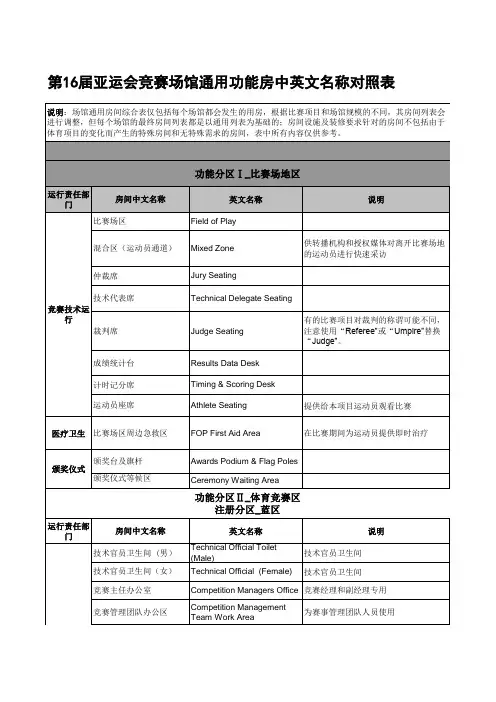
第 届亚运会竞赛场馆通用功能房中英文名称对照表
- 格式:xls
- 大小:152.00 KB
- 文档页数:14

亚运场馆介绍简报一、亚运会简介亚洲运动会(Asian Games)简称亚运会,是亚洲规模最大的综合性运动会,由亚洲奥林匹克理事会的成员国轮流主办,每四年举办一届。
亚运会不仅是一个体育盛会,也是一个文化交流的盛会,各国运动员在这里展示他们的技能和风采,增进友谊和团结。
二、亚运场馆介绍1. 杭州奥体中心杭州奥体中心是2023年杭州亚运会的主体育场,也是杭州地标性建筑之一。
该场馆可容纳观众6万人,举办过许多国内外大型体育赛事。
在这里,您可以欣赏到高水平的体育赛事和表演,感受亚运会的激情和魅力。
2. 杭州奥体中心游泳馆杭州奥体中心游泳馆是2023年杭州亚运会的重要场馆之一,也是国内最大的室内游泳馆之一。
该场馆拥有多个国际标准泳道,可举办各种级别的游泳比赛。
在这里,您可以欣赏到世界顶尖游泳选手的精彩表现,感受游泳运动的激情和魅力。
3. 杭州奥体中心体育馆杭州奥体中心体育馆是2023年杭州亚运会的重要场馆之一,也是国内最大的室内体育馆之一。
该场馆可容纳观众1.8万人,举办过许多国内外大型体育赛事。
在这里,您可以欣赏到各种体育比赛和表演,感受体育运动的激情和魅力。
4. 杭州奥体中心网球中心杭州奥体中心网球中心是2023年杭州亚运会的重要场馆之一,也是国内最大的网球场馆之一。
该场馆拥有多个国际标准网球场,可举办各种级别的网球比赛。
在这里,您可以欣赏到世界顶尖网球选手的精彩表现,感受网球运动的激情和魅力。
三、总结以上是对2023年杭州亚运会场馆的简要介绍。
这些场馆不仅为运动员提供了良好的比赛环境,也为观众提供了观赏比赛的绝佳场所。
在亚运会期间,这些场馆将举办各种体育比赛和表演,让观众们感受到运动的激情和魅力。

讲述亚运会场馆造型和功能的作文英文回答:The Asian Games, also known as the Asiad, is a major multi-sport event held every four years in Asia. It features athletes from all over Asia competing in various sports. The venues for the Asian Games are not only functional but also have unique and innovative designs.One example of a well-designed Asian Games venue is the Guangdong Olympic Stadium in Guangzhou, China. This stadium was built for the 2010 Asian Games and has a capacity of over 80,000 spectators. Its design is inspired by the shape of a blooming lotus flower, which is a symbol of purity and perfection in Chinese culture. The stadium's exterior is covered in a translucent material that allows natural light to filter through, creating a stunning visual effect both during the day and at night. The interior of the stadium is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities, including high-definition screens and sound systems, to enhance thespectators' experience.Another example is the Gelora Bung Karno Stadium in Jakarta, Indonesia, which hosted the Asian Games in 1962 and will host again in 2022. This stadium is considered an architectural masterpiece and is known for its unique shape and design. It features a distinctive roof structure that resembles a traditional Indonesian hat called "blangkon". The stadium has a seating capacity of over 80,000 and is equipped with modern facilities to ensure the comfort and safety of the spectators.中文回答:亚运会,也被称为亚洲运动会,是每四年在亚洲举办的一项重大多项运动赛事。

杭州亚运会的场馆介绍
杭州亚运会是计划于2022年9月10日至25日在中国杭州举
办的第19届亚洲运动会。
以下是一些杭州亚运会的场馆介绍:
1. 杭州奥体中心:作为亚运会的主场馆,杭州奥体中心位于钱塘江畔,总建筑面积约为400,000平方米。
该场馆包括一个主
体育场、一个室内游泳馆、一个室外游泳馆和若干训练馆。
主体育场可以容纳约80,000名观众,将举办开幕式、闭幕式和
田径比赛。
2. 头道温泉体育中心:位于杭州市下城区,总建筑面积约为52,500平方米。
该场馆将举办排球、跆拳道和摔跤比赛。
3.宁波国际会展中心:位于宁波市鄞州区,总占地面积约为220,000平方米。
该场馆包括室内体育馆和室外场地,将举办
羽毛球和射击比赛。
4. 京杭大运河体育公园:位于杭州市萧山区,总占地面积约为249,000平方米。
该场馆将举办侏儒花球、曲棍球、滑水和水
球比赛。
5. 湖墅南路篮球馆:位于杭州市西湖区,总建筑面积约为
21,500平方米。
该场馆将举办篮球比赛。
除了以上场馆,杭州还将利用现有的体育场馆和场地,如杭州馆、河坊街、杭州东站等,开展各项活动和竞赛。
整个赛事将
充分利用杭州市宽敞的道路、交通枢纽和接待设施,为来自亚洲各国的运动员和观众提供优质的体育赛事体验。

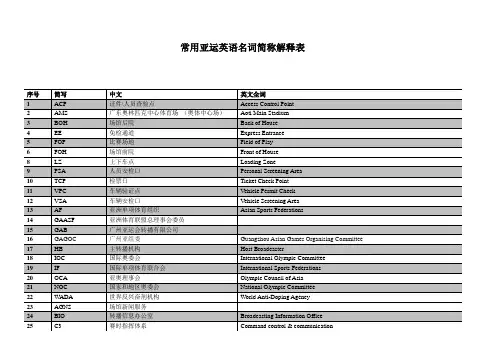
亚运英语1.火炬 torch2.火炬传递 torch relay3.观众spectator,而不用audience4.开幕式opening ceremony5.闭幕式closing ceremony6.无线电管理 radio management7.总赛程 general competition schedule8.新闻发布会 press conference9.公告 bulletin10.媒体公告 media notice11.奖牌榜 medal tally12.文化活动 cultural events,而不是 cultural activities(其实都可以,但不是很好)13.协办城市 co-host cities14.宗教场所 religious venue15.吉祥物 mascot16.亚运会理念 Vision of Asian games运动项目1.aquatic水上运动(即游泳)2.archery 射箭3.athletic 田径4.badminton 羽毛球5.baseball 棒球6.basketball 篮球7.billiard sports台球8.bowling 保龄球9.boxing拳击10.kayak,canoe皮划艇11.chess 棋类12.cricket 板球13.cycling 自行车14.dancesport 体育舞蹈15.dragon boat龙舟16.equestrian 马术17.fencing 击剑18.football 足球19.golf 高尔夫20.gymnastics 体操21.handball 手球22.hockey 曲棍球23.judo 柔道24.kabaddi 摔跤25.karate 空手道26.modern pentathlon 现代五项27.roller sport 滑轮28.rowing 划船29.rugby 橄榄球30.sailing 帆船31.sepaktakraw 藤球32.softball 垒球33.shooting 射击34.squash 壁球35.table tennis 乒乓球36.taekwondo 跆拳道37.tennis 网球38.triathlon 三项全能39.volleyball 排球40.weightlifting 举重41.wrestling 摔跤42.wushu 武术competition venue 比赛场馆1.Guangzhou international sports arena 广州国际体育演艺中心2.Aoti tennis center 奥体网球中心3.Aoti aquatic center 奥体游泳中心4.Haizhu sports center 海珠体育中心5.Guanggong cricket stadium 广工板球场6.Guangzhou chess institute 广州棋院n games town gymnasium 亚运城体育场馆8.Guangzhou velodrome 广州室内自行车馆9.Nansha gymnasium 南沙体育馆1、不要再用 more and more了;该词组被评为中国恶俗词组榜第一!!老师说。

杭州亚运会65个竞赛场馆答题(实用版)目录1.杭州亚运会简介2.竞赛场馆概况3.杭州奥体中心体育馆4.杭州奥体中心体育场5.杭州棋院(智力大厦)棋类馆6.杭州体育馆7.杭州奥体中心游泳馆8.中国轻纺城体育中心体育馆9.竞赛场馆分布正文杭州亚运会,即 2022 年第 19 届亚洲运动会,将于 2022 年在我国杭州市举行。
此次亚运会共设 40 个竞赛大项,其中有 31 个是奥运会项目,还有 9 个非奥运会项目,另外还增加了电子竞技和霹雳舞两个竞赛项目。
杭州亚运会的竞赛场馆共有 65 个,分布在杭州市的不同地区。
杭州奥体中心体育馆是杭州亚运会篮球项目的比赛场馆,位于杭州奥体中心南端。
该馆总建筑面积为 74470 平方米,约 18000 座,能够进行篮球、羽毛球、排球、乒乓球、手球、竞技体操、拳击、武术、室内足球等比赛。
杭州奥体中心体育场,又被称为“大莲花”,是杭州亚运会主体育场及田径项目比赛场地。
它位于杭州市滨江区、杭州城市新中心,距离亚运村约 3 公里。
场馆用地面积为 8.23 万平方米,总建筑面积约为 21.6万平方米,座席数约 80000 个。
杭州棋院(智力大厦)棋类馆是杭州亚运会棋类项目比赛场馆,位于杭州市萧山区奥体博览城区块。
该馆的 1-14 层为赛时用地,建筑面积为26633 平方米。
在完成现有亚运会赛事要求的同时,充分考虑赛后的利用,即保证亚运会赛后可快速转换成赛事、餐饮、商业配套的一体化智力运动大楼。
杭州体育馆是杭州亚运会拳击项目比赛场馆,位于杭州市拱墅区,地处亚运村西北侧且相距 10 公里,包含比赛馆及附属训练馆。
该馆始建于1966 年,为文保建筑,因其独特的马鞍形屋面造使得其成为 20 世纪杭州市标志性体育建筑设施。
总建筑面积 34202 平方米,观众席位数 4300 个。
杭州奥体中心游泳馆是杭州亚运会游泳、跳水、花样游泳项目比赛场馆及训练场馆,位于杭州奥体中心北端。
总建筑面积为 53959 平方米,观众席位数约 6000 个,是一个集游泳、跳水比赛和训练为一体的专业运动场馆。

杭州亚运会主要场馆
杭州亚运会主要场馆包括:
1. 杭州奥林匹克体育中心:是杭州亚运会的主场馆,包括主体育场和室内体育馆。
主体育场可容纳约8万观众,将用于举办开闭幕式、田径比赛等大型赛事;室内体育馆可容纳约1.6万观众,将用于举办篮球、排球等项目的比赛。
2. 杭州国际博览中心:作为亚运会的主要场馆之一,将举办羽毛球、举重等项目的比赛。
该场馆配备了包括主赛场和训练场在内的多个比赛场地,可满足多个项目的需求。
3. 杭州东湖体育中心:位于市中心的体育场馆,将举办足球、曲棍球等项目的比赛。
该场馆还包括一个标准的田径场和篮球场。
4. 杭州体育馆:位于杭州市郊区,是一座多功能体育场馆,将举办乒乓球、武术、跆拳道等项目的比赛。
5. 杭州亚运村:是为亚运会提供住宿的地方,包括运动员村、裁判员村和工作人员村。
亚运村中还设有训练场地,供各国运动员进行训练。
除了以上几个主要场馆外,杭州还将利用现有的体育场馆、游泳馆等设施进行一些比赛项目的举办。
同时,还将在市区的公共场所设置临时场馆,如体育公园、广场等,用于一些小型项
目的比赛。
杭州亚运会主要场馆的设施完善,将为运动员和观众提供良好的比赛和观赛环境。



Guangzhou (Canton), a prosperous metropolis full of vigor, is the capital city of GuangdongProvince located along the south coastline of China. Being an excellent port on the Pearl River navigable to the South China Sea, and with fast accessibility to Hong Kong and Macau, Guangzhou serves as the political, economic, scientific, educational and cultural center in Guangdong area.Being the first cities benefited from China's Reform and Opening Up policy since 1978, Guangzhou acts as the pioneer of the economic development of the country, with thousands of large, small and medium-sized enterprises, which offer more job opportunities and make the city a heavily populated area. The city is especially prosperous in commerce, tourism, dining, finance and real estate. For travelers, Guangzhou shows much attraction through its famous sights such as the Five Ram Statue in YuexiuPark, Pearl River and WhiteCloudMountain. Guangzhou History. from googleearthIt is believed that the first city built at the site of Guangzhou was Panyu (蕃禺, later simplifed to 番禺; the locals pronounced this in Cantonese as Poon Yu) founded in 214 BC. The city has been continuously occupied since that time. Panyu was expanded when it became the capital of the Nanyue Kingdom (南越) in 206 BC.Recent archaeological founding of her palace suggests that the citymight have traded frequently with foreigners by the sea routes. The foreign trade continued through every following dynasty and the city remains a major international trading port to this day.The Han Dynasty annexed Nanyue in 111 BC, and Panyu became a provincial capital and remains so until this day. In 226 AD, the city became the seat of the Guang Prefecture (廣州; Guangzhou). Therefore, 'Guangzhou' was the name of the prefecture, not of the city. However, people grew accustomed to calling the city Guangzhou, instead of Panyu. Although the Chinese name of Guangzhou replaced Panyu as the name of the walled city, Panyu was still the name of the area surrounding the walled city until the end of Qing era.Arabs and Persians sacked Guangzhou (known to them as Sin-Kalan) in AD 758, 2 according to a local Guangzhou government report on October 30, 758, which corresponded to the day of Guisi (癸巳) of the ninth lunar month in the first year of the Qianyuan era of Emperor Suzong of the Tang Dynasty.[1][2][3]During the Northern Song Dynasty, a celebrated poet called Su Shi visited Guangzhou's BaozhuangyanTemple and wrote the inscription 'Liu Rong' (Six Banyan Trees) because of the six banyan trees he saw there. It has since been called the Temple of the Six Banyan Trees.The Portuguese were the first Europeans to arrive to the city by sea, obtaining the monopoly for external trade with its harbour by 1511. They were later expelled from their settlements in Guangzhou (in Portuguese Canton or Cantao), but instead granted use of Macao (first occupied in 1511) as a trade base with the city in 1557. They would keep a near monopoly of foreign trade in the region until the arrival of the Dutch in the early XVII century.After China brought Taiwan under its control in 1683, the Qing government became open to encouraging foreign trade. Guangzhou quickly emerged as one of the most adaptable ports for negotiating commerce and before long, many foreign ships were going there to procure cargos. Portuguese in Macao, Spanish in Manila, and Armenians and Muslims from India were already actively trading in the port by the 1690s, when the French and English East India companies' ships began frequenting the port. Other companies were soon to follow: the Ostend General India Company in 1717; Dutch East India Company in 1729; the first Danish ship in 1731, which was followed by a Danish Asiatic Company ship in 1734; the Swedish East India Company in 1732; followed by an occasional Prussian and Trieste Company ship; the Americans in 1784; and the first ships from Australia in 1788. By themiddle of the 18th century, Guangzhou had emerged as one of the world's great trading ports, which was a distinction it maintained until the outbreak of the Opium War in 1839 and the opening of other ports in China in 1842.Guangzhou was one of the five Chinese treaty ports opened by the Treaty of Nanking (signed in 1842) at the end of the First Opium War between Britain and China. The other ports were Fuzhou, Xiamen, Ningbo, and Shanghai.In 1918, 'Guangzhou' became the official name of the city, when an urban council was established in it. Panyu became a county's name south of Guangzhou. In both 1930 and 1953, Guangzhou was promoted to the status of a Municipality, but each promotion was cancelled within the year.Japanese troops occupied Guangzhou from 1938-10-12 to 1945-09-16. Communist forces entered the city on October 14, 1949. Their urban renewal projects improved the lives of many residents. New housing on the shores of the Pearl River provided homes for the poor boat people. Reforms by Deng Xiaoping, who came to power in the late 1970s, led to rapid economic growth due to the city's close proximity to Hong Kong and access to the Pearl River.As labor costs increased in Hong Kong, manufacturers opened new plants in the cities of Guangdong including Guangzhou. As the largest city in one of China's wealthiest provinces, Guangzhou attracts farmers from the countryside looking for factory work. Cantonese links to overseas Chinese and beneficial tax reforms of the 1990s have aided the city's rapid growth.In 2000, Huadu and Panyu were merged into Guangzhou as districts, and Conghua and Zengcheng became county-level cities of Guangzhou.一、亚运会的主会场广州亚运会将使用70个场馆,设置的50个比赛场馆和20个训练场馆,形成了多中心、多功能的空间格局,即广东奥林匹克体育中心、天河体育中心、大学城、亚运城及花园酒店周边场馆等五大亚运场馆群,并辐射到广州市10个区2个县级市和佛山、东莞、汕尾3个分赛区城市。
亚运[yà yùn]基本翻译Asian Games网络释义亚运:Asian Games|Asienspiele|Juegos Asiáticos多哈亚运:Asienspiele 2006|Jeux asiatiques de 2006 釜山亚运:Asienspiele 2002|2002 Asian Games举重:Weightliftingbaseball 棒球basketball 篮球football/soccer 足球tennis 网球rugby 橄榄球softball 垒球handball 手球water polo 水球拳击:boxing男子1公里计时赛Men's/Women's Team Sprint 男子/女子个人追逐赛(男4000米,女3000米)Men's Team Sprint 男子团队追逐赛(4000米)Men's/Women's Points Race 男子/女子记分赛Men's Keirin 縚林赛Men's Madison 麦迪逊赛Cycling Mountain Bike:Cross Country 山地车:越野马术:equestriandiscus 铁饼weight throw 链球gavelock;javelin 标枪decathlon 男子十项全能(100米跑、跳远、铅球、跳高、400米跑,110米跨栏跑、铁饼、撑竿跳高、标枪、1500米跑)heptathlom 女子七项全能(100米跨栏跑、跳高、铅球、200米跑、跳远、标枪、800米跑)triathlon 铁人三项:游泳(1500米);自行车(40公里);跑步(10公里)射击: shooting男子/女子3米双人跳板游泳:swimming400 medley 400米混合泳freestyle 自由泳breaststroke 蛙泳butterfly 蝶泳backstroke 仰泳Men's/Women's 4x100 freestyle 男子/女子4x100混合泳接力Men's Artistic Gymnastics Parallel Bars 竞技体操男子双杠Men's Artistic Gymnastics horizontal Bar 竞技体操男子单杠Men's/Women's Artistic Gymnastics Team Finals 男子/女子团体竞技体操Men's/Women's Artistic Gymnastics All-Around Finals 竞技体操男子/女子个人全能决赛击剑:FencingMen’s/Women’s Fencing Sabre 击剑男子/女子长剑Men's Fencing (Team) Foil 击剑男子(团体)花剑Women’s Fencing Foil 击剑女子花剑final placing 决赛名次medal tally 奖牌榜lost to 败给defeat 击败win title 夺魁go for gold 夺取金牌defend title 卫冕road to 进军victory and ceremony/awarding ceremony 颁奖仪式The victory ceremony for … will now take place 颁奖仪式现在开始announce results 公布成绩The medals will be presented in descending order-1st, 2nd, 3rd. 按第一名、第二名、第三名顺序颁发奖牌。
杭州亚运会各个场馆的比赛项目杭州亚运会各个场馆的比赛项目是什么上城赛区上城体育中心体育场钱潮路12号-16号亚运会项目:足球杭州拱墅赛区杭州体育馆位置:体育场路200号亚运会项目:拳击,预计金牌数13枚亚残运会项目:硬地滚球中国杭州电竞中心位置:杭州北景园生态公园内,新天地对面(留石高架路北侧)亚运会项目:电子竞技,预计金牌数8枚拱墅运河体育公园体育馆位置:拱墅运河体育公园内亚运会项目:乒乓球、霹雳舞,预计金牌数9枚亚残运会项目:乒乓球拱墅运河体育公园体育场位置:拱墅运河体育公园内亚运会项目:曲棍球,预计金牌数2枚亚残运会项目:盲人足球西湖赛区黄龙体育中心体育场位置:黄龙路1号亚运会项目:足球,预计金牌数2枚亚残运会项目:田径黄龙体育中心体育馆位置:黄龙路1号亚运会项目:竞技体操、艺术体操、蹦床,预计金牌数18枚黄龙体育中心游跳馆位置:黄龙路1号亚运会项目:水球,预计金牌数2枚浙江大学(紫金港校区)体育馆位置:浙江大学紫金港校区内(余杭塘路866号)亚运会项目:五人制篮球西湖国际高尔夫球场位置:之江路200号亚运会项目:高尔夫球,预计金牌数4枚浙江工业大学(屏峰校区)板球场位置:浙江工业大学屏峰校区内(留和路288号)亚运会项目:板球,预计金牌数2枚滨江赛区滨江体育馆位置:江虹路996号亚运会项目:羽毛球,预计金牌数7枚亚残运会项目:羽毛球杭州奥体中心体育场位置:飞虹路闻涛路交叉口东北角亚运会项目:田径,预计金牌数48枚杭州奥体中心网球中心位置:飞虹路丹枫路交叉口北侧亚运会项目:软式网球、网球,预计金牌数10枚亚残运会项目:轮椅网球萧山赛区杭州奥体中心游泳馆位置:博奥路平澜路交叉口西南侧亚运会项目:游泳、花样游泳、跳水,预计金牌数53枚亚残运会项目:游泳杭州奥体中心体育馆位置:博奥路平澜路交叉口西南侧亚运会项目:五人制篮球,预计金牌数2枚亚残运会项目:轮椅篮球杭州奥体中心国博壁球馆位置:奔竞大道353号亚运会项目:壁球,预计金牌数5枚杭州棋院(智力大厦)棋类馆位置:博奥路利一路交叉口东侧亚运会项目:桥牌、象棋、围棋、国际象棋,预计金牌数13枚亚残运会项目:围棋、国际象棋萧山体育中心体育场位置:市心南路398号亚运会项目:足球萧山体育中心体育馆位置:市心南路398号亚运会项目:举重,预计金牌数14枚亚残运会项目:举重浙江师范大学(萧山校区)体育馆位置:浙江师范大学萧山校区内(耕文路1108号)亚运会项目:手球,预计金牌数2枚萧山临浦体育馆位置:临浦镇东藩路与人民路交叉口亚运会项目:柔道、柔术、克柔术,预计金牌数30枚亚残运会项目:盲人柔道萧山瓜沥文化体育中心位置:东灵路269号亚运会项目:卡巴迪、武术,预计金牌数17枚亚残运会项目:跆拳道余杭赛区杭州师范大学(仓前校区)体育场位置:杭州师范大学仓前校区内(余杭塘路2318号),良睦路东侧亚运会项目:七人制橄榄球,预计金牌数2枚杭州师范大学(仓前校区)体育馆位置:杭州师范大学仓前校区内(余杭塘路2318号),良睦路东侧亚运会项目:排球,预计金牌数2枚临平赛区临平体育中心体育场位置:东湖南路177号亚运会项目:足球临平体育中心体育馆位置:东湖南路177号亚运会项目:排球、空手道,预计金牌数12枚亚残运会项目:坐式排球钱塘赛区杭州电子科技大学体育馆位置:杭州电子科技大学内(下沙2号大街1158号)亚运会项目:击剑,预计金牌数12枚亚残运会项目:轮椅击剑浙江工商大学文体中心位置:浙江工商大学内(学正街18号)亚运会项目:手球钱塘轮滑中心位置:之江东路与拾里路交叉口东北侧亚运会项目:轮滑、滑板,预计金牌数16枚富阳赛区富阳银湖体育中心位置:龙溪南路与九龙大道交叉路口西侧亚运会项目:现代五项、射击(步枪、手枪、飞碟)、射箭,预计金牌数47枚亚残运会项目:射击、射箭富阳水上运动中心位置:东洲岛北支江南岸亚运会项目:赛艇、皮划艇(激流回旋、静水),预计金牌数30枚亚残运会项目:皮划艇、赛艇临安赛区临安文化体育会展中心位置:九州街599号亚运会项目:跆拳道、摔跤,预计金牌数31枚桐庐赛区桐庐马术中心位置:瑶琳镇瑶琳路西侧亚运会项目:马术,预计金牌数6枚淳安赛区淳安界首体育中心游泳赛场位置:千岛湖旅游度假区界首区块亚运会项目:马拉松游泳,预计金牌数2枚淳安界首体育中心小轮车赛场位置:千岛湖旅游度假区界首区块亚运会项目:小轮车,预计金牌数2枚淳安界首体育中心山地自行车赛场位置:千岛湖旅游度假区界首区块亚运会项目:山地自行车,预计金牌数2枚淳安界首体育中心公路自行车赛场位置:千岛湖旅游度假区界首区块亚运会项目:公路自行车,预计金牌数4枚淳安界首体育中心自行车馆千岛湖旅游度假区界首区块亚运会项目:场地自行车,预计金牌数12枚亚残运会项目:自行车(含公路)淳安界首体育中心铁人三项赛场千岛湖旅游度假区界首区块亚运会项目:铁人三项,预计金牌数3枚杭州亚运会赛事进程2023年4月25日上午,杭州亚运会代表团团长大会在杭州开幕。
杭州亚运会模拟赛场馆
1. 杭州奥体中心:作为亚运会的主场馆之一,杭州奥体中心是一个综合性运动场馆,包括主体育场、游泳馆和体育馆等多个场馆,可举办田径、足球、游泳等多项比赛。
2. 杭州国际会展中心:作为亚运会的另一主场馆,杭州国际会展中心内设有大型体育馆,可以承办室内项目的比赛,如羽毛球、乒乓球等。
3. 杭州未来科技城体育馆:该体育馆位于杭州未来科技城内,设施齐全,适合举办室内球类比赛,如篮球、排球等。
4. 杭州东部新城体育中心:位于杭州市东部的新城区域,该体育中心配备了多功能体育馆和游泳馆,可用于举办多项比赛。
5. 杭州奥林匹克体育中心:该体育中心是奥运会标准的综合性运动场馆,设有田径场、游泳馆、乒乓球馆等多个场馆,可承办各类比赛。
6. 浙江大学体育馆:作为浙江大学内的体育设施之一,该体育馆设备先进,适合举办室内球类比赛,如篮球、排球等。
7. 杭州市大运体育场:位于杭州市的大运体育场是一个大型综合性运动场馆,设施完备,适合举办田径、足球等项目的比赛。
8. 杭州绿城国际体育场:杭州绿城国际体育场是一个现代化的足球场馆,配备了专业的足球场地和看台设施,适合举办足球
比赛。
这些场馆将成为杭州举办亚运会模拟赛的重要场所,为运动员和观众提供优秀的比赛条件。
2023杭州亚运会场馆介绍2023杭州亚运会场馆介绍杭州亚运会共设有42个竞赛大项。
这42个竞赛大项包括31个奥运项目和11个非奥运项目,其中这11个非奥运项目具有浓郁的亚洲特色和中国特色。
下面小编为大家带来杭州亚运会场馆介绍,希望对您有所帮助!杭州亚运会场馆介绍从杭州亚组委获悉,原则上所有竞赛、训练场馆自2022年7月1日起惠民开放,按照“一场一策、一馆一策”制定开放方案计划。
杭州亚运会竞赛、训练场馆按照不同使用方向进行分门别类惠民开放。
第一类,已确定第三方运营单位实行市场化运营的场馆,比如杭州奥体中心体育场(“大莲花”),可收取适当费用,市场化引入各类体育文化资源和品牌,搭建平台组织开展体育赛事、培训会展、文艺演出等。
第二类,承担基本体育公共服务功能的各区县体育中心场馆,要发挥全民健身主阵地作用,运维成本比较低的体育馆、广场、田径场免费为市民开放。
第三类,部分尚不具备市场化运营和全民健身条件的专用场馆,比如赛艇、皮划艇、马术、射击、自行车等专用运动场地,可通过引进相关专业队伍作为训练基地,磨合场馆设施设备,并对外适度开展体验活动。
第四类,已建成的高校场馆,在满足日常教学外,可以承办各类体育赛事活动,倡导向社会开放,提高使用效率。
杭州亚运会吉祥物介绍04月3日,2022年第19届亚运会组委会发布杭州亚运会吉祥物“江南忆”组合,“琮琮”、“莲莲”、“宸宸”三个机器人造型的吉祥物分别代表了世界遗产良渚古城遗址、世界遗产西湖和世界遗产京杭大运河。
琮琮“琮琮”以机器人的造型代表世界遗产良渚古城遗址,名字源于良渚古城遗址出土的代表性文物玉琮。
具有精美绝伦纹饰的玉琮是良渚文化的重要标志物,散发着永恒的魅力。
“琮琮”实证了中华五千多年文明史,全身以源自大地、象征丰收的黄色为主色调,头部装饰的纹样取自良渚文化的标志性符号“饕餮纹”,意寓“不畏艰险、超越自我”。
“琮琮”坚强刚毅、敦厚善良、体魄强健、热情奔放,展现了不屈不挠的创业精神,鼓舞人们激发生命活力,创造美好生活。