meta分析量表模板
- 格式:xls
- 大小:56.00 KB
- 文档页数:2
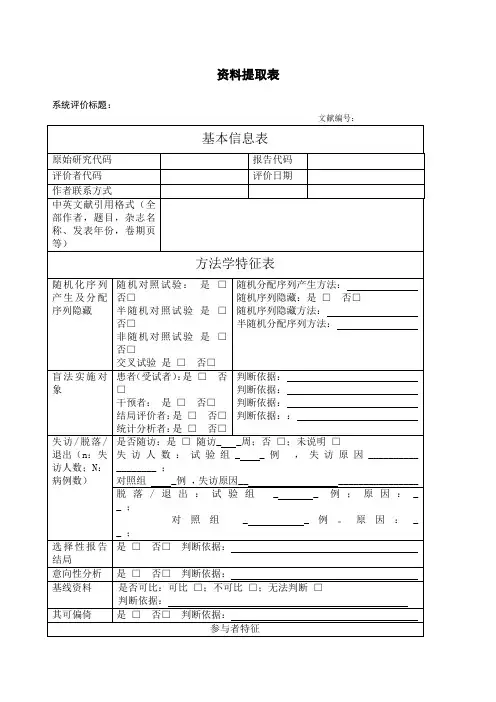
资料提取表系统评价标题:文献编号:基本信息表原始研究代码报告代码评价者代码评价日期作者联系方式中英文献引用格式(全部作者,题目,杂志名称、发表年份,卷期页等)方法学特征表随机化序列产生及分配序列隐藏随机对照试验:是□否□半随机对照试验是□否□非随机对照试验是□否□交叉试验是□否□随机分配序列产生方法:随机序列隐藏:是□否□随机序列隐藏方法:半随机分配序列方法:盲法实施对象患者(受试者):是□否□干预者:是□否□结局评价者:是□否□统计分析者:是□否□判断依据:判断依据:判断依据:判断依据::失访/脱落/退出(n:失访人数;N:病例数)是否随访:是□随访_ _周;否□;未说明□失访人数:试验组_ _例,失访原因__________ ________ ;对照组 _例,失访原因__ ________________ 脱落/退出:试验组_ _ 例;原因:_ _ ;对照组_ _例。
原因:_ _ ;选择性报告结局是□否□判断依据:意向性分析是□否□判断依据:基线资料是否可比:可比□;不可比□;无法判断□判断依据:其可偏倚是□否□判断依据:参与者特征项目试验组对照组性别(男/女)年龄(Mean±SD) 平均:±岁平均: ±岁被试者来源被试者特征健康人群:是□否□患病人群:是□否□;所患疾病名称:;诊断标准:研究持续时间干预措施人数干预措施描述具体方法描述(干预强度、频率及持续时间等)试验组对照组应急处理结局指标表结局指标定义(诊断方法、量表名称、阈值设定等)评定时间及标准1.TMT(The TrailMaking Test)2.MMSE3.N4004.P3005.记忆能力6.反应时间...结果数据表计量资料(结局指标)治疗组对照组测量时间指标名称单位例数均值标准差例数均值标准差认知能力分数思维能力分数计算能力分数执行能力分数记忆能力分数TMT Part A sTMT Part B s注意集中时间s注意分散次数次平均反应时间s最佳反应时间s手脚交叉运动总时间s正确次数s平均时间s手臂稳定性分数表象旋转s自我效能感x ±s应激性x ±sN40 0 潜伏期ms 波幅uVP30 0 潜伏期ms 波幅uV 反应时SMMSE评分分数ANT评分x ±s生活质量评分x ±s计数资料(结局指标)试验组对照组指标总例数显效有效无效加重总例数显效有效无效加重1.心血管事件2.骨骼肌损伤(如摔倒、扭伤和肌肉拉伤)3.热损伤4.不良事件5....经济学指标(成本)...综合判断纳入标准(符合①②③中任意一项且符合第④⑤项即可纳入)①随机、或半随机对照试验是□否□②对照试验是□否□③交叉研究第一阶段是□否□④对照组空白是□否□⑤采用与治疗组相同的常规基础治疗是□否□排除标准(一项及以上不符合者均排除)①研究对象不是脑卒中后患者是□否□②干预手段未采用有氧运动是□否□③干预手段采用有氧运动合并其他运动是□否□④未设立对照是□否□⑤对照组非空白是□否□⑥对照组采用除基础治疗之外的其他运动干预是□否□⑦结局指标与认知无关是□否□⑧数据不可提取是□否□⑨自身前后试验是□否□其他条件是否符合是□否□判断依据:综合判断是否合格是□否□注:原始研究代码(第一作者的姓和研究发表年份组成)评价者代码:资料提取者的姓名或代码评价日期:填写该表格的时间文献引用:刊登该文的全部作者,题目,杂志名称、发表年份,卷期页等。

AMSTAR ChecklistArticle Name:1. Did the research questions and inclusion criteria for the review include the components of PICO?For Yes: Optional (recommended)PopulationTimeframe for follow upYesNo InterventionComparator groupOutcome2. Did the report of the review contain an explicit statement that the review methods were established prior to the conduct of the review and did the report justify any significant deviations from the protocol?For Partial Yes:The authors state that they had awritten protocol or guide thatincluded ALL the following:For Yes:As for partial yes, plus the protocolshould be registered and should alsohave specified:review question(s)a meta-analysis/synthesisplan, if appropriate, andYesPartialYesNoa search strategy a plan for investigating causesof heterogeneityinclusion/exclusion criteria a plan for investigating causesof heterogeneitya risk of bias assessment3. Did the review authors explain their selection of the study designs for inclusion in the review?For Yes, the review should satisfy ONE of the following:Explanation for including only RCTs YesOR Explanation for including only NRSINoOR Explanation for including both RCTs and NRSI4. Did the review authors use a comprehensive literature search strategy? For Partial Yes (all the following): For Yes, should also have (all the following):searched at least 2 databases (relevant to research question) searched the reference lists / bibliographies of included studies YesPartialYesNoprovided key word and/or search strategy searched trial/study registriesjustified publication restrictions (e.g. language) included/consulted content experts in the fieldwhere relevant, searched for grey literatureconducted search within 24 months of completion of the review5. Did the review authors perform study selection in duplicate? For Yes, either ONE of the following:at least two reviewers independently agreed on selection of eligible studies and achieved consensus on which studies to includeYesNoOR two reviewers selected a sample of eligible studies and achieved good agreement (at least 80 percent), with the remainder selected by one reviewer.6. Did the review authors perform data extraction in duplicate? For Yes, either ONE of the following:at least two reviewers achieved consensus on which data to extract from included studiesYesNoOR two reviewers extracted data from a sample of eligible studiesand achieved good agreement (at least 80 percent), with the remainder extracted by one reviewer.7. Did the review authors provide a list of excluded studies and justify the exclusions? For Partial Yes:For Yes, must also have:provided a list of all potentially relevant studies that were read in full-text form butexcluded from the reviewJustified the exclusion from thereview of each potentially relevant studyYes Partial Yes No8. Did the review authors describe the included studies in adequate detail?For Partial Yes (ALL thefollowing): For Yes, should also have ALL the following:described populations described populationin detail YesPartial YesNodescribed interventionsdescribed intervention in detail (including doses where relevant)described comparatorsdescribed comparatorin detail(including doses where relevant)described outcomesdescribed study’s setting described research designstimeframe for follow-up9. Did the review authors use a satisfactory technique for assessing the risk of bias (RoB) in individual studies that were included in the review? RCTsFor Partial Yes, must have assessed RoB fromFor Yes, must also have assessed RoB from:unconcealed allocation, andallocation sequence that wasnot truly random, andYesPartial YesNolack of blinding of patients and assessors when assessing selection of the reported result from among multipleoutcomes (unnecessary for objective outcomes such as all-cause mortality) measurements or analyses of aspecified outcome Includes only NRSI NRSIFor Partial Yes, must have assessed RoB:For Yes, must also have assessed RoB:from confounding, andmethods used to ascertainexposures and outcomes, and YesPartial YesNoIncludesonly RCTsfrom selection biasselection of the reported result from among multiple measurements or analyses of a specified outcome10. Did the review authors report on the sources of funding for the studies included in the review? For YesMust have reported on the sources of funding for individual studies included in the review. Note: Reporting that the reviewers looked for this information but it was not reported by study authors also qualifiesYes No11. If meta-analysis was performed did the review authors use appropriate methods for statistical combination of results?RCTs For Yes:The authors justified combining the data in a meta-analysis YesNo Nometa-analysis conducted AND they used an appropriate weighted technique to combine study results and adjusted for heterogeneity if present.AND investigated the causes of any heterogeneity For NRSI For Yes:The authors justified combining the data in a meta-analysisYes NoNometa-analysisconducted AND they used an appropriate weighted technique to combine study results, adjusting for heterogeneity if presentAND they statistically combinedeffect estimates from NRSI that were adjusted for confounding, rather than combining raw data, or justified combining raw data when adjusted effect estimates were not available AND they reported separate summary estimates for RCTs and NRSI separately when both were included in the review12. If meta-analysis was performed, did the review authors assessthe potential impact of RoB in individual studies on the results of the meta-analysis or other evidence synthesis?For Yes:included only low risk of bias RCTsYesNoNo meta-analysis conductedOR, if the pooled estimate was based on RCTs and/or NRSI at variableRoB, the authors performed analyses to investigate possible impact of RoBon summary estimates of effect.13. Did the review authors account for RoB in individualstudies when interpreting/ discussing the results of the review?For Yes:included only low risk of bias RCTsYes NoOR, if RCTs with moderate or high RoB, or NRSI were included the review provided a discussion of the likely impact of RoB on the results14. Did the review authors provide a satisfactory explanation for, and discussion of, any heterogeneity observed in the results of the review?For Yes:There was no significant heterogeneity in the resultsYes NoOR if heterogeneity was present the authors performed aninvestigation of sources of any heterogeneity in the results and discussed the impact of this on the results of the review15. If they performed quantitative synthesis did the review authors carry out an adequate investigation of publication bias (small study bias) and discuss its likely impact on the results of the review? For Yes:performed graphical or statistical tests for publication bias anddiscussed the likelihood and magnitude of impact of publication biasYes No Nometa-analysis conducted16. Did the review authors report any potential sources of conflict of interest, including any funding they received for conducting the review? For Yes:The authors reported no competing interests ORYesNoThe authors described their funding sources and how they managed potential conflicts of interestTo cite this tool: Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, Moher D, Tugwell P, Welch V, Kristjansson E, Henry DA. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ. 2017 Sep 21;358:j4008.。

竭诚为您提供优质文档/双击可除meta分析数据提取表格篇一:meta分析资料提取表资料提取表系统评价标题:文献编号:注:原始研究代码(第一作者的姓和研究发表年份组成)评价者代码:资料提取者的姓名或代码评价日期:填写该表格的时间文献引用:刊登该文的全部作者,题目,杂志名称、发表年份,卷期页等篇二:meta分析步骤(1)明确简洁地提出需要解决的问题。
(2)制定检索策略,全面广泛地收集随机对照试验。
(3)确定纳入和排除标准,剔除不符合要求的文献。
(4)资料选择和提取。
(5)各试验的质量评估和特征描述。
(6)统计学处理。
a.异质性检验(齐性检验)。
b.统计合并效应量(加权合并,计算效应尺度及95%的置信区间)并进行统计推断。
c.图示单个试验的结果和合并后的结果。
d.敏感性分析。
e.通过“失安全数”的计算或采用“倒漏斗图”了解潜在的发表偏倚。
(7)结果解释、作出结论及评价。
(8)维护和更新资料。
提高国内随机对照试验meta-分析的质量何成奇,赵晓玲(四川大学华西医院康复中心,四川省成都市610041)[摘要]高质量的随机对照试验(Rct)的meta-分析结果与国际公认的大样本Rct结果一起被各国列为最高等级的证据,可为临床实践和卫生决策提供更真实的科学依据,引导临床医师在实践中做出正确的决策。
但质量差的meta-分析反而可能导致错误的结论。
国外meta-分析方法的应用已趋于成熟和规范。
然而目前国内由于应用时间不长,且缺乏统一规范的实施标准,文献质量参差不齐,很多方面还存在着较为严重的缺陷。
探讨如何提高国内Rctmeta-分析的质量,尽快与国际接轨,以便为循证医学、药学提供更科学真实的证据。
以进行Rctmeta-分析的步骤为线索,对国内meta-分析存在的问题和解决的办法进行了综述。
具体内容包括:提出一个好问题(研究目的),全面收集相关的Rct,制定严格的纳入/排除标准,正确提取数据资料,对符合纳入标准的Rct进行质量评价,应用正确的统计方法,必须进行敏感性分析,根据结果做出正确、全面的结论。

竭诚为您提供优质文档/双击可除meta分析数据提取表格篇一:meta分析资料提取表资料提取表系统评价标题:文献编号:注:原始研究代码(第一作者的姓和研究发表年份组成)评价者代码:资料提取者的姓名或代码评价日期:填写该表格的时间文献引用:刊登该文的全部作者,题目,杂志名称、发表年份,卷期页等篇二:meta分析步骤(1)明确简洁地提出需要解决的问题。
(2)制定检索策略,全面广泛地收集随机对照试验。
(3)确定纳入和排除标准,剔除不符合要求的文献。
(4)资料选择和提取。
(5)各试验的质量评估和特征描述。
(6)统计学处理。
a.异质性检验(齐性检验)。
b.统计合并效应量(加权合并,计算效应尺度及95%的置信区间)并进行统计推断。
c.图示单个试验的结果和合并后的结果。
d.敏感性分析。
e.通过“失安全数”的计算或采用“倒漏斗图”了解潜在的发表偏倚。
(7)结果解释、作出结论及评价。
(8)维护和更新资料。
提高国内随机对照试验meta-分析的质量何成奇,赵晓玲(四川大学华西医院康复中心,四川省成都市610041)[摘要]高质量的随机对照试验(Rct)的meta-分析结果与国际公认的大样本Rct结果一起被各国列为最高等级的证据,可为临床实践和卫生决策提供更真实的科学依据,引导临床医师在实践中做出正确的决策。
但质量差的meta-分析反而可能导致错误的结论。
国外meta-分析方法的应用已趋于成熟和规范。
然而目前国内由于应用时间不长,且缺乏统一规范的实施标准,文献质量参差不齐,很多方面还存在着较为严重的缺陷。
探讨如何提高国内Rctmeta-分析的质量,尽快与国际接轨,以便为循证医学、药学提供更科学真实的证据。
以进行Rctmeta-分析的步骤为线索,对国内meta-分析存在的问题和解决的办法进行了综述。
具体内容包括:提出一个好问题(研究目的),全面收集相关的Rct,制定严格的纳入/排除标准,正确提取数据资料,对符合纳入标准的Rct进行质量评价,应用正确的统计方法,必须进行敏感性分析,根据结果做出正确、全面的结论。


用症状自评量表(SCL-9 0 )评估中国大学生心理健康状况的Meta分析(?1广东工业大学心理学教学研究所,广州510006 ?2 广东白云学院心理健康辅导中心,广州510450? 通信作者Email:hyp0911126 )Meta分析(Meta analysis )又称荟萃分析、整合分析、汇总分析等,Glass :5]首次提出并使用,主要是对已有的研究结果进行综合量化分析,它可以对具有不一致结论的研究进行整合,得出一个所有研究的共同效应。
现今该方法已经在社会科学、医学领域得到了普遍的应用,但在心理学领域中使用还为数不多,本研究拟对搜集到的大学生心理健康状况研究进行Meta分析,以期发现大学生心理健康的真实状况,为大学生心理健康教育工作提供科学的根据。
?1对象与方法?1.1文献检索? 在中国期刊网的中国期刊全文数据库和中国优秀博硕士论文数据库(CDMD以及维普数据中以“ SCL为检索词,共搜索到1979~2008年29年间的研究成果764篇(检索截至时间为2008 年4 月25 日),以“大学”或“大学生”或“高校”等为检索词进行二次检索,得到有关文献345篇;再以“心理健康”进行一级检索,然后以“大学”“大学生”“高校”等进行二级检索,检索到文献532篇,排除重复文献后共搜索到文献381 篇,对已查得文献进行文献追溯和手工检索,得到文献7 篇,共388 篇。
?1.2文献剔除?文献纳入标准:①调查对象为在校大学生;②调查工具为SCL-90;③报告了这个群体总的完整的SCL-90因子分数与标准差。
文献排除标准:①贫困大学生、独生子女、网瘾大学生等特殊群体大学生调查结果;②资料不完整,如没有被试数量,没有交代标准差等;③一批数据多篇论文或者重复发表的论文;④有明显错误而导致结果不可信的文献。
最后检索到1979~2008年间符合标准文献共214 篇,232 个样本,文献中样本容量最少的为30 个,样本最大为12357 人,包括华北、东北、华东、中南、西南、西北24 个省市共263775 个大学生被试。
Revised Standards for Quality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE 2.0)Table 2. Glossary of key terms used in SQUIRE 2.0. This Glossary provides the intended meaning of selected words and phrases as they are used in the SQUIRE 2.0 Guidelines. They may, and often do, have different meanings in other disciplines, situations, and settings. AssumptionsReasons for choosing the activities and tools used to bring about changes in healthcare services at the system level.ContextPhysical and sociocultural makeup of the local environment (for example, external environmental factors, organizational dynamics, collaboration, resources, leadership, and the like), and the interpretation of these factors (“sense-making”) by the healthcare delivery professionals, patients, and caregivers that can affect the effectiveness and generalizability of intervention(s).Ethical aspectsThe value of system-level initiatives relative to their potential for harm, burden, and cost to the stakeholders. Potential harms particularly associated with efforts to improve the quality, safety, and value of healthcare services include opportunity costs, invasion of privacy, and staff distress resulting from disclosure of poor performance.GeneralizabilityThe likelihood that the intervention(s)in a particular report would produce similar results in other settings, situations, or environments (also referred to as external validity).Healthcare improvementAny systematic effort intended to raise the quality, safety, and value of healthcare services, usually done at the system level. We encourage the use of this phrase rather than “quality improvement,” which often refers to more narrowly defined approaches.InferencesThe meaning of findings or data, as interpreted by the stakeholders in healthcare services –improvers, healthcare delivery professionals, and/or patients and familiesInitiativeA broad term that can refer to organization-wide programs, narrowly focused projects, or the details of specific interventions (for example, planning, execution, and assessment)Internal validityDemonstrable, credible evidence for efficacy (meaningful impact or change) resulting from introduction of a specific intervention into a particular healthcare system.Intervention(s)The specific activities and tools introduced into a healthcare system with the aim of changing its performance for the better. Complete description of an intervention includes its inputs, internal activities, and outputs (in the form of a logic model, for example), and the mechanism(s) by which these components are expected to produce changes in a system’s performance.Opportunity costsLoss of the ability to perform other tasks or meet other responsibilities resulting from the diversion of resources needed to introduce, test, or sustain a particular improvement initiativeProblemMeaningful disruption, failure, inadequacy, distress, confusion or other dysfunction in a healthcare service delivery system that adversely affects patients, staff, or the system as a whole, or that prevents care from reaching its full potentialProcessThe routines and other activities through which healthcare services are deliveredRationaleExplanation of why particular intervention(s)were chosen and why it was expected to work, be sustainable, and be replicable elsewhere.SystemsThe interrelated structures, people, processes, and activities that together create healthcare services for and with individual patients and populations. For example, systems exist from the personal self-care system of a patient, to the individual provider-patient dyad system, to the microsystem, to the macrosystem, and all the way to the market/social/insurance system. These levels are nested within each other.Theory or theoriesAny “reason-giving” account that asserts causal relationships between variables (causal theory) or that makes sense of an otherwise obscure process or situation (explanatory theory). Theories come in many forms, and serve different purposes in the phases of improvement work. It is important to be explicit and well-founded about any informal and formal theory (or theories) that are used.。

meta分析结构式模板prisma举行上一次FS线上沙龙的时候,有不少小伙伴问有没有meta学习的简易资料,应大家的要求,这次猴哥发一个meta分析的八股文结构模板~prisma 说明与描述条目一:标题条目二:结构式摘要条目三:理论基础条目四:目的条目五:方案和注册条目六:合格标准条目七:信息来源条目八:检索条目九:研究选择条目十:资料提取条目十一:资料条目条目十二:单个研究存在的偏倚条目十三:概括效应指标条目十四:综合的分析方法条目十五:研究偏倚条目十六:其他方法条目十七:研究选择条目十八:特征研究条目十九:研究内部偏倚条目二十:单个研究的结果条目二十一:结果的综合条目二十二:研究间的偏倚条目二十三:附加分析条目二十四:证据总结条目二十五:局限性条目二十六:结论条目二十七:资金今天就写到这里,请大家多多批评指正~(图片不够高清?发送 sunmeta1 到后台,获得ppt全文)META专栏主编猴哥:Freescience公众号meta分析栏目现任主编。
副主任医师,武汉大学肿瘤学博士,专注于胃肠道肿瘤分子生物学机制、系统评价/Meta分析、数据挖掘、临床统计研究。
科研路,不孤单!Freescience医学科研联盟全国火热招募ing50家高校及医院的小伙伴已经加入啦具体点这里想围观一篇SCI论文是怎样写成的吗?Freescience线上沙龙之SCI论文合作呼唤你具体点这里FS科研软件库,集合50+医学科研必备神器,现在统统打包分享,点这里还有freescience科研交流群。

㊃6163㊃C H I N E S EE V I D E N C E-B A S E D N U R S I N G O c t o b e r,2023V o l.9N o.20不同角度采集桡动脉血临床效果的M e t a赵亚丽,万蕊星,张海军*兰州大学第一医院(麻醉手术科),甘肃省生物治疗与再生医学重点实验室,甘肃730000C l i n i c a l e f f e c t s o f c o l l e c t i n g r a d i a l a r t e r y b l o o d f r o md i f f e r e n t a n g l e s:aM e t a-a n a l y s i sZ H A OY a l i,W A NR u i x i n g,Z H A N G H a i j u nT h eF i r s tH o s p i t a lo fL a n z h o u U n i v e r s i t y,K e y L a b o r a t o r y o fB i o t h e r a p y a n d R e g e n e r a t i v e M e d i c i n eo fG a n s u P r o v i n c e,G a n s u730000C h i n aC o r r e s p o n d i n g A u t h o r Z H A N G H a i j u n,E-m a i l:l d y y_h a i j u n z h a n g@l z u.e d u.c nA b s t r a c t O b j e c t i v e:T o s y s t e m a t i c a l l y e v a l u a t e t h e c l i n i c a l e f f e c t so f d i f f e r e n t a n g l e s i nc o l l e c t i n g r a d i a l a r t e r y b l o o do nt h e s u c c e s s r a t e o f o n e-t i m e p u n c t u r ea n dt h e i n c i d e n c eo f l o c a l c o n g e s t i o na n de c c h y m o s i s.M e t h o d s:C o m p a r et h ec l i n i c a l e f f e c t so fc o l l e c t i n g r a d i a l a r t e r y b l o o d f r o md i f f e r e n t a n g l e s i na r a n d o m i z e d c o n t r o l l e d t r i a lw e r e r e t r i e v e d f r o m P u b M e d,W e bo fS c i e n c e,t h eC o c h r a n e L i b r a r y,C N K I,W a n F a n g D a t a b a s e,a n dV I P.T h e r e t r i e v a l t i m ew a s f r o mJ a n u a r y2000t oM a r c h2022,a n d t h e r e f e r e n c e s i n c l u d e d i n t h e s t u d y w e r e r e t r o s p e c t i v e l y a n a l y z e d.T w o r e s e a r c h e r s i n d e p e n d e n t l y s c r e e n e d l i t e r a t u r e,e x t r a c t e dd a t a,a n d e v a l u a t e d q u a l i t y b a s e d o n i n c l u s i o na n de x c l u s i o nc r i t e r i a,a n dc o n d u c t e d M e t a-a n a l y s i su s i n g R e v M a n5.3s o f t w a r e.R e s u l t s:A t o t a lo f8r a n d o m i z e d c o n t r o l l e d t r i a l sw e r ei n c l u d e d,w i t hat o t a lo f1799p a t i e n t s.T h e M e t a-a n a l y s i sr e s u l t ss h o w e dt h a tc o m p a r e d w i t ht h eo b l i q u e p u n c t u r em e t h o d,t h ed i r e c t p u n c t u r e m e t h o d h a dah i g h e ro n e-t i m e p u n c t u r es u c c e s sr a t e,a n dt h ed i f f e r e n c e w a ss t a t i s t i c a l l y s i g n i f i c a n t(R R=0.89,95%C I0.81-0.98,P=0.02).T h e r ew a sn os t a t i s t i c a l l y s i g n i f i c a n td i f f e r e n c e i nt h e i n c i d e n c eo f l o c a lb l o o d s t a s i s a n de c c h y m o s i sb e t w e e n t h e o b l i q u en e e d l i n g m e t h o da n d t h e d i r e c t n e e d l i n g m e t h o d(R R=1.66,95%C I0.48-5.77,P=0.43).C o n c l u s i o n:C u r r e n t e v i d e n c e s u g g e s t s t h a t t h es u c c e s sr a t eo fo b l i q u e p u n c t u r e i s l o w e r t h a nt h a to fd i r e c t p u n c t u r e.T h e r ew a sn o s i g n i f i c a n t d i f f e r e n c e i n t h e i n c i d e n c e o f l o c a l b l o o d s t a s i s a n de c c h y m o s i sb e t w e e n t h e t w o g r o u p s o f p u n c t u r em e t h o d s.K e y w o r d s a r t e r i a l p u n c t u r e;o b l i q u e p u n c t u r e;d i r e c t p u n c t u r e;t h e s u c c e s s r a t e o f o n e-t i m e p u n c t u r e;b l o o d s t a s i s;e c h y m o s i s;s y s t e m e v a l u a t i o n;M e t a-a n a l y s i s;r a n d o m i z e d c o n t r o l l e d t r i a l s;e v i d e n c e-b a s e dn u r s i n g摘要目的:系统评价不同角度采集桡动脉血一次穿刺成功率㊁局部淤血瘀斑发生率的临床效果㊂方法:计算机检索P u b M e d㊁W e b o f S c i e n c e㊁t h eC o c h r a n eL i b r a r y㊁中国知网㊁万方数据库和维普数据库,纳入比较不同角度采集桡动脉血的临床效果的随机对照试验,检索时限为2000年1月 2022年3月,并追溯纳入研究的参考文献㊂由2名研究者按照纳入与排除标准独立筛选文献㊁提取资料和质量评价,采用R e v M a n5.3软件进行M e t a分析㊂结果:共纳入8项随机对照试验,共计1799例病人㊂M e t a分析结果显示,与采用斜刺法相比,直刺法一次穿刺成功率较高,差异有统计学意义[R R=0.89,95%C I(0.81,0.98),P=0.02];采用斜刺法比直刺法局部瘀血㊁瘀斑发生率差异无统计学意义[R R=1.66,95%C I(0.48,5.77),P=0.43]㊂结论:现有证据表明,斜刺法一次穿刺成功率低于直刺法;两组方法穿刺的局部瘀血㊁瘀斑发生率差异无统计学意义㊂关键词动脉穿刺;斜刺法;直刺法;一次穿刺成功率;瘀血;瘀斑;系统评价;M e t a分析;随机对照试验;循证护理d o i:10.12102/j.i s s n.2095-8668.2023.20.002基金项目甘肃省自然科学基金项目,编号:22J R11R A021;甘肃省卫生行业项目,编号:G S W S K Y2022-11作者简介赵亚丽,护士,本科*通讯作者张海军,E-m a i l:l d y y_h a i j u n z h a n g@l z u.e d u.c n引用信息赵亚丽,万蕊星,张海军.不同角度采集桡动脉血临床效果的M e t a分析[J].循证护理,2023,9(20):3616-3620.Copyright©博看网. All Rights Reserved.动脉穿刺采血是临床诊疗过程中的重要手段,在麻醉手术过程及急危重症病人的管理中具有不可忽视的地位[1-2]㊂桡动脉因位置表浅㊁暴露少㊁病人配合度较高㊁穿刺后易于压迫止血等优点,是临床工作中有创动脉血压监测和血气分析较常选择的动脉[3]㊂当前临床上采集桡动脉血常采取斜刺法和直刺法两种方式,但是对于两种采血方式哪种是最佳选择且对病人的危害最小目前还是存在很多争议㊂有研究发现:斜刺法比直刺法更有利于儿童病人桡动脉的穿刺采血[4];直刺法采集桡动脉血的一次穿刺成功率高㊁局部瘀血瘀斑发生率低[5-10];但也有研究表明,直刺法与斜刺法采集桡动脉血时一次穿刺成功率差异无统计学意义[11]㊂检索国内外多个数据库,发现国内外针对动脉采血和动脉穿刺领域的研究主要聚焦于临床治疗和检验方面,对于不同采血方法比较方面的研究十分匮乏,尤其是国外对于该方面的研究尚未发现文献报道,而国内目前现有文献针对不同角度穿刺桡动脉血的比较实验中所采用的结局指标都不尽相同,对采取桡动脉血的最佳方法各执一词,难以对两种采血方式进行综合比较㊂另一方面,国内针对该领域的研究进展㊁荟萃分析和系统评价更是寥寥无几㊂因此,本研究采用M e t a 分析评价斜刺法和直刺法采集桡动脉血的临床效果,选取采血一次穿刺成功率和局部瘀血㊁瘀斑发生率作为结局指标,旨在为临床上采集桡动脉血的最佳方法提供科学依据㊂1资料与方法1.1纳入标准1.1.1研究设计随机对照试验(r a n d o m i z e d c o n t r o l l e d t r i a l, R C T),无论是否采用盲法㊂1.1.2研究对象意识清醒,能够进行正常的沟通交流;穿刺部位皮肤正常;对本研究内容了解且自愿签署知情同意书;经医院伦理委员会批准㊂1.1.3干预措施试验组采用斜刺法采集桡动脉血;对照组采用直刺法采集桡动脉血㊂1.1.4结局指标一次穿刺成功率;局部瘀血㊁瘀斑发生率㊂1.2排除标准患有血液系统疾病㊁血管壁功能异常㊁血小板异常㊁凝血功能异常的病人;重复发表的文献㊂1.3检索策略计算机检索P u b M e d㊁W e b o f S c i e n c e㊁t h e C o c h r a n eL i b r a r y㊁中国知网㊁万方数据库和维普数据库,全面收集不同角度穿刺桡动脉的临床效果的随机对照试验,检索时限为2000年1月 2022年3月,并追溯纳入研究的参考文献㊂以P u b M e d为例英文检索式:("r a d i a l a r t e r y b l o o d"O R"a r t e r i a l b l o o d c o l l e c t i o n"O R"a r t e r i o p u n c t u r e")A N D("n e e d l e e n t r y a n g l e"O R"p u n c t u r ea n g l e")A N D("a r t e r i a l p u n c t u r e"O R"r a d i a l a r t e r i a l p u n c t u r e");中文检索式: ( 桡动脉血 O R 动脉采血 O R 动脉穿刺 )A N D ( 进针角度 O R 穿刺角度 O R 不同角度 O R 不同方法 )㊂1.4纳入研究的方法学质量评价纳入研究方法学质量评价采用C o c h r a n e H a n d b o o k5.0所推荐的 偏倚风险评估工具 ,由2名研究者独立评估纳入研究偏倚的风险性㊂内容包括: 1)随机分配方法;2)隐蔽分组;3)盲法;4)结果数据的完整性;5)选择性报告研究结果;6)其他偏倚来源㊂所有评价条目根据研究具体情况按 是 否 不清楚 进行评价㊂1.5统计学方法采用R e v M a n5.3软件进行统计分析㊂定量资料采用均方差(M D)或标准化均方差(S M D)及其95%置信区间(C I)描述,定性资料采用相对危险度(R R)或比值比(O R)及95%C I为疗效分析统计量㊂各纳入研究结果间的异质性检验采用χ2检验㊂当各研究结果间有同质性(Pȡ0.05且I2<50%)时,采用固定效应模型进行M e t a分析㊂如各研究结果间异质性较大(P< 0.05且I2ȡ50%),分析其异质性来源,对可能导致异质性的因素进行亚组分析,若研究结果间存在统计学异质性而无临床异质性,或差异无统计学意义时,可采用随机效应模式进行M e t a分析;如两组间异质性过大或无法找寻数据来源时,采用描述性分析㊂当纳入研究数>9个时,采用漏斗图分析是否存在发表偏倚㊂2结果2.1文献检索结果与纳入研究的基本特征初检获得相关文献共182篇,依据纳入和排除标准逐层筛选后,最终纳入8篇随机对照试验研究[4-11],文献筛选流程及结果见图1,纳入研究的基本特征见表1㊂㊃7163㊃循证护理2023年10月第9卷第20期(总第112期)Copyright©博看网. All Rights Reserved.图1 文献筛选流程及结果表1 纳入研究的基本特征纳入研究年龄(岁) 样本量(例)试验组对照组干预措施试验组对照组一次穿刺成功(例)试验组对照组局部淤血㊁瘀斑(例)试验组对照组任秋红[5]201459~87514445~60ʎ斜刺法直刺法3941和欢[6]201738~82747445~60ʎ斜刺法直刺法5467132张格格等[4]20211~11505030~45ʎ斜刺法直刺法464237张燕[7]202042~836060斜刺法直刺法4656王安祥[8]201813~6925025030~45ʎ斜刺法直刺法200226246贺敬等[9]201540~82686840~60ʎ斜刺法直刺法5363113赵亚娟等[10]201921~69909030~45ʎ斜刺法直刺法6582高林玲等[11]200941~6426026045~60ʎ斜刺法直刺法2412318222.2 纳入研究的偏倚风险评估结果(见图2)图2 偏倚风险评估比例图2.3 M e t a 分析结果2.3.1 一次穿刺成功率针对2种角度采集桡动脉血一次穿刺成功率,纳入8项研究[4-11],共计1799例病人,M e t a 分析结果显示,斜刺法采集桡动脉血的一次穿刺成功率低于直刺法[R R=0.89,95%C I (0.81,0.98),P =0.02]㊂见图3㊂㊃8163㊃C H I N E S EE V I D E N C E -B A S E D N U R S I N G O c t o b e r ,2023V o l .9N o .20Copyright ©博看网. All Rights Reserved.图3两组采集桡动脉血一次穿刺成功率比较的M e t a分析2.3.2局部淤血㊁瘀斑发生率针对2种角度采集桡动脉血局部淤血㊁瘀斑的发生率,纳入5项研究[4,6,8-9,11],共计1404例病人,M e t a 分析结果显示,斜刺法与直刺法相比,局部瘀血㊁瘀斑发生率差异无统计学意义[R R=1.66,95%C I(0.48, 5.77)]㊂见图4㊂图4两组采集桡动脉血局部淤血、瘀斑发生率比较的M e t a分析3讨论动脉采血在临床工作中是一项非常关键的操作,尤其在急救过程中更是医护人员必须掌握的重要技能之一,桡动脉穿刺采血是获取动脉血样用于血气分析的优选方法,从血气分析可以快速获得病人的氧分压㊁二氧化碳分压㊁p H值㊁血红蛋白及离子平衡等重要内环境信息,在病人的病情评估和诊疗过程中具有重要的价值[1]㊂一般情况下,麻醉手术及重症病人监护过程中,进行动脉血压监测时也常常选择桡动脉进行穿刺,因为其简便易行而且手部有双重的血液供应,并发症的发生率相对较低㊂然而如果动脉穿刺采血或置管不当,可能会导致感染㊁血肿㊁血管痉挛和神经损伤等并发症,研究表明超声引导可以提高动脉插管的成功率,并能减少相关并发症的发生[12],超声引导下血管穿刺或许是未来的趋势㊂本研究探讨斜刺法和直刺法两种穿刺角度对采集桡动脉血一次穿刺成功率㊁局部瘀血与瘀斑发生率的影响,根据临床效果分为两个结局指标进行分析㊂1)研究分析不同角度采集桡动脉血的一次穿刺成功率,共纳入8项研究,其中6项研究[5-10]结果显示差异有统计学意义,2项研究[4,11]结果显示差异无统计学意义,而M e t a分析显示直刺法比斜刺法采集桡动脉血的一次穿刺成功率更高㊂2)研究分析不同角度采集桡动脉血对局部瘀血㊁瘀斑发生率的影响,纳入的4项研究[6,8-9,11]结果均显示差异有统计学意义,而M e t a分析显示斜刺法比直刺法穿刺的局部瘀血瘀斑发生率差异无统计学意义㊂垂直穿刺法根据桡动脉的解剖特点进行准确定位,利用食指的触觉感知桡动脉的搏动,进针时可缩短进针距离,减少穿刺进入血管的时间,一方面避免了反复多次穿刺血管造成的血管和组织损伤,另一方面,避免了针头刺入血管旁引起的血管痉挛,增加了穿刺的成功率[13]㊂而且,垂直穿刺进针时针头与皮肤接触面积小,对穿刺点局部组织损伤的程度较小,致痛物质释放也少,疼痛相对较轻,并且垂直进针能够直接㊁快速进入皮下,对皮下神经纤维的刺激相对也会减少,缩短了伤害性刺激的速度和时间,可有效减轻疼痛[14]㊂采用斜角穿刺法时护士的左手只能固定桡动脉的一端,进针时会刺激到血管导致血管游走,从而增加了穿刺失败率,当一次穿刺失败时,护士需要在皮下反复调整㊃9163㊃循证护理2023年10月第9卷第20期(总第112期)Copyright©博看网. All Rights Reserved.进针角度和针尖方向,不仅增加了局部瘀血㊁瘀斑的发生率,而且由于桡动脉位置较静脉深,靠近神经㊁肌腱㊁穴位,穿刺时疼痛明显,对于很多对疼痛敏感的病人难以配合,使病人的体验感明显变差[15]㊂在临床工作中,护理人员针对采集动脉血的方法如何做出最佳选择,不仅需要掌握不同穿刺角度的操作技术,了解2种方法各自的优缺点,而且更要重视方法的选择因人而异㊂比如在实际穿刺过程中需要判断病人血管的深浅,一般来说病人越胖㊁血管越深,进针角度越大,所以直刺法相对于斜刺法是一种较好的用于孕妇桡动脉穿刺采集动脉血的方法,适合产科临床护理应用[16]㊂此外,闵腊英等[17]也认为垂直穿刺法不仅适用于桡动脉穿刺,而且在足背动脉穿刺方面也是不错的选择,足背动脉位置表浅,皮下脂肪分布较少,采用垂直法穿刺足背动脉不仅穿刺成功率高,而且拔针后能准确按压穿刺点,不易发生皮下淤血㊁瘀斑㊂桡动脉穿刺采血是一项有创操作,除非病人处于麻醉手术过程等特殊状态,临床上桡动脉采血时一般不常规使用局部麻醉或其他镇痛方法,据报道,有70%的病人希望在动脉穿刺时给予镇痛,但常常得不到满足[18]㊂由于不同病人对于疼痛的敏感程度会有较大差别,疼痛和应激或许同样是影响穿刺成功率的重要因素,所以需要引起操作者的关注㊂当然,穿刺是否成功和疼痛还有可能与病人的情绪紧张有关,所以操作者在穿刺之前一定要做好解释工作,消除病人的顾虑,征得病人的配合,并嘱咐病人放松心情,避免直视穿刺过程,减轻紧张感,以便在穿刺过程中减轻疼痛感,保证穿刺成功率㊂4小结综上所述,不同角度采集桡动脉血时,垂直穿刺法相较于斜角穿刺法一次穿刺成功率更高,而两者对于穿刺部位局部淤血㊁瘀斑发生率差异无统计学意义㊂比较遗憾的是,本研究中只有4项研究进行了疼痛程度的评估,且每篇研究中对疼痛程度的评估标准各不相同,故不能对疼痛程度的临床效果进行系统评价㊂且由于本系统评价纳入研究均为随机对照试验研究,其中绝大部分研究未能准确判断分配隐藏情况,也无法采用盲法,而且研究包含成人和儿童病人,但儿童与成人的解剖结构不完全相同,且在采集过程中,患儿配合度低,容易对研究结果产生影响,造成一定程度的偏差㊂所以,针对该领域的研究希望未来采用更为严谨的研究设计开展,从而获得更为科学的研究结果,为临床桡动脉穿刺的方法选择提供最佳依据㊂参考文献:[1] D E VSP,H I L L M E R M D,F E R R IM.A r t e r i a l p u n c t u r e f o r b l o o d g a sa n a l y s i s[J].N e wE n g l a n d J o u r n a l o fM e d i c i n e,2011,364(5):e7.[2]J E N S E N P R,MA R K E W I T Z B A.I m p r o v e d s u c c e s s r a t e o fa r t e r i a l p u n c t u r ef o rb l o o d g a sa n a l y s i st h r o u g hs t a n d a r d i z a t i o n[J].L a b o r a t o r y M e d i c i n e,2018,49(2):175-178.[3]殷梦兰,刘宣言,黄劼,等.一种动脉穿刺针穿刺角度导向装置的设计与应用[J].中国中西医结合急救杂志,2021,38(5):631-633.[4]张格格,王玲玲,郭娜娜.不同进针角度对桡动脉穿刺成功率的影响分析[J].临床研究,2021,29(1):181-183.[5]任秋红.B D预设型动脉采血器经桡动脉采血两种不同进针方法的效果比较[J].中国民族民间医药,2014,23(3):96-99. [6]和欢.桡动脉采血进针角度与一次成功率㊁疼痛之间关系的探讨[J].锦州医科大学学报,2017,38(2):62-64.[7]张燕.不同方法采集桡动脉血穿刺成功率的临床效果观察[J].实用临床护理学电子杂志,2020,5(35):64.[8]王安祥.桡动脉采血进针角度的比较[J].健康前沿,2018,27(10):282-283.[9]贺敬,蒋慧娟,孙哲.一指定位垂直快速进针法在桡动脉采血中的应用[J].护理研究,2015,29(24):3027-3028.[10]赵亚娟,孙海宁.桡动脉血气分析血液采集中应用一指垂直采血法对患者疼痛程度的影响[J].中国民康医学,2019,31(23):111-112.[11]高林玲,任小红.两种桡动脉采血穿刺方法的效果比较[J].长治医学院学报,2009,23(5):377-378.[12] B A IB,T I A N Y,Z HA N G Y L,e t a l.D y n a m i c n e e d l e t i pp o s i t i o n i n g v e r s u st h ea n g l e-d i s t a n c et e c h n i q u ef o ru l t r a s o u n d-g u i d e d r a d i a l a r t e r y c a n n u l a t i o n i n a d u l t s:a r a n d o m i z e dc o n t r o l l ed t r i a l[J].B M CA ne s t h e s i o l o g y,2020,20(1):231.[13]陈丹.桡动脉穿刺采血中进针角度的探讨[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2010,19(32):4206-4207.[14]张亚军,何瑛.腕横纹定位垂直进针法在骨科老年患者桡动脉采血中的实践研究[J].临床医学研究与实践,2016,1(23):157-158.[15]潘海燕,颜波儿.一指垂直采血法在桡动脉血气分析标本采集中的应用[J].护理学报,2013,20(6):47-48.[16]杨月,陆进.孕妇桡动脉穿刺的临床应用分析[J].赣南医学院学报,2016,36(2):289-291.[17]闵腊英,聂成慧,胡静.足背动脉采血两种不同进针角度效果研究[J].内蒙古中医药,2013,32(10):42-43.[18] G O N E L L A S,C L A R I M,C O N T I A,e t a l.I n t e r v e n t i o n st or e d u c ea r t e r i a l p u n c t u r e-r e l a t e d p a i n:as y s t e m a t i cr e v i e w a n dM e t a-a n a l y s i s[J].I n t e r n a t i o n a l J o u r n a l o fN u r s i n g S t u d i e s,2022, 126:104131.(收稿日期:2023-03-08;修回日期:2023-10-09)(本文编辑孙玉梅)㊃0263㊃C H I N E S EE V I D E N C E-B A S E D N U R S I N G O c t o b e r,2023V o l.9N o.20Copyright©博看网. All Rights Reserved.。

观察性研究Meta分析的NOS量表Adjusted Effect Estimates for CoronaryHeart Disease(All Events) (HRT: Estrogen Ever Use)Case-Control Studies Selection Comparability Exposure Adjusted Effect Estimates for Coronary Heart Disease(All Events) (HRT: Estrogen + Progestin Ever Use)Case-Control Studies Selection Comparability Exposure Adjusted Effect Estimates for Coronary Heart Disease(All Events) (HRT: Estrogen Current Use) Cohort Studies Selection Comparability Outcome Adjusted EffectEstimates for Coronary Heart Disease(All Events) (HRT: Estrogen Ever Use)Cohort Studies Selection Comparability Outcome Current Development: Validity Face/content validity Criterion validity compare to more comprehensive scales compare to expert judgement Construct validity external criteria ‘convergent validity’‘divergent validity’internal structure ‘factorial validity’Current Development: Reliability Inter-rater reliability Intra-rater reliability Future Development: Scoring Identify threshold score disti nguishing between ‘good’and ‘poor’quality studies The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomized Studies in Meta-Analysis NOS Quality Assessment Scales: Case-control studies Cohortstudies Manual for NOS Scales The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomized Studies in Meta-Analysis G. Wells, B. Shea, D. O’Connell, J. Robertson, J. Peterson, V. Welch, M.Losos, P. Tugwell Development Applications Current Developments Development: Item Selection Newcastle quality assessment form Ottawa comprehensive list Panel review Critical review by experts Development: Grouping Items Cohort studies Selection of cohorts Comparability of cohorts Assessment of outcome Case-Control studies Selection of case and controls Comparability of cases and controls Ascertainment of exposure Development: Identifying Items Identify ‘high’quality choices with a ‘star’A imum of one ‘star’for each h item within the ‘Selection’and ‘Exposure/Outcome’categories; imum of two ‘stars’for‘Comparability’Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale:Case-Control Studies Selection (4) Comparability (1) Exposure (3) A study can be awarded a imum of one star for each numbered item within the Selection and Exposure categories. A imum of two stars can be given for Comparability 1. Is the case definition adequate? a) yes, with independent validation b) yes, eg record linkage or based on self reports c) no description 2. Representativeness of the cases a) consecutive or obviously representative series of cases b) potential for selection biases or not stated 3. Selection of Controls a) community controls b) hospital controls c) no description 4. Definition of Controls a) no history of disease (endpoint) b) no description of source Selection >1 person/record/time/process to extract information, or reference to primary record source such as x-rays or medical/hospital records e.g. ICDcodes in database or self-report with no reference to primary record or no description Comparability 1. Comparability of cases and controls on the basis of the design or analysis a) study controls for ___________ (select the most important factor) b) study controls for any additional factor (This criteria could be modified to indicate specific control for a second important factor.) Exposure 1. Ascertainment of exposure a) secure record (eg surgical records) b) structured interview where blind to case/control status c) interview not blinded to case/control status d) written self report or medical record only e) no description 2. Same method of ascertainment for cases and controls a) yes b) no 3. Non-Response Rate a) same rate for both groups b) non respondents described c) rate different and no designation Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale: Cohort Studies Selection (4) Comparability (1) Outcome (3) A study can be awarded a imum of one star for each numbered item within the Selection and outcome categories. A imum of two stars can be given for Comparability Selection 1. Representativeness of the exposed cohort a) truly representative of the average ___________ (describe) in the community b) somewhat representative of the average ___________ in the community c) selected group of users eg nurses, volunteers d) no description of the derivation of the cohort 2. Selection of the non exposed cohort a) drawn from the same community as the exposed cohort b) drawn from a different source c) no description of the derivation of the non exposed cohort 3. Ascertainment of exposure to implants a) secure record (eg surgical records) b) structured interview c) written self report d) no description 4. Demonstration that outcome of interest was not present atstart of study a) yes b) no In the case of mortality studies, outcome of interest is still the presence of a disease/ incident, rather than death; that is a statement of no history of disease or incident earns a star Comparability 1. Comparability of cohorts on the basis of the design or analysis a) study controls for ___________ (select the most important factor) b) study controls for any additional factor (This criteria could be modified to indicate specific control for a second important factor.) Outcome 1. Assessment of outcome a) independent blind assessment b) record linkage c) self report d) no description 2. Was follow up long enough for outcomes to occur a) yes (select an adequate follow up period for outcome of interest) b) no 3. Adequacy of follow up of cohorts a) complete follow up - all subjects accounted for b) subjects lost to follow up unlikely to introduce bias - small number lost - > ___ % (select an adequate %) follow up, or description of those lost) c) follow up rate < ___% (select an adequate %) and no description of those lost d) no statement Applications: Assess quality of nonrandomized studies Incorporate assessments in interpretation of meta-analytic results Design, content and ease of use Long Term Hormone Replacement Therapy and Coronary Heart Disease Events Clearly formulated question Comprehensive data search Unbiased selection and abstraction process Critical appraisal of data Synthesis of data Perform sensitivity and subgroup analyses if appropriate and possible Prepare a structured report Steps of a Cochrane Systematic Review Objective Is there a relationship between hormone replacement therapy and the incidence of coronary heart disease in postmenopausal women Inclusion Criteria Types of studies case-control,cohort or cross-sectional studies Population postmenopausal womenIntervention women exposed to hormone replacement therapy (estrogen orestrogen + progesterone) ever, current, past Outcomes coronary heartdisease (events) fatal, non-fatal, both Clearly formulated questionComprehensive data search Unbiased selection and abstraction processCritical appraisal of data Synthesis of data Perform sensitivity andsubgroup analyses if appropriate and possible Prepare a structured reportSteps of a Cochrane Systematic Review Search Strategy Electronic Search of: MEDLINE (1966 to May 2000) Current Contents (to May 2000)。
