Proe ISDX曲线使用全集
- 格式:doc
- 大小:923.50 KB
- 文档页数:22





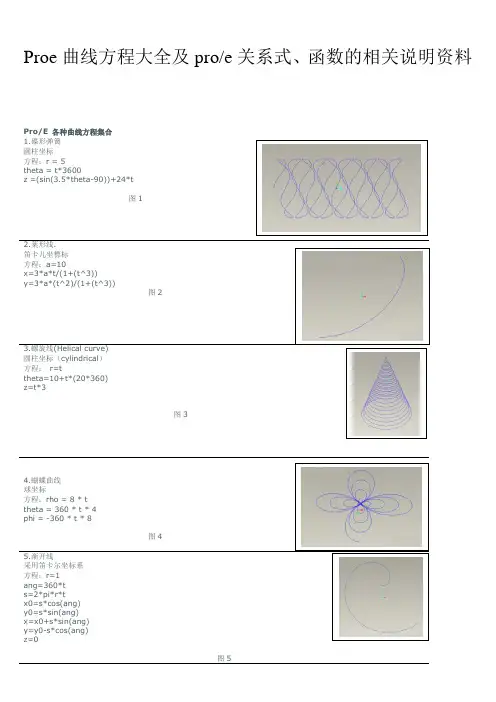
Proe曲线方程大全及pro/e关系式、函数的相关说明资料Pro/E 各种曲线方程集合1.碟形弹簧圓柱坐标方程:r = 5theta = t*3600z =(sin(3.5*theta-90))+24*t图12.葉形线.笛卡儿坐標标方程:a=10x=3*a*t/(1+(t^3))y=3*a*(t^2)/(1+(t^3))图23.螺旋线(Helical curve)圆柱坐标(cylindrical)方程:r=ttheta=10+t*(20*360)z=t*3图34.蝴蝶曲线球坐标方程:rho = 8 * ttheta = 360 * t * 4phi = -360 * t * 8图45.渐开线采用笛卡尔坐标系方程:r=1ang=360*ts=2*pi*r*tx0=s*cos(ang)y0=s*sin(ang)x=x0+s*sin(ang)y=y0-s*cos(ang)z=0图56.螺旋线.笛卡儿坐标方程:x = 4 * cos ( t *(5*360))y = 4 * sin ( t *(5*360))z = 10*t图6 7.对数曲线笛卡尔坐标系方程:z=0x = 10*ty = log(10*t+0.0001)图78.球面螺旋线采用球坐标系方程:rho=4theta=t*180phi=t*360*20图8 9.双弧外摆线卡迪尔坐标方程:l=2.5b=2.5x=3*b*cos(t*360)+l*cos(3*t*360)Y=3*b*sin(t*360)+l*sin(3*t*360)图910.星行线卡迪尔坐标方程:a=5x=a*(cos(t*360))^3y=a*(sin(t*360))^3图10 11.心脏线圓柱坐标方程:a=10r=a*(1+cos(theta))theta=t*360Pro/E 各种曲线方程集合(二)22.外摆线迪卡尔坐标方程:theta=t*720*5b=8a=5x=(a+b)*cos(theta)-b*cos((a/b+1)*theta)y=(a+b)*sin(theta)-b*sin((a/b+1)*theta)z=0图22 23. Lissajous 曲线theta=t*360a=1b=1c=100n=3x=a*sin(n*theta+c)y=b*sin(theta)图23 24.长短幅圆内旋轮线卡笛尔坐标方程:a=5b=7c=2.2theta=360*t*10x=(a-b)*cos(theta)+c*cos((a/b-1)*theta)y=(a-b)*sin(theta)-c*sin((a/b-1)*theta)图24 25.长短幅圆外旋轮线卡笛尔坐标方程:theta=t*360*10a=5b=3c=5x=(a+b)*cos(theta)-c*cos((a/b+1)*theta)y=(a+b)*sin(theta)-c*sin((a/b+1)*theta)图25 26. 三尖瓣线a=10x = a*(2*cos(t*360)+cos(2*t*360))y = a*(2*sin(t*360)-sin(2*t*360))图26 27.概率曲线!方程:笛卡儿坐标x = t*10-5y = exp(0-x^2)图27 28.箕舌线笛卡儿坐标系a = 1x = -5 + t*10y = 8*a^3/(x^2+4*a^2)图28 29.阿基米德螺线柱坐标a=100theta = t*400r = a*theta图29 30.对数螺线柱坐标theta = t*360*2.2a = 0.005r = exp(a*theta)图30 31.蔓叶线笛卡儿坐标系a=10y=t*100-50solvex^3 = y^2*(2*a-x)for x图31 32.tan曲线笛卡儿坐标系x = t*8.5 -4.25y = tan(x*20)图32 33.双曲余弦x = 6*t-3y = (exp(x)+exp(0-x))/2图33 34.双曲正弦x = 6*t-3y = (exp(x)-exp(0-x))/2图34 35.双曲正切x = 6*t-3y = (exp(x)-exp(0-x))/(exp(x)+exp(0-x))图35 36.一峰三驻点曲线x = 3*t-1.5y=(x^2-1)^3+1图36 37.八字曲线x = 2 * cos ( t *(2*180))y = 2 * sin ( t *(5*360))z = 0图37 38.螺旋曲线r=t*(10*180)+1theta=10+t*(20*180)z=t图38 39.圆x = cos ( t *(5*180))y = sin ( t *(5*180))z = 0图39 40.封闭球形环绕曲线rho=2theta=360*tphi=t*360*10图40 41.柱坐标螺旋曲线x = 100*t * cos ( t *(5*180))y = 100*t * sin ( t *(5*180))z = 0Pro/E 各种曲线方程集合(三)42.蛇形曲线x = 2 * cos ( (t+1) *(2*180))y = 2 * sin ( t *(5*360))z = t*(t+1)图42 43.8字形曲线柱坐标theta = t*360r=10+(8*sin(theta))^2图43 44.椭圆曲线笛卡尔坐标系a = 10b = 20theta = t*360x = a*cos(theta)y = b*sin(theta)图44 45.梅花曲线柱坐标theta = t*360r=10+(3*sin(theta*2.5))^2图45 46.另一个花曲线theta = t*360r=10-(3*sin(theta*3))^2z=4*sin(theta*3)^2图46 47.改一下就成为空间感更强的花曲线了;)theta = t*360r=10-(3*sin(theta*3))^2z=(r*sin(theta*3))^2图4748.螺旋上升的椭圆线a = 10b = 20theta = t*360*3x = a*cos(theta)y = b*sin(theta)z=t*12图48 49.甚至这种螺旋花曲线theta = t*360*4r=10+(3*sin(theta*2.5))^2z = t*16图49 50 鼓形线笛卡尔方程r=5+3.3*sin(t*180)+ttheta=t*360*10z=t*10图50 51 长命锁曲线笛卡尔方程:a=1*t*359.5b=q2*t*360c=q3*t*360rr1=w1rr2=w2rr3=w3x=rr1*cos(a)+rr2*cos(b)+rr3*cos(c)y=rr1*sin(a)+rr2*sin(b)+rr3*sin(c)图51 52 簪形线球坐标方程:rho=200*ttheta=900*tphi=t*90*10图52 53.螺旋上升曲线r=t^10theta=t^3*360*6*3+t^3*360*3*3z=t^3*(t+1)图53 54.蘑菇曲线rho=t^3+t*(t+1)theta=t*360phi=t^2*360*20*20图54 55. 8字曲线a=1b=1x=3*b*cos(t*360)+a*cos(3*t*360)Y=b*sin(t*360)+a*sin(3*t*360)图55 56.梅花曲线theta=t*360r=100+50*cos(5*theta)z=2*cos(5*theta)图56 57.桃形曲线rho=t^3+t*(t+1)theta=t*360phi=t^2*360*10*10图57 58.名稱:碟形弹簧建立環境:pro/e圓柱坐r = 5theta = t*3600z =(sin(3.5*theta-90))+24图58 59.环形二次曲线笛卡儿方程:x=50*cos(t*360)y=50*sin(t*360)z=10*cos(t*360*8)图59 60 蝶线球坐标:rho=4*sin(t*360)+6*cos(t*360^2)theta=t*360phi=log(1+t*360)*t*360图60 61.正弦周弹簧笛卡尔:ang1=t*360ang2=t*360*20x=ang1*2*pi/360y=sin(ang1)*5+cos(ang2)z=sin(ang2)Pro/E 各种曲线方程集合(四)62.环形螺旋线x=(50+10*sin(t*360*15))*cos(t*360)y=(50+10*sin(t*360*15))*sin(t*360)z=10*cos(t*360*5)图62 63.内接弹簧x=2*cos(t*360*10)+cos(t*180*10)y=2*sin(t*360*10)+sin(t*180*10)z=t*6图63 64.多变内接式弹簧x=3*cos(t*360*8)-1.5*cos(t*480*8)y=3*sin(t*360*8)-1.5*sin(t*480*8)z=t*8图64 65.柱面正弦波线柱坐标:方程r=30theta=t*360z=5*sin(5*theta-90)图65 66. ufo (漩涡线)球坐标:rho=t*20^2theta=t*log(30)*60phi=t*7200图66 67. 手把曲线thta0=t*360thta1=t*360*6r0=400r1=40r=r0+r1*cos(thta1)x=r*cos(thta0)y=r1*sin(thta1)z=0图67 68.篮子圆柱坐标r=5+0.3*sin(t*180)+ttheta=t*360*30z=t*5图68 69. 圆柱齿轮齿廓的渐开线方程:afa=60*tx=10*cos(afa)+pi*10*afa/180*sin(afa)x=10*sin(afa)-pi*10*afa/180*cos(afa)z=0注:afa为压力角,取值范围是0到60,10为基圆半径。


基于Pro/E由ISDX曲线构建自行车车垫曲面分析摘要在逆向工程中,用户可以通过强大的三维软件功能,测绘出空间位置上的点,然后在造型功能环境下,由若干空间位置上的点描出ISDX架构线;最后由ISDX架构线铺出线条流畅、饱满的曲面特征。
这种造型曲面创建方法,在现代工业产品设计中得到广泛使用。
自行车车垫曲面的构建,先测绘出空间位置上的点,在造型环境下由空间位置上的点描出ISDX曲线,再由ISDX曲线铺出曲面特征。
在曲面特征的创建过程中,如何创建渐消渐隐、流畅光滑、高质量的ISDX曲线是创建高质量曲面特征的关键。
关键词Pro/E;ISDX曲线;图形曲率;法向1 创建ISDX曲线11.1 创建ISDX曲线1参考点点击点按钮→【草绘】/【完成】→选取基准平面FRONT为绘图平面→【缺省】→绘制(-250,0)、(180,0)两点→【√】。
生成如图1所示基准点PNT0、PNT1。
1.2 创建ISDX曲线1【插入】→【造型】→选取造型曲线按钮→【平面的】→选取基准平面TOP→进入ISDX曲线绘制界面→绘制ISDX曲线1。
(1)编辑ISDX曲线1【编辑】→先按住shift键,左键点选ISDX曲线端点,拖动光标至基准点PNT0处,松开shift键,按住Alt键,ISDX曲线1自动捕捉到基准点PNT0上。
按住shift键,左键点选ISDX曲线1另一端点,拖动光标至基准点PNT1处,松开shift键,按住Alt键,ISDX曲线1自动捕捉到基准点PNT1上。
按住shift键,左键点选ISDX曲线1上的插入点,将其拖动到合适位置。
【编辑】→选取ISDX曲线1端点(靠近基准点PNT0)→出现一条黄色相切指示线→拖动相切指示线,改变曲线的形状。
右键单击相切指示线→【法向】→选取基准平面FRONT,使ISDX曲线1与基准平面FRONT垂直→【√】。
生成如图1所示ISDX1曲线1。
点击显示图形曲率按钮,得到如图1所示图形曲率图。

22.外摆线迪卡尔坐标方程:theta=t*720*5b=8a=5x=(a+b)*cos(theta)-b*cos((a/b+1)*theta)y=(a+b)*sin(theta)-b*sin((a/b+1)*theta)z=0图2223. Lissajous 曲线theta=t*360a=1b=1c=100n=3x=a*sin(n*theta+c)y=b*sin(theta)图2324.长短幅圆内旋轮线卡笛尔坐标方程:a=5b=7c=2.2theta=360*t*10x=(a-b)*cos(theta)+c*cos((a/b-1)*theta)y=(a-b)*sin(theta)-c*sin((a/b-1)*theta)图2425.长短幅圆外旋轮线卡笛尔坐标方程:theta=t*360*10a=5b=3c=5x=(a+b)*cos(theta)-c*cos((a/b+1)*theta)y=(a+b)*sin(theta)-c*sin((a/b+1)*theta)图2526. 三尖瓣线a=10x = a*(2*cos(t*360)+cos(2*t*360))y = a*(2*sin(t*360)-sin(2*t*360))图2627.概率曲线!方程:笛卡儿坐标x = t*10-5y = exp(0-x^2)图2728.箕舌线笛卡儿坐标系a = 1x = -5 + t*10y = 8*a^3/(x^2+4*a^2)图2829.阿基米德螺线柱坐标a=100theta = t*400r = a*theta图2930.对数螺线柱坐标theta = t*360*2.2a = 0.005r = exp(a*theta)图3031.蔓叶线笛卡儿坐标系a=10y=t*100-50solvex^3 = y^2*(2*a-x)for x图3132.tan曲线笛卡儿坐标系x = t*8.5 -4.25y = tan(x*20)图3233.双曲余弦x = 6*t-3y = (exp(x)+exp(0-x))/2图3334.双曲正弦x = 6*t-3y = (exp(x)-exp(0-x))/2图3435.双曲正切x = 6*t-3y = (exp(x)-exp(0-x))/(exp(x)+exp(0-x))图35 36.一峰三驻点曲线x = 3*t-1.5y=(x^2-1)^3+1图3637.八字曲线x = 2 * cos ( t *(2*180))y = 2 * sin ( t *(5*360))z = 0图3738.螺旋曲线r=t*(10*180)+1theta=10+t*(20*180)z=t图3839.圆x = cos ( t *(5*180))y = sin ( t *(5*180))z = 0图39</P< p>Pro/E 各种曲线方程集合(二)日期:2007-1-2 13:48:41 人气:1146 [大中小]上一页[1][2]下一页40.封闭球形环绕曲线rho=2theta=360*tphi=t*360*10图4041.柱坐标螺旋曲线x = 100*t * cos ( t *(5*180))y = 100*t * sin ( t *(5*180))z = 0图41。
PROE 野火5.0之曲面造型(style isdx) 新功能Styling window (Note: styling features are super features, and there can be father son relationships between common features)4 window points, select 4 window icon switch. 1 window changes, 4 windows are updated simultaneously.1 new 4 NEWThe CTRL +D key is restored to the standard four window viewStandard four lookAdjust the window, drag the window, the boundary cross line, adjust the size of each windowSelect the graphic of the activity plane and select the datum plane (the drawing plane attribute).Facing the right side of the plane the direction of the moving plane (the point of view attribute).The inner plane diagram is in the same column as the movable plane. The same plane construction method, but the same characteristics as modeling. The constructed datum plane changes into active plane in real time. Note: the difference between free curve and the plane curve, the reference slide within the "reference" can change the active plane, "offset" can offset existing activities to establish a new plane moving plane, while the internal surface in a more flexible way to establish a new plane activities.Environment settings modeling preferencesMolding curveThe free curve creates a curve icon, draws a line, ends the middle key, then draws another line, and the middle key ends... To complete the green tick curve (or press button), black tick exit featureDrag into 3D. By editing the curve icon, you can drag it into a 3D curve, while a flat curve does not. Before dragging, you'd better set the moving plane and make it look straight.Plane curveNot 3DCos curveDo not cross the boundary without crossing the boundary between the surfaces (the boundary of the surface will have the geometry of the surface) and the boundary between the surfaces (regardless of whether the surface is merged).An inner boundary that can cross a boundary but can cross a boundary to blend a surface or a curved surface.The drag plug allows one to pull one, more, or more points online (in conjunction with Ctrl) at one time.And directional control and coordinate control can be implemented.Direction control points on the slide: free, horizontal, vertical, vertical.The coordinates of control points (both absolute and relative to the direction of the axis defined Si). Check the relative, in a certain direction, enter a value, continuous press ENT, can realize continuous relative movement.Soft point control if the insertion point with the lock point (with Shift crawl) is a soft reference point, cannot coordinate control, can only use soft point editing type: length ratio, length, parameter (usually not only length ratio can be offset from the plane), and the lock lock to point (the point is no longer mobile freedom), link (when crawling into the surface and solid surface or datum, the point to point type grid display, soft switch to link).Remove soft point, select soft point, right key, disconnect.A curve conversion can only convert curves to free or flat surfaces, and cannot be converted into Cos attributes.Delete the curve modeling environment, double-click any curve to the right button, delete the curve.Extension curve, Shift+Alt point, line selection end drag. The extension is in the upper slider of the point: free, tangent, and curvature.Usually extends near the target and matches the Shift lock point.Cut the curve and delete the endpoint.Cut the curve, select the insertion point, the right key, and the segmentation. The split two curves have father son relation, and the segmentation point becomes the soft point of the subsystem.Endpoint combination curve Shift drag a curve to lock another curve (or lock to another curve near the end, and then set the soft point editing type "lock point to another automatically lock the ends of the curve), right click, combination.Offset curve Cos curve offset or normal surface offset in surface: modeling offset curve. Note: CosThe curve is referenced to the two surface, and the resulting offset of the surface will be offset by different directions, the normal surfaceThe offset will not; the offset is allowed to be greater than the minimum radius; delete the curve: right click "Edit"Definition, deletion, reference, or reset reference. The offset curve is the original Cos curve and the reference surfaceSubsystem.The selection of loading curve shape characteristics curve outside (can Ctrl more) and other, from a reference curve, V (loading curve become free curve). The loading curve has nothing to do with the original curve.Surface line support surfaces: IGES, Pro/E surfaces, surfaces within the same modeling feature, etc..Curve form: Cos or freedom. Cos can be converted into freedom afterwards.Father son relationship: drag Shift to tow the points at the ends and re lock the points to the curveIn addition to the father and son relation of the surface.Vertical and horizontal directions: press Ctrl to select the surface again to change the direction of the vertical and horizontal directions.The construction steps of modeling, curve from surface to surface, left click tickThe falling curve is similar to the Pro/E projection curve. For the original curve and the reference surface of the subsystem.Plane curve, move the copy is only applicable to modeling characteristics of free curve, circle and arc.The pair of plane curves does not violate the plane constraint.Motion and copy functions can be translated, rotated, scaled, or geometrically variable. A curve that has a soft point constraint (which can be removed if necessary) cannot be freely controlled, and when it is copied, it can be checked to "disconnect"". A plane curve can be translated, rotated, or scaled only on its plane.Translation: precise control using relative coordinates.Rotation: can input each shaft rotation angle.Scaling: allows locking of proportional values (proportionally).Control rod: can enter absolute or relative position coordinates; can input relative rotation angle; willThe control rod is positioned at the center of the cover frame or aligned with the movable plane; the curve rotates around the center of the control rod; the control lever rod can be moved, and the end of the control rod can be rotated to rotate.Conversion mode: Select (allow cover box, zoom curve, control lever translation and rotation curve) and cover frame (only allow box frame zoom curve).Mode of movement: freedom; horizontal / vertical (relative to the active plane); normal (relative to the active plane, but must be active, the plane is in a non positive state before it becomes effective).Zoom mode: reverse (one-way); Center (i.e., two-way).The proportion of updates to a soft point, and the overall scale of the curve is scaled.Location: curve, icon, tick, tick, scale, updateCondition: there are at least two soft points in the curve.Must be soft dragging.Must be free or flat curve, Cos curve cannot be renewed in proportion.The proportion of copy editors, copy, according to the proportion of selected curve (default check disconnected), drag the arrow replication curve (ratio of movement can cancel the option on the skateboard "unification" and "unified" height control. After you uncheck, change to equal height copy To B.The main difference with replication: you can match Shift, drag arrows, catch, locate, and use the unified function".Tangent constraint: natural (natural to edit to make the re set of constraints) and free, fixed angle, horizontal and vertical (horizontal and vertical reference plane, usually value) method (to start to choose a reference plane collector surface), the current alignment (tangent plane or parallel to another fall in the curve the symmetric (two), the average value of the tangent angle, explicit single arrow) and tangent (from paternal tangent angle value, explicit single arrow) andcurvature (from tangent angle value and the value of paternal length, four lines tangent to the surface (arrow) and tangent to the surface, do not show the arrow. Curvature of a surface or curvature of a surface can preserve the properties of a plane curve And the surface curvature (tangent curvature continuity to the surface, four line arrow), tangent draft; length (tangent vector length), angle (tangent projection in reference plane angle), height (tangent and the reference surface elevation, can only specify the free curve for elevation, tangent draft height is not available, will be converted into slope, slope) how to understand? Drag constraint: free, length, projection angle + elevation angle. Note: drag constraints affect only the tangents that are currently directly dragged by the mouse.Select display curvature shape feature, right click to edit the definition of curvature diagrams, to check the "save the selected curve (Ctrl optional multiple) - curvature check box (optional curvature box definition, set the curvature cable precision, accuracy refers to the cable density) to edit the curve, adjusting the curvature, the hidden" save the analysis "to show the" save the analysis box set shows that the curvature line again, re adjust the curvature of a curve.The keys are repeated in the styling environment by pressing a middle key or performing a double rotation icon, meaning repeating the menu instructions just now. For example, setting the base level, creating curves or editing curves, etc..Ctrl + D default view.The curve symmetry must make the curve be symmetrical to the designated base plane, except the coordinate point must be symmetrical,The tangent of the points at both ends should also be set symmetrically, in which the parameters to be adjusted are length, angle, and height. Special attention to angle symmetry input: when the input tangent angle at one end, and the other end of negative input can be, ENTER, the system will deduct 360 for the final calculation.A complete regeneration of the two curve can be established from the soft point father son relationship. When modifying the parent curve, the regeneration icon is shown in yellow and needs to be turned green to be fully regenerated. Note: the segmentation curve is also the case.。
ProE曲线方程式大集合目录第1页:1碟形弹簧、2葉形线、3螺旋线(Helical curve)、4蝴蝶曲线和、5渐开线;第2页:6螺旋线、7对数曲线、8球面螺旋线、9双弧外摆线和、10星行线;第3页:11心脏线、12圆内螺旋线、13正弦曲线、14太阳线和、15费马曲线(有点像螺纹线);第4页:16Talbot 曲线、17-4叶线、18Rhodonea 曲线、19抛物线和、20螺旋线;第5页:21三叶线、22外摆线、23Lissajous 曲线、24长短幅圆内旋轮线和、25长短幅圆外旋轮线;第6页:26三尖瓣线、27概率曲线、28箕舌线、29阿基米德螺线和、30对数螺线;第7页:31蔓叶线、32tan曲线、33双曲余弦、34双曲正弦和、35双曲正切;第8页:36一峰三驻点曲线、37八字曲线、38螺旋曲线、39圆和、40封闭球形环绕曲线;第9页:41柱坐标螺旋曲线、42蛇形曲线、43-8字形曲线、44椭圆曲线和、45梅花曲线;第10页:46花曲线、47空间感更强的花曲线、48螺旋上升的椭圆线、49螺旋花曲线和、50鼓形线;第11页:51长命锁曲线、52簪形线、53螺旋上升曲线、54蘑菇曲线和、55-8字曲线;第12页:56梅花曲线、57桃形曲线、58碟形弹簧、59环形二次曲线和、60蝶线;第13页:61正弦周弹簧、62环形螺旋线、63内接弹簧、64多变内接式弹簧和65、柱面正弦波线;第14页:66ufo(漩涡线)、67手把曲线、68篮子、69圆柱齿轮齿廓的渐开线方程和、70对数螺旋曲线;第15页:71罩形线、72向日葵线、73太阳线、74塔形螺旋线和、75花瓣线;第16页:76双元宝线、77阿基米德螺线的变形、78渐开线方程、79双鱼曲线和、80蝴蝶结曲线;第17页:81“两相望”曲线、82小蜜蜂、83弯月、84热带鱼和、85燕尾剪;第18页:86天蚕丝、87心电图、88变化后的星形线、89小白兔和、90大家好;第19页:91蛇形线、92五环、93蜘蛛网、94次声波和、95十字渐开线;第20页:96内五环和、97蜗轨线;1.碟形弹簧圓柱坐标方程:r = 5theta = t*3600z =(sin(3.5*theta-90))+24*t 此主题相关图片如下:1.jpg2.葉形线.笛卡儿坐標标方程:a=10x=3*a*t/(1+(t^3))y=3*a*(t^2)/(1+(t^3))此主题相关图片如下:2.jpg3.螺旋线(Helical curve)圆柱坐标(cylindrical)方程:r=ttheta=10+t*(20*360)z=t*3此主题相关图片如下:3.jpg4.蝴蝶曲线球坐标方程:rho = 8 * ttheta = 360 * t * 4phi = -360 * t * 8此主题相关图片如下:4.jpg5.渐开线采用笛卡尔坐标系方程:r=1ang=360*ts=2*pi*r*tx0=s*cos(ang)y0=s*sin(ang)x=x0+s*sin(ang)y=y0-s*cos(ang)z=0此主题相关图片如下:5.jpg6.螺旋线.笛卡儿坐标方程:x = 4 * cos ( t *(5*360)) y = 4 * sin ( t *(5*360))z = 10*t此主题相关图片如下:6.jpg7.对数曲线笛卡尔坐标系方程:z=0x = 10*ty = log(10*t+0.0001)此主题相关图片如下:7.jpg8.球面螺旋线采用球坐标系方程:rho=4theta=t*180phi=t*360*20此主题相关图片如下:8.jpg9.双弧外摆线方程:l=2.5b=2.5x=3*b*cos(t*360)+l*cos(3*t*360) Y=3*b*sin(t*360)+l*sin(3*t*360) 此主题相关图片如下:9.jpg10.星行线卡迪尔坐标方程:a=5x=a*(cos(t*360))^3y=a*(sin(t*360))^3此主题相关图片如下:10.jpg11.心脏线圓柱坐标方程:a=10r=a*(1+cos(theta))theta=t*360此主题相关图片如下:11.jpg采用柱座标系方程:theta=t*360r=10+10*sin(6*theta)z=2*sin(6*theta)此主题相关图片如下:12.jpg13.正弦曲线笛卡尔坐标系方程:x=50*ty=10*sin(t*360)z=0此主题相关图片如下:13.jpg14.太阳线(这本来是做别的曲线的,结果做错了,就变成这样了)此主题相关图片如下:14.jpg15.费马曲线(有点像螺纹线)数学方程:r*r = a*a*theta圓柱坐标方程1: theta=360*t*5a=4r=a*sqrt(theta*180/pi)方程2: theta=360*t*5a=4由于Pro/e只能做连续的曲线,所以只能分两次做此主题相关图片如下:15.jpg16.Talbot 曲线卡笛尔坐标方程:theta=t*360a=1.1b=0.666c=sin(theta)f=1x = (a*a+f*f*c*c)*cos(theta)/ay = (a*a-2*f+f*f*c*c)*sin(theta)/b此主题相关图片如下:16.jpg17.4叶线(一个方程做的,没有复制)此主题相关图片如下:17.jpg18.Rhodonea 曲线采用笛卡尔坐标系方程:theta=t*360*4x=25+(10-6)*cos(theta)+10*cos((10/6-1)*theta) y=25+(10-6)*sin(theta)-6*sin((10/6-1)*theta)此主题相关图片如下:18.jpg19. 抛物线笛卡儿坐标方程:x =(4 * t)y =(3 * t) + (5 * t ^2)z =0此主题相关图片如下:19.jpg20.螺旋线圓柱坐标方程:r = 5theta = t*1800z =(cos(theta-90))+24*t此主题相关图片如下:20.jpg21.三叶线圆柱坐标方程:a=1theta=t*380b=sin(theta)r=a*cos(theta)*(4*b*b-1)此主题相关图片如下:21.jpg22.外摆线迪卡尔坐标方程:theta=t*720*5b=8a=5x=(a+b)*cos(theta)-b*cos((a/b+1)*theta) y=(a+b)*sin(theta)-b*sin((a/b+1)*theta) z=0此主题相关图片如下:22.jpg23. Lissajous 曲线theta=t*360a=1b=1c=100n=3x=a*sin(n*theta+c)y=b*sin(theta)此主题相关图片如下:23.jpg24.长短幅圆内旋轮线卡笛尔坐标方程:a=5b=7c=2.2theta=360*t*10x=(a-b)*cos(theta)+c*cos((a/b-1)*theta) y=(a-b)*sin(theta)-c*sin((a/b-1)*theta) 此主题相关图片如下:24.jpg25.长短幅圆外旋轮线卡笛尔坐标方程:theta=t*360*10a=5b=3c=5x=(a+b)*cos(theta)-c*cos((a/b+1)*theta) y=(a+b)*sin(theta)-c*sin((a/b+1)*theta)此主题相关图片如下:25.jpg26. 三尖瓣线a=10x = a*(2*cos(t*360)+cos(2*t*360)) y = a*(2*sin(t*360)-sin(2*t*360)) 此主题相关图片如下:26.jpg27.概率曲线!方程:笛卡儿坐标x = t*10-5y = exp(0-x^2)此主题相关图片如下:27.jpg28.箕舌线笛卡儿坐标系a = 1x = -5 + t*10y = 8*a^3/(x^2+4*a^2)此主题相关图片如下:28.jpg29.阿基米德螺线柱坐标a=100theta = t*400r = a*theta此主题相关图片如下:29.jpg30.对数螺线柱坐标theta = t*360*2.2a = 0.005r = exp(a*theta)此主题相关图片如下:30.jpg31.蔓叶线笛卡儿坐标系a=10y=t*100-50solvex^3 = y^2*(2*a-x)for x此主题相关图片如下:31.jpg32.tan曲线笛卡儿坐标系x = t*8.5 -4.25y = tan(x*20)此主题相关图片如下:32.jpg33.双曲余弦x = 6*t-3y = (exp(x)+exp(0-x))/234.双曲正弦x = 6*t-3y = (exp(x)-exp(0-x))/2此主题相关图片如下:34.jpg35.双曲正切x = 6*t-3y = (exp(x)-exp(0-x))/(exp(x)+exp(0-x))36.一峰三驻点曲线x = 3*t-1.5y=(x^2-1)^3+1此主题相关图片如下:36.jpg37.八字曲线x = 2 * cos ( t *(2*180))y = 2 * sin ( t *(5*360))z = 0此主题相关图片如下:37.jpg38.螺旋曲线r=t*(10*180)+1theta=10+t*(20*180)z=t39.圆x = cos ( t *(5*180))y = sin ( t *(5*180))z = 0此主题相关图片如下:39.jpg40.封闭球形环绕曲线rho=2theta=360*tphi=t*360*1041.柱坐标螺旋曲线x = 100*t * cos ( t *(5*180)) y = 100*t * sin ( t *(5*180)) z = 0此主题相关图片如下:41.jpg42.蛇形曲线x = 2 * cos ( (t+1) *(2*180)) y = 2 * sin ( t *(5*360))z = t*(t+1)43.8字形曲线柱坐标theta = t*360r=10+(8*sin(theta))^2此主题相关图片如下:43.jpg44.椭圆曲线笛卡尔坐标系a = 10b = 20theta = t*360x = a*cos(theta)y = b*sin(theta)此主题相关图片如下:44.jpg45.梅花曲线柱坐标theta = t*360r=10+(3*sin(theta*2.5))^2此主题相关图片如下:45.jpg46.另一个花曲线theta = t*360r=10-(3*sin(theta*3))^2z=4*sin(theta*3)^2此主题相关图片如下:46.jpg47.改一下就成为空间感更强的花曲线了;) theta = t*360r=10-(3*sin(theta*3))^2z=(r*sin(theta*3))^2此主题相关图片如下:47.gif48.螺旋上升的椭圆线a = 10b = 20theta = t*360*3x = a*cos(theta)y = b*sin(theta)z=t*1249.甚至这种螺旋花曲线theta = t*360*4r=10+(3*sin(theta*2.5))^2z = t*16此主题相关图片如下:49.jpg50 鼓形线笛卡尔方程r=5+3.3*sin(t*180)+t theta=t*360*10z=t*1051 长命锁曲线笛卡尔方程:a=1*t*359.5b=q2*t*360c=q3*t*360rr1=w1rr2=w2rr3=w3x=rr1*cos(a)+rr2*cos(b)+rr3*cos(c) y=rr1*sin(a)+rr2*sin(b)+rr3*sin(c)此主题相关图片如下:51.jpg52 簪形线球坐标方程:rho=200*ttheta=900*tphi=t*90*10此主题相关图片如下:52.jpg53.螺旋上升曲线r=t^10theta=t^3*360*6*3+t^3*360*3*3 z=t^3*(t+1)此主题相关图片如下:53.jpg54.蘑菇曲线rho=t^3+t*(t+1)theta=t*360phi=t^2*360*20*20此主题相关图片如下:54.jpg55. 8字曲线a=1b=1x=3*b*cos(t*360)+a*cos(3*t*360) Y=b*sin(t*360)+a*sin(3*t*360)此主题相关图片如下:55.jpg56.梅花曲线theta=t*360r=100+50*cos(5*theta)z=2*cos(5*theta)此主题相关图片如下:56.jpg57.桃形曲线rho=t^3+t*(t+1)theta=t*360phi=t^2*360*10*10此主题相关图片如下:57.jpg58.名稱:碟形弹簧建立環境:pro/e圓柱坐r = 5theta = t*3600z =(sin(3.5*theta-90))+2459.环形二次曲线笛卡儿方程:x=50*cos(t*360)y=50*sin(t*360)z=10*cos(t*360*8)此主题相关图片如下:59.jpg60 蝶线球坐标:rho=4*sin(t*360)+6*cos(t*360^2) theta=t*360phi=log(1+t*360)*t*36061.正弦周弹簧笛卡尔:ang1=t*360ang2=t*360*20x=ang1*2*pi/360y=sin(ang1)*5+cos(ang2)z=sin(ang2)此主题相关图片如下:61.jpg62.环形螺旋线x=(50+10*sin(t*360*15))*cos(t*360) y=(50+10*sin(t*360*15))*sin(t*360)z=10*cos(t*360*5)63.内接弹簧x=2*cos(t*360*10)+cos(t*180*10)y=2*sin(t*360*10)+sin(t*180*10)z=t*6此主题相关图片如下:63.jpg64.多变内接式弹簧x=3*cos(t*360*8)-1.5*cos(t*480*8) y=3*sin(t*360*8)-1.5*sin(t*480*8)z=t*865.柱面正弦波线柱坐标:方程r=30theta=t*360z=5*sin(5*theta-90)此主题相关图片如下:65.jpg66. ufo (漩涡线)球坐标:rho=t*20^2theta=t*log(30)*60phi=t*720067. 手把曲线thta0=t*360thta1=t*360*6r0=400r1=40r=r0+r1*cos(thta1)x=r*cos(thta0)y=r1*sin(thta1)z=0此主题相关图片如下:67.jpg68.篮子圆柱坐标r=5+0.3*sin(t*180)+ttheta=t*360*30z=t*569. 圆柱齿轮齿廓的渐开线方程:afa=60*tx=10*cos(afa)+pi*10*afa/180*sin(afa)x=10*sin(afa)-pi*10*afa/180*cos(afa)z=0注:afa为压力角,取值范围是0到60,10为基圆半径。
第41卷 第3期 2019-03 【117】基于Pro/E 由ISDX 曲线构建渐消失曲面Construction of gradual disappearing surface by ISDX curve based on Pro/e李志刚LI Zhi-gang(武汉宸冈科技有限公司,武汉 430000)摘 要:渐消失曲面,是沿主体曲面走势延伸至某处自然消失的曲面,它能体现速度感和流畅感,是曲面增强设计效果的一种常用手段。
渐消失曲面的构建:首先是创建出主体曲面;然后创建投影曲线、边界曲线和ISDX曲线作为骨架线;最后由边界曲线产生渐消失曲面。
在渐消失曲面的创建过程中,如何创建高质量的ISDX曲线是创建高质量曲面特征的关键。
除此之外,还有一个重要的因素影响ISDX曲面质量,这就是相邻曲面间的连接形式。
通过设置相切或曲率连接方式,使两个相邻曲面间光滑过渡。
关键词:Pro/E;ISDX曲线;渐消失曲面;相切;投影曲线中图分类号:Tb472 文献标识码:b 文章编号:1009-0134(2019)03-0117-03收稿日期:2018-04-28作者简介:李志刚(1972 -),男,湖北人,工程师,本科,主要从事机电一体化方面的工作。
0 引言渐消失曲面是一种概念性很强、艺术性和技术性相对完美结合的曲面特征,在建筑装潢饰品外观设计上,加上渐消失曲面特征,它不仅可以创建出很多令人赏心悦目的建筑装潢饰品,还可以提升建筑装潢饰品的质感和层次感,并吸引消费者的目光,使得渐消失曲面在工业、民用建筑装饰饰品外观上运用的比例呈上升趋势。
1 创建主体曲面【特征】→【创建】→【曲面】→【旋转】/【完成】→【单侧】/【开放终点】/【完成】→选取FRONT 平面→【正向】→【缺省】→ 绘制2D 截面→【√】→【360】/【完成】→【确定】。
绘制如图1所示主体 曲面。
2 创建曲面构架曲线2.1 创建基准平面点击平面按钮,【穿过】→选取轴线→【角】/【平面】→选取基准平面FRONT →【完成】/【输入值】→输入角度:22.5→【√】.生成DTM1平面。
1.将PRO/E的图形放到word文档里方法一:先在Pro/E中在线框模式(在绘图模式下也可以)下直接另存为*.CGM文件,然后在WORD中插入,此方法效果非常好,图像是矢量图形,所以可以任意缩放也不会模糊,此方法适合线条图方法二:直接使用抓图软件(如HyperSnap-DX)抓图,朔椒ㄊ屎喜噬 牡阄煌?2.POR/E渲染用自定义图片视图>颜色和外观(野火版)中3.如何将Pro/E中的零件调入3D MAX中进行渲染先将零件输出为igs文件(方法为File > Save a Copy > 出现Save a Copy对话框,在type栏中选择IGES(*. igs)在3D MAX中调入igs文件进行渲染4.渲染功能野火版的使用了CDRS相同的渲染引擎,效果好多了;渲染功能在View > Model Setup > PhotoRender改变零件中的实体或曲面的颜色功能在View > Model Setup > Color and Appearance5.关联视图view->Relate View ,点选视图,点选需要关联的Item。
6.创建打死边Wall。
Sheetmetal---Wall---Extrude---use radius,一:使用钣金件内侧边拉伸建立特征,其inside radius必需为0;二:使用钣金件外侧边拉伸建立特征,其inside radius必需为0;要画外侧轮廓线。
7.创建压边先切除缺口;Sheetmetal---Wall---Extrude---use radius在切除边上拉伸特征。
inside radius设为0。
8. 翻孔攻丝打底孔;Sheetmetal---Wall---Swept-.>Use Radius 草绘翻孔高度直线;定义Radius;Cosmetics---Thread,注意选择翻孔上来的直孔璧。
9. 修改Partial view或detail view的显示边界View-〉Modify View-〉Boundary;10. 将视图转换为与模型无关Modify view-〉Snapshot11. 伪造Drawing尺寸选尺寸-〉Proparents-〉在Text中将D改为O;写你自己的尺寸;也可以标注公差:如:@O300@++0.05@#@--0.02@# 基本尺寸300,上偏差0.05,下偏差-0.02注意:只对手工添加的尺寸有效,show的尺寸不行。
ISDX曲线使用全集
ISDX模块的功能:1。
构建2D或3D曲线2。
配合锁点功能定义曲线端点所参考的对象3。
打断或连接曲线4。
构建投影曲线或在曲面上构建曲线5。
以相切或曲率连续在曲面上延伸曲线6。
构建独立或参考破衣特征的自由曲面,所参考的边界不需要端点相接7。
设置曲线端点或曲面边界以相切或曲率连续方式顺接参考对象8。
构建具有内部父子关系的对象以定义造型特征9。
在造型特征与破衣特征建立参数关系10。
具有独立解决问题的造型特征功能。
11。
具有独立的内部更新功能12。
配合逆向工程构建自由曲面ISDX的造型曲线与破衣的基准曲线有何差别ISDX模块有曲线的构建功能,用户可以构建3种造型曲线,它们分别是自由曲线(FREE)在平面上的曲线(PLANR)与在平面上的曲线(COS)。
所构建的曲线不会有任何尺寸标注,也就是说,用户无法通过修改尺寸改变曲线,但可以与其它破衣特征,曲线作参数性连接,因此只要修改所附着的特征尺寸,造型特征也会自动更新。
ISDX的曲线构建方式,类似基准曲线的通过点(Thru Points)功能,只不过前者可以在空间任何一点定义曲线通过的点,而通过点(Thru Points)必须选取对象,才能定义曲线。
在编缉曲线造型上,前者具有更大的自由度ISDX造型曲面与破衣的构建的曲面有何差别ISDX所定义的造型曲面类似破衣的边界曲面,它必须以4条边界定义曲面,所构建的特征以Style符号图标显示在Model Tree中。
所使用的边界并没有选取方向性的问题,而且边界只要相交便可(不必端点相接),若需要可加入多条内部曲线帮助定义造型曲面。
ISDX界面介绍:
命令介绍:
各种快捷菜单:
绘图区按右键
点选对象按右键
以右键选Soft Point或FIX POINT
以右键选黄色切线
以四个窗口进行模型显示:
点选如下图标:
系统会默认查看:(default)(top) (front) (right) 4个不同方法查看,供我们操作。
何谓作用平面:
构建自由(free)或平面上(planar)的曲线时,系统默认会把曲线先投影在
一平面上,称为作用平面,如图所示。
利用在平面上的(PLANAR)的方式构建曲线,它会先投影在作用平面上(以网格显示),用户可以调整平的偏移量改变曲线的放置位置
以planar作此线
除了可以旋转查看之外,还可以在绘图区按右键执行active-plane orientation
如何使用styling perferences对话框
不要勾选off when shaded 选项,便着色时仍可显示网面,并以surface mes h
调整网面密度
FREE--用法
选取此图标,勾选free选项,在空间上定义三个点,所构建的曲线会投影在作用平面上20
21
若需要,在曲线上按右键点ADD,在曲线上插入点,,在用左键点插入点进行拖拉,,使其成为
3D曲线
22
23
planar-用法:
点选此图标,勾选planar选项,在平面上点曲线要通过的点,构建在平面上的曲线,
若需要,可以planar的offset上输入偏移距离。
24
cos--用法:
在实体表面或曲面上点曲线要通过的点,构建曲线,只有实体或曲面存在时才可构建cos 曲线
系统只允许在同一个表面上构建曲线,无法横跨二曲面构建,
25
锁点用法:
以小方格符号显示,点曲线编缉图标,按住shift键再配合左左健使曲线端点锁在曲面上,不管如何拖拉伸仍在曲面上移动
26
以小圆圈符号显示,点曲线编缉图标,按住shift,再配合左健使曲线端点锁在曲面边界线上
或已存在曲线上,松开shift键,可在曲面边界上或已知曲线上随意拖动,,并可拖到曲面边界
线的端点或已知曲线的端点,再点选此端点,便出现一个黄色的线条,在此黄色线条上按右键,
可设置;相切,曲率连续,垂直等。
27
28
29
固定点:: 30
31
32
soft point 连接功能的应用
length ratio--系统以比例长度显示示该点在对象上的位置,输入0-1之间的数值33
34
parameter--用法跟length ratio类似
length---输入数值,以确定点在对象上长度的实际位置,
offset from plane ---当插入点或端点锁住边界或曲线时,或切换此形式控制该点与参考平面的参考距离。
使用此选项时,必须选取定义偏移距离的平面。
如何打断曲线
35
如何连接曲线:36
37
如何延伸:
extend free--在空间任何位置点选,系统会以曲率连续的方式顺接曲线端点与该点extend tangent--在空间任何位置点选,系统会以相切的方式延伸端点
extend curvature--在空间任何位置上点选,系统会以曲率连续方式延伸端点
如何构建投影曲线:
执行下图图标,先点选一个或多个要投影的曲面,再选取一条或多条曲线,最后选取
定义投影方向,使能构建投影曲线,
连续性设置
左键点端点,系统会显示切线方向与长度,(黄色线条),我们可拖位黄色线条改变方向与长
度
差调整曲线曲率,还可右键点此黄线设置连续性,前面粗略提到过,这里还是要说明一下
构建曲线后,端点的切线的长度与角度由系统定义
free-----切换此形式后,可以在对话框的length angle字段用输入方式精确定义
fix angle-以目前角度锁定切线方向
horizontal-以目前的工作平面定义水平方向
vertical---以指定的工作平面定义垂直方向
normal-----以指定平面的法向定义切线
align------以指定的曲线依参考定义切线方向
symmetric--以指定的曲线端点切作参考,同时调整二者的切线至平均值以修正切线方向。