高中英语语法讲义 ——简单句
- 格式:doc
- 大小:59.77 KB
- 文档页数:6

十、简单句1、简单句的特点:简单句通常只由一个主语(或并列主语)和一个谓语(或并列谓语)构成。
2、简单句的种类:简单句一般分为陈述句、疑问句、感叹句和祈使句四种。
3、陈述句:用来说明一个事实的句子叫陈述句。
它有肯定式和否定式两种形式。
▲陈述句的肯定式:He is a middle school student.(他是个中学生)/ I have a hammer in my hand.(我手上有把锤子)/ She teaches us geography.(她教我们地理)/ The new play was good enough and everybody enjoyed it.(新的话剧非常好大家都喜欢)▲陈述句的否定式:1)谓语动词如果是be 、助动词、情态动词时,在它们的后面加“not”。
如:My brotheris not a teacher.(我的弟弟不是教师)/ He does not have a cousin.(他没有堂兄弟)/ I will not go there tomorrow.(明天我不去那儿)/ My mother is not cooking a meal inthe kitchen.(我母亲现在不在厨房里做饭)/ You must not make such mistakes again.(你不该再犯类似错误了)/ We haven’t discussed the question yet(我们还没有讨论那个问题呢).2)谓语动词如果没有上述词语而是其他动词时,须在它的前面加do not(don’t).如:Idon’t know anything about it.(此事我一无所知) / Li Ming does not feed pigs in thecountryside.(李明不在农村养猪)/ We didn’t expect to meet her right here.(我们没指望着在这里见到她)/ We didn’t have a meeting yesterday afternoon.(昨天下午我们没有开会)3)如果“have”作“有”讲,也可以在它后面加not构成否定式,其形式与have got的否定式相同。



高考英语复习:简单句主谓宾结构详解讲义1)高考英语简单句主谓宾结构详解高考英语中,简单句的主谓宾结构是一个基础且重要的语法点。
下面,我将详细解释主谓宾结构的知识点,并给出相应的例句。
一、主谓宾结构知识点主谓宾结构是句子的基本框架,其中主语是句子所描述的主体,谓语描述主语的动作或状态,而宾语则是动作的对象或接受者。
主语(Subject):通常是句子中的名词或代词,表示句子所描述的人或事物。
谓语(Verb):描述主语的动作或状态,通常由动词担任。
宾语(Object):是动作的对象或接受者,也是由名词或代词来担任。
二、例句基本形式:主语+ 谓语+ 宾语I love music.(我爱音乐。
)在这个例子中,“I”是主语,“love”是谓语,“music”是宾语。
不同时态的主谓宾结构She reads books every day.(她每天读书。
)一般现在时,表示经常性或习惯性的动作。
He will buy a new car next month.(他下个月会买一辆新车。
)一般将来时,表示将来某个时间将要发生的动作。
They had finished their homework before dinner.(他们晚饭前已经完成了作业。
)过去完成时,表示在过去某个时间之前已经完成的动作。
不同动词类型的主谓宾结构She eats an apple.(她吃一个苹果。
)及物动词,直接带宾语。
I feel happy.(我感到快乐。
)系动词,后接形容词作表语,而非直接宾语。
三、注意事项在构建主谓宾结构的句子时,需要注意以下几点:主语和谓语在人称和数上必须保持一致。
宾语通常需要与谓语动词在逻辑上保持一致,即宾语通常是动词行为的直接承受者。
在实际运用中,主谓宾结构可以与其他句子成分(如状语、定语等)结合,形成更复杂但逻辑清晰的句子。
四.例句基本形式:主语+ 谓语+ 宾语She writes a letter.(她写一封信。

简单句、并列句及附加疑问句一.简单句按照句子中动词的语法功能, 英语句子可归纳为五种基本句型, 各种各样的句子都可以看成是这五种句型的扩展. 学习, 掌握这五种基本句型, 对于认识英语句子的基本结构, 提高连词造句, 阅读理解和书面表达的能力将会有很大的帮助.五种基本句型:第一种: 主语+谓语第二种: 主语+谓语+宾语第三种: 主语+谓语+表语第四种: 主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语第五种: 主语+谓语+宾语+宾语补足语1.主语+谓语(不及物动词)在这个句型中的动词是不及物的行为动词, 不能带宾语. 这种动词表示主语的行为动作, 意义基本完整, 所以不再需要宾语. 不及物动词没有被动语态形式. 在这个句型中, 谓语后面有时不再附加任何成分, 而大多数情况下有状语性质的修饰语. 这种修饰语可以由副词, 介词短语, 不定式短语, 分词短语以及从句等来担任. 例如:Tom is writing. (Little Tom is writing at the desk now.)He stopped. (He stopped to have a look.)The boy stood there, begging. (The boy whose parents died stood there, begging.)2.主语+谓语+宾语本句型中的及物动词同样也为行为动词, 表明一个具体实在的动作, 但其本身所表示的意义并不完整, 需要有一个宾语, 才能表达一个完整的概念. 例如:We have a TV set.You may use my pen. I will use hers.He doesn’t like the first. He likes the third.3.主语+系动词+表语在本句型中, 由系动词及表语构成表性状的复合谓语, 说明主语的身份, 特征, 性质, 状态等. 英语中除了最常见的系动词be以外, 还有表示感官的连系动词look, feel, sound, taste, smell等; 表示变化的连系动词get, turn, become, grow, fall, come等; 表示状态的连系动词keep, remain, stay, continue, seem等. 例如:Rose is an English boy.The boy looks like his father.4.主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语有些动词后面, 可以有两个宾语, 这个宾语一个指人, 一个指物, 指人的叫间接宾语, 表示动作的方向和目标; 指物的叫直接宾语, 表示动作的承受者, 间接宾语一般放在直接宾语之前. 例如:She brought me some fruit.Can you do us a favour?这两个句子中的间接宾语都可以变成介词短语放在直接宾语后面. 例如:She brought some fruit to me.Can you do a favour for me?5.主语+谓语+宾语+宾语补足语宾语和补足语之间的关系是逻辑上的主谓关系, 即宾语是宾语补足语的逻辑主语。


简单句简单句(Simple Sentence)是只包含一个主谓结构的句子。
简单句分成四类:陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。
陈述句1.陈述句(Declarative Sentence)否定的表示方法(1)使用“助动词+not”构成谓语动词。
若谓语动词为be,其否定式为“be+not”。
例如:Bram does not like to eat sweet food.布莱姆不喜欢吃甜食。
She has not had her breakfast.她还没吃早餐。
They are not typists.他们不是打字员。
(2)使用含有否定意义的代词、副词或有否定前缀的词。
例如:Nothing could be found in the sunken ship.沉船上没发现什么东西。
Scarcely any enemy planes were left undamaged after the attack.敌机遭到攻击后几乎没有不受破坏的。
They were unhappy about my answer.他们对我的回答不满意。
(3)使用含否定意义的结构和词汇。
例如:She was too excited to say a word.她激动得一句话也说不出来。
This is more than we can stand.我们忍受不了。
The city has greatly changed beyond our recognition. 城市变化很大,我们认不出来了。
He is above cheating in the exams.他不会在考试中作弊。
2. 肯定词、否定词与非肯定词肯定词否定词非肯定词one -onesome no-body -thing any-body thing-where -wheresomehow in no way in any waysometimes never everstill no longer any longerno more any moreone or the other neither eithersome no/none any否定结构可以由否定词构成,也可以由not+非肯定词构成。

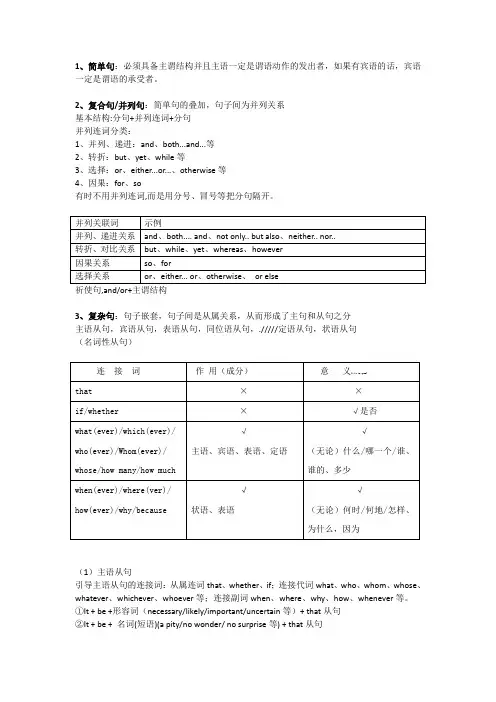
1、简单句:必须具备主谓结构并且主语一定是谓语动作的发出者,如果有宾语的话,宾语一定是谓语的承受者。
2、复合句/并列句:简单句的叠加,句子间为并列关系基本结构:分句+并列连词+分句并列连词分类:1、并列、递进:and、both...and...等2、转折:but、yet、while等3、选择:or、either...or...、otherwise等4、因果:for、so有时不用并列连词,而是用分号、冒号等把分句隔开。
祈使句,and/or+主谓结构3、复杂句:句子嵌套,句子间是从属关系,从而形成了主句和从句之分主语从句,宾语从句,表语从句,同位语从句,./////定语从句,状语从句(名词性从句)(1)主语从句引导主语从句的连接词:从属连词that、whether、if;连接代词what、who、whom、whose、whatever、whichever、whoever等;连接副词when、where、why、how、whenever等。
①It + be +形容词(necessary/likely/important/uncertain等)+ that从句②It + be + 名词(短语)(a pity/no wonder/ no surprise等) + that从句③It + be + 过去分词(said/ reported/decided/believed等) + that从句④It+不及物动词( seems/ appears/ happens等) + that从句只用Whether的两种情况:①句首②whether... or not③介词+ whether 从句(2)宾语从句●引导宾语从句的连接词:从属连词that、whether、if;连接代词what、who、whose、whatever、whichever、whoever等;连接副词when、where、why、how等。
从句用陈述句语序。
高考英语句子成分和简单句的基本句型一、句子成分1、主语:说明句子所谈的是:“什么人”或“什么物”,主语通常由名词、代词或相当于名词的词或短语充当。
EG:Lucy likes her new car very much. 露西喜欢她的新车。
【名词作主语】He goes to and from schoolby bike every day.他每天都起得很早。
(代词作主语)To learn English well is a challenge.学好英语是一项挑战性工作。
【不定式短语作主语】2、谓语:说明主语“做什么”、“是什么”或“怎么样”,英语中谓语只能用动词充当。
例如:We work hard.我们努力工作。
The boy caught a bird. 那个男孩逮住一只鸟。
He is like his father. 他像他父亲。
注意:介词不能作谓语,必须与be动词连用,构成系表结构,一起作谓语。
谓语和主语在人称和数方面必须保持一致。
EG:Music is the utmost pleasure in life.音乐是人生最大的快乐。
As I take each bite, the sweet and mild flavour of the red beanfilling slowly fills my mouth.3、宾语:宾语是动作的对象。
由名词、代词或相当于名词的词或短语充当,说明主语做“什么”。
EG:Tom bought a story-book.汤姆买了一本故事书。
【名词作宾语】I saw him yesterday. 昨天我看到他了。
【代词宾语】He decided to run away from home. 他决定离家出走。
【不定式短语作宾语】注意:宾语分为直接宾语和间接宾语:有些及物动词可以有两个宾语,一个指人,一个指物,指人的叫作间接宾语,指物的叫直接宾语;合称双宾语。
EG:I bought my sona box of Mark pens last night. 他给了我一些墨水。
一、句子成分构成句子的各个部分叫作句子成分。
句子成分包括主语、谓语、表语、宾语、宾语补足语、定语和状语等。
主语(subject)、谓语(predicate)、宾语(object)、定语(attribute)状语(adverbial)、补语(complement)表语(predicative)二、什么是简单句?只包含一个主谓结构的句子(有时有并列主语或并列谓语动词)叫简单句。
They gave me a lot of advice.My relatives and friends all came.三、基本句子结构英语句子的结构可以归纳成八种基本句型。
英语句子都可以看作是这八种句型及其扩大、组合、省略或倒装构成的。
掌握这八种基本句型,是掌握各种英语句子结构的基础,也是学好其他语法知识的必备前提。
用符号表示为:①SV(主+谓)②SVO(主+谓+宾)③SVoO(主+谓+间宾+直宾)④SVOC(主+谓+宾+宾补)⑤SVP(主+系+表)⑥There be 现存句⑦S+V+ A)主+谓+状)⑧S+V+O+ A(主+谓+宾+状语)1、SVP(主+系+表)本结构是由主语+系动词+表语组成,主要用以说明主语的特征,类属,状态,身份等。
Deep water stays still.The trouble is that they are short of money.2、SV(主+谓)S(主)+ Vi(不及物动词)(谓)本结构是由主语加不及物的谓语动词构成,常用来表示主语的动作。
Who cares?这类句子的谓语动词都是不及物动词,都不带宾语,但可以带状语。
Gradually a smile appeared on her face.3、SVO(主+谓+宾)S (主)+ Vt(及物动词)(谓)+ O(宾)本结构是由主语+及物的谓语动词+宾语构成。
宾语成分的多样化使得这一结构异常复杂。
谓语动词都具有实义,都是主语产生的动作,但不能表达完整的意思,必须跟有一个宾语,即动作的承受者,才能使意思完整。
高中英语语法讲义简单句简单句四句话一陈述句(肯、否)五种1,主谓SVi (不及物动词)You are listening (to me) . I’ve come (to Bangde)2,主系表SVP *系动词:be动词,You are cute/ a girl.感官动词feel/look/sound/smell/taste. You look young.成为动词become/get/turn/go/fall等, *become a teacher= turn teacherturn +颜色get +温度go +好坏fall +ill/asleep.保持:keep,stay, remain 等. You should remain quiet.似乎:seem(表可能)/appear(实则否) (to be)+adj结果是:prove /turn out (to be)+adj3,主谓宾SVO I hit you (on the head/ in the face)4,主谓宾宾SVOO 人+ 物= 物to +人I gave you a pen= I gave a pen to you .但make, buy, cook, find, get, order, sing, spare, fetch等用for+人5,主谓宾宾补SVOOc*find, think, elect, name, call, appoint, consider, make, leave等+O+名词They all call me Wangwang.*keep, get, make, leave, find, paint, set, turn, drive, call, cut, consider等+O+adjWe should keep our room tidy.*keep, find ,catch, leave等+O+ doing.He found a purse lying on the ground.*ask/tell/want/wish/order/request/demand等+O+(not)to doI wish you to learn English well.*feel / hear, listen to / let, make, have / look at, see, watch, notice, observe +O +do/doing.注意let, make不能接doing. 但be seen/made…+to do.Jim saw a girl go upstairs / playing under the tree.* think, find, consider等+it+Oc+to do. I think it useful to learn English.变否定句:在be/情态/助动词后+not。
不同的时态有不同的助动词,但一般现在时和一般过去时无助动词。
一般现在时需加don’t/doesn’t+V. 一般过去时需加didn’t+V附动词时态表(16种时态32种谓语结构)时:现在过去将来过去将来态一般V/Vs Ved will V would V进行am/is/are/Ving was/were Ving will be Ving would be Ving完成have/has Ved had Ved will have Ved would have Ved 完成进行have/has been Ving had been Ving will have been Ving would have been Ving 变被动态:主——V, 被——be Ved. 把被动态的be变成主动态的V的形式V ed不变。
Eg, Ved-----was/were Ved , have/has been Ving----have/has been being Ved,.课堂练习变否定句:1,Huang Meng has a new iphone 7plus.2, she’ll tell you something important.3, They had a great time last night.4, The boy often does sports after school.5, Her father has been to Wuhan many times.二感叹句2种1 What + a/an +adj + n + (SV) ! What a cute girl (you are) !+adj + ns + (SV)!What beautiful flowers ( they are )!+ adj + u + (SV) ! What fine weather ( it is ) !2 How + adj ( a/an + n ) + SV ! How cute (a girl) you are !+ adv + SV ! How carefully you are listening to me !+ ---- + SV ! How I miss you !课堂练习:变感叹句1,English is a useful tool.2 You’re a very honest student.3 The young man drives a car too carelessly.4 We’ve bought very interesting books.5 I wish to meet you right away.三疑问句4种1 一般疑问句== Be/情态/助动词(提前) + SV ? 但一般现在时要加Do/Does + SV ?一般过去时要加Did + SV ? 需要Yes/ No 回答。
We can speak correct English.----Can you speak correct English ? Yes, we can ./ No, we can’t.The boy often does sports after school. ——Does the boy often do sports after school? Yes, he does./No, he doesn’t.2 选择疑问句= 一般疑问句or 选择部分?不需要Yes/ No 回答。
Do you like English ( or math ) ? –I like English/ math. Both.3 特殊疑问句==疑问部分+ 一般疑问句?但疑问部分为S + 谓语?How many times a week do you come to Xue da ?Who teaches you English ?4 反意疑问句==SV ,+ 一般问句简略式(Be/情态/助动词+ S)? 前肯后否,前否后肯(Yes/No反译)。
*陈述部分有not/ no /seldom/hardly/rarely/scarcely/never/few/little/nothing/nobody等表否定的词,后用肯定形式反问,但有表否定前缀的词不算否定句,后要用否定形式反问。
There used to be nothing in the area 10 years ago, did there ? Yes, there did. 不,有。
No, there didn’t.是的,没有。
Huiling dislikes playing soccer , doesn’t she ? Yes, she does.是的,她不喜欢。
No, she doesn’t.不,她喜欢。
*有must/may/might/could的反意问句,接实意动词否定反问用needn’t,接be动词去掉情态反问,接have done 时有时间状语当过去时反问,无时间状语当现在完成时反问。
You must go home now, needn’t you ? You mustn’t make noise here, must/may you?You must /may/might/could be a little hungry, aren’t you ?He must have come here just now , didn’t he ? He must have come here, hasn’t he ?*宾语从句的反意问句,一般变主句,但I/We +think/believe/guess/suppose/expect/imagine+宾从时需变从句,注意否定前移.Jin Jie doesn’t believe his mother will come, does he ?I don’t think he can solve the problem, can he ?*不定代词做主语指人用he / they反问,指物用it 反问,不定式、动名词做主语也用it反问。
Nothing is difficult if you put your heart into it, is it ?Everyone likes moon cakes in China, doesn’t he ? / don’t they ?Learning English will cost us too much time , won’t it ?课堂练习1Xiao kong has a little bread and milk for break.(变一般问句)2It was extremely rainy yesterday. (变特殊问句)3They often come to school by bus.(用on foot变选择问句)4What she did is wrong, ___________ ?5Jia qi ,with her parents, usually travels abroad during holidays,__________ ?四祈使句表命令:肯定式:(You)+ V , will/would/ won’t you? Pass me the reference book, will/would/won’t you?否定式:Don’t/Never + V/ No Ving , will/ would you? 答语Sorry, I won’t.强调试:Do come here on time.●表建议:Let’s + V , shall we ? Let’s play basketball, shall we ?(一起打)Let us + V, will you ? Let us play basketball, will you?(你不打)总结:祈使句除了Let’s 用shall we,其余都可用will you反问。