抗心律失常药物的介绍和发展英文版
- 格式:doc
- 大小:55.50 KB
- 文档页数:10

抗心律失常药物【药品名称】通用名:酒石酸美托洛尔胶囊英文名:Metoprolol Tartrate Capsules本品主要成分及其化学名称为:1-异丙氨基-3-[对-(2-甲氧乙基)苯氧基]-2-丙醇L(+)-酒石酸盐其结构式为:分子式:(C15H25NO3)2·C4H6O6分子量:【性状】本品为胶囊剂【药物别名】倍他乐克,美多心安,美多洛尔Betaloc,lopressor,【药理毒理】本药属于2A类即无部分激动活性的β1-受体阻断药(心脏选择性β-受体阻断药)。
它对β1-受体有选择性阻断作用,无PAA(部分激动活性),无膜稳定作用。
其阻断β-受体的作用约与普萘洛尔(PP)相等,对β1-受体的选择性稍逊于阿替洛尔。
美托洛尔对心脏的作用如减慢心率、抑制心收缩力、降低自律性和延缓房室传导时间等与普萘洛尔、阿替洛尔(AT)相似,其降低运动试验时升高的血压和心率的作用也与PP、AT相似。
其对血管和支气管平滑肌的收缩作用较PP为弱,因此对呼吸道的影响也较小,但仍强于AT。
美托洛尔也能降低血浆肾素活性。
本品无致突变作用;对胎儿无影响;大鼠服用本品2年,800mg/天未发现良性及恶性新生物。
【药代动力学】美托洛尔的脂溶性介于普萘洛尔(PP)与阿替洛尔(AT)之间。
口服吸收迅速完全,吸收率大于90%,但肝脏代谢率达95%,首过效应为25~60%,故生物利用度仅为40~75%,与AT相近。
口服血浆浓度高峰时间一般在小时,最大作用时间为1~2小时。
血压的降低与血药浓度不平行,而心率的降低则与血药浓度呈直线关系。
主要在肝脏中被代谢为羟基美托洛尔,其在体内的代谢受遗传因素的影响。
在白种人中90%为快代谢型,t1/2为3~4小时;10%为慢代谢型,t1/2可达小时。
血浆高峰浓度的个体差异可达20倍。
肾功能不全时无明显改变。
在肝内代谢,经肾排泄,尿内以代谢物为主,仅少量(<5%)为原形物。
不能经透析排出。
![[精选]第22章抗心律失常药--资料](https://uimg.taocdn.com/79a295ed7f1922791688e8eb.webp)

抗心律失常药物的分类,作用机制及不良反应1药物简介英文名称:antiarrhythmic drugs抗心律失常药是一类用于治疗心脏节律紊乱的药物。
随着对心脏电生理特性以及抗心律失常药物作用机制的了解,使心律失常的药物治疗有了较大的进展。
心律失常是心动频率和节律的异常,它可分为快速型与缓慢型二类。
缓慢型心律失常可用阿托品或拟肾上腺素类药物治疗。
快速型心律失常比较复杂,它包括房性期前收缩、房性心动过速、心房纤颤、心房扑动、阵发性室上性心动过速、室性早搏、室性心动快速及心室颤动等。
本章主要讨论治疗快速型心律失常的药物。
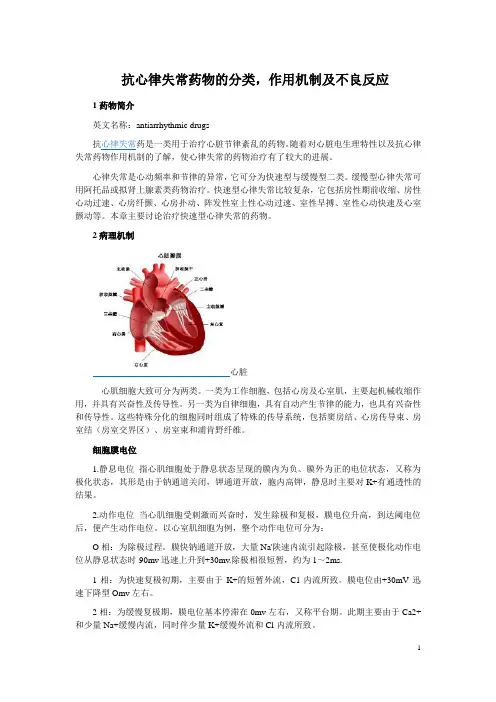
2病理机制心脏心肌细胞大致可分为两类。
一类为工作细胞,包括心房及心室肌,主要起机械收缩作用,并具有兴奋性及传导性。
另一类为自律细胞,具有自动产生节律的能力,也具有兴奋性和传导性。
这些特殊分化的细胞同时组成了特殊的传导系统,包括窦房结、心房传导束、房室结(房室交界区)、房室束和浦肯野纤维。
细胞膜电位1.静息电位指心肌细胞处于静息状态呈现的膜内为负、膜外为正的电位状态,又称为极化状态,其形是由于钠通道关闭,钾通道开放,胞内高钾,静息时主要对K+有通透性的结果。
2.动作电位当心肌细胞受刺激而兴奋时,发生除极和复极,膜电位升高,到达阈电位后,便产生动作电位。
以心室肌细胞为例,整个动作电位可分为:O相:为除极过程。
膜快钠通道开放,大量Na'陕速内流引起除极,甚至使极化动作电位从静息状态时-90mv迅速上升到+30mv.除极相很短暂,约为1~2ms.1相:为快速复极初期,主要由于K+的短暂外流,C1-内流所致。
膜电位由+30mV迅速下降型Omv左右。
2相:为缓慢复极期,膜电位基本停滞在0mv左右,又称平台期。
此期主要由于Ca2+和少量Na+缓慢内流,同时伴少量K+缓慢外流和Cl-内流所致。
3相:为快速复极末期,由于K+快速外流引起。
4相:复极完毕,心室肌细胞即为静息期。
此期由于Na+,K+-ATP酶的作用,细胞泵出Na+而摄入K+,恢复静息电位的离子分布。




Introduction and development ofanti-arrhythmic drugsAuthor:赵恒军Instructor:刘静庭Abstract Objective:summaries of the classification, progress and security applications of antiarrhythmic drugs. Methods:searching and retrieving relevant documents about the latestanti-arrhythmia at home and abroad. Results: this paperreviewed the classification, the latest progress and securityapplications of antiarrhythmic drugs. And it will help toformulate the proper treatment of rational anti-arrhythmia.Conclusions: the paper can be used to help people get basicknowledge of anti-arrhythmic drugs rapidly.Key words Antiarrhythmic agents, application, and development The concept of arrhythmiaUnder normal circumstances, the impulse of the heart comes from the sinus node, through the atrium, atrioventricular node, atrioventricular bundle and Purkinje fibers in turn and then to ventricular muscle finally which cause the contraction of the heart in a rhythm. Cardiac arrhythmia is a serious heart disease which is caused by abnormal of heartbeat law and frequency. At the same time, normal atrial and ventricular activationand movement sequence are disordered. The disease has slow and fast types, the former can be treated by isoproterenol (β agonist or atropine (M receptor blocker). The drug therapy of the latter is more complex, we usually say that the anti- arrhythmic drugs is for the fast type of arrhythmia.MechanismThe mechanism of anti-arrhythmic drugs is mainly through the influence of the Na+, Ca2+ and K+ transport of myocardial cell membrane, affecting the period of cardiac action potential, inhibition of self-regulation and (or) stop reentry to correct the arrhythmias.Since the mechanism of arrhythmia is complex, the side effects of various anti-arrhythmic drugs are different in many aspects. So it must be fully taken into account when select drugs. We also should pay attention to the dose of medication and methods to achieve the desired effects.CategoriesThe classification of antiarrhythmic drugs, proposed by the Vaughan Williams and completed by Harris etc., has been used for nearly 30 years. Vaughan Williams classified drugs into four categories based on the electrophysiological characteristics of the drugs. Ⅰclass medicines block sodium channels and inhibit atrial, ventricular and Purkinje fiber of fast response organizations conduction velocity.Ⅱ class medicinescan be further divided into 3 categories. Ⅰa sodium channel block in a medium speed, extended the period of repolarization, such as quinidine, procainamide, double disopyramide.Ⅰb sodium channel block in a fast speed such as lidocaine , mexiletine, Ⅰc sodium channel block in a slow speed, such as fluorine Cain, propafenone. Ⅱclass is a β-receptor blocker.Ⅲclass medicines prolong cardiac repolarization process and block potassium channel in the action potential of 2,3 phase. Thereby prolong the refractory period of cardiac tissue, such as amiodarone, sotalol. Ⅳclass medicines block calcium channels and inhibit sinus node, slow response organizations of atrioventricular node, such as verapamil, diltiazem.Antiarrhythmic drug efficacy and potential hazardsAlthough antiarrhythmic drugs can reduce or eliminate the symptoms which caused by the arrhythmia itself and / or risk of death, it may cause some potential dangers, including non-cardiac adverse reactions (such as dizziness, nausea), organ toxicity (eg, agranulocytosis, hepatitis), cardiac events, post-induced arrhythmia or arrhythmic death.Cardiac adverse reactions of antiarrhythmic drugs including: ① "early" arrhythmogenic effect, which refers to the treatment of early antiarrhythmic drug induced arrhythmia, or new deterioration of the existing arrhythmia. ②induce congestive heart failure or to the deterioration, ③induce cardiac conduction disturbances, such as theheight of atrioventricular block or "sick sinus syndrome."The most serious potential risk of antiarrhythmic drugs is to increase risk of late arrhythmia death, which known as the "late proarr-hythmiceffect ". Organ toxicity, such as agranulocytosis or hepatitis, are specifically found in quinidine, procainamide, tocainide, as well as amiodarone treatment. Treatment cases of flecainide, encainide shown it can effectively suppress ventricular arrhythmia and also well tolerated, but the risk of death in the late arrhythmia is still higher than placebo 2 to 3 times.This dangerous of "late proarr-hythmiceffect", can be seen in 10 months later of follow-up visit. Quinidine, mexiletine, Morrissey throat, also can make the late cause arrhythmogenic risk of death increased. So far known only when the β blockers treatment can reduce the risk of cardiac arrhythmias sudden death and total cardiac death.Progress in anti-arrhythmic drugsThe advance in antiarrhythmic drug research is rapid. There are nearly 20 varieties clinical application drugs. Quinidine, which started for clinical purposes in 1918, is the broad-spectrum anti-arrhythmic drug. And it was used as standard drugs in this class of preparations. Due to side effects, earlier application such as Procainamide and Lidocaine current consumption diminished.After 80 years of the 20th century, propafenone, flecainide, Encainidehave been applied in succession. These drugs, which can work directly on the cell membrane and make a difference, are the sodium channel blocker of strong activity. In 1995, pirmenol, anti-malignant ventricular arrhythmia drugs, go public in Japan. In 1999, the development of nifekalant by the Japanese Mitsui Corporation was approved listed on the treatment of ventricular arrhythmias which known as the only progress in drug.Looking from our antiarrhythmic drugs structure, the mature drug applying has little difference compared with abroad.Treatment of supraventricular, ventricular tachycardia drug propafenone, sotalol and amiodarone have high popularizing rate. Verapamil and diltiazem that control atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter also occupy a certain amount of market share. The new type Ⅲ class potassium channel Blockers has been the general concern of the indust.Type Ⅲnew potassium channel blocker ibutilide, dofetilide and sematilide is a recent development of products which is the class Ⅲantiarrhythmic drugs with a certain class Ⅰactivity. New Heart Ⅲdrugs has smaller side effects than amiodarone.However, the torsade type of tachycardia (TDP) incidence is not less than amiodarone. Ibutilide which belongs to methyl sulfonamide derivatives, is a new type of class Ⅲantiarrhythmic drugs with ion channel activity used on acute atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter patients. Pharmacia & Upjohnwhich researched and developed by the United States, come into the market in the United States in 1996. It has listed 11 countries in Europe and America. The treatment effect of intravenous administration is more significant. It provide a new type of good medicine to cure atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter to sinus rhythm.Duofeilite, which developed by the U.S. Pfizer and come into the market the first times in the United States in 2000, is the third-generation oral administration anti-arrhythmic drug. Duofeilite is a new type of potassium channel agonist with similar mechanism of action as ibutilide. The function on atrial is more obvious than ventricular.It is used in clinical to treat atrial fibrillation and atrial flapping and to make the rhythm of the heart to sinus rhythm. The main side effect is the torsade type of tachycardia. The occurrence rate of intravenous application is about 3%, while the incidence of oral administration is about 1%. Most adverse events happened within 3d after treatment. The torsade type of tachycardia risk factors are QT interval prolongation, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia and bradycardia.Dronedarone is a new antiarrhythmic drug which was reported in the Europe heart meetingin the August 2004. It is an analogue of amiodarone, because they are free of iodine compared with amiodarone, there is no organ toxicity. It is easier to adjust the dose with the half-life of 1 ~ 2d. EURIDS study shown, 77 European Hospital with 612 patientswith 2: 1 randomized into the group were due to auricular fibrillation or atrial flapping to try this medicine. All patients confirmed atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter within the first 3 months of at least 1 ECG before taking part in the group. 411 patients received dronedarone 400mg, 2 times a day, 201 patients received placebo treatment for 12 months. The results observed from random assignment to the first occurrence of atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter recurrence time for comparison (ECG confirmed onset time at least more than 10min). The results, from the random assignment to first atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter onset, shown that dronedarone group was 2.3 times longer than placebo group. The dronedarone reduced the recurrence rate of 33%, while medication side effects was similar to the placebo group, medicine group 59.4%, 58.2% in the placebo group, no significant difference.The drug was well tolerated, so it is very promising in control of atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter episode. Because it improves the amine iodine AZD7009 which is the drug being developed with sodium, potassium channel blocking effect, it has obvious effect on atrial muscles and is effective in treating atrial arrhythmias. It also can prolong QT interval, but no the torsade type of tachycardia happened. AZD7009 will enter Phase Ⅲclinical trials.RSD1235 is a new, fast acting and can be intravenous administration antiarrhythmic drugs. It has been shown to be effective in treating atrialfibrillation. It is of high degree of selection in the atrium, and almost no effect on the ventricle. The drug is safe and relatively well tolerated and no drug-related the torsade type of tachycardia. Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) meeting announced the arrhythmia cardioversion trial, that RSD1235 AF cardioversion rate is about 50% to 60% in America in 2005. In summary, for a long period of time, represented by amiodarone class Ⅲantiarrhythmic drugs will remain our first line of drug clinical arrhythmia. And the complex class Ⅲantiarrhythmic drug therapy with multi-channel block (IKr, IKs, Ito, INa etc.) effects may shed light on arrhythmic drugs.References[1] Vaughan Williams EM. A classification of antiarrhythmic actions reassessed after a decade of new drugs. J Clin Pharmacol, 1984, 24: 129- 147.[2] Morganroth J. Am J Cardiol, 1993, 72(4):3A~7A.[3] Saliba WI,Natale A.Ventricular Syndrome[J].Med Clin Nor Am,2001,85(2):267.[4] Jiang Zhirong, Dong fruit Xiong, Liu Chengyu, et al. Electrocardiogram and Clinical Practice [M]. Qingdao: Qingdao Publishing House, 2003.10[5] Liying,YangYanMin, Pu Kai Lin, et al. the Sodium Channel Block Effects of Acehytisine Hydrochloride in Guinea Pig Ventricular Myocytes[J]. Chinese Journal of Cardiac Arrhythmias, 2007.1 (11) :47-52.[6] Gerlach U.IKs channel blockers:potential antiarrhythmic agents[J]. Curt Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents, 2003, 1(3):243-252.[7] Saliba WI, Natale A. Ventricular Syndrome [J].Med Clin Nor Am, 2001, 85(2):267.[8] Wang Minghe. Antiarrhythmic Drug Induced Arrhythmias. World Clinical Drugs 2003, 24 (1): 21 – 25.[9] Working Group on Arrhythmias of the European Society of Car-diology. Atral fibrillation: current knowledge and recommendations for management. Eur Heart, J 1998, 19: 1294- 1330.[10] Chu Yingjie. in Common Use of Oral Anti-arrhythmic Drugs in the Clinical Application Points. Postgraduates of Medicine (Internal Medicine), 2004, 7 (1): 6 – 7.[11] Chinese Biomedical Engineering Society of Cardiac Electrophysiology Section, Chinese Medical Society of Cardiology Council, Editorial Board of Journal of Cardiology, China cardiac pacing and cardiac electrophysiology Journal Editorial Board. Amiodarone Antiarrhythmic Therapy Application Guide. Chinese Journal of Cardiology, 2004, 32 (12): 1065-1071.[12] Chen Haozhu. Drug Interactions Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease Journal of Clinical Electrocardiology, 1997. (4) :171-173. [13] Lijia Geng, Li Peisheng. Treating Arrhythmia experience [J]Traditional Chinese Medicine, 1995, 36 (11): 653-655.[14]Chen Xiu and others. Cardiovascular Pharmacology (First Edition). Beijing People's Medical Publishing House. 1997, 440-445.[15] Wang Shaoqu, Yin Ruixing. β-blocker Treatment of Dilated Cardiomyopathy Clinical Research Fair, 2005, 8 (12): 337.。