核燃料管理与优化-2 PPT
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:9.42 MB
- 文档页数:152






核污染治理ppt
这是一个关于核污染治理的PPT演示文稿。
幻灯片1:标题
- 核污染治理
幻灯片2:介绍
- 核污染是指核能源产生和使用过程中释放出的有害物质污染环境的问题。
- 核污染对健康和环境造成严重威胁,需要采取有效措施进行治理。
幻灯片3:影响
- 核污染对生态系统和人类健康的影响很大。
- 可能导致疾病发生、环境恶化以及物种灭绝等问题。
幻灯片4:核污染种类
- 辐射污染:核能源的释放会产生辐射,对人体和环境造成危害。
- 核废料污染:核能产生的废料需要妥善处理,否则会造成严重的污染问题。
幻灯片5:核污染治理方法
- 废物处理:开展废物处理工作,确保核能产生的废料得到合理处置,减少对环境的影响。
- 辐射防护:加强辐射防护工作,减少辐射对人体的危害。
- 安全监管:加强核能的安全监管,预防事故的发生,并及时
处理事故后果。
幻灯片6:核污染治理的挑战
- 技术难题:核污染治理需要先进的技术手段和设备。
- 资金问题:核能治理需要大量投入资金,对于一些发展中国家来说存在困难。
- 社会认知:大众对核能治理的认知程度不同,需要加强宣传和教育。
幻灯片7:案例分析
- 核事故后的核污染治理:福岛核事故后的核污染治理工作。
- 核武器开发及废弃物处理:核武器开发产生的核污染及其处理方法。
幻灯片8:结论
- 核污染治理是一个复杂且需要长期关注和努力的任务。
- 需要加强国际合作,共同应对核污染问题。
幻灯片9:致谢
- 感谢大家的聆听。
幻灯片10:提问环节
- 欢迎大家提问和讨论。

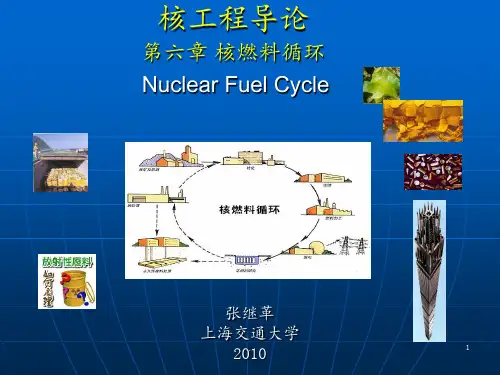
核燃料循环技术的优化与效率提升Optimization and Efficiency Enhancement of Nuclear FuelCycle TechnologyThe nuclear fuel cycle, an intricate process involving the mining, refining, use, and disposal of radioactive materials, stands at the heart of sustainable energy production. As the world increasingly turns to nuclear power as a clean and efficient source of energy, optimizing this cycle becomes paramount for maximizing efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.Mining operations form the initial stage in the nuclear fuel cycle. Here, precision and technology converge to extract uranium ore with minimal waste. Advanced geological surveys identify rich deposits, while modern drilling techniques ensure only targeted extraction. This meticulous approach not only enhances yields but also reduces the need for extensive processing later in the cycle. Refining, or milling, transforms raw uranium into usable fuel. Refinery operators must strike a delicate balance between purifying uranium enough to be viable yet retaining enough impurities to prevent criticality accidents. The introduction of automated systems has revolutionized this phase, enhancing purity levels while drastically reducing human error.Once refined, uranium is loaded into reactors where it undergoes fission to generate heat – ultimately convertingwater into steam that powers turbines to generate electricity. Reactor design plays a pivotal role in efficiency; advanced reactor technologies like molten salt reactors promise higher conversion rates and reduced radioactive waste.Spent fuel management poses unique challenges. Radioactive byproducts require careful handling to safeguard public health and protect ecosystems. Advanced reprocessing techniques allow the recovery of unused fissile material from spent fuel, extending its useful life while reducing waste volume. Storage solutions are being continually innovated to provide long-term safety without compromising space utilization.Finally, disposing of high-level radioactive waste remains a pressing issue. Deep geologic repositories offer one potential solution, safely isolating waste far below Earth’s surface. Ongoing research explores innovative materials and methods to further enhance containment integrity over millennia.In conclusion, optimizing the nuclear fuel cycle requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing advancements in mining, refinement, reactor design, spent fuel management, and waste disposal. By harnessing technological innovation and adopting best practices across all stages of the cycle, we can achieve greater efficiencies while safeguarding our planet's future.。

核反应堆燃料管理:对整个核燃料循环提出安全经济的管理策略堆前管理:核燃料的勘探和制造堆内燃料管理:反应堆运行期间的管理堆后管理:燃烧后的乏燃料的处理管理核燃料转换:通过中子俘获,将可裂变核素转换成易裂变核素转换比(CR):反应堆中每消耗一个易裂变材料原子所产生新的易裂变材料的原子数。
剩余反应性:除去控制毒物,反应堆所具有的初始反应性循环长度:一次装料后,反应堆满功率运行的时间换料周期:反应堆两次停堆换料之间的时间间隔燃耗深度:装入堆芯的单位质量燃料所发出的能量卸料燃耗深度:从堆芯中卸除的燃料所达到的燃耗深度初始循环:反应堆首次启动运行的第一个循环过渡循环:从第二循环开始一直延续到平衡循环为止的循环平衡循环:每个循环的性能参数都保持相同扰动循环:由于燃料棒破损等原因导致平衡循环被破坏,直至新的平衡循环建立前所有循环。
平均卸料燃耗:燃料循环结束后,将要从堆芯中卸掉的燃料组件的末期平均燃耗值。
三步法:将整个种子学计算分为栅元计算,组件计算和堆芯计算两步法:直接由栅元计算到堆芯计算栅元:一般是由燃料芯块,包壳和慢化剂构成的非均匀系统非燃料栅元:常规反应堆中除了燃料栅元以为的其他各种栅元,包括控制棒、可燃毒物、测量导管水洞等栅元单通道模型:将冷却剂通道等效成水力当量直径为De的圆管通道,并对该通道求解质量守恒,能量守恒以及状态方程咬量:限制主调节棒组的最小插入深度的位置慢化剂温度系数:慢化剂平均温度每变化1°C引起的堆芯反应性变化Doppler功率系数:功率每变化额定功率的1%时由于Doppler 效应引起的反应性变化微分硼价值:堆芯单位硼浓度变化引起的反应性变化落棒事故:功率运行时一束或几束控制棒落入堆芯引起功率畸变的瞬态事故提棒事故:在次临界状态和功率运行状态下一束或几束控制棒失控抽搐的事故堆芯换料优化:通过寻求满足约束条件的最优布料方案和可燃毒物布置方案,来达到最安全或最经济的目标。
任务:在多循环燃料管理所确定的燃料管理策略下,在确保核电厂安全运行的前提下,寻求堆内燃料组件和可燃毒物的最优空间布置,以是核燃料循环能量成本最小。