水化脱胶工艺
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:745.00 KB
- 文档页数:3

连续水化脱胶工艺流程英文回答:Continuous hydration and de-gelling process is a commonly used technique in various industries, including food processing, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. This process involves the removal of water from a gel-like substance to obtain a more stable and solid product.The process begins with the preparation of the gel-like substance, which can be a mixture of various ingredients. For example, in food processing, it could be a mixture of starch, water, and other additives. In pharmaceuticals, it could be a mixture of active ingredients, excipients, and water.Once the gel-like substance is prepared, it is then subjected to the continuous hydration and de-gelling process. This process typically involves the use of heat and mechanical agitation to remove water from the gel andpromote the formation of a solid product.During the process, the gel-like substance is heated to a specific temperature, which is typically above theboiling point of water. This heat helps in evaporating the water present in the gel and promoting the gelatinizationof starch or other gelling agents. The mechanical agitation, such as stirring or mixing, helps in breaking down the gel structure and facilitating the removal of water.As the water is evaporated and the gelatinization process occurs, the gel-like substance transforms into a more solid and stable product. This solid product can then be further processed or used directly in various applications.For example, in food processing, the continuous hydration and de-gelling process can be used to produce instant noodles. The dough-like mixture of flour, water,and other ingredients is subjected to the process,resulting in the formation of solid noodles that can be cooked quickly by consumers.In the pharmaceutical industry, this process can be used to produce tablets or capsules. The gel-like mixture of active ingredients and excipients is subjected to the process, leading to the formation of solid dosage forms that are easier to handle and administer.Overall, the continuous hydration and de-gelling process is a versatile technique that allows for the transformation of gel-like substances into more stable and solid products. It is widely used in various industries to improve the quality, stability, and usability of products.中文回答:连续水化脱胶工艺流程是在食品加工、制药和化妆品等各个行业中常用的技术。

水化脱胶的原理
嘿,让我们来聊聊水化脱胶的原理吧!想象一下,就好像我们在清理一个混乱的房间。
水化脱胶呢,就像是要把房间里那些不需要的、杂乱的“小颗粒”给清理出去。
在食用油或者其他油脂中,会有一些杂质,比如磷脂等。
这些杂质就像房间里的灰尘和杂物一样。
水化脱胶就是通过加水这个巧妙的办法,让这些杂质凝聚起来。
水就像是一个神奇的“召集令”,让那些磷脂之类的杂质乖乖地聚集在一起。
就好像小朋友们听到集合的哨声会跑过来集合一样,磷脂遇到水后也会聚集起来形成胶团。
然后呢,我们就可以像把垃圾打包一样,把这些胶团分离出去,从而让油脂变得更加纯净。
比如说,我们平时吃的植物油,如果不进行水化脱胶,可能就会有一些不好的口感或者影响其质量。
通过这个过程,就能让油变得更清亮、更好用啦!是不是很有趣呢?其实很多看似复杂的原理,就藏在我们生活的点点滴滴中,只要我们细心去发现和理解,就能掌握它们哦!。


油脂水化脱胶实验报告1. 实验目的本实验旨在通过油脂水化脱胶实验,观察不同条件下油脂脱胶的效果,并分析实验结果,为工业生产中的油脂脱胶工艺提供参考。
2. 实验原理油脂水化脱胶是利用水对油脂中的成分进行水解反应,进而分离油脂和脱胶物质的一种方法。
在实验中,我们采用碱法水化脱胶的方法,通过将含有油脂的试样与碱溶液反应,使油脂中的蛋白质与水中的碱发生反应,将油脂中的杂质和胶质物质与水分离开来。
3. 实验步骤3.1 准备工作- 准备试样:选取不同来源的油脂样品,如动物油、植物油等。
- 准备试剂:碱溶液、去离子水等。
3.2 油脂水化脱胶实验1. 取一定量的试样,加入适量的碱溶液,在温度控制下进行搅拌反应。
2. 设定不同的实验条件,如温度、碱溶液的浓度等,进行实验。
3. 实验一段时间后,停止搅拌,静置一段时间,使油脂和胶质沉淀。
4. 将上层的油脂和胶质物质倒掉,并取出沉淀物。
5. 将沉淀物进行过滤、洗涤和干燥。
6. 对油脂样品进行质量测定。
4. 实验结果与分析根据实验操作和观察结果,我们可以得到不同实验条件下的油脂水化脱胶效果。
4.1 不同油脂样品比较经过实验,我们发现不同来源的油脂在水化脱胶时具有不同的脱胶效果。
例如,动物油相较于植物油在一定条件下更容易发生水化脱胶反应,脱胶效果更好。
这可能是由于动物油中的脂肪酸较多,与水和碱发生反应较为容易。
4.2 不同反应温度比较实验中,我们选取了不同的反应温度,观察其对脱胶效果的影响。
结果显示,在温度较高的条件下,比如60C,油脂中的胶质物质能够更快地与水分离,脱胶效果更好。
这是因为在较高的温度下,反应速度加快,胶质物质更容易从油脂中脱离。
4.3 不同碱溶液浓度比较我们还对不同浓度的碱溶液进行了比较实验。
结果显示,较高浓度的碱溶液能够更快速地与油脂中的脱胶物质反应,从而实现较好的脱胶效果。
然而,过高浓度的碱溶液也可能对油脂的质量产生一定的负面影响。
5. 实验结论本次油脂水化脱胶实验结果表明:1. 不同来源的油脂在水化脱胶时具有不同的脱胶效果,动物油相较于植物油更容易脱胶。
收稿日期:2001—10—23作者简介:黄菊莲(1968-),女,工程师;主要从事生产油脂精炼设备的技术开发工作。
文章编号:1003—7969(2002)02—0052—02 中图分类号:TS224.6 文献标识码:A几种连续水化脱胶工艺的特点黄菊莲,严建国(南京绿洲机器厂,210039南京市中华门外新建) 摘要:随着油脂精炼加工技术的不断发展,脱胶工序显得越来越重要,根据设计和调试的经验对喷射式快速水化工艺、大豆油的水化脱胶工艺和通用的水化脱胶工艺进行阐述和比较。
关键词:水化脱胶;原理;参数;特点 在不同的油脂精炼加工过程中,脱胶工序不仅必不可少,而且是非常重要的,胶质脱除得是否彻底将直接影响得率和产品的最终质量。
本文根据我厂这几年来为满足用户需要而设计和调试的几种水化脱胶工艺并对它们的特点进行探讨和总结,望能给读者以一定的启示和帮助。
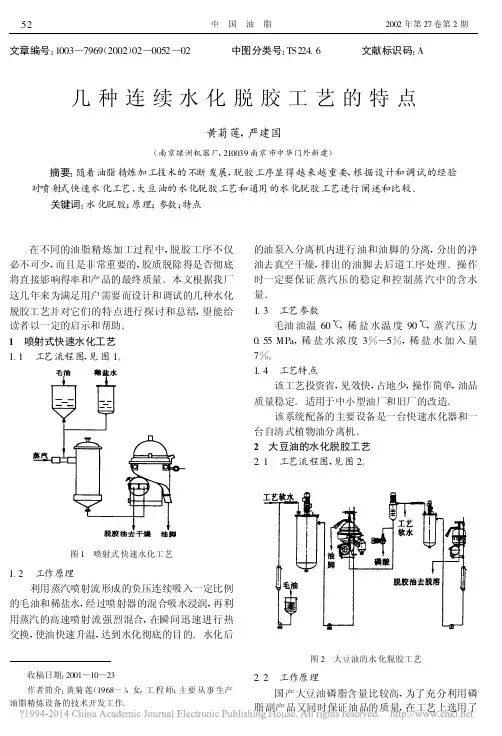
1 喷射式快速水化工艺1.1 工艺流程图,见图1。
图1 喷射式快速水化工艺1.2 工作原理利用蒸汽喷射流形成的负压连续吸入一定比例的毛油和稀盐水,经过喷射器的混合吸水浸润,再利用蒸汽的高速喷射流强烈混合,在瞬间迅速进行热交换,使油快速升温,达到水化彻底的目的。
水化后的油泵入分离机内进行油和油脚的分离,分出的净油去真空干燥,排出的油脚去后道工序处理。
操作时一定要保证蒸汽压的稳定和控制蒸汽中的含水量。
1.3 工艺参数毛油油温60℃,稀盐水温度90℃,蒸汽压力0.55MPa ,稀盐水浓度3%—5%,稀盐水加入量7%。
1.4 工艺特点该工艺投资省,见效快,占地少,操作简单,油品质量稳定。
适用于中小型油厂和旧厂的改造。
该系统配备的主要设备是一台快速水化器和一台自清式植物油分离机。
2 大豆油的水化脱胶工艺2.1 工艺流程图,见图2。
图2 大豆油的水化脱胶工艺2.2 工作原理国产大豆油磷脂含量比较高,为了充分利用磷脂副产品又同时保证油品的质量,在工艺上选用了52中 国 油 脂 2002年第27卷第2期图3 通用的水化脱胶工艺二次水化工艺。

水化油脚的胶体化学及对脱胶工艺的指导意义
水化油脚的胶体化学是一种新兴的技术,它利用碱性材料制备胶体和胶水,使油脚固化成聚合物。
水化油脚是由水溶性有机碱(如乙酰胺、乙酸乙酯)和均相胶水溶剂(如二甲基硅氧烷、氢氧化氢和醋酸)制成的胶水,可
以用来修补一些不可见的抽水沟。
要想获得良好的水化油脚修复效果,必须正确地使用胶体材料。
该材料
必须选择具有良好的粘附性能,固化速度要快,不同的材料的固化时间也有
所不同,在配制胶水时,要按照定容体积和比例将胶水物质配制成混合物,
以便得到良好的固化效果。
有时,由于修复材料本身的原因,可能会出现水化油脚脱胶现象。
此时
就要使用专用的脱胶剂,而不是简单地借助抛光机进行处理。
专用的脱胶剂,它的作用原理是破坏固体牢固状态的胶体物质,从而使胶体脱离表面。
总结来说,胶体化学技术可用于水化油脚的修补,而正确使用胶体材料
可以获得良好的固化效果;当出现水化油脚脱胶现象时,可以采用专用的脱
胶剂,以便良好地处理。


连续水化脱胶工艺流程英文回答:Continuous hydration and gelatinization process is a widely used method in the food industry for the production of various products such as starch-based snacks, breakfast cereals, and instant noodles. This process involves the hydration and gelatinization of starch, which is an important step in the production of these food products.The continuous hydration and gelatinization process typically consists of the following steps:1. Mixing: In this step, dry starch is mixed with water to form a slurry. The slurry is then pumped into a continuous cooker.2. Cooking: The slurry is heated in the continuous cooker to a specific temperature and held for a certain period of time. This step is crucial for the gelatinizationof starch, which is necessary for the desired texture and functionality of the final product.3. Cooling: After cooking, the hot slurry is cooled down to a lower temperature to stop the gelatinization process. This is usually done by passing the slurry through a heat exchanger.4. Drying: The cooled slurry is then dried to remove excess moisture and obtain the desired moisture content of the final product. This can be achieved through various drying methods such as hot air drying or extrusion.5. Milling: The dried product is then milled to the desired particle size. This step is important for the texture and appearance of the final product.6. Packaging: The milled product is finally packaged in suitable packaging materials to ensure its shelf life and quality.Continuous hydration and gelatinization process offersseveral advantages over batch processing. It allows for higher production capacity, better control of process parameters, and consistent product quality. Additionally, it reduces labor and energy costs compared to batch processing.中文回答:连续水化脱胶工艺流程是食品工业中广泛使用的方法,用于生产各种产品,如淀粉基零食、早餐谷物和方便面。



菜籽油水化脱脂工艺
菜籽油水化脱脂工艺是一种常见的油脂精炼工艺,其主要步骤如下:
1. 将菜籽毛油加入水化罐中,加入一定量的水,搅拌均匀。
2. 加热油脂,使其升温至一定温度,以便水化作用的进行。
3. 保持一定的反应时间,使磷脂等杂质吸水膨胀并凝聚。
4. 通过静置、沉淀或离心分离等方式,将水化后的油脂和沉淀物分离。
5. 对油脂进行干燥、过滤等处理,得到脱脂菜籽油。
在菜籽油水化脱脂过程中,需要控制好水的用量、油脂的温度和反应时间等参数,以确保脱脂效果和油脂质量。
同时,水化脱脂工艺只能去除水化磷脂等部分杂质,对于非水化磷脂等杂质的去除能力有限。
因此,在实际生产中,通常采用深度水化脱胶工艺,即在水化之前添加磷酸、柠檬酸等物质,起到螯合金属离子的作用,以提高脱胶效果。
油脂加工水化脱胶工艺概述1水化脱胶的概念、作用水化脱胶是利用磷脂等胶溶性杂质的亲水性,将一定量的热水或稀碱、食盐水溶液、磷酸等电解质水溶液,在搅拌下加入到一定温度的毛油中,使其中的胶溶性杂质凝聚沉降分离的一种脱胶方式。
在水化脱胶过程中,被分离出不溶的物质以磷脂为主,还有与磷脂结合在一起的蛋白质、糖基甘油二酯、粘液质和金属离子等。
2水化脱胶的原理在水化过程中能被凝聚沉降的物质以磷脂为主,磷脂中有又以卵磷脂为代表。
这种磷脂属于‘双亲媒性分子“,即在其分子结构中,即有疏水的非极性基团,又有亲水的极性基团。
当毛油中含水量很少时,磷脂呈内盐式结构,此时极性很弱,溶于油中,不到临界温度,不会凝聚沉降析出。
水化时,在毛油当中加入热水之后,磷脂的亲水基团投入水相之中,水分子与成盐的原子团结合,致使分子结构由内盐转化为水化式。
在水化式结构中,磷脂分子中的亲水基团(游离态羟基),具有更强的吸水能力,随吸水量的增加,磷脂由最初极性基团倾入水中呈含水胶束,然后转变成有规则的定向排列。
分子中疏水基团在油相尾尾相连,亲水基团伸向水相形成脂质双分子层(又称液晶形态)。
在脂质分子层中,水分子进入磷脂双分子层间,并未破坏磷脂的分子结构,却引起磷脂的体积膨胀,发生水合作用。
有时脂质体双分子层还能自发膨胀成多层的类似洋葱状的封闭球形结构---“多层脂质体”。
多层脂质体的每个片层都是脂质双分子层结构,片层之间和中心部分充满水相和油相(O/W),若经高频声波处理,可变成磷脂双分子层围成的球状的单层脂质体。
水化后的磷脂和其他胶体物质,极性基团周围吸引了许多水分子之后,在油脂之中的溶液解度减小。
吸水量逐渐增大,膨胀之后,双分子层或多分子层的片状和球状胶体彼此影响,有的甚至开成胶束。
小颗粒的胶体在极性力的作用下,相碰后形成絮凝状胶团,同时水化后的磷脂能吸附油中的其它胶质,而使其颗粒增大,比重增大,为沉降和离心分离创造条件。
磷脂中除上述水化磷脂之外,还存在少量的“非水化磷脂”。