedure vector_add_vector end interface interface operator(-) module procedure vector_sub_vector end interface interface operator(*) module procedure real_mul_vector module procedure vector_mul_real module procedure vector_dot_vector end interface interface operator(.dot.) module procedure vector_dot_vector end interface contains type(vector) function vector_add_vector(a,b) type(vector), intent(in) :: a,b vector_add_vector = vector(a%x+b%x, a%y+b%y) end function type(vector) function vector_sub_vector(a,b) type(vector), intent(in) :: a,b vector_sub_vector = vector(a%x-b%x, a%y-b%y) end function type(vector) function real_mul_vector(a,b) real, intent(in) :: a type(vector), intent(in) :: b real_mul_vector = vector( a*b%x, a*b%y ) end functiontype(vector) function vector_mul_real(a,b) type(vector), intent(in) :: a real, intent(in) :: b vector_mul_real = real_mul_vector(b,a) end function real function vector_dot_vector(a,b) type(vector), intent(in) :: a,b vector_dot_vector = a%x*b%x + a%y*b%y end function subroutine output(vec) type(vector) :: vec write(*,"('('F6.2','F6.2')')") vec end subroutine end module program main use vector_utility implicit none type(vector) a,b,ca=vector(1.0, 2.0) b=vector(2.0, 1.0) c=a+b call output(c) c=a-b call output(c) write(*,*) a*b end program main。
FORTRAN90FORTRAN 90第一章绪论一、特点在FORTRAN 77的基础上增添了许多具有现代特性的功能、递归、数组直接运算、派生类型、指针和过程。
二、与FORTRAN 77的区别1、不区分书写格式2、不赞成语句标号3、不使用BLOCK DATA 数据块子程序、语句函数4、主程序以PROGRAM 开头,以END PROGRAM为结尾函数子程序:区分函数名与函数值5、不使用GOTO 10、STOP、PAUSE语句6、不使用DO 10 I=1,3,而以DO与END DO 匹配使用。
7、不使用:I-N规则、双精度、DATA语句、多条RETURN语句。
而使用REAL ::A=0,B=2.58、不使用COMMON语句,而用模块MODULE9、用假定形状数组取代假定大小数组10、DIMENSION A(10)在FORTRAN 90中不再定义数组11、FORMAT 语句不再使用第二章F ORTRAN 90 基础知识第2.1节语言元素一、字符集1、A-Z (26个)2、0-9 (10个)3、_(下划线)(1个)4、特殊符号(21个):空格、等号、加号、减号、*、/、(、)、,、.、’、:、!、”、%、&、;、<、>、?、$二、数据类型本身:INTEGER real complex character logical派生类型种别参数:对可移值数据精度和范围进行选择的机制,他提供了对每种内部数据类型的不同机器表示进行选择的参数化方式,种别参数均为整数。
用法:KIND=种别参数。
函数KIND(X)表示返回X的种别参数。
1、常量(字符型:双、单引号表示)常数的种别标示:例15_2 14.36_3 .false._4 5_’ang’带种别参数的常量的运算:15_2+14.36_3=29.36_3定义常量:REAL(KIND=2),PARAMETER::N=52、变量(1)变量名(程序名、常量、虚参、派生类型)命名规则:长度小于等于31个字符、须以字母开头、由字母、数字、下划线构成,其中不出现空格。
参考答案:习题七7.1 运用Euler 方法和改进Euler 方法求下列初值问题在给定区间上的数值解, 计算结果保留四位小数。
(1) ⎪⎩⎪⎨⎧=≤≤=-=04.0,2.00,1)0(22h x y y x dxdy; (2) ⎪⎩⎪⎨⎧=≤≤=-=1.0,5.00,1)0(h x y ydxdy。
解:(1) 5,4,3,2,1,0,,04.0,1)0(,),(22====-=n nh x h y y x y x f n8360.08635.08935.09262.09616.01Euler 8299.08583.08894.09232.096.01Euler 2.016.012.008.004.00改进k x (2) 5,4,3,2,1,0,,1.0,1)0(,),(====-=n nh x h y y y x f n6071.06708.07412.0819.0905.01Euler 5905.06561.0729.081.09.01Euler 5.04.03.02.01.00改进k x 7.2 用Euler 方法和改进Euler 方法求初值问题⎪⎩⎪⎨⎧=+=0)0(y bax dx dy的解在),2,1(, ==n hn x n 处的近似值。
bnh ah n n bnh n ah bh anh h n a y bhanh y b anh h y b ax h y y x hf y y y x b ax y x f n n n n n n n n n ++=+++++==++-+=++=++=++=+===+=-+2222121002)1()...210(...2)1()()(),(0,0,),(7.3 运用标准四阶Runge--Kutta 法求初值问题⎪⎩⎪⎨⎧=+=1)1(32y yx x dx dy的解在x =1.1,1.2,1.3处的近似值, 计算结果保留三位小数。
102.2)3.1(,587.1)2.1(,24.1)1.1(===y y y7.4 运用标准四阶Runge--Kutta 法求初值问题⎪⎩⎪⎨⎧=--=1)0(2y xy y dx dy在区间[0,1]上的数值解, 取步长h =0.2, 将计算结果与准确值1)12()(---=x e x y x 进行比较。
fortran习题答案【篇一:fortran习题1答案】txt>上机目的:练习c语言的书写、循环和判断结构1. 编写程序实现摄氏度和华氏度的相互转换:f?c*9/5?32#include stdio.hint main(void){ float c,f;printf(请输入摄氏温度:\n);scanf(%f,c);f=c*9/5+32;printf(对应的华氏温度为:\n);printf(%.2f\n,f);}2. 打印出6行杨辉三角形如下图:11 11 2 11 3 3 11 4 6 4 11 5 10 10 5 1#include stdio.h#define n 6int main(){int a[n][n],i,j; for (i=0;in;i++) { a[i][0]=1; a[i][i]=1; } for(i=2;in;i++) for (j=1;ji;j++)a[i][j]=a[i-1][j-1]+a[i-1][j]; for(i=0;in;i++) {}for (j=0;j=i;j++)printf(%4d,a[i][j]); printf(\n); } return 0;3. 求出数列2/1,3/2,5/3,8/5,13/8,21/13...的前10项之和。
#include stdio.hint main(void){} float a,b,c,i,s; a=1;b=2;s=0; for (i=1;i=10;i++) { } printf(数列前10项的和为:%f\n,s); s=s+b/a; c=a+b; a=b; b=c;4. 输入若干实数,请编写程序用于统计每个正数和负数的个数。
5. 从键盘上输入三条边长,判断是否能组成三角形。
#include stdio.hint main(void){float a,b,c;printf(请输入三个边长:\n); scanf(%f%f%f,a,b,c);if (a+bca+cbb+ca) printf(这三条边可以围成三角形\n);} else printf(这三条边不可以围成三角形\n);6. 输入某个点的坐标(a, b),判断该点是否位于圆心(x, y)、半径为r的圆内。
FORTRAN90模拟测验一(笔试部分)一.选择题(从4个可选答案中选择一个正确答案添入空白处)1.FORTRAN 90规定程序中名称的长度不能超过个字符。
A.8 B.15 C.31 D.632.关于FORTRAN 90程序单元,以下四种说法中正确的是。
A.一个FORTRAN 90程序由多个程序单元组成,其中有一个且只能有一个主程序单元B.一个FORTRAN 90程序由多个程序单元组成,其中有一个且只能有一个模块单元C.一个FORTRAN 90程序允许有多个程序单元,但每类程序单元只能有一个D.一个FORTRAN 90程序允许有多个程序单元,但主程序单元和模块单元只能有一个3.FORTRAN 90程序中允许使用的三个通用标志符是。
A.!% & B.@ , ; C.! ; & D.; & *4. 下列中,所指的FORTRAN 90表达式都是正确的。
①∣A*x+B*y+C*z∣② b*b+4*a*c③ .NOT. .TRUE. .AND. .FALSE. ④‘A’<= ch <= ‘Z’⑤ X>100 = = .TRUE. ⑥ SQRT(A2+B2)⑦π*R**2 ⑧‘HAPPY ’+‘NEW ’+‘YEAR.’A. ①②⑤B.②③④⑧C.②③⑤D.②⑤⑥⑦5. FORTRAN 90规定,变量类型声明从高到低的优先顺序是。
A.隐含约定(I-N规则)、IMPLICIT声明、类型声明B.类型声明、隐含约定(I-N规则)、IMPLICIT声明C.类型声明、IMPLICIT声明、隐含约定(I-N规则)D.IMPLICIT声明、类型声明、隐含约定(I-N规则)6.数组声明语句为:INTEGER,DIMENSION(-5:-1,-3:3,11:15) ::num 数组元素num(-2,1,13)是存储结构中第个元素。
A.70 B.85 C.90 D.947.类型声明语句为:INTEGER(2) I 数据输出语句为:PRINT *,I变量I中数据输出域宽是字符。
第七章目标代码生成7.1 对下列四元式序列生成目标代码:T=A-BS=C+DW=E-FU=W/TV=U*S其中,V是基本块出口的活跃变量,R0和R1是可用寄存器。
【解答】简单代码生成算法依次对四元式进行翻译。
我们以四元式T=a+b为例来说明其翻译过程。
汇编语言的加法指令代码形式为ADD R, X其中,ADD为加法指令;R为第一操作数,第一操作数必须为寄存器类型;X为第二操作数,它可以是寄存器类型,也可以是内存型的变量。
ADD R,X指令的含意是:将第一操作数R与第二操作数相加后,再将累加结果存放到第一操作数所在的寄存器中。
要完整地翻译出四元式T=a+b,则可能需要下面三条汇编指令:MOV R, aADD R, bMOV T, R第一条指令是将第一操作数a由内存取到寄存器R中;第二条指令完成加法运算;第三条指令将累加后的结果送回内存中的变量T。
是否在翻译成目标代码时都必须生成这三条汇编指令呢?从目标代码生成的优化角度考虑,即为了使生成的目标代码更短以及充分利用寄存器,上面的三条指令中,第一条和第三条指令在某些情况下是不必要的。
这是因为,如果下一个四元式紧接着需要引用操作数T,则第三条指令就不急于生成,可以推迟到以后适当的时机再生成。
此外,如果必须使用第一条指令,即第一操作数不在寄存器而是在内存中,且此时所有可用寄存器都已分配完毕,这时就要根据寄存器中所有变量的待用信息(也即引用点)来决定淘汰哪一个寄存器留给当前的四元式使用。
寄存器的淘汰策略如下:(1) 如果某寄存器中的变量已无后续引用点且该变量是非活跃的,则可直接将该寄存器作为空闲寄存器使用。
(2) 如果所有寄存器中的变量在基本块内仍有引用点且都是活跃的,则将引用点最远的变量所占用寄存器中的值存放到内存与该变量对应的单元中,然后再将此寄存器分配给当前的指令使用。
因此,本题所给四元式序列生成的目标代码如下:MOV R0, ASUB R0, C /*R0=T*/MOV R1, CADD R1, D /*R1=S*/MOV S, R1 /*S引用点较T引用点远,故将R1的值送内存单元S*/MOV R1, ESUB R1, F /*R1=W*/SUB R1, R0 /*R1=U*/MUL R1, S /*R1=V*/7.2 假设可用的寄存器为R0和R1,且所有临时单元都是非活跃的,试将以下四元式基本块:T1=B-CT2=A*T1T3=D+1T4=E-FT5=T3*T4W=T2/T5用简单代码生成算法生成其目标代码。
第6章自底向上优先分析第1题已知文法G[S]为:S T a|A |(T)T,S|S(1)计算 G[S]的 FIRSTVT 和 LASTVT。
(2)构造G[S]的算符优先关系表并说明G[S]是否为算符优先文法。
⑶计算G[S]的优先函数。
(4)给出输入串(a,a)#和(a,(a,a))#的算符优先分析过程。
答案:文法展开为:S^aS T AS T (T)T T T,ST T S猱符优先关系表:友情提示:记得增加拓广文法S' T#S#,所以# FIRSTVT(S) , LASTVT(S) # 。
Success!对输入串(a,(a,a) ) #的算符优先分析过程为:栈〔STACK) 为询字符WH恋)剩余输入笊(INPUT_STRING)动作〔ACTION)岸n a.(a.a))# e ill * a 伽)># itove iiima{aa)> Reduce: S—q <a.a)># Move iii( a.a))# Move iiia 讪Move iiia))# Reduce: S—日#(N,(N i a))# \tove iii#(N.(N a Move m粼屈)Reduce: S—R粼N(N.N)Reduce; T—丁占)h【ovE iii)#Reduce: S—*(T) #(N,N )#Reduce: T—*T,S #(N )Move iiiKN) ##Reduce: S—"(T) Success!第2题已知文法G[S]为:S T a|A |(T)T,S|S(1)给出(a,(a,a))和(a,a)的最右推导,和规范归约过程。
⑵ 将⑴和题1中的⑷进行比较给出算符优先归约和规范归约的区另叽答案:(1 ) (n・a)的授右推导过程为: sn(T) =(T.S)=^(T.a)=>(S.a)=>(a.a)(a.(a.a))的最右推导过程为:S=>(T)O(T.S)=(T.(T))=>(r.(r.s))=>(T.(T.a))=>(T.(S.a))=>(T-(a.a))=>(S.(a.a))=>(a.(a.a))(a.(a.a))的规范归约过程:(冇)的规范!H约过阻(2)非终结符无关,只需知道把当前可归约串归约为某一个非终结符,不必知道该非终结符的名字是什么,因此去掉了单非终结符的归约。
1.输入整数,判断能否被3或5整除,如能整除,则打印,否则不打印。
编写程序实现之。
解答:
!判断可以被3或5整除的整数
PROGRAM exam61
INTEGER :: n
PRINT*, '请输入一个整数:'
READ*, n
IF(mod(n,15)==0) THEN
WRITE(*, "(1X,I5,'是一个可以被3和5整除的整数')") n
ELSE IF(mod(n,3)==0) THEN
WRITE(*, "(1X,I5,'是一个可以被3整除的整数')") n
ELSE IF(mod(n,5)==0) THEN
WRITE(*, "(1X,I5,'是一个可以被5整除的整数')") n
ENDIF
END
2.计算职工工资,工人每周工作40小时,超过40小时的部分应该按加班工资计算(为正常工资的2倍。
输入工作时间和单位报酬,计算出该职工应得的工资,并打印输出。
编写程序实现之。
解答:
!计算职工工资
PROGRAM exam62
INTEGER t,p,pt
PRINT*, '请输入工人工作的时间t和单位报酬pt'
READ*, t,pt
IF(t>40)then
p=40*pt+(t-40)*2*pt
ELSE
p=t*pt
ENDIF
PRINT*, '该工人本周的应得工资为:',p,'元'
END
1.已知:x=0︒、10︒、20︒、…、180︒,输出x、sin(x)、cos(x)、tg(x)的值。
编写程序实现之。
解答:
! 输出x、xin(x)、cos(x)、tan(x)的值
PROGRAM exam71
PARAMETER(pi=3.1415926)
INTEGER i
REAL :: x,sinx,cosx,tanx
PRINT *,' x sin(x) cos(x) tg(x)'
DO i=0,180,10
x=i/180.0*pi
sinx=sin(x)
cosx=cos(x)
tanx=tan(x)
PRINT '(I3,3(2X,F10.7))',i,sinx,cosx,tanx
END DO
END
2.已知:x=1.0、1.1、1.2、…、2.9,输出x、x2、ex、ln(x)的值。
编写程序实现之。
解答:
! 计算x、x平方、e的x次方、ln(x)的值
PROGRAM exam72
INTEGER i
REAL :: x,x2,ex,lnx
PRINT*,' x x**2 exp(x) ln(x) '
DO i=10,29
x=i/10.0
x2=x*x
expx=exp(x)
lnx=log(x)
PRINT '(F3.1,2X,F4.2,2X,F10.5,2X,F10.5)',x,x2,expx,lnx
END DO
END
3.输入10个整数,计算它们的和、积、平方和、和的平方。
编写程序实现之。
解答:
! 计算和,积,平方和,和的平方
PROGRAM exam73
INTEGER i
REAL :: s1=0.0,s2=1.0,s3=0.0,s4=0.0
PRINT*,'请输入十个实数(每行一个)'
DO i=1,10
READ*,a
s1=s1+a
s2=s2*a
s3=s3+a**2
END DO
s4=s1**2
PRINT*,'10个数之和',s1
PRINT*,'10个数之积',s2
PRINT*,'10个数平方和',s3
PRINT*,'10个数和的平方',s4
END
4.输入20个数,统计其中正数、零、负数的个数。
编写程序实现之。
解答:
!统计其中正数、负数和零的个数
PROGRAM exam74
INTEGER :: i,s1=0,s2=0,s3=0
REAL a
PRINT*,'请输入二十个数(每行一个):'
DO i=1,20
READ*,a
IF (a>0) s1=s1+1
IF (a==0) s2=s2+1
IF (a<0) s3=s3+1
END DO
PRINT*,'正数个数',s1
PRINT*,'0的个数',s2
PRINT*,'负数个数',s3
END。