英文版工艺流程图l
- 格式:doc
- 大小:44.50 KB
- 文档页数:2

工艺流程英文# The Art of Process Flow: A Journey Through the Steps of ProductionIn the realm of manufacturing and production, the term "process flow" refers to the sequence of steps that are followed to create a product or service. It is a systematic approach that ensures efficiency, quality, and consistency. Understanding the process flow is crucial for businesses to optimize their operations and meet the demands of the market. Let's delve into the intricacies of this vital concept.## 1. Design and PlanningThe process begins with the design and planning phase. Here, the product concept is developed, and the specifications are outlined. Engineers and designers work together to create a blueprint that will guide the subsequent steps. This is where the foundation for the entire process is laid.## 2. Material ProcurementOnce the design is finalized, the next step is material procurement. This involves sourcing the raw materials needed for production. It is a critical step as the quality of the materials directly impacts the final product.## 3. Production PreparationBefore the actual production can commence, the productionline must be prepared. This includes setting up machinery,calibrating tools, and ensuring that all necessary equipment is in place and functioning properly.## 4. ManufacturingThe manufacturing phase is where the raw materials are transformed into the final product. This step can involve various processes such as casting, forging, machining, and assembly, depending on the nature of the product.## 5. Quality ControlQuality control is an integral part of the process flow. It involves inspecting the products at various stages of production to ensure they meet the required standards. This step helps to identify and rectify any defects early on, reducing waste and improving product reliability.## 6. PackagingAfter the products have passed the quality control checks, they are packaged. This step is crucial for protecting the products during transportation and storage. It also plays a significant role in the presentation of the product to the end consumer.## 7. Storage and Inventory ManagementProper storage and inventory management are essential to ensure that products are available when needed. This step involves organizing the finished goods in a way that optimizes space and facilitates easy access.## 8. DistributionThe distribution phase involves getting the products to theend consumer or the market. This can include transportation, warehousing, and logistics management.## 9. Sales and MarketingThe final step in the process flow is sales and marketing. This is where the products are promoted and sold to the customers. Effective marketing strategies can significantly impact the success of a product in the market.## ConclusionThe process flow is a comprehensive framework that guides the production of goods and services. It encompasses a wide range of activities, from the initial design to the final sale. By understanding and optimizing each step in the process flow, businesses can enhance their efficiency, reduce costs, and improve the quality of their products. This, in turn, can lead to greater customer satisfaction and a competitive edge in the market.。
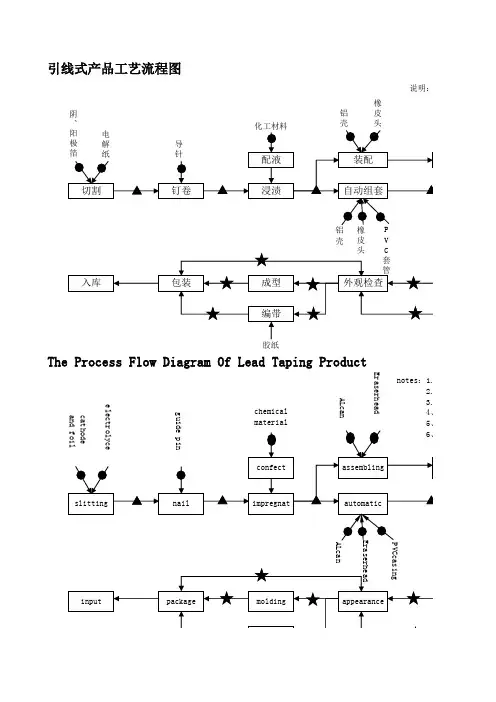
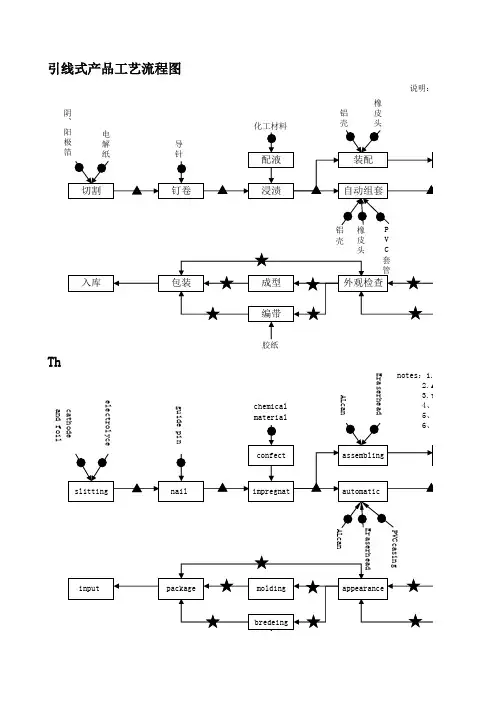
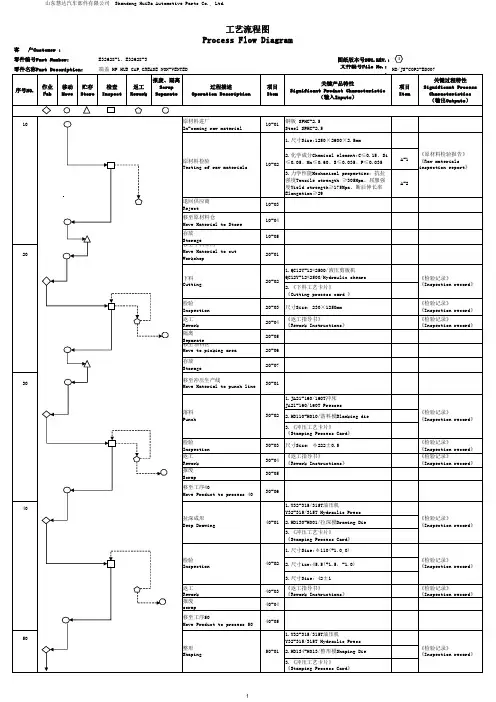


工序流程图英语作文Title: Process Flowchart: An Essential Tool for Streamlining Operations。
In today's fast-paced and competitive business environment, efficiency is paramount. To ensure smooth operations and optimize productivity, businesses often rely on process flowcharts. A process flowchart, also known as a process map or workflow diagram, is a visual representation of the steps involved in a process. It provides a clear and systematic overview of how tasks are performed, helping organizations identify bottlenecks, streamline operations, and improve overall efficiency.First and foremost, a process flowchart serves as a comprehensive guide, outlining each step of a process in a sequential manner. From start to finish, every task and decision point is documented, offering a complete picture of the workflow. This clarity is invaluable, especially in complex processes involving multiple departments orstakeholders. By visually mapping out the process, teams can better understand their roles and responsibilities, reducing confusion and ensuring everyone is on the same page.Moreover, a process flowchart facilitates analysis and optimization. By examining each step in the process, organizations can identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. For example, bottlenecks or delays may become apparent when certain steps take longer than anticipated or when tasks are repeatedly sent back for revisions. Withthis insight, businesses can implement targeted solutions to address these issues, such as reallocating resources, redesigning workflows, or automating certain tasks.Additionally, a process flowchart promotes transparency and accountability within an organization. By documenting the entire process, including decision points and responsible parties, stakeholders can easily track the progress of tasks and identify potential roadblocks. This transparency fosters a culture of accountability, as team members are aware of their roles and performanceexpectations. Furthermore, it enables managers to monitor performance metrics and identify areas where additional support or training may be needed.Furthermore, a process flowchart serves as a valuable communication tool, particularly when collaborating with external partners or clients. Instead of relying on lengthy written descriptions or verbal explanations, organizations can use visual diagrams to convey complex processes in a clear and concise manner. This not only enhances understanding but also minimizes the risk of miscommunication or misunderstandings. Whether presenting to stakeholders, training new employees, or onboarding clients, a well-designed process flowchart can effectively communicate key information and expectations.In conclusion, a process flowchart is an essential tool for streamlining operations and optimizing productivity in today's business environment. By providing a visual representation of processes, facilitating analysis and optimization, promoting transparency and accountability, and enhancing communication, process flowcharts empowerorganizations to achieve greater efficiency and effectiveness. As businesses continue to evolve and adapt to changing market dynamics, the importance of process flowcharts in driving operational excellence cannot be overstated.。


工艺流程图英文The Process Flowchart of a Production LineThe production line described in this flowchart is used to manufacture a popular consumer product "Product X". It involves a series of sequential steps and processes to transform raw materials into the final product. Let's take a look at the detailed process flowchart:Step 1: Raw Material ProcurementRaw materials for Product X, such as metal, plastic, and electronic components, are sourced from approved suppliers. The purchasing department is responsible for ensuring the quality, quantity, and timely delivery of these materials.Step 2: Material Inspection and StorageUpon arrival, the raw materials are inspected for quality and compliance with specifications. Any defective or non-compliant materials are rejected and returned to the supplier. Approved materials are properly labeled and stored in designated storage areas.Step 3: Material PreparationTo ensure the materials are ready for manufacturing, they go through several preparation processes. For example, metal sheets may need to be cut to the required size using cutting machines, and plastic components may need to be molded according to product design specifications.Step 4: Assembly Line SetupThe assembly line is prepared for production by setting up required machinery, tools, and equipment. Workers are assigned to specific workstations along the line and provided with necessary training and instructions.Step 5: Component AssemblyIn this step, different parts and components of Product X are assembled together. Workers follow a specific order and assembly instructions to ensure each component is correctly attached or assembled. This may involve the use of specialized tools or equipment.Step 6: Quality Control and InspectionAt various points along the assembly line, quality control and inspection checks are performed. Quality control supervisors closely monitor the assembly process and visually inspect the products for any defects or non-compliance. Any defective products are immediately removed from the line for rework or disposal.Step 7: Testing and CalibrationAfter assembly, the finished product undergoes testing and calibration. This may include electrical or functional testing to ensure it meets the required performance standards. Any product that fails the testing is again removed for further diagnosis and rectification.Step 8: Packaging and LabelingOnce the product has passed all quality checks and testing, it is ready for packaging. Packaging materials, such as boxes or blisterpacks, are selected and assembled. The product is carefully placed inside the packaging, and relevant labels and instructions are attached.Step 9: Storage and Inventory ManagementThe packaged products are stored in a central warehouse before distribution. Inventory management systems are used to track the quantity, location, and movement of products within the warehouse. This ensures efficient storage, retrieval, and distribution of the finished products to customers.Step 10: Distribution and Customer DeliveryCustomer orders are received and processed by the sales department. The packaged products are then picked from the warehouse, prepared for shipping, and delivered to the end customers or retailers.In conclusion, the production line for Product X involves a seriesof steps starting from raw material procurement to final product delivery. Each step is carefully planned, executed, and monitored to ensure the highest quality standards and customer satisfaction.。
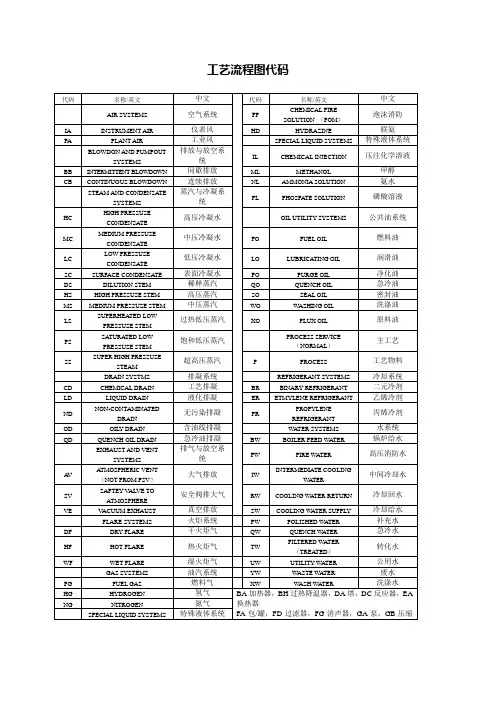
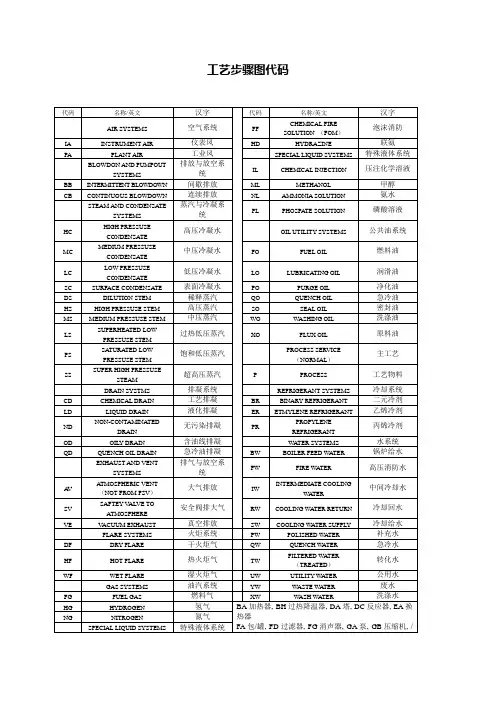
PID图纸中德英文注译自己整理pipinginstrumentdiagram工艺流程图MISCELLANEOUS ABBREBIATIONS 各种缩写ATMOS ATMOSPHERE 大气压BF BLANK FLANGE 盲板法兰B/L CONNECTION 连接CSC CAR SEALED CLOSED 汽车密封CSO CAR SEALED OPEN 汽车密封开放DR DRAIN 排水管,下水道EL ELEVATION 标高(F) FURNISHED BY OTHERS 提供的FB FULL BORE 等径孔道GR GRADE 等级HLL HIGH LIQUID LEVEL 高液位HOR HORIZONTAL 地平线的HP HIGH PRESSURE 高压LC LOCKED CLOSED 锁住LLL LOW LIQUID LEVEL 低液位LO LOCKED OPEN 解锁LP LOW PRESSURE 低压MAX MAXIMUM 最大量MIN MINIMUN 最低量MP MEDIUM PRESSURE 中等压力NC NORMAL LIQUID LEVEL 正常水位NO NORMALLY OPEN 正常断开的N2 NITROGEN 氮气OWS OILY WATER SEWER 含油污水RS REMOVABLE SPOOL 可移动卷轴SO STEAM OUT 蒸汽吹出T TEMPORARY 暂时的TAN TANGENT LINE 切线TP TERMINAL POINT 端点TYP TYPICAL 典型的UC UTILITY CONNECTION 接驳公用设施V VENT 通风孔VAC VACUUM 真空VERT VERTICAL 垂直的VFA VAPOUR FRACTION ANALYSER 蒸汽馏分分析仪----------------------------------------------------------------------------SERVICE ABBREVIATIONSBD BOILER BLOWDOWN 锅炉排污管BFW BOILER FEEDWATER 锅炉补给水CD CHEMICAL DOSING 化学计量CG CONVERTED GAS 换气CHW CHILLED WATER 冷冻水CWR COOLING WATER RETURN 循环冷却回水CWS COOLING WATER SUPPLY 循环冷却给水DR DRAIN 排水管DW DEMINERALISED WATER 脱离子水EW EXTRACTOR WATER 分离水FG FUEL GAS 燃料气FW FRESH WATER 淡水H HYDROGEN 氮气HO HOT OIL(HEATING MEDIUM) 热油HPC HIGH PRESSURE STEAM 高压蒸汽IA INSTRUMENT AIR 仪表空气IW INDUSTRIAL WATER 工业用水LLC LOW LOW PRESSURE CONDENSATE(STEAM) 超低压凝结LLS LOW LOW PRESSURE STEAM 超低压蒸汽LD LUBE OIL 润滑油LPC LOW PRESSURE CONDENATE(STEAM) 低压凝结LPS LOW PRESSURE STEAM 低压蒸汽N NITROGEN 氮P PROCESS 步骤PA PLANT AIR 工厂用的压缩空气PW POTABLE (DRINKING)WATER 饮用水TWR TEMPERED WATER RETURN 软化水回水TWS TEMPEREDWATER SUPPLY 软化水给水UC UTILITY CONNECTIONS 效用连接VA VENT TO ATMOSPHERE 大气排放VB VENT TO BOILER 锅炉排放VE VACUUM EXHAUST 真空排放VF VENT TO FLARE 火炬排放WW WASTE WATER/WASH WATER 废水/冲洗水----------------------------------------------------------------------INSULATION ABBREVIATIONS 隔离缩写A ACOUSTIC 听觉的C COLD CONSERVATION 冷保护FP HEAT CONSERVATION 热保护P PERSONNEL PROTECTION 人身保护S SOLAR 太阳的W WINTERISATION 准备过冬------------------------------------------------------------------------INSTRUMENT ABBREVIVATIONS 装置缩写ES ELECTRIC SUPPLY 供电AS AIR SUPPLY 空气供给E VOLTAGE SIGNAL 电压信号FC FAIL CLOSED 故障时自动关闭FI FAIL INTERMEDIATE 失败中间FL FAIL LOCKED 故障时锁住FL/SC FAIL LOCKED/SPRING TO CLOSED FL/SO FAIL LOCKED/SPRING TO OPEN FO FAIL OPENI CURRENT SIGNAL 电流信号MV MEASURED VALUE 测量值P PNEUMATIC SIGNAL 气压信号R RESISTANCE SIGNAL 电阻信号源SP SET POINT 设定值COMP. COMPENSATION 补偿。
液体汽化制冷的工艺流程图英语Liquid Vaporization Refrigeration (LVR)。
Introduction.Liquid vaporization refrigeration (LVR) is arefrigeration cycle that uses a refrigerant to absorb heat from a cold source and release it to a hot source. The refrigerant is first vaporized in an evaporator, which absorbs heat from the cold source. The vaporizedrefrigerant is then compressed in a compressor, which increases its pressure and temperature. The high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant is then condensed in a condenser, which releases heat to the hot source. The condensed refrigerant is then allowed to expand in an expansion valve, which reduces its pressure and temperature. The low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant is then returned to the evaporator, where the cycle repeats.Advantages of LVR.LVR has several advantages over other refrigeration cycles, including:High efficiency: LVR cycles are very efficient, with COPs (coefficients of performance) of up to 4.0.Low noise: LVR cycles are relatively quiet, making them ideal for use in residential and commercial applications.Environmentally friendly: LVR cycles do not use ozone-depleting refrigerants, making them environmentally friendly.Disadvantages of LVR.LVR also has some disadvantages, including:High cost: LVR systems are more expensive to install and maintain than other refrigeration cycles.Complex design: LVR cycles are more complex to design and build than other refrigeration cycles.Applications of LVR.LVR cycles are used in a wide variety of applications, including:Air conditioning.Refrigeration.Heat pumps.Industrial cooling.Process Flow Diagram.The process flow diagram for an LVR cycle is shown below.[Image of an LVR process flow diagram]The following is a description of the process flow diagram:1. The refrigerant enters the evaporator as a liquid.2. The refrigerant absorbs heat from the cold source and vaporizes.3. The vaporized refrigerant exits the evaporator and enters the compressor.4. The compressor compresses the refrigerant, increasing its pressure and temperature.5. The high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant exits the compressor and enters the condenser.6. The refrigerant condenses in the condenser, releasing heat to the hot source.7. The condensed refrigerant exits the condenser andenters the expansion valve.8. The expansion valve expands the refrigerant, reducing its pressure and temperature.9. The low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant exits the expansion valve and enters the evaporator.10. The cycle repeats.Conclusion.LVR is a reliable and efficient refrigeration cycle that is used in a wide variety of applications. LVR cycles have several advantages over other refrigeration cycles, including high efficiency, low noise, and environmental friendliness. However, LVR cycles are also more expensive to install and maintain than other refrigeration cycles.。
smt工艺图流程英文介绍The process flow of Surface Mount Technology (SMT) mainly includes the following steps:1. Substrate preparation: Firstly, select the appropriate substrate material, commonly used are FR4, metal substrates, etc. Then, perform necessary cleaning and surface treatment on the substrate to ensure welding quality.2. Attachment of surface-mounted components: Accurately attach surface-mounted components (such as resistors, capacitors, chips, etc.) that have been prepared in the component inventory to the substrate according to the process requirements. This step is usually completed by an automatic placement machine.3. Curing and bonding: Fix the surface-mounted components already attached to the substrate through reflow soldering or wave soldering, ensuring a secure connection.4. Soldering of through-hole components: For components that require through-hole assembly (such as sockets, connectors, etc.), insert them into the corresponding positions on the substrate for connection with other components.5. Soldering of leaded components: For components thatneed to be soldered for connection (such as IC chips, diodes, etc.), use appropriate soldering methods (such as wave soldering, manual soldering, etc.) to solder them to the substrate.6. Cleaning and inspection: Clean and inspect the assembled substrate to ensure that there are no residual solder flux or other contaminants, and make necessary corrections if needed.7. Testing and debugging: Perform functional testing and debugging on the assembled circuit board to verify its performance, reliability, and stability.8. Packaging and delivery: The final step is to package the finished substrate and label, categorize, and deliver it according to customer requirements.。