变量数据的获得方法2(实验性分离和)
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.61 MB
- 文档页数:18

实验心理学知识点1、在实验心理学上具有里程碑意义的人物有费希纳、冯特和艾宾浩斯。
2、费希纳的贡献:(1)联系内部世界和外部世界:费希纳定律(2)心理现象的定量研究方法:最小可觉差法、正误法和均差法。
(这三种针对的都只是感觉)费希纳对现代实验心理学的影响:一方面,他关于感觉测量的思想被后人进一步深化:对各种心理现象都试图进行科学量化研究,并用数字形式表现出来。
另一方面,从费希纳阈限思想的不足和缺陷出发,后人发展出了新的心理物理方法——信号检测论。
3、冯特的贡献:(1)冯特倡导用心理现象作为心理学的研究内容,反对把神学和哲学上的灵魂作为自己的研究对象,为心理学的独立开辟了道路(2)冯特提出必须用试验方法研究心理学,并于1879年在莱比锡大学建立了第一个心理学实验室,对心理现象进行量化的科学研究,从而创立了实验心理学这门新学科,使心理学真正地走进了科学殿堂。
(3)冯特的伟大之处还在于运用莱比锡大学的心理实验室培养了一大批学生,撒遍心理学国际性发展的种子。
冯特的影响:他的研究实践和大量著述宣告了实验心理学的诞生,搭建了实验心理学这座大厦的框架。
4、艾宾浩斯的贡献:(1)证明了试验方法可以用来研究高级心理过程(2)从根本上变革了实验心理学的研究范式(3)为实验心理学提供了新的变量测量方法,解决了高级心理过程的量化问题(4)通过实验研究,建立了第一个和高级心理过程有关的函数关系---遗忘曲线。
艾宾浩斯的影响:(1)诱使后背心理学家们不断尝试将实验法应用于各种心理现象(2)他采用的人工条件下实验研究的方法,成为此后所有实验心理学研究的金科玉律,保证了实验心理学结论的客观性(3)仅从记忆研究这一点来说,艾宾浩斯对现代实验心理学的影响也是巨大的。
5、科学的目标:描述、解释、预测、控制。
6、非科学方法的特点:听信权威之言、注意凝聚、先验7、科学方法的特点:强调系统的经验观察、能够自我校正、8、实验室实验的优势:实验室情景比真实生活更可靠、实验室情景得出的结果更具说服力、不会直接将实验室结论无限推广到真实生活中去。

江西省2024—2025学年上学期调研测试高三生物学(答案在最后)试卷共6页,21小题,满分100分。
考试用时75分钟。
注意事项:1.考查范围:必修1,必修2第1章~第3章。
2.答卷前,考生务必将自己的姓名、准考证号等填写在答题卡指定位置上。
3.回答选择题时,选出每小题答案后,用铅笔把答题卡上对应题目的答案标号涂黑。
如需改动,用橡皮擦干净后,再选涂其他答案标号。
回答非选择题时,将答案写在答题卡上。
写在本试卷上无效。
4.考生必须保持答题卡的整洁。
考试结束后,请将答题卡交回。
一、选择题:本题共12小题,每小题2分,共24分。
在每小题给出的4个选项中,只有1项符合题目要求,答对得2分,答错得0分。
1.生命系统是由物质组成的,生命活动的完成都离不开系统内的物质。
下列关于细胞中的元素和化合物的叙述,正确的是()A.微量元素在人体内含量很少,因此其作用不大B.人摄食的蛋白质,可直接被小肠上皮细胞吸收C.缺Mg会影响植物叶绿素和人体血红素的合成D.脂质存在于所有细胞中,通常表现为不溶于水2.下列关于细胞器结构和功能的叙述,正确的是()A.通过光学显微镜可以看到叶绿体的内部含有许多圆饼状的基粒B.内质网上都有核糖体附着,是蛋白质合成、加工、分类的场所C.线粒体具有内外双层膜,能通过内膜折叠形成嵴来增大膜面积D.液泡内含有糖类、光合色素等物质,能调节植物细胞内的环境3.细胞代谢离不开酶和ATP。
下列关于酶和ATP的叙述,错误的是()A.酶的组成单位是氨基酸或脱氧核苷酸B.溶菌酶溶解细菌需要适宜的温度和pHC.植物合成ATP时所需的能量可来自呼吸作用D.正常活细胞中ATP和ADP的比值保持相对稳定4.规范的实验操作是实验能否成功的关键。
下列对实验中出现异常实验现象的原因分析,不合理的是()选项实验名称异常实验现象可能原因A检测生物组织中的还原糖没有出现砖红色沉淀未进行水浴加热B观察根尖分生区组织细胞的有丝分裂看到的细胞呈长方形按压盖玻片时用力过大C绿叶中色素的提取和分离观察到的色素带颜色浅加入无水乙醇过多D性状分离比的模拟实验性状分离比与预期相差较大实验次数过少5.为探究植物细胞的吸水和失水,某同学使用0.3mol/L的KNO3溶液处理洋葱鳞片叶外表皮细胞,观察到其原生质体(除细胞壁外的细胞结构)体积相对值的变化如下图所示。

心理学:实验心理学(题库版)1、填空题变量是指在()或()可变的事物的()。
在实验中实验者()、()的变量称为自变量;由操纵而引起的被试者的()称为因变量。
正确答案:数量上、质量上、属性、所操纵的、对被试的反应产生影响(江南博哥)、自变量、某种特定反应2、名词解释次级内隐自尊效应正确答案:意指个体作出的判断通常是与个体的自尊密切相联的,都有维护和促进自尊的功能,但是,个体本身对此并没有明确的意识。
3、填空题反应时实验中有二个基本因变量,即()和()。
因此,反应时间实验中的一个突出问题就是()它们之间的相互关系。
正确答案:速度、准确性、权衡4、填空题最能够最有效运用实验控制策略的是().正确答案:实验室实验5、名词解释被试内设计正确答案:指每一个被试都接受自变量的所有水平处理的设计。
被试内设计不但节省了被试人数,而且不同组的被试个体差异也得到了最好的控制。
被试内设计比被试间设计更有力,能更好的考察实验组和控制组之间的差异,这个优点使得许多研究者更倾向于使用被试内设计。
和被试间设计相反,被试内设计不会受到来自被试个体差异的困扰,但却必须面对实验处理之间相互污染的问题。
可以采用平衡技术来控制这些差异。
6、填空题斯腾伯格曾借助加因素法揭示了短时记忆信息提取过程的四个独立加工阶段,即刺激编码阶段、()、()和反应组织阶段。
正确答案:顺序比较阶段、决策阶段7、填空题脑磁图(简称MEG)的工作原理是:大脑工作时所形成的(),在头颅外表产生(),脑磁图通过捕捉这些(),便可反映大脑内部的神经活动。
正确答案:电流、感应磁场、极微弱的磁信号8、填空题社会测量设计的首要任务是().正确答案:确定测量标准9、填空题心理学上关于反应时间的研究可划分为两个时期。
第一时期称(),它是由唐德斯奠定基础的。
又称()或唐德斯三成分说。
第二个时期称(),它是由斯顿伯格奠定基础的。
正确答案:减数法时期、唐德斯反应时ABC、加因素法时期10、单选使用直线内插法计算阈限的方法是()A、极限法B、恒定刺激法C、阶梯法D、平均差误法正确答案:B11、名词解释直接验证正确答案:是一种对实验效度进行验证的方法,指在尽可能保持原实验方法的情况下在实际中重复实验。

实验心理学第一章1、实验心理学的诞生:1879年冯特在莱比锡大学创建了世界上第一个心理学实验室。
2、对实验心理学有突出贡献的心理学家:(1)费希纳:(1801~1887)是德国著名的哲学家、物理学家、心理物理学家、实验美学家。
他是实验心理学奠基人和实验美学的创始人。
费希纳对心理学的贡献:1、联系心理与物理世界 2. 心理现象的定量研究方法对现代心理学的影响:创立了实验计量心理学(2)冯特:研究贡献:1. 冯特倡导以心理现实作为心理学的研究内容2.冯特提出必须用实验方法研究心理学3. 冯特的伟大之处还在于运用莱比锡实验室培养了一大批学生对现代实验心理学的影响:开创的心理学是以实验方法研究现实的人类心理。
是实验心理学的开山人物。
(3)艾宾浩斯:研究贡献:1.证明了实验方法可以用来研究高级心理过程。
2.从根本上变革了实验心理学的研究范式。
3.为实验心理学提供新的变量测量方法,解决了高级心理过程的量化问题。
4.通过实验研究,建立了第一个和高级心理过程有关的函数关系——遗忘曲线。
对现代心理学的影响:1. 开创性地采用实验方法研究高级心理现象2. 作为记忆研究的开山鼻祖,为记忆的实验心理学研究奠定了根基。
3、实验心理学研究方法上的新突破:(1)脑功能成像技术(2)元分析:元分析是对已有研究结果的总体分析,也有人称为“总分析”。
元分析运用了测量和统计分析技术对分别进行了的一些实验或研究进行定量化的总结,找出一组相同课题研究的结果所反映的共同效应。
元分析的特点:元分析是一种定量分析元分析是一种全面的评价元分析寻求普遍性的结论元分析的步骤:1、以往研究的检索2、研究的分类和编码3、研究结果的预测效果量=(实验组的因变量平均值-对照组的因变量平均值)/对照组的标准差4、分析与评价(3)反应时新法(4)实验性分离第二章1、除科学方法之外,还有三种确立信念的方法:权威、先验、注意凝聚2、科学的方法:客观观察、自我校正3、影响实验效度的因素:(1)主试—被试间的相互作用:霍桑效应、实验者效应、安慰剂效应(2)统计回归回归假象指在许多测量情景中,第一次测验时的高分组与低分组这两个极端组在第二次测量时向平均数回归;高分组的得分比第一次低些,低分组的得分高些。


---------------------------------------------------------------最新资料推荐------------------------------------------------------ 人教版高中生物课标教材中的科学方法体系人教版高中生物课标教材中的科学方法体系课程教材研究所赵占良新课程十分注重培养学生的科学探究能力。
科学探究能力的培养离不开三个要素:知识、方法和过程技能。
人教版普通高中生物课程标准实验教科书在着力构建知识体系的同时,也力图构建符合高中学生探究能力发展需要的科学方法体系和技能体系。
下面对教材中的科学方法体系作简要的分析。
科学研究的方法大致包括三个层次:第一层次是学科内的特殊的方法,如生物学研究中的同位素标记示踪法、分离细胞器的方法、解剖的方法等;第二层次是科学研究的一般方法,这些方法是从物理、化学、生物学等自然科学研究中概括出来的适用于各门自然科学研究的共同方法;第三层次是最具有普遍意义的哲学方法,如唯物辩证法、矛盾分析法等,这些方法适用于自然科学、社会科学和思维科学。
教材中强调的科学方法主要指科学研究的一般方法,因为这些方法对所有学生的发展都具有重要价值。
科学研究的一般方法包括获取经验性材料的方法和理性思维的方法两大方面(见下图)。
图人教版高中生物新课标教材中的科学方法体系1/ 161.观察法观察法是指人们在自然发生的条件下,通过感官或借助于仪器,有目的有计划地考察研究对象,从而获得有关经验性材料的方法。
人教版初中生物学教科书中对观察法已经做过这样的表述:观察是科学探究的一种基本方法。
科学观察可以直接用肉眼,也可以借助放大镜、显微镜等仪器,或利用照相机、录音机、摄像机等工具,有时还需要测量。
科学观察不同于一般的观察,要有明确的目的;观察时要全面、细致和实事求是,并及时记录下来;对于需要较长时间的观察,要有计划,有耐心;观察时要积极思考,多问几个为什么。

变量分离原理
变量分离原理是指将总变量分解为两个或多个部分变量,以便更好地理解和分析问题。
通过这种分离,问题可以被更详细地描述和解释,从而使问题的解决变得更加直观和便捷。
变量分离原理的基本思想是将一个复杂的变量进行分步骤的分解,每一步骤都只考虑整个过程的一部分内容。
这样,问题不再是一团糟的复杂性,而是被分解成几个可以独立处理的相对简单的问题。
这些部分问题可以通过独立的分析方法进行研究,最终得到整个过程的全面分析结果。
变量分离原理一般涉及两个主要步骤。
首先,将总变量分解为独立的部分变量。
这种分解可以基于物理、经济或其他相关因素进行。
其次,通过对每个部分变量的独立分析,得到每个部分变量对总变量的影响程度,并确定它们之间的相互作用关系。
这样,我们就可以更好地理解和解释整个过程。
变量分离原理的应用非常广泛。
在物理学中,我们常常会将复杂的物理问题分解为几个较小的部分问题,以便更好地理解和求解。
在经济学中,我们可以将总产出分解为几个独立的生产要素,以便研究它们对总产出的贡献。
在统计学中,我们可以通过控制其他可能的影响因素,来研究某个变量真正的影响效应。
总之,变量分离原理是一种有效的分析方法,通过将总变量分解为部分变量,帮助我们更好地理解和解释问题。
它为我们提
供了研究复杂问题的一种有力工具,使得问题的求解过程更加清晰和可行。

实验性分离(Experimental isolation)Psychological Science2000 thVolume 234Four hundred and twelveExperimental separation between implicit and explicit memory tasks:The degree of coding and the requirement of extractionXComponent(Department of education, Liaoning Normal University116029)Coding level is manipulated(Experiment1) and extraction requirements(Experiment2) compare the operations between implicit and explicit memory tasksChange. The result showsThere is a tendency of mutual inhibition between semantic and non semantic processing in encodingMore awareness in the extraction requirementsThe participation of ingredients leads to more extraction of semantic components in earlier plotsAnd rarely affect the extraction of non semantic componentsCoding levelThere is interaction between the extraction requirements and the extraction requirements.Key wordThe extraction of coding degree requires implicit memory and explicit memory1 PrefaceA comparative study of implicit and explicit memory tasks wascarried out using experimental dissociation techniquesThe manipulation of coding will make explicitMemory produces significant processing level effectsImplicit memory is rarely affected[1]. Further research findingsEncoding from semantics to nonVarying degrees of semanticsThe semantic component increases as the processing stimulus increasesThe priming effect of explicit memory also increaseslargeThe priming effect of implicit memory is reduced[2]. Does this mean that different types of coded processing are complementary?Brown?(1991) research supports this finding[3]. howeverCraik, Moscovitch, andMcDowd (1994) considersProcessedComplementarity occurs mainly in comparison within the same task[3].Information encoded in varying degreesHow much of the extraction is affected by different extraction requirements?As stated aboveExplicitIn memoryRecall of deep processing items is superior to that of shallow processing itemsImplicit memory, however, remained unaffected. But some studies have shown that,Some implicit memory tests also produce processing level effects[5]. thusImplicit memory has been shown to be contaminated by explicit memory(Contamination) and pure(Pure) the debate about implicit memory.Jacoby presents a procedure separation procedure(Process -Disso2Ciation, Procedure) modelAttempts are made to resolve the dispute[6]. The authors believe thatExplicitImplicit division and consciousnessUnconscious DivisionIt is not a one-to-one correspondenceThe degree of consciousness in the process of extraction isclosely related to the degree and extent of information encodingImplicit and explicitThere may be conscious or unconscious effects in memory.2 Experiment 1211 experimental method21111 subjectsLiaoning normal university undergraduate students24Half and half of men and womenVision and vision correction are normal.21112 instrumentSeagull4400L a baby lampCK - J intelligent test controller one21113 materialsFrom the dictionary of modern Chinese frequency(Chinese Language Press)1986 EditionSelect low-frequency Chinese characters190Frequency of occurrencestayBetween 0100006 and 010016Average stroke1514 strokes. The characters in the learning phase are bothNumber 4 boldface is filmed on slideupperHalf of the Chinese characters are underlinedThe paired Chinese characters presented in the test phase are also used4 boldface is shown on the slide.21114 test environmentThe subjects sit at the distance from the screen5 metersAt the same level as the center of the screenThe interior is natural lightSlide showX this article is well received by Mr. Yang ZhiliangSpecial thanks for.1995-2005, Tsinghua, Tongfang, Optical, Disc, Co., Ltd., All, rights, reserved.No.4 issue of Zhou RenlaiExperimental separation between implicit and explicit memory tasksThe degree of coding and the requirement of extractionMachine located on screen6 metersThe rendered Chinese characters fall into the middle of the screen20 * 30cm rangeEach subject was tested individually.21115 design adoption2 (among subjects)* 2 (subject to factor)Mixed variance design. Among the subjects were recognition and word determinationTwo test formsAnd within subject factors for grapheme and meaning two levels of processingTotal.4 conditionsFor each condition12 people.21116 programThere are two stages of study and test. Learning phaseThe subjects were randomly presented130 Chinese charactersAmong them, the official Chinese charactersOne hundred and twentyindividualAnd the restThe 10 halves are placed before and after the official project as a buffer item. Each Chinese character presents1Intervals2 secondsBy intelligenceTester automatic control. The subjects were asked to type the underlined charactersIt is divided into three kinds: the left and right, the upper and the lower, and the middleYes, no!The underlined Chinese characters of meaning of judgmentAsk for a word that is similar or opposite to the meaning of the word. After practiceOfficially beginBefore and afterThe operation of 5 Chinese characters is not included in the result. Cover after learning phase. Present to the subjects10 cards with the name of the city in our countrysliceThe subjects were asked to sketch out the name of the province where the city was located. Test phase. Present to the subjects65 pairs of Chinese charactersAmong them60For formal projectsOn the other,The 5 one is exercise. One of each pair of characters is previously studiedAnd the other one is not studied. eachStimulus presentation015 secondsIntervalsOne second. The first group of subjects was tested for word determinationThe subjects were asked to judge which of the Chinese characters that appeared in pairsOne word is correctThe proportion of the words that appear in the learning stage is judged as the proportion of the correct words as the index of the words. The second group underwent re - operationRecognition testThe subjects were asked to quickly identify which pairs of Chinese characters they had just metCorrect the words that appear in the learning phaseThe proportion of judgment as an indicator of recognition. Officially begin after practice.212 results and analysis1 subjects were operated wrongThe results have been cancelledActual statistics23 people. All the experimental data are usedSPSS software processing.surface1 word determination and recognition operations under different coding conditionsGrapheme meaning processingWord determination01630155Recognition01740182Table1 data were analyzed by means of an overall variance analysisThere was significant difference between the main effectsF (1,21) =15116, MSE =4832116, P =01001; the main effect within the group was not significantF (1,21), =0114, MSE=16152, P, =01709; between groups and within groupsThe interaction is remarkableF (1,21) =8118, MSE = 946107, P, =01009. Further simple effect tests are shownWord meaningThere are significant differences in the processing of the confirmation and recognition test under the condition of font processingF (1, 21) = 4136, MSE = 750199, P, =01049,There was a significant difference in word processing conditionsF (1, 21) = 19118, MSE = 5027124, P = 01000; word determination test byThe effect of different coding operationsThe font, the machining operation is significantly greater than the meaning of the machining operationF (1,21) =5148, MSE =633186, P = 01029, recognition did not show significant processing level effectsF (1,21) =2195, MSE = 341144, P =0110. chart1 showsWith the increasing semantic components in codingThe achievement of word determination tends to decreaseWhile the recognition results areTend to rise.chart1 word determination and recognition operations under different encoding1995-2005, Tsinghua, Tongfang, Optical, Disc, Co., Ltd., All,rights, reserved.Psychological ScienceVolume 23Four hundred and fourteenin additionWe0150 as the baseline level of words,Asked the learned words just try to complete the current radical If you can't do itJust use the first word to think of it.Exclusion groupParticipants were asked to complete the Chinese.But you must not use the words presented in the learning phase. Implicit groupThe subjects are asked to finish the current as soon as theyBaseline groupThis group did not participate in the learning phaseOnly ask them as soon as possible, the complete word radical thought.312 results and analysis1995-2005, Tsinghua, Tongfang, Optical, Disc, Co., Ltd., All, rights, reserved.No.4 issue of Zhou RenlaiExperimental separation between implicit and explicit memory tasksThe degree of coding and the requirement of extractionAll the experimental data are usedSPSS software for processing.surface2 the operations of inclusion, elimination, implicit and baseline complement are given under different encoding. The sumAnalysis of body variance showedThere was significant difference between the main effectsF (2,33) =8134, MSE = 20816, P = 01001; difference in intra group main effectsremarkableF (2,33), =39194, MSE = 450180, P, =01000 showed significant interaction between groupsF (2,33) =12154,surface2 supplementary pen operation under different extraction requirementsGrapheme meaning processingContaining group01130123Exclusion group01120113Implicit group01140118Baseline group01080109MSE = 12154, MSE = 145118, P, =01000. Further single factor differences in the operations of the three groups under font processingTest displayF (2,33), =11948, MSE = 121438, P, =01159, the difference was not significantIndicateUnder the font encoding conditionGuidanceThe language has the same effect on the three groups. The difference test of single factor on the meaning processing operation under the condition of the three groups show, F (2,33) =131647, MSE = 74119, P, =01000, the difference is extremely significantFurther matching, comparison, displayInclude groupImplicit group> excludegroup(P are less than0105), show that in the condition of encoding meaningThe guidance language had different effects on the operation of the three groups. For different groupsThe difference between the test operation and the meaning of the display fontBaseline group: P > 0105; contains groups: T=6151, DF, =11, P=0100, platoonIn addition to the group: T=0.00, DF, =11, P=1100, implicit group: T, =2107, DF, =11, P=01024, graphs2 shows each group in different encodingsOperating trends under conditions and extraction requirements.in additionWe performed a difference test between the first three groups and the baseline group under different coding conditionsThe result showsIn addition,There was no significant difference between the operation of removing group font and baseline groupThe operation of the other groups was significantly greater than the baseline leveldo(all)P<0105).chart2 supplementary pen manipulation under different coding conditions313 discussionExperiment 2The inclusion group, the excluded group, and the implicit group are the same in terms of activation, coding requirements, target stimulus, task nature, etc.TheThe instructions are different only when they are extracted. The result showsUnder the condition of non semantic codingDifferent extraction instructions do not affect the phaseSame task operationUnder the condition of semantic assimilationEncoding stage the semantic processing of priming stimuli to enable subsequent pen fillingWhether it's explicit or notImplicit) produced a catalytic effect. The experiment confirmed thatAlthough both of these three experiments have strongdata-driven propertiesBut the guiding languageIn the case of semantic assimilation coding, the extraction of prior plot is better than that of non semantic encodingThat is only the first.When more semantic information is stored in the plotImplicit and explicit instructions may have different effects.Another important result of this study is that,The explicit complement operation of the inclusion group and the implicit supplementary pen operation show a strong additionLevel effectHowever, the effect of processing level was not shown by the pen manipulation. This shows that the subjects obeyed the guidelines in the test1995-2005, Tsinghua, Tongfang, Optical, Disc, Co., Ltd., All, rights, reserved.Psychological ScienceVolume 23Four hundred and sixteenRequirementsThe degree of waking consciousness was greatly reduced during the extraction processOtherwiseThe pens of the excluded group should show the effect of processing levelShould. As a group containing known explicit effects of additional levels of processing manipulation remains easy to understandThe stem, the implicit completion is plusThere may be some ambiguity in the interpretation of horizontal manipulation effects. Jacoby et al(1994a) proposed by [6], is likely to stem the implicit task completion byTo the "extraction" of "pollution", that is, implicit penThe external extraction strategy was adopted unconsciously to complete the current taskInternallyThe invisible pen becomes a certain amount of external makeup. This inference seems to imply such an ideaImplicit tasks are just a matter of the unconsciousProcess of cognitionIf the participants did not take explicit extraction strategyIt will not show the effect of machining level. We thinkImplicit indexThe memory task under the lead is not a pure unconscious processAs far as implicit task requirements are concernedThere is no ban on the subjectsExplicit strategies are not allowedWhether explicit or conscious elements exist in implicit pens does not depend entirely on whether the guiding language is implicit or notExplicitThere is no complete one-to-one correspondence betweenimplicit / explicit and unconscious / conscious division. thereforeAs in earlier episodesWhen the physical information of the stimulus is storedThe function of the guiding language is not obviousThe level of conscious and unintentional impact is relatively smallWhen.In earlier episodes, more semantic information is stored when stimuli are storedWith the increase of consciousness in the guiding languageThe effect of the previous plot on the extraction is alsoIt's getting bigger. The number of semantic components in the previous plot is closely related to the arousal level of the acquisition. Implicit and explicit memoryBoth conscious and unconscious influences can existWhich one is more likely to dominate?.4 general discussionExperimentManipulation of the physical and semantic features of the stimulus during the encoding phaseIt confirms the data driven word determinationMore benefit from processing physical features that stimulate the encoding phaseThe concept driven recognition task is more stimulated from the encoding phaseThe semantic features benefit from processing. In experiment two, the effects of different extraction requirements were further explored on the basis of experiment 1. Show differentThe extraction orientation allows differences in the extraction of previous plotsThere is an interaction between coding requirements and extraction requirements. Emphasis on codingProcessing of non semantic featuresDifferent extraction requirements do not affect the operation of the same memory taskWhile encoding emphasizes semantic feature processing,Increase semantic information in a previous plotDifferent extraction requirements have different effects on the same memory taskThe guiding language is pleasing to the eyeAn increase in knowledge adds more semantic information to the previous plot.5 referencesThe "Stephan B. Hamann.Level2of 2Processing Effects in Conceptually Driven Implicit of Tasks.Journal Experimental Psy2"Chology:Learning, Memory, andCognition, 1990; 16 (6): 9702977The "Jeffrey P. Toth and R. Reed Hunt. Effect of Generation on a Word2Identification Task.Journal of Experimental Psy2"Chology:Learning, Memory, andCognition, 1990; 16 (6): 99321003ThreeFergus, I., M., Craik, Morris, Moscovitch, and, Joan, M.MC Dowd。
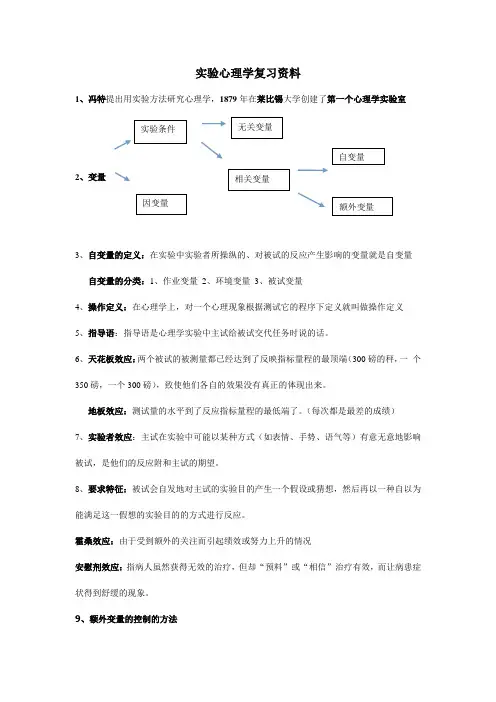
实验心理学复习资料1、冯特提出用实验方法研究心理学,1879年在莱比锡大学创建了第一个心理学实验室2、变量3、自变量的定义:在实验中实验者所操纵的、对被试的反应产生影响的变量就是自变量 自变量的分类:1、作业变量 2、环境变量 3、被试变量4、操作定义:在心理学上,对一个心理现象根据测试它的程序下定义就叫做操作定义5、指导语:指导语是心理学实验中主试给被试交代任务时说的话。
6、天花板效应:两个被试的被测量都已经达到了反映指标量程的最顶端(300磅的秤,一 个 350磅,一个300磅),致使他们各自的效果没有真正的体现出来。
地板效应:测试量的水平到了反应指标量程的最低端了。
(每次都是最差的成绩)7、实验者效应:主试在实验中可能以某种方式(如表情、手势、语气等)有意无意地影响被试,是他们的反应附和主试的期望。
8、要求特征:被试会自发地对主试的实验目的产生一个假设或猜想,然后再以一种自以为能满足这一假想的实验目的的方式进行反应。
霍桑效应:由于受到额外的关注而引起绩效或努力上升的情况安慰剂效应:指病人虽然获得无效的治疗,但却“预料”或“相信”治疗有效,而让病患症状得到舒缓的现象。
9、额外变量的控制的方法 实验条件 因变量 无关变量 相关变量 自变量额外变量1、排除法:把额外变量从实验中排除出去。
如:双盲实验2、恒定法:使额外变量在实验过程中保持恒定不变。
3、匹配法:使实验组和控制组中的被试属性相等的一种办法。
4、随机化法和抵消平衡法:把被试随机地分派到各处理组中去的技术。
5、统计控制法:在实验完成后通过一定的统计技术来事后避免实验中额外变量的干扰。
10、交互作用:自变量之间的相互关系。
当一个自变量产生的效果在第二个自变量的每一个水平上不一样时,交互作用就发生了。
11、P73 例B12、被试间设计:每一种水平接受不同的被试优点:每一个人只接受一种处理方式,而一种处理方式不可能影响或污染另一种处理方式,因此避免了练习效应和疲劳效应等由实验顺序造成的误差.缺点:⑴所需要的被试数量巨大:由于每一个自变量的每一个水平都需要不同的被试,当实验因素增加时,实验所需要的被试数量就会迅速增加.⑵由于接受不同处理的总是不同的个体,因此被试间设计从根本上是不能排除个体差异对实验结果的混淆的,而匹配和随机化技术也只是尽可能地缓解而不是根治这一问题.被试内设计:每一个被试分到每一个水平。


因子分析是一种多变量统计方法,用于了解变量之间的关系和发现隐藏在数据背后的结构。
在因子分析中,变量的筛选和因子的提取是非常重要的步骤。
本文将从变量筛选和因子提取两个方面来探讨因子分析中的方法。
一、变量筛选在进行因子分析之前,需要对变量进行筛选,只有选择合适的变量才能得到有意义的结果。
变量筛选的方法有很多种,常用的有相关性分析、方差分析和因子载荷等。
在相关性分析中,可以通过计算变量之间的相关系数来判断它们之间的相关性,选择相关系数较高的变量作为分析对象。
方差分析则可以用来比较不同组别之间的变量差异,从而选择具有显著差异的变量进行分析。
而因子载荷则是因子分析中的重要参数,它可以反映出变量对特定因子的影响程度,通过观察因子载荷大小来筛选变量。
在变量筛选过程中,需要注意的是要考虑变量的相关性、独立性和可解释性,选择具有代表性和丰富信息的变量进行分析,避免出现冗余和重复的变量。
二、因子提取方法在变量筛选之后,接下来就是因子提取的步骤。
因子提取的目的是将原始变量转化为更少的几个因子,以便于后续的数据分析和解释。
常用的因子提取方法包括主成分分析法、最大似然法和最小残差法等。
主成分分析法是一种常用的因子提取方法,它通过线性变换将原始变量转化为一组新的互相无关的变量,这些新变量即为主成分。
主成分分析法的优势在于能够保留大部分原始变量的信息,对于高维数据的处理效果较好。
最大似然法则是一种参数估计方法,它通过最大化样本数据的似然函数来估计模型参数,从而得到最合适的因子提取结果。
而最小残差法则是一种基于残差平方和的优化方法,通过最小化原始变量与因子之间的残差来提取因子。
在选择因子提取方法时,需要根据具体的数据情况和研究目的来进行选择,不同的方法有着不同的适用范围和假设条件。
因此,在进行因子提取时,需要综合考虑数据的结构、特点和研究需求,选择最适合的方法进行因子提取。
综上所述,因子分析中的变量筛选和因子提取是非常重要的步骤,它们直接影响着最终的分析结果和结论。
什么是实验设计:广义的实验设计指科学研究的一般程序的知识,它包括从问题的提出,假说的形成,变量的选择等一直到结果的分析,论文的写作一系列内容。
狭义的实验设计指实施实验处理的一个计划方案及与计划方案有关的统计分析。
包括:1、建立与研究假设有关的统计假说2、确定实验中使用的实验处理和必须控制的多余条件3、确定实验中需要的被试的数量及被试抽样的总体4、确定将实验条件分配给被试的方法5、确定因变量和使用的统计分析因素:指研究者在实验中感兴趣的一个变量,研究者通过操纵改变它来评估它对因变量的影响,这个变量也叫自变量。
因素水平:指实验中所操纵的变量的每个特定的值,因素水平有的是自然的,有的是人为控制的。
处理与处理水平的结合:都是指实验中一个特定独特的实验条件,对于单因素,一个实验条件为一个实验处理,对于多因素,一个实验条件作为一个实验处理水平的结合。
主效应:指实验中一个因素的不同水平引起的变异,叫因素的主效应。
交互效应:在一个多因素实验中,当一个因素的水平在另一个因素的不同水平上变化趋势不一致时,称两个因素之间存在交互效应。
自变量的控制:1、通过操作定义2、通过规定自变量的不同水平3、校准测量自变量的仪器因变量的控制:1、通过操作定义固定因变量2、良好因变量的标准:a因变量要有客观性b反应指标要准确c因变量数量化d因变量要有有效性无关变量的控制:1、随机化:随机选择被试,随机安排实验处理2、匹配3、消除:使无关变量在实验中消失4、附加自变量5、统计分析心理实验研究的程序:1、问题的提出与假设的建立2、实验中变量的选择和控制3、被试的确定,包括选择与安排4、实验操作5、结果的统计与分析内部效度:指研究的自变量与因变量之间的关系的明确程度,还指实验数据偏离真值的程度或指系统误差的大小。
影响内部效度的因素:1、历史:指在实验过程中,与实验变量同时发生,并对实验结果产生影响的特定事件。
2、成熟或自然发展的影响,指在实验过程中随着时间的延续,被试身心发生变化,如变得较为成熟,变得疲倦,对实验失去兴趣或饥渴等。
广东省佛山市南海区2023-2024学年高三上学期摸底测试生物试题学校:___________姓名:___________班级:___________考号:___________B.根据信息可推测gasdermin基因是一种有效的肿瘤抑制基因C.上述细胞死亡过程中细胞内的mRNA种类并未发生变化D.gasdermin成孔蛋白结构正常时才具备使细胞膜成孔的作用4.科学的研究方法是取得成功的关键,下列关于人类探索遗传奥秘历程中的科学实验方法及技术的叙述,错误的说法是()A.孟德尔运用“假说—演绎法”提出了基因的分离定律和自由组合定律B.摩尔根发现了基因的连锁互换定律,且证明了基因在染色体上呈线性排列C.艾弗里利用自变量控制中的“加法原理”设计了肺炎链球菌的体外转化实验D.沃森和克里克研究DNA分子结构时,运用了建构物理模型的方法5.①~④是在某种因素影响下生物的性状表现。
下列相关分析正确的是()①镰状细胞贫血患者的红细胞呈现镰刀状;②F1圆粒豌豆自交产生的子代出现皱粒;③柳穿鱼花的形态结构与Lcyc基因的表达直接相关;④同一株水毛茛在水中和空气中的叶片表现出两种不同形态。
A.①②中的性状可遗传,③④中的性状不可遗传B.①中的性状是基因通过控制酶的合成来控制代谢而形成的C.②中的皱粒豌豆产生的根本原因是细胞中的淀粉分支酶异常D.发生③④现象的生物体的基因碱基序列并没有发生改变6.研究发现,印度洋中多个丽鱼物种都来源于早期的同一个物种,其形成的原因是不同颜色的雌雄丽鱼专挑与自己颜色相同的丽鱼作为交配对象,形成生殖上相对隔离的族群,而不同的族群以不同生物为食,最终导致新物种的形成。
下列有关说法错误的是()A.不同颜色丽鱼变异产生的根本来源是基因重组B.对比不同丽鱼物种的基因序列,是研究它们进化关系的分子水平证据C.新物种的形成不一定要经过地理隔离,但一定要经过生殖隔离D.上述新物种形成过程中必然存在着种群基因频率的定向改变7.水中毒又称为稀释性低钠血症,指当机体所摄入水总量大大超过了排出水量,导致水分在体内滞留。
高中生物简答题知识点除了知识和学问之外,世上没有其他任何力量能在人们的精神和心灵中,在人的思想、想象、见解和信仰中建立起统治和权威。
下面小编给大家分享一些高中生物简答题知识,希望能够帮助大家,欢迎阅读!高中生物简答题知识1.哺乳动物成熟的红细胞,用来提取较纯净的细胞膜的原因是没有核膜和其他的细胞器膜;其他的动物细胞提取的膜面积大于细胞膜2倍的原因是有细胞核膜和细胞器膜增大了膜面积;不能用其进行DNA 的粗提和鉴定的原因是没有细胞核而无核DNA,难以提取。
哺乳动物成熟的红细胞不能称为原核细胞的原因是红细胞幼小时是具有细胞核与细胞器的,只是后来发育过程中才丢失细胞核,所以仍是真核生物。
2.病毒不能在细胞外独立增殖的原因是缺乏相应的酶系统、原料、能量与特定的结构。
灭活的病毒可用作疫苗的原因是它没有感染性而有抗原性,使机体不患病又能刺激机体产生特异性抗体。
含单链核酸的病毒容易发生突变(或不易制备疫苗)的原因单链的核酸不稳定易发生基因突变。
3.植物细胞可看成一个渗透装置的原因是植物细胞的原生质层相当于半透膜,而细胞内外存在着浓度差。
用一定的硝酸钾溶液能使植物细胞发生质壁分离和复原的原因是硝酸钾溶液的浓度比细胞液的浓度高,使植物细胞失水而发生质壁分离,但当硝酸钾被植物细胞吸收后,使细胞液的浓度升高,细胞又从外界吸水而使质壁分离复原。
夏季晴天,植物光合作用会出现“午休”现象的原因是:由于光照强,植物失水过多,气孔关闭,使CO2固定减少,光合作用效率下降。
4.同一生物体细胞结构和功能不同的原因是由于基因选择性表达,细胞发生了分化,但是其核基因组成相同原因是它们是由同一个受精卵经过有丝分裂产生,遗传物质保持稳定。
5.在动物细胞核移植克隆动物时用卵细胞作受体细胞原因是卵细胞大利于操作,细胞质中有使细胞核基因得以表达的物质和条件。
6.动物激素广泛分布在体液中,但只能作用于特定的靶细胞,原因是只有靶细胞才有与激素发生特异性结合的受体。
中考生物申请科学实验的数据处理与分析数据处理与分析是科学实验的重要环节,对于中考生物实验来说,更是至关重要的一步。
本文将探讨中考生物实验中数据处理与分析的方法和技巧,以帮助学生更好地应对实验环节。
一、收集实验数据中考生物实验通常需要进行数据收集,例如对于种子萌发的实验,我们可以记录每组种子的发芽数目,发芽时间以及根长度等。
为确保数据的准确性,我们可以对每个组别进行重复实验,并记录每次实验的数据。
二、数据整理与清洗在收集到一定量的数据后,我们需要对数据进行整理和清洗。
首先,由于实验中可能出现的误差,我们需要找出异常值并删去。
其次,对于多组数据,可以计算平均值并记录,以减小数据的随机误差。
此外,需要注意在数据整理的过程中保留足够的有效数字,避免舍入误差。
三、绘制数据图表数据图表是数据处理与分析的重要工具,它能够直观地反映数据的分布和趋势。
根据实验的需要,我们可以采用折线图、柱状图、散点图等不同类型的图表来展示数据。
在绘制图表时,要注意选择合适的比例尺和坐标轴,以准确地显示数据。
四、数据分析方法1. 描述性统计分析:通过计算均值、中位数、众数、标准差等指标,可以对数据进行描述性统计分析,揭示数据的中心趋势和变异程度。
2. 相关性分析:通过计算相关系数,可以研究两个变量之间的相关性。
例如,我们可以在实验中探究光照强度和光合作用速率之间的关系。
3. 统计假设检验:根据实验的目的,我们可以制定假设并进行统计假设检验,从而判断实验结果是否具有统计学意义。
例如,我们可以通过方差分析等方法比较不同处理组之间的差异。
五、结果解读与讨论在数据处理与分析的基础上,我们需要对结果进行解读与讨论。
通过对结果的分析,我们可以得到对实验问题的答案或结论,并对实验结果的可靠性进行评价。
此外,还可以对实验中的不确定因素和偏差进行讨论,并提出进一步研究和改进的建议。
六、注意事项1. 数据处理与分析中应遵循科学原则和规范,确保数据的准确性和可信度。