Element_Period_Table-元素周期表
- 格式:xls
- 大小:35.00 KB
- 文档页数:1
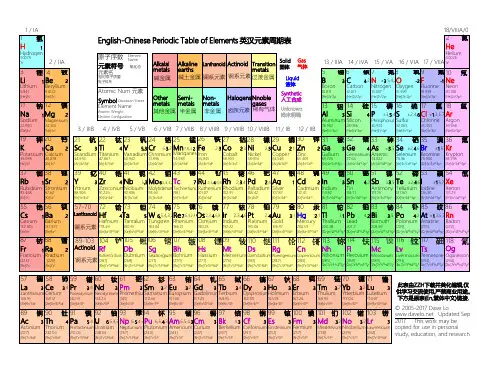

元素周期表的构成和规律一、元素周期表的构成1.元素周期表是一个表格,其中横向称为周期,纵向称为族。
2.周期表中的元素按照原子序数递增排列,原子序数相同的元素位于同一周期。
3.周期表共有7个周期,从第1周期到第7周期,周期数越大,元素的原子序数越大。
4.周期表共有18个族,包括7个主族、7个副族、1个0族和1个第Ⅷ族。
5.主族元素包括第1A到第7A族,副族元素包括第1B到第7B族,0族元素为稀有气体,第Ⅷ族元素为过渡金属。
二、元素周期表的规律1.周期规律:同一周期内,元素的原子半径随着原子序数的增加而减小;元素的金属性随着原子序数的增加而减弱,非金属性随着原子序数的增加而增强。
2.族规律:同一族元素具有相似的化学性质,族数相同的元素具有相同的最外层电子数。
3.电子层数规律:元素周期表中,电子层数等于周期数。
4.价电子规律:元素的价电子数等于其族序数。
5.原子半径规律:同一主族元素,原子半径随着周期数的增加而增大;同一周期元素,原子半径随着族序数的增加而增大。
6.金属性和非金属性规律:同一周期内,金属性随着族序数的增加而减弱,非金属性随着族序数的增加而增强;同一族内,金属性随着周期数的增加而增强,非金属性随着周期数的增加而减弱。
7.化合价规律:主族元素的化合价等于其最外层电子数;副族元素的化合价较为复杂,具有一定的可变性。
三、重要概念1.原子序数:元素在周期表中的序号,等于其核内质子数。
2.电子层:原子中电子分布的层次,等于元素周期表中的周期数。
3.价电子:原子最外层参与化学反应的电子数,等于元素周期表中的族序数。
4.主族元素:周期表中第1A到第7A族和第1B到第7B族的元素。
5.副族元素:周期表中第1B到第7B族的元素(除主族元素外)。
6.过渡金属:周期表中第Ⅷ族的元素。
7.稀有气体:周期表中0族的元素,具有稳定的电子层结构。
元素周期表是化学中的重要工具,通过其构成和规律,我们可以了解元素的性质、预测化学反应等。
镧系57 La镧5d16s2138.958 Ce铈4f15d16s2140.159 Pr镨4f36s2140.960 Nd钕4f46s2144.261 Pm钷4f56s2〔145〕62 Sm钐4f66s2150.463 Eu铕4f76s2152.064 Gd钆4f75d16s2157.365 Tb铽4f96s2158.966 Dy镝4f106s2162.567 Ho钬4f116s2164.968 Er铒4f126s2167.369 Tm铥4f136s2168.970 Yb镱4f146s2173.071 Lu镥4f145d16s2175.0锕系89 Ac锕6d17s2〔227〕90 Th钍6d27s2232.091 Pa镤5f26d17s2231.092 U铀5f36d17s2238.093 Np镎5f46d17s2〔237〕94 Pu钚5f67s2〔244〕95 Am镅*5f77s2〔243〕96 Cm锔*5f76d17s2〔247〕97 Bk锫*5f97s2〔147〕98 Cf锎*5f107s2〔251〕99 Es锿*5f117s2〔252〕100 Fm镄*5f127s2〔257〕101 Md钔*5f137s2〔258〕102 No锘*5f147s2〔259〕103 Lr铹*5f146d17s2〔262〕/'silv ə(r)//'læθənaid//'haidr əd ʒən/氢/'li θi əm/锂/b ə'rili əm/铍/'b ɔːr ɒn/硼/'k ɑːb ən/碳/'naitr əd ʒən/氮/'ɒksid ʒən/氧/'hi ːli əm/氦/'ni ːɒn/氖/'fl ɔːri ːn/氟/ælj ə'mini əm/铝/'silik ən/硅 /'f ɒsf ər əs/磷/‘s ʌlf ə(r)/硫/'kl ɔːri ːn/氯/’ɑːg ɒn/氩 /‘gæli əm/镓/d ʒɜː'meini əm/锗 /'ɑːsnik/砷/s ə'li ːni əm/硒/'br əʊmi ːn/ 溴/'kript ɒn/氪/'indi əm/铟/tin/锡/'æntim əni/锑 /'telj ʊəri əm/碲 /'ai ədi ːn/碘/'zen ɒn/氙/'θæli əm/铊/li ːd/铅/'bizm əθ/铋/'p əl əʊni əm/钋/'æst əti ːn/砹/'reid ɒn/氡/'s əʊdi əm/钠/mæg'ni ːzi əm/镁/p ə‘tæsi əm/钾/'kælsi əm/钙/'skændi əm/钪/ti'teini əm/钛/v ə'neidi əm/钒/'kr əʊmi əm/铬/'mæŋg əni ːz/锰/ai ən/铁/'k əʊb ɔːlt/钴/'nikl/镍/'k ɒp ə(r)/铜 /zi ŋk/锌/r ʊ'bidi əm/铷/'str ɒnti əm/锶/'itri əm/钇/z ɜː'k əʊni əm/钇/nai'əʊbi əm/铌/m ə'libd ən əm/钼/tek'ni ːʃɪəm/锝/ru ː'θi ːni əm/钌/'r əʊdi əm/铑/p ə'leidi əm/钯/'kædmi əm/镉/'m ɜːkj əri/汞/g əʊld/金/'plætin əm/铂/I'ridi əm/铱/'ɒzmi əm/锇/'ri ːni əm/铼/'t ʌŋst ən/钨/'tænt əl əm/钽/'hæfni əm/铪 /'silv ə(r)/银 /'læn θənaid/镧/'be əri əm/钡/'si ːzi əm/铯/'frænsi əm/钫/'reidi əm/镭/æk'tini əm/锕/'læn θən əm/镧/'si əri əm/铈/preizi əʊdimi əm/镨/ni ːəʊ'dimi əm/钕/pr ə'mi ːθi əm/钜/s ə'me əri əm/钐/j ʊər'əʊpi əm/铕/gæd ə'lini əm/钆/'t ɜːbi əm/铽/dis'pr əʊzi əm/镝/dis'pr əʊzi əm/镝 /'ɜːbi əm/铒 /'θu ːli əm/铥/i't ɜːbi əm/镱/lu ː'ti ːʃi əm/镏/æk'tini əm/锕/'θɔːri əm/钍/pr əʊtæk'tini əm/镤/ju'reini əm/铀/'ælk əlai/ 碱金属/'ælk əlain/ 碱土金属金属/'metl ɔɪd/类金属非金属/'hæl əd ʒən/ 卤素/'n əʊbl/ 稀有气体/'læn θənaid/ or /æk'tinaid/ 稀土元素NOBLE GASES1H 1.008Hydrogen1s1Oxidation States Electroneg.12.2Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 37–Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.7513.603Li 6.94Lithium 1s 22s 1Oxidation States Electroneg.10.98Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 152(+1)76Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.62 5.394Be 9.01Beryllium1s 22s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.2 1.57Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 111(+2)45Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.Unstable Anion 9.3212Mg 24.31Magnesium [Ne]3s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.2 1.31Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 160(+2)72Electron Affinity1st Ion. Pot.Unstable Anion 7.6521Sc 44.96Scandium [Ar]3d 14s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3 1.36Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 161(+3)75Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.19 6.5639Y 88.91Yttrium [Kr]4d 15s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3 1.22Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 178(+3)102Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.31 6.2257La 138.9Lanthanum [Xe]5d 16s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3 1.10Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 187(+3)116Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.5 5.7789Ac 227Actinium [Rn]6d 17s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3 1.1Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 188(+3) -Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 5.17104Rf 261Rutherfordium [Rn]5f 146d 27s 2disc.1964105Db 262Dubnium [Rn]5f 146d 37s 2disc.196758Ce 140.1Cerium [Xe]4f 15d 16s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3,4 1.12Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 183(+3)114Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 5.5459Pr 140.9Praseodymium [Xe]4f 36s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3,4 1.13Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 182(+3)113Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 5.4660Nd 144.2Neodymium [Xe]4f 46s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3 1.14Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 181(+3)114Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 5.5361Pm 145Promethium [Xe]4f 56s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3–Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 181(+3)109Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 5.5562Sm 150.4Samarium [Xe]4f 66s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3,2 1.17Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 180(+3)108Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 5.6463Eu 152.0Europium [Xe]4f 76s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3,2–Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 199(+3)107Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 5.6764Gd 157.3Gadolinium [Xe]4f 75d 16s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3 1.20Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 179(+3)105Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 6.1565Tb 158.9Terbium [Xe]4f 96s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3,4–Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 176(+3)118Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 5.8666Dy 162.5Dysprosium [Xe]4f 106s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3 1.22Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 175(+3)103Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 5.9467Ho 164.9Holmium [Xe]4f 116s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3 1.23Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 174–Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 6.0268Er 167.3Erbium [Xe]4f 126s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3 1.24Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 173(+3)100Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 6.1169Tm 168.9Thulium [Xe]4f 136s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3,2 1.25Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 173(+3)109Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 6.1870Yb 173.0Ytterbium [Xe]4f 146s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3,2–Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 194(+3)99Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 6.2571Lu 175.0Lutetium [Xe]4f 145d 16s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3 1.0Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 172(+3)98Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 5.4390Th 232.0Thorium [Rn]6d 27s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.4 1.3Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 180(+4)94Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 6.0891Pa 231.0Protactinium [Rn]5f 26d 17s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.5,4 1.5Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 161(+5)78Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 5.8992U 238.0Uranium [Rn]5f 36d 17s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.6,5,4,3 1.7Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 139(+6)73Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 6.1993Np 237Neptunium [Rn]5f 46d 17s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.6,5,4,3 1.3Atomic Radius Ionic Radius –(+5)75Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 6.2794Pu 244Plutonium [Rn]5f 67s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.6,5,4,3 1.3Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 151(+4)86Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 6.0695Am 243Americium [Rn]5f 77s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.6,5,4,3–Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 131(+3)98Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 5.9996Cm 247Curium [Rn]5f 76d 17s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3–Atomic Radius Ionic Radius –(+3)97Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 6.0297Bk 247Berkelium [Rn]5f 97s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.4,3–Atomic Radius Ionic Radius –(+3)96Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 6.2398Cf 251Californium [Rn]5f 107s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3–Atomic Radius Ionic Radius –(+3)95Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 6.3099Es 252Einsteinium [Rn]5f 117s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3–Atomic Radius Ionic Radius ––Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 6.42100Fm 257Fermium [Rn]5f 127s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3–Atomic Radius Ionic Radius ––Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 6.50101Md 258Mendelevium [Rn]5f 137s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3,2–Atomic Radius Ionic Radius ––Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 6.58102No 259Nobelium [Rn]5f 147s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3,2–Atomic Radius Ionic Radius ––Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 6.65103Lr 262Lawrencium [Rn]5f 146d 17s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.3–Atomic Radius Ionic Radius ––Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.––106Sg 266Seaborgium [Rn]5f 146d 47s 2disc.1974107Bh 264Bohrium [Rn]5f 146d 57s 2disc.1981108Hs 269Hassium [Rn]5f 146d 67s 2disc.1984109Mt 268Meitnerium [Rn]5f 146d 77s 2disc.1982110Ds 281Darmstadtium [Rn]5f 146d 97s 1Darmstats, Germany111Uuu 272Unununium disc.1994Darmstats, Germany 112Uub 277Ununbium disc.1996Darmstats, Germany 113Uut 284Ununtrium disc.2004Dubna, Russia 114Uuq 289Ununquadium disc.1999Dubna, Russia 115Uup 288Ununpentium disc.2004Dubna, Russia 116??Notdiscovered - -117??Notdiscovered --118??Notdiscovered - -72Hf 178.5Hafnium [Xe]4f 145d 26s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.4 1.3Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 156(+4)83Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.~0 6.8373Ta 180.9Tantalum [Xe]4f 145d 36s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.5 1.5Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 143(+5)64Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.327.8974W 183.8Tungsten [Xe]4f 145d 46s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.6,5,4,3,2 1.7Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 137(+6)60Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.867.9875Re 186.2Rhenium [Xe]4f 145d 56s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.7,6,4,2,-1 1.9Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 137(+7)53Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.157.8876Os 190.2Osmium [Xe]4f 145d 66s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.2,3,4,6,8 2.2Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 134(+4)63Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.1.108.777Ir 192.2Iridium [Xe]4f 145d 76s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.2,3,4,6 2.2Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 136(+4)63Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.1.579.178Pt 195.1Platinum [Xe]4f 145d 96s 1Oxidation States Electroneg.2,4 2.2Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 139(+4)63Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.2.139.079Au 197.0Gold [Xe]4f 145d 106s 1Oxidation States Electroneg.3,1 2.4Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 144(+3)85Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.2.319.2380Hg 200.6Mercury [Xe]4f 145d 106s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.2,11.9Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 150(+2)102Electron Affinity1st Ion. Pot.Unstable Anion 10.4481Tl 204.4Thallium [Xe]4f 145d 106s 2p 1Oxidation States Electroneg.3,1 1.8Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 170(+1)159Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.2 6.1182Pb 207.2Lead [Xe]4f 145d 106s 2p 2Oxidation States Electroneg.4,2 1.8Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 175(+2)119Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.367.4283Bi 209.0Bismuth [Xe]4f 145d 106s 2p 3Oxidation States Electroneg.3,5 1.9Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 155(+3)103Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.957.2984Po 209Polonium [Xe]4f 145d 106s 2p 4Oxidation States Electroneg.4,2 2.0Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 118(+4)–Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.1.98.4240Zr 91.22Zirconium [Kr]4d 25s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.4 1.33Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 159(+4)84Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.43 6.6341Nb 92.91Niobium [Kr]4d 45s 1Oxidation States Electroneg.5,3 1.60Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 143(+5)64Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.90 6.7642Mo 95.94Molybdenum [Kr]4d 55s 1Oxidation States Electroneg.6,5,4,3,2 2.16Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 136(+6)59Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.757.0943Tc 98Technetium [Kr]4d 55s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.7 2.10Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 135–Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.557.2844Ru 101.1Ruthenium [Kr]4d 75s 1Oxidation States Electroneg.2,3,4,6,8 2.20Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 133(+3)68Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.1.057.3645Rh 102.9Rhodium [Kr]4d 85s 1Oxidation States Electroneg.2,3,4 2.28Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 135(+3)67Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.1.147.4646Pd 106.4Palladium [Kr]4d 10Oxidation States Electroneg.2,4 2.20Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 138(+2)64Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.568.3447Ag 107.9Silver [Kr]4d 105s 1Oxidation States Electroneg.1 1.93Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 145(+1)115Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.1.307.5848Cd 112.4Cadmium [Kr]4d 105s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.2 1.69Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 149(+2)95Electron Affinity1st Ion. Pot.Unstable Anion 8.9949In 114.8Indium [Kr]4d 105s 2p 1Oxidation States Electroneg.3 1.78Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 163(+3)80Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.30 5.7950Sn 118.7Tin [Kr]4d 105s 2p 2Oxidation States Electroneg.4,2 1.96Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 141(+4)45Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.1.117.3422Ti 47.87Titanium [Ar]3d 24s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.4 1.54Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 145(+4)61Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.08 6.8323V 50.94Vanadium [Ar]3d 34s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.5.3 1.63Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 131(+5)54Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.53 6.7524Cr 52.00Chromium [Ar]3d 54s 1Oxidation States Electroneg.6,3,2 1.66Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 125(+3)62Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.67 6.7725Mn 54.94Manganese [Ar]3d 54s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.7,6,4,2,3 1.55Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 137(+2)67Electron Affinity1st Ion. Pot.Unstable Anion 7.4326Fe 55.85Iron [Ar]3d 64s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.2,3 1.83Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 124(+3)55Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.1517.9027Co 58.93Cobalt [Ar]3d 74s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.2,3 1.88Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 125(+2)65Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.667.8828Ni 58.69Nickel [Ar]3d 84s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.2,3 1.91Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 125(+2)69Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.1.167.6429Cu 63.55Copper [Ar]3d 104s 1Oxidation States Electroneg.2,1 1.90Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 128(+2)73Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.1.247.7330Zn 65.39Zinc [Ar]3d 104s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.2 1.65Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 133(+2)74Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.Unstable Anion 9.3931Ga 69.72Gallium [Ar]3d 104s 2p 1Oxidation States Electroneg.3 1.81Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 122(+3)62Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.3 5.1013Al 26.98Aluminum [Ne]3s 2p 1Oxidation States Electroneg.3 1.61Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 143(+3)54Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.44 5.995B 10.81Boron 1s 22s 2p 1Oxidation States Electroneg.3 2.04Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 80–Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.288.306C 12.01Carbon 1s 22s 2p 2Oxidation States Electroneg.4,2 2.55Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 77(+4)16Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.1.2611.267N 14.01Nitrogen 1s 22s 2p 3Oxidation States Electroneg.3,5,4,2 3.04Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 74(+3)16Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.Unstable Anion 14.538O 16.00Oxygen 1s 22s 2p 4Oxidation States Electroneg.-2 3.44Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 74(-2)140Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.1.4613.629F 19.00Fluorine 1s 22s 2p 5Oxidation States Electroneg.-1 3.98Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 71(-1)133Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.3.4017.4210Ne 20.18Neon 1s 22s 2p 6Oxidation States Electroneg.––Atomic Radius Ionic Radius ––Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.Unstable Anion 21.572He 4.003Helium 1s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.––Atomic Radius Ionic Radius ––Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.Unstable Anion 24.5914Si 28.09Silicon [Ne]3s 2p 2Oxidation States Electroneg.4 1.90Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 118(+4)40Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.1.398.1515P 30.97Phosphorus [Ne]3s 2p 3Oxidation States Electroneg.3,5,42.19Atomic RadiusIonic Radius 110(+5)17Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.7510.4933As 74.92Arsenic [Ar]3d 104s 2p 3Oxidation States Electroneg.3,5 2.18Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 125(+3)58Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.819.8152Te 127.6Tellurium [Kr]4d 105s 2p 4Oxidation States Electroneg.2,4,62.10Atomic RadiusIonic Radius 143(-2)221Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.1.979.0185At 210Astatine [Xe]4f 145d 106s 2p 5Oxidation States Electroneg.1,3,5,72.2Atomic RadiusIonic Radius ––Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.2.8-20Ca 40.08Calcium [Ar]4s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.2 1.00Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 197(+2)100Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.04 6.1138Sr 87.62Strontium [Kr]5s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.20.95Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 215(+2)126Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.11 5.7056Ba 137.3Barium [Xe]6s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.20.89Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 217(+2)142Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.15 5.2188Ra 226Radium [Rn]7s 2Oxidation States Electroneg.20.9Atomic Radius Ionic Radius –(+2)162Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.– 5.2811Na 22.99Sodium [Ne]3s 1Oxidation States Electroneg.10.93Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 186(+1)102Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.55 5.1419K 39.10Potassium[Ar]4s1Oxidation States Electroneg.10.82Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 227(+1)151Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.50 4.3437Rb 85.47Rubidium[Kr]5s1Oxidation States Electroneg.10.82Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 248(+1)161Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.49 4.1855Cs 132.9Cesium[Xe]6s1Oxidation States Electroneg.10.79Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 265(+1)174Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.47 3.8987Fr 223Francium[Rn]7s1Oxidation States Electroneg.10.7Atomic Radius Ionic Radius ––Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.0.46–+–34Se 78.96Selenium [Ar]3d 104s 2p 4Oxidation States Electroneg.2,4,62.55Atomic RadiusIonic Radius 116(-2)198Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.2.029.75+–35Br 79.90Bromine [Ar]3d 104s 2p 5Oxidation States Electroneg.1,5 2.96Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 114(-1)196Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.3.3611.81+–36Kr 83.80Krypton [Ar]3d 104s 2p 6Oxidation States Electroneg.––Atomic Radius Ionic Radius ––Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.Unstable Anion 14.00+–+–16S 32.07Sulfur [Ne]3s 2p 4Oxidation States Electroneg.2,4,62.58Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 103(-2)184Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.2.0810.36+–17Cl 35.45Chlorine [Ne]3s 2p 5Oxidation States Electroneg.1,3,5,73.16Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 99(-1)181Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.3.6112.97+–18Ar 39.95Argon [Ne]3s 2p 6Oxidation States Electroneg.––Atomic Radius Ionic Radius ––Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.Unstable Anion 15.76+–53I 126.9Iodine [Kr]4d 105s 2p 5Oxidation States Electroneg.1,5,72.66Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 133(-1)220Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.3.0610.45+–54Xe 131.3Xenon [Kr]4d 105s 2p 6Oxidation States Electroneg.– 2.60Atomic Radius Ionic Radius ––Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.Unstable Anion 12.13+–86Rn 222Radon [Xe]4f 145d 106s 2p 6Oxidation States Electroneg.––Atomic Radius Ionic Radius ––Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.Unstable Anion 10.7551Sb 121.8Antimony [Kr]4d 105s 2p 3Oxidation States Electroneg.3,5 2.05Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 145(+3)76Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.1.078.64+–32Ge 72.61Germanium [Ar]3d 104s 2p 2Oxidation States Electroneg.4 2.01Atomic Radius Ionic Radius 123(+4)53Electron Affinity 1st Ion. Pot.1.237.90ALKALIMETALS A C T I N I D ES E R I E S L A N T H A N I D E S E R I E S Atomic Number:number of protons Atomic Weight:weighted average of atomic masses of natural isotopes - mass number of the most stable isotope for each radioactive element 23456789111210131415161718ALKALINE EARTHMETALSHALOGENS Electronegativity:Pauling scale; measures ability of atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond Atomic Radius:given in “pm”; 1 pm = 1x10-12mIonic Radius:given in “pm”; 1 pm = 1x10-12mElectron Affinity:energy released in the formation of ananion: given in “eV”1st Ionization Potential:energy required to remove one electron,forming a cation; given in “eV” $4.95 U.S. / $7.50 CAN REFERENCE: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics • 81st edition, 2000-2001CONTENT ADVISOR: Mark Jackson, PhD Chemistry Professor - Florida Atlantic UniversityDESIGN / LAYOUT: John Ford, CEO -Customer Hotline # 1.800.230.9522March 2005ISBN 142320003-9visit us at All rights reserved.No part of this publica-tion may be reproduced or transmitted in anyform, or by any means, electronic or mechan-ical, including photocopy , recording, or anyinformation storage and retrieval sy stem,without written permission from the publisher.©2002, 2005 BarCharts, Inc.1.00791 4.0026220.1801014.007739.9481835.4531718.998915.999883.8036131.2954(222)8612.0116C 10.811B 526.982Al 1328.086Si 1430.9741532.065S 166.941Li 39.0122Be 422.9901124.305Mg1239.0981940.078Ca 2044.956Sc 2147.867Ti 2250.942V 2351.996Cr 2454.938Mn 2555.845Fe 2658.933Co 2758.693Ni 2863.546Cu 2965.39Zn 3069.7233172.64Ge 3274.922As 3378.96Se 3479.9043585.4683787.62Sr 3888.906Y 3991.224Zr 4092.906Nb 4195.94Mo 42132.9155137.33Ba 56138.91La La-Lu 57-7157178.49Hf 72180.95Ta 73183.84W 74(223)87(226)Ra 88(227)AcAc-Lr 89-10389(98)Tc43126.90I 53101.07Ru 44102.91Rh 45106.42Pd 46107.87Ag 47112.41Cd 48186.21Re 75190.23Os 76192.22Ir 77195.08Pt 78196.97Au 79200.59P Na K Ga RbCsFrHg 80204.38Tl 81207.2Pb 82208.98Bi 83(209)Po 84(210)At 85114.82In 49118.71Sn 50121.76Sb 51127.60Te 52H He Ne N Ar Cl F O Kr Xe Rn Br IA IIA IIIB IVB VB VIB VIIB IB IIB IVA VA VIA VIIA VIIIB VIIIA 154231314151617186789101112IIIA 174.97Lu 71140.12Ce 58232.04Th 90231.04Pa 91238.03U 92140.91Pr 59144.24Nd 60(262)Lr 103(145)Pm 61(237)Np 93(244)Pu 94(243)Am 95(247)Cm 96(247)Bk 97(251)Cf 98(252)Es 99(257)Fm 100(258)Md 101(259)No 102150.36Sm 62151.96Eu 63157.25Gd 64158.93Tb 65162.50Dy 66164.93Ho 67167.26Er 68168.93Tm 69173.04Yb 70(264)Bh 107(261)Rf 104(262)Db 105(266)Sg 106(277)Hs 108(268)Mt 109Copyright EniG. (eni@ktf-split.hr)© 1998-200310.811B 513(281)Uun 110(272)Uuu 111(285)Uub 112(289)Uuq 114Ne Ga Fe Tc 123456711621718HYDROGEN HELIUM NEON NITROGEN ARGON CHLORINE FLUORINE OXYGEN KRYPTON XENON RADON CARBON BORON ALUMINIUM SILICON PHOSPHORUS SULPHUR LITHIUM BERYLLIUM SODIUM MAGNESIUM POTASSIUM CALCIUM SCANDIUM TITANIUM VANADIUM CHROMIUM MANGANESE COBALT NICKEL COPPER ZINC GALLIUM GERMANIUM ARSENIC SELENIUM BROMINE RUBIDIUM STRONTIUM YTTRIUM ZIRCONIUM NIOBIUM MOLYBDENUM CAESIUM BARIUM LANTHANUM HAFNIUM TANTALUM TUNGSTEN FRANCIUM RADIUM ACTINIUM TECHNETIUM IODINE RUTHENIUM RHODIUM PALLADIUM SILVER CADMIUM RHENIUM OSMIUM IRIDIUM PLATINUM GOLD THALLIUM LEAD BISMUTH POLONIUM ASTATINE INDIUM TIN ANTIMONY TELLURIUM P E R I O D GROUPIRON MERCURY LANTHANIDEACTINIDE LUTETIUM CERIUM THORIUM PROTACTINIUM URANIUM PRASEODYMIUM NEODYMIUM LAWRENCIUMPROMETHIUM NEPTUNIUM PLUTONIUM AMERICIUM CURIUM BERKELIUM CALIFORNIUM EINSTEINIUM FERMIUM MENDELEVIUM NOBELIUM SAMARIUM EUROPIUM GADOLINIUM TERBIUM DYSPROSIUM HOLMIUM ERBIUM THULIUM YTTERBIUM BOHRIUM RUTHERFORDIUM DUBNIUM SEABORGIUM HASSIUM MEITNERIUM http://www.ktf-split.hr/periodni/en/Lanthanide Actinide PERIODIC TABLE OF THE ELEMENTS BORON ATOMIC NUMBERELEMENT NAME SYMBOL (1) Pure Appl. Chem.,, No. 4, 667-683 (2001)73Editor:Aditya Vardhan (adivar@)Relative atomic mass is shown with fivesignificant figures.For elements have no stablenuclides,the value enclosed in bracketsindicates the mass number of the longest-livedisotope of the element.However three such elements (Th,Pa,and U)do have a characteristic terrestrial isotopiccomposition,and for these an atomic weight istabulated.Metal Alkali metal Alkaline earth metal Transition metals LanthanideActinide Chalcogens element Halogens elementNoble gas Semimetal Nonmetal - gas - liquid - solid - syntheticSTANDARD STATE (100 °C; 101 kPa)UNUNNILIUM UNUNUNIUM UNUNQUADIUMUNUNBIUM RELATIVE ATOMIC MASS (1)GROUP CAS GROUP IUPACNotes- I UPAC 2011 Standard atomic weights abridged to four significant digits (Table 4 published in Pure Appl. Chem. 85, 1047-1078 (2013); /10.1351/PAC-REP-13-03-02. The uncertainty in the last digit of the standard atomic weight value is listed in parentheses following the value. In the absence of parentheses, the uncertainty is one in that last digit. An interval in square brackets provides the lower and upper bounds of the standard atomic weight for that element. No values are listed for elements which lack isotopes with a characteristic isotopic abundance in naturalterrestrial samples. See PAC for more details. - “Aluminum” and “cesium” are commonly used alternative spellings for “aluminium” and “caesium.”- Claims for the discovery of all the remaining elements in the last row of the Table, namely elements with atomic numbers 113, 115, 117 and 118, and for which no assignments have yet been made, are being considered by a IUPAC and IUPAP Joint Working Party.For updates to this table, see /reports/periodic_table/. This version is dated 1 May 2013.Copyright © 2013 IUPAC, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.InternatIonal UnIon of PUre and aPPlIed ChemIstry1Hhydrogen[1.007; 1.009]1183Li lithium[6.938; 6.997]4Be beryllium 9.01211Nasodium22.9912Mg magnesium 24.3119Kpotassium39.1020Ca calcium 40.0837Rbrubidium85.4738Sr strontium 87.6255Cscaesium132.956Ba barium 137.387Frfrancium 88Ra radium 5B boron [10.80; 10.83]13Al aluminium 26.9831Ga gallium 69.7249In indium 114.881Tl thallium [204.3; 204.4]6C carbon [12.00; 12.02]14Si silicon [28.08; 28.09]32Ge germanium 72.6350Sn tin 118.782Pb lead 207.27N nitrogen [14.00; 14.01]15P phosphorus 30.9733As arsenic 74.9251Sb antimony 121.883Bi bismuth 209.08O oxygen [15.99; 16.00]16S sulfur [32.05; 32.08]34Se selenium 78.96(3)52Te tellurium 127.684Po polonium 9F fluorine 19.0017Cl chlorine [35.44; 35.46]35Br bromine 79.9053I iodine 126.985At astatine 10Ne neon 20.182He helium 4.00318Ar argon 39.9536Kr krypton 83.8054Xe xenon 131.386Rn radon22Ti titanium 47.8740Zr zirconium 91.2272Hf hafnium 178.5104Rf rutherfordium23V vanadium 50.9441Nb niobium 92.9173Ta tantalum 180.9105Db dubnium 24Cr chromium 52.0042Mo molybdenum 95.96(2)74W tungsten 183.8106Sg seaborgium 25Mn manganese 54.9443Tc technetium 75Re rhenium 186.2107Bh bohrium 26Fe iron 55.8544Ru ruthenium 101.176Os osmium 190.2108Hs hassium 27Co cobalt 58.9345Rh rhodium 102.977Ir iridium 192.2109Mt meitnerium 28Ni nickel 58.6946Pd palladium 106.478Pt platinum 195.1110Ds darmstadtium 29Cu copper 63.5547Ag silver 107.979Au gold 197.030Zn zinc 65.38(2)48Cd cadmium 112.480Hg mercury 200.6111Rg roentgenium 112Cn copernicium57Lalanthanum138.989Acactinium 58Ce cerium 140.190Th thorium232.059Pr praseodymium 140.991Pa protactinium 231.060Nd neodymium 144.292U uranium 238.061Pm promethium 93Np neptunium 62Sm samarium 150.494Pu plutonium 63Eu europium 152.095Am americium 64Gd gadolinium 157.396Cm curium 65Tb terbium 158.997Bk berkelium 66Dy dysprosium 162.598Cf californium 67Ho holmium 164.999Es einsteinium 68Er erbium 167.3100Fm fermium 69Tm thulium 168.9101Md mendelevium 70Yb ytterbium 173.1102No nobelium 71Lu lutetium 175.0103Lr lawrencium21Sc scandium 44.9639Y yttrium 88.9157-71lanthanoids 89-103actinoids atomic numberSymbol standard atomic weight 213 14 15 16 17 Key: 34 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 name For updates to this table, see /reports/periodic_table/. This version is dated 21 January 2011.Copyright © 2011 IUPAC, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.Notes- IUPAC 2009 Standard atomic weights abridged to four significant digits (Table 4 published in Pure Appl. Chem. 83, 359-396 (2011);doi:10.1351/PAC-REP-10-09-14). The uncertainty in the last digit of the standard atomic weight value is listed in parentheses following the value.In the absence of parentheses, the uncertainty is one in that last digit. An interval in square brackets provides the lower and upper bounds of thestandard atomic weight for that element. No values are listed for elements with no stable isotopes. See PAC for more details.- “Aluminum” and “cesium” are commonly used alternative spellings for “aluminium” and “caesium.”IUPAC Periodic Table of the Elements镧系La镧 Ce铈Pr镨Nd钕Pm钷Sm钐Eu铕Gd钆Tb铽Dy镝Ho钬Er铒Tm铥Yb镱Lu镥lán shìpǔnǚpǒshān yǒu gátèdīhuǒěr diūyìlǔlanthanun cerium praseodymium neodymium promethium samarium europium gadolinium terbium dysprosium holmium erbium thulium ytterbium lutetium 57138.958140.159140.960144.261[145]62150.46315264157.365158.966162.567164.968167.369168.97017371175锕系Ac锕Th钍Pa镤U铀Np镎Pu钚Am镅*Cm锔*Bk锫*Cf锎*Es锿*Fm镄*Md钔*No锘*Lr铹*ātǔpúyóu nábùméi jūpéi kāiāi fèi mén nuòláo actinium thorium protactinium uranium neptunium plutonium americium curium berkelium californium einsteinium fermium mendelevium nobelium lawrencium 89[227]90232912319223893[237]94[244]95[243]96[247]97[247]98[251]99[252]100[257]101[258]102[259]103[262]。

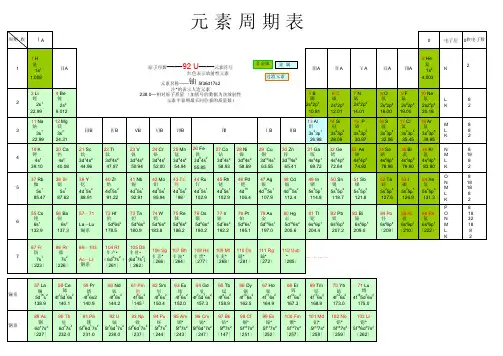
元素周期表(高清英文版)元素周期表(高清英文版)---概述元素周期表是一种以化学元素按一定规律排列的表格,用于系统地组织和展示化学元素的相关信息。
元素周期表包含了所有已知的化学元素,以及它们的原子序数、原子量和化学性质等重要信息。
本文档将介绍高清英文版的元素周期表,为化学爱好者和科学研究人员提供详细的参考信息。
元素周期表的排列元素周期表的排列基于元素的原子序数,即元素中原子的个数。
在英文版的元素周期表中,元素按照原子序数递增的顺序从左到右排列,每行包含一定数量的元素。
具体的排列方式如下:---- 1 ---- 2 ----------:------:-------- H ---- He -------- Li ---- Be ---- B ---- C ---- N ---- O ---- F ---- Ne -------- Na ---- Mg ---- Al ---- Si ---- P ---- S ---- Cl ---- Ar -------- K ---- Ca ---- Sc ---- Ti ---- V ---- Cr ---- Mn ---- Fe ---- Co ---- Ni ---- Cu ---- Zn ---- Ga ---- Ge ---- As ---- Se ---- Br ---- Kr -------- Rb ---- Sr ---- Y ---- Zr ---- Nb ---- Mo ---- Tc ---- Ru ---- Rh ---- Pd ---- Ag ---- Cd ---- In ---- Sn ---- Sb ---- Te ---- I ---- Xe -------- Cs ---- Ba ---- La-Lu ---- Hf ---- Ta ---- W ---- Re ---- Os ---- Ir ---- Pt ---- Au ---- Hg ---- Tl ---- Pb ---- Bi ---- Po ---- At ---- Rn -------- Fr ---- Ra ---- Ac-Lr ---- Rf ---- Db ---- Sg ---- Bh ---- Hs ---- Mt ---- Ds ---- Rg ---- Cn ---- Nh ---- Fl ---- Mc ---- Lv ---- Ts ---- Og ----元素周期表的信息元素周期表提供了丰富的化学元素信息,以下为其中的一些重要信息:元素符号每个元素都有一个独特的化学符号,用于标识该元素。
preface前言;序文;卷首语Textbook教材;教科书;课本prerequisite前提;先决条件;必备条件quantum mechanics量子力学Annex附件;附录crystallography晶体学manipulate操作;控制;处理vector矢量matrices矩阵Instructor指导者;教员;导师graphically以图表形式;用图解法;形象地;生动地;逼真地parameter参数;参量;指标参数capacitor电容元件;电容substrate基板;基材;衬底lattice 晶格;点阵;格点lattice parameter晶格常数bipolar transistor双极性晶体管numerical数值的;用数表示的finite-difference有限差分depletion耗尽approximation近似;粗略估算generation-recombination phenomena产生复合现象illustrate说明;举例说明;阐明visualize想象;设想;使形象化;构思quantum mechanical effects量子效应energy band structure能带结构carrier transport载流子输运electron and hole behavior电子和空穴的行为electric field电场;静电场space-charge region空间电荷区solar cells太阳能电池charge and potential distributions电荷和电位分布two-dimensional field二维场(2D)pinch-off夹断second-order effects二阶效应channel length modulation沟道长度调制效应surface channel mobility reduction表面沟道迁移率减小threshold voltage roll-off阈值电压下降Scaling rules缩放;缩放比例准则hot-carrier degradation effects热载流子退化效应non-volatile memory固定存储器;非易失性存储器silicon-on-insulator devices绝缘体上硅器件?construct simple circuits构建简单的电路bipolar junction transistor (BJT) 双极型晶体管heterojunction异质结tunnel effect隧道效应tunnel diode隧道二级管silicon processing techniques硅加工技术ion implantation离子注入lithography光刻;微影技术oxidation氧化(作用)etching蚀刻法silicide formation硅化物的形成?fabrication processes制造工艺phosphorus磷donor捐赠者;献血者;捐赠机构electric potential difference电势差thermal 热的;热量的and electric equilibria平衡Outline概述;轮廓线;梗概Discrete分离的;互不相连的semiconductor deviceIntermediate中间的;中等的;适合中等程度者的resistivity电阻系数;抵抗力;电阻率;conductivity传导性[力];导电率insulator隔热或绝缘、隔音等的材料conductor导线;导体Element Periodic Table元素周期表Elemental Semiconductor : Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge)Compound Semiconductor :IV-IV: SiC; III-V: AlP, AlAs, AlSb, GaN,GaP, GaAs,GaSb,InP, InAs; II-VI: ZnO, ZnS, ZnSe,ZnTe,CdS,CdTe,HgSAlloy Semiconductor:Binary Alloys: Si1-xGexTriple Alloys: AlxGa1-xAs, AlxIn1-xAs, Cd1-xMnxTe,GaAs1-xPxHybridize v.杂化;〔生〕杂交;杂混electrons in the conduction band and holes in the valence band of a semiconductorzero Kelvin 0开vacant seat 空位covalent共价的bond债券;键;结合recombination〔遗〕重组;〔物〕复合Conversely adv.相反地;反过来generation of an electron-hole pairthermodynamic equilibrium热平衡illumination照明;启示gallium arsenide (GaAs)momentum动量;势头;动力;推进力direct-bandgap semiconductorband-to-band recombinationphoton光子Planck's constant---hcorresponding符合的;相应的;相关的visible可见的;明显的near-infrared light近红外线radiative发光的;发射的;【物】辐射性的recombinationexploit v.开发;利用respectively分别;各自;顺序为indirect-bandgap semiconductorhomojunction同质结heterojunction异质结生物物理学Biophysics真空冷冻干燥技术Vacuum Freezing & Drying Technology16位微机16 Digit MicrocomputerALGOL语言ALGOL LanguageBASIC 语言BASIC LanguageBASIC 语言及应用BASIC Language & ApplicationC 语言C LanguageCAD 概论Introduction to CADCAD/CAM CAD/CAMCOBOL语言COBOL LanguageCOBOL语言程序设计COBOL Language Program DesigningC与UNIX环境C Language & Unix EnvironmentC语言与生物医学信息处理C Language & Biomedical Information Processing dBASE Ⅲ课程设计C ourse Exercise in dBASE ⅢFORTRAN语言FORTRAN LanguageIBM-PC/XT Fundamentals of Microcomputer IBM-PC/XTIBM-PC微机原理Fundamentals of Microcomputer IBM-PCLSI设计基础Basic of LSI DesigningPASCAL大型作业PASCAL Wide Range WorkingPASCAL课程设计Course Exercise in PASCALX射线与电镜X-ray & Electric MicroscopeZ-80汇编语言程序设计Z-80 Pragramming in Assembly Languages板壳理论Plate Theory板壳力学Plate Mechanics半波实验Semiwave Experiment半导体变流技术Semiconductor Converting Technology半导体材料Semiconductor Materials半导体测量Measurement of Semiconductors半导体瓷敏元件Semiconductor Porcelain-Sensitive Elements半导体光电子学Semiconductor Optic Electronics半导体化学Semiconductor Chemistry半导体激光器Semiconductor Laser Unit半导体集成电路Semiconductor Integrated Circuitry半导体理论Semiconductive Theory半导体器件Semiconductor Devices半导体器件工艺原理Technological Fundamentals of Semiconductor Device 半导体物理Semiconductor Physics半导体专业Semiconduction Specialty半导体专业实验Specialty Experiment of Semiconductor薄膜光学Film Optics报告文学专题Special Subject On Reportage报刊编辑学Newspaper & Magazine Editing报纸编辑学Newspaper Editing泵与风机Pumps and Fans泵与水机Pumps & Water Turbines毕业设计Graduation Thesis编译方法Methods of Compiling编译技术Technique of Compiling编译原理Fundamentals of Compiling变电站的微机检测与控制Computer Testing & Control in Transformer Substation变分法与张量Calculus of Variations & Tensor变分学Calculus of Variations变质量系统热力学与新型回转压Variable Quality System Thermal Mechanics & Neo-Ro表面活性物质Surface Reactive Materials并行算法Parallel Algorithmic波谱学Wave Spectrum材料的力学性能测试Measurement of Material Mechanical Performance材料力学Mechanics of Materials财务成本管理Financial Cost Management财政学Public Finance财政与金融Finance & Banking财政与信贷Finance & Credit操作系统Disk Operating System操作系统课程设计Course Design in Disk Operating System操作系统原理Fundamentals of Disk Operating System策波测量技术Technique of Whip Wave Measurement测量原理与仪器设计Measurement Fundamentals & Meter Design 测试技术Testing Technology测试与信号变换处理Testing & Signal Transformation Processing 产业经济学Industrial Economy产业组织学Industrial Organization Technoooligy场论Field Theory常微分方程Ordinary Differentical Equations超导磁体及应用Superconductive Magnet & Application超导及应用Superconductive & Application超精微细加工Super-Precision & Minuteness Processing城市规划原理Fundamentals of City Planning城市社会学Urban Sociology成组技术Grouping Technique齿轮啮合原理Principles of Gear Connection冲击测量及误差Punching Measurement & Error冲压工艺Sheet Metal Forming Technology抽象代数Abstract Algebra传动概论Introduction to Transmission传感器与检测技术Sensors & Testing Technology传感器原理Fundamentals of Sensors传感器原理及应用Fundamentals of Sensors & Application传热学Heat Transfer传坳概论Introduction to Pass Col船舶操纵Ship Controling船舶电力系统Ship Electrical Power System船舶电力系统课程设计Course Exercise in Ship Electrical Power System 船舶电气传动自动化Ship Electrified Transmission Automation船舶电站Ship Power Station船舶动力装置Ship Power Equipment船舶概论Introduction to Ships船舶焊接与材料Welding & Materials on Ship船舶机械控制技术Mechanic Control Technology for Ships船舶机械拖动Ship Mechamic Towage船舶建筑美学Artistic Designing of Ships船舶结构力学Structual Mechamics for Ships船舶结构与制图Ship Structure & Graphing船舶静力学Ship Statics船舶强度与结构设计Designing Ship Intensity & Structure船舶设计原理Principles of Ship Designing船舶推进Ship Propeling船舶摇摆Ship Swaying船舶阻力Ship Resistance船体建造工艺Ship-Building Technology船体结构Ship Structure船体结构图Ship Structure Graphing船体振动学Ship Vibration创造心理学Creativity Psychology磁测量技术Magnetic Measurement Technology磁传感器Magnetic Sensor磁存储设备设计原理Fundamental Design of Magnetic Memory Equipment 磁记录技术Magnetographic Technology磁记录物理Magnetographic Physics磁路设计与场计算Magnetic Path Designing & Magnetic Field Calculati磁盘控制器Magnetic Disk Controler磁性材料Magnetic Materials磁性测量Magnetic Measurement磁性物理Magnetophysics磁原理及应用Principles of Catalyzation & Application大电流测量Super-Current Measurement大电源测量Super-Power Measurement大机组协调控制Coordination & Control of Generator Networks大跨度房屋结构Large-Span House structure大型锅炉概况Introduction to Large-Volume Boilers大型火电机组控制Control of Large Thermal Power Generator Networks大学德语College German大学俄语College Russian大学法语College French大学日语College Japanese大学英语College English大学语文College Chinese大众传播学Mass Media代用运放电路Simulated Transmittal Circuit单片机原理Fundamentals of Mono-Chip Computers单片机原理及应用Fundamentals of Mono-Chip Computers & Applications 弹性力学Theory of Elastic Mechanics当代国际关系Contemporary International Relationship当代国外社会思维评价Evaluation of Contemporary Foreign Social Thought 当代文学Contemporary Literature当代文学专题Topics on Contemporary Literature当代西方哲学Contemporary Western Philosophy当代戏剧与电影Contemporary Drama & Films党史History of the Party导波光学Wave Guiding Optics等离子体工程Plasma Engineering低频电子线路Low Frequency Electric Circuit低温传热学Cryo Conduction低温固体物理Cryo Solid Physics低温技术原理与装置Fundamentals of Cryo Technology & Equipment 低温技术中的微机原理Priciples of Microcomputer in Cryo Technology 低温绝热Cryo Heat Insulation低温气体制冷机Cryo Gas Refrigerator低温热管Cryo Heat Tube低温设备Cryo Equipment低温生物冻干技术Biological Cryo Freezing Drying Technology低温实验技术Cryo Experimentation Technology低温物理导论Cryo Physic Concepts低温物理概论Cryo Physic Concepts低温物理概念Cryo Physic Concepts低温仪表及测试Cryo Meters & Measurement低温原理Cryo Fundamentals低温中的微机应用Application of Microcomputer in Cryo Technology 低温装置Cryo Equipment低噪声电子电路Low-Noise Electric Circuit低噪声电子设计Low-Noise Electronic Designing低噪声放大与弱检Low-Noise Increasing & Decreasing低噪声与弱信号检测Detection of Low Noise & Weak Signals地理Geography第二次世界大战史History of World War II电测量技术Electric Measurement Technology电厂计算机控制系统Computer Control System in Power Plants电磁测量实验技术Electromagnetic Measurement Experiment & Technology 电磁场计算机Electromagnetic Field Computers电磁场理论Theory of Electromagnetic Fields电磁场数值计算Numerical Calculation of Electromagnetic Fields电磁场与电磁波Electromagnetic Fields & Magnetic Waves电磁场与微波技术Electromagnetic Fields & Micro-Wave Technology电磁场中的数值方法Numerical Methods in Electromagnetic Fields电磁场中的数值计算Numerical Calculation in Electromagnetic Fields电磁学Electromagnetics电动力学Electrodynamics电镀Plating电分析化学Electro-Analytical Chemistry电工测试技术基础Testing Technology of Electrical Engineering电工产品学Electrotechnical Products电工电子技术基础Electrical Technology & Electrical Engineering电工电子学Electronics in Electrical Engineering电工基础Fundamental Theory of Electrical Engineering电工基础理论Fundamental Theory of Electrical Engineering电工基础实验Basic Experiment in Electrical Engineering电工技术Electrotechnics电工技术基础Fundamentals of Electrotechnics电工实习Electrical Engineering Practice电工实验技术基础Experiment Technology of Electrical Engineering 电工学Electrical Engineering电工与电机控制Electrical Engineering & Motor Control电弧电接触Electrical Arc Contact电弧焊及电渣焊Electric Arc Welding & Electroslag Welding电化学测试技术Electrochemical Measurement Technology电化学工程Electrochemical Engineering电化学工艺学Electrochemical Technology电机测试技术Motor Measuring Technology电机电磁场的分析与计算Analysis & Calculation of Electrical Motor & Electromagnetic Fields电机电器与供电Motor Elements and Power Supply电机课程设计Course Exercise in Electric Engine电机绕组理论Theory of Motor Winding电机绕组理论及应用Theory & Application of Motor Winding电机设计Design of Electrical Motor电机瞬变过程Electrical Motor Change Processes电机学Electrical Motor电机学及控制电机Electrical Machinery Control & Technology电机与拖动Electrical Machinery & Towage电机原理Principle of Electric Engine电机原理与拖动Principles of Electrical Machinery & Towage电机专题Lectures on Electric Engine电接触与电弧Electrical Contact & Electrical Arc电介质物理Dielectric Physics电镜Electronic Speculum电力电子电路Power Electronic Circuit电力电子电器Power Electronic Equipment电力电子器件Power Electronic Devices电力电子学Power Electronics电力工程Electrical Power Engineering电力生产技术Technology of Electrical Power Generation电力生产优化管理Optimal Management of Electrical Power Generation 电力拖动基础Fundamentals for Electrical Towage电力拖动控制系统Electrical Towage Control Systems电力系统Power Systems电力系统电源最优化规划Optimal Planning of Power Source in a Power System电力系统短路Power System Shortcuts电力系统分析Power System Analysis电力系统规划Power System Planning电力系统过电压Hyper-Voltage of Power Systems电力系统继电保护原理Power System Relay Protection电力系统经济分析Economical Analysis of Power Systems电力系统经济运行Economical Operation of Power Systems电力系统可靠性Power System Reliability电力系统可靠性分析Power System Reliability Analysis电力系统无功补偿及应用Non-Work Compensation in Power Systems & Applicati电力系统谐波Harmonious Waves in Power Systems电力系统优化技术Optimal Technology of Power Systems电力系统优化设计Optimal Designing of Power Systems电力系统远动Operation of Electric Systems电力系统远动技术Operation Technique of Electric Systems电力系统运行Operation of Electric Systems电力系统自动化Automation of Electric Systems电力系统自动装置Power System Automation Equipment电路测试技术Circuit Measurement Technology电路测试技术基础Fundamentals of Circuit Measurement Technology电路测试技术及实验Circuit Measurement Technology & Experiments电路分析基础Basis of Circuit Analysis电路分析基础实验Basic Experiment on Circuit Analysis电路分析实验Experiment on Circuit Analysis电路和电子技术Circuit and Electronic Technique电路理论Theory of Circuit电路理论基础Fundamental Theory of Circuit电路理论实验Experiments in Theory of Circuct电路设计与测试技术Circuit Designing & Measurement Technology电器学Electrical Appliances电器与控制Electrical Appliances & Control电气控制技术Electrical Control Technology电视接收技术Television Reception Technology电视节目Television Porgrams电视节目制作Television Porgram Designing电视新技术New Television Technology电视原理Principles of Television电网调度自动化Automation of Electric Network Management电影艺术Art of Film Making电站微机检测控制Computerized Measurement & Control of Power Statio 电子材料与元件测试技术Measuring Technology of Electronic Material and Element电子材料元件Electronic Material and Element电子材料元件测量Electronic Material and Element Measurement电子测量与实验技术Technology of Electronic Measurement & Experiment电子测试Electronic Testing电子测试技术Electronic Testing Technology电子测试技术与实验Electronic Testing Technology & Experiment电子机械运动控制技术Technology of Electronic Mechanic Movement Control 电子技术Technology of Electronics电子技术腐蚀测试中的应用Application of Electronic Technology in Erosion Measurement电子技术基础Basic Electronic Technology电子技术基础与实验Basic Electronic Technology & Experiment电子技术课程设计Course Exercise in Electronic Technology电子技术实验Experiment in Electronic Technology电子理论实验Experiment in Electronic Theory电子显微分析Electronic Micro-Analysis电子显微镜Electronic Microscope电子线路Electronic Circuit电子线路设计与测试技术Electronic Circuit Design & Measurement Technology电子线路实验Experiment in Electronic Circuit电子照相技术Electronic Photographing Technology雕塑艺术欣赏Appreciation of Sculptural Art调节装置Regulation Equipment动态规划Dynamic Programming动态无损检测Dynamic Non-Destruction Measurement动态信号分析与仪器Dynamic Signal Analysis & Apparatus锻压工艺Forging Technology锻压机械液压传动Hydraulic Transmission in Forging Machinery 锻压加热设备Forging Heating Equipment锻压设备专题Lectures on Forging Press Equipments锻压系统动力学Dynamics of Forging System锻造工艺Forging Technology断裂力学Fracture Mechanics对外贸易概论Introduction to International Trade多层网络方法Multi-Layer Network Technology多目标优化方法Multipurpose Optimal Method多项距阵Multi-Nominal Matrix多元统计分析Multi-Variate Statistical Analysis发电厂Power Plant发电厂电气部分Electric Elements of Power Plants法律基础Fundamentals of Law法学概论An Introduction to Science of Law法学基础Fundamentals of Science of Law翻译Translation翻译理论与技巧Theory & Skills of Translation泛函分析Functional Analysis房屋建筑学Architectural Design & Construction非电量测量Non-Electricity Measurement非金属材料Non-Metal Materials非线性采样系统Non-Linear Sampling System非线性光学Non-Linear Optics非线性规划Non-Linear Programming非线性振荡Non-Linear Ocsillation非线性振动Non-Linear Vibration沸腾燃烧Boiling Combustion分析化学Analytical Chemistry分析化学实验Analytical Chemistry Experiment分析力学Analytical Mechanics风机调节Fan Regulation风机调节.使用.运转Regulation,Application & Operation of Fans风机三元流动理论与设计Tri-Variate Movement Theory & Design of Fans 风能利用Wind Power Utilization腐蚀电化学实验Experiment in Erosive Electrochemistry复变函数Complex Variables Functions复变函数与积分变换Functions of Complex Variables & Integral Transformation复合材料力学Compound Material Mechanics傅里叶光学Fourier Optics概率论Probability Theory概率论与数理统计Probability Theory & Mathematical Statistics 概率论与随机过程Probability Theory & Stochastic Process钢笔画Pen Drawing钢的热处理Heat-Treatment of Steel钢结构Steel Structure钢筋混凝土Reinforced Concrete钢筋混凝土及砖石结构Reinforced Concrete & Brick Structure钢砼结构Reinforced Concrete Structure高层建筑基础设计Designing bases of High Rising Buildings高层建筑结构设计Designing Structures of High Rising Buildings 高等材料力学Advanced Material Mechanics高等代数Advanced Algebra高等教育管理Higher Education Management高等教育史History of Higher Education高等教育学Higher Education高等数学Advanced Mathematics高电压技术High-Voltage Technology高电压测试技术High-Voltage Test Technology高分子材料High Polymer Material高分子材料及加工High Polymer Material & Porcessing高分子化学High Polymer Chemistry高分子化学实验High Polymer Chemistry Experiment高分子物理High Polymer Physics高分子物理实验High Polymer Physics Experiment高级英语听说Advanced English Listening & Speaking高能密束焊High Energy-Dense Beam Welding高频电路High-Frenquency Circuit高频电子技术High-Frenquency Electronic Technology高频电子线路High-Frenquency Electronic Circuit高频电子线路High-Frenquency Electronic Circuit高压测量技术High-Voltage Measurement Technology高压测试技术High-Voltage Testing Technology高压电场的数值计算Numerical Calculation in High-Voltage Electronic Field 高压电器High-Voltage Electrical Appliances高压绝缘High-Voltage Insulation高压实验High-Voltage Experimentation高压试验技术High-Voltage Experimentation Technology工程材料的力学性能测试Mechanic Testing of Engineering Materials工程材料及热处理Engineering Material and Heat Treatment工程材料学Engineering Materials工程测量Engineering Surveying工程测试技术Engineering Testing Technique工程测试实验Experiment on Engineering Testing工程测试信息Information of Engineering Testing工程动力学Engineering Dynamics工程概论Introduction to Engineering工程概预算Project Budget工程经济学Engineering Economics工程静力学Engineering Statics工程力学Engineering Mechanics工程热力学Engineering Thermodynamics工程项目评估Engineering Project Evaluation工程优化方法Engineering Optimizational Method工程运动学Engineering Kinematics工程造价管理Engineering Cost Management工程制图Graphing of Engineering工业分析Industrial Analysis工业锅炉Industrial Boiler工业会计学Industrial Accounting工业机器人Industrial Robot工业技术基础Basic Industrial Technology工业建筑设计原理Principles of Industrial Building Design 工业经济理论Industrial Economic Theory工业经济学Industrial Economics工业企业财务管理Industrial Enterprise Financial Management工业企业财务会计Accounting in Industrial Enterprises工业企业管理Industrial Enterprise Management工业企业经营管理Industrial Enterprise Adminstrative Management 工业社会学Industrial Sociology工业心理学Industrial Psychology工业窑炉Industrial Stoves工艺过程自动化Technics Process Automation公差Common Difference公差技术测量Technical Measurement with Common Difference公差与配合Common Difference & Cooperation公共关系学Public Relations公文写作Document Writing古代汉语Ancient Chinese古典文学作品选读Selected Readings in Classical Literature固体激光Solid State Laser固体激光器件Solid Laser Elements固体激光与电源Solid State Laser & Power Unit固体物理Solid State Physics管理概论Introduction to Management管理经济学Management Economics管理数学Management Mathematics管理系统模拟Management System Simulation管理心理学Management Psychology管理信息系统Management Information Systems光波导理论Light Wave Guide Theory光电技术Photoelectric Technology光电信号处理Photoelectric Signal Processing光电信号与系统分析Photoelectric Signal & Systematic Analysis 光辐射探测技术Ray Radiation Detection Technology光谱Spectrum光谱分析Spectral Analysis光谱学Spectroscopy光纤传感Fibre Optical Sensors光纤传感器Fibre Optical Sensors光纤传感器基础Fundamentals of Fibre Optical Sensors光纤传感器及应用Fibre Optical Sensors & Applications光纤光学课程设计Course Design of Fibre Optical光纤技术实验Experiments in Fibre Optical Technology光纤通信基础Basis of Fibre Optical Communication光学Optics光学测量Optical Measurement光学分析法Optical Analysis Method光学计量仪器设计Optical Instrument Gauge Designing光学检测Optical Detection光学设计Optical Design光学信息导论Introduction of Optical Infomation光学仪器设计Optical Instrument Designing光学仪器与计量仪器设计Optical Instrument & Gauge Instrument Designing 光学仪器装配与校正Optical Instrument Installation & Adjustment广播编辑学Broadcast Editing广播新闻Broadcast Journalism广播新闻采写Broadcast Journalism Collection & Composition广告学Advertisement锅炉燃烧理论Theory of Boiler Combustion锅炉热交换传热强化Boiler Heat Exchange,Condction & Intensification锅炉原理Principles of Boiler国际金融International Finance国际经济法International Economic Law国际贸易International Trade国际贸易地理International Trade Geography国际贸易实务International Trade Affairs国际市场学International Marketing国际市场营销International Marketing国民经济计划National Economical Planning国外社会学理论Overseas Theories of Sociology过程(控制)调节装置Process(Control) Adjustment Device过程调节系统Process Adjustment System过程控制Process Control过程控制系统Process Control System海洋测量Ocean Surveying海洋工程概论Introduction to Ocean Engineering函数分析Functional Analysis焊接方法Welding Method焊接方法及设备Welding Method & Equipment焊接检验Welding Testing焊接结构Welding Structure焊接金相Welding Fractography焊接金相分析Welding Fractography Analysis焊接冶金Welding Metallurgy焊接原理Fundamentals of Welding焊接原理及工艺Fundamentals of Welding & Technology焊接自动化Automation of Welding汉语Chinese汉语与写作Chinese & Composition汉语语法研究Research on Chinese Grammar汉字信息处理技术Technology of Chinese Information Processing毫微秒脉冲技术Millimicrosecond Pusle Technique核动力技术Nuclear Power Technology合唱与指挥Chorus & Conduction合金钢Alloy Steel宏观经济学Macro-Economics宏微观经济学Macro Micro Economics红外CCD Infrared CCD红外电荷耦合器Infrared Electric Charge Coupler红外探测器Infrared Detectors红外物理Infrared Physics红外物理与技术Infrared Physics & Technology红外系统Infrared System红外系统电信号处理Processing Electric Signals from Infrared Systems厚薄膜集成电路Thick & Thin Film Integrated Circuit弧焊电源Arc Welding Power弧焊原理Arc Welding Principles互换性技术测量基础Basic Technology of Exchangeability Measurement互换性技术测量Technology of Exchangeability Measurement互换性与技术测量Elementary Technology of Exchangeability Measurement 互换性与技术测量实验Experiment of Exchangeability Measurement Technology画法几何及机械制图Descriptive Geometry & Mechanical Graphing画法几何与阴影透视Descriptive Geometry,Shadow and Perspective 化工基础Elementary Chemical Industry化工仪表与自动化Chemical Meters & Automation化工原理Principles of Chemical Industry化学Chemistry化学反应工程Chemical Reaction Engineering化学分离Chemical Decomposition化学工程基础Elementary Chemical Engineering化学计量学Chemical Measurement化学文献Chemical Literature化学文献及查阅方法Chemical Literature & Consulting Method化学粘结剂Chemical Felter环境保护理论基础Basic Theory of Environmental Protection环境化学Environomental Chemistry环境行为概论Introduction to Environmental Behavior换热器Thermal Transducer回旧分析与试验设计Tempering Analysis and Experiment Design回转式压缩机Rotary Compressor回转压缩机数学模型Mathematical Modeling of Rotary Compressors 会计学Accountancy会计与财务分析Accountancy & Financial Analysis会计与设备分析Accountancy & Equipment Analysis会计原理及外贸会计Principles of Accountancy & Foreign Trade Accountancy 会计原理与工业会计Principles of Accountancy & Industrial Accountancy活力学Energy Theory活塞膨胀机Piston Expander活塞式制冷压缩机Piston Refrigerant Compreessor活塞式压缩机Piston Compressor活塞式压缩机基础设计Basic Design of Piston Compressor活塞压缩机结构强度Structural Intensity of Piston Compressor活赛压机气流脉动Gas Pulsation of Piston Pressor货币银行学Currency Banking基本电路理论Basis Theory of Circuit基础写作Fundamental Course of Composition机床电路Machine Tool Circuit机床电器Machine Tool Electric Appliance机床电气控制Electrical Control of Machinery Tools机床动力学Machine Tool Dynamics机床设计Machine Tool design机床数字控制Digital Control of Machine Tool机床液压传动Machinery Tool Hydraulic Transmission机电传动Mechanical & Electrical Transmission机电传动控制Mechanical & electrical Transmission Control机电耦合系统Mechanical & Electrical Combination System机电系统计算机仿真Computer Simulation of Mechanic/Electrical Systems 机电一体化Mechanical & Electrical Integration机构学Structuring机器人Robot机器人控制技术Robot Control Technology机械产品学Mechanic Products机械产品造型设计Shape Design of Mechanical Products机械工程控制基础Basic Mechanic Engineering Control机械加工自动化Automation in Mechanical Working机械可靠性Mechanical Reliability机械零件Mechanical Elements机械零件设计Course Exercise in Machinery Elements Design机械零件设计基础Basis of Machinery Elements Design机械设计Mechanical Designing机械设计基础Basis of Mechanical Designing机械设计课程设计Course Exercise in Mechanical Design机械设计原理Principle of Mechanical Designing机械式信息传输机构Mechanical Information Transmission Device机械原理Principle of Mechanics机械原理和机械零件Mechanism & Machinery机械原理及机械设计Mechanical Designing机械原理及应用Mechanical Principle & Mechanical Applications机械原理课程设计Course Exercise of Mechanical Principle机械原理与机械零件Mechanical Principle and Mechanical Elements机械原理与机械设计Mechanical Principle and Mechanical Design机械噪声控制Control of Mechanical Noise机械制造概论Introduction to Mechanical Manufacture机械制造工艺学Technology of Mechanical Manufacture机械制造基础Fundamental of Mechanical Manufacture机械制造基础(金属工艺学) Fundamental Course of Mechanic Manufacturing (Meta机械制造系统自动化Automation of Mechanical Manufacture System机械制造中计算机控制Computer Control in Mechanical Manufacture机制工艺及夹具Mechanical Technology and Clamps积分变换Integral Transformation积分变换及数理方程Integral Transformation & Mathematical Equations积分变换控制工程Integral Transformation Control Engineering积分变换与动力工程Integral Transforms & Dynamic Engineering激光电源Laser Power Devices激光焊Laser Welding激光基础Basis of Laser激光技术Laser Technology激光加工Laser Processing激光器件Laser Devices激光器件与电源Laser Devices & Power Source激光原理Principles of Laser激光原理与技术Laser Principles & Technology极限分析Limit Analysis集合论与代数结构Set Theory & Algebraical Structure技术管理Technological Management技术经济Technological Economy技术经济学Technological Economics技术市场学Technological Marketing计量经济学Measure Economics计算方法Computational Method计算机导论Introduction to Computers计算机导论与实践Introduction to Computers & Practice计算机辅助设计CAD计算机辅助设计与仿真Computer Aided Design & Imitation 计算机辅助语言教学Computer-Aided Language Teaching 计算机辅助制造Computer-Aided Manufacturing计算机概论Introduction to Computers计算机绘图Computer Graphics计算机基础Basis of Computer Engineering计算机接口技术Computer Interface Technology计算机接口与通讯Computer Interface & Communication计算机局域网Regional Network of Computers计算机控制Computer Controling计算机设计自动化Automation of Computer Design计算机实践Computer Practice计算机数据库Computer Database计算机算法基础Basis of Computer Algorithm计算机图形显示Computer Graphic Demonstration计算机图形学Computer Graphics计算机网络Computer Networks计算机系统结构Computer Architecture计算机语言处理Computer Language Processing计算机原理Principle of Computer Engineering计算机在化学中的应用Application of Computer in Chemistry 计算机组成原理Principles of Computer Composition计算力学Computational Mechanics计算力学基础Basis of Computational Mechanics计算流体Fluid Computation继电保护新技术New Technology of Relay Protection继电保护原理Principles of Relay Protection继电保护运行Relay-Protected Operation检测技术Measurement Technique检测系统动力学Detection System Dynamics检测与控制Detection & Controling简明社会学Concise Sociology简明世界史Brief World History减振设计Vibration Absorption Designing渐近方法Asymptotical Method建筑材料Building Materials建筑初步Elementary Architecture建筑防火Building Fire Protection建筑概论Introduction to Architecture建筑构造Architectural Construction建筑结构Architectural Structure建筑结构抗震设计Anti-quake Architectural Structure Design建筑经济与企业管理Architectural Economy & Enterprise Management 建筑力学Architectural Mechanics建筑名作欣赏Appreciation of Architectural Works建筑入门Elementary Architecture建筑摄影Architectural Photographing建筑设备Architectural Equipment建筑设计Architectural Design建筑施工Construction Technology建筑绘画Architectural Drawing建筑物理Architecural Physics。

化学专业英语一、无机化学1. periodic table 元素周期表element 元素metal 金属nonmetal 非金属transition metal 过渡金属group / family 族alkali metal 碱金属alkaline earth metal 碱土金属chalcogen 氮族元素halogen 卤素noble gas 稀有气体period 周期lanthanide 镧系元素actinide 锕系元素block 区s-block s区(H、He、碱金属、碱土金属)p-block p区(IIIA~VIIA族、稀有气体(He除外))d-block d区(过渡金属)f-block f区(镧系元素、锕系元素)2. electron configuration 电子排布,电子构型electron shell 电子层shell (电子)层subshell (电子)亚层atomic orbital 原子轨道structure 结构molecule 分子molecular 分子的atom 原子atomic nucleus 原子核electron 电子electron cloud 电子云ion 离子anion /ˈæn.aɪ.ən/ 阴离子cation /ˈkæt.aɪ.ən/ 阳离子3. quantum number 量子数principal quantum number 主量子数(n)1≤nazimuthal quantum number 角量子数(ℓ)0≤ℓ≤n-1magnetic quantum number 磁量子数(m)- ℓ≤m ≤ℓspin quantum number 自旋量子数(s或m s)±1/2Pauli exclusion principle(泡利不相容原理):Two electrons cannot occupy the same quantum state within a quantum system simultaneously.Hund’s principle / Hund’s rule(洪特规则):If two orbitals of equal energy are available, electrons will occupy them singly before filling them in pairs.4. chemical bond 化学键ionic bond 离子键ionization energy 电离能electron affinity 电子亲和能ionic polarization 离子极化dipole 偶极covalent bond 共价键metallic bond 金属键(=metallic bonding)intermolecular force 分子间作用力van der Waals force 范德华力5. Lewis structure 路易斯结构lone pairs 孤电子对,孤对电子valence electron 价电子single bond 单键multiple bond 多重键(double bond 双键,triple bond 三键)6. chemical reaction 化学反应四种基本反应类型(four basic types):combination reaction 化合反应 C + O2= C O2decomposition reaction 分解反应Cu(OH)2 = CuO + H2Odisplacement reaction (single displacement reaction) 置换反应Fe + CuSO4 = FeSO4 + Cumetathesis reaction (double displacement reaction) 复分解反应AgNO3 + NH4I = NH4NO3+ AgI↓precipitation 沉淀(作用)precipitate 沉淀物其它反应:reduction-oxidation reaction (=redox reaction) 氧化还原反应oxidation 氧化reduction 还原combustion 燃烧(=burning)stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɪtri/ 化学计量stoichiometric ration 化学计量比reactivity series of metals / activity series of metals 金属活动性顺序standard electrode potential 标准电极电势(符号Eθ)chemical stability 化学稳定性acid-base reaction 酸碱(中和)反应conjugated acid 共轭酸conjugated base 共轭碱Lewis acid 路易斯酸Lewis base 路易斯碱Brønsted acid Brønsted酸Brønsted base Brønsted碱7. solution 溶液solute 溶质solvent 溶剂concentration 浓度concentrated 浓的dilute 稀的molality 质量摩尔浓度(mol溶质/kg溶剂) mole fraction 摩尔分数mass fraction 质量分数mass concentration 质量浓度(kg/m3)osmotic pressure 渗透压molar concentration 摩尔浓度(mol/L)solubility 溶解度solubility product 溶度积(K sp)soluble 可溶的slightly soluble 微溶的insoluble 难溶的,不溶的solvation 溶剂化作用solvate 溶剂合物(如CaCl2·C2H5OH)hydration 水合作用hydrate 水合物(如CuSO4·5H2O)hemihydrate 半水合物monohydrate 一水合物dihydrate 二水合物(tri- 3, tetra- 4, penta- 5, hexa- 6, hepta- 7, octa- 8, nona- 9, deca- 10, undeca- 11, dodeca- 12)8. compound (=chemical compound) 化合物inorganic compound 无机化合物organic compound 有机化合物nomenclature /nəˈmenklətʃə(r)/ 命名法chemical formula 化学式empirical formula 实验式,简式structural formula 结构式molecular formula 分子式macromolecule 高分子polymer 聚合物coordination complex 配合物,络合物元素名以ium(或um)结尾的,去掉后缀,某化物加ide,如硫化钠sodium sulfide。


原本打算每人交一篇论文,但估计一部分同学会网上下载,凑数,所以,我们考试就是词汇,范围包括下面我列出来的和课后的,只要能根据英语写出汉语即可。
下周上课时间我们简单考一下,请大家复习一下。
第一课element(元素), fundamental particles(基本粒子),protons, neutrons and electrons(质子,中子,电子),chemical identity(化学特性),nucleus (原子核),positively charged (带正电的),uncharged(不带电的),negatively charged (带负电的),electrically neutral(电中性的),atomic number(原子序数),Periodic Table(元素周期表),mass number(质量数),nucleon(核子),carbon(碳),orbital electrons(轨道电子),innermost electron(内壳层电子),naturally occurring(天然存在的),stable isotope(稳定同位素),unstable (不稳定的)or radioactive(放射性的),artificial means(人工手段),chemical bonds(化学键),nuclei(原子核nucleus的复数),chemical symbol(化学符号), subscript(下角标),superscript (上角标),oxygen(氧),radioactive isotopes(放射性同位素),Hydrogen(氢),nuclear engineering(核工程),heavy hydrogen(重氢)or deuterium(氘),tritium(氚)mass and charge(质量和电荷), atomic and nuclear physics(原子和原子核物理),atomic mass unit (u)(原子质量单位),one twelfth (十二分之一)carbon 12 (碳12),weighted mean (加权平均数),Avogadro’s Number(阿伏加德罗常数),compounds and molecules(化合物和分子),equal in magnitude and opposite in sign(数量相等,符号相反),electron-volt(电子伏特),mega electron-volt(兆电子伏特)( MeV),unit electronic charge(单位电荷),potential difference (势差),classical principle(经典原理),conservation of mass(质量守恒定律),mass defect (质量亏损),principle of the equivalence of mass and energy(质能相当原理),interchange of mass and energy(质能转换),laws of conservation of mass and conservation of energy(质量守恒和能量守恒定律),release of energy(能量的释放), absorption of energy(能量的吸收),equivalence between mass and energy(质能相当),force of electrostatic repulsion between like charge(同种电荷之间的静电排斥力), force of attraction(吸引力),nuclear force(核力),nucleon(核子),Binding Energy(结合能),energy of chemical binding(化学结合能),Energy Level(能级),ground state of energy(能量基态),nuclear reaction (核反应),excited states or levels (激发态或激发能级),discrete excited states (分立的激发态),spacing of the levels (能级间隔),excitation energy (激发能),average lifetime (平均寿命),decay, or become de-excited(衰变或退激发),emission of high energy electromagnetic radiation (发射高能电磁辐射),fission (裂变),uranium (铀),transuranium elements(超铀元素),radioactive barium 139(放射性钡139),split into fragments (分裂成碎片),intermediate mass elements (中间质量的元素),medium mass number(中等质量数), chain reaction (链式反应)uranium 235(铀235), Thorium 232(钍232), fissionable (可裂变的), fissile(易裂变的),uranium 233 and plutonium 239(钚239), low energy neutrons(低能中子),liquid drop model(液滴模型),short range nuclear forces(短程核力), surface tension (表面张力), action of the nuclear forces(核力作用),dumbbell shape (哑铃形),Coulomb force of repulsion (库仑排斥力),emission of gamma radiation(发射伽玛辐射),fission fragments (裂变碎片),neutrinos (中微子),macroscopic(宏观的)第二课radiation(辐射),material or electromagnetic origin(物质或电磁起源), nuclear decay(核衰变),particle accelerator(粒子加速器), cosmic rays(宇宙射线), molecules, atoms, electrons, and nuclei(分子,原子,电子,原子核),photons(光子),target(靶),projectile (入射粒子),nuclear energy field(核能领域),nuclear reactor(核反应堆), inert substances(惰性物质),protective shielding(防护屏),Excitation and Ionization (电离和激发),fluorescent light bulb(荧光灯泡), vacuum tube (真空管),impart energy to (传递能量),excitation of electrons to higher energy states(激发电子到更高能态),emission of light(发光).inner orbits (内层轨道),high energy radiation(高能辐射),heavy element target(重元素靶,X-rays due to transitions in the electronic orbits(电子在轨道间跃迁产生的X射线), bremsstrahlung (韧致辐射),ion pair(离子对),range(射程), millimeter(毫米),meter (米),Charged particles(带电粒子),fragments of fission (裂变碎片),heavy particles (重离子), inertia(惯性),electrostatic interaction (静电相互作用),kinetic energy (动能),inversely proportional to(成反比例),million-electron-volt (百万电子伏特)high-speed charged ion (高速带电离子),mutual repulsion (相互排斥),hyperbolic path (双曲线轨迹),scatter(散射),initial energy (初始能量),scattering of the photon(光散射), ionization by the photon(光电离), pair production(电子对产生). Photon-Electron Scattering(光-电子散射),rest mass (静止质量),bound to their nucleus(受原子核的束缚), free stationary particles(自由静止粒子),physical principles of energy and momentum conservation(能量和动量守恒物理原理. Compton effect(康普顿效应), scattered backward(背散射),the special theory of relativity (狭义相对论),cross section(截面),Photoelectric Effect(光电效应),incident photon (入射光子),light emission (发光), Electron-Positron Pair Production(电子正电子对产生),be converted into matter(转变成物质),theory of the equivalence of mass and energy(质能相当理论),law of conservation of charge (电荷守恒定律),be annihilated as material particles(作为物质粒子湮灭), substance(物质), attenuation of gamma rays in matter (伽马射线在物质中的衰减),mean free path (平均自由程),helium 4 (氦4),positive charge(正电荷),density of the material (物质密度),aluminum (铝),health hazard (健康危害),alpha-emitting isotope(α放射性同位素),be ingested in the body(摄入人体),radioactive isotope(放射性同位素),a spectrum of energies(能谱),ingestion hazard(摄入危害). penetrating power(穿透本领),radiation hazards (辐射危害),reactor shielding(反应堆屏蔽).light elements (轻元素),beryllium(铍),Neutron(中子),average lifetime (平均寿命),Neutron Source(中子源),radium 226(镭226),potential scattering (势散射),compound nucleus formation(复合核形成),capture(俘获)。

化学专业英语一、无机化学1. periodic table 元素周期表element 元素metal 金属nonmetal 非金属transition metal 过渡金属group / family 族alkali metal 碱金属alkaline earth metal 碱土金属chalcogen 氮族元素halogen 卤素noble gas 稀有气体period 周期lanthanide 镧系元素actinide 锕系元素block 区s-block s区(H、He、碱金属、碱土金属)p-block p区(IIIA~VIIA族、稀有气体(He除外))d-block d区(过渡金属)f-block f区(镧系元素、锕系元素)2. electron configuration 电子排布,电子构型electron shell 电子层shell (电子)层subshell (电子)亚层atomic orbital 原子轨道structure 结构molecule 分子molecular 分子的atom 原子atomic nucleus 原子核electron 电子electron cloud 电子云ion 离子anion /ˈæn.aɪ.ən/ 阴离子cation /ˈkæt.aɪ.ən/ 阳离子3. quantum number 量子数principal quantum number 主量子数(n)1≤nazimuthal quantum number 角量子数(ℓ)0≤ℓ≤n-1magnetic quantum number 磁量子数(m)- ℓ≤m ≤ℓspin quantum number 自旋量子数(s或m s)±1/2Pauli exclusion principle(泡利不相容原理):Two electrons cannot occupy the same quantum state within a quantum system simultaneously.Hund’s principle / Hund’s rule(洪特规则):If two orbitals of equal energy are available, electrons will occupy them singly before filling them in pairs.4. chemical bond 化学键ionic bond 离子键ionization energy 电离能electron affinity 电子亲和能ionic polarization 离子极化dipole 偶极covalent bond 共价键metallic bond 金属键(=metallic bonding)intermolecular force 分子间作用力van der Waals force 范德华力5. Lewis structure 路易斯结构lone pairs 孤电子对,孤对电子valence electron 价电子single bond 单键multiple bond 多重键(double bond 双键,triple bond 三键)6. chemical reaction 化学反应四种基本反应类型(four basic types):combination reaction 化合反应 C + O2= C O2decomposition reaction 分解反应Cu(OH)2 = CuO + H2Odisplacement reaction (single displacement reaction) 置换反应Fe + CuSO4 = FeSO4 + Cumetathesis reaction (double displacement reaction) 复分解反应AgNO3 + NH4I = NH4NO3+ AgI↓precipitation 沉淀(作用)precipitate 沉淀物其它反应:reduction-oxidation reaction (=redox reaction) 氧化还原反应oxidation 氧化reduction 还原combustion 燃烧(=burning)stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɪtri/ 化学计量stoichiometric ration 化学计量比reactivity series of metals / activity series of metals 金属活动性顺序standard electrode potential 标准电极电势(符号Eθ)chemical stability 化学稳定性acid-base reaction 酸碱(中和)反应conjugated acid 共轭酸conjugated base 共轭碱Lewis acid 路易斯酸Lewis base 路易斯碱Brønsted acid Brønsted酸Brønsted base Brønsted碱7. solution 溶液solute 溶质solvent 溶剂concentration 浓度concentrated 浓的dilute 稀的molality 质量摩尔浓度(mol溶质/kg溶剂) mole fraction 摩尔分数mass fraction 质量分数mass concentration 质量浓度(kg/m3)osmotic pressure 渗透压molar concentration 摩尔浓度(mol/L)solubility 溶解度solubility product 溶度积(K sp)soluble 可溶的slightly soluble 微溶的insoluble 难溶的,不溶的solvation 溶剂化作用solvate 溶剂合物(如CaCl2·C2H5OH)hydration 水合作用hydrate 水合物(如CuSO4·5H2O)hemihydrate 半水合物monohydrate 一水合物dihydrate 二水合物(tri- 3, tetra- 4, penta- 5, hexa- 6, hepta- 7, octa- 8, nona- 9, deca- 10, undeca- 11, dodeca- 12)8. compound (=chemical compound) 化合物inorganic compound 无机化合物organic compound 有机化合物nomenclature /nəˈmenklətʃə(r)/ 命名法chemical formula 化学式empirical formula 实验式,简式structural formula 结构式molecular formula 分子式macromolecule 高分子polymer 聚合物coordination complex 配合物,络合物元素名以ium(或um)结尾的,去掉后缀,某化物加ide,如硫化钠sodium sulfide。

化学专业英语版翻译 Modified by JEEP on December 26th, 2020.01T H E E L E M E N T S A N D T H E P E R I O D I C T A B L E01 元素和元素周期表The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is referred to as the atomic number, or proton number, Z. The number of electrons in an electrically neutral atom is also equal to the atomic number, Z. The total mass of an atom is determined very nearly by the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. This total is called the mass number, A. The number of neutrons in an atom, the neutron number, is given by the quantity A-Z.质子的数量在一个原子的核被称为原子序数,或质子数、周淑金、电子的数量在一个电中性原子也等于原子序数松山机场的总质量的原子做出很近的总数的质子和中子在它的核心。
这个总数被称为大量胡逸舟、中子的数量在一个原子,中子数,给出了a - z的数量。
The term element refers to, a pure substance with atoms all of a single kind. To the chemist the "kind" of atom is specified by its atomic number, since this is the property that determines its chemical behavior. At present all the atoms from Z = 1 to Z = 107 are known; there are 107 chemical elements. Each chemical element has been given a name and a distinctive symbol. For most elements the symbol is simply the abbreviated form of the English name consisting of one or two letters, for example:这个术语是指元素,一个纯物质与原子组成一个单一的善良。
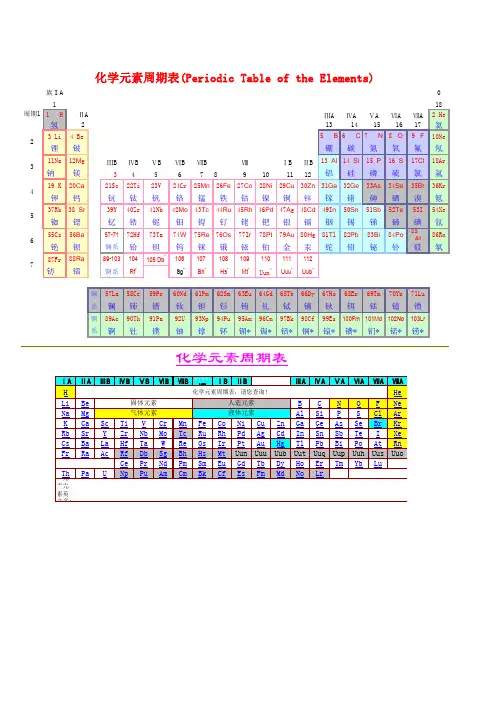
H氢qīngPeriodic Table of the Elements化学元素周期表He氦hàiLi锂l ǐBe铍p íSolids 固态Liquids 液态Gases 气态Man Made Elements人造元素B硼péngC碳tànN氮dànO氧yǎngF 氟f úNe氖nǎiNa 钠n àMg 镁měiAl 铝l ǚSi硅guīP磷línS硫liúCl 氯l ǜAr氩y àK钾jiǎ Ca钙gàiSc钪kàngTi钛tàiV钒fánCr 铬g èMn锰měngFe铁tiěCo 钴g ǔNi镍nièCu铜tóngZn锌xīnGa镓jiāGe锗zhěAs砷shēnSe 硒x īBr溴xiùKr 氪k èRb 铷r úSr 锶s īY 钇y ǐZr 锆gàoNb 铌n íMo钼m ùTc 锝d éRu钌liǎoRh铑lǎo Pd 钯p áAg银yínCd 镉g éIn铟yīnSn 锡x īSb 锑t īTe 碲d ìI碘diǎnXe氙xiān Cs 铯s èBa 钡bèi La-Lu镧lán系Hf 铪h āTa 钽tǎnW 钨w ūRe铼lái Os 锇éIr 铱y īPt 铂b ó Au金jīnHg汞gǒng Tl铊t āPb铅qiānBi 铋b ìPo 钋p ōAt 砹àiRn氡dōngFr 钫fāng Ra镭léiAc-Lr 锕ā系 Rf Db Sg Bh HsMtUunUuu Uub Uut Uuq Uup Uuh Uus UuoLa镧lán Ce铈shìPr镨p ǔNd 钕n ǚPm 钷p ǒSm钐shānEu铕yǒuGd 钆g áTb 铽t èDy 镝d íHo钬huǒEr 铒ěrTm铥diūYb 镱y ìLu 镥l ǔAc 锕āTh 钍t ǔPa 镤p úU铀yóuNp 镎n áPu 钚b ùAm镅méiCm 锔j ūBk锫péi Cf锎kāi Es 锿āiFm镄fèi Md钔ménNo锘nuòLr铹láo Name: 名称Number: 原子序数 Weight: 原子量 Shells: 核外电子排布Orbital: 价电子 Melt: 熔点Boil: 沸点制成:。
1. 概述element table树状结构在现代科学和工程领域中,element table(元素周期表)是一张表格,用于表示各种元素的化学性质。
它按照元素的原子序数、原子量和化学性质等进行排列,呈现出一种树状结构。
这个树状结构的排布方式,使得我们能够更好地理解元素之间的关系以及它们的物理、化学性质。
在本文中,我们将深入探讨element table树状结构的深度和广度,同时带您一同探寻这一主题。
2. element table树状结构的深度解析element table树状结构的深度包括了元素周期律的排列规律、元素的周期性趋势、元素化合物的形成等方面。
我们从元素周期律的排列规律出发,可以看到元素周期表上的元素是按照它们的原子序数从小到大排列的。
这种排列方式使得相邻元素之间的性质具有一定的相似性,例如同一周期内元素的化合价和化学反应性相似。
我们可以进一步探讨元素的周期性趋势,包括原子半径、电负性、离子半径等特性。
这些周期性趋势的变化规律,可以帮助我们理解元素周期表上不同位置元素之间的性质差异。
3. element table树状结构的广度分析在element table树状结构的广度方面,我们可以深入探讨元素之间的关系、元素的分类、元素化合物的性质等内容。
我们可以从元素周期表的分组来讨论元素之间的关系,例如惰性气体、碱金属、卤素等,每一组元素都有着相似的化学性质。
我们还可以探讨元素的分类,包括金属、非金属、过渡金属等类别,这些分类有助于我们更好地理解元素的性质和用途。
另外,在元素化合物的性质方面,我们可以讨论元素之间的化合关系,包括共价键、离子键、金属键等,以及化合物的性质、命名规则等内容。
4. 总结与展望通过本文的深度和广度分析,我们对element table树状结构有了更深入的理解。
从元素周期表的排列规律、周期性趋势到元素之间的关系、分类和化合物的性质,我们逐步深入探讨了这一主题。
希望本文能够帮助读者更全面、深刻地理解element table树状结构,并在相关领域有所启发。