机械振动第1章习题
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.39 MB
- 文档页数:25

机械振动复习题第⼀章⼀填空题1.机械运动是⼀种特殊形式的运动,在这种运动过程中,机械系统将围绕作运动。
2.从能量的⾓度看,惯性是保持的元素,恢复性是贮存的元素,阻尼是使能量散逸的元素。
3.⼀个质点在空间作⾃由运动,决定其位置需要个独⽴的坐标,⾃由度数为,⽽由n个相对位置可变的质点组成的质点系,其⾃由度数为,当系统收到r个约束条件时,系统的⾃由度数是。
4、系统的⾃由度是表明能够描述系统各部分在任⼀瞬时位置的独⽴的最⼩数⽬。
⼆、判断题1、简谐振动的加速度,其⼤⼩与位移呈正⽐,⽽⽅向与位移相反,始终指向平衡位置。
()2、简谐运动是周期运动。
()3、所有表⽰周期振动的周期函数都可以展开成Fourier级数的形式。
()4、⼴义坐标必须能完整地描述系统的运动。
()5、两个同频率的简谐振动在同⽅向的合成运动是该频率的简谐振动。
()三、简答题1、构成机械振动系统的基本元素有哪些?其作⽤?四、选择题1、单摆的⾃由度是()。
A、1B、2C、3D、02、⼀个单⾃由度系统都可以⽤这样⼀个理论模型来描述:它是由以下哪三个基本元件组成()ωA.理想的弹簧kB.理想的阻尼cC.理想的质量mD.理想的固有频率nE.理想的阻尼⽐ξ五、名词解释1、⾃由度六、计算题P16 1-1、1-2⼀、⼀填空题填空题1、阻尼对抑制系统近旁的运动有决定作⽤,⽽对系统在⾮共振频率的运动影响不⼤。
2、冲击⼒的特点是数值很⼤,但作⽤时间很。
3、单位作⽤下单⾃由度系统的响应称为脉冲响应函数。
4、振动问题的全解由态解和瞬态解组成。
5、振动测试仪器有三种基本形式:测试、和的仪器。
它们都是根据引起系统振动的原理⼯作的。
5、对于线性系统,叠加原理成⽴,即各激励⼒共同作⽤所引起的系统稳态响应为各激励⼒()时引起的系统各稳态响应的总和。
⼆、选择题1、对于机械系统有三种典型的强迫振动的情况()A.系统本⾝的不平衡引起的强迫振动B.简谐激励⼒作⽤下强迫振动C.基础运动引起的强迫振动D⽀承运动引起的强迫振动三、判断题1、线性系统内各个激励产⽣的响应是互不影响的。
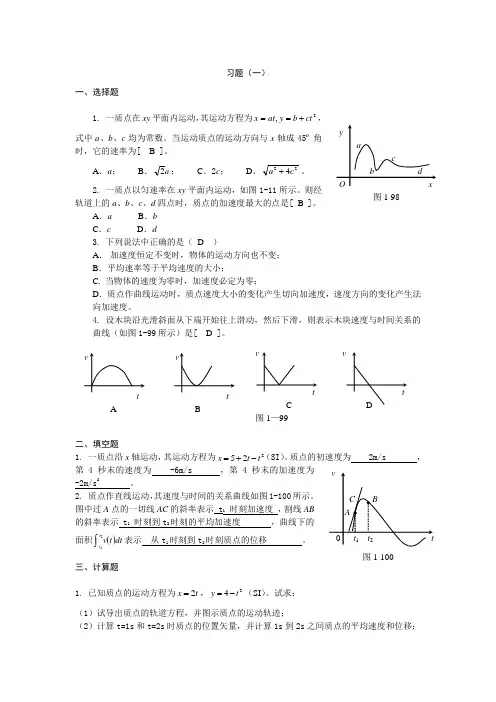
习题(一)一、选择题1. 一质点在xy 平面内运动,其运动方程为2,ct b y at x +==,式中a 、b 、c 均为常数。
当运动质点的运动方向与x 轴成45º角时,它的速率为[ B ]。
A .a ;B .a 2;C .2c ;D .224c a +。
2. 一质点以匀速率在xy 平面内运动,如图1-11所示。
则经轨道上的a 、b 、c 、d 四点时,质点的加速度最大的点是[ B ]。
A .aB .bC .cD .d3. 下列说法中正确的是( D )A . 加速度恒定不变时,物体的运动方向也不变;B .平均速率等于平均速度的大小;C. 当物体的速度为零时,加速度必定为零;D .质点作曲线运动时,质点速度大小的变化产生切向加速度,速度方向的变化产生法向加速度。
4. 设木块沿光滑斜面从下端开始往上滑动,然后下滑,则表示木块速度与时间关系的 曲线(如图1-99所示)是[ D ]。
二、填空题1. 一质点沿x 轴运动,其运动方程为225t t x -+=(SI )。
质点的初速度为 2m/s ,第4秒末的速度为 -6m/s ,第4秒末的加速度为-2m/s 2。
2. 质点作直线运动,其速度与时间的关系曲线如图1-100所示。
图中过A 点的一切线AC 的斜率表示 t 1 时刻加速度 ,割线AB 的斜率表示 t 1 时刻到t 2时刻的平均加速度 ,曲线下的面积()⎰21t t dt t v 表示 从t 1时刻到t 2时刻质点的位移 。
三、计算题1. 已知质点的运动方程为t x 2=,24t y -=(SI )。
试求:(1)试导出质点的轨道方程,并图示质点的运动轨迹;(2)计算t=1s 和t=2s 时质点的位置矢量,并计算1s 到2s 之间质点的平均速度和位移;(3)计算质点在第2秒末时的速度和加速度,并说明质点作何种运动?答:(1)由2x t =得2xt = ,代入22y t =-224x =-即为轨道方程。

第1章1。
单选题(本大题共94小题)1。
(1分)以零部件装备配或更换时不需要挑选、辅助加工与修配为条件的互换性,等于_______互换性。
A、绝对B、完全C、有限D、不完全2.(1分)分组装配法等于典型的________互换性,其方法是零件加工完后,根据零件实测尺寸的大小,将制成的零件分成若干组,使每组内的尺寸差别较小,然后对相应组的零件进行装配。
A、绝对B、不完全C、完全D、有限3.(1分)国际标准化组织的号是________。
A、ISOB、ANSIC、JISD、KS4.(1分)不属于国家标准的代号是_________。
A、GBB、GB/TC、JBD、QB5.(1分)__________℃为标准计量温度.A、20B、25C、0D、1006.(1分)关于孔和轴的概念,下列说法中错误的是_______.A、圆柱形的内表面为孔,圆柱形的外表面为轴B、孔和轴的形状一定都是圆的C、从装配关系上看,包容面为孔,被包容面为轴D、从加工过程上看,切削过程中尺寸由小变大的为孔,尺寸由大变小的为轴7。
(1分)基本尺寸是______.A、测量时得到的B、加工时得到的C、装备后得到的D、设计时给定的8。
(1分)最大极限尺寸与基本尺寸的关系是_______。
A、前者大于后者B、前者小于后者C、前者等于后者D、两者之间的大小无法确定9。
(1分)某尺寸的实际偏差为零,则实际尺寸_________.A、必定合格B、为零件的真实尺寸C、等于基本尺寸D、等于最小极限尺寸10。
(1分)当上偏差或下偏差为零时,在图样上进行标注时________。
A、必须标出B、不用标出C、标与不标皆可D、视具体情况而定11.(1分)极限偏差是________.A、设计时确定的B、加工后测量得到的C、实际尺寸减基本尺寸的代数差D、最大极限尺寸与最小极限尺寸之差12.(1分)关于尺寸公差,下列说法中正确的是_________。
A、尺寸公差只能大于零,故公差值前应标“+”号B、尺寸公差是用绝对值定义的,没有正、负的含义,故公差值不应标“+”号C、尺寸公差不能为负值,但可为零值D、尺寸公差为允许尺寸变动范围的界限值13.(1分)Φ200030 .0+mm与Φ2000072 .0+mm相比,其尺寸精确程度________.A、相同B、前者高,后者低C、前者低,后者高D、无法比较14.(1分)当孔的最大极限尺寸与轴的最小极限尺寸的代数差为正值时,此代数差称为_____。

机械振动考题第一章1.21.If energy is lost in any way during vibration, the system can be considered to be damped. (T)2.Superposition principle is valid for both linear and nonlinear systems(F)3.The frequency with which an initially disturbed system vibrates on its own is known as natural frequency(T)4.Any periodic function can be expanded into Fourier series(T)5.Harmonic motion is a periodic motion(T)6.The equivalent mass of several masses at different locations can be found using the equivalence of kinetic energy(T)7.The generalized coordinates are not necessarily Cartesian coordinates. (T)8.Discrete systems are same as lumped parameter systems(T)9.Consider the sum of harmonic motions,, withand The amplitude A is given by 30.8088(T)10.Consider the sum of harmonic motions, , withand The phase angle α is given by 1.57 rad. (F)第二章2.21.The amplitude of an undamped system will not change with time.(T)2.A system vibrating in air can be considered as a damped system(T)3.The equation of motion of a single degree of freedom system will be the same whether the mass moves in a horizontalplane or an inclined plane.(T)4.When a mass vibrates in a vertical direction, its weight can always be ignored in deriving the equation of motion(F)5.The principle of conservation of energy can be used to derive the equation of motion of both damped and undamped systems(F)6.The damped frequency can be larger that the undamped natural frequency of the system in some cases(F)7.The damped frequency can be zero in some cases. (T)8.The natural frequency of vibration of torsional system is given by where k and m denote the torsional spring constant and the polar mass moment of inertia, respectively(T)9.Rayleigh’s method is based on the principle of conservation of energy(T)10.The final position of the mass is always the equilibrium position in the case of Coulomb damping. (F)11.The undamped natural frequency of a system is given by , where is the static deflection of the mass(T)12.For an undamped system, the velocity leads the displacement by . (T)13.For an undamped system, the velocity leads the acceleration by (F)14.Coulomb damping can be called constant damping(T)15.The loss coefficient denotes the energy dissipated per radian per unit strain energy.(T)16.The motion diminishes to zero in both underdamped and overdamped cases. (T)17.The logarithmic decrement can be used to find the damping ratio(T)18.The hysteresis loop of the stress –strain curve of amaterial causes damping(T)19.The complex stiffness can be used to find the damping force in a system with hysteresis damping(T)20.The motion can be considered to be harmonic in the cases of hysteresis damping(T)第三章3.21.The magnification factor is the ratio of maximum amplitude and static deflection(T)2.The response will be harmonic if excitation is harmonic(T)3.The phase angle of the response depends on the system parameter m, c, k, and ω(T)4.The phase angle of the response depends on the amplitude of the forcing function.(F)5.During beating, the amplitude of the response builds up and then diminishes in a regular pattern (T)6.The Q-factor can be used to estimate the damping in a system (T)7.The half power points denote the values of frequency ratio where the amplification factor falls towhere Q is the Q-factor. (T)8.The amplitude ratio attains its maximum value at resonance in the case of hysteresis damping(F)9.The response is always in phase with the harmonic forcing function in the case of hysteresis damping(T)10.Damping reduces the amplitude ratio for all values of the forcing frequency. (T)11.The unbalance in a rotating machine causes vibration(T)12.The steady state solution can be assumed to be harmonicfor small values of dry friction force(T)13.In a system with rotational unbalance, the effect of damping becomes negligibly small at higher speeds. A set is a collection of objects(T)第四章4.21.The change in momentum is called impulse (T)2.The response of a system under arbitrary force can be found by summing the responses due toseveral elementary impulses (T)3.The response spectrum corresponding to base excitation is useful in the design of machinery subject to earthquakes (T)4.Some periodic functions can not be replaced by a sum of harmonic functions (F)5.The amplitudes of higher harmonics will be smaller in the response of a system. (T)6.The Laplace transform method takes the initial conditions into account automatically (T)7.The equation of motion can be integrated numerically even when the exciting force is nonperiodic (T)8.The response spectrum gives the maximum response of all possible single degree of freedom systems (T_9.For a harmonic oscillator, the acceleration and displacement spectra can be obtained from the velocity spectrum. (T)第五章5.21.The normal modes can also be called principal modes (T)2.The generalized coordinates are linearly dependent (F)3.Principal coordinates can be considered as generalizedcoordinates (T)4.The vibration of a system depends on the coordinate system (F)5.The nature of coupling depends in the coordinate system (T)6.The principal coordinates avoid both static and dynamic coupling.(T)7.The use of principal coordinates helps in finding the response of the system (T)8.The mass, stiffness, and damping matrices of a two degree of freedom system are symmetric (T)9.The characteristics of a two degree of freedom system are used in the design of dynamic vibration absorber (T)10.Semi-definite systems are also known as degenerate systems (T)11.A semi-definite system can not have non-zero natural frequencies (F)12.The generalized coordinates are always measured form the equilibrium position of the body (F)13.During free vibration, different degrees of freedom oscillate with different phase angles (F)14.During free vibration, different degrees of freedom oscillate at different frequencies (F)15.During free vibration, different degrees of freedom oscillate with different amplitudes (T)16.The relative amplitude of different degrees of freedom ina two degree of freedom system depend on the natural frequency (T)17.The modal vectors of a system denote the normal modes of vibration (T)第六章6.21.For a multidegree of freedom system, one equation of motion can be written for each degree of freedom (T) /doc/db13674645.html,grange’s equation cannot be used to derive the equations of motion of a multidegree of freedom system (F)3.The mass, stiffness, and damping matrices of a multidegree of freedom are always symmetric (T)4.The product of stiffness and flexibility matrices of a system is always an identity matrix (T)5.The modal analysis of a n-degree of freedom system can be conducted using r modes with r < n (T)6.For a damped multidegree of freedom system, all the eigenvalues can be complex (T)7.The modal damping ratio denotes damping in a particular normal mode (T)8.A multidegree of freedom system can have six of the natural frequencies equal to zero (T)9.The generalized coordinates will always have the unit of length (F)10.The generalized coordinates are independent of the conditions of constraint of the system (T)11.The generalized mass matrix of a multidegree of freedom system is always diagonal (F)12.The potential and kinetic energies of a multidegree of freedom system are always quadratic functions (T)13.The mass matrix of a system is always symmetric and positive definite (T)14.The stiffness matrix of a system is always symmetric andpositive definite (F)15.The rigid body mode is also called the zero mode. (T)16.An unrestrained system is also known as a semi-definite system. (T)17.Newton’s second law of motion can always be used to derive the equations of motion of a vibrating system (T) 第七章7.21.T he fundamental fr equency given by Durkerley’s formula will always be larger than the exact value (F)2.The fundamental frequency given by Rayleigh’s method will always be larger than the exact value (T)3.is a standard eigenvalue problem (F)4.is a standard eigenvalue problem (T)5.Jacobi method can find the eigenvalues of only symmetric matrices. (T)6.Jacobi method uses rotation matrices. (T)7.The matrix iteration method requires the natural frequencies to be distinct and well separated (T)8.In matrix iteration method, any computational error will not yield incorrect results (T)9.The matrix iteration method will never fail to converge to higher frequencies. (F)10.When Rayleigh’s method is used for a shaft carrying several rotors, the static deflection curve can be used as the appropriate mode shape. (T)11.Rayleigh’s method can be considered to be same as the conservation of energy for a vibrating system (T)第八章8.21.Continuous systems are same as distributed systems. (T)2.Continuous systems can be considered to have infinite number of degrees of freedom. (T)3.The governing equation of a continuous system is an ordinary differential equation. (F)4.The free vibration equations corresponding to the transverse motion of a string, the longitudinal motion of a bar and the torsional motion of a shaft have the same form. (T)5.The normal modes of a continuous system are orthogonal. (T)6.A membrane has zero bending resistance. (T)7.Rayleigh’s method can be considered as a method of conservation of energy.(T)8.Rayleigh-Ritz method assumes the solution as a series of functions that satisfy the boundary conditions of the problem. (T)9.For a discrete system, the boundary conditions are to be applied explicitly. (T)10.The Euler-Bernoulli beam theory is more accurate than the Timoshenko theory. (F)第九章9.21.Vibration can cause structural and mechanical failures. (T)2.The response of a system can be reduced by the use of isolators and absorbers (T)3.Vibration control means the elimination or reduction of vibration (T)4.The vibration caused by a rotating unbalanced disc can be eliminated by adding a suitable mass to the disc (T)5.Any unbalanced mass can be replaced by two equivalent unbalanced masses in the end planes of the rotor (T)6.The oil whip in the bearings can cause instability in a rotor system (T)7.The natural frequency of a system can be changed by varying its damping (F)8.The stiffness of a rotating shaft can be altered by changing the location of its bearings (T)9.All practical systems have damping. (T)10.High loss factor of a material implies less damping (F)11.Passive isolation systems require external power to function (F)12.The transmissibility is also called the transmission ratio. (T)13.The force transmitted to the foundation of an isolator with rigid foundation can never be infinity (F)14.Internal and external friction can cause instability in a rotating shaft at speeds above the first critical speed (T)。






1、简谐运动的概念①简谐运动的定义:____________________________________________________________。
②简谐运动的物体的位移x、回复力F、加速度a、速度v、动能E K、势能E P的变化规律:A.在研究简谐运动时位移的起点都必须在处。
B.在平衡位置:位移最、回复力最、加速度最;速度最、动能最。
C.在离开平衡位置最远时:_________________________________________。
D.振动中:注意以上各量的矢量性和对称性。
③简谐运动机械能守恒,但机械能守恒的振动不一定时简谐运动。
④注意:A.回复力是效果力。
B.物体运动到平衡位置不一定处于平衡状态(如单摆,最低点有向心力)。
C.简谐运动定义式F=-K x中的K不一定是弹簧的劲度系数,是振动系数(如双弹簧)。
1.A关于回复力,下列说法正确的是( )A.回复力一定是物体受到的合外力B.回复力只能是弹簧的弹力提供C.回复力是根据力的作用效果命名的D.回复力总是指向平衡位置答案:CD2.A下列的运动属于简谐运动的是( )A.活塞在气缸中的往复运动B.拍皮球时,皮球的上下往复运动C.音叉叉股的振动D.小球在左右对称的两个斜面上来回滚动答案:C3.A一质点做简谐运动,当位移为正的最大值时,质点的( )A.速度为正的最大值,加速度为零B.速度为负的最大值,加速度为零C.速度为零,加速度为正的最大值D.速度为零,加速度为负的最大值答案:D4.A关于简谐运动的位移、加速度和速度的关系,正确的说法是( )A.位移减小时,加速度增大,速度增大B.位移方向总和加速度方向相反,和速度方向相同C.物体的速度增大时,加速度一定减小D.物体向平衡位置运动时,速度方向和位移方向相同答案:C6.B关于简谐运动中的平衡位置,下列说法正确的是( )A.平衡位置就是物体所受合外力为零的位置B.平衡位置就是加速度为零的位置C.平衡位置就是回复力为零的位置D.平衡位置就是受力平衡的位置答案:C7.B一平台沿竖直方向做简谐运动,一物体置于平台上随台一起运动,当振动平台处于什么位置时,物体对台面的压力最大( )A.振动平台在最高位置时B.振动平台向下振动经过平衡位置时C.振动平台在最低位置时D.振动平台向上运动经过平衡位置时答案:C8.B简谐运动是下列哪一种运动( )A.匀速直线运动B.匀加速运动C.匀变速运动D.变加速运动答案:D9.B做简谐运动的物体每次经过同一位置时,一定相同的物理量是( )A.速度B.位移C.回复力D.加速度答案:BCD10.B 对于弹簧振子,其回复力和位移的关系,在下图中正确的是()答案:C11.C 对简谐运动的回复力F=-kx 的理解,正确的是()A.k 只表示弹簧的劲度系数B.式中负号表示回复力总是负值C.位移x 是相对平衡位置的位移D.回复力只随位移变化,不随时间变化答案:C12.C 弹簧振子的质量是0.2kg,在水平方向做简谐运动,当它运动到平衡位置左侧x 1=2cm 的位置时,受到的回复力大小F 1=4N,则当它运动到平衡位置右侧x 2=4cm 的位置时,它的加速度是()A.20m/s 2,方向向左 B20m/s 2,方向向右C.40m/s 2,方向向左 D.40m/s 2,方向向右答案:C二、计算题(共16分)13.C 试证明:用轻弹簧悬挂一个振子,让它在竖直方向振动起来,在弹性限度内,振子是做简谐运动.(如图)答案:设振子的平衡位置为O,令向下为正方向,此时弹簧的形变为x 0,根据胡克定律及平衡条件有mg-kx 0=0.当振子向下偏离平衡位置x 时,有F=mg-k(x+x 0) 整理可得F=-kx(紧扣简谐运动特征及对称性)故重物的振动满足简谐运动的条件 2、总体上描述简谐运动的物理量①振幅A :_ _称为振幅。

1.1 试举出振动设计、系统识别和环境预测的实例。
1.2 如果把双轴汽车的质量分别离散到前、后轴上去,在考虑悬架质量和非悬架质量两个离散质量的情况下,画出前轴或后轴垂直振动的振动模型简图,并指出在这种化简情况下,汽车振动有几个自由度?1.3 设有两个刚度分别为1k ,2k 的线性弹簧如图T —1.3所示,试证明:1)它们并联时的总刚度eq k 为:21k k k eq +=2)它们串联时的总刚度eq k 满足:21111k k k eq +=解:1)对系统施加力P ,则两个弹簧的变形相同为x ,但受力不同,分别为:1122P k x P k x=⎧⎨=⎩由力的平衡有:1212()P P P k k x =+=+故等效刚度为:12eq Pk k k x ==+2)对系统施加力P ,则两个弹簧的变形为: 1122Px k P x k ⎧=⎪⎪⎨⎪=⎪⎩,弹簧的总变形为:121211()x x x P k k =+=+故等效刚度为:122112111eq k k P k x k k k k ===++1.4 求图所示扭转系统的总刚度。
两个串联的轴的扭转刚度分别为1t k ,2t k 。
解:对系统施加扭矩T ,则两轴的转角为: 1122t t Tk T k θθ⎧=⎪⎪⎨⎪=⎪⎩系统的总转角为:121211()t t T k k θθθ=+=+,12111()eq t t k T k k θ==+故等效刚度为:12111eq t t k k k =+1.5 两只减振器的粘性阻尼系数分别为1c ,2c ,试计算总粘性阻尼系数eq c1)在两只减振器并联时,2)在两只减振器串联时。
解:1)对系统施加力P ,则两个减振器的速度同为x,受力分别为: 1122P c x P c x =⎧⎨=⎩由力的平衡有:1212()P P P c c x =+=+ 故等效刚度为:12eq P c c c x ==+ 2)对系统施加力P ,则两个减振器的速度为: 1122P x c P x c ⎧=⎪⎪⎨⎪=⎪⎩,系统的总速度为:121211()x x x P c c =+=+ 故等效刚度为:1211eq P c x c c ==+1.6 一简谐运动,振幅为0.5cm,周期为0.15s,求最大速度和加速度。
习题课及考前复习(24题)
一、考试知识点
二、考题分布情况
三、作业题
四、课堂练习题
五、经典例题
一、考试知识点
第一章
1、单自由度系统振动方程。
2、无阻尼单自由度系统的自由振动。
3、等效单自由度系统。
4、有阻尼单自由度系统的自由振动。
5、简谐力激励下的受迫振动。
6、基础简谐激励下的受迫振动。
第二章
1、多自由度系统的振动方程。
2、建立系统微分方程的方法。
3、无阻尼系统的自由振动。
4、无阻尼系统的受迫振动。
二、考题分布情况
1、主要围绕作业题、课堂练习题、经典例题题型展开。
2、复习时把握每章知识要点,理解基础题型解题方法。
3、考卷共6道大题。
习题课及考前复习(24题)
一、考试知识点
二、考题分布情况
三、作业题
四、课堂练习题
五、经典例题
m
222(2)m l θ= ⎧⎨⎩211
(2)m l θ= 212(22)2k l l l θθ−⋅−⋅⋅11k l l θ−⋅221(22)2k l l l
θθ−⋅−⋅⋅
习题课及考前复习(24题)
一、考试知识点
二、考题分布情况
三、作业题
四、课堂练习题
五、经典例题
m
m
m
m
m
m
习题课及考前复习(24题)
一、考试知识点
二、考题分布情况
三、作业题
四、课堂练习题
五、经典例题
m。
《机械振动学》课程习题库第一章1.1 何谓机械振动?表示物体运动特征的物理量有哪些? 1.2 按产生振动的原因分为几类?按振动的规律分为几类? 1.3 何谓线性系统、机械系统和等效系统?1.4 如何理解瞬态振动、稳态振动、自由振动、强迫振动、纵向振动。
横向振动、扭转振动、参数振动和非线性振动?1.5 写出频率、角频率、相位、幅值、有阻尼固有频率,并说明意义,注明单位值。
1.6 如何理解粘性阻尼系数、等效阻尼、临界阻尼系数、欠阻尼和过阻尼? 1.7 振动对机械产品有哪些影响?1.8 利用振动原理而工作的机电设备有哪些?试举例说明。
1.9 重温非简谐的周期性振动傅里叶级数,时间函数为f(t),其周期为T ,表达式为:)s i n c o s ()(10t n b t n an a t f n n ωω++=⎰∞=式中:⎰=Tdt t f Ta 00)(1⎰=Tn tdt n t f T a 0cos )(2ω⎰=Tn tdt n t f T b 0sin )(2ω 注:《手册》P91.10将下图所示的f(t)展成傅立叶级数。
参考答案:()∑∞===5.2.1sin 1440t np t f n pb n b n n n ωππ傅氏级数为奇数时,,当为偶数时,当 f(t)P 0 -Pπ/ω2π/ω 3π/ω 4π/ωt1.11今有一简谐位移x(t)(mm),其表达式为:()=8sin(24 -),3x t t π求:1. 振动的频率和周期;2. 最大位移、最大速度和最大加速度;3. t=0时的位移、速度和加速度;4. t=1.5s 时的位移、速度和加速度。
参考答案:24rad/s ,3.82Hz ,0.2618s ;192mm/s ,4608mm/s 2;-6.9282mm ,96mm/s ,3990.65 mm/s 2 ;-3.253mm ,175.4mm/s ,1874 mm/s 21.12一振动体作频率为50Hz 的简谐振动,测得其加速度为80 m/s 2 ,求它的位移幅值和速度幅值。