第三章国际市场营销双语
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:377.50 KB
- 文档页数:26

《国际市场营销(双语)》课程标准表1 课程基本信息1.1 课程定位与作用1.1.1 课程的定位本课程为双语课程,属于跨境电子商务(普高)专业核心课程,旨在培养学生跨境电商相关的专业核心能力。
跨境电商人才需求表明企业急需具有一定英语应用能力、营销推广能力的运营人才。
本课程将通过“做中学,学中做”,利用双语教学模式,培养学生跨境电商营销与推广的实践能力、创新能力、协作与沟通能力等,同时提高学生国际化素养。
1.1.2 课程的地位与作用国际市场营销是一门双语课程,是跨境电子商务专业核心课。
本专业对双语课程的学分提出了一定要求,本课程是归属国际贸易实务专业的唯一一门双语课程,因此具有重要地位。
本课程的开设是为了培养适应跨境电子商务和网络经济发展需要的、应用型的、高层次的专业人才为目标的。
本课程根据跨境电商营销岗位的工作任务及能力要求设计教学项目,要求学生熟练地、系统地掌握跨境电商营销推广的工作内容和方法。
在教学过程中,向学生完整介绍跨境电商营销的知识体系与操作方法;同时,在实践过程中,训练学生开展各项跨境电商网络营销活动,培养学生成为具有国际市场调研分析能力和跨境电商营销推广能力的综合型人才,为学生将来的工作和创业打下坚实的基础。
符合国际贸易实务专业人才培养目标和专业相关技术领域岗位任职要求,对在培养学生具备处理国际贸易市场营销尤其是互联网+外贸背景下国际市场营销与推广工作的实践能力、创新能力、协作与沟通能力等方面有明显的支撑作用。
1.1.3 与其他课程的关系本课程针对大二学生开设,前期课程主要包括互联网+外贸实务、跨境电商实务、跨境电商应用英语等专业核心课,这些课程是国际市场营销双语课程顺利开展的基础。
保证学生英语知识与英语应用技能达到一定水平,双语教学的质量才能得到保障;后续课程包括国际贸易综合实训(POCIB+)、跨境电商模拟软件实训、品牌策划与推广等,学生还可参加跨境电商项目运营(基地/园区)等实践项目,本课程将为这些课程的开展提供基础与准备。

国际市场营销双语教学教案第一章:国际市场营销概述1.1 教学目标了解国际市场营销的定义和重要性掌握国际市场营销的基本概念和原则理解国际市场营销的环境和趋势1.2 教学内容国际市场营销的定义和重要性国际市场营销的基本概念和原则国际市场营销的环境和趋势1.3 教学方法讲授:讲解国际市场营销的定义和重要性,介绍基本概念和原则案例分析:分析国际市场营销的成功案例,让学生更好地理解国际市场营销的应用1.4 教学评估小组讨论:学生分组讨论国际市场营销的成功案例,分享自己的观点和经验课堂测试:设计相关的选择题和简答题,测试学生对国际市场营销的基本概念和原则的理解第二章:国际市场营销环境分析2.1 教学目标了解国际市场营销环境的组成和影响因素掌握PESTEL分析工具,对国际市场营销环境进行分析了解国际市场营销环境的发展趋势2.2 教学内容国际市场营销环境的组成和影响因素PESTEL分析工具的介绍和应用国际市场营销环境的发展趋势2.3 教学方法讲授:讲解国际市场营销环境的组成和影响因素,介绍PESTEL分析工具小组讨论:学生分组讨论国际市场营销环境的案例,运用PESTEL分析工具进行分析2.4 教学评估小组报告:学生分组进行报告,分享他们对国际市场营销环境案例的分析结果课堂测试:设计相关的问题,测试学生对PESTEL分析工具的应用和国际市场营销环境的发展趋势的理解第三章:国际市场营销策略3.1 教学目标了解国际市场营销策略的类型和选择掌握国际市场营销策略的基本原则和步骤了解国际市场营销策略的成功案例3.2 教学内容国际市场营销策略的类型和选择国际市场营销策略的基本原则和步骤国际市场营销策略的成功案例3.3 教学方法讲授:讲解国际市场营销策略的类型和选择,介绍基本原则和步骤案例分析:分析国际市场营销策略的成功案例,让学生更好地理解策略的应用3.4 教学评估小组讨论:学生分组讨论国际市场营销策略的成功案例,分享自己的观点和经验课堂测试:设计相关的问题,测试学生对国际市场营销策略的理解和应用能力第四章:国际市场营销渠道和物流4.1 教学目标了解国际市场营销渠道的类型和功能掌握国际市场营销渠道的选择和管理了解国际市场营销物流的流程和重要性4.2 教学内容国际市场营销渠道的类型和功能国际市场营销渠道的选择和管理国际市场营销物流的流程和重要性4.3 教学方法讲授:讲解国际市场营销渠道的类型和功能,介绍选择和管理的方法案例分析:分析国际市场营销渠道和物流的成功案例,让学生更好地理解应用4.4 教学评估小组讨论:学生分组讨论国际市场营销渠道和物流的成功案例,分享自己的观点和经验课堂测试:设计相关的问题,测试学生对国际市场营销渠道和物流的理解和应用能力第五章:国际市场营销推广和沟通5.1 教学目标了解国际市场营销推广的工具和策略掌握国际市场营销推广的基本原则和步骤了解国际市场营销沟通的重要性和方法5.2 教学内容国际市场营销推广的工具和策略国际市场营销推广的基本原则和步骤国际市场营销沟通的重要性和方法5.3 教学方法讲授:讲解国际市场营销推广的工具和策略,介绍基本原则和步骤案例分析:分析国际市场营销推广和沟通的成功案例,让学生更好地理解应用5.4 教学评估小组讨论:学生分组讨论国际市场营销推广和沟通的成功案例,分享自己的观点和经验课堂测试:设计相关的问题,测试学生对国际市场营销推广和沟通的理解和应用能力第六章:国际市场营销文化差异与适应6.1 教学目标了解不同文化对国际市场营销的影响掌握跨文化沟通的原则和策略了解如何适应不同文化的市场营销策略6.2 教学内容不同文化对国际市场营销的影响跨文化沟通的原则和策略适应不同文化的市场营销策略6.3 教学方法讲授:讲解不同文化对国际市场营销的影响,介绍跨文化沟通的原则和策略小组讨论:学生分组讨论文化差异对国际市场营销的影响,分享跨文化沟通的实践经验6.4 教学评估小组报告:学生分组进行报告,分享他们对文化差异对国际市场营销的影响的理解和跨文化沟通的实践经验课堂测试:设计相关问题,测试学生对不同文化对国际市场营销的影响和适应不同文化的市场营销策略的理解第七章:国际市场营销法律、伦理和社会责任7.1 教学目标了解国际市场营销中的法律和伦理问题掌握国际市场营销中的法律和伦理原则了解国际市场营销中的社会责任7.2 教学内容国际市场营销中的法律和伦理问题国际市场营销中的法律和伦理原则国际市场营销中的社会责任7.3 教学方法讲授:讲解国际市场营销中的法律和伦理问题,介绍法律和伦理原则小组讨论:学生分组讨论国际市场营销中的法律和伦理问题,分享对社会责任的理解7.4 教学评估小组报告:学生分组进行报告,分享他们对国际市场营销中的法律、伦理和社会责任的理解课堂测试:设计相关问题,测试学生对国际市场营销中的法律和伦理问题的理解以及对社会责任的认识第八章:国际市场营销计划和实施8.1 教学目标了解国际市场营销计划的结构和内容掌握国际市场营销计划的制定和实施步骤了解国际市场营销计划的评估和调整方法8.2 教学内容国际市场营销计划的结构和内容国际市场营销计划的制定和实施步骤国际市场营销计划的评估和调整方法8.3 教学方法讲授:讲解国际市场营销计划的结构和内容,介绍制定和实施的步骤案例分析:分析国际市场营销计划的案例,让学生更好地理解应用8.4 教学评估小组讨论:学生分组讨论国际市场营销计划的案例,分享自己的观点和经验课堂测试:设计相关问题,测试学生对国际市场营销计划的理解和应用能力第九章:国际市场营销案例分析9.1 教学目标了解国际市场营销案例分析的方法和技巧掌握国际市场营销案例分析的工具和步骤了解国际市场营销案例的成功经验和教训9.2 教学内容国际市场营销案例分析的方法和技巧国际市场营销案例分析的工具和步骤国际市场营销案例的成功经验和教训9.3 教学方法讲授:讲解国际市场营销案例分析的方法和技巧,介绍工具和步骤小组讨论:学生分组讨论国际市场营销案例,运用分析和技巧进行深入探讨9.4 教学评估小组报告:学生分组进行报告,分享他们对国际市场营销案例分析的理解和应用课堂测试:设计相关问题,测试学生对国际市场营销案例分析的方法和技巧的掌握第十章:国际市场营销的未来趋势10.1 教学目标了解国际市场营销的最新发展趋势掌握影响国际市场营销未来发展的因素了解国际市场营销的未来挑战和机遇10.2 教学内容国际市场营销的最新发展趋势影响国际市场营销未来发展的因素国际市场营销的未来挑战和机遇10.3 教学方法讲授:讲解国际市场营销的最新发展趋势,介绍影响未来发展的因素小组讨论:学生分组讨论国际市场营销的未来挑战和机遇,分享自己的观点和看法10.4 教学评估小组报告:学生分组进行报告,分享他们对国际市场营销最新发展趋势的理解和对未来挑战和机遇的认识课堂测试:设计相关问题,测试学生对国际市场营销的未来发展趋势的理解和认识重点和难点解析1. 教学目标:明确教学目标,确保教学内容能够满足学生的学习需求。

《国际市场营销学》双语教学方法改革探析高校教育中的教学是体现我国教育与国际接轨的一个重要方面。
吸收和借鉴国外先进的教学方法是培养本土化复合型国际化人才的必然趋势。
本文基于《国际市场营销学》双语教学改革的必要性,对课程进行教学改革探析,以教为主转变为以学为主,增加了双语互动教学法、课堂学生自主学习法、情景模拟教学法,以增强学生对所学知识的理解,培养学生的实践能力与创新能力。
国际市场营销学教学改革高校教育随着国际交流的加快,国际市场营销中越来越凸显出对既有专业知识又能在国际销售中施展才干的复合型人才的需求,而高校中的教学成为培养这类人才的一个主要途径。
尽管现在许多高校都开设了《国际市场营销学》双语教学课程,然而其教学依旧沿袭传统的教学方法,致使培养出来的学生虽有宽厚的国际营销知识基础,但缺乏实践的分析与解决问题能力。
很难适应社会对国际营销人才的要求。
所以,《国际市场营销学》双语教学成为我国教育理论和教学实践广为关注的一个热点教改问题。
一、《国际市场营销学》双语教学方法改革的必要性1.人才市场对《国际市场营销学》双语教学方法改革的要求近年来,随着就业压力的逐步加大,各类企业对营销类人才的需求也逐步从以前的重文凭转为重能力,人才市场对国际营销人才的综合素质和实践能力要求越来越高,很多企业更愿意招聘一些具有实践能力或实践经验的人才。
所以,培养学生具有较强的综合分析、解决实践问题能力成为《国际市场营销学》教学的另一重要目标。
2.课程自身特点的需求《国际市场营销学》是以国际营销活动过程及规律为研究对象的,它是一门实践性很强的学科。
随着经济全球化,国际营销市场出现了许多新的营销形式,这不仅丰富了国际市场营销的内容,同时也要求学生既掌握丰富的理论知识,更具备强的动口和动手能力。
而双语教学,不仅可以激发学生的学习兴趣,还可以帮助学生了解西方的营销环境。
同时,随着专业课程改革的逐步深入,新的教学理念正不断地冲击着传统的教学模式,必须强调对学生自主探究、综合应用能力的培养。


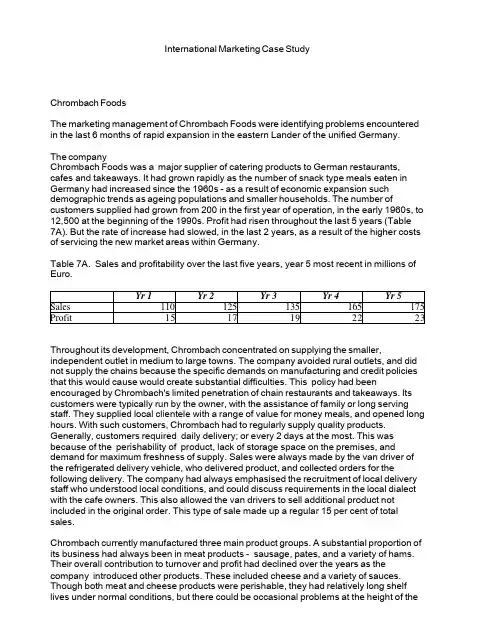
International Marketing Case StudyChrombach FoodsThe marketing management of Chrombach Foods were identifying problems encountered in the last 6 months of rapid expansion in the eastern Lander of the unified Germany.The companyChrombach Foods was a major supplier of catering products to German restaurants, cafes and takeaways. It had grown rapidly as the number of snack type meals eaten in Germany had increased since the 1960s - as a result of economic expansion such demographic trends as ageing populations and smaller households. The number of customers supplied had grown from 200 in the first year of operation, in the early 1960s, to 12,500 at the beginning of the 1990s. Profit had risen throughout the last 5 years (Table7A). But the rate of increase had slowed, in the last 2 years, as a result of the higher costs of servicing the new market areas within Germany.Table 7A. Sales and profitability over the last five years, year 5 most recent in millions of Euro.Yr 1Yr 2Yr 3Yr 4Yr 5 Sales110125135165175 Profit1517192223 Throughout its development, Chrombach concentrated on supplying the smaller, independent outlet in medium to large towns. The company avoided rural outlets, and did not supply the chains because the specific demands on manufacturing and credit policies that this would cause would create substantial difficulties. This policy had been encouraged by Chrombach's limited penetration of chain restaurants and takeaways. Its customers were typically run by the owner, with the assistance of family or long serving staff. They supplied local clientele with a range of value for money meals, and opened long hours. With such customers, Chrombach had to regularly supply quality products. Generally, customers required daily delivery; or every 2 days at the most. This was because of the perishability of product, lack of storage space on the premises, and demand for maximum freshness of supply. Sales were always made by the van driver of the refrigerated delivery vehicle, who delivered product, and collected orders for the following delivery. The company had always emphasised the recruitment of local delivery staff who understood local conditions, and could discuss requirements in the local dialect with the cafe owners. This also allowed the van drivers to sell additional product not included in the original order. This type of sale made up a regular 15 per cent of total sales.Chrombach currently manufactured three main product groups. A substantial proportion of its business had always been in meat products - sausage, pates, and a variety of hams. Their overall contribution to turnover and profit had declined over the years as the company introduced other products. These included cheese and a variety of sauces. Though both meat and cheese products were perishable, they had relatively long shelf lives under normal conditions, but there could be occasional problems at the height of the。



国际市场营销课件英文版chapter3Chapter 3 History and Geography: Foundation of Culture 1. Lead in: an Panama issueHistory of USA interventionViewpoints of some Americans to USAViewpoints of Panamanians to USAHistorical Sino-US conflictsDomination of part of ChinaGeographical importancePanama – ChinaTIMEFormation of Viewpoints2.Effects of history and geographyattitudes and behaviorsBusiness opportunities and cross-culture marketing Historical eventsgeographicaluniquenessefforts toimproveadaptionto it3. Historical perceptive in global businessJapanese behaviors:1. 8><#004699'>A distribution system sodifficult for an outsider todevelop2. Decisions made byconsensus3. Loyalty to family, tocountry, to company, and tosocial group4. CooperationJapanese history and Confucian philosophy in which loyalty is to countryAnswers found in4.Subjective understanding of historyHistory help understand why <#004699'>a country behaves as it does ——it helps define <#004699'>a natio n’s “mission”, how it perceives it neighbors, and how it sees its place in the world.Understanding any nation’s business and political culture is the subjective perception of its history, with biases and SRC (Self reference criterion)—— the unconscious reference to one><039;s own culturalvalues or one&#<039;s home country frame of reference.5.Establish <#004699'>a historical perspectiveTo understand <#004699'>a country’s attitudes, prejudices,and fears, it is necessary to look beyond thesurface of current events to the inner subtletiesof the country’s entire past for clues.6. Geography and Global MarketsPopulationResource, climate, surface, neighboring countries…Efforts made for improvementCultureIndustries,Economy7.Climate and TopographyClimateUse and FunctionProduct FitnessConsuming SeasonsDistribution BarrierTopographic VariationInfrastructureConstruction8.Climate difference and adaptation to it Climate differenceAfricaEuropeAdaptation to climate difference9.Topography barrierand improvement of itGeographic barrierSouth America48% is jungle and forest, 5% arable; separation by mountain ranges with high altitute of 4<0<0<0m, population concentrate on outer periphery.China,Russia, India,and Canada1<0.Topography barrierand improvement of itImprovement of Geographic barrierEuropeEnglish ChannelSweden-Denmark bridgeSouth America(Argentina, Brazil,Paraguay, and Uruguay)Colonia Bridge in South America//.oceansatlas4>#ff66ff'>/unatlas/about/oceansofthefuture/backgro und/seemore2.html11.Geography, Nature, and Economic GrowthUnprivileged countries suffer economic stagnation, many among poorest countries.-----Most people live and work as they do because the resources of their part of country have opened certain opportunities and closed others.12.Geography, Nature,and Economic GrowthOvercoming nature barriers, with social and environmental cost.DisplacementSilt clog (in reservoir)Ecosystem13.Geography, Nature,and Economic GrowthProblems in process of development:Disruption of ecosystemInadequate hazardous waste managementRelocation of peopleIndustrial pollutionExtractive growth14.Geography in Some Typical Countries15.Social Responsibility &Environmental ManagementManufacturing plants see regulations everywhere against pollution(industrial wastes) and the disposal of hazardous waste.Strengthen environmental crisis —— Whether economic development and protection for the environment can coexist.16.Social Responsibility &Environmental ManagementSustainable developmentWise resource management,Equitable distribution of benefits,Reduction of negative efforts on people andthe environment—— from the process of economic growth.17. Sustainable Development: Key Propositions that Serve as <#004699'>a Foundation for PracticeThere is <#004699'>a crucial and potentially positive link between economic development and the environment.The costs of inappropriate economic policies on the environment are very high.Addressing environmental problems requires that poverty be reduced.Economic growth must be guided by prices that incorporate environmental values.Since environmental problems pay no respect to borders, global and regional collaboration is sometimes needed to complement national and regional regions.18,ResourcesHuman labor provides the preponderanceof energy in underdeveloped countriesImportance of oil and gas in world energyconsumptionOther energy resources: wood, nuclear power, ocean’s tides, geothermal power, sun.19.World energy consumption2<0.Dynamics of Global Population TrendsPeople CONSTITUTE markets for various categories of goods——Changesin the composition and distribution of the population will affect future demand.Necessary to know about:(1) rural/urban population shifts(2) rates of growth(3) age levels, and(4) population control(5) rural-urban migration ofworld population(6) population decline and aging(7) worker shortage and immigrationRussia-China Oil PlanRussia-China Oil Plan21.Rural & Urban Population, 1996~2<03<022.Change in world populationThe developing world’s population is increasingwhile the industrialized world’s is decl ining.23. World Population by Major Areas & Life Expectancy24. Percentage of World Population by Age-Group Density25. World Trade Routes and Communication LinksKnowledge about trade routes over land,sea, and air important in makingmarketing decisionsThe majority of world trade is among themost industrialized and industrializingcountries of Europe, North America, andAsiaNeed to be aware about communicationlinks—the underpinning of all commerceImpact of the Internet revolutionespecially for global marketing of products26. World Trade Routes and Communication Links27. The Triad: Trade between USA and Canada,the European Community, and Japan ($ billions)EUROPEANCOMMUNITYUNITED STATES & CANADAJAPANFor additional figures see: “Indicators of Market Size for 115 Countries I” Crossborder Monitor, August, 1997, pp.4-8 195.466.3151.689.<091.5141.7。

《国际市场营销(双语)》课程教学大纲课程编号:11263制定单位:国际经贸学院制定人(执笔人):陈琦*******制定(或修订)时间:2016年2月28日江西财经大学教务处《国际市场营销(双语)》课程教学大纲一、课程总述本课程大纲是以2014年全校本科专业人才培养方案为依据编制的。
二、教学时数分配三、单元教学目的、教学重难点和内容设置Chap.1. The Scope and Challenge of International Marketing教学目的:理解国际市场营销的动因、国际市场营销的职能以及文化差异对国际市场营销的影响。
教学重难点:理解自我参考准则和民族优越感的概念、联系与区别;了解自我参考准则和民族优越感对跨文化沟通和认知的影响。
内容设置:1. The changing face of U.S. business2. The scope of the international marketing task3. The increasing importance of global awareness4. The progression of becoming a global marketer5. The importance of the SRC in international marketingChap.2. The Global Environment of International Marketing教学目的:了解国际市场营销的区域和全球环境。
教学重难点:理解国际收支状况对一国贸易政策的影响;了解主要的区域经济一体化组织的异同;了解区域和全球一体化组织对国际市场营销的影响。
内容设置:1. The basis for the reestablishment of world trade following World War II2. The importance of balance-of-payment figures to a country’s economy3. The effects of protectionism on world trade4. The seven types of trade barriers5. The importance of GATT and WTOChap.3. History and Geography: The Foundations of Culture教学目的:了解历史和地理与文化的形成、特质之间的关系。
国际市场营销双语教学教案第一章:国际市场营销概述1.1 教学目标了解国际市场营销的定义和重要性掌握国际市场营销的基本概念和原则理解国际市场营销的挑战和机遇1.2 教学内容国际市场营销的定义和重要性国际市场营销的基本概念和原则国际市场营销的挑战和机遇1.3 教学方法讲授和案例分析相结合小组讨论和角色扮演互动式教学和问题解决1.4 教学资源教材和参考书籍网络资源和案例研究教学幻灯片和图表1.5 教学评估课堂参与和讨论角色扮演和小组讨论课后作业和案例分析报告第二章:国际市场营销环境2.1 教学目标了解国际市场营销环境的构成因素掌握国际市场营销环境的变化趋势理解国际市场营销环境的挑战和机遇2.2 教学内容国际市场营销环境的构成因素国际市场营销环境的变化趋势国际市场营销环境的挑战和机遇2.3 教学方法讲授和案例分析相结合小组讨论和角色扮演互动式教学和问题解决2.4 教学资源教材和参考书籍网络资源和案例研究教学幻灯片和图表2.5 教学评估课堂参与和讨论角色扮演和小组讨论课后作业和案例分析报告第三章:国际市场营销战略3.1 教学目标了解国际市场营销战略的制定过程掌握国际市场营销战略的基本要素理解国际市场营销战略的实施和评估3.2 教学内容国际市场营销战略的制定过程国际市场营销战略的基本要素国际市场营销战略的实施和评估3.3 教学方法讲授和案例分析相结合小组讨论和角色扮演互动式教学和问题解决3.4 教学资源教材和参考书籍网络资源和案例研究教学幻灯片和图表3.5 教学评估课堂参与和讨论角色扮演和小组讨论课后作业和案例分析报告第四章:国际市场营销产品策略4.1 教学目标掌握国际市场营销产品策略的基本要素理解国际市场营销产品策略的实施和评估4.2 教学内容国际市场营销产品策略的重要性国际市场营销产品策略的基本要素国际市场营销产品策略的实施和评估4.3 教学方法讲授和案例分析相结合小组讨论和角色扮演互动式教学和问题解决4.4 教学资源教材和参考书籍网络资源和案例研究教学幻灯片和图表4.5 教学评估课堂参与和讨论角色扮演和小组讨论课后作业和案例分析报告第五章:国际市场营销渠道策略5.1 教学目标了解国际市场营销渠道策略的重要性理解国际市场营销渠道策略的实施和评估5.2 教学内容国际市场营销渠道策略的重要性国际市场营销渠道策略的基本要素国际市场营销渠道策略的实施和评估5.3 教学方法讲授和案例分析相结合小组讨论和角色扮演互动式教学和问题解决5.4 教学资源教材和参考书籍网络资源和案例研究教学幻灯片和图表5.5 教学评估课堂参与和讨论角色扮演和小组讨论课后作业和案例分析报告第六章:国际市场营销传播策略6.1 教学目标理解国际市场营销传播策略的基本概念掌握国际市场营销传播策略的制定和实施方法6.2 教学内容国际市场营销传播策略的基本概念国际市场营销传播策略的制定和实施方法国际市场营销传播策略的有效运用6.3 教学方法讲授和案例分析相结合小组讨论和角色扮演互动式教学和问题解决6.4 教学资源教材和参考书籍网络资源和案例研究教学幻灯片和图表6.5 教学评估课堂参与和讨论角色扮演和小组讨论课后作业和案例分析报告第七章:国际市场营销价格策略7.1 教学目标理解国际市场营销价格策略的重要性掌握国际市场营销价格策略的基本要素学习国际市场营销价格策略的制定和评估7.2 教学内容国际市场营销价格策略的重要性国际市场营销价格策略的基本要素国际市场营销价格策略的制定和评估7.3 教学方法讲授和案例分析相结合小组讨论和角色扮演互动式教学和问题解决7.4 教学资源教材和参考书籍网络资源和案例研究教学幻灯片和图表7.5 教学评估课堂参与和讨论角色扮演和小组讨论课后作业和案例分析报告第八章:国际市场营销服务策略8.1 教学目标理解国际市场营销服务策略的基本概念掌握国际市场营销服务策略的制定和实施方法学习国际市场营销服务策略的有效运用8.2 教学内容国际市场营销服务策略的基本概念国际市场营销服务策略的制定和实施方法国际市场营销服务策略的有效运用8.3 教学方法讲授和案例分析相结合小组讨论和角色扮演互动式教学和问题解决8.4 教学资源教材和参考书籍网络资源和案例研究教学幻灯片和图表8.5 教学评估课堂参与和讨论角色扮演和小组讨论课后作业和案例分析报告第九章:国际市场营销风险管理9.1 教学目标理解国际市场营销风险的基本概念掌握国际市场营销风险的识别和管理方法学习国际市场营销风险的有效应对策略9.2 教学内容国际市场营销风险的基本概念国际市场营销风险的识别和管理方法国际市场营销风险的有效应对策略9.3 教学方法讲授和案例分析相结合小组讨论和角色扮演互动式教学和问题解决9.4 教学资源教材和参考书籍网络资源和案例研究教学幻灯片和图表9.5 教学评估课堂参与和讨论角色扮演和小组讨论课后作业和案例分析报告第十章:国际市场营销伦理和社会责任10.1 教学目标理解国际市场营销伦理和社会责任的重要性掌握国际市场营销伦理和社会责任的基本原则学习国际市场营销伦理和社会责任的最佳实践10.2 教学内容国际市场营销伦理和社会责任的重要性国际市场营销伦理和社会责任的基本原则国际市场营销伦理和社会责任的最佳实践10.3 教学方法讲授和案例分析相结合小组讨论和角色扮演互动式教学和问题解决10.4 教学资源教材和参考书籍网络资源和案例研究教学幻灯片和图表10.5 教学评估课堂参与和讨论角色扮演和小组讨论课后作业和案例分析报告重点解析本文档为“国际市场营销双语教学教案”,共包含十个章节。
双语示范课程《国际市场营销》教学《国际市场营销学》International Marketing(双语)教学大纲学分/总学时:3/54一,课程的性质,目的和任务."国际市场营销学"(International Marketing)是市场营销专业的专业必修课.采用双语教学,使用英语原版教材,并结合课程内容,组织学生以小组的形式开展研究,制定针对相关国家的国际市场营销计划,并将研究成果在课堂上作演说汇报.本课程的教学目的是使学生能较为系统地理解和掌握国际市场营销的基本理论和实践.课程的主要内容包括国际营销的范围和挑战,国际营销的全球环境,全球市场评估中的文化因素,国际营销调研,全球营销管理,国际营销渠道,国际广告及国际市场定价.本课程在教学中坚持理论分析与实例,案例分析相结合的方法,为学生提供大量的案例陈述,分析和讨论的机会,锻炼和培养学生分析问题和解决问题的能力.课程全部章节均使用英语授课.课件全部用英语.要求学生尽量用英语参与课堂讨论,完成作业.试卷的出题全部使用英语.通过双语教学,培养学生用英语获取和交流专业知识的水平和能力.二,学习本课程学生应掌握的前设课程知识经济学,管理学原理,市场营销学,英语综合运用知识和能力三,学时分配1. The Scope and Challenge of International Marketing(国际营销的范围和挑战)(4学时)2. The Global Environment of International Marketing (国际营销的全球环境)(4学时)3. History and Geography: The Foundations of Culture(历史与地理–文化的基础) (3学时)4. Cultural Dynamics in Assessing Global Markets(全球市场评估中的文化因素)(3学时)5. Culture, Management Style, and Business Systems(文化,管理风格与经营方式) (3学时)6. The Political Environment(政治环境) (3学时)7. The International Legal Environment(国际法律环境) (4学时)8. Developing a Global Vision through Marketing Research(通过营销调研建立全球视野) (4学时)9. Global Marketing Management: Planning and Organization(全球营销管理–计划和组织) (4学时)10. Products and Services for Consumers(面向消费者的产品和服务) (4学时)11. International Marketing Channels(国际营销渠道) (4学时)12. Integrated Marketing Communications and International Advertising(一体化的营销沟通与国际广告) (4学时)13. Personal Selling and Sales Management(人员推销与销售管理) (4学时)14. Pricing for International Markets(国际市场定价) (4学时)15. Review(2学时)四,课程基本要求和内容Part One: An OverviewChapter1:The Scope and Challenge of International Marketing(国际营销的范围和挑战)4学时Learning Objectives(基本要求):T o learn and understand the followings: the scope of the international marketing task; the importance of the cross-cultural analysis in international marketing; the progression of becominga global marketer; the increasing importance of global awareness.1. International Marketing Defined2. The International Marketing Task3. Environmental Adaptation Needed4. The Self-Reference Criterion and Ethnocentrism5. Developing a Global Awareness6. Stages of International Marketing Involvement7. Strategic Orientation8. The Orientation of International MarketingChapter2:The Global Environment of International Marketing (国际营销的全球环境)4学时Learning Objectives(基本要求):To learn and understand the followings: the importance of GA TT and the World Trade Organization; the emergence of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank Group; the evolution of the European Community to the European Union; the trade linkage of NAFTA and South America and its regional effects; the development of trade within the Asia-Pacific Rim; the growth of developing markets and their importance to regional trade.1. GATT and WTO2. The International Monetary Fund and World Bank Group3. Protests against Global Institutions4. Global Markets and Multinational Market Groups5. Marketing in a Developing CountryPart Two: The Cultural Environment of Global MarketsChapter3: History and Geography: The Foundations of Culture(历史与地理–文化的基础)3学时Learning Objectives(基本要求):To learn and understand the following: the importance of history and geography in the understanding of international markets; the effects of history on a country's culture; effect of geographic diversity on economic profiles of a country; economic effects of controlling population growth versus aging population.1. Historical Perspective in Global Business2. Geography and Global Markets3. Dynamics of Global Population Trends4. World Trade RoutesChapter4: Cultural Dynamics in Assessing Global Markets(全球市场评估中的文化因素)3学时Learning Objectives(基本要求):To learn and understand the following: the importance of culture to an international marketer; the origins and elements of culture; the impact of cultural borrowing;the strategy of planned change and its consequences.1. Culture's Pervasive Impact2. Definitions and Origins of Culture3. Elements of Culture4. Cultural Knowledge5. Cultural ChangeChapter5: Culture, Management Style, and Business Systems(文化,管理风格与经营方式)4学时Learning Objectives(基本要求):To learn and understand the following: the necessity for adapting to cultural differences; how and why management styles vary around the world; the extent and implications of gender bias in some countries; the importance of cultural differences in business ethics; the differences between relationship-oriented and information-oriented cultures.1. Required Adaptation2. Management Styles around the World3. Gender Bias in International Business4. Business Ethics5. Culture's Influence on Strategic Thinking6. A Synthesis, Relationship-Oriented versus Information-Oriented CulturesChapter6: The Political Environment: A Critical Concern (政治环境)4学时Learning Objectives(基本要求):To learn and understand the following: what the sovereignty of nations means and how it affects the stability of government policies, political parties, and nationalism; the political risks of global business and the factors that affect stability; the importance of the political system to international marketing and its effects on foreign investments; assessing and reducing the effects of political vulnerability.1. The Sovereignty of Nations2. Stability of Government Policies3. Political Risks of Global Business4. Assessing Political Vulnerability5. Reducing Political VulnerabilityChapter7: The International Legal Environment(国际法律环境)4学时Learning Objectives(基本要求):To learn and understand the following: the four heritages of today's legal systems; the important factors in jurisdiction of legal disputes; issues associated with jurisdiction of legal disputes and the various methods of dispute resolution; the unique problemsof protecting intellectual property rights internationally; ways to protect against piracy and counterfeiting; the legal differences between countries and how the differences can affect international marketing plans.1. Bases for Legal Systems2. Jurisdiction in International Legal Disputes3. International Dispute Resolution4. Protection of Intellectual Property Rights5. Commercial Law within CountriesPart three: Developing Global Marketing StrategiesChapter 8: Developing a Global Vision through MarketingResearch(通过营销调研建立全球视野)4学时Learning Objectives(基本要求):To learn and understand the following: the importance of problem definition in international research; the problems of availability and use of secondary data; quantitative and qualitative research methods; sources of secondary data; how to analyze and use research information.1. Breadth and Scope of International Marketing Research2. The Research Process3. Defining the Problem and Establishing Research Objectives4. Problems of Availability and Use of Secondary Data5. Gathering Primary Data: Quantitative and Qualitative Research6. Multicultural Research: A Special Problem7. Research on the Internet: A Growing Opportunity8. Estimating Market Demand9. Problems in Analyzing and Interpreting Research Information10. Responsibility for Conducting Marketing Research11. Communicating with Decision MakersChapter9: Global Marketing Management: Planning and Organization(全球营销管理–计划和组织)4学时Learning Objectives(基本要求):To learn and understand the following: how global marketing management differs from international marketing management; the increasing importance of international strategic alliances; the need for planning to achieve company goals; the important factors for each alternative market-entry strategy.1. Global Marketing Management: An Old Debate and a New View2. Planning for Global Markets3. Alternative Market-Entry Strategy4. Organizing for Global CompetitionChapter10: Products and Services for Consumers(面向消费者的产品和服务)4学时Learning Objectives(基本要求):To learn and understand the following: the importance of offering a product suitable for the intended market; the importance of quality and how quality is defined; country-of-origin effects on product image; physical, mandatory, and cultural requirements for product adaptation; the need to view all attributes of a product in order to overcome resistance to acceptance.1. Quality2. Products and Culture3. Analyzing Product Components for Adaptation4. Marketing Consumer Services Globally5. Brands in International MarketsChapter11: International Marketing Channels(国际营销渠道)4学时Learning Objectives(基本要求):To learn and understand the followings: the variety of distribution channels and how they affect cost and efficiency in marketing; how distribution patterns affect the various aspects of international marketing; the growing importance of e-commerce as a distribution alternative; the functions, advantages, and disadvantages of various kinds of middlemen; the importance of middlemen to a product's success and the importance of selecting and maintaining middlemen.1. Channel-of-Distribution Structures2. Distribution Patterns3. Alternative Middleman Choices4. Factors Affecting Choices of Channels5. Locating, Selecting, and Motivating Channel Members6. The InternetChapter12: Integrated Marketing Communications and International Advertising(一体化的营销沟通与国际广告)4学时Learning Objectives(基本要求):To learn and understand the followings: local market characteristics that affect the advertising and promotion of products; the strengths and weaknesses of sales promotion and public relations in global marketing; when global advertising is most effective; when modified advertising is necessary; the effect of limited media, excessive media, and government regulations on advertising and promotion budgets.1. Sales Promotions in International Markets2. International Public Relations3. International Advertising4. Advertising Strategy and Goals5. The Message: Creative Challenge6. Media Planning and Analysis7. Campaign Execution and Advertising Agency8. International Control of AdvertisingChapter13: Personal Selling and Sales Management(人员推销与销售管理)4学时Learning Objectives(基本要求):To learn and understand the followings: the role of interpersonal selling in international marketing; the considerations in designing an international sales force; the steps to recruiting three types of international sales people; selection criteria for international sales and marketing positions; the special training needs of international personnel; motivation techniques for international sales representatives; how to design compensation systems for an international salesforce; the changing profile of the global sales and marketing manager.1. Designing the Sales Force2. Recruiting Marketing and Sales Personnel3. Selecting Sales and Marketing Personnel4. Training for International Marketing5. Motivating Sales Personnel6. Designing Compensation Systems7. Evaluating and Controlling Sales Representatives8. Developing Cultural Awareness9. The Changing Profile of the Global Manager10. Foreign Language SkillsChapter14: Pricing for International Markets(国际市场定价)4学时Learning Objectives(基本要求):To learn and understand the following: components of pricing as competitive tools in international marketing; the pricing pitfalls directly related to international marketing; how to control pricing in parallel imports or gray markets; price escalation and how to minimize its effect; countertrading and its place in international marketing practices; the mechanisms of price quotations.1. Pricing Policy2. Approaches to International Pricing3. Price Escalation4. Approaches to Lessening Price Escalation5. Leasing in International Markets6. Countertrade as a Pricing Tool7. Transfer Pricing Strategy8. Price Quotation9. Administered PricingPart Four :Supplementary Material五,教材及学生参考书教材:Philip Cateora等著International Marketing(国际营销)12th Edition(第12版) 中国人民大学出版社2005年3月参考书:1,Michael R. Czinkota著International Marketing(国际商务) 8th Edition(第8版) 北京大学出版社2007年10月。