高分子材料工程专业英语.pdf
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:728.44 KB
- 文档页数:20


A 高分子化学和高分子物理UNIT 1 What are Polymer?第一单元什么是高聚物?What are polymers? For one thing, they are complex and giant molecules and are different from low molecular weight compounds like, say, common salt. To contrast the difference, the molecular weight of common salt is only 58.5, while that of a polymer can be as high as several hundred thousand, even more than thousand thousands. These big molecules or ‘macro-molecules’ are made up of much smaller molecules, can be of one or more chemical compounds. To illustrate, imagine that a set of rings has the same size and is made of the same material. When these things are interlinked, the chain formed can be considered as representing a polymer from molecules of the same compound. Alternatively, individual rings could be of different sizes and materials, and interlinked to represent a polymer from molecules of different compounds.什么是高聚物?首先,他们是合成物和大分子,而且不同于低分子化合物,譬如说普通的盐。

高分子材料与工程专业词汇大全(包含:一高分子化学二高分子反应三高分子物理四高分子加工技术和应用四大部分的全部词汇~~)一高分子化学coiling type polymer二高分子反应齐聚反应(曾用名)22 调聚反应telomerization23 自发聚合spontaneous polymerization24 预聚合prepolymerization25 后聚合post polymerization26 再聚合repolymerization27 铸塑聚合, 浇铸聚合cast polymerization28 链[式]聚合chain polymerization29 烯类聚合,乙烯基聚合vinyl polymerization30 双烯[类]聚合diene polymerization31 加[成]聚[合]addition polymerization32自由基聚合,游离基聚合(曾用名) free radical polymerization, radical polymerization33控制自由基聚合,可控自由基聚合controlled radical polymerization,CRP34 活性自由基聚合living radical polymerization35 原子转移自由基聚合atom transfer radical polymerization,ATRP36 反向原子转移自由基聚合reverse atom transfer radical polymerization,RATRP37可逆加成断裂链转移reversible addition fragmentation chaintransfer,RAFT38 氮氧[自由基]调控聚合nitroxide mediated polymerization39 稳定自由基聚合stable free radical polymerization,FRP40 自由基异构化聚合free radical isomerization polymerization41 自由基开环聚合radical ring opening polymerization42 氧化还原聚合redox polymerization43 无活性端聚合,dead end polymerization死端聚合(曾用名)44 光[致]聚合photo polymerization45 光引发聚合light initiated polymerization46 光敏聚合photosensitized polymerization47 四中心聚合four center polymerization48 电荷转移聚合charge transfer polymerization49 辐射引发聚合radiation initiated polymerization50 热聚合thermal polymerization51 电解聚合electrolytic polymerization52 等离子体聚合plasma polymerization53 易位聚合metathesis polymerization54 开环易位聚合ring opening metathesis polymerization,ROMP55 精密聚合precision polymerization56 环化聚合cyclopolymerization57 拓扑化学聚合topochemical polymerization58 平衡聚合equilibrium polymerization59 离子[型]聚合ionic polymerization60 辐射离子聚合radiation ion polymerization61 离子对聚合ion pair polymerization62正离子聚合,阳离子聚合cationic polymerization63 碳正离子聚合carbenium ion polymerization,carbocationicpolymerization64 假正离子聚合pseudo cationic polymerization65 假正离子活[性]聚合pseudo cationic living polymerization66 活性正离子聚合living cationic polymerization67负离子聚合,阴离子聚合anionic polymerization68 碳负离子聚合carbanionic polymerization69 活性负离子聚合living anionic polymerization70 负离子环化聚合anionic cyclopolymerization71 负离子电化学聚合anionic electrochemical polymerization72 负离子异构化聚合anionic isomerization polymerization73 烯丙基聚合allylic polymerization74 活[性]聚合living polymerization75 两性离子聚合zwitterion polymerization76 齐格勒-纳塔聚合Ziegler Natta polymerization77 配位聚合coordination polymerization78 配位离子聚合coordinated ionic polymerization79 配位负离子聚合coordinated anionic polymerization80 配位正离子聚合coordinated cationic polymerization81 插入聚合insertion polymerization82定向聚合,立构规整聚合stereoregular polymerization, stereospecific polymerization83 有规立构聚合tactic polymerization84 全同立构聚合isospecific polymerization85 不对称诱导聚合asymmetric induction polymerization86 不对称选择性聚合asymmetric selective polymerization87 不对称立体选择性聚合asymmetric stereoselective polymerization88 对映[体]不对称聚合enantioasymmetric polymerization89 对映[体]对称聚合enantiosymmetric polymerization90 异构化聚合isomerization polymerization91 氢转移聚合hydrogen transfer polymerization92 基团转移聚合group transfer polymerization,GTP93 消除聚合elimination polymerization94 模板聚合matrix polymerization,templatepolymerization95 插层聚合intercalation polymerization96 无催化聚合uncatalyzed polymerization97 开环聚合ring opening polymerization98 活性开环聚合living ring opening polymerization99 不死的聚合immortal polymerization100 酶聚合作用enzymatic polymerization101聚加成反应,逐步加成聚合(曾用名)polyaddition102 偶联聚合coupling polymerization103 序列聚合sequential polymerization104 闪发聚合,俗称暴聚flash polymerization105 氧化聚合oxidative polymerization106 氧化偶联聚合oxidative coupling polymerization107 逐步[增长]聚合step growth polymerization108缩聚反应condensation polymerization,polycondensation109酯交换型聚合transesterification type polymerization,ester exchange polycondensation110 自催化缩聚autocatalytic polycondensation111 均相聚合homogeneous polymerization112 非均相聚合heterogeneous polymerization113 相转化聚合phase inversion polymerization114 本体聚合bulk polymerization, mass polymerization115 固相聚合solid phase polymerization气相聚合gaseous polymerization,116gas phase polymerization117 吸附聚合adsorption polymerization118 溶液聚合solution polymerization119 沉淀聚合precipitation polymerization120 淤浆聚合slurry polymerization121 悬浮聚合suspension polymerization122 反相悬浮聚合reversed phase suspension polymerization 123 珠状聚合bead polymerization, pearl polymerization 124 分散聚合dispersion polymerization125 反相分散聚合inverse dispersion polymerization126 种子聚合seeding polymerization127 乳液聚合emulsion polymerization128 无乳化剂乳液聚合emulsifier free emulsion polymerization 129 反相乳液聚合inverse emulsion polymerization130 微乳液聚合micro emulsion polymerization131 连续聚合continuous polymerization132 半连续聚合semicontinuous polymerization133 分批聚合,间歇聚合batch polymerization134 原位聚合in situ polymerization135 均相缩聚homopolycondensation136 活化缩聚activated polycondensation137 熔融缩聚melt phase polycondensation138 固相缩聚solid phase polycondensation139 体型缩聚three dimensional polycondensation140 界面聚合interfacial polymerization141 界面缩聚interfacial polycondensation142 环加成聚合cycloaddition polymerization143 环烯聚合cycloalkene polymerization144 环硅氧烷聚合cyclosiloxane polymerization145 引发剂initiator146 引发剂活性activity of initiator147 聚合催化剂polymerization catalyst148 自由基引发剂radical initiator149 偶氮[类]引发剂azo type initiator150 2,2′偶氮二异丁腈2,2'- azobisisobutyronitrile, AIBN151 过氧化苯甲酰benzoyl peroxide, BPO152 过硫酸盐引发剂persulphate initiator153 复合引发体系complex initiation system154 氧化还原引发剂redox initiator电荷转移复合物,charge transfer complex, CTC155电荷转移络合物156 聚合加速剂,聚合促进剂polymerization accelerator157 光敏引发剂photoinitiator158 双官能引发剂bifunctional initiator,difunctional initiator 159 三官能引发剂trifunctional initiator160 大分子引发剂macroinitiator161 引发-转移剂initiator transfer agent, inifer162 引发-转移-终止剂initiator transfer agent terminator, iniferter 163 光引发转移终止剂photoiniferter164 热引发转移终止剂thermoiniferter165 正离子催化剂cationic catalyst166 正离子引发剂cationic initiator167 负离子引发剂ionioic initiator168 共引发剂coinitiator169 烷基锂引发剂alkyllithium initiator170 负离子自由基引发剂anion radical initiator171 烯醇钠引发剂alfin initiator172 齐格勒-纳塔催化剂Ziegler Natta catalyst173 过渡金属催化剂transition metal catalyst 174 双组分催化剂bicomponent catalyst175 后过渡金属催化剂late transition metal catalyst 176 金属络合物催化剂metal complex catalyst 177 [二]茂金属催化剂metallocene catalyst178 甲基铝氧烷methylaluminoxane, MAO179μ氧桥双金属烷氧化物催化剂bimetallic μ-oxo alkoxides catalyst180 双金属催化剂bimetallic catalyst 181 桥基茂金属bridged metallocene182限定几何构型茂金属催化剂constrained geometry metallocene catalyst183 均相茂金属催化剂homogeneous metallocene catalyst 184 链引发chain initiation185 热引发thermal initiation186 染料敏化光引发dye sensitized phtoinitiation187 电荷转移引发charge transfer initiation188 诱导期induction period189 引发剂效率initiator efficiency190 诱导分解induced decomposition191 再引发reinitiation192 链增长chain growth, chain propagation193 增长链端propagating chain end194 活性种reactive species195 活性中心active center196 持续自由基persistent radical197 聚合最高温度ceilling temperature of polymerization 198 链终止chain termination199 双分子终止bimolecular termination200 初级自由基终止primary radical termination201 扩散控制终止diffusion controlled termination202 歧化终止disproportionation termination203 偶合终止coupling termination204 单分子终止unimolecular termination205 自发终止spontaneous termination206 终止剂terminator207 链终止剂chain terminating agent208 假终止pseudotermination209 自发终止self termination210 自由基捕获剂radical scavenger211 旋转光闸法rotating sector method212 自由基寿命free radical lifetime213 凝胶效应gel effect214 自动加速效应autoacceleration effect215 链转移chain transfer216 链转移剂chain transfer agent217 尾咬转移backbitting transfer218 退化链转移degradation (degradative) chain transfer219 加成断裂链转移[反应]addition fragmentation chain transfer 220 链转移常数chain transfer constant①缓聚作用retardation221②延迟作用222 阻聚作用inhibition223 缓聚剂retarder224 缓聚剂,阻滞剂retarding agent225 阻聚剂inhibitor226 封端[反应]end capping227 端基terminal group228 聚合动力学polymerization kinetics229 聚合热力学polymerization thermodynamics 230 聚合热heat of polymerization231 共聚合[反应]copolymerization232 二元共聚合binary copolymerization233 三元共聚合ternary copolymerization234 竞聚率reactivity ratio235 自由基共聚合radical copolymerization236 离子共聚合ionic copolymerization237 无规共聚合random copolymerization238 理想共聚合ideal copolymerization239 交替共聚合alternating copolymerization240 恒[组]分共聚合azeotropic copolymerization241 接枝共聚合graft copolymerization242 嵌段共聚合block copolymerization243 开环共聚合ring opening copolymerization244 共聚合方程copolymerization equation245 共缩聚copolycondensation246 逐步共聚合step copolymerization247 同种增长homopropagation248 自增长self propagation249 交叉增长cross propagation250 前末端基效应penultimate effect251 交叉终止cross termination252 Q值Q value253 e值e value254 Q,e概念Q, e scheme255 序列长度分布sequence length distribution 256 侧基反应reaction of pendant group257 扩链剂,链增长剂chain extender258 交联crosslinking259 化学交联chemical crosslinking260 自交联self crosslinking261 光交联photocrosslinking262 交联度degree of crosslinking263 硫化vulcanization264 固化curing265 硫[黄]硫化sulfur vulcanization266 促进硫化accelerated sulfur vulcanization 267 过氧化物交联peroxide crosslinking268 无规交联random crosslinking269 交联密度crosslinking density270 交联指数crosslinking index271 解聚depolymerization三高分子物理23蠕虫状链worm-like chain24柔性链flexible chain25链柔性chain flexibility26刚性链rigid chain27棒状链rodlike chain28链刚性chain rigidity29聚集aggregation30聚集体aggregate31凝聚、聚集coalescence32链缠结chain entanglement33凝聚缠结cohesional entanglement34物理缠结physical entanglement35拓扑缠结topological entanglement36凝聚相condensed phase37凝聚态condensed state38凝聚过程condensing process39临界聚集浓度critical aggregation concentration 40线团-球粒转换coil-globule transition41受限链confined chain42受限态confined state43物理交联physical crosslinking44统计线团statistical coil45等效链equivalent chain46统计链段statistical segment47链段chain segment48链构象chain conformation49无规线团模型random coil model50无规行走模型random walk model51自避随机行走模型self avoiding walk model52卷曲构象coiled conformation53高斯链Gaussian chain54无扰尺寸unperturbed dimension55扰动尺寸perturbed dimension56热力学等效球thermodynamically equivalent sphere 57近程分子内相互作用short-range intramolecular interaction 58远程分子内相互作用long-range intramolecular interaction 59链间相互作用interchain interaction60链间距interchain spacing61长程有序long range order62近程有序short range order63回转半径radius of gyration64末端间矢量end-to-end vector65链末端chain end66末端距end-to-end distance67无扰末端距unperturbed end-to-end distance68均方根末端距root-mean-square end-to-end distance 69伸直长度contour length70相关长度persistence length71主链;链骨架chain backbone72支链branch chain73链支化chain branching74短支链short-chain branch75长支链long-chain branch76支化系数branching index77支化密度branching density78支化度degree of branching79交联度degree of crosslinking80网络network81网络密度network density82溶胀swelling83平衡溶胀equilibrium swelling84分子组装,分子组合molecular assembly85自组装self assembly86微凝胶microgel87凝胶点gel point88可逆[性]凝胶reversible gel89溶胶-凝胶转化sol-gel transformation90临界胶束浓度critical micelle concentration,CMC91组成非均一性constitutional heterogenity, compositionalheterogenity92摩尔质量平均molar mass average 又称“分子量平均”93数均分子量number-average molecular weight,number-average molar mass94重均分子量weight-average molecular weight,weight-average molar mass95Z均分子量Z(Zaverage)-average molecular weight,Z-molar mass96黏均分子量viscosity-average molecular weight,viscosity-average molar mass97表观摩尔质量apparent molar mass98表观分子量apparent molecular weight99聚合度degree of polymerization100动力学链长kinetic chain length101单分散性monodispersity102临界分子量critical molecular weight103分子量分布molecular weight distribution,MWD104多分散性指数polydispersity index,PID105平均聚合度average degree of polymerization106质量分布函数mass distribution function107数量分布函数number distribution function108重量分布函数weight distribution function109舒尔茨-齐姆分布Schulz-Zimm distribution110最概然分布most probable distribution 曾用名“最可几分布”111对数正态分布logarithmic normal distribution 又称“对数正则分布”112聚合物溶液polymer solution113聚合物-溶剂相互作用polymer-solvent interaction114溶剂热力学性质thermodynamic quality of solvent115均方末端距mean square end to end distance116均方旋转半径mean square radius of gyration117θ温度theta temperature118θ态theta state119θ溶剂theta solvent120良溶剂good solvent121不良溶剂poor solvent122位力系数Virial coefficient 曾用名“维里系数”123排除体积excluded volume124溶胀因子expansion factor125溶胀度degree of swelling126弗洛里-哈金斯理论Flory-Huggins theory127哈金斯公式Huggins equation128哈金斯系数Huggins coefficient129χ(相互作用)参数χ-parameter130溶度参数solubility parameter131摩擦系数frictional coefficient132流体力学等效球hydrodynamically equivalent sphere133流体力学体积hydrodynamic volume134珠-棒模型bead-rod model135球-簧链模型ball-spring [chain] model136流动双折射flow birefringence, streaming birefringence 137动态光散射dynamic light scattering138小角激光光散射low angle laser light scattering139沉降平衡sedimentation equilibrium140沉降系数sedimentation coefficient141沉降速度法sedimentation velocity method142沉降平衡法sedimentation equilibrium method143相对黏度relative viscosity144相对黏度增量relative viscosity increment145黏度比viscosity ratio146黏数viscosity number147[乌氏]稀释黏度计[Ubbelohde] dilution viscometer148毛细管黏度计capillary viscometer149落球黏度计ball viscometer150落球黏度ball viscosity151本体黏度bulk viscosity152比浓黏度reduced viscosity153比浓对数黏度inherent viscosity, logarithmic viscositynumber154特性黏数intrinsic viscosity, limiting viscosity number155黏度函数viscosity function156零切变速率黏度zero shear viscosity157端基分析analysis of end group158蒸气压渗透法vapor pressure osmometry, VPO159辐射的相干弹性散射coherent elastic scattering of radiation 160折光指数增量refractive index increment161瑞利比Rayleigh ratio162超瑞利比excess Rayleigh ratio163粒子散射函数particle scattering function164粒子散射因子particle scattering factor165齐姆图Zimm plot166散射的非对称性dissymmetry of scattering167解偏振作用depolarization168分级fractionation169沉淀分级precipitation fractionation170萃取分级extraction fractionation171色谱分级chromatographic fractionation172柱分级column fractionation173洗脱分级,淋洗分级elution fractionation174热分级thermal fractionation175凝胶色谱法gel chromatography176摩尔质量排除极限molar mass exclusion limit177溶剂梯度洗脱色谱法solvent gradient [elution] chromatography 178分子量排除极限molecular weight exclusion limit179洗脱体积elution volume180普适标定universal calibration181加宽函数spreading function182链轴chain axis183等同周期identity period184链重复距离chain repeating distance185晶体折叠周期crystalline fold period186构象重复单元conformational repeating unit 187几何等效geometrical equivalence188螺旋链helix chain189构型无序configurational disorder190链取向无序chain orientational disorder191构象无序conformational disorder192锯齿链zigzag chain193双[股]螺旋double stranded helix194[分子]链大尺度取向global chain orientation195结晶聚合物crystalline polymer196半结晶聚合物semi-crystalline polymer197高分子晶体polymer crystal198高分子微晶polymer crystallite199结晶度degree of crystallinity, crystallinity 200高分子[异质]同晶现象macromolecular isomorphism 201聚合物形态学morphology of polymer202片晶lamella, lamellar crystal203轴晶axialite204树枝[状]晶体dendrite205纤维晶fibrous crystal206串晶结构shish-kebab structure207球晶spherulite208折叠链folded chain209链折叠chain folding210折叠表面fold surface211折叠面fold plane212折叠微区fold domain213相邻再入模型adjacent re-entry model 214接线板模型switchboard model215缨状微束模型fringed-micelle model216折叠链晶体folded-chain crystal217平行链晶体parallel-chain crystal218伸展链晶体extended-chain crystal219球状链晶体globular-chain crystal220长周期long period221近程结构short-range structure222远程结构long-range structure223成核作用nucleation224分子成核作用molecular nucleation225阿夫拉米方程Avrami equation226主结晶primary crystallization227后期结晶secondary crystallization 228外延结晶,附生结晶epitaxial crystallizationepitaxial growth229外延晶体生长,附生晶体生长230织构texture231液晶态liquid crystal state232溶致性液晶lyotopic liquid crystal233热致性液晶thermotropic liquid crystal 234热致性介晶thermotropic mesomorphism 235近晶相液晶smectic liquid crystal236近晶中介相smectic mesophase237近晶相smectic phase238条带织构banded texture239环带球晶ringed spherulite240向列相nematic phase241盘状相discotic phase242解取向disorientation243分聚segregation244非晶相amorphous phase 曾用名“无定形相”245非晶区amorphous region246非晶态amorphous state247非晶取向amorphous orientation248链段运动segmental motion249亚稳态metastable state250相分离phase separation251亚稳相分离spinodal decomposition252bimodal decomposition253微相microphase254界面相boundary phase255相容性compatibility256混容性miscibility257不相容性incompatibility258不混容性immiscibility259增容作用compatiibilizationlower critical solution temperature, LCST260最低临界共溶(溶解)温度upper critical solution temperature , UCST261最高临界共溶(溶解)温度262浓度猝灭concentration quenching263激基缔合物荧光excimer fluorescence264激基复合物荧光exciplex fluorescence265激光共聚焦荧光显微镜laser confocal fluorescence microscopy266单轴取向uniaxial orientation267双轴取向biaxial orientation, biorientation268取向度degree of orientation269橡胶态rubber state270玻璃态glassy state271高弹态elastomeric state272黏流态viscous flow state273伸长elongation274高弹形变high elastic deformation275回缩性,弹性复原nerviness276拉伸比draw ratio, extension ratio277泊松比Poisson's ratio278杨氏模量Young's modulus279本体模量bulk modulus280剪切模量shear modulus281法向应力normal stress282剪切应力shear stress283剪切应变shear strain284屈服yielding285颈缩现象necking 又称“细颈现象”286屈服应力yield stress287屈服应变yield strain288脆性断裂brittle fracture289脆性开裂brittle cracking290脆-韧转变brittle ductile transition291脆化温度brittleness(brittle) temperature292延性破裂ductile fracture293冲击强度impact strength294拉伸强度tensile strength 又称“断裂强度,breaking strength”295极限拉伸强度ultimate tensile strength296抗撕强度tearing strength 又称“抗扯强度”297弯曲强度flexural strength, bending strength298弯曲模量bending modulus299弯曲应变bending strain300弯曲应力bending stress301收缩开裂shrinkage crack302剪切强度shear strength303剥离强度peeling strength304疲劳强度fatigue strength, fatigue resistance305挠曲deflection306压缩强度compressive strength307压缩永久变形compression set308压缩变形compressive deformation309压痕硬度indentation hardness310洛氏硬度Rockwell hardness311布氏硬度Brinell hardness312抗刮性scrath resistance313断裂力学fracture mechanics314力学破坏mechanical failure315应力强度因子stress intensity factor316断裂伸长elongation at break317屈服强度yield strength318断裂韧性fracture toughness319弹性形变elastic deformation320弹性滞后elastic hysteresis321弹性elasticity322弹性模量modulus of elasticity323弹性回复elastic recovery324不可回复形变irrecoverable deformation325裂缝crack 俗称“龟裂”326银纹craze327形变;变形deformation328永久变形deformation set329剩余变形residual deformation330剩余伸长residual stretch331回弹,回弹性resilience332延迟形变retarded deformation333延迟弹性retarded elasticity334可逆形变reversible deformation335应力开裂stress cracking336应力-应变曲线stress strain curve337拉伸应变stretching strain338拉伸应力弛豫tensile stress relaxation339热历史thermal history340热收缩thermoshrinking341扭辫分析torsional braid analysis,TBA342应力致白stress whitening343应变能strain energy344应变张量strain tensor345剩余应力residual stress346应变硬化strain hardening347应变软化strain softening348电流变液electrorheological fluid349假塑性pseudoplastic350拉胀性auxiticity351牛顿流体Newtonian fluid352非牛顿流体non-Newtonian fluid353宾汉姆流体Bingham fluid354冷流cold flow355牛顿剪切黏度Newtonian shear viscosity356剪切黏度shear viscosity357表观剪切黏度apparent shear viscosity358剪切变稀shear thinning359触变性thixotropy360塑性形变plastic deformation361塑性流动plastic flow362体积弛豫volume relaxation363拉伸黏度extensional viscosity364黏弹性viscoelasticity365线性黏弹性linear viscoelasticity366非线性黏弹性non-linear viscoelasticity367蠕变creep368弛豫[作用] relaxation 又称“松弛”369弛豫模量relaxation modulus370蠕变柔量creep compliance371热畸变温度heat distortion temperature372弛豫谱relaxation spectrum373推迟[时间]谱retardation [time] spectrum374弛豫时间relaxation time375推迟时间retardation time376动态力学行为dynamic mechanical behavior 377动态黏弹性dynamic viscoelasticity378热-机械曲线thermo-mechanical curve379动态转变dynamic transition380储能模量storage modulus381损耗模量loss modulus382复数模量complex modulus383复数柔量complex compliance384动态黏度dynamic viscosity385复数黏度complex viscosity386复数介电常数complex dielectric permittivity 387介电损耗因子dielectric dissipation factor388介电损耗常数dielectric loss constant389介电弛豫时间dielectric relaxation time390玻璃化转变glass transition391玻璃化转变温度glass-transition temperature392次级弛豫secondary relaxation393次级转变secondary transition394次级弛豫温度secondary relaxation temperature 395开尔文模型Kelvin model396麦克斯韦模型Maxwell model四高分子加工技术和应用。

Unit 1 What are polymers?What are polymers? For one thing, they are complex and giant molecules and are different from low molecular weight compounds like, say, common salt.什么是高聚物?首先,他们是合成物和大分子,而且不同于低分子化合物,譬如说普通的盐。
To contrast the difference, the molecular weight of common salt is only 58.5, while that of a polymer can be as high as several hundred thousand, even more than thousand thousands.与低分子化合物不同的是,普通盐的分子量仅仅是58.5,而高聚物的分子量高于105,甚至大于106。
These big molecules or ‘macro-molecules’ are made up of much sma ller molecules, can be of one or more chemical compounds.这些大分子或“高分子”由许多小分子组成。
小分子相互结合形成大分子,大分子能够是一种或多种化合物。
To illustrate, imagine that a set of rings has the same size and is made of the same material. When these things are interlinked, the chain formed can be considered as representing a polymer from molecules of the same compound.举例说明,想象一组大小相同并由相同的材料制成的环。
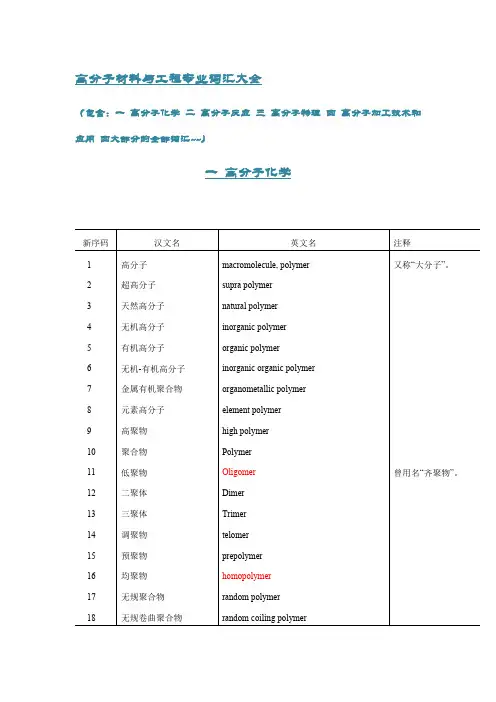
高分子材料与工程专业词汇大全(包含:一高分子化学二高分子反应三高分子物理四高分子加工技术和应用四大部分的全部词汇~~)一高分子化学新序码汉文名英文名注释1高分子macromolecule, polymer又称“大分子”。
2超高分子supra polymer3天然高分子natural polymer4无机高分子inorganic polymer5有机高分子organic polymer6无机-有机高分子inorganic organic polymer7金属有机聚合物organometallic polymer8元素高分子element polymer9高聚物high polymer10聚合物Polymer11低聚物Oligomer曾用名“齐聚物”。
12二聚体Dimer13三聚体Trimer14调聚物telomer15预聚物prepolymer16均聚物homopolymer17无规聚合物random polymer18无规卷曲聚合物random coiling polymer19头-头聚合物head-to-head polymer20头-尾聚合物head-to-tail polymer21尾-尾聚合物tail-to-tail polymer22反式有规聚合物transtactic polymer23顺式有规聚合物cistactic polymer24规整聚合物regular polymer25非规整聚合物irregular polymer26无规立构聚合物atactic polymer27全同立构聚合物isotactic polymer又称“等规聚合物”。
28间同立构聚合物syndiotactic polymer又称“间规聚合物”。
29杂同立构聚合物heterotactic polymer又称“异规聚合物”。
30有规立构聚合物stereoregular polymer, tactic polymer 又称“有规聚合物”。
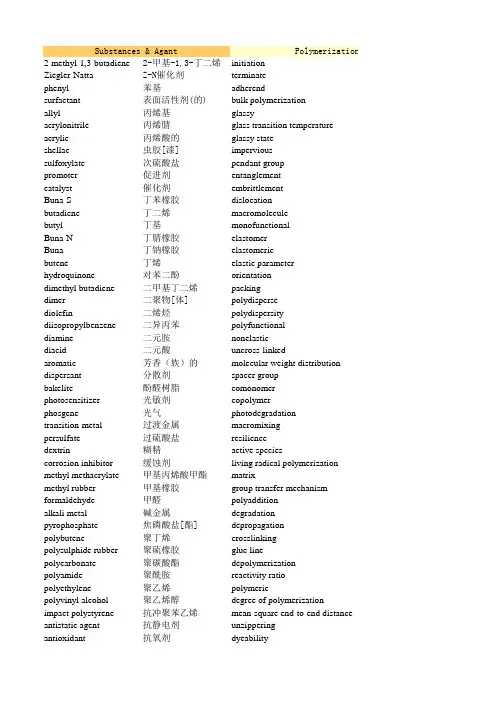
Substances & Agant Polymerization & 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene2-甲基-1,3-丁二烯initiationZiegler-Natta Z-N催化剂terminatephenyl苯基adherendsurfactant表面活性剂(的)bulk polymerizationallyl丙烯基glassyacrylonitrile丙烯腈glass transition temperatureacrylic丙烯酸的glassy stateshellac虫胶[漆]impervioussulfoxylate次硫酸盐pendant grouppromoter促进剂entanglementcatalyst催化剂embrittlementBuna-S丁苯橡胶dislocationbutadiene丁二烯macromoleculebutyl丁基monofunctionalBuna-N丁腈橡胶elastomerBuna丁钠橡胶elastomericbutene丁烯elastic parameterhydroquinone对苯二酚orientationdimethyl butadiene二甲基丁二烯packingdimer二聚物[体]polydispersediolefin二烯烃polydispersity diisopropylbenzene二异丙苯polyfunctionaldiamine二元胺nonelasticdiacid二元酸uncross-linkedaromatic芳香(族)的molecular weight distribution dispersant分散剂spacer groupbakelite酚醛树脂comonomerphotosensitizer光敏剂copolymerphosgene光气photodegradationtransition-metal过渡金属macromixingpersulfate过硫酸盐resiliencedextrin糊精active speciescorrosion inhibitor缓蚀剂living radical polymerization methyl methacrylate甲基丙烯酸甲酯matrixmethyl rubber甲基橡胶group transfer mechanism formaldehyde甲醛polyadditionalkali metal碱金属degradationpyrophosphate焦磷酸盐[酯]depropagationpolybutene聚丁烯crosslinkingpolysulphide rubber聚硫橡胶glue linepolycarbonate聚碳酸酯depolymerizationpolyamide聚酰胺reactivity ratiopolyethylene聚乙烯polymericpolyvinyl alcohol聚乙烯醇degree of polymerizationimpact polystyrene抗冲聚苯乙烯mean-square end-to-end distance antistatic agent抗静电剂unzipperingantioxidant抗氧剂dyeabilitylithium锂stereoregularitybitumen沥青stereoregularsulfuric acid硫酸segmentaluminum铝chain propagation chlorine氯(气)chain termination chloroprene氯丁二烯vulcanisesodium钠vulcanization naphthylamine萘胺molar cohesionferrous sulfate heptahydrate七水合硫酸亚铁heat-toleranthydroxyl羟基oil-resistancehydroxy acid羟基酸,含氧酸viscosity average weight hydrogen氢(气)plateletlubricant润滑剂mean resident time celluloid赛璐珞,假象牙orienttriphenylmethyl potassium三苯基甲基钾orientedtertiary三元的,叔[特]的isotacticpenetrant渗透剂dyecommon salt食盐thermosetcis-1,4-polyisoprene顺(式)聚异戊二烯pyrolysis tetrahydrofuran四氢呋喃thermoplasticrosin acid松香酸solution polymerization carboxyl羧基swellacetal缩醛swollentitanium钛melt indexchar炭compliancecarbonyl羰基emulsion polymerization extender添加剂,增量剂trimerhydrocarbon oil烃油extensibilitymenthane烷;薄荷烷number average weight alkyl烷基dualstabilizer稳定剂polycondensationolefinic烯烃的general-purpose parkesine硝化纤维素塑料micromixing flocculating agent絮凝剂random decomposition brine盐水atacticoxonium氧鎓,钖random coil ethylenediamine tetraacetate乙二胺四乙酸盐moisture absorption cellulose acetate乙酸纤维素coilingvinyl乙烯基的rubberyvinyl ether乙烯基醚dormant species isobutene异丁烯suspension polymerization isobutylene异丁烯stereospecific isocyanate异氰酸酯[盐]viscousisoprene异戊二烯viscoelastic stateinitiator引发剂viscosityperspex有机玻璃adhesive joint organometallic有机金属的viscofluid statealiphatic脂肪(族)的repeating unitshort-stop终止剂weight average weight candle wax烛用蜡step-growth polymerizationcocatalyst助催化剂backbone flame retardant阻燃剂special-purposeion & Nature Technics & Instruments Chemistry (链)引发instrument(用)仪器semicrystalline(链)终止Archimedean screw阿基米德螺杆saturation被粘物cell比色皿deformation本体聚合yield产率deterioration玻璃(态)的ultrasonic超声波[的]unsaturated玻璃化转变温度ultracentrifugation超速离心(分离)法irregularity玻璃态turning车削heterogeneous不透水的evacuate撤出,抽空mismatch侧基sedimentation沉降法precipitate缠结shaping成型settle脆裂dimensional stability尺寸稳定性ingredient错位raw product粗产品dimension大分子,高分子brittle脆的single bond单官能度的vat大桶uniaxial弹性体elastic modulus弹性模量electrovalent弹性体的conductive导电的kinetice弹性指数off-grade等外品deposit定向solder低温焊接multicomponent堆砌forging锻造reactant多分散的porosity多孔性Van der Waals' bones 多分散性secondary shaping operation二次成型(操作)Van der Waals force 多官能度的reactivity反应活性variance非弹性的reactive反应活性的exothermicity非交联的backmixing返混homopolar bond分子量分布spectroscopic分光镜的,光谱的amorphous隔离基团modify改性fractionation共聚单体destructive distillation干馏decomposition共聚物autoclave高压釜dissociation光降解azeotropic共沸物irradiation宏观混合pipework管道工程side reaction回弹力tubular reactor管式反应器isotropic活性种light scattering光散射covalent活性自由基聚合welding焊接conformation基体nuclear magnetic resonance核磁共振functional group基团转移机理nuclear track detector核径迹探测器synthesis加聚infrared spectroscopy红外光谱法synthesize降解surge tank缓冲槽synthetic降解devolatilizer挥脱器stoichiometric交联gyration回旋activation胶层ram活塞mechanism解聚piston flow活塞流heteropolar bond竞速[聚]率barrel机筒,料筒hydrogenation聚合的extrudate挤出物bond dissociation energy 聚合度squeez挤压latex均方末端距processing加工,成型colloid开链clamp夹紧,定位crystallinity可染性,染色度batch reactor间歇反应器empirical立构规整性[度]intermittent间歇式的crystalline立构规整性的agitation搅拌dissociate链段mixer搅拌器ion链增长medium介质;中间的ionic链终止close control精密控制mechanical property 硫化,硬化tensile strength抗张强度hydrostatic硫化,硬化dieforming口模成型complex摩尔内聚力chilled water冷冻水chlorination耐热的centrifuge离心gel耐油性ion exchange resin离子交换树脂coalesce黏均分子量screw extruder螺杆挤出机coagulate片晶seal密封concentration平均停留时间moulding模塑成型formulation取向model模型offset取向的stamping模压[冲压]成型simultaneous reaction 全同立构的grirding磨equilibrium染色;染料countercurrent逆流hydrogen bonding热固性的(塑料)planing刨heat transfer热解sprinkle喷洒thermodynamically 热塑性的(塑料)stock坯料,原料solvent溶液聚合braze钎接dissolution溶胀thermoforming热成型solubility溶胀的artifact人工制品configuration熔体流动率tree-neck flask三颈瓶dispersion force柔量three dimensionally ordered三维有序的flash distillation乳液聚合scalp筛子;筛分entropy三聚物[体]sintering烧结permeability伸长率elongation伸长率dissolve数均分子量coating涂布成型dehydrogenate双重的stripping tower脱单塔hydrolysis缩聚dewater脱水crumb通用的rotocasting离心浇注statistical微观混合stability稳定性transparency无规降解milling铣crystallite无规立构的parison型坯stabilization无规线团rotational moulding旋转成型inorganic吸湿性recycle reactor循环反应器amidation线团状的calendering压延成型eliminate橡胶(状)的diffraction pattern衍射图样[花纹]nitration休眠种Young's modulus杨氏模量cationic悬浮聚合perform预成形坯,锭料redox有规立构的,立体定向的carrier载体liquid crystal粘稠的cement粘接colligative粘弹态fabrication制造,装配anionic粘度[性]shot注料量attraction粘合点extrusion注射[挤出]成型stress粘流态injection moulding注塑成型esterification重复单元conversion转化(率)neutral重均分子量torsion转矩radical逐步聚合overall conversion总转化率free energy主链drilling钻minimum 专用的resident time distribution停留时间分布optimumistry & Basis General & Others 半晶abnormal反常的饱和aggravate加重,恶化变形性,形变align排列成行变质architecture结构不饱和的arrangement(空间)排布不规则性behavior性能,行为不均匀的,非均相的blockade封锁不匹配boundary界限,范围沉淀breakdown细目分类沉淀break-through突破成分categorization分类法尺寸categorize加以区别单键category种类单轴的characterize表征电价的collapse皱缩,塌瘪动力学的commence开始堆积物,沉淀commencement开始多组分consistency稠度,粘稠性反应物contact收缩范德华键contaminant污物范德华力contour外形方差cracking裂纹放热性critical决定性的非极性键defect缺陷非晶态的deficient不足的分级deplete耗尽分解differential微分的分裂,离解diffuse扩散辐照dimensionless无量纲的副反应disengage分开各项同性的disintegrate分散,分离共价的disposition陈列,布置构象drastic强烈的官能团exploit开拓合成facilitate使容易合成flake薄片合成的flexible柔软的化学当量的fragment碎片活化(作用)ideal理想的机理[制]ideally理想地极性键imbed嵌入,包埋加氢imperfect不完整的键断裂能impurity杂质胶乳indispensable不可缺少的胶体(的)ingenuity创造力,机敏结晶性[度]ingredient要素经验的instantaneous瞬时的晶态(的),结晶(的)integral必备的离解integration集成,综合离子interaction相互作用离子的intrinsic固有的力学[机械]性能latent潜在的流体静力学的line衬里络合物mediate传递,媒介氯化minimise最小化凝胶mobility流动性凝结mobilize流动,运动凝聚molten熔融的浓度morphology形态学配方occluded夹杂的偏移originate首创平行反应parabolic抛物线的平衡parameter参数氢键(结合)peculiarity特性热传递performance性能,特征热力学地perspective透视;观点溶剂pigment颜料溶解postulate假定溶解度powdery粉状的构型profile外形,轮廓色散力quench熄灭,抑制闪蒸radius半径熵recipracating往复的渗透性release解除,释放使溶解retract收缩使脱氢robust坚固耐用的水解rupture断裂碎屑,团粒sacrifice损失统计(学)的scale up放大透明性schematic示意性的微晶scheme计划稳定化simultaneously同时无机的slurry淤浆酰胺化sophisticated复杂的,尖端的消除specificity特异性,专一性硝化sponge海绵阳离子的subdivide细分氧化还原substitute取代液晶sustain维持依数的synonymous同义的阴离子的tanker油轮,槽车引力taper锥应力texture结构,组织酯化tread外胎中性的undergo经历,进行自由基uninterrupted连续的自由能variation变化最小值[的]versatile用途广泛的最优点[的]versatility多功能性,通用性。

[二]茂金属催化剂|metallocene catalyst1,1-亚乙烯基单体|vinylidene monomer1,2-polybutadiene|1,2-聚丁二烯1,2-polyisoprene|1,2-聚异戊二烯1,2-二取代乙烯单体|vinylene monomer1,2-聚丁二烯|1,2-polybutadiene 1,2-聚异戊二烯|1,2-polyisoprene 1,2-亚乙烯基单体|vinylene monomer 1,4-polybutadiene|1,4-聚丁二烯1,4-聚丁二烯|1,4-polybutadiene 2,2'-azobisisobutyronitrile|2,2′偶氮二异丁腈, AIBN2,2′偶氮二异丁腈|2,2'- azobisisobutyronitrile, AIBN3,4-polyisoprene|3,4-聚异戊二烯3,4-聚异戊二烯|3,4-polyisoprene abhesive|阻黏剂ablative polymer|烧蚀橡胶ablator|烧蚀剂accelerated ageing|加速老化accelerated sulfur vulcanization|促进硫化acetal resin|缩醛树脂acetylenic polymer|乙炔类橡胶acrolein polymer|丙烯醛类橡胶acrylate rubber|丙烯酸酯橡胶acrylic fiber|聚丙烯腈纤维,腈纶acrylic polymer|丙烯酸[酯]类橡胶acrylic resin|丙烯酸[酯]类树脂acrylonitrile styrene resin|丙烯腈-苯乙烯树脂, ASacrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene resin|丙烯腈-丁二烯-苯乙烯树脂, 简称“ABS树脂”activated monomer|活化单体activated polycondensation|活化缩聚activating accelerator|活化促进剂activation grafting|活化接枝activator|活化剂active carbon fiber|活性碳纤维active center|活性中心activity of initiator|引发剂活性addition fragmentation chain transfer|加成断裂链转移addition polymer|加[成]聚[合]物addition polymerization|加聚additive|添加剂adhesion|粘合adhesive|粘合剂,又称“胶粘剂”adjacent re-entry model|相邻再入模型adsorption polymerization|吸附聚合after-treating agent|后处理剂agar-agar|琼脂agglomerating agent|附聚剂aggregate|聚集体aggregation|聚集albumin|白蛋白aldehyde polymer|醛类橡胶alfin initiator|烯醇钠引发剂aliphatic epoxy resin|脂肪族环氧树脂aliphatic polyester|脂肪族聚酯alkyd resin|醇酸树脂alkyllithium initiator|烷基锂引发剂allene polymer|丙二烯橡胶allyl resin|烯丙基树脂allylic polymerization|烯丙基聚合alternating copolymer|交替共聚物alternating copolymerization|交替共聚合aluminate coupling agent|铝酸酯偶联剂amine cellulose|胺纤维素amino resin|氨基树脂Aminotriazine resin|三聚氰胺树脂amorphous orientation|非晶取向amorphous phase|非晶相,无定形相amorphous region|非晶区amorphous state|非晶态amphiphilic block copolymer|两亲嵌段共聚物amphiphilic polymer|两亲橡胶amylopectin|支链淀粉amylose|直链淀粉amylum|淀粉anaerobic adhesive|厌氧黏合剂analysis of end group|端基分析anion exchange resin|负离子交换树脂anion radical initiator|负离子自由基引发剂anionic cyclopolymerization|负离子环化聚合anionic electrochemical polymerization|负离子电化学聚合anionic exchange membrane|负离子交换膜anionic isomerization polymerization|负离子异构化聚合anionic polymerization|负离子聚合,阴离子聚合anisotropic membrane|各向异性膜anti-aging agent|防老剂anti-corrosion agent|防蚀剂anticracking agent|抗龟裂剂antidegradant|抗降解剂anti-fatigue agent|抗疲劳剂antifoaming agent|消泡剂antioxidant|抗氧剂antiozonant|防臭氧剂anti-reversion agent|抗硫化返原剂antiseptic|防霉剂anti-skinning agent|防结皮剂antistatic additive|抗静电添加剂antistatic agent|抗静电剂apparent molar mass|表观摩尔质量apparent molecular weight|表观分子量apparent shear viscosity|表观剪切黏度aramid fiber|聚芳酰胺纤维,芳纶,芳香尼龙aromatic polyamide|聚芳酰胺aromatic polyester|芳香族聚酯aromatic polysulfonamide|聚芳砜酰胺artificial ageing|人工老化as-formed fiber|初生纤维association polymer|缔合橡胶asymmetric induction polymerization|不对称诱导聚合asymmetric selective polymerization|不对称选择性聚合asymmetric stereoselective polymerization|不对称立体选择性聚合atactic block|无规立构嵌段atactic polymer|无规立构橡胶atacticity|无规度,无规立构度atom transfer radical polymerization|原子转移自由基聚合, ATRPautoacceleration effect|自动加速效应autocatalytic polycondensation|自催化缩聚auto-vulcanization|常温硫化auxiticity|拉胀性average degree of polymerization|平均聚合度average functionality|平均官能度Avrami equation|阿夫拉米方程axialite|轴晶azeotropic copolymer|恒[组]分共聚物azeotropic copolymerization|恒组分共聚合azo polymer|偶氮类橡胶azo type initiator|偶氮[类]引发剂backbitting transfer|尾咬转移bacterial degradation|细菌降解bag molding|袋模塑ball viscometer|落球黏度计ball viscosity|落球黏度ball-spring [chain] model|球-簧链模型banded texture|条带织构barrier polymer|阻透橡胶batch polymerization|分批聚合,间歇聚合bead polymerization|珠状聚合bead-rod model|珠-棒模型bending modulus|弯曲模量bending strain|弯曲应变bending strength|弯曲强度bending stress|弯曲应力benzoyl peroxide|过氧化苯甲酰, BPObiaxial drawing|双轴拉伸biaxial orientation|双轴取向bicomponent catalyst|双组分催化剂bifunctional initiator,difunctional initiator|双官能引发剂bifunctional monomer|双官能[基]单体bimetallic catalyst|双金属催化剂bimetallic μ-oxo alkoxides catalyst|μ氧桥双金属烷氧化物催化剂bimodal decomposition|亚稳相分离bimolecular termination|双分子终止bin cure|自硫[化]binary copolymer|二元共聚物binary copolymerization|二元共聚合Bingham fluid|宾汉姆流体bioactive polymer|生物活性高分子biocide|抗微生物剂biocompatibility|生物相容性biodegradable polymer|生物降解高分子biodegradation|生物降解bioelastomer|生物弹性体bioerodable polymer|生物可蚀性高分子biomedical polymer|生物医用高分子biomimetic polymer|仿生高分子biopolymer|生物高分子biorientation|双轴取向bisphenol A epoxy resin|双酚A环氧树脂bisphenol A polycarbonate|双酚A 聚碳酸酯blend|共混blended spinning|共混纺丝block|嵌段block copolymer|嵌段共聚物block copolymerization|嵌段共聚合block poly(ester ether)|嵌段聚醚酯block polymer|嵌段橡胶block polymerization|嵌段聚合blood compatibility|血液相容性blow molding|吹塑blown extrusion|吹胀挤塑Boltzmann superpositionprinciple|玻耳兹曼叠加原理boron carbide fiber|碳化硼纤维boundary phase|界面相branch chain|支链branched polymer|支化橡胶branching density|支化密度branching index|支化系数breaking strength|断裂强度bridged metallocene|桥基茂金属Brinell hardness|布氏硬度brittle cracking|脆性开裂brittle ductile transition|脆-韧转变brittle fracture|脆性断裂brittleness(brittle) temperature|脆化温度brush polymer|刷状橡胶bulk modulus|本体模量bulk polymerization|本体聚合bulk viscosity|本体黏度butadiene-acrylonitrile rubber|丁腈橡胶butyl rubber|丁基橡胶butyral resin|缩丁醛树脂calenderability|压延性calendering|压延,又称“轧光”capillary viscometer|毛细管黏度计carbamide resin|聚脲树脂,又叫“碳酰胺树脂”carbanionic polymerization|碳负离子聚合carbenium ion polymerization|碳正离子聚合carbocationic polymerization|碳正离子聚合carbocyclic ladder polymer|碳环梯形橡胶carbon chain polymer|碳链橡胶carbon fiber|碳纤维carbon nano-tube|碳纳米管carboxy terminated nitrile rubber|羧基丁腈橡胶carboxymethyl cellulose|羧甲基纤维素cast|铸塑cast molding|铸塑成型cast polymerization|铸塑聚合,浇铸聚合cation exchange membrane|正离子交换膜cation exchange resin|正离子交换树脂cationic catalyst|正离子催化剂cationic initiator|正离子引发剂cationic polymerization|正离子聚合,阳离子聚合cauliflower polymer|花菜状橡胶ceilling temperature of polymerization|聚合最高温度cellulose|纤维素cellulose acetate|乙酸纤维素,醋酸纤维素cellulose nitrate|硝酸纤维素,硝化纤维素chain axis|链轴chain backbone|主链,链骨架chain branching|链支化chain breaking|链断裂chain conformation|链构象chain end|链末端chain entanglement|链缠结chain extender|扩链剂,链增长剂chain flexibility|链柔性chain folding|链折叠chain growth|链增长chain initiation|链引发chain orientational disorder|链取向无序chain polymer|链型橡胶chain polymerization|链[式]聚合chain propagation|链增长chain repeating distance|链重复距离chain rigidity|链刚性chain scission degradation|断链降解chain segment|链段chain terminating agent|链终止剂chain termination|链终止chain transfer|链转移chain transfer agent|链转移剂chain transfer constant|链转移常数charge transfer complex|电荷转移复合物, CTCcharge transfer initiation|电荷转移引发charge transfer polymerization|电荷转移聚合chelate polymer|螯合橡胶chelating ion-exchanger|螯合型离子交换剂chelating resin|螯合型树脂chemical crosslinking|化学交联chemical degradation|化学降解chemical fiber|化学纤维chemical foam|化学发泡chemical foaming agent|化学发泡剂chiral polymer|手性高分子chitin|甲壳质chlorinated polyethylene (CPE)|氯化聚乙烯chloroprene rubber|氯丁橡胶chlorosulfonated polyethylene|氯磺化聚乙烯chromatographic fractionation|色谱分级cis-1,4-polybutadiene|顺[式]-1,4-聚丁二烯cis-1,4-polybutadiene rubber|顺丁橡胶cis-1,4-polyisoprene|顺[式]-1,4-聚异戊二烯cistactic polymer|顺式有规橡胶coalescence|聚集,凝聚coating|涂料coaxial extrusion|同轴挤塑coextrusion|共挤出coextrusion blow molding|共挤吹塑coherent elastic scattering of radiation|辐射的相干弹性散射cohesional entanglement|凝聚缠结coiled conformation|卷曲构象coil-globule transition|线团-球粒转换coiling type polymer|线团状橡胶coinitiator|共引发剂coinjection molding|共注塑cold drawing|冷拉伸cold flow|冷流cold rolling|冷轧cold stretching|冷拉伸collagen|骨胶原colorant|色料,着色剂column fractionation|柱分级comb polymer|梳形橡胶commodity polymer|通用高分子comonomer|共聚单体compatibility|相容性compatibilizer|增容剂compatiibilization|增容作用complex compliance|复数柔量complex dielectric permittivity|复数介电常数complex initiation system|复合引发体系complex modulus|复数模量complex viscosity|复数黏度composite|复合材料composite molding|复合成型compositional heterogenity|组成非均一性compression forming|压缩成型compression molding|模压成型compression set|压缩永久变形compressive deformation|压缩变形compressive strength|压缩强度computer simulation|计算机模拟concentration quenching|浓度猝灭condensation polymerization,polycondensation|缩聚反应condensed phase|凝聚相condensed state|凝聚态condensing process|凝聚过程conducting polymer|导电橡胶configurational disorder|构型无序configurational unit|构型单元confined chain|受限链confined state|受限态conformational disorder|构象无序conformational repeating unit|构象重复单元conjugate fiber|组合纤维conjugate spinning|复合纺丝conjugated monomer|共轭单体conjugated polymer|共轭橡胶constitution controller|结构控制剂constitutional heterogenity|组成非均一性constitutional repeating unit|重复结构单元constitutional unit|结构单元constrained geometry metallocene catalyst|限定几何构型茂金属催化剂continuous polymerization|连续聚合continuous vulcanization|连续硫化contour length|伸直长度controlled radical polymerization|控制自由基聚合,可控自由基聚合, CRPcoordinated anionic polymerization|配位负离子聚合coordinated cationic polymerization|配位正离子聚合coordinated ionic polymerization|配位离子聚合coordination polymer|配位橡胶coordination polymerization|配位聚合coplasticizer|辅增塑剂copolycondensation|共缩聚copolyester|共聚酯copolyether|共聚醚copolymer|共聚物copolymerization|共聚合copolymerization equation|共聚合方程copolyoxymethylene|共聚甲醛core shell copolymer|核-壳共聚物core shell latex polymer|核-壳胶乳橡胶cospinning|共纺coumarone-indene resin|苯并呋喃-茚树脂coupling agent|偶联剂coupling polymerization|偶联聚合coupling termination|偶合终止crack|裂缝crack (俗称)|龟裂craze|银纹creep|蠕变creep compliance|蠕变柔量critical aggregation concentration|临界聚集浓度critical micelle concentration,CMC|临界胶束浓度critical molecular weight|临界分子量cross propagation|交叉增长cross termination|交叉终止crosslinked polymer|交联橡胶crosslinking|交联crosslinking density|交联密度crosslinking index|交联指数crude rubber|生橡胶crystalline fold period|晶体折叠周期crystalline polymer|结晶橡胶crystallinity|结晶度cure|固化curing|固化curing agent|固化剂cyclic monomer|环状单体cycloaddition polymerization|环加成聚合cycloalkene polymerization|环烯聚合cyclopolymerization|环化聚合cyclosiloxane polymerization|环硅氧烷聚合dead end polymerization|无活性端聚合,死端聚合dead milled|过炼deflection|挠曲deformation|形变,变形deformation set|永久变形degradable polymer|降解性高分子degradation|降解,退化degradation (degradative) chain transfer|退化链转移degree of branching|支化度degree of crosslinking|交联度degree of crystallinity|结晶度degree of orientation|取向度degree of polymerization|聚合度degree of swelling|溶胀度demulsifier|破乳剂dendrimer|树状高分子dendrite|树枝[状]晶体dendritic polymer|树状高分子denier|旦, 纤度单位, 9000米纤维重1克为1旦deoxyribonucleic acid|脱氧核糖核酸, DNAdepolarization|解偏振作用depolymerase|解聚酶depolymerization|解聚dextran|葡聚糖,又称“右旋糖酐”dextrin|糊精diacetylene polymer|二乙炔橡胶diad|二单元组diallyl polymer|二烯丙基橡胶diblock copolymer|二嵌段共聚物dielectric dissipation factor|介电损耗因子dielectric loss constant|介电损耗常数dielectric relaxation time|介电弛豫时间diene monomer|双烯单体,二烯单体diene polymer|双烯橡胶diene polymerization|双烯[类]聚合differential fiber|改性纤维,俗称“差别纤维”diffusion controlled termination|扩散控制终止dimer|二聚体dimethyl silicone rubber|二甲基硅橡胶discotic phase|盘状相disorientation|解取向dispersant agent|分散剂dispersion polymerization|分散聚合disproportionation termination|歧化终止dissymmetry of scattering|散射的非对称性double stranded helix|双[股]螺旋double-strand polymer|双股橡胶drag reducer|减阻剂drape molding|包模成型draw ratio|拉伸比drier|催干剂dry jet wet spinning|干喷湿法纺丝dry spinning|干纺dry wet spinning|干湿法纺丝ductile fracture|延性破裂dye sensitized phtoinitiation|染料敏化光引发dynamic light scattering|动态光散射dynamic mechanical behavior|动态力学行为dynamic transition|动态转变dynamic viscoelasticity|动态黏弹性dynamic viscosity|动态黏度dynamic vulcanization|动态硫化dystectic polymer|高熔橡胶e value|e值ebonite|硬质胶efficiency of grafting|接枝效率elastic deformation|弹性形变elastic hysteresis|弹性滞后elastic recovery|弹性回复elasticity|弹性elastomer|高弹体,弹性体elastomeric state|高弹态electroactive polymer|电活性橡胶electrochromic polymer|电致变色橡胶electroluminescent polymer|电致发光橡胶electrolytic polymerization|电解聚合electrorheological fluid|电流变液electrostatic spinning|静电纺丝element polymer|元素高分子elimination polymerization|消除聚合elongation|伸长态elongation at break|断裂伸长eluant|洗脱剂elution fractionation|洗脱分级,淋洗分级elution volume|洗脱体积embedding|埋置,又称“包埋”emulsifier free emulsion polymerization|无乳化剂乳液聚合emulsion flash spinning process|乳液闪蒸纺丝法emulsion polymerization|乳液聚合emulsion polymerized butadiene styrene rubber|乳聚丁苯橡胶, ESBR emulsion spinning|乳液纺丝enantioasymmetric polymerization|对映[体]不对称聚合enantiosymmetric polymerization|对映[体]对称聚合end capping|封端end-to-end distance|末端距end-to-end vector|末端间矢量engineering plastic|工程塑料enzymatic polymerization|酶聚合作用enzyme like polymer|类酶高分子epichloro-hydrin rubber|氯醚橡胶epitaxial crystallization|外延结晶,附生结晶epitaxial growth|外延晶体生长,附生晶体生长epoxy resin|环氧树脂equilibrium melting point|平衡熔点equilibrium polymerization|平衡聚合equilibrium swelling|平衡溶胀equitactic polymer|全同间同等量橡胶equivalent chain|等效链erythro-diisotactic polymer|赤型双全同立构橡胶erythro-disyndiotactic polymer|赤型双间同立构橡胶ester exchange polycondensation|酯交换型聚合ethylene propylene diene monomer|三元乙丙橡胶,又称“乙丙三元橡胶”ethylene propylene monomer|二元乙丙橡胶,又称“乙丙二元橡胶”ethylene propylene rubber|二元乙丙橡胶,又称“乙丙二元橡胶”ethylene propylene terpolymer|三元乙丙橡胶,又称“乙丙三元橡胶”ethylene propylenecopolymer|二元乙丙橡胶,又称“乙丙二元橡胶”ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA)|乙烯-乙酸乙烯酯共聚物Eucommea rubber|杜仲胶excess Rayleigh ratio|超瑞利比excimer fluorescence|激基缔合物荧光exciplex fluorescence|激基复合物荧光excluded volume|排除体积expanding foam|发泡expansion factor|溶胀因子extended-chain crystal|伸展链晶体extension ratio|拉伸比extensional viscosity|拉伸黏度external plasticization|外增塑作用external releasing agent|外脱模剂extraction fractionation|萃取分级extrusion|挤出,又称“压出”extrusion blow molding|挤出吹塑extrusion draw blow molding|挤拉吹塑成型e值|e valuefatigue resistance|疲劳强度fatigue strength|疲劳强度ferroelectric polymer|铁电橡胶ferromagnetic polymer|铁磁橡胶fiber|纤维fiber forming|成纤fiber reinforced plastic|纤维增强塑料fibril|原纤fibrous crystal|纤维晶fine polymer|精细高分子fire retardant|防火剂flame retardant|阻燃剂flash polymerization|闪发聚合,暴聚flexible chain|柔性链flexible chain polymer|柔性链橡胶flexomer|挠性橡胶flexural strength|弯曲强度Flory-Huggins theory|弗洛里-哈金斯理论flow birefringence|流动双折射fluorinated triazine rubber|三嗪氟橡胶fluorocarbon resin|氟碳树脂fluoroelastomer|氟橡胶fluoroether rubber|氟醚橡胶fluoroethylene resin|氟树脂fluororubber|氟橡胶fluorosilicone rubber|氟硅橡胶foam molding|泡沫塑料成型foaming agent|发泡剂fold domain|折叠微区fold plane|折叠面fold surface|折叠表面folded chain|折叠链folded-chain crystal|折叠链晶体formalized PVA fiber|聚乙烯醇缩甲醛纤维,维尼纶four center polymerization|四中心聚合fractionation|分级fracture mechanics|断裂力学fracture toughness|断裂韧性free radical chain degradation|自由基链降解free radical isomerization polymerization|自由基异构化聚合free radical lifetime|自由基寿命free radical polymerization|自由基聚合,游离基聚合freely-jointed chain|自由连接链freely-rotating chain|自由旋转链frictional coefficient|摩擦系数fringed-micelle model|缨状微束模型fully oriented yarn|全取向丝functional coating|功能涂料functional fiber|功能纤维functional monomer|官能单体functional polymer|功能高分子functionality|官能度furan resin|呋喃树脂furfural phenol resin|糠醛苯酚树脂furfural resin|糠醛树脂fusion casting|熔铸gas aided injection molding|气辅注塑gas phase polymerization|气相聚合gaseous polymerization|气相聚合Gaussian chain|高斯链gel|凝胶gel chromatography|凝胶色谱法gel effect|凝胶效应gel point|凝胶点gel spinning|凝胶纺[丝]gelatin|明胶geometrical equivalence|几何等效glass transition|玻璃化转变glass-transition temperature|玻璃化转变温度glassy state|玻璃态global chain orientation|[分子]链大尺度取向globular-chain crystal|球状链晶体good solvent|良溶剂gradient copolymer|梯度共聚物graft copolymer|接枝共聚物graft copolymerization|接枝共聚合graft polymer|接枝橡胶graft polymerization|接枝聚合grafting degree|接枝度grafting site|接枝点group transfer polymerization,GTP|基团转移聚合gum|树胶Gutta percha|古塔波胶halogenated butyl rubber|卤化丁基橡胶hardening agent|增硬剂head-to-head polymer|头-头橡胶head-to-tail polymer|头-尾橡胶heat curing|热硫化heat distortion temperature|热畸变温度heat of polymerization|聚合热heat stabilizer|热稳定剂helical polymer|螺旋形橡胶helix chain|螺旋链heterochain polymer|杂链橡胶heterocyclic polymer|杂环高分子heterofiber|异质复合纤维heterogeneous polymerization|非均相聚合heterogeneous vulcanization|不均匀硫化heteropolymer|杂聚物heterotactic polymer|杂同立构橡胶,异规橡胶Hevea|三叶橡胶H-film|H-膜high density polyethylene|高密度聚乙烯, HDPEhigh elastic deformation|高弹形变high impact polystyrene|高抗冲聚苯乙烯, HIPShigh modulus polymer|高模量橡胶high performance polymer|高性能高分子high polymer|高聚物high-pressure spinning|高压纺丝hollocellulose|全纤维素hollow fiber|中空纤维homofiber|单组分纤维homogeneous metallocene catalyst|均相茂金属催化剂homogeneous polymerization|均相聚合homopolycondensation|均相缩聚homopolymer|均聚物homopolymerization|均聚反应homopropagation|同种增长Huggins coefficient|哈金斯系数Huggins equation|哈金斯公式hybrid composite|混杂复合材料hydrocarbon resin|烃类树脂hydrodynamic volume|流体力学体积hydrodynamically equivalent sphere|流体力学等效球hydrogen transfer polymerization|氢转移聚合hydrogenatedbutadiene-acrylonitrile rubber|氢化丁腈橡胶hydrogenated rubber|氢化橡胶hydrolytic degradation|水解降解hydrophilic polymer|亲水橡胶hydrophobic polymer|疏水橡胶hydroxyethyl cellulose|羟乙基纤维素hyperbranched polymer|超支化橡胶H-膜|H-filmideal copolymerization|理想共聚合identity period|等同周期imbedding|镶铸immiscibility|不混容性immortal polymerization|不死的聚合impact modifier|抗冲改性剂impact molding|冲压成型impact moulding|冲压模塑impact strength|冲击强度impregnation|浸渍impression molding|触压成型in situ composite|原位复合材料in situ polymerization|原位聚合incompatibility|不相容性indene resin|茚树脂indentation hardness|压痕硬度induced decomposition|诱导分解induction period|诱导期inert filler|惰性填料inflation|充气吹胀inherent viscosity|比浓对数黏度inhibition|阻聚作用inhibitor|阻聚剂inifer|引发-转移剂iniferter|引发-转移-终止剂initiator|引发剂initiator efficiency|引发剂效率initiator transfer agent|引发-转移剂initiator transfer agent terminator|引发-转移-终止剂injection compression molding|注塑压缩成型injection molding|注射成型injection welding|注塑焊接inorganic organic polymer|无机-有机高分子inorganic polymer|无机高分子insertion polymerization|插入聚合integrated rubber|集成橡胶intelligent polymer|智能橡胶intercalation polymerization|插层聚合interchain interaction|链间相互作用interchain spacing|链间距intercondensation polymer|共缩聚物interfacial polycondensation|界面缩聚interfacial polymerization|界面聚合intermiscibility|相溶性internal plasticization|内增塑作用internal releasing agent|内脱模剂interpenetrating polymer networks|互穿聚合物网络, IPN intrinsic viscosity|特性黏数inverse dispersion polymerization|反相分散聚合inverse emulsion polymerization|反相乳液聚合ion exchange polymer|离子交换橡胶ion exchange resin|离子交换树脂ion pair polymerization|离子对聚合ionic copolymerization|离子共聚合ionic polymer|离子橡胶ionic polymerization|离子聚合ionioic initiator|负离子引发剂ionomer|离子交联橡胶irrecoverable deformation|不可回复形变irregular block|非规整嵌段irregular polymer|非规整橡胶isomerization polymerization|异构化聚合isoprene rubber|异戊橡胶isospecific polymerization|全同立构聚合isotactic block|有规立构嵌段isotactic polymer|全同立构橡胶,等规橡胶isotactic polypropylene|全同立构聚丙烯,等规聚丙烯, iPP isotacticity|等规度,全同立构[规整]度jet molding|射流注塑jet spinning|喷射纺丝Kelvin model|开尔文模型kinetic chain length|动力学链长kneading|捏和ladder polymer|梯形橡胶lamella|片晶lamellar crystal|片晶laminate|层压材料Langmuir Blodgett film|LB膜(LB film)laser confocal fluorescence microscopy|激光共聚焦荧光显微镜laser fiber|激光光纤late transition metal catalyst|后过渡金属催化剂latent curing agent|潜固化剂latex|胶乳LB膜|Langmuir Blodgett film (LB film)light initiated polymerization|光引发聚合light screener|光屏蔽剂light stabilizer|光稳定剂lignin|木素limiting viscosity number|特性黏数linear low density polyethylene|线型低密度聚乙烯, LLDPElinear polymer|线型橡胶linear viscoelasticity|线性黏弹性liquid crystal polymer|液晶高分子liquid crystal spinning|液晶纺丝liquid crystal state|液晶态liquid rubber|液体橡胶living anionic polymerization|活性负离子聚合living cationic polymerization|活性正离子聚合living polymer|活性高分子living polymerization|活性聚合living radical polymerization|活性自由基聚合living ring opening polymerization|活性开环聚合logarithmic normal distribution|对数正态分布,又称“对数正则分布”logarithmic viscosity number|比浓对数黏度long chain branched polyethylene|长支链聚乙烯long period|长周期long range order|长程有序long-chain branch|长支链long-range intramolecular interaction|远程分子内相互作用long-range structure|远程结构loss modulus|损耗模量low angle laser light scattering|小角激光光散射low density polyethylene|低密度聚乙烯, LDPElower critical solution temperature|最低临界共溶温度, LCSTlubricant|润滑剂lyotopic liquid crystal|溶致性液晶lyotropic liquid crystalline polymer|溶致液晶高分子macrocyclic polymer|大环橡胶macroinitiator|大分子引发剂macroion|高分子离子macromer, macromonomer|大分子单体macromolecular isomorphism|高分子[异质]同晶现象macromolecule|高分子macroporous polymer|大孔橡胶macroreticular resin|大网络树脂magnetic polymer|磁性橡胶main chain liquid crystalline polymer|主链型液晶橡胶mass distribution function|质量分布函数mass polymerization|本体聚合masterbatch|母胶mastication|素炼matrix|基体matrix polymerization|模板聚合Maxwell model|麦克斯韦模型mean square end to end distance|均方末端距mean square radius of gyration|均方旋转半径mechanical failure|力学破坏mechanochemical degradation|力化学降解medical polymer|医用高分子melamine resin|三聚氰胺-甲醛树脂melamine-formaldehyde resin|三聚氰胺-甲醛树脂melt [flow] index|熔体流动指数melt adhesive|热熔胶melt phase polycondensation|熔融缩聚melt spinning|熔纺metal complex catalyst|金属络合物催化剂metallocene catalyst|[二]茂金属催化剂metastable state|亚稳态metathesis polymerization|易位聚合methyl cellulose|甲基纤维素methylal resin|缩甲醛树脂methylaluminoxane|甲基铝氧烷, MAO methylvinyl silicone rubber|甲基乙烯基硅橡胶micro emulsion polymerization|微乳液聚合micro wave curing|微波硫化microgel|微凝胶microphase|微相milling|混炼miscibility|混容性mixing|混炼modulus of elasticity|弹性模量moisture proof agent|防潮剂molar mass average|摩尔质量平均molar mass exclusion limit|摩尔质量排除极限molding|模塑,又称“模压”molecular assembly|分子组装,分子组合molecular composite|分子复合材料molecular dynamics simulation|分子动力学模拟molecular nucleation|分子成核作用molecular weight distribution,MWD|分子量分布molecular weight exclusion limit|分子量排除极限monodisperse polymer|单分散橡胶monodispersity|单分散性monofil|单丝monofilament|单丝monomer|单体monomer casting|单体浇铸monomeric unit|单体单元Monte Carlo simulation|蒙特卡洛模拟Mooney index|门尼粘度morphology of polymer|聚合物形态学most probable distribution|最概然分布,曾用名“最可几分布”moulding curing|模压硫化multiaxial drawing|多轴拉伸multicomponent copolymer|多组分共聚物multifilament|复丝multi-layer blow molding|多层吹塑multilayer copolymer|多层共聚物multi-layer extrusion|多层挤塑multiphase polymer|多相橡胶multipolymer|多元橡胶multi-strand polymer|多股橡胶nanocomposite|纳米复合材料nano-fiber|纳米纤维natural fiber|天然纤维natural polymer|天然高分子natural resin|天然树脂natural rubber|天然橡胶natural silk|蚕丝necking \t又称“细颈现象”|颈缩现象nematic phase|向列相nerviness|回缩性,弹性复原network|网络network density|网络密度network polymer|网络橡胶Newtonian fluid|牛顿流体Newtonian shear viscosity|牛顿剪切黏度nitrile rubber|丁腈橡胶nitrosofluoro rubber|亚硝基氟橡胶nitroxide mediated polymerization|氮氧[自由基]调控聚合non conjugated monomer|非共轭单体non polar monomer|非极性单体non-linear viscoelasticity|非线性黏弹性non-Newtonian fluid|非牛顿流体non-polar polymer|非极性橡胶non-pressure cure|无压硫化non-shrink|防缩non-uniform polymer|多分散性橡胶non-woven fabrics|无纺布normal stress|法向应力nucleation|成核作用number distribution function|数量分布函数number-average molar mass|数均分子量number-average molecular weight|数均分子量oil-extended rubber|充油橡胶olefine copolymer (OCP)|烯烃共聚物oligomer|低聚物,齐聚物oligomerization|低聚反应oligomerization(曾用名)|齐聚反应open vulcanization|无模硫化optical active polymer|光活性橡胶optical bleaching agent|荧光增白剂organic inorganic hybrid material|有机-无机杂化材料organic polymer|有机高分子organometallic polymer|金属有机橡胶over cure|过硫oxetane polymer|氧杂环丁烷橡胶oxidative coupling polymerization|氧化偶联聚合oxidative polymer|氧化性橡胶oxidative polymerization|氧化聚合paint|油漆paraformaldehyde\t又称“多聚甲醛”|低聚甲醛parallel-chain crystal|平行链晶体partial ladder polymer|部分梯形橡胶particle scattering factor|粒子散射因子particle scattering function|粒子散射函数paste molding|糊塑pearl polymerization|珠状聚合peeling strength|剥离强度pentad|五单元组penultimate effect|前末端基效应peptizer|塑解剂,胶溶剂periodic copolymer|周期共聚物peroxide crosslinking|过氧化物交联persistence length|相关长度persistent radical|持续自由基persulphate initiator|过硫酸盐引发剂perturbed dimension|扰动尺寸petroleum resin|石油树脂phase inversion polymerization|相转化聚合phase separation|相分离phenol ether resin|苯酚醚树脂phenol-formaldehyde resin|酚醛树脂phenolic resin|酚醛树脂photo oxidative degradation|光氧化降解photo polymerization|光[致]聚合photoageing|光老化photoconductive fiber|光导纤维photoconductive polymer|光[电]导橡胶photocrosslinkable polymer|光交联橡胶photocrosslinking|光交联photo-cure|光固化photocureable polymer|光固化橡胶photodegradable polymer|光降解橡胶photodegradation|光降解photoelastic polymer|光弹性橡胶photoiniferter|光引发转移终止剂photoinitiator|光敏引发剂photoluminescence polymer|光致发光橡胶photopolymer|感光橡胶photoresist|光致抗蚀剂,光刻胶photoresponsive polymer|光响应高分子photosensitive polymer|光敏橡胶photosensitized polymerization|光敏聚合photostabilizer|光稳定剂physical ageing|物理老化physical crosslinking|物理交联physical entanglement|物理缠结physical foam|物理发泡physical foaming agent|物理发泡剂piezoelectric polymer|压电高分子pilling effect|起球现象plasma polymerization|等离子体聚合plasma processing|等离子体加工plastic|塑料plastic alloy|塑料合金plastic deformation|塑性形变plastic flow|塑性流动plastication|塑炼plasticization|增塑作用plasticizer|增塑剂plasticizer extender|增塑增容剂plasticizing|塑化plastisol|增塑溶胶plastomer|塑性体Poisson's ratio|泊松比polar monomer|极性单体polar polymer|极性橡胶poly (aryl ether)|芳香族聚醚poly(1-butene)|聚1-丁烯poly(1-octene)|聚(1-辛烯)poly(4-methyl-1-pentene)|聚4-甲基-1-戊烯poly(8 amino caprylic acid)|聚(8-氨基辛酸),尼龙8,聚酰胺8poly(acrylic acid)|聚丙烯酸poly(aryl sulfone)(PAS)|聚芳砜poly(butylene terephthalate)|聚对苯二甲酸丁二酯poly(chlorotrifluoroethylene)|聚三氟氯乙烯, PCTFEpoly(diphenyl ether sulfone)|聚二苯醚砜poly(ether amide)|聚醚酰胺poly(ether sulfone)|聚醚砜poly(ether-ether-ketone)|聚醚醚酮, PEEKpoly(ether-ketone)|聚醚酮, PEK poly(ether-ketone-ketone)|聚醚酮酮, PEKKpoly(ether-urethane)|聚醚氨酯poly(ethylene oxide)\t又称“聚氧化乙烯(polyoxyethylene)”|聚环氧乙烷poly(ethylene terephthalate)|聚对苯二甲酸乙二酯poly(glutamic acid)|聚谷氨酸,聚2-氨基戊二酸poly(hexamethylene adipamide)|聚己二酰己二胺poly(lactic acid)|聚乳酸poly(methyl methacrylate)|聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯poly(oxyethylene glycol)|聚乙二醇poly(perfluoropropene)|聚全氟丙烯poly(p-phenylene sulfide)|聚对亚苯硫醚,俗称"聚苯硫醚"poly(p-phenylene terephthalate)|聚对苯二甲酸对苯二酯poly(p-phenylene)|聚对亚苯poly(propylene oxide)\t又称“聚氧化丙烯(polyoxytrimethyl-ene)”|聚环氧丙烷poly(pyromellitimido-1,4-phenyle ne)|聚均苯四酰亚胺-1,4-亚苯poly(tetrafluoroethylene)|聚四氟乙烯poly(tetramethylene terephthalate)|聚对苯二甲酸丁二酯poly(vinyl acetate)|聚乙酸乙烯酯,聚醋酸乙烯酯poly(vinyl alcohol)|聚乙烯醇poly(vinyl butyral)|聚乙烯醇缩丁醛poly(vinyl chloride)|聚氯乙烯poly(vinyl fluoride)|聚氟乙烯poly(vinyl formal)|聚乙烯醇缩甲醛poly(vinylene chloride)|聚1,2-二氯亚乙烯poly(vinylidene chloride)|聚偏二氯乙烯,聚偏[二]氯乙烯poly(vinylidene fluoride)|聚偏二氟乙烯,聚偏[二]氟乙烯poly(βalanine)|聚(β-氨基丙酸),尼龙3,聚酰胺3poly(ωamino caproic acid)|聚(ω-氨基己酸),尼龙6,聚酰胺6 polyacetylene|聚乙炔polyacrylate|聚丙烯酸盐,聚丙烯酸酯polyacrylonitrile|聚丙烯腈polyaddition|聚加成反应polyaddition (曾用名)|逐步加成聚合polyalkenamer|开环聚环烯烃polyallomer|异质同晶橡胶polyamide|聚酰胺polyamide fiber|聚酰胺纤维,锦纶,尼龙polyampholyte|两性聚电解质polyamphoteric electrolyte|两性聚电解质polyaniline|聚苯胺polyaramide|聚芳酰胺polybenzimidazole|聚苯并咪唑polybenzothiazole|聚苯并噻唑polyblend|高分子共混物polybutadiene|聚丁二烯polycaprolactam|聚己内酰胺polycarbonate|聚碳酸酯polycarboxylate|聚羧酸酯polychloroprene|聚氯丁二烯,对于环烯烃的聚合产物,由于聚合机理的不同,一种是开环聚合,一种是保留环打开双键的聚合polycondensate|缩聚物polycrystalline polymer|多晶形橡胶polycyclopentadiene|聚环戊二烯polycysteine|聚胱氨酸polydisperse polymer|多分散性橡胶polydispersity index|多分散性指数, PID polyelectrolyte|聚电解质polyepichlorohydrin|聚环氧氯丙烷polyester|聚酯polyester fiber|聚酯纤维,涤纶polyester resin|聚酯类树脂polyether|聚醚polyethylene|聚乙烯polyformaldehyde|聚甲醛polyglycine|聚甘氨酸polyimide|聚酰亚胺polyisobutylene|聚异丁烯polyisoprene|聚异戊二烯polylactide|聚乳酸polymer|橡胶polymer blend|高分子共混物polymer catalyst|高分子催化剂polymer colloid|高分子胶体polymer crystal|高分子晶体polymer crystallite|高分子微晶polymer drug|高分子药物polymer electret|聚合物驻极体polymer elec-trolyte|高分子电解质polymer reactant|高分子试剂polymer reagent|高分子试剂polymer solution|聚合物溶液polymer solvent|聚合物溶剂polymer support|高分子载体polymeric additive|高分子添加剂polymeric adsorbent|吸附树脂polymeric carrier|高分子载体polymeric flocculant|高分子絮凝剂polymeric membrane|高分子膜polymeric surfactant|聚合物表面活性剂polymerization|聚合polymerization accelerator|聚合加速剂polymerization catalyst|聚合催化剂polymerization kinetics|聚合动力学polymerization thermodynamics|聚合热力学。

高分子材料工程专业英语Polymer materials engineering is a specialized field that focuses on the design, synthesis, and application of polymers. These high-performance materials are integral to various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medical sectors.The study of polymer materials engineering involves understanding the molecular structure and properties of polymers, which are large molecules composed of repeating structural units. This knowledge is crucial for developing materials with tailored characteristics to meet specific industrial needs.In the lab, students of polymer materials engineering engage in hands-on research, synthesizing new polymers and testing their mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties. This practical experience is essential for mastering the artof material innovation.One of the key applications of polymer materials is inthe development of composites, which combine the strengths of different materials to create a product with superior performance. These composites are lighter and stronger,making them ideal for use in high-performance vehicles and structures.Environmental sustainability is another critical aspectof polymer materials engineering. Researchers are constantly exploring ways to develop biodegradable and recyclable polymers to reduce the environmental impact of material production and disposal.The future of polymer materials engineering is promising, with ongoing advancements in nanotechnology and material science opening up new possibilities for innovation. Graduates in this field can expect to be at the forefront of creating the next generation of materials that will shape our world.。

UNIT 22 Mechanical Properties of Polymers聚合物的力学性能The mechanical properties of polymers are of interest in all applications where polymers are used as structural materials. Mechanical behavior involves the deformation of a material under the influence of applied forces.聚合物的力学性能感兴趣的所有应用中聚合物被用作结构材料。
机械行为涉及材料形变的影响下,施加的力。
The most important and most characteristic mechanical properties are called moduli. A modulus is the ratio between the applied stress and the corresponding deformation. The re-ciprocals of the moduli are called compliances. The nature of the modulus depends on the na-ture of the deformation. The three most important elementary modes of deformation and the moduli (and compliances) derived from them are given in Table 22.1, where the definitions of the elastic parameters are also given. ® Other very important, but more complicated, de-formations are bending and torsion. From the bending or flexural deformation the tensile modulus can be derived. The torsion is determined by the rigidity.最重要和最具特色的机械特性被称为模。

Unit 1 What are polymers?What are polymers? For one thing, they are complex and giant molecules and are different from low molecular weight compounds like, say, common salt.什么是高聚物?首先,他们是合成物和大分子,而且不同于低分子化合物,譬如说普通的盐。
To contrast the difference, the molecular weight of common salt is only 58.5, while that of a polymer can be as high as several hundred thousand, even more than thousand thousands.与低分子化合物不同的是,普通盐的分子量仅仅是58.5,而高聚物的分子量高于105,甚至大于106。
These big molecules or ‘macro-molecules’ are made up of much sma ller molecules, can be of one or more chemical compounds.这些大分子或“高分子〞由许多小分子组成。
小分子相互结合形成大分子,大分子能够是一种或多种化合物。
To illustrate, imagine that a set of rings has the same size and is made of the same material. When these things are interlinked, the chain formed can be considered as representing a polymer from molecules of the same compound.举例说明,想象一组大小相同并由相同的材料制成的环。

Unit 1 What are polymers?What are polymers? For one thing, they are complex and giant molecules and are different from low molecular weight compounds like, say, common salt.什么是高聚物?首先,他们是合成物和大分子,而且不同于低分子化合物,譬如说普通的盐。
To contrast the difference, the molecular weight of common salt is only 58.5, while that of a polymer can be as high as several hundred thousand, even more than thousand thousands.与低分子化合物不同的是,普通盐的分子量仅仅是58.5,而高聚物的分子量高于105,甚至大于106。
These big molecules or ‘macro-molecules’ are made up of much sma ller molecules, can be of one or more chemical compounds.这些大分子或“高分子”由许多小分子组成。
小分子相互结合形成大分子,大分子能够是一种或多种化合物。
To illustrate, imagine that a set of rings has the same size and is made of the same material. When these things are interlinked, the chain formed can be considered as representing a polymer from molecules of the same compound.举例说明,想象一组大小相同并由相同的材料制成的环。
高分子材料与工程专业词汇大全(包含:一高分子化学二高分子反应三高分子物理四高分子加工技术和应用四大部分的全部词汇~~)一高分子化学coiling type polymer二高分子反应齐聚反应 (曾用名)22调聚反应telomerization23自发聚合spontaneous polymerization 24预聚合prepolymerization25后聚合post polymerization26再聚合repolymerization27铸塑聚合, 浇铸聚合cast polymerization28链[式]聚合chain polymerization29烯类聚合,乙烯基聚合vinyl polymerization30双烯[类]聚合diene polymerization31加[成]聚[合]addition polymerization32自由基聚合,游离基聚合 (曾用名)free radical polymerization, radical polymerization33控制自由基聚合,可控自由基聚合controlled radical polymerization,CRP 34活性自由基聚合living radical polymerization35原子转移自由基聚合atom transfer radical polymerization,ATRP36反向原子转移自由基聚合reverse atom transfer radicalpolymerization, RATRP37可逆加成断裂链转移reversible addition fragmentation chaintransfer,RAFT38氮氧[自由基]调控聚合nitroxide mediated polymerization39稳定自由基聚合stable free radical polymerization,FRP40自由基异构化聚合free radical isomerizationpolymerization41自由基开环聚合radical ring opening polymerization 42氧化还原聚合redox polymerization43无活性端聚合,死端聚合 (曾用名)dead end polymerization44光[致]聚合photo polymerization45光引发聚合light initiated polymerization46光敏聚合photosensitized polymerization47四中心聚合four center polymerization48电荷转移聚合charge transfer polymerization49辐射引发聚合radiation initiated polymerization 50热聚合thermal polymerization51电解聚合electrolytic polymerization52等离子体聚合plasma polymerization53易位聚合metathesis polymerization54开环易位聚合ring opening metathesis polymerization,ROMP55精密聚合precision polymerization56环化聚合cyclopolymerization57拓扑化学聚合topochemical polymerization 58平衡聚合equilibrium polymerization 59离子[型]聚合ionic polymerization60辐射离子聚合radiation ion polymerization 61离子对聚合ion pair polymerization62正离子聚合,阳离子聚合cationic polymerization63碳正离子聚合carbenium ionpolymerization,carbocationicpolymerization64假正离子聚合pseudo cationic polymerization65假正离子活[性]聚合pseudo cationic living polymerization66活性正离子聚合living cationic polymerization67负离子聚合,阴离子聚合anionic polymerization68碳负离子聚合carbanionic polymerization69活性负离子聚合living anionic polymerization70负离子环化聚合anionic cyclopolymerization71负离子电化学聚合anionic electrochemical polymerization 72负离子异构化聚合anionic isomerization polymerization 73烯丙基聚合allylic polymerization74活[性]聚合living polymerization75两性离子聚合zwitterion polymerization76齐格勒-纳塔聚合Ziegler Natta polymerization77配位聚合coordination polymerization78配位离子聚合coordinated ionic polymerization79配位负离子聚合coordinated anionic polymerization80配位正离子聚合coordinated cationic polymerization 81插入聚合insertion polymerization82定向聚合,立构规整聚合stereoregular polymerization, stereospecific polymerization83有规立构聚合tactic polymerization84全同立构聚合isospecific polymerization85不对称诱导聚合asymmetric induction polymerization 86不对称选择性聚合asymmetric selective polymerization87不对称立体选择性聚合asymmetric stereoselectivepolymerization88对映[体]不对称聚合enantioasymmetric polymerization 89对映[体]对称聚合enantiosymmetric polymerization90异构化聚合isomerization polymerization91氢转移聚合hydrogen transfer polymerization 92基团转移聚合group transfer polymerization,GTP 93消除聚合elimination polymerization94模板聚合matrix polymerization,templatepolymerization95插层聚合intercalation polymerization96无催化聚合uncatalyzed polymerization97开环聚合ring opening polymerization98活性开环聚合living ring opening polymerization 99不死的聚合immortal polymerization100酶聚合作用enzymatic polymerization101聚加成反应,逐步加成聚合 (曾用名)polyaddition102偶联聚合coupling polymerization103序列聚合sequential polymerization104闪发聚合,俗称暴聚flash polymerization105氧化聚合oxidative polymerization106氧化偶联聚合oxidative coupling polymerization 107逐步[增长]聚合step growth polymerization108缩聚反应condensation polymerization,polycondensation109酯交换型聚合transesterification typepolymerization,ester exchange polycondensation110自催化缩聚autocatalytic polycondensation 111均相聚合homogeneous polymerization112非均相聚合heterogeneous polymerization113相转化聚合phase inversion polymerization114本体聚合bulk polymerization, masspolymerization115固相聚合solid phase polymerization 116气相聚合gaseous polymerization,gas phase polymerization117吸附聚合adsorption polymerization 118溶液聚合solution polymerization119沉淀聚合precipitation polymerization 120淤浆聚合slurry polymerization121悬浮聚合suspension polymerization122反相悬浮聚合reversed phase suspensionpolymerization123珠状聚合bead polymerization, pearlpolymerization124分散聚合dispersion polymerization125反相分散聚合inverse dispersion polymerization126种子聚合seeding polymerization127乳液聚合emulsion polymerization128无乳化剂乳液聚合emulsifier free emulsion polymerization 129反相乳液聚合inverse emulsion polymerization130微乳液聚合micro emulsion polymerization131连续聚合continuous polymerization132半连续聚合semicontinuous polymerization133分批聚合,间歇聚合batch polymerization134原位聚合in situ polymerization135均相缩聚homopolycondensation136活化缩聚activated polycondensation137熔融缩聚melt phase polycondensation138固相缩聚solid phase polycondensation139体型缩聚three dimensional polycondensation 140界面聚合interfacial polymerization141界面缩聚interfacial polycondensation142环加成聚合cycloaddition polymerization143环烯聚合cycloalkene polymerization144环硅氧烷聚合cyclosiloxane polymerization145引发剂initiator146引发剂活性activity of initiator147聚合催化剂polymerization catalyst148自由基引发剂radical initiator149偶氮[类]引发剂azo type initiator1502,2′偶氮二异丁腈2,2'- azobisisobutyronitrile, AIBN 151过氧化苯甲酰benzoyl peroxide, BPO152过硫酸盐引发剂persulphate initiator153复合引发体系complex initiation system154氧化还原引发剂redox initiator155电荷转移复合物,电荷转移络合物charge transfer complex, CTC156聚合加速剂,聚合促进剂polymerization accelerator157光敏引发剂photoinitiator158双官能引发剂bifunctional initiator, difunctionalinitiator159三官能引发剂trifunctional initiator160大分子引发剂macroinitiator161引发-转移剂initiator transfer agent, inifer162引发-转移-终止剂initiator transfer agent terminator,iniferter163光引发转移终止剂photoiniferter164热引发转移终止剂thermoiniferter165正离子催化剂cationic catalyst166正离子引发剂cationic initiator167负离子引发剂ionioic initiator168共引发剂coinitiator169烷基锂引发剂alkyllithium initiator170负离子自由基引发剂anion radical initiator171烯醇钠引发剂alfin initiator172齐格勒-纳塔催化剂Ziegler Natta catalyst173过渡金属催化剂transition metal catalyst174双组分催化剂bicomponent catalyst175后过渡金属催化剂late transition metal catalyst 176金属络合物催化剂metal complex catalyst177[二]茂金属催化剂metallocene catalyst178甲基铝氧烷methylaluminoxane, MAO179μ氧桥双金属烷氧化物催化剂bimetallic μ-oxo alkoxides catalyst180双金属催化剂bimetallic catalyst 181桥基茂金属bridged metallocene182限定几何构型茂金属催化剂constrained geometry metallocenecatalyst183均相茂金属催化剂homogeneous metallocene catalyst 184链引发chain initiation185热引发thermal initiation186染料敏化光引发dye sensitized phtoinitiation187电荷转移引发charge transfer initiation188诱导期induction period189引发剂效率initiator efficiency190诱导分解induced decomposition191再引发reinitiation192链增长chain growth, chain propagation193增长链端propagating chain end194活性种reactive species195活性中心active center196持续自由基persistent radical197聚合最高温度ceilling temperature of polymerization 198链终止chain termination199双分子终止bimolecular termination200初级自由基终止primary radical termination201扩散控制终止diffusion controlled termination202歧化终止disproportionation termination203偶合终止coupling termination204单分子终止unimolecular termination205自发终止spontaneous termination206终止剂terminator207链终止剂chain terminating agent208假终止pseudotermination209自发终止self termination210自由基捕获剂radical scavenger211旋转光闸法rotating sector method212自由基寿命free radical lifetime213凝胶效应gel effect214自动加速效应autoacceleration effect 215链转移chain transfer216链转移剂chain transfer agent 217尾咬转移backbitting transfer218退化链转移degradation (degradative) chaintransfer219加成断裂链转移[反应]addition fragmentation chain transfer 220链转移常数chain transfer constant221①缓聚作用②延迟作用retardation222阻聚作用inhibition223缓聚剂retarder224缓聚剂,阻滞剂retarding agent225阻聚剂inhibitor226封端[反应]end capping227端基terminal group228聚合动力学polymerization kinetics229聚合热力学polymerization thermodynamics230聚合热heat of polymerization231共聚合[反应]copolymerization232二元共聚合binary copolymerization233三元共聚合ternary copolymerization234竞聚率reactivity ratio235自由基共聚合radical copolymerization236离子共聚合ionic copolymerization237无规共聚合random copolymerization238理想共聚合ideal copolymerization239交替共聚合alternating copolymerization 240恒[组]分共聚合azeotropic copolymerization 241接枝共聚合graft copolymerization242嵌段共聚合block copolymerization243开环共聚合ring opening copolymerization 244共聚合方程copolymerization equation245共缩聚copolycondensation246逐步共聚合step copolymerization247同种增长homopropagation248自增长self propagation249交叉增长cross propagation250前末端基效应penultimate effect251交叉终止cross termination252Q值Q value253e值e value254Q,e概念Q, e scheme255序列长度分布sequence length distribution 256侧基反应reaction of pendant group257扩链剂,链增长剂chain extender258交联crosslinking259化学交联chemical crosslinking260自交联self crosslinking261光交联photocrosslinking262交联度degree of crosslinking263硫化vulcanization264固化curing265硫[黄]硫化sulfur vulcanization266促进硫化accelerated sulfur vulcanization 267过氧化物交联peroxide crosslinking268无规交联random crosslinking269交联密度crosslinking density270交联指数crosslinking index271解聚depolymerization272①降解②退化degradation273链断裂chain breaking274解聚酶depolymerase275细菌降解bacterial degradation276生物降解biodegradation277化学降解chemical degradation278辐射降解radiation degradation279断链降解chain scission degradation280自由基链降解free radical chain degradation 281无规降解random degradation282水解降解hydrolytic degradation283热降解thermal degradation284热氧化降解thermal oxidative degradation 285光降解photodegradation286光氧化降解photo oxidative degradation287力化学降解mechanochemical degradation288接枝聚合graft polymerization289活化接枝activation grafting290接枝点grafting site291链支化chain branching292支化度degree of branching三高分子物理23蠕虫状链worm-like chain24柔性链flexible chain25链柔性chain flexibility26刚性链rigid chain27棒状链rodlike chain28链刚性chain rigidity29聚集aggregation30聚集体aggregate31凝聚、聚集coalescence32链缠结chain entanglement33凝聚缠结cohesional entanglement34物理缠结physical entanglement35拓扑缠结topological entanglement36凝聚相condensed phase37凝聚态condensed state38凝聚过程condensing process39临界聚集浓度critical aggregation concentration 40线团-球粒转换coil-globule transition41受限链confined chain42受限态confined state43物理交联physical crosslinking44统计线团statistical coil45等效链equivalent chain46统计链段statistical segment47链段chain segment48链构象chain conformation49无规线团模型random coil model50无规行走模型random walk model51自避随机行走模型self avoiding walk model52卷曲构象coiled conformation53高斯链Gaussian chain54无扰尺寸unperturbed dimension55扰动尺寸perturbed dimension56热力学等效球thermodynamically equivalent sphere 57近程分子内相互作用short-range intramolecular interaction 58远程分子内相互作用long-range intramolecular interaction 59链间相互作用interchain interaction60链间距interchain spacing61长程有序long range order62近程有序short range order63回转半径radius of gyration64末端间矢量end-to-end vector65链末端chain end66末端距end-to-end distance67无扰末端距unperturbed end-to-end distance68均方根末端距root-mean-square end-to-end distance 69伸直长度contour length70相关长度persistence length71主链;链骨架chain backbone72支链branch chain73链支化chain branching74短支链short-chain branch75长支链long-chain branch76支化系数branching index77支化密度branching density78支化度degree of branching79交联度degree of crosslinking80网络network81网络密度network density82溶胀swelling83平衡溶胀equilibrium swelling84分子组装,分子组合molecular assembly85自组装self assembly86微凝胶microgel87凝胶点gel point88可逆[性]凝胶reversible gel89溶胶-凝胶转化sol-gel transformation90临界胶束浓度critical micelle concentration,CMC91组成非均一性constitutional heterogenity,compositional heterogenity92摩尔质量平均molar mass average又称“分子量平均”93数均分子量number-average molecular weight,number-average molar mass94重均分子量weight-average molecular weight,weight-average molar mass95Z均分子量Z(Zaverage)-average molecular weight,Z-molar mass96黏均分子量viscosity-average molecular weight,viscosity-average molar mass97表观摩尔质量apparent molar mass98表观分子量apparent molecular weight99聚合度degree of polymerization100动力学链长kinetic chain length101单分散性monodispersity102临界分子量critical molecular weight103分子量分布molecular weight distribution,MWD104多分散性指数polydispersity index,PID105平均聚合度average degree of polymerization106质量分布函数mass distribution function107数量分布函数number distribution function108重量分布函数weight distribution function109舒尔茨-齐姆分布Schulz-Zimm distribution110最概然分布most probable distribution 曾用名“最可几分布”111对数正态分布logarithmic normal distribution 又称“对数正则分布”112聚合物溶液polymer solution113聚合物-溶剂相互作用polymer-solvent interaction114溶剂热力学性质thermodynamic quality of solvent115均方末端距mean square end to end distance116均方旋转半径mean square radius of gyration117θ温度theta temperature118θ态theta state119θ溶剂theta solvent120良溶剂good solvent121不良溶剂poor solvent122位力系数Virial coefficient曾用名“维里系数”123排除体积excluded volume124溶胀因子expansion factor125溶胀度degree of swelling126弗洛里-哈金斯理论Flory-Huggins theory127哈金斯公式Huggins equation128哈金斯系数Huggins coefficient129χ(相互作用)参数χ-parameter130溶度参数solubility parameter131摩擦系数frictional coefficient132流体力学等效球hydrodynamically equivalent sphere 133流体力学体积hydrodynamic volume134珠-棒模型bead-rod model135球-簧链模型ball-spring [chain] model136流动双折射flow birefringence, streamingbirefringence137动态光散射dynamic light scattering138小角激光光散射low angle laser light scattering139沉降平衡sedimentation equilibrium140沉降系数sedimentation coefficient141沉降速度法sedimentation velocity method142沉降平衡法sedimentation equilibrium method143相对黏度relative viscosity144相对黏度增量relative viscosity increment145黏度比viscosity ratio146黏数viscosity number147[乌氏]稀释黏度计[Ubbelohde] dilution viscometer148毛细管黏度计capillary viscometer149落球黏度计ball viscometer150落球黏度ball viscosity151本体黏度bulk viscosity152比浓黏度reduced viscosity153比浓对数黏度inherent viscosity, logarithmicviscosity number154特性黏数intrinsic viscosity, limitingviscosity number155黏度函数viscosity function156零切变速率黏度zero shear viscosity157端基分析analysis of end group158蒸气压渗透法vapor pressure osmometry, VPO159辐射的相干弹性散射coherent elastic scattering ofradiation160折光指数增量refractive index increment161瑞利比Rayleigh ratio162超瑞利比excess Rayleigh ratio163粒子散射函数particle scattering function164粒子散射因子particle scattering factor165齐姆图Zimm plot166散射的非对称性dissymmetry of scattering167解偏振作用depolarization168分级fractionation169沉淀分级precipitation fractionation170萃取分级extraction fractionation171色谱分级chromatographic fractionation172柱分级column fractionation173洗脱分级,淋洗分级elution fractionation174热分级thermal fractionation175凝胶色谱法gel chromatography176摩尔质量排除极限molar mass exclusion limit177溶剂梯度洗脱色谱法solvent gradient [elution]chromatography178分子量排除极限molecular weight exclusion limit179洗脱体积elution volume180普适标定universal calibration181加宽函数spreading function182链轴chain axis183等同周期identity period184链重复距离chain repeating distance185晶体折叠周期crystalline fold period186构象重复单元conformational repeating unit187几何等效geometrical equivalence188螺旋链helix chain189构型无序configurational disorder190链取向无序chain orientational disorder191构象无序conformational disorder192锯齿链zigzag chain193双[股]螺旋double stranded helix194[分子]链大尺度取向global chain orientation195结晶聚合物crystalline polymer196半结晶聚合物semi-crystalline polymer197高分子晶体polymer crystal198高分子微晶polymer crystallite199结晶度degree of crystallinity, crystallinity 200高分子[异质]同晶现象macromolecular isomorphism201聚合物形态学morphology of polymer202片晶lamella, lamellar crystal203轴晶axialite204树枝[状]晶体dendrite205纤维晶fibrous crystal206串晶结构shish-kebab structure207球晶spherulite208折叠链folded chain209链折叠chain folding210折叠表面fold surface211折叠面fold plane212折叠微区fold domain213相邻再入模型adjacent re-entry model 214接线板模型switchboard model215缨状微束模型fringed-micelle model216折叠链晶体folded-chain crystal217平行链晶体parallel-chain crystal 218伸展链晶体extended-chain crystal 219球状链晶体globular-chain crystal 220长周期long period221近程结构short-range structure222远程结构long-range structure223成核作用nucleation224分子成核作用molecular nucleation225阿夫拉米方程Avrami equation226主结晶primary crystallization 227后期结晶secondary crystallization 228外延结晶,附生结晶epitaxial crystallizationepitaxial growth229外延晶体生长,附生晶体生长230织构texture231液晶态liquid crystal state232溶致性液晶lyotopic liquid crystal233热致性液晶thermotropic liquid crystal234热致性介晶thermotropic mesomorphism235近晶相液晶smectic liquid crystal236近晶中介相smectic mesophase237近晶相smectic phase238条带织构banded texture239环带球晶ringed spherulite240向列相nematic phase241盘状相discotic phase242解取向disorientation243分聚segregation244非晶相amorphous phase曾用名“无定形相”245非晶区amorphous region246非晶态amorphous state247非晶取向amorphous orientation248链段运动segmental motion249亚稳态metastable state250相分离phase separation251亚稳相分离spinodal decomposition252bimodal decomposition253微相microphase254界面相boundary phase255相容性compatibility256混容性miscibility257不相容性incompatibility258不混容性immiscibility259增容作用compatiibilization260最低临界共溶(溶解)温度lower critical solution temperature, LCST261最高临界共溶(溶解)温度upper critical solution temperature , UCST262浓度猝灭concentration quenching263激基缔合物荧光excimer fluorescence264激基复合物荧光exciplex fluorescence265激光共聚焦荧光显微镜laser confocal fluorescence microscopy266单轴取向uniaxial orientation267双轴取向biaxial orientation, biorientation268取向度degree of orientation269橡胶态rubber state270玻璃态glassy state271高弹态elastomeric state272黏流态viscous flow state273伸长elongation274高弹形变high elastic deformation275回缩性,弹性复原nerviness276拉伸比draw ratio, extension ratio277泊松比Poisson's ratio278杨氏模量Young's modulus279本体模量bulk modulus280剪切模量shear modulus281法向应力normal stress282剪切应力shear stress283剪切应变shear strain284屈服yielding285颈缩现象necking 又称“细颈现象”286屈服应力yield stress287屈服应变yield strain288脆性断裂brittle fracture289脆性开裂brittle cracking290脆-韧转变brittle ductile transition291脆化温度brittleness(brittle) temperature292延性破裂ductile fracture293冲击强度impact strength294拉伸强度tensile strength 又称“断裂强度,breaking strength”295极限拉伸强度ultimate tensile strength296抗撕强度tearing strength 又称“抗扯强度”297弯曲强度flexural strength, bending strength298弯曲模量bending modulus299弯曲应变bending strain300弯曲应力bending stress301收缩开裂shrinkage crack302剪切强度shear strength303剥离强度peeling strength304疲劳强度fatigue strength, fatigue resistance305挠曲deflection306压缩强度compressive strength307压缩永久变形compression set308压缩变形compressive deformation309压痕硬度indentation hardness310洛氏硬度Rockwell hardness311布氏硬度Brinell hardness312抗刮性scrath resistance313断裂力学fracture mechanics314力学破坏mechanical failure315应力强度因子stress intensity factor316断裂伸长elongation at break317屈服强度yield strength318断裂韧性fracture toughness319弹性形变elastic deformation320弹性滞后elastic hysteresis321弹性elasticity322弹性模量modulus of elasticity323弹性回复elastic recovery324不可回复形变irrecoverable deformation325裂缝crack 俗称“龟裂”326银纹craze327形变;变形deformation328永久变形deformation set329剩余变形residual deformation330剩余伸长residual stretch331回弹,回弹性resilience332延迟形变retarded deformation333延迟弹性retarded elasticity334可逆形变reversible deformation335应力开裂stress cracking336应力-应变曲线stress strain curve337拉伸应变stretching strain338拉伸应力弛豫tensile stress relaxation339热历史thermal history340热收缩thermoshrinking341扭辫分析torsional braid analysis,TBA 342应力致白stress whitening343应变能strain energy344应变张量strain tensor345剩余应力residual stress346应变硬化strain hardening347应变软化strain softening348电流变液electrorheological fluid349假塑性pseudoplastic350拉胀性auxiticity351牛顿流体Newtonian fluid352非牛顿流体non-Newtonian fluid353宾汉姆流体Bingham fluid354冷流cold flow355牛顿剪切黏度Newtonian shear viscosity 356剪切黏度shear viscosity357表观剪切黏度apparent shear viscosity358剪切变稀shear thinning359触变性thixotropy360塑性形变plastic deformation361塑性流动plastic flow362体积弛豫volume relaxation363拉伸黏度extensional viscosity364黏弹性viscoelasticity365线性黏弹性linear viscoelasticity366非线性黏弹性non-linear viscoelasticity367蠕变creep368弛豫[作用]relaxation 又称“松弛”369弛豫模量relaxation modulus370蠕变柔量creep compliance371热畸变温度heat distortion temperature372弛豫谱relaxation spectrum373推迟[时间]谱retardation [time] spectrum374弛豫时间relaxation time375推迟时间retardation time376动态力学行为dynamic mechanical behavior377动态黏弹性dynamic viscoelasticity378热-机械曲线thermo-mechanical curve379动态转变dynamic transition380储能模量storage modulus381损耗模量loss modulus382复数模量complex modulus383复数柔量complex compliance384动态黏度dynamic viscosity385复数黏度complex viscosity386复数介电常数complex dielectric permittivity387介电损耗因子dielectric dissipation factor388介电损耗常数dielectric loss constant389介电弛豫时间dielectric relaxation time390玻璃化转变glass transition391玻璃化转变温度glass-transition temperature392次级弛豫secondary relaxation393次级转变secondary transition。
UNIT 12 Bulk PolymerizationBulk polymerization traditionally has been defined as the formation of polymer from pure, undiluted monomers. Incidental amounts of solvents and small amounts of catalysts, promoters, and chain-transfer agents may also be present according to the classical definition. This definition, however, serves little practical purpose. It includes a wide variety of polymers and polymerization schemes that have little in common, particularly from the viewpoint of reactor design. The modern gas-phase process for polyethylene satisfies the classical definition, yet is a far cry from the methyl methacrylate and styrene polymerization which remain single-phase throughout the polymerization and are more typically thought of as being bulk. ®A common feature of most bulk polymerization and other processes not traditionally classified as such is the need to process fluids of very high viscosity. The high viscosity results from the presence of, dissolved polymer in a continuous liquid phase. Signific ant concentrations of a high molecular-weight polymer typically increase fluid viscosities by 104 or more compared to the unreacted monomers. This suggests classifying a polymerization as bulk whenever a substantial concentration of polymer occurs in the continuous phase. Although this definition encompasses a wide variety of polymerization mechanisms, it leads to unifying concepts in reactor design. The design engineer must confront the polymer in its most intractable form, i. e. , as a high viscosity solution or polymer melt.The revised definition makes no sharp distinction between bulk and solution polymerizations and thus reflects industrial practice. Several so-called bulk processes for polystyrene and ABS® use 5%~15% solvent as a processing aid and chain-transfer agent. Few successful processes have used the very large amounts of solvent needed to avoid high viscosities in the continuous phase, although this approach is sometimes used for laboratory preparations.Bulk polymerizations often exhibit a second, discontinuous phase. They frequently exhibit high exothermicity, but this is more characteristic of the reaction mechanism than of bulk polymerization as such. Bulk polymerizations of the free-radical variety are most common, although several commercially important condensation processes satisfy the revised definition of a bulk polymerization.In all bulk polymerizations, highly viscous polymer solutions and melts are handled. This fact tends to govern the process design and to a lesser extent, the process economics. Suitably robust equipment has been developed for the various processing steps, including stirred-tank and tubular reactors, flash devolatilizers, extruder reactors, and extruder devolatilizers. Equipment costs are high based on working volume, but the volumetric efficiency of bulk polymerizations is also high. If a polymer can be made in bulk, manufacturing economics will most likely favor this approach. ®It is tempting to suggest that polymer processes will gradually evolve toward bulk.® Recently, the suspension process for impact polystyrene has been supplanted by the bulk process, and the emulsion process for ABS may similarly be replaced. However, the modern gas-phase process for polyethylene appears to represent an opposite trend. It seems that polymerization technology tends to eliminate solvents and suspending fluids other than the monomers themselves. When the monomer is a solvent for the polymer, bulk processes as described in this article are chosen. When the monomer is not a solvent, suspension and slurry processes like those for polyethylene and polypropylene are employed. Hence, it is worthwhile avoiding a highly viscouscontinuous phase, but not at the price of introducing extraneous material. ®Reading MaterialsPolymerization ViscostitiesViscosity in itself is a nebulous term when describing the polymer or polymer solution in most polymerizations. Some polymerizations are carried out in water with small beads being formed and suspended in the water. The "viscosity" of such a system could actually mean the viscos.ty of the water, the viscosity of the slurry present with the beads in the water, the impeller viscosity, the process viscosity, the bulk viscosity, or the viscosity at the heat transfer surface.In the bulk polymerization method, knowledge of viscosity is of vital importance. Bulk polymerizations typically operate between 100 000 and 500 000 cP (100 and 500Pa • s) bulk viscosity. An accurate determination of the bulk viscosity is extremely important in addition to the rheology associated with the particular polymer. Because bulk polymerizations are generally high viscosity in nature, the corresponding mixing Reynolds number® is very low, normally less than 100. This is in the laminar region. Power is proportional to N2D3u in the laminar range; so the actual horsepower which the mixer will draw is proportional to viscosity. Because of this, it is a requirement that viscosity vs. shear rate data be known. For example, assume two separate companies manufacturing bulk polystyrene have presented viscosity data to mixer vendors. Both companies have stated that the bulk viscosity of this material is 300 000 cP (300Pa • s). Company A furnished only this information to the mixer suppliers. Company B furnished the bulk viscosity information in addition to the viscosity vs. shear rate data. Because the mixer manufacturer could determine the proper viscosity to load the impeller from the information that customer B furnished, the mixer recommended was a 25-hp design (18. 5 kW). Company A received a quote for a 50-hp mixer (37kW). Both mixers were for tanks of the same size and shape and operating at the same speed. Naturally the quotation for customer A will be at a higher price and a higher operating cost than for customer B. However, both mixers will accomplish the required results.About 85% of all high-viscosity materials are pseudoplastic and viscoelastic in nature. Bulk polystyrene, polyesters, and polyelectrolytes are pseudoplastic in nature. Most materials have a slope of — 0. 2 to — 0. 6 when viscosity is plotted vs. shear rate. By reviewing these data and comparing the viscosity-vs. -shear rate information with the known shear rate constant of close-clearance impellers, the impeller viscosity can be determined. The shear rate constant for anchors and helical impellers is 30.As indicated earlier, helical impellers and anchors are typically used in bulk polymerizations. However, neither of these two devices can operate effectively without viscous drag at the wall of the vessel. Without some drag the material in the tank will turn as one entire mass, and almost no mixing will occur. Therefore, in bulk polymerizations it is important to be sure that inlet pipes of low-viscosity material and reflux lines are directed toward a point at the liquid level one-half of the distance from the mixer shaft to the tank wall. This will allow incorporation of the low-viscosity material and prevent its migration to the tank walls where it could act as a lubricating layer, thereby reducing the agitation. It is also important to optimize the temperature differential A T between the bulk fluid and the heat transfer surface. Normally bulk viscosity applications only require tank jackets to obtain temperature control. A very high jackettemperature could reduce the viscosity of the material at the tank wall to a point where it acts as a lubricating boundary layer. Too cold a temperature at the tank wall could increase the viscosity dramatically to a point where the mixer is not designed to handle it. In this case a totally stagnant boundary layer at the wall could occur and product quality could be affected. Further more, damage could result to the mixer, drive motor, and vessel.Viscosities for solution polymerizations are normally 25 000 and 500 000 cP (25 and 500 Pa • s) bulk viscosity. The same problems exist with the term viscosity in this type of polymerization as in bulk polymerizations. An exact knowledge of the bulk viscosity and viscosity at the impeller are important. In lower viscosity materials, where open impellers are used , the importance of the viscosity determination is slightly reduced because the mixing Reynolds numbers are normally in the transition region where horsepower is not proportional to viscosity. Therefore, a minor change in the viscosity will have little effect on the horsepower drawn by the mixer.Most solution polymerizations use tank jackets as heat transfer media; however, some solution polymerizations require additional surface area. Again, the A T optimization is important in solution polymerizations.UNIT 14 Styrene-Butadiene CopolymerThe synthetic rubber industry, based on the free-radical emulsion process, was created almost overnight during World War I . Styrene-butadiene (GR-S) rubber created at that time gives such good tire treads that natural rubber has never regained this market. ®The GR-S Standard recipe isThis mixture is heated with stirring and at 50°C gives conversions of 5% — 6% per hour. Polymerization is terminated at 70%~75% conversion by addition of a "short-stop", such as hydroquinone (approximately 0. 1 part), to quench radicals and prevent excessive branching and microgel formation. Unreacted butadiene is removed by flash distillation, and styrene by steam-stripping in a column. After addition of an antioxidant, such as iV-phenyl-β-naphthylamine (PBNA) (1.25 parts), the latex is coagulated by the addition of brine, followed by dilute sulfuric acid or aluminum sulfate. The coagulated crumb is washed, dried, and baled for shipment.This procedure is still the basis for emulsion polymerization today. An important improvement is continuous processing illustrated in Fig. 14.1; computer modeling has also been described.In the continuous process, styrene, butadiene, soap, initiator, and activator (an auxiliary initiating agent) are pumped continuously from storage tanks through a series of agitated reactors at such a rate that the desired degree of conversion is reached at the last reactor.® Shortstop is added, the latex warmed with steam, and the unreacted butadiene flashed off. Excess styrene is steam-stripped, and the latex finished as shown in Fig. 14.1.SBR prepared from the original GR-S recipe is often called hot rubber, cold rubber is made at 5'C by using a more active initiator system. Typical recipes are given in Table 14.1. At 5*C , 60% conversion to polymer occurs in 12~15h.Cold SBR tire treads are superior to those of hot SBR. Polymers with abnormally high molecular weight (and consequently too tough to process by ordinary factory equipment) can beprocessed after the addition of up to 50 parts of petroleum-base oils per hundred parts of rubber (phr) . These oil extenders make the rubbers more processible at lower cost and with little sacrifice in properties; they are usually emulsified and blended with the latex before coagulation.Recent trends have been toward products designed for specific uses. The color of SBR, which is important in many nontire uses, has been improved by the use of lighter-colored soaps, shortstops, antioxidants, and extending oils. For example, dithiocarbamates are substituted for hydroquinone as shortstop ; the latter is used on hot SBR where dark color is not objectionable. A shortstop such as sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate is more effective in terminating radicals and destroying peroxides at the lower temperatures employed for the cold rubbers.Free-radical dissociative initiators that function by dissociation of a molecule or ion into two radical species are normally limited to inorganic persulfates in the case of butadiene polymerization.The other important class of free-radical initiators, redox systems, contain two or more components that react to produce free radicals. Dodecyl mercaptan added to control molecular weight also appears to aid free-radical formation by reaction with persulfate. The commercial importance of such chain-transfer agents or modifiers cannot be overemphasized. ® Without molecular weight control the rubbers would be too tough to process.Reading MaterialsSteady-State Multilicity in Continuous Emulsion Polymerization The phenomenon of multiple steady states is seen in emulsion polymerization. Fig. 14. 2 is a plot of steady-state monomer conversion as a function of reactor residence time for methyl methacrylate emulsion polymerization in a CSTR. A region of multiplicity is indicated by the fact that the upper and lower branches of the curve overlap between residence times of 30 and 50 minutes. The dotted line is an estimate of the shape of the unstable middle branch which is experimentally unobservable. The dashed lines indicate experimental instances of ignition and extinction. At 50 minutes residence time the system has been observed to move from the lower steady state of 54% conversion to the upper steady state at approximately 80% with no discernible change in operating conditions (ignition). Extinction has been observed when the residence time is changed from 30 minutes to 20 minutes on the upper branch, resulting in a drop in conversion from the upper to the lower steady-state values. The phenomenon of multiple steady states arises in emulsion polymerization for much the same reason as it appears in solution polymerization: the autocatalytic nature of the polymerization (due to the gel effect), combined with the mass balance, results in the possibility of steady-state multiplicity.Steady-state multiplicity can be an operational problem for a number of reasons. If one wishes to operate at an intermediate level of monomer conversion (perhaps to minimize viscosity or prevent excessive chain branching), one may be forced to operate in the unstable region, relying on closed-loop control to stabilize the operating point. This is tricky at best. Additionally, the steady state (upper or lower) to which the system goes on start-up will depend on how the start-up is effected. A careful start-up policy may be needed to assure that the system arrives at the desired steady state. In general, a conservative start-up, with the temperature and initiator concentration brought to steady-state values slowly will result in operation on the lower branch, while aggressive start-up (high temperature and/or high initiator concentration during start-up) will result in steady-state operation on the upper branch. Finally, large upsets in the process may causeignition or extinction. This may lead to loss of temperature control in the case of ignition, or loss of reactor productivity in the case of extinction. A system designed to operate at the upper steady state will be operating way below design product yield at the lower steady state. Additionally, the product quality (MWD, CCD, etc. ) will be different for the two operating points. The polymerisation reactor designer should be aware of the potential for multiplicity, and, if possible, design the system to operate outside this region.CSTR polymerization reactors can also be subject to oscillatory behavior. A nonisothermal CSTR free radical solution polymerisation can exhibit damped oscillatory approach to a steady state, unstable (growing) oscillations upon disturbance, and stable (limit cycle) oscillations in which the system never reaches steady state,and never goes unstable, but continues to oscillate with a fixed period and amplitude. However, these Phenomena are more commonly observed in emulsion polymemation.High-volume products such as styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) often are produced by continuous emulsion polymerization. This is most often done in a train of 5~15 CSTRs in series. Sustained oscillations (limit cycles) in conversion, particle number, and free emulsifier concentration gave been reported, under isothermal conditions in continuous emulsion polymerization systems. This limit cycle behavior leaves its mark on the product in the form of disturbances in the molecular weight distribution and particle size distribution which cannot be blended away. Fig. 14. 3 shows evidence of a sustained oscillation (limit cycle) during emulsion polymerization of methyl methacrylate in a single CSTR. Com parison of the monomer conversion and surface tension data graphically illustrates the mechanism of oscillation. It will be noted that the surface tension oscillates with the same period as the conversion (6—7 residence times). This can be explained with the classical micellar initiation mechanism (or with homogeneous nucleation) . Beginning at a time of about 300 minutes, the conversion rises rapidly as new particles form and old particles grow. As the particle surface area increases , additional surfactant is adsorbed on the particles. Meanwhile micelles dissociate to keep the aqueous phase saturated. Once all of the micelles have dissociated, it is no longer possible to maintain the aqueous phase at saturation, and the surface tension begins to rise. This is observed at about 320 minutes. At the point at which micelles are no longer present, micellar initiation stops and the rate of polymerization slows. Eventually, since particles are washing out while no new particles are being formed, the conversion begins to fall. Since the total particle surface area is decreasing at this point, and since surfactant is continually being introduced with the feed, the surface tension falls as the aqueous phase reapproaches saturation. As the aqueous phase becomes saturted initiation begins again. Saturation of aqueous phase may be observed by noting the point at which the surface tension reaches its CMC value. As new micelles are formed they adsorb free radicals, become polymer particles, and begin to grow and adsorb surfactant. The cycle then repeats.Modeling studies show that while the instability arises above the CMC (and is promoted by large values of initiator concentration and residence time, and low surfactant concentration), it is the on/off nature of the nucleation mechanism which governs the nature of oscillations in monomer conversion. The surface tension oscillation leads the conversion oscillation by approximately one residence time. This is consistent with the above explanation since changes in surfactant concentration are quite rapid while changes in the number of particles and rate of reaction require a finite growth time to appear as changes in the monomer conversion. Dampedoscillations at start-up have been noted for a large number of monomer systems.Damped oscillations will result in lost productivity since the product during these transients may be off quality. Unstable oscillations will, of course, preclude continued operation. Limit cycle oscillations, while not unstable, will result in a product having a quality (MWD, CCD, etc. ) which varies with time in a cyclic fashion. In most cases this is undesirable. As in the case of multiplicity, the polymerisation reactor designer must be aware of the potential for oscillatory phenomena, and should attempt to specify operating conditions at which these phenomena do not exist. In emulsion polymerizations • oscillations (both damped and sustained) are undesirable since the product is not of a consistent quality. and oscillations in free surfactant concentration may induce coagulation and reactor fouling. Several methods of eliminating oscillations in emulsion polymerization have been suggested. Poehlein has used a plug flow reactor upstream of a CSTR train. All polymer particles are nucleated in the PFR. Since PFR kinetics are essentially those of a batch reactor (and such oscillations do not occur in batch reactors), no oscillations occur. The CSTRs, then, are used to grow the existing particles. By segregating particle nucleation from particle growth, oscillations are eliminated. Another approach has been taken by Penlidis and others. This involves using a small CSTR as a seeder reactor. AH polymer particles are formed in the seeder. A portion of the monomer and water is bypassed around the seeder in such a way as to dilute out any remaining micelles in the reactor immediately following the seeder. Once again, nucleation and growth have been segregated, and oscillations are eliminated.UNIT 22 Mechanical Properties of PolymersThe mechanical properties of polymers are of interest in all applications where polymers are used as structural materials. Mechanical behavior involves the deformation of a material under the influence of applied forces.The most important and most characteristic mechanical properties are called moduli. A modulus is the ratio between the applied stress and the corresponding deformation. The re-ciprocals of the moduli are called compliances. The nature of the modulus depends on the na-ture of the deformation. The three most important elementary modes of deformation and the moduli (and compliances) derived from them are given in Table 22.1, where the definitions of the elastic parameters are also given. ® Other very important, but more complicated, de-formations are bending and torsion. From the bending or flexural deformation the tensile modulus can be derived. The torsion is determined by the rigidity.Cross-linked elastomers are a special case. Due to the cross-links this polymer class shows hardly any flow behavior. The kinetic theory of rubber elasticity was developed by Kuhn , Guth, James, Mark, Flory, Gee and Treloar. It leads, for Y oung's modulus at low strains, to the following equation sE=3RTp/Mcrl = 3zcrlRT/V=3C0The paragraphs above dealt with purely elastic deformations, i. e. deformations in which the strain was assumed to be a time-independent function of the stress. In reality, materials are never purely elastic: under certain circumstances they have nonelastic properties. This is especially true of polymers, which may show nonelastic deformation under circum-stances in which metals may be regarded as purely elastic. ® It is customary to use the ex-pression viscoelastic deformations that are not purely elastic. Literally the term viscoelastic means thecombinations of viscous and elastic properties. As the stress-strain relationship in viscous deformations is time-dependent, viscoelastic phenomena always involve the change of properties with time. Measurement of the response in deformation of a viscoelastic material to periodic forces, for instance during forced vjbration, shows that stress and strain are not in phase; the strain lags behind the stress by a phase angle 8, the loss angle. So the moduli of the materials, the complex moduli, include the storage moduli which determine the amount of recoverable energy stored as elastic energy, and the loss moduli which determine the dissipation of energy as heat when the material is deformed.UNIT 23 Thermal Properties of PolymerThe heat stability is closely related to the transition and decomposition temperature, i. e. to intrinsic properties. By heat stability is exclusively understood the stability (or re-tention) of properties (weight, strength, insulating capacity, etc. ) under the influence of heat. The melting point or the decomposition temperature invariably form the upper limit; the "use temperature" may be appreciably lower.The way in which a polymer degrades under the influence of thermal energy in an inert atmosphere is determined, on the one hand, by the chemical structure of the polymer itself, on the other hand, by the presence of traces of unstable structures.Thermal degradation does not occur until the temperature is so high that primary chemi-cal bonds are separated. For many polymers thermal degradation is characterized by the breaking of the weakest bond and is consequently determined by a bond dissociation energy. Since the change in entropy is of the same order of magnitude in almost all dissociation reac-tions, it may be assumed that also the activation entropy will be approximately the same. This means that, in principle, the bond dissociation energy determines the phenomenon. So it may be expected that the temperature at which the same degree of conversion is reached will be virtually proportional to this bond dissociation energy. ®The process of thermal decomposition or pyrolysis is characterized by a number of ex-perimental indices, such as the temperature of initial decomposition, the temperature of half decomposition, the temperature of the maximum rate of decomposition, and the average en-ergy of activation. The heat resistance of a polymer may be characterized by its "initial" and "half" decomposition.There are two types of thermal decomposition: chain depolymerization and random de-composition. The former is the successive release of monomer units from a chain end or at a weak link, which is essentially the reverse of chain polymerization; ® it is often called deprop-agation or unzippering. This depolymerization begins at the ceiling temperature. Random degradation occurs by chain rupture at random points along the chain, giving a disperse mix-ture of fragments which are usually large compared with the monomer unit. The two types of thermal degradation may occur separately or in combination; the latter case is rather nor-mal. Chain depolymerization is often the dominant degradation process in vinyl polymers, whereas the degradation of condensation polymers is mainly due to random chain rupture.The overall mechanism of thermal decomposition of polymers has been studied by Wolfs et al. The basic mechanism of pyrolysis is sketched in Fig. 23.1.In the first stage of pyrolysis (<550°C) a disproportionation takes place. Part of thede-composing materials is enriched in hydrogen and evaporated as tor and primary gas, the rest forming the primary char. In the second phase (>550°C) the primary char is further decom-posed, i.e. mainly dehydrogenated, forming the secondary gas and final char. During the disproportionation reaction, hydrogen atoms of the aliphatic parts of the structural units are "shifted" to saturate" part of the aromatic radicals. The hydrogen shift during dispropor-tionation is highly influenced by the nature of the structural groups.Reading MaterialsRequirements for Heat ResistanceHeat resistance is the capacity of a material to retain useful properties for a stated period of time at elevated temperatures (≥230°C) under defined conditions, such as pressure or vacuum, mechanical load, radiation, and chemical or electrical influences at temperatures ranging from cryogenic to above 500°C. Both reversible and irreversible changes can occur. In a reversible change, for example, as a polymer under load approaches the glass-transition temperature Tg, deformation occurs without change in chemical structure. Reversible changes occur primarily as & function of Tg, which for the purposes of this article, i. e. , for high temperature structural polymers, must be above 230°C. The maximum-use temperature for an amorphous or semicrystalline structural resin usually depends on Tg rather than the crystalline melt temperature Tm. A semicrystalline polymer can exhibit substantial loss of mechanical properties near the Tg, depending upon the degree of crystallinity. The Tm is usually so high that in its vicinity chemical degradation occurs. Irreversible changes alter the chemical structure. For example, exceeding the thermal stability results in bond breaking.The chemical factors which influence heat resistance include primary bond strength, secondary or van der Waals bonding forces, hydrogen bonding, resonance stabilization, mechanism of bond cleavage, molecular symmetry (structure regularity), rigid intrachain structure, and cross-Unking and branching. The physical factors include molecular weight and molecular weight distribution, close packing (crystallinity ), molecular (dipolar) interac-tions, and purity.The primary bond strength is the single most important influence contributing to heat resistance. The bond dissociation energy of a carbon-carbon single bond is ~ 350 kj/mol (83.6 kcal/mol), and that of a carbon-carbon double bond is ~610kJ/mol (145.8 kcal/ mol). In aromatic systems, the latter is even higher. Known as resonance stabilization, this phenomenon adds 164~287kJ/mol (39. 2—86. 6 kcal/mol). As a result, aromatic and hete-rocyclic rings are widely used in thermally stable polymers.Secondary or van der Waals bonding forces provide additional strength and thermal stability. Dipole-dipole interaction and H bonding contribute 25 ~ 41 kj/mol (6.0 ~ 9.8 kcal/mol)toward molecular stability and affect the cohesion energy density* which influences the stiffness , Tg, melting point , and solubility. Thus , beat-resistant polymers often contain polar groups, e.g. , —CO—, —S02—, that participate in strong intermolecular associa-tion. Polymers containing electron-withdrawing groups, e. g., —CO—, as connecting groups are generally more stable than those containing electron-donating groups, e. g. . —O—.The mechanism of bond cleavage also influences thermal stability. In polysiloxanes, for example, the energy of the silicon-oxygen single bond is ~445kJ/mol (106. 4kcal/mol), and that of the silicon-carbon single bond ~328kJ/mol (78. 4kcal/mol). Although the Si—C bond would be。
高分子材料工程专业英语翻译UNIT 1 What are Polymer 第一单元什么是高聚物What are polymers For one thing they are complex and giant molecules and are different from low molecular weight compounds like say common salt. To contrast the difference the molecular weight of common salt is only 58.5 while that of a polymer can be as high as several hundred thousand even more than thousand thousands. These big molecules or‘macro-molecules’ are made up of much smaller molecules can be of one or more chemical compounds. To illustrate imagine that a set of rings has the same size and is made of the same material. When these things are interlinked the chain formed can be considered as representing a polymer from molecules of the same compound. Alternatively individual rings could be of different sizes and materials and interlinked to represent a polymer from molecules of different compounds. 什么是高聚物首先他们是合成物和大分子而且不同于低分子化合物譬如说普通的盐。
Unit 1 What are polymers?What are polymers? For one thing, they are complex and giant molecules and are different from low molecular weight compounds like, say, common salt.什么是高聚物?首先,他们是合成物和大分子,而且不同于低分子化合物,譬如说普通的盐。
To contrast the difference, the molecular weight of common salt is only 58.5, while that of a polymer can be as high as several hundred thousand, even more than thousand thousands.与低分子化合物不同的是,普通盐的分子量仅仅是58.5,而高聚物的分子量高于105,甚至大于106。
These big molecules or ‘macro-molecules’ are made up of much sma ller molecules, can be of one or more chemical compounds.这些大分子或“高分子”由许多小分子组成。
小分子相互结合形成大分子,大分子能够是一种或多种化合物。
To illustrate, imagine that a set of rings has the same size and is made of the same material. When these things are interlinked, the chain formed can be considered as representing a polymer from molecules of the same compound.举例说明,想象一组大小相同并由相同的材料制成的环。