第10章_植物遗传转化
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:2.60 MB
- 文档页数:83


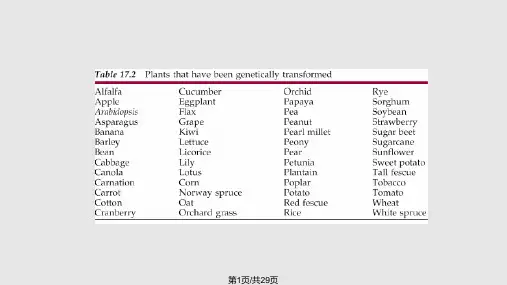
鳞茎球根植物的遗传转化英文回答:Genetic transformation of bulbous plants is a technique that allows for the introduction of foreign genes into the genome of these plants. This process involves the transfer of desired genes into the cells of the plant, which are then integrated into the plant's DNA. This genetic modification can result in a variety of traits, such as enhanced disease resistance, improved yield, or altered flower color.One example of genetic transformation in bulbous plants is the introduction of a gene for insect resistance in lilies. By inserting a gene from the bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), which produces a toxin lethal tocertain insects, lilies can become resistant to pests such as aphids or thrips. This transformation can significantly reduce the need for chemical pesticides, making the plant more environmentally friendly.Another example is the modification of flower color in tulips. Through genetic transformation, scientists havebeen able to introduce genes responsible for the production of pigments such as anthocyanins or carotenoids. This has allowed for the creation of tulips with unique and vibrant colors that are not naturally found in these plants. These genetically modified tulips have become popular in the horticultural industry due to their aesthetic appeal.Genetic transformation in bulbous plants can beachieved through various methods, including Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and biolistic (gene gun) transformation. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation involves the use of a soil bacterium called Agrobacterium tumefaciens, which naturally transfers DNA into plant cells. This bacterium is genetically engineered to carry the desired gene and then introduced to the plant tissue. The bacterium transfers the gene into the plant cells,resulting in genetic transformation.Biolistic transformation, on the other hand, involvesthe use of a gene gun to deliver DNA-coated particles into the plant cells. The gene gun shoots tiny gold or tungsten particles coated with the desired gene into the plant tissue. The particles penetrate the cell walls and deliver the foreign DNA into the plant cells, leading to genetic transformation.In both methods, the transformed plant cells are then cultured in a laboratory to encourage their growth into whole plants. Once the plants have grown, they are screened for the presence of the desired trait, such as insect resistance or altered flower color. This screening process involves various molecular techniques, such as PCR or gene expression analysis, to confirm the successful integration of the foreign gene into the plant's genome.Overall, genetic transformation of bulbous plantsoffers a powerful tool for improving their traits and characteristics. It allows for the introduction of desired genes that can confer benefits such as pest resistance, enhanced color, or increased yield. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the horticultural industry bycreating novel and improved varieties of bulbous plants.中文回答:鳞茎球根植物的遗传转化是一种将外源基因引入这些植物基因组的技术。



![[农学]第十章 园艺植物遗传转化1](https://uimg.taocdn.com/9bf315e7a1c7aa00b52acbb0.webp)

《植物生物技术》教学大纲一、课堂教学大纲1、教学目的该课程系统地论述了植物生物技术的理论和方法,既介绍了基本知识,也反映了该领域的最新研究进展。
全课程共分三大部分:植物组织培养、植物基因工程和植物分子标记及应用。
要求学生全面系统地了解植物生物技术的发展过程和发展趋势;理解各部分的基本理论、原理和概念;融会贯通三大部分的内容,并能运用所学技术解决生产中的实际问题。
通过学习,使学生学习掌握现代生物技术知识的技能和方法,尤其要求学生具有将植物生物技术与传统方法相结合改良植物、培育新品种、设计高新技术产业的能力,提高学生综合分析问题,系统利用专业知识的综合素质。
2、教学内容第一章绪论(2学时)•生物技术的产生与发展•植物生物技术与农业革命•植物生物技术在未来农业生产中所起的作用第二章植物细胞培养实验室建设与操作技术(2学时)本章重点、难点:植物组织培养所涉及的基本概念;培养基的组成、特点和用途;植物组织培养实验室建设;无菌操作的原理与技术等。
•植物组织培养实验室建设•实验室的设置•主要仪器设备、用途和使用方法•无菌操作器械•培养基及其制备•培养基的成分组成•常用培养基及其特点•培养基的改良与效应分析•培养基的制备•植物组织培养离体操作技术•培养用品的清洗与洗涤液的使用•灭菌与消毒•无菌操作技术•无菌操作中应注意的事项第三章胚胎培养(2学时)本章重点、难点:胚培养、胚珠培养和胚乳培养的意义,在育种工作中的实用价值。
•胚培养•胚培养的意义和用途•胚培养的方法•影响胚培养效果的因素•培养条件下的胚发育•胚珠培养•胚珠培养的意义•胚珠培养操作技术•胚乳培养•胚乳培养的意义•影响胚乳培养效果的因素•植株再生•离体授精第四章植物愈伤组织的诱导与分化培养(2学时)本章重点、难点:愈伤组织诱导、继代、培养与分化的基本术语和概念;器官发生;体细胞胚胎发生与植株再生;促进细胞分化的方法手段。
•愈伤组织的诱导与继代培养•脱分化、再分化的概念•愈伤组织的诱导、时期划分,各时期愈伤组织的特征特性•继代培养及继代培养的意义•悬浮培养及其用途•愈伤组织分化与植株再生•器官发生与植株再生•体细胞胚胎发生与植株再生•体细胞胚胎发生过程•体细胞胚的概念与内涵•体细胞胚胎发生与器官发生的区别•影响体细胞胚胎发生的外部因素•影响体细胞胚胎发生的外部因素•影响体细胞胚胎发生的内在因素•试管苗的移栽与护理•试管苗与自然苗的生理区别•试管苗移栽时应注意的事项第五章体细胞无性系变异与植物改良(2学时)本章重点、难点:体细胞克隆变异产生的遗传基础;体细胞克隆变异的育种应用。


资源植物遗传转化体系开发与应用
资源植物是指具有经济、生态、科学价值的植物,包括药用植物、食用植物、观赏植物等。
资源植物的遗传转化体系开发与应用是指通过基因工程技术对资源植物进行遗传改良,以提高其经济、生态、科学价值。
资源植物遗传转化体系的开发包括以下几个方面:
1. 基因克隆:通过PCR扩增、限制性酶切、连接等技术,将资源植物中的有用基因克隆出来。
2. 基因转化:将克隆的有用基因导入到资源植物中,使其表达出有用的性状。
3. 基因编辑:通过CRISPR/Cas9等技术,对资源植物中的基因进行编辑,以改变其性状。
4. 基因组学研究:通过对资源植物基因组的研究,了解其基因组结构、功能和调控机制,为遗传转化提供理论基础。
资源植物遗传转化体系的应用包括以下几个方面:
1. 药用植物的遗传改良:通过基因转化和基因编辑技术,提高药用植物的药效和药物含量,以满足临床需求。
2. 食用植物的遗传改良:通过基因转化和基因编辑技术,提高食用
植物的产量、品质和抗病性,以满足人们对食品的需求。
3. 观赏植物的遗传改良:通过基因转化和基因编辑技术,提高观赏植物的花色、花型和花期,以满足人们对美的追求。
4. 生态修复:通过基因转化和基因编辑技术,提高植物的抗逆性和生长速度,以加速生态修复过程。
资源植物遗传转化体系的开发与应用,可以为资源植物的保护、利用和开发提供新的思路和方法,为人类的生产和生活带来更多的福祉。
构树遗传转化近年来,构树遗传转化技术在农业领域引起了广泛关注。
构树遗传转化是指利用基因工程技术将外源基因导入植物细胞,并使其稳定地整合到植物基因组中,从而实现对植物性状的改良和优化。
这一技术在农作物育种、病虫害防治、抗逆性提高等方面具有巨大潜力,并对农业的可持续发展起到了积极的推动作用。
构树遗传转化的基本原理是通过载体将外源基因导入目标植物细胞中。
载体通常采用农杆菌或冷冻法介导的方式,将外源基因转移到目标植物细胞中。
农杆菌介导的构树遗传转化是最常用的方法,其基本原理是利用农杆菌感染植物组织,使其在植物细胞中引入外源基因。
冷冻法介导的构树遗传转化则是将目标植物细胞暴露在低温条件下,使其细胞壁破裂,然后将外源基因导入细胞中。
构树遗传转化技术在农业领域的应用非常广泛。
首先,构树遗传转化可以用于农作物的品质改良。
通过导入特定基因,可以使农作物产生更高的产量、更好的品质和更强的抗病能力。
例如,在水稻中导入抗病基因可以提高水稻的抗病能力,减少病害对产量的影响。
其次,构树遗传转化可以用于农作物的抗逆性提高。
通过导入耐盐碱、耐干旱等基因,可以使作物在恶劣环境下生长更加健壮,提高产量和品质。
此外,构树遗传转化还可以用于农作物的病虫害防治。
通过导入抗虫害基因,可以减少农药的使用,降低环境污染,提高农作物的产量和质量。
构树遗传转化技术在实际应用中仍面临一些挑战和难题。
首先,构树遗传转化的效率仍然较低。
目前,构树遗传转化的成功率通常只有1%左右,这限制了其在农业生产中的应用。
其次,构树遗传转化的安全性问题也备受关注。
外源基因的导入可能会引起植物的突变,导致不可预测的副作用。
因此,对于构树遗传转化的安全性评估和监管非常重要。
最后,构树遗传转化技术的成本较高,限制了其在大规模农业生产中的应用。
因此,需要进一步降低构树遗传转化的成本,提高其经济效益。
为了推动构树遗传转化技术的应用和发展,需要加强研究和合作。
一方面,需要不断探索新的构树遗传转化方法,提高转化效率和安全性。