刃型位错的原子模型
Atomic Model of an Edge Dislocation
刃位错的基本特征: 柏氏矢量与位错线垂直
滑移面唯一
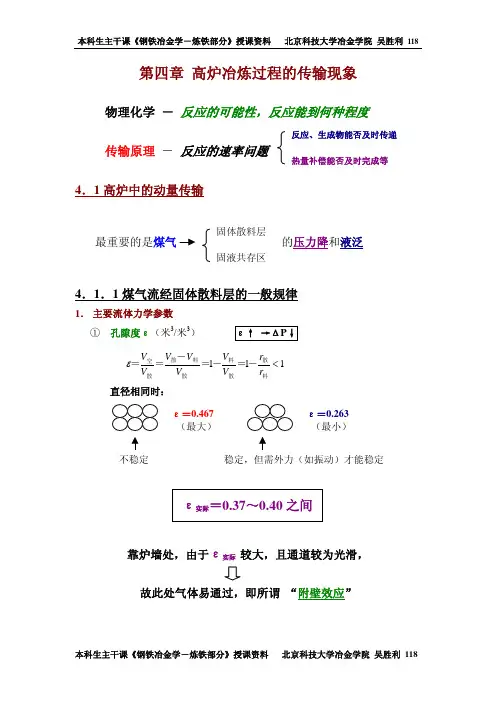
b x line 运动
滑移(glide)
攀移(climb)
形状: 直线、平面曲线 平面折线、环状
刃位错的形状: 直线\平面折线\任何平面曲线
滑 移 面
Atoms near the boundaries must be Dislocated! Dislocations位错
2、位错的基本性质:边界
1)宏观上属“线性”缺陷; 2)在晶体内部呈自封闭曲线或
终止于晶体表面或晶界; 3)恒定的滑移矢量
位错的滑移矢量-柏氏矢量
Burger’s Vector: 大小:位错滑移量的大小 方向:位错滑移方向 守恒性: 一条位错线,无论其形状如
二、间隙原子 Interstitial Atoms
热力学不稳定的晶体缺陷
自间隙原子(Self-Interstitials):
除经高能粒子辐照外(如核装备零件,同时产生 空位空位群空洞:缺陷)、一般不存在
溶质间隙原子(Solute Interstitials) :
C、N、B、O、H等,固溶强化效果极强!
《Science》 299 (2003)5607, 686-688.
2004年中国十大科技新闻(位列第二)
Microstructure in the surface layer of a pure iron plate was refined at the nanometer scale by a surface mechanical attrition treatment that generates repetitive severe plastic deformation of the surface layer. The subsequent nitriding kinetics were greatly enhanced, so that the nitriding temperature could be as low as 300°C, which is much lower than conventional nitriding temperatures (above 500°C). This enhanced processing method demonstrates the technological significance of nanomaterials in improving traditional processing techniques.