静态与动态翻译课件
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.14 MB
- 文档页数:47



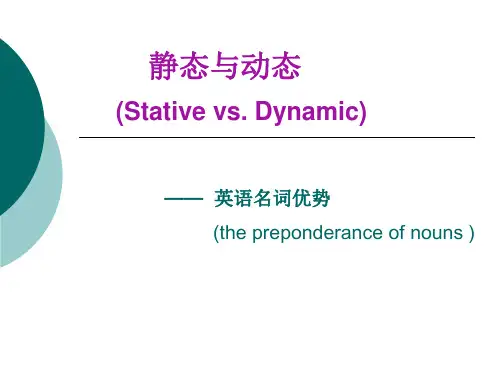
第七章静态与动态(Stative vs.Dynamic)英语倾向于多用名词,因而叙述呈静态(stative);汉语倾向于多用动词,因而叙述呈动态(dynamic)。
R.Quirk等人对静态和动态曾作如下解释:Broadly speaking, nouns can be characterized naturally as ‘stative’in that they refer to entities that are regarded as stable.whether these are concrete (physical) like house,table,paper,or abstract (of the mind)like hope,botany,length.At the opposite pole,verbs can be equally naturally characterized as ‘dynamic’:they are fitted (by their capacity to show tense and aspect,for example) to indicate action,activity and temporary or changing conditions.These relations between the open classes can be summarized thus:STA TIVE noun ↔ adjectiveDYNAMIC verb adverb英语的静态倾向,主要表现在以下几方面:一、名词化(Nominalization)是英语常见的现象。
名词化主要指用名词来表达原来属于动词(或形容词)所表达的概念,如用抽象名词来表达动作、行为、变化、状态、品质、情感等概念。
S.Potter在“Changing E nglish”一书中曾指出英语“名词优势于动词”的倾向(preponderance of nouns over verbs)。