遗传信息的翻译资料
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:2.57 MB
- 文档页数:31

遗传信息的翻译遗传信息翻译为英文:Genetic InformationGenetic information refers to the genetic material or DNA sequence that is inherited from one generation to another. It carries the instructions for the development, growth, functioning, and reproduction of living organisms.Genetic information is found in the nucleus of cells in the form of chromosomes. Each chromosome is made up of DNA strands that are tightly coiled. The DNA molecule consists of a long chain of nucleotides, which are the building blocks of DNA. These nucleotides are made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. There are four types of nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). The sequence of these bases along the DNA strand determines the genetic code.The genetic code is universal, meaning that it is the same for all living organisms. It consists of sets of three bases, known as codons, which specify the order of amino acids in a protein. Proteins are essential for the structure and function of cells, and they are responsible for various biological processes. The genetic code is read by ribosomes, which are cellular structures that translate the information from DNA into proteins.Genetic information is passed from parents to offspring through the transmission of genetic material during reproduction. In sexualreproduction, genetic information from both parents is combined to create a unique combination of traits in the offspring. This is why offspring inherit characteristics from their parents.Genetic information can also be influenced by environmental factors. Environmental factors can affect gene expression, which refers to the activation or deactivation of genes. Gene expression can be influenced by factors such as diet, stress, and exposure to toxins. These environmental factors can alter the phenotype, or the physical characteristics of an organism, without changing the genetic code.Advances in technology have made it possible to study and manipulate genetic information. Scientists can sequence the entire DNA of an organism to identify genes and study their functions. They can also use genetic engineering techniques to modify the genetic code of organisms and create new traits. These advancements have significant implications for various fields, including medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology.In conclusion, genetic information is the inheritance of genetic material from one generation to another. It carries the instructions for the development, growth, functioning, and reproduction of living organisms. It is found in the DNA molecule, which consists of nucleotides with nitrogenous bases that determine the genetic code. Genetic information is passed from parents to offspring and can be influenced by environmental factors. Advances in technology have allowed scientists to study and manipulate genetic information, leading to significant advancements in various fields.。
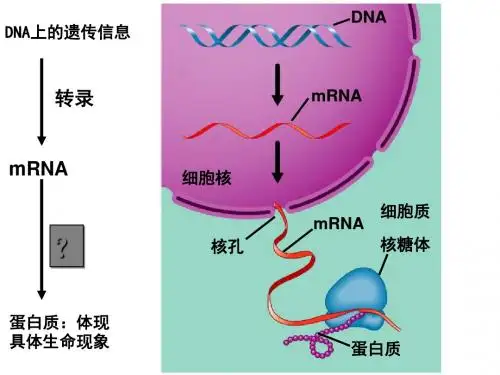





遗传信息的翻译:在细胞质中,以信使RNA为模板,合成具有一定氨基酸顺序的蛋白质的过程。
密码子:mRNA上3个相邻的碱基决定1个氨基酸,这样的3个碱基成为1个密码子。
反密码子:tRNA上与mRNA上密码子互补配对的3个碱基。
tRNA:翻译过程中,将游离氨基酸运到核糖体上的RNA。
密码子(在mRNA上)64种,决定蛋白质的61种(3种终止密码子),tRNA 61种,反密码子(在tRNA上)可以与密码子互补配对,tRNA有特异性。
相关计算:经翻译合成的蛋白质分子中氨基酸数目是mRNA中碱基数目的1/3,是双链DNA碱基数目的1/6。
常见酶:(1)淀粉酶:作用是催化淀粉水解为麦芽糖。
按其产生部位分为唾液淀粉酶、胰淀粉酶、肠淀粉酶和植物淀粉酶。
(淀粉遇碘变蓝)(2)麦芽糖酶:作用是催化麦芽糖水解成葡萄糖,主要分布在发芽的大麦中。
(3)蔗糖酶:作用是催化蔗糖水解成葡萄糖和果糖,主要分布在甘蔗等生物体内。
(4)脂肪酶:作用是催化脂肪水解为脂肪酸和甘油。
在动物体内分为胰脂肪酶和肠脂肪酶等。
在动物的胰液、血浆和植物的种子中均有分布。
(5)蛋白酶:作用是催化蛋白质水解为短肽。
在动物体内分为胰蛋白酶和胃蛋白酶等。
在动物的胰液、胃液,植物组织和微生物中都有分布。
(6)纤维素酶:作用是催化纤维素水解成葡萄糖。
在真菌、细菌和高等植物中含有。
(7)溶菌酶:广泛存在于动植物、微生物及其分泌物中,能溶解细菌细胞壁中的多糖,可使细菌失活。
还可激活白细胞的吞噬功能,增强机体抵抗力。
(8)固氮酶:能使大气中的氮还原为氨,由两种含金属的蛋白质组成,一种为铁蛋白,另一种为钼铁蛋白。
根瘤菌、蓝藻和土壤中各种固氮菌中都含有此酶。
(9)限制酶―磷酸二酯键、解旋酶―碱基间氢键、ATP水解酶―高能磷酸键、蛋白酶―肽键。



