ACCA P3知识要点汇总(下)
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:1023.74 KB
- 文档页数:54

ACCA P3知识点:PESTEL分析模型在ACCA P3考试中分析企业外部环境时,常用PESTEL模型,PESTEL分析模型又称大环境分析,是分析宏观环境的有效工具,不仅能够分析外部环境,而且能够识别一切对组织有冲击作用的力量。
它是分析组织外部影响因素的方法,其每一个字母代表一个因素,可以分为6大因素:政治因素(Political)、经济因素(Economic)、社会因素(Social)、技术要素(Technological)、环境因素(Environmental)和法律因素(Legal)。
The PESTEL framework (sometimes also called "SLEPT" framework) analyses external forces under the headings:·Political;·Economic;·Socio-Cultural;·Technological;·Environmental; and·Legal.(1)政治因素(Political):是指对组织经营活动具有实际与潜在影响的政治力量和有关的政策、法律及法规等因素。
(2)经济因素(Economic):是指组织外部的经济结构、产业布局、资源状况、经济发展水平以及未来的经济走势等。
(3)社会因素(Social):是指组织所在社会中成员的历史发展、文化传统、价值观念、教育水平以及风俗习惯等因素。
(4)技术因素(Technological):技术要素不仅仅包括那些引起革命性变化的发明,还包括与企业生产有关的新技术、新工艺、新材料的出现和发展趋势以及应用前景。
(5)环境因素(Environmental):一个组织的活动、产品或服务中能与环境发生相互作用的要素。
(6)法律因素(Legal):组织外部的法律、法规、司法状况和公民法律意识所组成的综合系统。

ACCA P3、P5新知识点Big Data 的探讨2016年,Big data (大数据技术)作为新的知识点纳入P3,P5的知识体系。
这一知识体系上的调整,正确地反映了在互联网信息技术时代,以云计算技术为支撑的大数据技术在组织发展中的日益重要的背景。
本文就Big Data作一基本的探讨。
——基本定义DefinitionBig Data is a term for a collection of data which is so large that it becomes difficult to store and process using traditional databases and data processing applications.大数据就是一种归集的数据;这些数据涉及的资料量规模巨大,无法通过传统的主流软件工具管理、处理、整理。
Extremely large collections of data (data sets) that may be analysed to reveal patterns, trends, and associations, especially relating to human behaviour and interactions.'超级强大的数据归集,对此分析以揭示某种模式、趋势和关联;尤其是人类社会行为方面的模式、趋势和关联。
基于如上的释义,可以看出:1)Big Data应时而生。
当今社会数据量井喷式的增长是大数据的存在的理由。
这种井喷式的数据增长,可以分为有意识的(主动性的)或无意识的(被动性的)。
有意识的,可理解为组织自发地主动地制造了大数据。
Delivery company UPS equips its delivery vehicles with sensors which monitor data on speed, direction, braking performance and other mechanical aspects of the vehicle. UPS公司自发在其运输车辆上安装传感器以检测车辆的各项参数,以此制造大量数据。
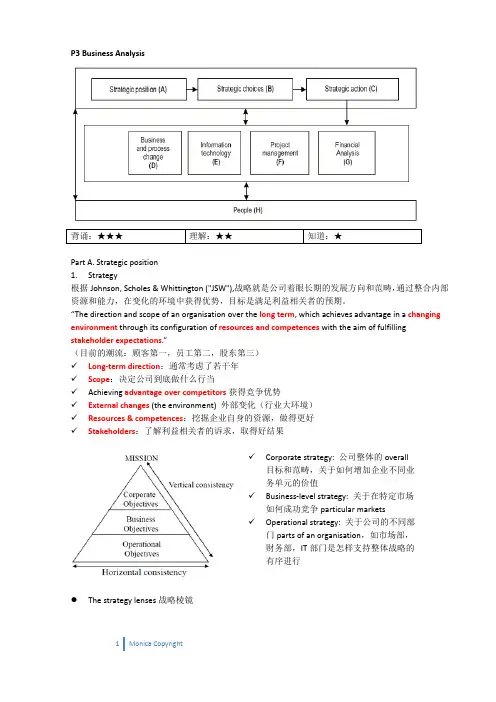
P3 Business Analysis背诵:★★★ 理解:★★ 知道:★Part A. Strategic position1.Strategy根据Johnson, Scholes & Whittington ("JSW"),战略就是公司着眼长期的发展方向和范畴,通过整合内部资源和能力,在变化的环境中获得优势,目标是满足利益相关者的预期。
“The direction and scope of an organisation over the long term, which achieves advantage in a changing environment through its configuration of resources and competences with the aim of fulfilling stakeholder expectations.”(目前的潮流:顾客第一,员工第二,股东第三)✓Long‐term direction:通常考虑了若干年✓Scope:决定公司到底做什么行当✓Achieving advantage over competitors获得竞争优势✓External changes (the environment) 外部变化(行业大环境)✓Resources & competences:挖掘企业自身的资源,做得更好✓Stakeholders:了解利益相关者的诉求,取得好结果✓Corporate strategy: 公司整体的overall 目标和范畴,关于如何增加企业不同业务单元的价值✓Business‐level strategy: 关于在特定市场如何成功竞争particular markets✓Operational strategy: 关于公司的不同部门parts of an organisation,如市场部,财务部,IT部门是怎样支持整体战略的有序进行●The strategy lenses战略棱镜✓Design: 战略的设计应该是理性的rational,自上而下的top‐down process,中级管理层根据战略设定来分析信息,确认一个清晰的行动方案。

国际知名的ACCA(特许公认会计师)因为其权威性让许多人望而生畏,很多考生因为处理不好考试中思维方式、法律制度和答题技巧等方面的与国内考试的差异,使考试成了艰苦而漫长的过程。
其实,国际职业资格考试并不像一般人想象的那样可望而不可及,再难也是有规律可循的。
记者近日专门请教了有关专家,探寻到ACCA考试的一些规律和秘密。
经验1:鼓励人们以乐观态度看待未来据专家介绍,ACCA鼓励人们从战略的角度去思考问题,以乐观态度看待未来,提倡考生自己对问题有独到的见解。
由于其培养的是高级管理人才,面对的许多问题并不仅局限于会计的领域,因此需要站在更高的角度去拓展自己的思路。
在学习过程中一方面要培养自己用英语进行思维的习惯、发散性分析能力和归纳能力,另一方面要从最基本的要义和逻辑分析入手,培养自己在复杂环境下的决策、判断能力和心理承受能力。
这些能力的培养可通过对其提供的大量案例的反复研究、分析和体会,逐渐使自己形成灵活、独立、辩证地分析问题、解决问题的能力。
经过一段学习之后,你可能会发现这些能力在实际生活中也是十分有益的。
经验2:尝试分析历年考试内容ACCA考题规律性比较强,重点的内容会反复出现在历年的考题中。
尽管教材提供的内容很多,信息量大,而每次实际考试不会超过教材内容的三分之一,更不会出偏题和怪题。
考生不妨尝试分析历年考试内容,找出考官的出题规律,针对这些重点反复练习,这样有利于把握考试要点,同时提高学习效率,对考过关会有极大的帮助。
但这种分析是须建立在对书本内容全面理解的基础上的。
经验3:充分利用学员简讯扩大知识面除了要掌握课本和习题上提供的知识外,还要充分利用学员简讯,不断扩大自己的知识面,了解最新信息和接受不同的观点。
有条件的考生不妨浏览ACCA的网站,上面提供了许多专家甚至主考官的文章和历年考试分析,从中可以了解最新考试信息,不至于盲人摸象。
也可参加一些培训机构提供的相关培训提高对学习内容的认识。
据介绍,在最后几门难度较大的管理策划和财务策划等课程中,专家认为,课本似乎只提供了一个知识框架,应不断地补充知识面.例如,企业核心竞争力的不断培育、竞争优势、绩效评价体系、全球经济一体化对企业的影响等均可以和当前我国的一些知名企业相联系,这些理念在跨国公司的实际运作中有许多贴切的运用,有助于对课本知识的理解和应用。

acca考试知识点总结ACCA全称为Association of Chartered Certified Accountants,是全球最有影响力的专业会计师协会之一。
ACCA会员遍布全球180个国家,是世界上最大的国际专业会计师组织。
ACCA证书不仅在英国和欧洲有很高的认可度,而且在亚洲、非洲和中东等地区也备受青睐。
ACCA证书是一个标志,是对专业能力、行业经验和国际视野的认可。
ACCA考试是全球专业会计师考试,它涵盖了财务管理和会计领域的所有知识点,需要考生具备相当的知识储备和能力。
下面我们来总结一下ACCA考试的知识点。
第一部分:核心基础知识1.管理会计管理会计是一门研究如何为组织做决策和分配资源的学科,主要包括成本管理、预算管理、绩效评价和风险管理等知识点。
2.财务报告财务报告是组织向外部利益相关者提供的关于其财务状况和经营业绩的信息,主要包括财务报表分析、财务信息披露和国际财务报告准则等知识点。
3.税收税收是政府为了筹集财政收入而向纳税人征收的一种收费,主要包括个人所得税、公司所得税、增值税和财产税等知识点。
4.审计与保险审计是一种独立的评价活动,用来评估组织内部控制的有效性和财务报告的可靠性,主要包括内部审计、外部审计和信息系统审计等知识点。
第二部分:商业专业化知识1.企业法企业法是一门研究组织和企业在商业活动中的法律关系的学科,主要包括合同法、公司法、竞争法和知识产权法等知识点。
2.财务管理财务管理是一种为组织提供资金和资本的管理活动,主要包括投资决策、资金成本、风险管理和财务市场等知识点。
3.商业伦理商业伦理是一种研究商业活动中道德规范和价值观的学科,主要包括道德决策、企业社会责任和道德风险管理等知识点。
4.财务分析财务分析是一种评估组织财务状况和经营业绩的方法,主要包括财务比率分析、现金流量分析和经济附加值分析等知识点。
以上就是ACCA考试的知识点总结,希望对考生有所帮助。
在备考过程中,考生需要充分理解和掌握这些知识点,并且进行大量的练习和模拟考试,才能在考试中取得好成绩。

ACCA P1P2P3复习以及答题技巧汇总ACCA P1《公司治理,风险和道德》是ACCA专业核心模块的第一门课程,它总共分为四个部分。
1.介绍在代理关系的环境下,企业的整个治理。
这个部分主要是董事的角色和责任以及外部审计师和内部审计师的角色和责任;2.介绍内部监察、内部控制以及实施有效的治理得到的反馈,包括关于决策和决策支持部门的合规问题;3.介绍管理层如何识别、评估和控制风险;4.介绍在会计师责任的背景下个人的以及职业道德和道德框架-职业价值观以及在各种各样的情况下的职业行为。
ACCA P1学习方法首先大家注意公司治理来自于F4中的agency thoery也就是我们经常说的代理理论。
正因为公司的投资人不直接参与公司的管理,从而导致管理者与持有人之间产生一些利益上的冲突,所以上市公司通过完善公司治理来增强监督、减少冲突、降低风险,从而达到股东投资回报最大化。
其次,大家要关注NED(非执行董事)在公司治理中的重要作用,以及他们发挥监督作用具备的条件,这其中要求NED要充分独立。
虽然NED不是公司雇员,和公司之间没有雇佣关系,但是他们对完善和实施公司的发展战略有着重要的作用,另外NED要有足够的时间参与公司的日常经营。
再次,我请同学们关注TURNBULL REPORT和COMBINED CODE中对internal control和risk management的要求。
什么样的internal control system是完善而且有效的,如何进行risk assessment以及如何进行风险处理。
需要强调的五点:第一、考官的历年考题中只有两种格式:Memo 和letter。
烦请大家注意这两种格式第二、大家注意自己写出来的句子要专业,比如有效的内部控制要写sound internal control system, risk embedded等等第三、答题要有逻辑性,适当的通过分段,分层次来讲述自己的观点第四、要注意senario中引号的句子,这些句子一般是考点最后,希望大家多动笔,少用眼睛考虑问题。


ACCA P3重要知识点DEADL Y SIN ONETHE STRATEGY IS NOT WORTH IMPLEMENTINGIn too many cases, what is referred to as business strategy, is deficient in analytical rigor, creative insight, ambition or practicality. If the strategy is going to get the active support of management and staff, it needs to be specific, realistic and give the organisation something to strive for. Strategy making is often considered to be easy. It is easy if the strategy development process limits the scope of discovery, the breadth of involvement and the amount of intellectual effort expended. The strategy should not just be more of the same, incremental or comfortable. It needs to be stretching or innovative.DEADL Y SIN TWOPEOPLE ARE NOT CLEAR HOW THE STRA TEGY WILL BE IMPLEMENTEDWhen the strategy has been developed and evaluated, it then requires a plan to prepare the organisation for its implementation. There is always a strong desire to get started and make the strategy happen. The time spent on implementation planning is often seen as time wasting. However, there are a number of important issues that need to be addressed including:▎priorities for management;▎timescale;▎lessons learnt from previous strategy implementations;▎impact on structure and staff at all levels;▎participation; and▎risks.DEADL Y SIN THREECUSTOMERS AND STAFF DO NOT FULL Y UNDERSTAND THE STRA TEGYThere is a tendency for chief executives and senior management to communicate the business strategy on a ''need to know'' basis. If you don't put in the effort to sell and explain the strategy, how can you hope to have it implemented? Your front-line supervisory staff must understand what the strategy is about, why it is important and how it will affect them. The strategy implementation plan should include a communications plan, which sets out who needs to be told about the strategy. The plan should not only include senior management but also middle management, supervisors,staff, customers, suppliers and other key stakeholders.DEADL Y SIN FOURINDIVIDUAL RESPONSIBILITIES FOR IMPLEMENTING THE CHANGE ARE NOT CLEARIt is not sufficient just to develop a very insightful and relevant strategy and hope that the logic behind the strategy will be enough to make it a reality. People should be given clear and specific responsibilities for making strategy work. The more people you directly involve in the implementation process the better. This will create a wider sense of ownership, commitment and responsibility for making the strategy happen. Accountability must go hand in hand with responsibility. If someone has been given an implementation task, make sure they do it. Part of assigning staff responsibility is giving clear, understandable instructions and tasks and reviewing progress at regular intervals.DEADL Y SIN FIVECHIEF EXECUTIVES AND SENIOR MANAGERS STEP OUT OF THE PICTURE ONCE IMPLEMENTATION BEGINSIt is very important that strong leadership is provided during the implementation phase. People will be looking for clues. If staff feel that senior management are not fully committed to the strategy, their commitment and enthusiasm for it will wane. Staff must believe that implementing the strategy is one of the organisation's top priorities. From the time the strategy is developed, senior management must sell and continue to sell the strategy to the organisation and to the other stakeholders. They need to explain the vision and communicate the importance of the strategy for the future of the organisation.DEADL Y SIN SIXTHE 'BRICK WALLS' ARE NOT RECOGNISEDNothing ever goes exactly according to plan. Organisations operate in an ever changing and dynamic environment. It is important that those brick walls, which inevitably will be encountered along the way, are acknowledged and addressed. When those moments of crisis or uncertainty occur, staff should be encouraged to develop creative and innovative solutions to surmount these obstacles.DEADL Y SIN SEVENFORGETTING TO 'MIND THE SHOP'There is a risk that the process of developing and implementing strategy becomes theconsuming concern of senior management. They forget that they have a business to run, targets to meet, a service to provide and customers to serve. Both management and staff must believe that implementing the strategy is as important as doing the day job. One is not more important than the other and the strategy, if it is relevant and meaningful, should become an integral part of the day job.Shareholders will not thank senior management for developing and implementing a very well crafted strategy while at the very same time, letting profitability fall significantly or customer service to deteriorate.It is important that strategy is a continuous activity and not a once-off event. Periodic checks are necessary. Check that the assumptions are still valid. Identify and anticipate events or developments, both internal and external, which may require a revision or addition to the strategy. Make the changes quickly and communicate them to all concerned; however make sure that the changes are really required and the strategy is not being adjusted in a frivolous manner.Strategy implementation is always going to be difficult and fraught with danger of being abandoned through inertia or resistance. Change is never easy. However, the task of putting strategy to work can be made much easier and have greater chances of success by avoiding the seven deadly sins outlined above.。

1.FrameworkThe value chain describes the activities within and around an organisation that create a product or service.The value chain provides a framework for analysing an organisation by breaking it down into"strategically significant"activities that add value to the product or service in the eyes of the customer.2.Activities2.1.Primary Activities*Primary activities directly create or deliver a product or service.(a)Inbound logistics are activities concerned with receiving,storing and distributing inputs to the product or service including materials handling, inventory control,transport,etc.(b)Operations transform these inputs into the final product or service (e.g.machining,packaging,assembly,testing,etc)。
(c)Outbound logistics collect,store and distribute the product to customers(e.g.warehousing,materials handling,distribution,etc)。

ACCAP3知识点总结ACCAP3是ACCA(特许公认会计师)课程的第三阶段,在ACCA考试的过程中是非常重要的一个阶段。
在这个阶段,学员需要掌握更加深入复杂的会计知识,具备扎实的专业能力和解决问题的能力。
以下是ACCAP3的知识点总结:1.管理会计管理会计是指为企业内部管理决策服务的会计。
在ACCAP3课程中,学员需要掌握管理会计的基本概念和技巧,包括成本-收益分析、成本分类、成本控制、绩效评估等方面的知识。
此外,学员还需要了解现代管理会计技术的应用,如活动基础成本管理、质量成本管理、目标成本管理等。
2.管理决策管理决策是管理会计的核心内容之一,涉及企业内部各个方面的决策。
在ACCAP3课程中,学员需要掌握管理决策的基本原理和方法,包括差异分析、边际成本、机会成本等概念。
此外,学员还需掌握现代管理决策模型的应用,如线性规划、灵敏度分析、风险分析等。
3.财务管理财务管理是企业财务决策的核心内容,包括资金管理、投资管理、风险管理等方面。
在ACCAP3课程中,学员需要掌握财务管理的基本原理和技巧,包括财务报表分析、资本预算、财务风险管理等。
此外,学员还需了解国际财务管理的相关规范和标准,如国际金融报告准则(IFRS)。
4.企业战略企业战略是企业长期发展的规划和决策,包括市场定位、竞争战略、资源配置等方面。
在ACCAP3课程中,学员需要掌握企业战略的基本概念和方法,包括SWOT分析、价值链分析、波特五力分析等。
此外,学员还需了解战略规划的实施过程和方法,如平衡计分卡、战略地图等。
5.风险管理6.企业伦理企业伦理是企业社会责任的核心内容,包括企业与员工、客户、股东、社会等各方面的道德义务。
在ACCAP3课程中,学员需要掌握企业伦理的基本原则和规范,包括公平、诚信、责任等。
此外,学员还需了解企业伦理的实施要求和方法,如道德决策模型、伦理审计等。
P3 走近60分 ( Final review of knowledge & Skill Part)1.Strategy can be defined as:‘the direction and scope of an organisation over the long-term, which achieves advantage in a changing environment through its configuration of resources and competences with the aim of fulfilling stakeholder expectations’.CAI’s selection 12. Major TypesStrategic planning involves formal analysis of each of the stages of strategic position before a final strategic choice is made. Strategic planning is useful because:•It forces managers to consider each stage of the strategic process•It forces managers to justify their actions•It forces managers to consider the effect of a strategy on all aspects of the business•It allows managers to be proactive rather than reactive.Emergent strategies involve no long-term strategic plan – in effect, making up the strategy as the organisation goes along. An emergent strategy is useful because:•It allows managers to quickly exploit changing circumstances•It is quicker and cheaper than strategic planning.CAI’s selection 23.Position,Choice,and actionUnder the rational planning model, there are a number of stages. Each of these will be discussed in more detail later in the notes.Stage 1 – Strategic Position1 Identify key stakeholders and their expectations.2 Develop long-term objectives to satisfy these stakeholder expectations.3 Calculate financial and nonfinancial ratios to show position of organisation.4 Identify core resources and competences within the organisation.5 Identify key factors changing the environment outside the organisation.6 Use SWOT analysis (also known as a corporate appraisal) to summarise the strategic position.Stage 2 – Strategic Choices1 Consider possible exit from existing industries.2 Consider diversification into new industries.3 Consider developing new competitive advantages.4 Consider entry into new markets.5 Consider development of new products.Stage 3 – Strategy into Action1. Evaluate above options and choose strategy to be followed.2. Implement any necessary changes in the organisation.3.This might involve changing processes, people etc.CAI’s selection 34.Model Johnson and Scholes – three lensesThis model argues that strategy can be set in different ways:•Strategy as experience.Here the strategy is basically repeating what has been done in the past.•Strategy as ideas.Here the strategy aims to encourage innovation. Culture will be very important here.•Strategy as design.Here the strategy is driven from the top in order to meet the objectives of the organisation. The process is very similar to that given earlier in this chapter.5.MODEL – Mendelow stakeholder mappingThere will always be a conflict of interest between what different groups want. For example giving employees better pay levels reduces the profit available for shareholders. Stakeholders can be divided into:•High Interest with High Power = Key players•Low Interest with High Power = Keep satisfied•High Interest with Low Power = Keep informed•Low Interest with Low Power = Minimal effort.Stakeholders matter because objectives should be geared towards the needs of those with high power. Stakeholders matter because any strategy followed will need to be acceptable to the key players and keep satisfied.CAI’s selection 46.Corporate governanceJohnson and Scholes suggest that corporate governance is about answering two questions:1. Who is the organisation there to serve (i.e. who are the key stakeholders?)?2. How should the priorities of the organisation be decided (i.e. should strategy e planned or should the organisation be opportunistic?)?Johnson and Scholes define the main ethical position for a company as: The extent to which an organisation will exceed its minimum obligations toshareholders.The four main ethical positions are:1. Short-term shareholder interest.2. Longer-term shareholder interest.3. Multiple stakeholder obligations.4. Shaper of society.7.Core values are the principles that guide the behaviour of an organisation.A mission statement explains to the external world and to those managers making strategic decisions inside the organisation, the basic principles theorganisation should be following.A mission statement will commonly contain the following:•Purpose of the organisation.•Overall strategy of the organisation.•The core values of the organisation.Supporters of mission statements claim they help:•Resolve stakeholder conflict.•To guide managers when setting strategy.•Communicate the values of the organisation to employees.•Help with marketing the organisation.CAI’s selection 58.MODEL – Charles Handy types of cultureOrganisational culture consists of the beliefs, attitudes, practices and customs to which people are exposed during their interaction with the organisation.•Power – Heavily centralised with few decision-makers. Allows quick responses to changes in the environment.•Role – Lots of formalised procedures. Can be very useful in an environment that is stable.•Task – Emphasis on getting the job done rather than following rules. Works well in complex, unstable environments.•Person – Purpose is purely to look after the individuals (found where self-employed people are the norm).This may impact on whether a strategy chosen by the Directors is likely to be accepted by the employees.9.MODEL – Miles and Snow – Strategic cultures•Defenders – like strategic options that have worked in the past / low risks / secure markets.•Prospectors – like options that could deliver results even if they entail high risk.•Analysers – will move into new areas but only after someone else has proved they work.•Reactors – do not plan ahead.•The above may impact on the type of decisions made by the organisation.10.MODEL – Johnson and Scholes the cultural web•Rituals and routines – Which procedures are emphasised?•Symbols – Are status symbols used within the organisation as rewards?•Control systems – What is most closely monitored?•Organisational structures – How tall / flat is the organisation?•Power structures – How much centralisation is there?•Stories – Does news within the organisation focus on successes or failures?•The paradigm – What assumptions are taken for granted?CAI’s selection 611.Model – Johnson and Scholes Key drivers of change•Market globalisation•Cost globalisation•Global competition.In addition to the above, if you have a UK company, use:•Economic – conditions as they are at the time of the exam.•Environmental – the move towards more environmentally friendly products (this includes things like materials and packaging).•Legal – minimum wage for unskilled labour.12. MODEL – PESTEL•Political – includes government policies on education and infrastructure.•Economic – includes the state of the economy, interest rates and tax levels.•Social – includes attitudes, demographics and household structure.•Technological – includes new technologies making current products obsolete.•Environmental – includes the move towards environmentally cleaner products.•Legal – includes changes in law making it e.g. harder / more expensive to operate.CAI’s selection 713.Scenario planning•These methods look at what might happen (scenarios) and then decide what the organisation should do if they occur.14.Time Series AnalysisTime Series Analysis is used when sales tend to be seasonal. The time series is made up of two parts:•The long-term trend (calculated using moving averages).•The seasonal variation (calculated as the average of actual figures against the trend).Regression Analysis is used when sales tend to be steady throughout the year.15.MODEL – Porter’s national diamondCompanies based in certain countries seem to be more competitive than companies from other countries. Porter’s diamond looks at why.Porter comes up with 4 reasons for this:•Factor conditions•Firm strategy, structure and rivalry•Demand conditions•Related and supporting industries.CAI’s selection 816.Industries LifecycleIndustries grow and then shrink over time. It is important for a company to consider which industries it is involved in so that it can deliver profits to shareholders over the long-term. The stages the industry goes through are:Introduction•The industry is only just being established.•The industry may be seen as a niche.•At this point there may be only a few competitors (or maybe only one).•Customers may not be entirely sure why they need the product.Growth•An increasing number of customers start to buy the product and reasonable profits can be made.•The industry becomes more attractive and new competitors attempt to join.Maturity•The industry typically goes through a period of consolidation.•Weaker companies might leave.Decline•Customers are buying different products and so total sales are falling.•The industry may again become a niche.•As part of its corporate strategy, a company should regularly review the industries it is in to decide whether to:•Exit from existing industries.•Enter into new ones.CAI’s selection 917.Porter’s 5 forcesPorter’s 5 forces model looks at why some industries might be more profitable than others. In general the more of the forces that are favourable within an industry the more profits will be earned. Unfortunately as the industry becomes more attractive then more rivals will want to enter it.The 5 forces are:•Competitors (new)•Competitors (existing)•Customers•Suppliers•Substitutes.18.MODEL – The marketing mix•Product – What the customer receives•Price – the Cost to the customer•Place – the convenience to the customer•Promotion – how does the company Communicates with the customer19.CSF & KPICritical success factors are those elements that an organisation must perform properly in order to succeed. These often link with competences.•Threshol d competence•Core competen ces.CAI’s selection 10A common way of thinking about KPI’s is to group them into various categories. One common approach is to use:•Econo my – the amount spent on inputs (materials, labour, marketing etc).•Effectiveness – whether customers are satisfied with the products / services provided (customer satisfaction, repeat customers etc).•Efficiency – how good the organisation is at turning inputs into outputs (wastage, idle time etc).20.MODEL – the nine M’s modelThis model gives nine possible areas an organisation might be strong in•Machinery•Money•Materials•Men and Women•Makeup (culture)•Markets (products)•Management information•Management•Methods (processes).In the exam, look at the numbers that the Examiner gives you (particularly ones that do not fit into Financial Accounting areas). These often indicate weaknesses. Examples could include:•Sales per employee•Age of machinery•Time taken to process orders.CAI’s selection 1121.Cost controlOne common threshold competence in the exam is cost control.This is important to public sector organisations as they may have a fixed income.This is important to companies as they are trying to make a profit. If costs increase then either they have to accept lower profits or attempt to pass this on to customers through higher prices. The likelihood of costs rising will be affected by the power of the organisation’s suppliers.The possibility of raising sales prices will be affected by the power of customers. Costs could be reduced through:•Economies of scale•Low supply costs•Sensible design•Experience.CAI’s selection 1222.Sustainable competitive advantageSustainable competitive advantage is about the reasons a customer buys from one firm rather than another.The key word here is “sustainable”, a resource may give an organisation an advantage in the short-term but this will not be sustainable if it is easy for competitors to acquire as well.Similarly a competence that can easily be copied by others will only give a short-term advantage.Sustainable competitive advantage will need to focus on resources and capabilities which are:•Rare (this could include patents or a skill).•Robust (things that are difficult to imitate). Examples include:o Complex procedureso Uncertainty to outsiders.•Difficult for a customer to substitute with somethi• A final thing to remember is that the customer must be willing to pay for this unique resource or core competence.CAI’s selection 1323.MODEL – Porter’s value chainPorter divides a business into nine different areas. The five primary activities are:•Inbound logistics•Operations•Outbound logistics•Marketing and sales•Service.The four secondary activities are:•Firm infrastructure•Human Resource Management•Technology Development•Procurement.Porter argues that each cost in the business is one of two types.•Value-adding – the extra cost is outweighed by the extra the customer is willing to pay•Non value-adding – the extra cost is not valued by the customer.CAI’s selection 1424.Knowledge managementThe knowledge that an organisation has is a resource that may be difficult for other organisations to acquire and so can be a source of competitive advantage.For this to happen the organisation must record the knowledge of its employees and make it available to others.Knowledge management is the collective and shared experience accumulated through systems, routines and activities of sharing across the organisation.25.MODEL – Nonaka and Takeuchi on tacit and explicit knowledgeTacit knowledge is knowledge that staff possess. They are often unaware of how important this knowledge is. Explicit knowledge is knowledge that has been recorded by the organisation.Nonaka and Takeuchi say knowledge can be transferred by:•Socialisation•Externalisation•Internalisation•Combination.CAI’s selection 1526.SWOTOnce the organisation has analysed the external and internal environments it should be able to identify:•Strengths•Weaknesses•Opportunities•Threats.It is important to remember that strengths and weaknesses are in the eye of the customer not the company.It is important to remember in the exam that opportunities and strengths need to match up. If there is an opportunity for which the organisation does not have a matching strength – then the organisation will not be able to exploit the opportunity.Strategic capability can be improved by:•Extending competences•Ceasing nonessential activities•Extending best practices•Adding or improving activities•Remedying weaknesses.CAI’s selection 1627.Benchmarking•Historical comparisons are made between actual and past figure to see if the organisation is improving / deteriorating.•Strategic– comparisons are made between actual and budget (note that the budget should be set at a level so that meeting the budget should mean the critical success factor is achieved).•Industry – comparisons are made between actual and performance of others to see if we are performing better or worse than our rivals (this will identify strengths and weaknesses).28.Balanced scorecardAll processes must be as efficient and effective as possible in order to support the strategy. This means the organisation will need some method of measuring performance. One common method is to use the balanced scorecard. Processes can be measured to see if they are helping the following perspectives:•Financial•Customers•Internal business•Innovation and learning.CAI’s selection 1729.MODEL – Ansoff’s growth vector matrixIgor Ansoff came up with a simple method of identifying strategic options. The areas for a business to consider are:•Should they carry on selling their existing products?•Should they carry on selling to their existing market (this means the types of customer they already target)?Ansoff comes up with four possibilities:•Market penetration – existing products and existing markets•Market development – existing products and a new market•Product development – new products and an existing market•Diversification – new products to a new market.30.Methods?We will look at all of these in turn in this sectioWhichever of these is chosen there is an additional decision to be made. Should the organisation:•Grow organically – should the organisation launch a new product / go into a new market themselves?•Grow by acquisition – should the organisation buy another company that sells a new product / operates in a different market?A company can attempt to enter a foreign market in a number of ways. The main ones for a manufacturer are:Direct exporting – selling directly to overseas customers.•Advantages – the company gets to know the needs of the final customer•Disadvantages – it may be costly to build up customer awareness.Indirect exporting – selling to intermediaries such as retailers who then sell to final consumer.CAI’s selection 18•Advantages – the company gets access to the local company’s knowledge•Disadvantages – the company will not see all of the profits.Overseas production– the company manufactures and sells the products in the target country.•Advantages – distribution costs will be reduced•Disadvantages – may require a large capital investment.Contract manufacture (licensing) – the product is made abroad by another company.•Advantages – lower risk since no need to build manufacturing plant•Disadvantages – may lose control over areas such as quality.Joint ventures – the company goes into partnership with a local company.•Advantages – lower risk since local knowledge gained and costs shared•Disadvantages – lower returns since profits shared.CAI’s selection 1931.MODEL – Porter’s generic strategiesA further possibility would be to change HOW the company competes (the business strategy). This means changing the reason why customers should buy theproduct. Porter comes up with three possibilities:•Cost leadership•Product differentiation•Focussing on a particular type of customer.32.MODEL – The BCG matrixIn the exam you may have to calculate the market share of a product. If the information is available it would also be useful to calculate profit margins for each product.•Cash cows are in the mature or decline stage of the life cycle:o The threat of new competitors is low and the high market share makes the threats from substitutes and existing competitors low as well.o This product should be earning reasonable profits.o The product cannot grow any further (since the market is already mature).•Stars also have a high market share:o The market is growing (introduction or growth stage of the lifecycle) so new competitors will be attracted into the marketo Prices may need to be kept low to maintain market shareo Marketing costs might also need to be high to keep sales upo Profits may not be high.•Question marks have a lot of potential due to the high growth. Decision is whether to:o Spend money to build up market shareCAI’s selection 20o Spend money to hold market shareo Leave market.•Dogs have low market share and low growth. They should be closed unless needed by one of the other products.33.Related diversificationRelated diversification (also known as concentric diversification) means moving into areas that are similar to those the business already operates in.The idea is use the current strengths of the company to exploit new opportunities. In the exam look for examples of:•Horizontal integration – e.g. a shirt manufacturer that starts manufacturing shoes•Backwards integration – e.g. a shirt manufacture that starts manufacturing cloth•Forwards integration – e.g. a shirt manufacturer that starts retailing clothes.CAI’s selection 2134.Model Johnson and Scholes strategic rationale•P ortfolio Managers•Synergy managers•Parental developers35.Ashridge ModelThe four groups are:•High Feel / High BenefitHeartland businesses which gain most benefit from the attention of the parent (concentrate on these).•High Feel / Low BenefitBallast businesses which would be just as viable if they were independent businesses (so leave these ones alone to run themselves).•Low Feel / High BenefitValue Trap businesses which do not have much overlap with the skills of the parent (these may have been acquired as a method of unrelateddiversification). Unless the parent can develop these skills the business may not be of much benefit.•Low / Feel / Low BenefitAlien businesses which should be sold off.From this follows the idea that the amount of cost being spent by the parent should reflect the value it adds to the divisions.CAI’s selection 2236.Model – Johnson and Scholes SFA testJohnson and Scholes suggest that for any option to be considered seriously it must pass three tests. The option must be:•Suitable•Feasible•Acceptable.A strategic option is suitable if:•It builds on strengths/ reduces weaknesses / exploits opportunities / avoids threats.•Gives a new competitive advantage / maintains an existing one.•Suits the organisation’s culture .•It fits with the current strategies already being aA strategic option is feasible if:•The organisation has enough finance to pursue it.•The organisation has the rights skills / knowledge / experience to pursue it.•The company will be able to deal with any responses from competitors.•The company has enough time to follow the strategy.A strategic option is acceptable if:•The additional reward if the strategy is successful is greater than the risk if it is unsuccessful.•The additional risk is acceptable to shareholders / banks etc.•It helps the company to meet its financial objectives (ROCE etc) – shareholders.•Any interest payments will be maintained – banks.•It does not break any regulations – government.•It does not adversely affect connected stakeholders – customers / suppliers.CAI’s selection 2337.Financial RatiosThe following are common causes for ADVERSE variances;•Materials price Powerful supplier Change of supplier•Materials usage Poor quality material•Labour rate Powerful supplier•Labour usage Poor quality labour•Overhead efficiency Poor levels of maintenance•Sales price Powerful customersMany substitutes•Sales volume Sales lost to new entrantsMany competitorsCAI’s selection 2438.Decision treeA decision tree is another quantitative method for looking at uncertainty.A decision tree is a diagrammatic approach to solving problems involving probabilities and decision making.MethodStep1: Draw the tree from left to right showing appropriate decisions andUsefor a decision point,and an outcome point.Label tree and cash inflows/outflows and probabilities associated with outcomes.Step2: Evaluate the tree from right to left.•Calculate an expected value at each outcome point.•Select the option to maximise expected payoff at each decision point.Step3: Recommend a course of action to management.CAI’s selection 2539.Model Harmon’s process-strategy matrixThere are four approaches to change depending on:•Is the pro cess strategically important? (does it tie up with SWOT); and•Is the proces s complex?This leads to•High importance / complex Improve processes focusing on staff•High importance / simple Use an automated ERP solution•Low importance / complex Outsource•Low import ance / simple Automate.40.OutsourcingIt will often be more efficient to outsource these since the outsourcing company can obtain economies of scale.Problems with outsourcing processes include:•Fragmentat ion of complex processes (outsourcers can only do part of the process).•Concerns with relying on others for key business processes.•Concerns about quality.•Unwillingness to be locked into long-term contracts.41.Evaluating Business ProcessesProcess improvement methods•Lean proce sses – eliminate nonvalue adding activities or time between activities.CAI’s selection 26•Human perfor mance analysis – redesign incentives, improve training.Process redesign methods•Automa te activities.•Integrate processes – to reduce gaps and disconnects.•Process Measu rement schemes – develop or redesign the way performance ids measured.42.Model – Skidmore and Eva – stages in selecting software package•The company may decide to have a software package written especially (known as a bespoke package). There are five stages the company goes through:•Obtain tenders•First pass selection•Second pass selection•Implementation•Managing long-term relationship.CAI’s selection 2743.6C- the benefits of E-businessThe above definition does NOT mean that goods / services have to be sold to customers over the internet – this is referred to as ecommerce. Benefits of adopting e-business include:•Cost reduction•Capability•Communication•Control•Customer service•Competitive.44.Model – McFarlan’s gridMcFarlan’s grid looks at how important IT is to the organisation, in particular, how it can help with the organisation’s strategy.•The impact of current IT systems on gaining an advantage.•The potential impact of future IT systems on gaining an advantage.1. Current Low / Future low SupportIT is useful but no advantage is being achieved (e.g. payroll).2. Current High / Future low FactoryIT is crucial to the current operations but it is unlikely that it can be developed further to give an advantage in the future( e.g. a JIT system).CAI’s selection 283. Current Low / Future High TurnaroundIT can be used to develop new advantages over the long-term (e.g. Amazon’s Kindle e-reader and store).4. Current High / Future High StrategicIT will be fundamental to the ongoing success of the business.45.Model 6i’s for emarketing1 Interactivity – Customers can be asked for contact details.2 Integration – Adverts on the web can be clicked to go straight to purchasing.3 Intelligence – websites can record how many visitors they have and what they do on the website.4 Industry structure – Websites can change distribution channels (by cutting out intermediaries and selling direct).5 Independence of location.6 Individualisation – if a customer regularly visits a website it can be tailored to that individual.46.Model – Adcock’s guide to CRMCRM is the establishment, development, maintenance and optimisation of long-term mutually valuable relationships between consumers and organisations.CRM has many benefits including:•Improved retention•Improved cross-sellingCAI’s selection 29Improved profitability.In order to build relationships with customers, businesses need to:•Build a customer database•Develop customer oriented service systems•Have more direct contacts with customers.As part of this process, businesses should think about their long-term relationship with customers and what that is likely to be worth over the customer’s lifetime. CAI’s selection 30。
environmental and legal. It describes a framework of macro-environmental factors used in the environmental scanning component of strategic management.Political factors are basically how the government intervenes in the economy. Specifically, political factors has areas including tax policy, labourlaw, environmental law, trade restrictions, tariffs, and politicalstability.Economic factors include economic growth, interest rates, exchange rates, the inflation rate. These factors greatly affect how businesses operate and make decisions. (Interest rates impacts company's cost of capital, business growth and expands. Exchange rate impacts the cost, supply and price of imported goods.) Social factors include the cultural aspects and health consciousness, population growth rate, age distribution, career attitudes and emphasis on safety. Technological factors include technological aspectslike R&D activity, automation, technology incentives and the rateof technological change. These can determine barriers to entry, minimum efficient production level and influence the outsourcing decisions. Technological shifts would affect costs, quality, and lead to innovation.Legal factors include discrimination law, consumer law, antitrustlaw, employment law, and health and safety law. These factors can affect how a company operates, its costs, and the demand for its products.Environmental factors include ecological and environmental aspects such as weather, climate, and climate change, which may especially affect industries such as tourism, farming, and insurance.Porter's five forces analysis is a framework for analyzing the level of competitionwithin an industry and business strategy development.Threat of new entrants:The existence of barriers to entry (patents, rights, etc.). Government disadvantages independent of of of product costs or sunk to loyalty to established profitability (the more profitable the industry the more attractive it will be to new competitors).Network effect.Threat of substitutes:Buyer propensity to price performance of switching level of product of substitute products available in the of of close substitute. Bargaining power of customers:Buyer concentration to firm concentration of dependency upon existing channels of leverage, particularly in industries with high fixed switching costs relative to firm switching information down of existing substitute price advantage (uniqueness) of industry (customer value) total amount of trading.Bargaining power of suppliers:Supplier switching costs relative to firm switching of differentiation of of inputs on cost and of substitute of distribution concentration to firm concentration solidarity . labor unions).Supplier competition: the ability to forward vertically integrate and cut out the buyer. Industry rivalry:Sustainable competitive advantage through between online and offline of advertising competitive concentration of transparency.The National Diamond is a tool for analyzing the organization’s task environment. The National Diamond highlights that strategic choices should not only be a function of industry structure and a firm’s resources. And this model states fou r principal determinants of national competitive advantage: a. Factor conditions b. Firm strategy structure and rivalry c. Demand conditions d. Related and supporting industriesa. Factor conditionsHuman Resources(skill,price)/ physical resources(land,climate,location relative)/knowledge (科技, educational institution)/capital(investment)/infrastructure(transport, communication, housing)b. Firm strategy structure and rivalryNational performance in particular sectors is inevitably related to the strategies and the structure of the firms in that sector. Competition plays a big role in driving innovation and the subsequent upgradation of competitive advantage. Since domestic competition is more direct and impacts earlier than steps taken by foreign competitors, the stimulus provided by them is higher in terms of innovation and efficiency.c. Demand conditionsDemand conditions in the domestic market provide the primary driver of growth, innovation and quality improvement.d. Related and supporting industriesFor many firms, the presence of related and supporting industries is of critical importance to the growth of that particular industry. A critical concept here is that national competitive strengths tend to be associated with "clusters" of industries.Besides above four factors, chance and government always are the essential elements impacting on four principal determinants of national competitive advantage. OpportunitiesOpportunities always are hard to come by and uncontrollable, hence once facing a chance, we will firmly grasp. Under this new era, polity, economy and various factors bring a great deal of opportunities, and the more fierce competition also bring more chances.Government"acting as a catalyst and challenger; it is to encourage - or even push - companies to raise their aspirations and move to higher levels of competitive performance …" . They must encourage companies to raise their performance, stimulate early demand for advanced products, focus on specialized factor creation and to stimulate local rivalry by limiting direct cooperation and enforcing anti-trust regulations.The Boston classification classifies business units in terms of their capacity for growth within the market and the market's capacity for growth as a whole. Assessing rate of market growth as high or low depends on the conditions in the market. High market growth rate can indicate good opportunities for profitable operations. Relative market share is assessed as a ratio: it is market share compared with the market share of the largest competitor.Stars require capital expenditure in excess of the cash they generate, in order to maintain their position in their competitive growth market, but promise high returns in the future. Strategy: buildCash cows need very little capital expenditure, since mature markets are likely to be quite stable, and they generate high level of cash income. Cash cows can be used to finance the stars. Strategy: hold or harvest if weak.Question marks must be assessed as to whether they justify considerable capital expenditure in the hope of increasing their market share. Strategy: build or harvestDogs: may be ex-cash cows that have now fallen on hard times. Although they will show only a modest net cash outflow, or even a modest net cash inflow, they are cash traps which tie up funds and provide a poor return on investment. Strategy: divest or holdSWOT analysis(alternatively SWOT matrix) is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats and is a structured planning method that evaluates those four elements of an organization, project or business venture.Strengths: characteristics of the business or project that give it an advantage over others.Weaknesses: characteristics of the business that place the business or project at a disadvantage relative to others.Opportunities: elements in the environment that the business or project could exploit to its advantage.Threats: elements in the environment that could cause trouble for the business or project.Customer relationship management (CRM) is an approach to managing a company's interaction with current and potential customers. It uses data analysis about customers' history with a company and to improve business relationships with customers, specifically focusing on customer retention and ultimately driving sales growth.The CAGE Distance Framework identifies Cultural, Administrative, Geographic andEconomic differences or distances between countries that companies should address when crafting international strategies.。
ACCA P3/P4考前重点公布,赶快收藏!来源:浦江财经ACCA P3 Exam TipsKaplanEmbed your knowledge on the core models from Johnson and Scholes (the examiner based this paper on their work).When answering questions, write answers like you are writing to your senior management. Make it as professional as possible. Marks are allocated to this in section A.Do not start writing answers straightaway. Take a minute to think about the structure and presentation of the answers.It is important with this level to remember that writing lots of knowledge and theory will not get you through the exam. The key is application to the material and expanding the relevance to the scenario.We suggest watching the news / reading the papers, but with a critical eye. For instance when you see that a business has launched a new product or moved into a new market think about the theories you have learnt that may be relevant. In this case it could be:-Porter’s generic strategies-Ansoff-Bowman’s clockThen apply those theories to the real life situation –understand why they have created this product/why they have gone into this market. With practice you will find it easier to apply the theories to the scenario.And of course you can do this for other areas of the syllabus.There is nothing worse for a marker than getting a script which is just a page of writing. Try to think about making your script easier to read for the marker. Headings and Sub-headings along with a bit of space will help. Then use your paragraph to explain the point you are making.If it is easy for the marker to see the points being made this can make the difference between pass and fail for a borderline script, include application, plus relevance within your statement, avoid listing.If you use the word ‘and’in your answer, are you making two separate points? If yes, maybe you need to split your paragraph into two headings / sub-headings.There are 3 professional marks which will constitute professionalism, presentation and layout.-Know the theory and apply it.-Create mind maps of the key knowledge, then learn these.-Do practice questions under timed conditions and if possible, get them marked.-Make sure you’ve read all the current examiner articles, available on the ACCA website.-Get good business awareness –read a quality newspaper.-Use the reading time to select questions, and get frameworks for answer plans.-Do a section B question first.-Don’t focus on the numbers –do not spend more than 15 minutes on them per question. -Watch the clock –allocate your time efficiently –don’t overrun.-Layout your answers in a way that the marker can clearly read and understand.-Read the question carefully!ACCA P4 Exam TipsKaplanP4 is a technical paper with some complex calculations sometimes but DO NOT think of the exam as numbers-only. There are plenty of discursive parts which are usually easier than the calculations and easy marks can be picked up by applying commercial awareness and common sense.Analyse the individual requirements of the question. If you can do the wordy bits first then do so as you will not get bogged down in them like you will with the calculation elements.Do not expect to finish a question. You must stick to time, especially on the calculations which are very easy to over-run on. The exam is extremely time pressured and the secret to passing is to have a go at every part of every question, not to try and get 100% on every question –to do that you would need about 7 hours!If you are not sure what to do with a particular figure in a question, ignore it and move on –state assumptions, you haven’t got time to worry about it!If you get a Black-Scholes question, always list out the input variables as your first stage and assign the relevant values to them –there will be about 2-3 marks usually for doing this.Practice as many questions as possible but do as many as possible to time. You must get used to doing the questions in the time available and not spending too long on them.Practice as many questions as possible across the syllabus, and don’t only concentrate on what you consider to be the core areas.Choose carefully on section B of the paper –it is very limited choice but nonetheless it will becritical.Do not put down unnecessary workings; because as it will cost you heavily in lost time.If there is a calculation that you are unable to complete –for e.g. a WACC which prevents you from going on to do the NPV, then just make a reasonable assumption and estimate a WACC which you have been unable to calculate, this will then allow you to progress the calculation and get on to the often more generously rewarded discursive parts of the question.Look out for examinable articles –two in particular for June 2011:-24 August –The new examiner Shishir Malde gives his approach for the P4 paper-23 September –Another article by the new examiner Shishir Malde on Risk Management January/February articleTwo key topics are always NPV appraisal and capital structure, particularly CAPM and Betas. You will not pass if that is all you know but you will struggle to pass if you do not know them!欲知后续P5-P7详情,敬请听下回浦江财经分解~各科目重要考点汇总:ACCA F5/F6考前重点公布请戳这里!ACCA F7/F8考前重点公布请戳这里!ACCA F9考前重点公布请戳这里!ACCA P1/P2考前重点公布请戳这里!浦江财经创立财经培训新标准,专业师资团队打造专业财经培训!。
20.Business process change●Business processesThe value chain analyses the organisation as a collection of activities, but these activities are also joined together in processes. “A process is a bounded set of activities that are undertaken, in response to some event, in order to generate an output” (Harmon) 价值链分析了公司是由一系列活动构成的,而这些活动也充斥在各个流程中。
Harmon定义:流程是一组能够为客户创造有价值的结果的相互关联的活动。
Organisations may seek to improve their processes in order to:提高流程是为了实现:✓reduce costs, particularly during an economic downturn降低成本,尤其经济衰退时✓provide a scaleable platform for expanding production, or entering new markets建立可拓展的平台,拓展生产或进入一个新市场✓offer better products or services in order to be more competitive提供更好的产品或服务,提高竞争力✓exploit opportunities offered by technology (e.g. cheaper communication)通过新技术开拓机遇✓execute a new strategic direction 实行新战略●Process – strategy matrixHarmon’s process‐strategy matrix uses two criteria to categorise processes, and the best approach to improving them:哈默的过程战略矩阵使用了2个要素来分类流程Complexity – simple processes are fairly straightforward, with clearly defined rules to follow and little change over time. Complex processes require high levels of judgement and may changefrequently.复杂性:单一的过程相对简单明了,长期来看变化也少;复杂的过程需要很高的自主判断,而且会频繁变化。
ACCA知识点:P3-Equity Share Capital本文由高顿ACCA整理发布,转载请注明出处1. Types1.1. Ordinary shares—this represents the permanent capital and is most common.Ordinary shares normally have a nominal value, which is the limit of the shareholder's liability to contribute to the debts of the company on an insolvent liquidation.As initial costs for issuing shares are relatively low, companies will seek to obtain as much share capital as possible.An existing company can increase its share capital through a rights issue. Where applicable, pre-emptive rights allow existing shareholders first refusal to acquire new shares issued by a company in a rights issue.1.2. Preference shares—these shares pay a fixed dividend:They were popular with UK "building societies" (but most of them are now listed on the London Stock Exchange).There is great diversity in the preferred share market but two key categories are cumulative and non-cumulative preference shares.1.3. Convertible loan stock—these are fixed-return securities, either secured or unsecured, which may be converted into ordinary shares at a later date:Prior to conversion, the holders have creditor status;Sometimes conversion price is increased to stimulate early conversion; andPart conversion is also possible, whereby only a portion of the stock is converted into shares, normally 50%.Advantages of convertible loan stock include:Obtaining finance at a lower rate than a debenture;Encourage investors with the prospect of future profits;and Deferred equity with a tax break.2 Raising Equity FinanceEquity finance can be raised by two general methods:a. Issuing new share capital.b. Reinvesting profits (retaining earnings) rather than paying out dividends.3 Issuing Share CapitalFor large companies, whose shares are listed on a stock market, new shares can be issued using a rights issue (i.e. to existing shareholders in proportion to their existing shareholdings). The rights issue is usually organised by an investment bank or other authorised financial institution.*4. Retained EarningsFew organisations pay out all of their profits as dividends, and retained profits are the most important source of equity finance. The decision about how much capital to retain is the complement of the dividend decision.5.Advantages and Disadvantages of Share CapitalShare capital is a low-risk source of finance as there is no legal requirement to pay dividends if profits are insufficient to do so. The higher the portion of share capital in a company's capital structure, the lower its gearing (i.e. less financial risk).Because share capital is a low-risk source of finance to the company, it is of high risk to shareholders. They will, therefore, expect a higher return in terms of dividends and growth in share price. It is an expensive source of finance. If shareholders do not obtain the returnthey require, they will sell their shares, which will push down the market price of the company. This may lead to dissatisfaction with the management of the company.更多ACCA资讯请关注高顿ACCA官网:。
20.Business process change●Business processesThe value chain analyses the organisation as a collection of activities, but these activities are also joined together in processes. “A process is a bounded set of activities that are undertaken, in response to some event, in order to generate an output” (Harmon) 价值链分析了公司是由一系列活动构成的,而这些活动也充斥在各个流程中。
Harmon定义:流程是一组能够为客户创造有价值的结果的相互关联的活动。
Organisations may seek to improve their processes in order to:提高流程是为了实现:✓reduce costs, particularly during an economic downturn降低成本,尤其经济衰退时✓provide a scaleable platform for expanding production, or entering new markets建立可拓展的平台,拓展生产或进入一个新市场✓offer better products or services in order to be more competitive提供更好的产品或服务,提高竞争力✓exploit opportunities offered by technology (e.g. cheaper communication)通过新技术开拓机遇✓execute a new strategic direction 实行新战略●Process – strategy matrixHarmon’s process‐strategy matrix uses two criteria to categorise processes, and the best approach to improving them:哈默的过程战略矩阵使用了2个要素来分类流程Complexity – simple processes are fairly straightforward, with clearly defined rules to follow and little change over time. Complex processes require high levels of judgement and may changefrequently.复杂性:单一的过程相对简单明了,长期来看变化也少;复杂的过程需要很高的自主判断,而且会频繁变化。
20.Business process change●Business processesThe value chain analyses the organisation as a collection of activities, but these activities are also joined together in processes. “A process is a bounded set of activities that are undertaken, in response to some event, in order to generate an output” (Harmon) 价值链分析了公司是由一系列活动构成的,而这些活动也充斥在各个流程中。
Harmon定义:流程是一组能够为客户创造有价值的结果的相互关联的活动。
Organisations may seek to improve their processes in order to:提高流程是为了实现:✓reduce costs, particularly during an economic downturn降低成本,尤其经济衰退时✓provide a scaleable platform for expanding production, or entering new markets建立可拓展的平台,拓展生产或进入一个新市场✓offer better products or services in order to be more competitive提供更好的产品或服务,提高竞争力✓exploit opportunities offered by technology (e.g. cheaper communication)通过新技术开拓机遇✓execute a new strategic direction 实行新战略●Process – strategy matrixHarmon’s process‐strategy matrix uses two criteria to categorise processes, and the best approach to improving them:哈默的过程战略矩阵使用了2个要素来分类流程Complexity – simple processes are fairly straightforward, with clearly defined rules to follow and little change over time. Complex processes require high levels of judgement and may changefrequently.复杂性:单一的过程相对简单明了,长期来看变化也少;复杂的过程需要很高的自主判断,而且会频繁变化。
Strategic importance – how much value does the process add to an organisation’s products and services. A high strategic importance process is a core competency and a source of competitiveadvantage. A low strategic importance process simply needs to be done so that a company can do something else that adds value.战略重要性:这个过程会给产品和服务增加多少价值?战略重要性高,意味着关系核心竞争力和竞争优势的资源。
对于低战略重要性的过程,公司宁愿做些其他事来提高价值。
Based on this, processes can be categorised as follows:a)Low complexity‐low strategic importance processes need to be carried out as efficiently as possiblebut there is little scope for improving them. These should be automated as far as possible usingstandard off‐the‐shelf software and may be best outsourced, e.g. purchase ledger.这类流程要提高效率,但提升空间可能不大,考虑自动化(现成软件/系统)或外包,比如财务记账。
b)Low complexity‐high strategic importance processes are key to the organisation’s success.Automation should be used to reduce costs and gain efficiency. We should also be aiming to improve these processes, e.g. product assembly. 此类流程对公司成败很重要。
自动化可以有助于降低成本,提高效率,比如产品装配。
c)High complexity‐low strategic importance these processes will cause problems they aren’t done butdon’t add much value. Because they are complex, they may be hard to automate. Organisations may decide to outsource these processes to a specialist, e.g. large‐scale logistics and distribution这类流程不做的话会对公司造成麻烦,但做了的话,价值也不大。
这类通常有专业技能要求,所以最好外包,比如物流。
d)High complexity‐high strategic importance These are critical and involve a lot of human expertise.These processes will be a priority for major improvements, e.g. negotiating partnerships, newproduct development对公司至关重要,需要经验判断和专业技能。
如何提升这些流程是首要考量,比如谈判的合伙关系,新产品开发等。
Tips: Bear in mind that the same process may be in a different category for different companies. For a company that provides payroll services, efficient and accurate payroll processing is a core competenceand key to competitive advantage, but it is unlikely to be strategically important for other organisations.同一流程在不同公司有不同的意义,比如对于专业提供薪酬服务的公司,有效率和精准的薪酬流程是核心竞争力,但对于其他公司而言,战略上就没这么重要。
●OutsourcingIf processes are outsourced to an external provider, this may bring the following benefits:✓The provider should have economies of scale which will lead to cost reductions利用他人的规模经济来达到降低成本的目的✓Management time is freed up to focus on core competencies 集中精力提高核心竞争力✓The specialist provider may bring greater expertise than the organisation can supply internally 借助外包商的专家专业技能>胜于自己内部的能力On the other hand, some of the problems with outsourcing are:✓It leads to a reduction of control, particularly in relation to quality. Firms try to mitigate this by having clear service level agreements in place and devoting resources to relationship management失去控制,尤其是质量方面。
企业要有明确的服务水平协议来缓解这一关系,并将资源投入到关系管理中去。
✓Firms may be tied in to long‐term contracts and find it hard to change suppliers even if their supplier is unsatisfactory可能存在长期合同,即使不满意也很难轻易更换供应商✓Outsourcing can mean a firm loses competencies and becomes dependent on suppliers, giving them increased bargaining power even when the contract ends公司这方面能力不足,过度依赖供应商,提高对方议价能力Tips: When processes are outsourced they cannot be a basis of competitive advantage as any companycan use the same provider. These processes therefore become commodities and companies need to focus on their truly core processes.当流程外包时,它们不能成为公司竞争优势的基础,任何公司都可以使用相同的供应商来获得这种能力。