abaqus第五讲ABAQUS中的材料
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:312.50 KB
- 文档页数:22


abaqus铝合金材料参数摘要:1.Abaqus 简介2.铝合金材料概述3.Abaqus 中铝合金材料的参数4.参数对材料性能的影响5.结论正文:1.Abaqus 简介Abaqus 是一款广泛应用于工程领域的有限元分析软件,它可以模拟各种复杂结构的力学行为,为工程师提供可靠的数值模拟结果。
在Abaqus 中,用户可以自定义材料的参数,以满足不同工程需求。
2.铝合金材料概述铝合金材料因其优良的力学性能、良好的耐腐蚀性和较低的重量,在航空航天、汽车、建筑等领域得到广泛应用。
铝合金的主要成分是铝,同时还含有一定比例的铜、镁、锌等元素。
3.Abaqus 中铝合金材料的参数在Abaqus 中,铝合金材料的参数主要包括以下几类:(1) 弹性模量:描述材料刚性的指标,决定了材料在受到外力时的变形程度。
(2) 泊松比:描述材料在受到拉伸时的横向收缩程度,与弹性模量一起决定了材料的应力- 应变关系。
(3) 密度:描述材料单位体积的质量,影响材料的重量和刚度。
(4) 剪切模量:描述材料在受到剪切力时的变形程度,与弹性模量和泊松比一起决定了材料的应力- 应变关系。
(5) 硬度:描述材料抵抗划痕或穿透的能力,通常用布氏硬度或维氏硬度表示。
(6) 粘度:描述材料在高温下的流动性,影响铸造和焊接等加工过程。
4.参数对材料性能的影响(1) 弹性模量和泊松比:这两参数决定了材料的应力- 应变关系,影响材料的强度、刚度和韧性等性能。
(2) 密度:密度影响材料的重量和刚度,通常情况下,密度越大,材料的强度和刚度越高。
(3) 剪切模量:影响材料的剪切强度和韧性。
(4) 硬度:硬度影响材料的耐磨性和抗疲劳性能。
(5) 粘度:粘度影响材料的铸造性能和焊接性能。
5.结论通过对Abaqus 中铝合金材料的参数进行调整,可以实现对材料性能的调控,以满足不同工程应用的需求。

Department of Engineering University of Cambridge > Engineering Department > computing helpABAQUS Materials Input1. 5. ABAQUS - Materials2. Q5.1 : How do I find what material properties are needed for a particular analysis ?Read the relevant section in Chapter 6 : Analysis Procedures (User's manual Vol. I). This gives an overview about the analysis and has more information about the material properties.Read also the following sections in Chapter 17 : Materials Introduction of the ABAQUS User's manual.▪Section 17.1.1 - Material Library : Overview▪Section 17.1.2 - Material Data Definition▪Section 17.1.3 - Combining Material PropertiesSection 17.1.3 lists the material model combination tables. Several models are available to define the mechanical behaviour (elastic, plastic).Some material options require the presence of other material options. Some exclude the use of the other material options. For example *DEFORMATION PLASTICITY completely defines the material's mechanical behaviour and should not be used with *ELASTIC.Once you have all the relevant keywords to define the material properties consult the keyword Manual for each of the keywords. This will explain what data is required for each of the keyword.3. Q5.2 : What material properties need to be specified in a thermal-electrical analysis ?Referring to Section 17.1.3 of the ABAQUS User's manual you will require the heat transfer properties as well as the electrical properties. These are listed below :▪Heat Transfer properties▪*CONDUCTIVITY▪*LATENT HEAT▪*SPECIFIC HEAT▪*HEAT GENERATION▪Electrical properties▪*DIELECTRIC▪*ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY▪*JOULE HEAT FRACTION▪*PIEZOELECTRICThis forms the complete set of properties. If Piezoelectric elements are not used then*PIEZOELECTRIC and *DIELECTRIC properties will not be required.If only the steady state heat transfer response is of interest then *SPECIFIC HEAT properties are not required. Similarly if there are no phase changes involved then *LATENT HEAT is not required.*JOULE HEAT FRACTION is used to specify the fraction of electrical energy that will be released as heat.Example problem 5.2.1 - thermal-electrical modelling of an automotive fuse illustrates the thermal-electrical analysis.ABAQUS allows for redundant material properties to be specified. It will simply ignore the material properties not required for the current analysis.Typical example of material properties :*MATERIAL, NAME=ZINC*CONDUCTIVITY0.1121, 20.00.1103, 100.0*ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY16.75E3, 20.012.92E3, 100.0*JOULE HEAT FRACTION1.0*DENSITY7.14E-6*SPECIFIC HEAT389.04. Q5.3 : What material properties need to be specified in an analysis using temperature- displacement elements ?Referring to Section 17.1.3 of the ABAQUS User's manual you will require the heat transfer properties as well as the mechanical properties. These are listed below :▪Mechanical properties▪*ELASTIC▪Additional properties which may be required : example plastic ▪Heat Transfer properties▪*CONDUCTIVITY▪*LATENT HEAT▪*SPECIFIC HEAT▪*HEAT GENERATION5. Q5.4 : What material properties need to be specified in an analysis using piezoelectric elements?Referring to Section 9.1.3 of the ABAQUS User's manual you will require the electrical properties. These are listed below :▪Electrical properties▪*DIELECTRIC▪*ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY▪*JOULE HEAT FRACTION▪*PIEZOELECTRIC6. Q5.5 : What material properties need to be specified in modeling concrete with reinforcements?Use the concrete model available with rebar to model the reinforcements.Section 1.1.5 of the ABAQUS Example's manual gives an example of the collapse analysis of a concrete slab subjected to a central point load.The data file for that example is collapse example.The complete set of ABAQUS input files can be obtained by using the following command :abaqus fetch j=collapseconcslab**CONCRETE3000., 0. abs. value of compressive stress, abs. value of plastic strain. 5500., 0.0015 " "*FAILURE RATIOS1.16, 0.0836This is used to define the shape of the failure surface (see section 11.5.1 of the ABAQUSUSER's manual Vol. II).The first parameter is the ratio of the ultimate biaxial compression stress, to the uniaxial compressive stress. Default is 1.16.The second parameter is the absolute value of the ratio of uniaxial tensile stress at failure to the uniaxial compressive stress at failure. Default is 0.09.7. Tension Stiffening*TENSION STIFFENING1., 0.0., 2.E-3First parameter is the fraction of remaining stress to stress at cracking. The second parameter is the absolute value of the direct strain minus the direct strain at cracking.This defines the retained tensile stress normal to the crack as a function of the deformation in the direction of the normal to the crack.8. Shear Retention*SHEAR RETENTIONNot used for this example.9. Reinforcement modelling*REBAR is used to model the reinforcement.*REBAR,ELEMENT=SHELL,MATERIAL=SLABMT,GEOMETRY=ISOPARAMETRIC,NAME=YYSLAB, 0.014875, 1., -0.435, 4*REBAR,ELEMENT=SHELL,MATERIAL=SLABMT,GEOMETRY=ISOPARAMETRIC,NAME=XXSLAB, 0.014875, 1., -0.435, 1Here SLAB is the element name or name of the element set that contains these rebars. The geometry is ISOPARAMETRIC. Other choice is SKEW. ELEMENT can be BEAM, SHELL, AXISHELL or CONTINUUM type. The following are the other parameters specified :▪cross-sectional area of the rebar.▪spacing of the rebars in the plane of the shell▪position of the rebar. Distance from the reference surface. Here the mid-surface is the reference surface and the minus sign indicates that the distance is measured in theopposite direction to the direction of positive normal. The positive normal is defined by the right hand rule as the nodes are considered in an anti-clockwise sequence.▪edge number to which rebars are similar.10. Alternate Method o modelling REBAR ReinforcementsAlternatively REBAR can be modelled as follows :*NODE........**-------------------END NODES FOR REBAR BEAM ELEMENTS501, 0.0, 0.15, -0.02541, 1.5, 0.15, -0.02601, 0.0, 0.15, -0.07641, 1.5, 0.15, -0.07701, 0.0, 0.60, -0.02741, 1.5, 0.60, -0.02801, 0.0, 0.60, -0.07841, 1.5, 0.60, -0.07........**---------------------GENERATE INTERMEDIATE NODES*NGEN, NSET=BAR10TF701, 741, 2*NGEN, NSET=BAR10TB801, 841, 2......**--------------------GENERATE THE BEAM ELEMENTS*ELEMENT, TYPE=B31701, 701, 703801, 801, 803*ELGEN, ELSET=BAR10TF701, 20, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1*ELGEN, ELSET=BAR10TB801, 20, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1......**---------------------DEFINE THE MATERIAL PROPERTIES*MATERIAL, NAME=BAR8**** 8 mm dia bar***ELASTIC, TYPE=ISO197.E6, 0.3*PLASTIC354.E3, 0.364.E3, 0.0018****---------------------DEFINE THE SECTION PROPERTIES......*BEAM SECTION, SECTION=CIRC, MATERIAL=BAR10, ELSET=BAR10TF0.005*BEAM SECTION, SECTION=CIRC, MATERIAL=BAR10, ELSET=BAR10TB0.005...**--------------------DEFINE AN ELEMENT SET WHICH CONTAINS**--------------------THE ELEMENTS THROUGH WHICH THE REBAR**--------------------ELEMENTS PASSES.....*ELSET, ELSET=TOP, GENERATE5, 80, 5****--------------------*EMBEDDED ELEMENT,HOST ELSET=TOPBAR10TF,BAR10TB**11. Q5.6 : What material properties need to be specified in using the deformation plasticity model ?See section 11.2.11 of the users' manual (Vol. II). See also section 23.4.7 of the users' manual (Vol. III), keyword section.For example :*DEFORMATION PLASTICITY1.E3, 0.3,2., 3, 0.396Here the data line contains the Young's modulus, Poissons ratio, Yield stress, Exponent, Yield offset respectively. If it is necessary to define the dependence of these parameters on temperature then the 6th parameter will be the temperature. Then repeat the dataline for different temperatures as required.| Computing Help |[Finite Elements] | [Engineering Packages]© Cambridge University Engineering DeptInformation provided by Arul M Britto (amb2)Last updated: 28 September 2010。
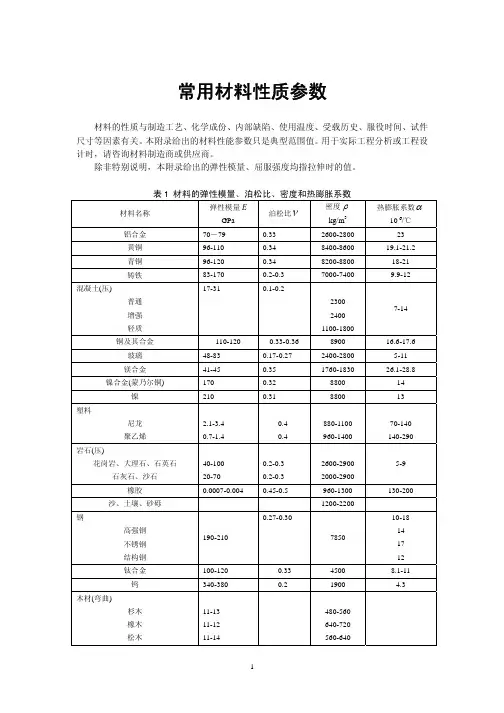
常用材料性质参数材料的性质与制造工艺、化学成份、内部缺陷、使用温度、受载历史、服役时间、试件尺寸等因素有关。
本附录给出的材料性能参数只是典型范围值。
用于实际工程分析或工程设计时,请咨询材料制造商或供应商。
除非特别说明,本附录给出的弹性模量、屈服强度均指拉伸时的值。
表1 材料的弹性模量、泊松比、密度和热膨胀系数材料名称弹性模量EGPa泊松比ν密度ρkg/m3热膨胀系数α10-6/℃铝合金 70-79 0.33 2600-2800 23 黄铜96-110 0.34 8400-8600 19.1-21.2 青铜96-120 0.34 8200-8800 18-21 铸铁83-170 0.2-0.3 7000-7400 9.9-12混凝土(压)普通增强轻质17-31 0.1-0.2230024001100-18007-14铜及其合金110-120 0.33-0.36 8900 16.6-17.6 玻璃48-83 0.17-0.272400-2800 5-11 镁合金41-45 0.35 1760-183026.1-28.8镍合金(蒙乃尔铜) 170 0.32 8800 14 镍210 0.31 8800 13 塑料尼龙聚乙烯2.1-3.40.7-1.40.40.4880-1100960-140070-140140-290岩石(压)花岗岩、大理石、石英石石灰石、沙石40-10020-700.2-0.30.2-0.32600-29002000-29005-9橡胶0.0007-0.004 0.45-0.5 960-1300 130-200 沙、土壤、砂砾1200-2200 钢高强钢不锈钢结构钢190-2100.27-0.30785010-18141712钛合金100-120 0.334500 8.1-11 钨340-380 0.2 1900 4.3 木材(弯曲)杉木橡木松木11-1311-1211-14480-560640-720560-640表2 材料的力学性能材料名称/牌号屈服强度sσMPa抗拉强度bσMPa伸长率5δ%备注铝合金LY12 35-500274100-5504121-4519 硬铝黄铜70-550 200-620 4-60 青铜82-690 200-830 5-60铸铁(拉伸) HT150HT250 120-290 69-4801502500-1铸铁(压缩) 340-1400混凝土(压缩) 10-70铜及其合金55-760 230-830 4-50玻璃平板玻璃玻璃纤维30-1000707000-20000镁合金80-280 140-340 2-20 镍合金(蒙乃尔铜) 170-1100 450-1200 2-50 镍100-620 310-760 2-50 塑料尼龙聚乙烯40-807-2820-10015-300岩石(压缩)花岗岩、大理石、石英石石灰石、沙石50-280 20-200橡胶1-7 7-20 100-800 普通碳素钢Q215 Q235 Q255 Q275 215235255275335~450375~500410~550490~63026~3121~2619~2415~20旧牌号A2旧牌号A3旧牌号A4旧牌号A5优质碳素钢25 35 45 55 2753153553804505306006452320161325号钢35号钢45号钢55号钢低合金钢15MnV 16Mn 390345530510182115锰钒16锰合金钢20Cr 40Cr 54078583598010920铬40铬30CrMnSi 88510801030铬锰硅铸钢ZG200-400 ZG270-500 2002704005002518钢线280-1000 550-1400 5-40钛合金760-1000 900-1200 10 钨 1400-40000-4 木材(弯曲)杉木橡木松木30-5030-4030-5040-7030-5040-70。

abaqus铝合金材料参数【原创实用版】目录1.Abaqus 铝合金材料概述2.Abaqus 铝合金材料参数说明3.Abaqus 铝合金材料参数应用实例正文一、Abaqus 铝合金材料概述Abaqus 是一款广泛应用于工程领域的有限元分析软件,其强大的功能和便捷的操作赢得了许多工程师的青睐。
在 Abaqus 中,铝合金材料是一种常见的金属材料,具有良好的机械性能和耐腐蚀性能,广泛应用于航空航天、汽车制造等领域。
二、Abaqus 铝合金材料参数说明Abaqus 中铝合金材料的参数主要包括以下几类:1.材料属性:包括弹性模量、泊松比、密度等,这些参数决定了铝合金材料的基本力学性能。
2.应力 - 应变曲线:描述了铝合金材料在拉伸过程中的应力 - 应变关系,可以帮助工程师了解材料的变形能力和破坏强度。
3.硬化模型:Abaqus 提供了多种硬化模型,如线性硬化模型、非线性硬化模型等,用于描述铝合金材料在变形过程中的硬化行为。
4.失效准则:包括屈服准则、断裂准则等,用于判断铝合金材料在受力过程中是否会发生失效。
三、Abaqus 铝合金材料参数应用实例假设我们要分析一个由铝合金制成的飞机机翼结构,在 Abaqus 中,我们可以按照以下步骤设置铝合金材料参数:1.创建一个新的材料卡片,输入铝合金材料的弹性模量、泊松比、密度等基本属性。
2.创建一个应力 - 应变曲线,输入拉伸过程中的应力 - 应变数据。
3.选择合适的硬化模型,并根据实际需求调整模型参数。
4.设置失效准则,如选择屈服强度和断裂强度等。
完成以上设置后,我们就可以使用该铝合金材料参数对飞机机翼结构进行有限元分析,从而得到结构在不同受力条件下的应力、应变和变形情况,为结构设计提供参考依据。

Department of EngineeringUniversity of Cambridge? ? Engineering Department? ? computing helpABAQUS Materials Input5. ABAQUS - MaterialsQ5.1 : How do I find what material properties are needed for a particular analysis ?Read the relevant section in Chapter 6 : Analysis Procedures User's manual Vol. I . This gives an overview about the analysis and has more information about the material properties.Read also the following sections in Chapter 17 : Materials Introduction of the ABAQUS User's manual.Section - Material Library : OverviewSection - Material Data DefinitionSection - Combining Material PropertiesSection lists the material model combination tables. Several models are available to define the mechanical behaviour elastic, plastic .Some material options require the presence of other material options. Some exclude the use of the other material options. For example *DEFORMATION PLASTICITY completely defines the material's mechanicalbehaviour and should not be used with *ELASTIC.Once you have all the relevant keywords to define the material properties consult the keyword Manual for each of the keywords. This will explain what data is required for each of the keyword.Q5.2 : What material properties need to be specified in a thermal-electrical analysis ?Referring to Section of the ABAQUS User's manual you will require the heat transfer properties as well as the electrical properties. These are listed below :Heat Transfer properties*CONDUCTIVITY*LATENT HEAT*SPECIFIC HEAT*HEAT GENERATIONElectrical properties*DIELECTRIC*ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY*JOULE HEAT FRACTION*PIEZOELECTRICThis forms the complete set of properties. If Piezoelectric elements are not used then *PIEZOELECTRIC and *DIELECTRIC properties will not be required.If only the steady state heat transfer response is of interest then *SPECIFIC HEAT properties are not required. Similarly if there are no phase changes involved then *LATENT HEAT is not required.*JOULE HEAT FRACTION is used to specify the fraction of electrical energy that will be released as heat.Example problem - thermal-electrical modelling of an automotive fuse illustrates the thermal-electrical analysis.ABAQUS allows for redundant material properties to be specified. It will simply ignore the material properties not required for the current analysis.Typical example of material properties :*MATERIAL, NAME ZINC*CONDUCTIVITY0.1121, 20.00.1103, 100.0*ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY16.75E3, 20.012.92E3, 100.0*JOULE HEAT FRACTION1.0*DENSITY7.14E-6*SPECIFIC HEAT389.0Q5.3 : What material properties need to be specified in an analysis using temperature- displacement elements ?Referring to Section of the ABAQUS User's manual you will require the heat transfer properties as well as the mechanical properties. These are listed below :Mechanical properties*ELASTICAdditional properties which may be required : example plasticHeat Transfer properties*CONDUCTIVITY*LATENT HEAT*SPECIFIC HEAT*HEAT GENERATIONQ5.4 : What material properties need to be specified in an analysis using piezoelectric elements?Referring to Section of the ABAQUS User's manual you will require the electrical properties. These are listed below :Electrical properties*DIELECTRIC*ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY*JOULE HEAT FRACTION*PIEZOELECTRICQ5.5 : What material properties need to be specified in modeling concrete with reinforcements?Use the concrete model available with rebar to model the reinforcements.Section of the ABAQUS Example's manual gives an example of the collapse analysis of a concrete slab subjected to a central point load.The data file for that example is collapse example.The complete set of ABAQUS input files can be obtained by using the following command :abaqus fetch j collapseconcslab**CONCRETE3000., 0. abs. value of compressive stress, abs. value of plastic strain.5500., 0.0015 " "*FAILURE RATIOS1.16, 0.0836This is used to define the shape of the failure surface see section of the ABAQUS USER's manual Vol. II .The first parameter is the ratio of the ultimate biaxial compression stress, to the uniaxial compressive stress. Default is 1.16.The second parameter is the absolute value of the ratio of uniaxial tensile stress at failure to the uniaxial compressive stress at failure. Default is 0.09.Tension Stiffening*TENSION STIFFENING1., 0.0., 2.E-3First parameter is the fraction of remaining stress to stress at cracking. The second parameter is the absolute value of the direct strain minus the direct strain at cracking.This defines the retained tensile stress normal to the crack as a function of the deformation in the direction of the normal to the crack.Shear Retention*SHEAR RETENTIONNot used for this example.Reinforcement modelling*REBAR is used to model the reinforcement.*REBAR,ELEMENT SHELL,MATERIAL SLABMT,GEOMETRY ISOPARAMETRIC,NAME YY SLAB, 0.014875, 1., -0.435, 4*REBAR,ELEMENT SHELL,MATERIAL SLABMT,GEOMETRY ISOPARAMETRIC,NAME XX SLAB, 0.014875, 1., -0.435, 1Here SLAB is the element name or name of the element set that containsthese rebars. The geometry is ISOPARAMETRIC. Other choice is SKEW. ELEMENT can be BEAM, SHELL, AXISHELL or CONTINUUM type. The following are the other parameters specified :cross-sectional area of the rebar.spacing of the rebars in the plane of the shellposition of the rebar. Distance from the reference surface. Here the mid-surface is the reference surface and the minus sign indicates that the distance is measured in the opposite direction to the direction of positive normal. The positive normal is defined by the right hand rule as the nodes are considered in an anti-clockwise sequence.edge number to which rebars are similar.Alternate Method o modelling REBAR ReinforcementsAlternatively REBAR can be modelled as follows :*NODE........**501, 0.0, 0.15, -0.02541, 1.5, 0.15, -0.02601, 0.0, 0.15, -0.07641, 1.5, 0.15, -0.07701, 0.0, 0.60, -0.02741, 1.5, 0.60, -0.02 801, 0.0, 0.60, -0.07 841, 1.5, 0.60, -0.07 ........***NGEN, NSET BAR10TF701, 741, 2*NGEN, NSET BAR10TB801, 841, 2......***ELEMENT, TYPE B31701, 701, 703801, 801, 803*ELGEN, ELSET BAR10TF701, 20, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1*ELGEN, ELSET BAR10TB801, 20, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1......*MATERIAL, NAME BAR8**** 8 mm dia bar***ELASTIC, TYPE ISO197.E6, 0.3*PLASTIC354.E3, 0.364.E3, 0.0018****......*BEAM SECTION, SECTION CIRC, MATERIAL BAR10, ELSET BAR10TF 0.005*BEAM SECTION, SECTION CIRC, MATERIAL BAR10, ELSET BAR10TB 0.005...*******ELSET, ELSET TOP, GENERATE5, 80, 5*****EMBEDDED ELEMENT,HOST ELSET TOPBAR10TF,BAR10TB**Q5.6 : What material properties need to be specified in using the deformation plasticity model ?See section of the users' manual Vol. II . See also section of the users' manual Vol. III , keyword section.For example :*DEFORMATION PLASTICITY1.E3, 0.3,2., 3, 0.396Here the data line contains the Young's modulus, Poissons ratio, Yield stress, Exponent, Yield offset respectively. If it is necessary to define the dependence of these parameters on temperature then the 6th parameter will be the temperature. Then repeat the dataline for different temperatures as required.| Computing Help |[Finite Elements] | [Engineering Packages]Cambridge University Engineering DeptInformation provided by Arul M Britto amb2 Last updated: 28 September 2010。


ABAQUS学习笔记一.AQUS-.inp编码介绍(一).ABAQUS头信息文件段(1-4)1.*PREPRINT 输出求解过程所要求的信息(在dat文件中)ie:*PREPRINT, ECHO=YES, HISTORY=YES, MODEL=YES2.*HEADING 标题输出文件(出现在POST/VIEW窗口中,且出现在结果输出文件中)ie:*HEADINGSTRESS ANALYSIS FOR A PLATE WITH A HOLE3.*RESTART 要求abaqus/standard输出其POST/view模块所需要的.res文件。
其中的FREQ=?控制结果在每次迭代(或载荷步)输出的次数。
ie:*RESTART, WRITE, FREQ=14.*FILE FORMAT 要求abaqus/standard输出到.fil中的某些信息。
它也用于post。
对于在后处理中得到x-y形式的诸如应力-时间、应力-应变图有用!ie: *FILE FORMAT, ZERO INCREMENT(二).ABAQUS网格生成段定义结点、单元,常用的命令有:结点定义(*NODE,*NGEN),单元定义(*ELEMENT,*ELGEN等)。
1.*NODE 定义结点,其格式为:*NODE结点号,x轴坐标,y轴坐标,(z轴坐标)2.*NGEN 在已有结点的基础上进行多个结点的生成,一般是在两结点间以某种方式(直线、圆)产生一定分布规律的结点。
如:*NGEN, LINE=C, NSET=HOLE,119, 1919, 100, 101 在两结点(结点号为119,1919)间以圆弧形式生成多个结点,100为任意相邻结点的单元号增量,101为圆弧形成时圆心位置的结点(对于直线形式生成没有此结点)。
所有这些生成的结点(包括119,1919)被命名成HOLE的集合(这样做的目的是以后的命令中使用到它,比如说对这些结点施加同等条件的边界条件或载荷等,HOLE就是这些结点的代称)。



Abaqus实例教程——材质特性处理Workshop 5材質與剖⾯特性(補充之物理特性): 幫浦模型Introduction(前⾔)在這個練習中你將會使⽤到 ABAQUS/CAE 中的Property 模組來為幫浦組裝中的組件定義材質資料跟剖⾯特性(補充之物理特性)(section properties). 其中的襯墊將會使⽤襯墊的材質特性. 其餘的組件(幫浦外殼, 底蓋, 跟螺絲)則是假設為使⽤鋼材. Defining a linear elastic material and solid section properties(定w5-define and assign 義⼀個線彈性材質資料以及實體的剖⾯特性)遵照以下的說明完成鋼材的材質定義與剖⾯特性定義並將之指定給幫浦的相對應組件. 注意本模型中使⽤的單位是英制的in, lb, 跟 psi.1.從幫浦組裝模型所在的⽬錄中開啟⼀個新的 ABAQUS/CAE 執⾏程序.2.在Start Session 的對話框中選⽤Open Database開啟Pump.cae.3.在其模型樹中的Materials上快點兩下, 可以在pump_ribs模型中產⽣出⼀個新的材質資料.ABAQUS/CAE也會⾃動切換到Property 模組, 同時材質資料編輯器會彈出來.4.定義⼀個線彈性材質資料叫做Steel. 指定楊⽒係數(Young’s modulus)為30.E6psi 以及浦松⽐(Poisson’s ratio)為0.3.5.在其模型樹中的Sections上快點兩下, 產⽣⼀個新的均質,實體的剖⾯特性; 將此剖⾯特性命名為steelSection,它會使⽤剛才定義好的材質資料Steel.6.在模型樹中, 將零件 PUMP-1展開並點選其上的Section Assignments來將這個steelSection的剖⾯特性指定給整個幫浦外殼.7.同樣的, 指定steelSection的剖⾯特性給bolt 跟 cover組件.Defining the gasket material and section properties(定義襯墊材質資料及剖⾯特性)在 ABAQUS 中傳統的襯墊材質特性給定⽅法是利⽤⼀個襯墊受壓與其厚度⽅向上的厚度值之列表來表⽰.在 ABAQUS 中所使⽤的襯墊受壓與厚度值之關係這樣的襯墊材質特性建構⽅法可以模擬很複雜的襯墊⾏為, 包括⾮線性彈性⾏為, 永久塑性變形, 以及不同路徑之負載施加與負載解除. 這些⾏為資料通常是透過實驗來測定的.對於襯墊材質的⾏為特性之細節討論, 已經超越了這個課程的範圍. 為了你的便利(以及使這個分析更逼真) 該襯墊的特性已經以⼀個命令檔(script)將之定義好了, 你可以直接將之讀進ABAQUS/CAE 裡.1.從上⽅的下拉式功能表中, 選⽤File→Run Script 功能指令.然後Run Script對話框會出現.2.選⽤gasket_material.py(這是⼀個python檔案). 按下對話框中的OK按鈕.3.在模型樹中, 將pump_ribs模型中的Materials容器展開.注意其中Gasket材質資料已經被加⼊到模型資料庫中了.4.在這個Gasket材質資料上快點兩下進⼊Gasket材質資料的編輯器.5.查看⼀下這個襯墊的材質資料特性. 注意這個襯墊的材質資料特性中有薄膜彈性係數 12155 psi, 剪⼒勁度 6435 psi, 還有熱膨脹係數 1.67 E?5 /°F.6.從對話框中可⽤的Material Options列表中選取Gasket Thickness Behavior,注意襯墊的負載施加與負載解除曲線的表格中的內容(參閱圖 W5–1).Figure W5–1 Edit Material dialog box.你可以使⽤ ABAQUS/CAE 中的畫圖功能來畫出這⼀條負載施加與負載解除曲線. 這可能有助於幫助你了解這個材質的⾏為.7.打開其中的Loading標籤⾴. 在這個表格的欄位的上⽅標題欄位處按⼀下滑⿏右鍵, 然後從彈出來的選項列表中選取Create XY Data選項. 當Create XY Data對話框中提⽰你給予名字時為他取名loading.重複相同的動作再為負載解除製做⼀條曲線並為之取名unloading.8.按⼀下Cancel按鈕關閉Edit Material對話框不需要做任何變動.9.從⼯具列之下的Module列表中, 選⽤Visualization以進⼊該模組中⼯作.10.從上⽅的下拉式功能表中, 選⽤Tools→XY Data→Manager 功能指令.然後XY Data Manager視窗會出現.11.在其列出的列表中選取該兩條曲線 (使⽤shift 鍵), 然後按⼀下Plot按鈕. 你會看到在圖形區會畫出與下圖 W5–2 類似的曲線.Figure W5–2 Loading and unloading gasket behavior.12.按⼀下Dismiss按鈕結束掉此XY Data Manager視窗.13.在模型樹中的Sections上快點兩下快速的回到物理特性(Property)模組然後製作⼀個襯墊剖⾯特性.14.在Create Section對話框中, 選⽤Other種類Gasket類別. 將此剖⾯特性取名gasketSection (參考圖 W5–3) 然後按下Continue.Figure W5–3 Create Section and Edit Section dialog boxes. 15. 在 Edit Section 對話框中(看圖 W5–3), 選取 Gasket 材質資料其餘的選項都使⽤預設值就好.16. 將這個剖⾯特性 gasketSection 指定給 gasket 組件.17. 將整個模型資料存檔為 Pump.cae .。
Abaqus铝合金材料参数1.引言本文档提供了关于Ab a qu s铝合金材料参数的详细介绍和使用指南。
A b aq us是一款强大的有限元分析软件,广泛应用于工程和科学领域。
了解铝合金材料参数对于在Ab aq us中进行材料模拟和分析非常重要。
2.铝合金材料参数的定义在A ba qu s中,铝合金材料参数是用来描述材料力学性质和行为的关键因素。
以下是一些常见的铝合金材料参数:-弹性模量(Yo un g's M od ul us):材料受力时的变形能力。
-屈服强度(Yi el dS t re ng th):材料开始产生塑性变形的应力水平。
-屈服后硬化斜率(H a rd en in gS lo pe):材料在屈服点之后逐渐增加硬度的程度。
-破断延伸率(F ra ct u re St ra in):材料在破断前的变形能力。
-破断应力(Fr ac tur e St re ss):材料发生破断时所受的最大应力。
3.如何使用Abaqu s进行铝合金材料参数设置以下是使用A ba qu s进行铝合金材料参数设置的步骤:3.1创建材料首先,在Ab aq us中创建一个新的材料,或者选择现有的材料。
在材料属性对话框中,可以设置并定义材料的力学性质和行为。
3.2设置材料参数在材料属性对话框的参数选项卡中,可以设置铝合金的弹性模量、屈服强度、屈服后硬化斜率、破断延伸率和破断应力等参数。
根据实际需求和材料测试结果,输入相应数值。
3.3材料模型选择根据需要选择适当的材料模型,常见的选择包括线性弹性模型、塑性模型和强化模型等。
选择合适的模型对于准确描述铝合金材料的力学性质非常重要。
4.温度对铝合金材料参数的影响温度是一个重要的因素,可以显著影响铝合金材料的力学性质。
以下是一些常见的温度相关参数:-热膨胀系数(C oe ff i ci en to fT he rm alE x pa ns io n):材料随温度变化而产生的长度变化。
Abaqus复合材料建模材料参数一、引言本文档旨在介绍如何在A ba qu s中建立复合材料模型以及相应的材料参数设置。
复合材料是由两种或两种以上不同性质的材料按一定的方式组合而成,具有轻质、高强度、高模量等特点,在航空航天、汽车工程等领域得到广泛应用。
二、复合材料建模方法1.宏观模型在A ba qu s中,建立复合材料模型的一种常用方法是使用宏观模型。
该方法将复合材料视为等效各向同性材料,通过指定等效材料的弹性常数和热膨胀系数来描述其宏观性能。
2.细观模型对于复材的更精细模拟,可以采用细观模型。
细观模型考虑了材料内部的细观数值,常用的方法包括单元层模型和单元纤维模型。
三、复合材料模型参数设置1.宏观模型参数设置宏观模型中的材料参数包括弹性常数和热膨胀系数。
弹性常数包括Y o un g'sM od ul us(杨氏模量)、Sh ea rM o du lu s(剪切模量)和P o is so n'sR at io(泊松比)。
热膨胀系数描述了材料在温度变化时的尺寸变化情况。
2.细观模型参数设置在细观模型中,除了上述宏观模型参数外,还需要设置与材料内部细观数值相关的参数。
例如,单元层模型需要设定层间剪切刚度和层内剪切刚度,单元纤维模型需要设置纤维体积分数、纤维方向和纤维间隔等。
四、复合材料模型示例下面通过一个简单的示例来说明复合材料模型的建立和参数设置过程。
1.示例问题描述考虑一个平面应力状态下的复合材料层合板,包含两层材料:上层为碳纤维复合材料,下层为环氧树脂基复合材料。
2.宏观模型参数设置示例对于这个示例,我们可以使用宏观模型来建立模型。
假设上层和下层材料的弹性常数已知,分别为:上层材料:-Y ou ng's Mo du lu s:200G Pa-S he ar Mo du lu s:80G P a-P oi ss on's Ra ti o:0.2下层材料:-Y ou ng's Mo du lu s:50GP a-S he ar Mo du lu s:20G P a-P oi ss on's Ra ti o:0.3同时,我们需要给定材料的热膨胀系数,用于考虑温度变化对材料性能的影响。
abaqus材料库Abaqus材料库。
Abaqus是一款广泛应用于工程领域的有限元分析软件,它的材料库是其中一个非常重要的组成部分。
材料库中包含了各种不同类型的材料模型,用户可以根据实际工程需求选择合适的材料模型进行分析和仿真。
本文将对Abaqus材料库进行介绍,并对其中一些常用的材料模型进行简要说明。
Abaqus材料库主要包括金属材料、塑料材料、复合材料、土壤材料等多种类型的材料模型。
在进行有限元分析时,选择合适的材料模型对于结果的准确性和可靠性至关重要。
因此,了解Abaqus材料库中各种材料模型的特点和适用范围是非常必要的。
金属材料是工程中应用最广泛的一类材料,Abaqus材料库中包含了多种金属材料模型,如弹性模型、塑性模型、强化模型等。
用户可以根据金属材料的实际力学性能选择合适的材料模型进行分析。
塑料材料是另一类在工程中应用广泛的材料,Abaqus材料库中也包含了多种塑料材料模型,如线性弹性模型、非线性弹性模型、本构模型等。
复合材料是由两种或两种以上的材料组合而成的材料,Abaqus材料库中也包含了多种复合材料模型,如层合板模型、细观模型、宏观模型等。
土壤材料是在土木工程中应用广泛的一类材料,Abaqus材料库中也包含了多种土壤材料模型,如弹性模型、塑性模型、本构模型等。
在使用Abaqus进行有限元分析时,用户可以根据实际工程需求选择合适的材料模型,并进行相应的参数设置。
在选择材料模型时,需要考虑材料的力学性能、温度效应、应变速率效应等因素,以确保分析结果的准确性和可靠性。
此外,用户还可以根据实际工程需求自定义材料模型,以满足特定的分析要求。
总之,Abaqus材料库是Abaqus软件中一个非常重要的组成部分,其中包含了多种类型的材料模型,用户可以根据实际工程需求选择合适的材料模型进行分析。
了解Abaqus材料库中各种材料模型的特点和适用范围,对于进行准确、可靠的有限元分析是非常必要的。
希望本文对Abaqus材料库有所帮助,谢谢阅读。
Abaqus中的复合材料分析Abaqus提供了不同方式对复合结构进行建模的功能。
根据被建模的复合材料的类型,可用的材料数据,边界条件以及期望的结果,某种特定方法可能比其他方法更好。
什么是复合结构?复合材料是嵌入基质材料内的增强材料的宏观混合物。
复合结构由复合材料制成,并且可以具有许多形式,如单向纤维复合材料,织物或蜂窝结构。
Abaqus使用几种不同的方法来模拟复合结构1)微观:在这种方法中,基体和增强材料被建模为单独的可变形连续体2)宏观:在这种方法中,基体和增强材料被建模为整体可变形连续体。
当单个纤维的微观行为及其与基体的相互作用不太重要的时,可以使用这种方法。
3)混合建模:在该方法中,复合结构被建模为单一正交各向异性(或各向异性)材料。
当结构的整体行为比微观层面的行为更重要时,这一点很重要。
单个材料定义(通常是各向异性的)足以预测全局行为。
复合材料层压板的分析:复合层压材料由多层制成。
每层具有独自的厚度,并且每层中的增强纤维以不同方式对齐。
布置层以形成层压板的顺序称为叠层或堆叠顺序。
在Abaqus中对此进行建模的最简单方法是使用混合建模方法。
这将包括为每个层定义正交各向异性,厚度,纤维取向和堆叠顺序,这反过来又决定其结构行为。
通常,层压性能直接从实验或其他应用中获得。
这些性质可以是A,B,D基质的形式,其定义了层压材料的刚度。
在这种情况下,宏观方法可用于层压板的结构分析。
这种方法在本质上可以被认为是宏观的,因为在Abaqus部分定义中导出并使用等效的截面属性。
还可以认为它是一种混合建模方法,因为截面刚度是基于层板铺设得出的。
下面的示例显示了A,B,D矩阵是如何从可用的上层信息中派生出来的,并在Abaqus的General Shell Section定义中使用。
经典层压理论的假设:这里显示的层压复合材料的宏观建模方法基于经典层压理论(CLT)。
为了准确实现CLT,假设需要满足:·通过层压材料的厚度的位移分量是连续的,并且在层压材料的相邻层之间没有滑动。
一、混凝土-土摩擦系数
二、钢材
弹性模量的符号为E,单位为GPa,钢材的弹性模量约为210GPa,
密度
工业应用:
灰口铸铁: 6.6~7.4g/cm^3;
白口铸铁:7.4~7.7g/cm^3;
铸钢:7.8g/cm^3;
工业纯铁:7.87g/cm^3;
普通碳素钢:7.85g/cm^3;
优质碳素钢:7.85g/cm^3
二、混凝土
混凝土结构设计规范GB50010-2002第4.1.5条。
C30混凝土受压和受拉时的弹性模量为:3.00X(10)^4 N/mm2,即30KN/mm2.
普通混凝土的密度是25kN/m3,也就是2500kg/m3
这要从混凝土的分类说起
重混凝土密度大于2800千克每立方米
普通混凝土2000到2800千克每立方米
轻质混凝土密度小于1950千克每立方米
一般工程中设计混凝土在2350到2450之间可以取2400
三、桩负摩阻力系数
四、粗砂
密实的粗砂压缩模量一般11-13mpa。
其弹性模量应更大。
五、桩土摩擦系数
一般在土体摩擦角比较小的时候,可以用经验公式tan(0.6~0.75摩擦角),在摩擦角比较小的时候,计算摩擦系数误差不大,但是土体摩擦角比较大,用此公式,计算摩擦系数误差会比较。
六、侧压力系数
一般来说K=1-sina 粘土 K=0.95-sina 砂土
也可以K=u/1-u u为泊松比。
Material Name and Condition. Density Yng's Poisslb/in^3 Modul Ratio Strs S msi ksi k acrylic lucite 0.0430 0.43 0.400 6.0 1 aluminum pure 99.996 annealed 0.0970 10.00 0.330 1.8 aluminum pure 99.45-o condition 0.0980 10.00 0.330 4.0 1 aluminum pure-h12 sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 12.0 1 aluminum pure-h16 sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 16.0 1 aluminum 1060-o sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 4.0 1 aluminum 1060-h12 sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 11.0 1 aluminum 1060-h18 sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 18.0 1 aluminum 1100-o sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 5.0 1 aluminum 1100-h14 sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 17.0 1 aluminum 1100-h18 sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 26.0 2 aluminum 2011-t3 bar 0.1020 10.20 0.330 43.0 5 aluminum 2011-t8 bar 0.1020 10.20 0.330 45.0 5 aluminum 2014-o bar 0.1010 10.60 0.330 14.0 2 aluminum 2014-t6 sheet 0.1010 10.60 0.330 68.0 7 aluminum 2014-t651 0.1010 10.60 0.330 63.5 6 aluminum 2017-o bar 0.1010 10.50 0.330 10.0 2 aluminum 2017-t4 bar 0.1010 10.50 0.330 40.0 6 aluminum 2021-o sheet 0.1030 10.70 0.330 10.0 2 aluminum 2021-t31 sheet 0.1030 10.70 0.330 40.0 6 aluminum 2021-t81 plate 0.1030 10.70 0.330 63.0 7 aluminum 2021-t8151 0.1030 10.70 0.330 66.6 7 aluminum 2024-o sheet 0.1000 10.60 0.330 11.0 2 aluminum 2024-t3 sheet 0.1000 10.60 0.330 51.0 6 aluminum 2024-t4 sheet 0.1000 10.60 0.330 47.0 6 aluminum 2024-t851 plate 0.1000 10.60 0.330 68.0 7 aluminum 2025-t6 plate 0.1010 10.40 0.330 37.0 5 aluminum 2219-o sheet 0.1020 10.60 0.330 11.0 2 aluminum 2219-t31 sheet 0.1020 10.60 0.330 45.0 5 aluminum 2219-t62 sheet 0.1020 10.60 0.330 39.0 5 aluminum 2219-t851 sheet 0.1020 10.60 0.330 51.0 6 aluminum 2219-t851 0.1020 10.60 0.330 53.8 6 aluminum 2618-t6 sheet 0.1000 10.50 0.330 56.0 6 aluminum 3003-o sheet 0.0990 10.00 0.330 6.0 1 aluminum 3003-h12 sheet 0.0990 10.00 0.330 18.0 1 aluminum 3003-h14 0.0990 10.00 0.330 21.1 2 aluminum 3003-h18 sheet 0.0990 10.00 0.330 27.0 2 aluminum 3004-o sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 10.0 2 aluminum 3004-h32 sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 25.0 3 aluminum 3004-h34 sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 29.0 3 aluminum 3004-h38 sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 36.0 4 aluminum 4032-t6 0.0970 11.40 0.330 46.0 5 aluminum 5050-o sheet 0.0970 10.00 0.330 8.0 2 aluminum 5050-h32 sheet 0.0970 10.00 0.330 21.0 2aluminum 5050-h38 sheet 0.0970 10.00 0.330 29.0 3 aluminum 5052-o sheet 0.0970 10.20 0.330 13.0 2 aluminum 5052-o 0.0970 10.20 0.330 12.0 2 aluminum 5052-h34 sheet 0.0970 10.20 0.330 31.0 3 aluminum 5052-h38 sheet 0.0970 10.20 0.330 38.0 4 aluminum 5083-o sheet 0.0960 10.30 0.330 22.0 4 aluminum 5083-o 0.0960 10.30 0.330 20.4 4 aluminum 5083-h12 sheet 0.0960 10.30 0.330 44.0 5 aluminum 5083-h32 sheet 0.0960 10.30 0.330 38.0 5 aluminum 5083-h34 sheet 0.0960 10.30 0.330 45.0 5 aluminum 5083-h321 0.0960 10.30 0.330 34.1 4 aluminum 5086-o sheet 0.0960 10.30 0.330 19.0 4 aluminum 5086-o 0.0960 10.30 0.330 17.0 3 aluminum 5086-h32 plate 0.0960 10.30 0.330 30.0 4 aluminum 5086-h34 sheet 0.0960 10.30 0.330 38.0 5 aluminum 5086-h34 plate 0.0960 10.30 0.330 38.0 5 aluminum 5154-o sheet 0.0960 10.20 0.330 16.0 3 aluminum 5154-h32 sheet 0.0960 10.20 0.330 31.0 4 aluminum 5154-h34 sheet 0.0960 10.20 0.330 38.0 4 aluminum 5154-h38 sheet 0.0960 10.20 0.330 43.0 4 aluminum 5454-o sheet 0.0970 10.20 0.330 16.0 3 aluminum 5454-o 0.0970 10.20 0.330 16.7 3 aluminum 5454-h32 sheet 0.0970 10.20 0.330 32.0 4 aluminum 5454-h32 0.0970 10.20 0.330 28.9 4 aluminum 5454-h34 sheet 0.0970 10.20 0.330 40.0 4 aluminum 5454-h32 plate 0.0970 10.20 0.330 38.0 4 aluminum 5456-o sheet 0.0960 10.30 0.330 25.0 4 aluminum 5456-o 0.0960 10.30 0.330 23.2 4 aluminum 5456-h24 sheet 0.0960 10.30 0.330 41.0 5 aluminum 5456-h321 sheet 0.0960 10.30 0.330 37.0 5 aluminum 5456-h321 plate 0.0960 10.30 0.330 34.0 5 aluminum 6061-o sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 8.0 1 aluminum 6061-t6 sheet thick 0.0980 10.00 0.330 41.0 4 aluminum 6061-t6 sheet thin 0.0980 10.00 0.330 43.0 4 aluminum 6061-t6 0.0980 10.00 0.330 42.2 4 aluminum 6061-t651 plate 0.0980 10.00 0.330 39.0 4 aluminum 6063-o sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 7.0 1 aluminum 6063-t4 sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 13.0 2 aluminum 6063-t6 sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 31.0 3 aluminum 6063-t6 0.0980 10.00 0.330 31.0 3 aluminum 6063-t832 sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 39.0 4 aluminum 6066-o sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 12.0 2 aluminum 6066-t4 sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 30.0 5 aluminum 6066-t6 sheet 0.0980 10.00 0.330 51.0 5 aluminum x7005-o sheet 0.1010 10.30 0.330 12.0 2 aluminum x7005-t6 sheet 0.1010 10.30 0.330 46.0 5aluminum 7039-o sheet 0.1010 10.10 0.330 15.0 3 aluminum 7039-t6 sheet 0.1010 10.10 0.330 55.0 6 aluminum 7039-t61 plate 0.1010 10.10 0.330 48.0 5 aluminum 7049-t73 die forgings 0.1020 10.20 0.330 61.0 7 aluminum 7049-t73511 extrusions 0.1020 10.20 0.330 62.0 7 aluminum 7049-t75511 extrusions 0.1020 10.20 0.330 69.0 7 aluminum 7050-t73652 hand forging 0.1010 10.30 0.330 60.0 7 aluminum 7050-t736 die forgings 0.1010 10.30 0.330 60.0 7 aluminum 7075-o sheet 0.1010 10.30 0.330 15.0 3 aluminum 7075-t6 sheet 0.1010 10.30 0.330 76.0 8 aluminum 7075-t651 plate 0.1010 10.40 0.330 76.0 8 aluminum 7075-t73 sheet 0.1010 10.30 0.330 63.0 7 aluminum 7076-t61 0.1020 9.70 0.330 60.0 7 aluminum 7079-o sheet 0.0990 10.40 0.330 15.0 3 aluminum 7079-t6 sheet 0.0990 10.40 0.330 70.0 7 aluminum 7079-t651 plate 0.0990 10.40 0.330 77.0 8 aluminum 7178-o sheet 0.1020 10.40 0.330 15.0 3 aluminum 7178-t6 sheet 0.1020 10.40 0.330 75.0 8 aluminum 7178-t76 plate 0.1020 10.20 0.330 72.0 8 aluminum 7178-t651 plate 0.1020 10.40 0.330 84.0 9 aluminum wrought 1060 o 0.0980 10.00 0.330 4.0 1 aluminum wrought 1060 h14 0.0980 10.00 0.330 13.0 1 aluminum wrought 1060 h18 0.0980 10.00 0.330 18.0 1 aluminum wrought 1100 o 0.0980 10.00 0.330 5.0 1 aluminum wrought 1100 h14 0.0980 10.00 0.330 17.0 1 aluminum wrought 1100 h18 0.0980 10.00 0.330 22.0 2 aluminum wrought 1350 o 0.0980 10.00 0.330 4.0 1 aluminum wrought 1350 h19 0.0980 10.00 0.330 24.0 2 aluminum wrought 2011 t3 0.1090 10.20 0.330 43.0 5 aluminum wrought 2011 t8 0.1090 10.20 0.330 45.0 5 aluminum wrought 2014 o 0.1010 10.60 0.330 14.0 2 aluminum wrought 2014 t6 0.1010 10.60 0.330 68.0 7 aluminum wrought 2017 o 0.1010 10.50 0.330 10.0 2 aluminum wrought 2017 t4 0.1010 10.50 0.330 40.0 6 aluminum wrought 2024 o 0.1010 10.60 0.330 11.0 2 aluminum wrought 2024 t3 0.1010 10.60 0.330 50.0 7 aluminum wrought 2024 t4 or t351 0.1010 10.60 0.330 47.0 6 aluminum wrought 2024 t361 0.1010 10.60 0.330 57.0 7 aluminum wrought 2036 t4 0.1000 10.30 0.330 28.0 4 aluminum wrought 2219 o 0.1030 10.60 0.330 11.0 2 aluminum wrought 2219 t31 or t351 0.1030 10.60 0.330 36.0 5 aluminum wrought 2219 t81 or t851 0.1030 10.60 0.330 51.0 6 aluminum wrought 3003 o 0.0990 10.00 0.330 6.0 1 aluminum wrought 3003 h12 0.0990 10.00 0.330 18.0 1 aluminum wrought 3003 h14 0.0990 10.00 0.330 21.0 2 aluminum wrought 3003 h18 0.0990 10.00 0.330 27.0 2aluminum wrought 3004 h32 0.0980 10.00 0.330 25.0 3 aluminum wrought 3004 h34 0.0980 10.00 0.330 29.0 3 aluminum wrought 3004 h38 0.0980 10.00 0.330 36.0 4 aluminum wrought 3105 o 0.0980 10.00 0.330 8.0 1 aluminum wrought 3105 h14 0.0980 10.00 0.330 22.0 2 aluminum wrought 3105 h18 0.0980 10.00 0.330 28.0 3 aluminum wrought 3105 h25 0.0980 10.00 0.330 23.0 2 aluminum wrought 4032 t6 0.0970 11.40 0.330 46.0 5 aluminum wrought 5005 o 0.0980 10.00 0.330 6.0 1 aluminum wrought 5005 h14 0.0980 10.00 0.330 22.0 2 aluminum wrought 5005 h18 0.0980 10.00 0.330 28.0 2 aluminum wrought 5005 h38 0.0980 10.00 0.330 27.0 2 aluminum wrought 5050 o 0.0970 10.00 0.330 8.0 2 aluminum wrought 5050 h34 0.0970 10.00 0.330 24.0 2 aluminum wrought 5050 h38 0.0970 10.00 0.330 29.0 3 aluminum wrought 5052 o 0.0970 10.20 0.330 13.0 2 aluminum wrought 5052 h34 0.0970 10.20 0.330 31.0 3 aluminum wrought 5052 h38 0.0970 10.20 0.330 37.0 4 aluminum wrought 5083 o 0.0960 10.30 0.330 21.0 4 aluminum wrought 5083 h321 or h116 0.0960 10.30 0.330 33.0 4 aluminum wrought 5086 0 0.0960 10.30 0.330 17.0 3 aluminum wrought 5086 h32 or h116 0.0960 10.30 0.330 30.0 4 aluminum wrought 5154 o 0.0960 10.20 0.330 17.0 3 aluminum wrought 5154 h34 0.0960 10.20 0.330 33.0 4 aluminum wrought 5154 h38 0.0960 10.20 0.330 39.0 4 aluminum wrought 5252 h25 0.0960 10.00 0.330 25.0 3 aluminum wrought 5454 o 0.0970 10.20 0.330 17.0 3 aluminum wrought 5454 h32 0.0970 10.20 0.330 30.0 4 aluminum wrought 5454 h34 0.0970 10.20 0.330 35.0 4 aluminum wrought 5456 o 0.0960 10.30 0.330 23.0 4 aluminum wrought 5456 h24 0.0960 10.30 0.330 41.0 5 aluminum wrought 5456 h34 0.0960 10.30 0.330 37.0 5 aluminum wrought 5657 h25 0.0970 10.00 0.330 20.0 2 aluminum wrought 5657 h38 or h28 0.0970 10.00 0.330 24.0 2 aluminum wrought 6061 o 0.0980 10.00 0.330 8.0 1 aluminum wrought 6061 t451 0.0980 10.00 0.330 21.0 3 aluminum wrought 6061 t651 0.0980 10.00 0.330 40.0 4 aluminum wrought 6063 o 0.0970 10.00 0.330 7.0 1 aluminum wrought 6063 t4 0.0970 10.00 0.330 13.0 2 aluminum wrought 6063 t6 0.0970 10.00 0.330 31.0 3 aluminum wrought 6066 o 0.0980 10.00 0.330 12.0 2 aluminum wrought 6066 t4 0.0980 10.00 0.330 30.0 5 aluminum wrought 6066 t6 0.0980 10.00 0.330 52.0 5 aluminum wrought 6101 t6 0.0970 10.00 0.330 28.0 3 aluminum wrought 7001 o 0.1030 10.30 0.330 22.0 3 aluminum wrought 7001 t6 0.1030 10.30 0.330 91.0 9aluminum wrought 7075 t6 or t651 0.1010 10.30 0.330 73.0 8 aluminum wrought 7075 t73 0.1010 10.30 0.330 63.0 7 aluminum wrought 7178 o 0.1020 10.40 0.330 15.0 3 aluminum wrought 7178 t6 or t651 0.1020 10.40 0.330 78.0 8 aluminum wrought 7178 t76 or t7651 0.1020 10.40 0.330 73.0 8 beryllium s-65 0.0670 42.00 0.029 30.0 4 beryllium s-200f 0.0670 42.00 0.029 35.0 4 beryllium 1319 0.0670 42.00 0.029 35.0 5 beryllium 1162 0.0670 42.00 0.029 25.0 3 beryllium qmv 0.0670 42.00 0.029 30.0 5 beryllium-copper 10 dead soft 0.3190 20.00 0.310 20.0 3 beryllium-copper 10 planished 0.3190 20.00 0.310 25.0 3 beryllium-copper 10 h temper 0.3190 20.00 0.310 55.0 7 beryllium-copper 10 at temper 0.3190 20.00 0.310 80.0 10 beryllium-copper 10 ht temper 0.3190 20.00 0.310 100.0 11 beryllium-copper 10 htr temper 0.3190 20.00 0.310 110.0 12 beryllium-copper 10 htc temper 0.3190 20.00 0.310 50.0 7 beryllium-copper 25 dead soft 0.3020 19.00 0.310 28.0 6 beryllium-copper 25 planished 0.3020 19.00 0.310 30.0 6 beryllium-copper 25 1/4 h temper 0.3020 19.00 0.310 60.0 7 beryllium-copper 25 1/2 h temper 0.3020 19.00 0.310 75.0 8 beryllium-copper 25 h temper 0.3020 19.00 0.310 90.0 10 beryllium-copper 25 at temper 0.3020 19.00 0.310 140.0 16 beryllium-copper 25 1/4 ht temper 0.3020 19.00 0.310 150.0 17 beryllium-copper 25 1/2 ht temper 0.3020 19.00 0.310 160.0 18 beryllium-copper 25 ht temper 0.3020 19.00 0.310 165.0 19 brass cartridge cu.7 zn.3 1/2 hard 0.3080 16.00 0.330 52.0 6 brass cartridge cu.7 zn.3 1/4 hard 0.3080 16.00 0.330 40.0 5 brass cartridge cu.7 zn.3 annealed 0.3080 16.00 0.330 19.0 5 bronze commercial cu.9 zn.1 1/2 hard 0.3180 17.00 0.330 45.0 5 bronze commercial cu.9 zn.1 annealed 0.3180 17.00 0.330 12.0 3 copper cold rolled 0.3220 17.00 0.330 45.0 5 copper hot rolled 0.3230 17.00 0.330 10.0 3 copper oxygen free (99.92) annealed 0.3210 17.00 0.330 10.0 3 gold pure (99.9) annealed 0.6980 12.00 0.420 1.0 1 gold pure (99.9) cold rolled 0.6980 12.00 0.420 30.0 3 inconel x annealed 0.3000 31.00 0.330 50.0 11 inconel x hot rolled 0.3000 31.00 0.330 120.0 18 iron gray cast 0.2600 13.00 0.300 32.0 3 iron ingot (99.9+) annealed 0.2840 30.10 0.290 19.0 3 iron ingot (99.9+) hot rolled 0.2840 30.10 0.290 19.0 3 iron wrought hat rolled 0.2780 29.00 0.290 30.0 4 lead pure 0.4100 2.00 0.420 1.9 magnesium az31b-h24 0.0640 6.50 0.350 22.0 3 magnesium hk31b-h24 0.0650 6.40 0.350 29.0 3 magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn h24 sheet 0.016/0.249 0.0643 6.50 0.330 32.0 4magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn h24 sheet 0.250/0.374 0.0643 6.50 0.330 magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn h24 sheet 0.375/0.500 0.0643 6.50 0.330 27.0 3 magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn h24 sheet 0.501/1.000 0.0643 6.50 0.330 24.0 3 magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn h24 sheet 1.001/2.000 0.0643 6.50 0.330 23.0 3 magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn h24 sheet 2.001/3.000 0.0643 6.50 0.330 21.0 3 magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn h26 sheet 0.250/0.374 0.0643 6.50 0.330 30.0 4 magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn h26 sheet 0.375/0.438 0.0643 6.50 0.330 28.0 4 magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn h26 sheet 0.439/0.500 0.0643 6.50 0.330 28.0 4 magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn h26 sheet 0.501/0.750 0.0643 6.50 0.330 28.0 4 magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn h26 sheet 0.751/1.000 0.0643 6.50 0.330 26.0 3 magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn h26 sheet 1.001/1.500 0.0643 6.50 0.330 25.0 3 magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn h26 sheet 1.501/2.000 0.0643 6.50 0.330 24.0 3 magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn o sheet 0.016/0.060 0.0643 6.50 0.330 22.0 3 magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn o sheet 0.061/0.249 0.0643 6.50 0.330 23.0 3 magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn o sheet 0.250/0.500 0.0643 6.50 0.330 22.0 3 magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn o sheet 0.501/2.000 0.0643 6.50 0.330 22.0 3 magnesium wrought az31b 3-al 1-zn o sheet 2.001/3.000 0.0643 6.50 0.330 21.0 3 magnesium wrought hk31a 3.2-th 0.7-zr h24 sheet 0.016/0.125 0.0647 6.50 0.330 30.0 3 magnesium wrought hk31a 3.2-th 0.7-zr h24 sheet 0.126/0.250 0.0647 6.50 0.330 30.0 3 magnesium wrought hk31a 3.2-th 0.7-zr h24 sheet 0.251/1.000 0.0647 6.50 0.330 31.0 3 magnesium wrought hk31a 3.2-th 0.7-zr h24 sheet 1.001/3.000 0.0647 6.50 0.330 29.0 3 magnesium wrought hk31a 3.2-th 0.7-zr o sheet 0.016/0.250 0.0647 6.50 0.330 20.0 3 magnesium wrought hk31a 3.2-th 0.7-zr o sheet 0.251/0.500 0.0647 6.50 0.330 19.0 3 magnesium wrought hk31a 3.2-th 0.7-zr o sheet 0.501/1.000 0.0647 6.50 0.330 18.0 3 magnesium wrought hk31a 3.2-th 0.7-zr o sheet 1.001/3.000 0.0647 6.50 0.330 17.0 3 magnesium wrought hm21a 2.0-th 0.8-mn t8 sheet 0.016/0.250 0.0643 6.50 0.330 28.0 3 magnesium wrought hm21a 2.0-th 0.8-mn t8 sheet 0.251/0.500 0.0643 6.50 0.330 30.0 3 magnesium wrought hm21a 2.0-th 0.8-mn t8 sheet 0.501/1.000 0.0643 6.50 0.330 28.0 3 magnesium wrought hm21a 2.0-th 0.8-mn t8 sheet 1.001/2.000 0.0643 6.50 0.330 25.0 3 magnesium wrought hm21a 2.0-th 0.8-mn t8 sheet 2.001/3.000 0.0643 6.50 0.330 26.0 3 magnesium wrought hm21a 2.0-th 0.8-mn t81 sheet 0.125/0.312 0.0643 6.50 0.330 30.0 3 magnesium wrought az31b 3.0-al 1.0-zn temper-f extrusion 0.0643 6.50 0.330 28.0 3 magnesium wrought az61a 6.5-al 1.0-zn temper-f extrusion 0.0650 6.50 0.330 33.0 4 magnesium wrought az80a 8.5-al 0.5-zn temper-f extrusion 0.0650 6.50 0.330 36.0 4 magnesium wrought az80a 8.5-al 0.5-zn temper-t5 extrusion 0.0650 6.50 0.330 40.0 5 magnesium wrought hm31a 3.25-th 1.2-mn temper-t5 extrusion 0.0653 6.50 0.330 39.0 4 magnesium wrought zk60a 5.5znh 0.45-zr temper-f extrusion 0.0661 6.50 0.330 40.0 4 magnesium wrought zk60a 5.5znh 0.45-zr temper-t5 extrusion 0.0661 6.50 0.330 44.0 5 magnesium wrought az31b 3.0-al 1.0-zn temper-f tubing 0.0643 6.50 0.330 24.0 3 magnesium wrought az61a 6.5-al 1.0-zn temper-f tubing 0.0650 6.50 0.330 24.0 4 magnesium wrought zk60a 5.5znh 0.45-zr temper-f tubing 0.0661 6.50 0.330 34.0 4 magnesium wrought zk60a 5.5znh 0.45-zr temper-t5 tubing 0.0661 6.50 0.330 40.0 5 magnesium wrought az31b 3.0-al 1.0-zn temper-f forging 0.0643 6.50 0.330 28.0 3 magnesium wrought az61a 6.5-al 1.0-zn temper-f forging 0.0650 6.50 0.330 26.0 4 magnesium wrought az80a 8.5-al 0.5-zn temper-f forging 0.0650 6.50 0.330 31.0 4 magnesium wrought az80a 8.5-al 0.5-zn temper-t5 forging 0.0650 6.50 0.330 34.0 5 magnesium wrought az80a 8.5-al 0.5-zn temper-t6 forging 0.0650 6.50 0.330 36.0 5magnesium wrought hm21a 2.0-th 0.8-mn temper-t5 forging 0.0643 6.50 0.330 magnesium wrought zk60a 5.5znh 0.45-zr temper-t5 forging 0.0661 6.50 0.330 30.0 4 magnesium wrought zk60a 5.5znh 0.45-zr temper-t6 forging 0.0661 6.50 0.330 39.0 4 magnesium cast am100a 10.0-al 0.3-zn temper-f 0.0654 6.50 0.330 12.0 2 magnesium cast am100a 10.0-al 0.3-zn temper-t4 0.0654 6.50 0.330 13.0 4 magnesium cast am100a 10.0-al 0.3-zn temper-t6 0.0654 6.50 0.330 16.0 4 magnesium cast am100a 10.0-al 0.3-zn temper-t61 0.0654 6.50 0.330 22.0 4 magnesium cast az63a 60.0-al 3.0-zn temper-f 0.0663 6.50 0.330 14.0 2 magnesium cast az63a 60.0-al 3.0-zn temper-t4 0.0663 6.50 0.330 14.0 4 magnesium cast az63a 60.0-al 3.0-zn temper-t5 0.0663 6.50 0.330 15.0 2 magnesium cast az63a 60.0-al 3.0-zn temper-t6 0.0663 6.50 0.330 19.0 4 magnesium cast az81a 7.5-al 0.7-zn temper-t4 0.0650 6.50 0.330 12.0 4 magnesium cast az91a 8.7-al 0.7-zn temper-f 0.0654 6.50 0.330 14.0 2 magnesium cast az91a 8.7-al 0.7-zn temper-t4 0.0654 6.50 0.330 13.0 4 magnesium cast az91a 8.7-al 0.7-zn temper-t6 0.0654 6.50 0.330 19.0 4 magnesium cast az92a 9.0-al 2.0-zn temper-f 0.0657 6.50 0.330 14.0 2 magnesium cast az92a 9.0-al 2.0-zn temper-t4 0.0657 6.50 0.330 14.0 4 magnesium cast az92a 9.0-al 2.0-zn temper-t5 0.0657 6.50 0.330 17.0 2 magnesium cast az92a 9.0-al 2.0-zn temper-t6 0.0657 6.50 0.330 22.0 4 magnesium cast ez33a 2.5-re 3.2-zn temper-t5 0.0660 6.50 0.330 16.0 2 magnesium cast hk31a 3.2-th 0.3-zn temper-t6 0.0646 6.50 0.330 15.0 3 magnesium cast hz32a 3.2-th 2.1-zn temper-t5 0.0660 6.50 0.330 15.0 2 magnesium cast k1a 0.7-zr temper-f 0.0629 6.50 0.330 8.0 2 magnesium cast qe22a 2.5-ag 2.2-re 0.7-zr temper-t6 0.0654 6.50 0.330 28.0 3 magnesium cast qh21a 2.5-ag 1-re 1.1-th 0.7-zr temper-t6 0.0657 6.50 0.330 30.0 4 magnesium cast ze41a 4.2-zn 1.25-re 0.7-zr temper-t5 0.0657 6.50 0.330 20.0 3 magnesium cast ze63a 5.75-zn 2.6-re 0.7-zr temper-t6 0.0672 6.50 0.330 28.0 4 magnesium cast ze62a 5.7-zn 1.8-th 0.75-zr temper-t5 0.0669 6.50 0.330 25.0 4 magnesium cast zk51a 4.6-zn 0.75-zr temper-t5 0.0654 6.50 0.330 24.0 4 magnesium cast zk61a 60.0-zn 0.8-zr temper-t6 0.0660 6.50 0.330 28.0 4 molybdenium drawn 14 min. 0.3680 42.00 0.320 60.0 21 monel sand cast ni.63 cu.32 si.012 0.3120 19.00 0.330 35.0 8 monel wrought ni.67 cu.30 annealed 0.3190 26.00 0.360 35.0 7 monel wrought ni.67 cu.30 cold drawn 0.3190 26.00 0.360 80.0 10 monel wrought ni.67 cu.30 cold rolled hard 0.3190 26.00 0.360 100.0 11 monel wrought ni.67 cu.30 hot rolled 0.3190 26.00 0.360 50.0 9 nickel silver cu.65 zn.2 ni.15 1/2 hard 0.3140 18.00 0.310 62.0 7 nickel silver cu.65 zn.2 ni.15 annealed 0.3140 18.00 0.310 19.0 5 nickel silver cu.65 zn.2 ni.15 full hard 0.3140 18.00 0.310 75.0 8 nickel wrought (99.0) annealed 0.3210 30.00 0.310 20.0 7 nickel wrought (99.0) cold drawn 0.3210 30.00 0.310 70.0 9 nickel wrought (99.0) cold rolled hard 0.3210 30.00 0.310 95.0 10 nickel wrought (99.0) hot rolled 0.3210 30.00 0.310 25.0 7 palladium commercial (99.5) annealed 0.4320 17.00 0.390 5.0 3 palladium commercial (99.5) cold rolled 0.4310 17.00 0.390 32.0 4 platinum pure (99.99) annealed 0.7220 21.00 0.390 10.0 2 platinum pure (99.99) cold rolled 0.7720 21.00 0.390 27.0 3plutonium alpha 0.6970 14.00 0.190 plutonium delta 0.5710 6.00 0.290 16.0 2 polycarbonate 0.0430 0.34 0.380 8.0 1 polyethylene type iii 0.0440 0.15 0.450 1.8 silver pure (99.9) annealed 0.3790 11.00 0.370 12.0 2 silver pure (99.9) cold rolled 0.3790 11.00 0.370 38.0 4 steel wrought stainless 201 sheet annealed 0.2800 28.60 0.290 55.0 11 steel wrought stainless 201 sheet 10% cr 0.2800 28.60 0.290 90.0 13 steel wrought stainless 201 sheet 40% cr 0.2800 28.60 0.290 165.0 19 steel wrought stainless 202 sheet annealed 0.2800 28.60 0.290 50.0 10 steel wrought stainless 202 sheet 10% cr 0.2800 28.60 0.290 98.0 12 steel wrought stainless 202 sheet 40% cr 0.2800 28.60 0.290 155.0 18 steel wrought stainless 203 ez 1 in. bar annealed 0.2840 28.60 0.290 45.0 8 steel wrought stainless 203 ez 1 in. bar cd 0.2840 28.60 0.290 80.0 11 steel wrought stainless 203 ez 1 in. bar full hard 0.2840 28.60 0.290 140.0 17 steel wrought stainless 301 sheet annealed 0.2860 29.00 0.290 40.0 12 steel wrought stainless 301 sheet 10% cr 0.2860 28.00 0.290 88.0 15 steel wrought stainless 301 sheet 40% cr 0.2860 28.00 0.290 170.0 19 steel wrought stainless 301 sheet 60% cr 0.2860 27.00 0.290 230.0 23 steel wrought stainless 302 sheet annealed 0.2870 27.90 0.290 40.0 9 steel wrought stainless 302 sheet 10% cr 0.2870 27.90 0.290 92.0 10 steel wrought stainless 302 sheet 40% cr 0.2870 27.90 0.290 132.0 15 steel wrought stainless 302b plate anealed 0.2870 27.90 0.290 40.0 9 steel wrought stainless 303 1 in. bar annealed 0.2900 28.00 0.290 37.0 9 steel wrought stainless 303 1 in. bar 10% cr 0.2900 28.00 0.290 45.0 10 steel wrought stainless 303 1 in. bar 40% cr 0.2900 28.00 0.290 80.0 17 steel wrought stainless 303 se 1 in. bar annealed 0.2860 28.00 0.290 35.0 9 steel wrought stainless 303 se 1 in. bar half hard 0.2860 28.00 0.290 105.0 13 steel wrought stainless 303 se 1 in. bar full hard 0.2860 28.00 0.290 137.0 17 steel wrought stainless 304 bar annealed 0.2900 28.10 0.290 34.0 8 steel wrought stainless 304 bar 10% cr 0.2900 28.10 0.290 70.0 9 steel wrought stainless 304 bar 40% cr 0.2900 28.10 0.290 135.0 14 steel wrought stainless 304l bar annealed 0.2860 28.00 0.290 32.0 8 steel wrought stainless 304l bar 10% cr 0.2860 28.00 0.290 73.0 10 steel wrought stainless 304l bar 40% cr 0.2860 28.00 0.290 137.0 15 steel wrought stainless 305 sheet annealed 0.2860 28.00 0.290 33.0 8 steel wrought stainless 305 sheet 10% cr 0.2860 28.00 0.290 70.0 9 steel wrought stainless 305 sheet 40% cr 0.2860 28.00 0.290 130.0 14 steel wrought stainless 308 sheet annealed 0.2900 28.00 0.290 33.0 8 steel wrought stainless 308 sheet 10% cr 0.2900 28.00 0.290 64.0 9 steel wrought stainless 308 sheet 40% cr 0.2900 28.00 0.290 128.0 15 steel wrought stainless 309 sheet annealed 0.2900 29.00 0.290 37.0 8 steel wrought stainless 309 sheet 10% cr 0.2900 29.00 0.290 57.0 8 steel wrought stainless 309 sheet 40% cr 0.2900 29.00 0.290 124.0 13 steel wrought stainless 310 sheet annealed 0.2870 28.20 0.290 45.0 8 steel wrought stainless 310 sheet 10% cr 0.2870 28.20 0.290 67.0 10 steel wrought stainless 310 sheet 40% cr 0.2870 28.20 0.290 138.0 15steel wrought stainless 316 sheet annealed 0.2870 28.10 0.290 38.0 8 steel wrought stainless 316 sheet 10% cr 0.2870 28.10 0.290 70.0 9 steel wrought stainless 316 sheet 40% cr 0.2870 28.10 0.290 128.0 14 steel wrought stainless 316l sheet annealed 0.2840 28.00 0.290 37.0 7 steel wrought stainless 316l sheet half hard 0.2840 28.00 0.290 90.0 12 steel wrought stainless 316l sheet full hard 0.2840 28.00 0.290 127.0 16 steel wrought stainless 317 1 in. bar annealed 0.2900 28.00 0.290 38.0 8 steel wrought stainless 317 1 in. bar 10% cr 0.2900 28.00 0.290 57.0 10 steel wrought stainless 317 1 in. bar 40% cr 0.2900 28.00 0.290 134.0 14 steel wrought stainless 321 sheet annealed 0.2850 28.00 0.290 32.0 9 steel wrought stainless 321 sheet 10% cr 0.2850 28.00 0.290 70.0 10 steel wrought stainless 321 sheet 40% cr 0.2850 28.00 0.290 133.0 15 steel wrought stainless 347 sheet annealed 0.2860 28.20 0.290 40.0 9 steel wrought stainless 347 sheet 10% cr 0.2860 28.20 0.290 77.0 10 steel wrought stainless 347 sheet 40% cr 0.2860 28.20 0.290 138.0 15 steel wrought stainless 348 bar 0.2900 28.20 0.290 37.0 9 steel wrought stainless 19-9dl sheet annealed 0.2870 29.50 0.290 67.0 11 steel wrought stainless 19-9dl sheet hr+sr at 1200f 0.2870 29.50 0.290 103.0 12 steel wrought stainless 21-6-9 sheet annealed 0.2830 29.40 0.290 68.0 11 steel wrought stainless 21-6-9 sheet cr 0.2830 29.40 0.290 130.0 14 steel wrought stainless 21-6-9 sheet 60 %cr 0.2830 29.40 0.290 182.0 20 steel wrought stainless 22-13-5 sheet annealed 0.2850 28.00 0.290 86.0 12 steel wrought stainless 22-13-5 sheet 60% cr 0.2850 28.00 0.290 199.0 21 steel wrought stainless 18-2mn 0.25 in bar annealed 0.2850 28.00 0.290 65.0 12 steel wrought stainless 18-2mn 0.25 in bar 20% cr 0.2850 28.00 0.290 135.0 17 steel wrought stainless 18-2mn 0.25 in bar 60% cr 0.2850 28.00 0.290 224.0 26 steel wrought stainless 400 sheet anealed 0.2800 29.00 0.290 32.0 6 steel wrought stainless 405 sheet annealed 0.2800 29.00 0.290 47.0 6 steel wrought stainless 405 sheet ??% cr 0.2800 29.00 0.290 65.0 9 steel wrought stainless 405 sheet ??% cr 0.2800 29.00 0.290 125.0 13 steel wrought stainless 430 sheet annealed 0.2800 29.00 0.290 52.0 7 steel wrought stainless 430 sheet ??% cr 0.2800 29.00 0.290 65.0 9 steel wrought stainless 430 sheet ??% cr 0.2800 29.00 0.290 125.0 13 steel wrought stainless 442 sheet annealed 0.2800 29.00 0.290 52.0 8 steel wrought stainless 442 sheet ??% cr 0.2800 29.00 0.290 70.0 9 steel wrought stainless 442 sheet ??% cr 0.2800 29.00 0.290 100.0 11 steel wrought stainless 446 sheet annealed 0.2700 29.00 0.290 52.0 8 steel wrought stainless 446 sheet ??% cr 0.2700 29.00 0.290 70.0 9 steel wrought stainless 446 sheet ??% cr 0.2700 29.00 0.290 109.5 11 steel wrought stainless 18 sr sheet annealed 0.2700 29.00 0.290 65.0 8 steel wrought stainless 261 e-brite strip annealed 0.2770 29.00 0.290 46.0 6 steel wrought stainless 261 e-brite strip 20% cr 0.2770 29.00 0.290 88.0 9 steel wrought stainless 261 e-brite strip 60% cr 0.2770 29.00 0.290 116.0 12 steel wrought stainless 403 bar annealed 0.2780 29.70 0.290 45.0 7 steel wrought stainless 403 bar temper 1200f 0.2780 29.70 0.290 85.0 11 steel wrought stainless 403 bar temper 600f 0.2780 29.70 0.290 140.0 18steel wrought stainless 410 1 in. bar temper 1000f 0.2790 29.00 0.290 104.0 11 steel wrought stainless 410 1 in. bar temper 600f 0.2790 29.00 0.290 143.0 18 steel wrought stainless 410 1 in. bar temper 300f 0.2790 29.00 0.290 148.0 18 steel wrought stainless 414 bar anealed 0.2800 28.50 0.290 90.0 11 steel wrought stainless 414 bar temper 1200f 0.2800 28.50 0.290 105.0 12 steel wrought stainless 414 bar temper 800f 0.2800 28.50 0.290 150.0 20 steel wrought stainless 416 bar anealed 0.2780 29.00 0.290 35.0 6 steel wrought stainless 416 bar temper 1200f 0.2780 29.00 0.290 90.0 11 steel wrought stainless 416 bar temper 600f 0.2780 29.00 0.290 140.0 18 steel wrought stainless 420 1 in. bar anealed 0.2770 29.00 0.290 50.0 9 steel wrought stainless 420 1 in. bar temper 1400f 0.2770 29.00 0.290 70.0 11 steel wrought stainless 420 1 in. bar temper 400f 0.2770 29.00 0.290 215.0 25 steel wrought stainless 422 bar anealed 0.2810 29.80 0.290 74.0 9 steel wrought stainless 422 bar temper 1400f 0.2810 29.80 0.290 90.0 12 steel wrought stainless 422 bar temper 1200f 0.2810 29.80 0.290 125.0 14 steel wrought stainless 422 bar temper 800f 0.2810 29.80 0.290 168.0 23 steel wrought stainless 431 1 in. bar anealed 0.2800 29.00 0.290 95.0 12 steel wrought stainless 431 1 in. bar temper 1100f 0.2800 29.00 0.290 115.0 14 steel wrought stainless 431 1 in. bar temper 500f 0.2800 29.00 0.290 149.0 19 steel wrought stainless 440a bar anealed 0.2800 29.00 0.290 60.0 10 steel wrought stainless 440a bar temper 600f 0.2800 29.00 0.290 240.0 26 steel wrought stainless 440b bar anealed 0.2800 29.00 0.290 62.0 10 steel wrought stainless 440b bar temper 600f 0.2800 29.00 0.290 270.0 28 steel wrought stainless 440c bar anealed 0.2800 29.00 0.290 65.0 11 steel wrought stainless 440c bar temper 600f 0.2800 29.00 0.290 275.0 28 steel wrought stainless 440f bar temper 600f 0.2800 29.00 0.290 275.0 28 steel wrought stainless 12 mov sheet annealed 0.2790 29.00 0.290 65.0 10 steel wrought stainless 12 mov temper 900f 0.2790 29.00 0.290 195.0 24 steel wrought stainless 12 mov temper 700f 0.2790 29.00 0.290 188.0 23 steel wrought stainless greek ascolony bar tmpr 1000f 0.2840 29.00 0.290 137.0 16 steel wrought stainless greek ascolony bar tmpr 500f 0.2840 29.00 0.290 175.0 20 steel wrought stainless 17-14 cu-mo bar 1350f wq 0.2870 29.00 0.290 41.0 8 steel wrought stainless hmn bar annealed 0.2790 29.00 0.290 56.0 11 steel wrought stainless hmn bar age 1400f 0.2790 29.00 0.290 110.0 17 steel wrought stainless hmn bar age 1300f 0.2790 29.00 0.290 135.0 18 steel wrought stainless 17-7ph sheet annealed 0.2820 29.00 0.290 40.0 13 steel wrought stainless 17-7ph sheet th 1050 0.2760 29.00 0.290 185.0 20 steel wrought stainless 17-7ph sheet rh 950 0.2760 29.00 0.290 220.0 23 steel wrought stainless 17-7ph sheet ch 900 0.2770 29.50 0.290 260.0 26 steel wrought stainless ph 15-7 mo sheet annealed 0.2820 29.00 0.290 55.0 13 steel wrought stainless ph 15-7 mo sheet th 1050 0.2770 29.00 0.290 200.0 21 steel wrought stainless ph 15-7 mo sheet rh 950 0.2770 29.00 0.290 225.0 24 steel wrought stainless ph 15-7 mo sheet ch 900 0.2770 29.00 0.290 260.0 26 steel wrought stainless ph 14-8 mo sheet annealed 0.2830 28.30 0.290 55.0 12 steel wrought stainless ph 14-8 mo sheet srh 1050 0.2830 28.30 0.290 205.0 21 steel wrought stainless ph 14-8 mo sheet srh 950 0.2780 28.30 0.290 220.0 23。