《电子技术专业英语》单元设计03
- 格式:doc
- 大小:72.00 KB
- 文档页数:4

《电子信息技术行业英语》课程标准
一、课程基本信息
二、课程的性质、目的和任务
1.课程性质
是学院电子信息工程技术专业物联网方向的专业基础课。
在第三学期开设的必修课,通过本课程的学习,使学生掌握相关英语词汇,旨在提高学生的专业英语读写和应用能力。
前导课程为基础英语,基础为本专业学习的相关理论。
2.目的和任务
通过本门课程的学习,使学生熟悉和掌握计算机专业英语的专业词汇,计算机专业技术术语,培养阅读英语科技资料的能力。
为形成综合职业能力奠定基础,为今后的学习和发展有着积极的作用。
三、课程教学的基本要求
四、课程的教学重点和难点、学时分配
教学重点:专业词汇的翻译教学难点:专业词汇和语法的翻译
课程学时分配一览表
五、相关课程的衔接
开设此门课程之前,学生应完成基础英语的学习。
六、其它
课程的考核与评价。
考核重点是考察学生是否掌握计算机应用中的英语知识,包括常见的专业英语语法、句型、常用词组,并具有一定的翻译能力。
考核方式为理论考核+过程考核。
考核内容除了考查学生对该门课程基础知识的掌握情况以外,增加了应用、创新知识的考核,考查学生运用所学课程知识分析问题和解决问题的能力。
学生成绩包括平时成绩和期末考试成绩,其中,平时成绩占50%,期末考核占50%。
成绩考核方法分为过程考核和理论考核两种。
平时成绩为过程考核,包括出勤表现20%、课堂提问20%、作业测评10%,期末考试为理论考核,重点考核学生的专业知识水平。
通过进行试卷分析,研究考核过程中出现的问题并提出解决的措施,以便在以后的教学过程中进行改进。

《专业英语》教学大纲English for Electronic Information Science and Technology学 时:32学 分:2 制订者:陈青春审核者:鲁植雄一、课程性质本课程为电子信息科学与技术专业科类选修课,授课对象为电子信息科学与技术专业高年级学生,宜安排在三年级进行。
二、教学目的与要求通过本课程学习,掌握电子信息科学与技术的英语表达方式和常用词汇,提高本专业英语原文文献的阅读能力。
三、教学内容及安排(一)课堂讲授部分(32学时)内 容学时 Course introduction 2 Unit 1 Electronic devices 3 Unit 2 Electronic circuits3 Unit 3 Electronic system components 3 Unit4 Electronic system 3 Unit5 Modern digital design 3 Unit6 Digital signal processing 3 Unit7 Audio and voice 3 Unit8 Image and video 3 Unit9 Embedded applications3 Unit 10 Electronic instruments and measurements3(二)实验部分(0学时)四、考核方式及成绩评定考核方式:开卷考试,120分钟,百分制成绩评定:平时成绩(作业、考勤、答疑)占总成绩30%; 期终考试占总成绩70%五、教材与参考书(一)教材1.任治刚编,《电子信息工程专业英语》,2004年,电子工业出版社,第一版(二)参考书1.李白萍编,《电子信息类专业英语》,2004年,西安电子科技大学出版社,第一版。
Teaching Design for Electronic Circuit Basics(English version)IntroductionThe electronic circuit is a fundamental tool for many industriesthat use electrical systems. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the basics of electronic circuits to ensure efficient and successful integration into designs. This document presents the teaching design for electronic circuit basics in English, targeting learners at the beginner to intermediate level. The course ms to guide learners through the construction, operation, and troubleshooting of fundamental electronic circuits.Course GoalsThe course has the following goals:1.An understanding of electronic circuit components and theirfunctionality.2.The ability to read and interpret electronic circuitdiagrams.3.The ability to design basic electronic circuits for specificapplications.4.The ability to test and troubleshoot electronic circuits.Course OutlineModule 1: Introduction to Electronic CircuitsThis module introduces learners to the fundamental concepts of electronic circuits. Topics covered include electronic components, circuit diagrams, and circuit analysis techniques. Learners will obtn a foundation that will enable them to safely and effectively work with electronic circuits.Module 2: Resistors and CapacitorsThis module explores the use of resistors and capacitors within electronic circuits. Learners will discuss the various technologies avlable for these components and how they can be utilized effectively within circuit design.Module 3: Diodes and TransistorsLearners will understand the basics of semiconductor technology and how it is used in diodes and transistors. The module covers the mode of operation of diodes and transistors and their practical applications in electronic circuits.Module 4: AmplifiersThis module teaches learners how amplifiers work and how they can strengthen signals. The module also covers the different types of amplifiers and their applications.Module 5: Digital ElectronicsThe final module of the course focuses on digital electronics, which is a crucial aspect of modern-day electronics. The module covers binary numbers, Boolean algebra, logic gates, and how to design basic digital circuits using these concepts.Course DeliveryThe course will be delivered in an e-learning environment, utilizing an online platform that enables the learners to access the course materials from any internet-connected device. The course will consist of video lectures, interactive quizzes, and hands-on practical exercises. The learners will also receive a certificate of completion after they successfully complete the course.AssessmentLearners will be assessed continually throughout this course to ensure that they have understood the fundamental concepts. Each module will conclude with a quiz that covers the course material.ConclusionThis teaching design for electronic circuit basics ms to provide learners with a fundamental understanding of the components and operations of electronic circuits. With these skills, learners will be equipped to design, build and troubleshoot basic electronic circuits. This course is structured to enable learners to work at their own pace while providing regular feedback to ensure that they have a comprehensive understanding of the concepts presented.。

1、汉译英1)直流电路direct current circuits2)放大器(扩音器)amplifier3)模拟电子技术analog electronics4)半导体二极管semiconductor diode5)晶体管效应transistor effect6)微处理器microprocessor7)电气工程electrical engineering8)能源工程(或电力工程)power engineering9)通信工程telecommunications engineering10)内部器件internal devices11)电子元件electrical components12)欧姆定律Ohm law13)限制电流limit current14)分压器voltage divider15)晶体管偏置电路transistor biasing circuits16)阻碍电流block DC current17)存储点能store electrical energy18)感抗inductive reactance19)绝缘材料insulating material20)交流阻抗AC resistancea)通用仪表general-purpose meterb)模拟仪表analog meterc)交换测试笔reverse the test leadsd)机械调节mechanical adjuste)测量电阻measure resistancef)正向电压positive voltageg)测量电流measure currenth)电压幅度voltage amplitudei)双踪示波器dual-trace oscilloscopej)信号发生器signal generator21)PN结PN junction22)三极管bipolar transistor23)电子和空穴electron and hole24)稳压电源electronic power supply或steady DC voltage source25)桥式整流器bridge rectifier26)脉冲直流电pulsating DC27)二极管的正极anode of diode28)峰值电压peak voltage29)电容滤波器capacitor filter30)充电和放电charge and discharge31)稳压管Zener diode32)电器电子工程师学会IEEE(Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers)33)专业技术组织technical professional association34)基尔霍夫电压定律Kirchhoff’s V oltage Law35)电压源voltage sources36)电荷守恒定律the law of conservation of electric charge37)在每一瞬时at every instant of time38)元件两端的电压voltages across elements39)无线电传输radio transmission40)频率调制或调频frequency modulation41)频域the frequency domain42)线性电阻linear resistor43)调幅波形amplitude modulation wave44)专用集成电路(ASIC)45)快速时间响应fast response time46)有效信号valid signal47)十进制数字系统decimal system48)逻辑运算logic operation1)控制信号线the control bus2)中断线interrupt lines1)结构化语言structured language2)局部变量local variables3)副作用side effect4)汇编语言指令assembly language instructions1)静止图像still image2)阴极射线管,显像管CRT or the cathode ray tube3)像素pixel4)电子束electron beam2、英译汉1)assembler language汇编语言2)alternating current circuits交流电路3)passive electrical circuits无源电路4)three phase circuits三相电路5)digital electronics数字电子技术6)logic gates逻辑门7)3D virtual reality image三维虚拟图像8)computer programming计算机编程9)major in(在大学里)主修10)advanced programming techniques高级编程技术1)known as capacitive reactance称为容抗2)with units ohms单位为欧姆3)prevent device from burning out防止器件烧掉4)has an AC resistance to AC current对交流电流由阻抗5)adjustment with a screw用一个螺丝调节6)in the shape of a cylinder 呈圆柱形式7)block DC current,but pass AC current阻直流通交流8)to vary the inductance改变电感9)be given by the formula 由公式给出10)the RF amplifier 音频放大器1)analog multimeter模拟万用表2)extended range扩展范围3)specific meters特殊仪表4)includes the function and range switches具有功能及范围选择旋钮5)present an electronic picture呈现一幅电子图像6)display the voltage waveform显示电压波形7)appear on the screen在屏幕上出现8)phase relationships相位关系9)an example例如,作为一个例子10)in series with the circuit串连接入电路1)Semiconductor material半导体材料2)forward biased正向偏置3)depend on the external circuit resistance取决于外部电路的电阻4)excessive reverse-biased voltage过高的反偏电压5)is directly proportional to the amount ofbase current是正比于基极电流6)may even appear almost as a short几乎可看成是短路7)cause stability problems for a transistorcircuit引起晶体管电路的稳定性问题8)digital technology数字技术9)the most popular technology最常用的技术10)use two complementary typeset oftransistors N-channel and P-channel用两种互补型的晶体管——N沟道和P沟道1)equipment operation设备的运行2)device that converts AC into DC把交流电转换成直流电的器件3)the power lines电源线4)depending on the value of DC voltageneeded 根据所需要的直流电压值5) a half-wave rectifier平波整流器6)so as to produce a constant DC output从而产生一个稳定的直流输出7)in the negative side of the capacitor在电容的负极8)flow through the load流过负载9)in the forward-biased condition在加正向偏置电压的条件下10) a series(current-limiting)resistor一个串联(限制电流)电阻1)current source电流源2)under this circumstance在这种情况下3)present the second of Kirchhoff’s laws给出基尔霍夫第二定律4)introduce the concept of a “loop”引入“回路”的概念5)An alternative statement of KVLKVL的另一种表述法6)voltages algebraically sum电压代数和7)sinusoidal steady-syate response正弦稳态响应8)ordinary household voltage日常用电的电压9)time-invariant circuit时不变电路10)percentage of modulation调制百分比reduce the power consumption减小消耗功率flip-flop 触发器the octal and hexadecimal systems当时钟脉冲信号来到时改变状态①直流电路direct current circuits②放大器(扩音器)amplifier③欧姆定律Ohm law④正极positive electrode⑤充电与放电Charge and discharge⑥无线电传输Radio transmission⑦模拟仪表Analogue Meters⑧模拟电子技术analog electronics⑨半导体二极管semiconductor⑩晶体管效应transistor effect⑪微处理器microprocessor⑫通信工程telecommunications engineering ⑬汇编语言assembler language⑭电子元件electrical components⑮限制电流limit current⑯分压器voltage divider⑰偏置电路biasing circuits⑱阻碍电流block DC current⑲感抗inductive reactance⑳容抗capacitive21正向电压positive voltage22扩展范围extended range23电压波形voltage waveform24连接入电路in series with the circuit25PN结PN junction 26三极管bipolar transistor27电子与空穴electron and hole28半导体材料semiconductor material29正向偏置forward biased30数字技术digital technology31桥式整流器bridge rectifier32稳压管Zener diode33电源线the power lines34在电容的负极in the negative side of the capacitor 在加正向偏置的条件下in the forward-biased condition一个串联电阻 a series (current-limiting)resistor35电压源voltage sources36在每一瞬时at every instant of time37无线电传输radio transmission38频率调制或调频frequency modulation39快速时间响应fast response time40有效信号valid signal41结构化语言structured language42局部变量local variables43副作用side effect44静止图像still image45阴极射线管pixel46电子束electron beam1.resistors are used to limit current flowing to adevice ,thereby preventing it from burning out, as voltage dividers to reduce voltage for other circuits, as transistor biasing circuits, and to serve as circuit loads.电阻常用做限流器,限制流过器件的电流防止烧坏器件,电阻也可用作分压器,以减小其他电路电压,还可以用在晶体管偏执电路中和作为电路负载。



电子科学与技术专业英语第三章大部分翻译(P139)3.1晶界生长与外延正如前面第一章所讨论的那样,在分立器件和集成电路中最重要的两种半导体是硅和砷化镓,在这一章我们叙述这两种半导体的常用的单晶生长技术,基本的工艺流程是从原料到抛光晶片,原料经过化学处理做成一个用来生长单晶的高纯多晶半导体。
单晶硅锭铸形,以定义材料的直径,这些晶片经过腐蚀和抛光来提供一个光滑的特定的且器件将做在上面的表面。
一种和单晶生长密切相关的技术包含一个单晶半导体层在一个单晶半导体衬底的生长,这叫外延,它是从希腊语epi和taxis得来的,外延工艺提供了一种重要的控制掺杂形貌的技术,以至于器件和电流性能可以被优化。
例如,一个掺杂浓度相称低的半导体层可以在一个同型掺杂而浓度很高的衬底外延生长,通过这种方式和衬底相关联的体电阻将被充分地减少,许多新的器件结构,特别是微波和光学器件,可以通过外延工艺制得。
在这章的后面我们将考虑讨论一些重要外延生长技术。
(p140)3.2从熔体生长单晶从熔体生长单晶有两种基本方法,直拉法和布里奇曼法,用于半导体行业的充足百分比的硅单晶是通过直拉法制备的,实际上所有的用于集成电路制造的硅都是用这方法制备的。
大部份的砷化镓,在另一方面,是通过布里奇曼法生长的。
然而,直拉法在生长大直径的砷化镓方面变得越来越流行。
3.2.1原始材料硅的起始材料是一种相当纯的叫做石英的沙子形式。
它和各种形式的碳被置于炉中,当很多反应在炉中发生时,总的反应式是SI+SIO2=这种工艺生产出纯度98%的冶金及的硅。
下一步,硅被磨碎和氯化氢反应生成三氯氢硅(SIHCL3)SI + 2HCL三氯氢硅在温室下是液体,液体分馏除去不要的杂质,净化过后的SIHCL3用于与氢气反应。
制备电子级的硅(EGS):SIHCL3+这个反应在包括为硅的沉积提供晶体成核点的电阻加热硅棒的反应堆中发生,纯度为电子级别的硅,也就是一个高纯的多晶硅材料,是用于制备器件级质量的单晶硅的未加工材料。

电子科学与技术专业专业英语教学大纲目录专业英语1教学大纲1一、课程开设目的与要求2二、教学中应注意的问题2三、课程内容及学时分配2Chapter 1Semiconductors Physics2Chapter 2Semiconductor Device2Chapter 3Processing Technology3Chapter 4Integrated Circuits3Chapter 5Microeleclromechanical Systems (MEMS)3Chapter 6Examples of Scientific and Technological Papers3四、授课学时分配4五、教材及参考书目4一、课程开设目的与要求电子科学与技术专业英语是电子科学与技术专业的一门专业必修课程。
主要目标是培养学生以英语为工具获取专业信息,及应用英语进行口头、书面专业交流的能力。
通过本课程的学习,使学生学习专业英语的常用语法和惯用法;掌握电子科学与技术领域常用的专业词汇、术语和缩略词;了解电子科学与技术专业领域的最新技术和发展动向;掌握基本的专业英语阅读和翻译技巧,为毕业后阅读专业英文文献打下良好的基础,培养学生能够借助工具阅读电子科学与技术专业书籍,并能够对相关资料进行翻译的能力。
二、教学中应注意的问题1.专业英语的先修课程:大学英语、大学物理、高等数学、电磁场、集成电路设计等;2.本课程教学应采用互动式的教学方式。
即通过将示范讲解和课上练习相互结合的方式,既能够调动学生们学习的主动性,也可以及时检查学生的学习效果。
示范讲解着重专业术语和句子的理解,重点培养学生的专业文献阅读能力和翻译能力。
三、课程内容及学时分配Chapter 1 Semiconductors Physics重点内容:学习半导体物理中的常用词汇和专业术语。
了解阅读的基本要素和基本的阅读方法。
基本要求:1.掌握半导体物理学中的常用词汇和专业术语;2. 了解阅读的基本要素和基本的阅读方法。
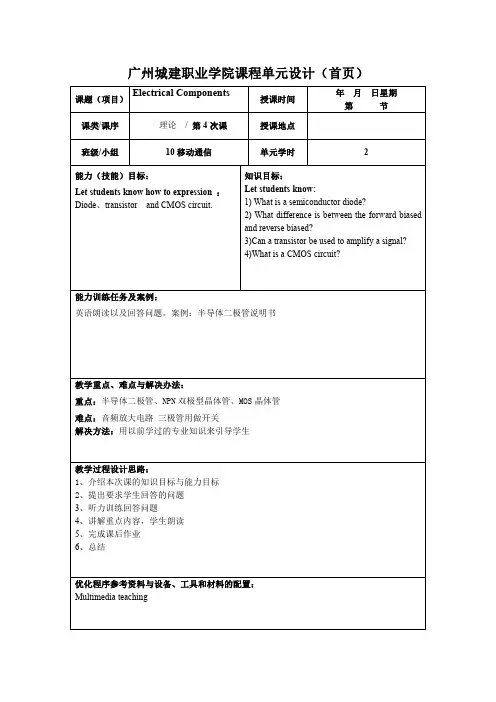
广州城建职业学院课程单元设计(首页)课题(项目)Electrical Components授课时间年月日星期第节课类/课序理论/第4次课授课地点班级/小组10移动通信单元学时2能力(技能)目标:Let students know how to expression:Diode、transistor and CMOS circuit.知识目标:Let students know:1)What is a semiconductor diode?2)What difference is between the forward biased and reverse biased?3)Can a transistor be used to amplify a signal?4)What is a CMOS circuit?能力训练任务及案例:英语朗读以及回答问题。
案例:半导体二极管说明书教学重点、难点与解决办法:重点:半导体二极管、NPN双极型晶体管、MOS晶体管难点:音频放大电路三极管用做开关解决方法:用以前学过的专业知识来引导学生教学过程设计思路:1、介绍本次课的知识目标与能力目标2、提出要求学生回答的问题3、听力训练回答问题4、讲解重点内容,学生朗读5、完成课后作业6、总结优化程序参考资料与设备、工具和材料的配置:Multimedia teaching课程单元设计(续页)教学内容(训练项目)设计教学方法与手段设计学生活动(训练任务)设计时间分配(分钟)ReviewKnowledge goal andAbility goalListening and answerquestionCurriculum content1Semiconductor DiodeMultimediateach+demonstrate+discussionAnswer question ListeningListening and Answer questionListening and Answer questionReadingA semiconductor diode (refers to diode in short)is the simplest possible semiconductor device.A diode consists of a PN junction made of semiconductor material. The P-type material is called the anode,while theN-type material is called the cathode(Fig4.1).A diode is forward biased when the anode is more positive than the cathode (greater than the turn-on voltage,which is approximately0.3V for germanium and0.7V for silicon).In this condition the internal resistance of the diode is low and a large current will flow through5315152NPN Bipolar3MOS Transistors4Audio Amplitifiers 5summary the diode(depending on the external circuit resistance).Listening and Answer questionReadingThere are two types of standard bipolar transistors,NPN and PNP, with different circuit symbols(Fig 4.4).The letters refer to the layers of semiconductor material used to make the transistor. Most transistors used today are NPN because this is the easiest type to make from silicon.Listening and Answer questionReadingListening and Answer questionReadingListening、discussion and Answer question1512105课后作业布置:Translation:A semiconductor diode(refers to diode in short)is the simplest possible semiconductor device.A diode consists of a PN junction made of semiconductor material.The P-type material is called the anode,while the N-type material is called the cathode(Fig4.1).A diode is forward biased when the anode is more positive than the cathode(greaterthan the turn-on voltage,which is approximately0.3V for germanium and0.7V for silicon).In this condition the internal resistance of the diode is low and a large current will flowthrough the diode(depending on the external circuit resistance).教学效果评价与改进措施:检查评价:检查人:年月日。
电子技术基础英文改编版课程设计1. IntroductionThis course is designed for Chinese students who want to learn electronic technology basics in English. The course covers the fundamental concepts and principles of electronic technology, including electronics, digital circuits, and microprocessors. The mn goal of this course is to help students improve their English skills while developing their understanding of electronic technology.2. Course Objectives•Develop a basic understanding of electronic technology concepts and principles.•Learn how to read and write technical documentation and communicate effectively in English.•Gn practical experience by building electronic circuits and designing simple systems using microprocessors.•Develop critical thinking skills and apply them to electronic technology problems.3. Course ContentsThe course consists of the following mn topics:3.1 Electronics•Introduction to electronic technology and basic electronic components•AC and DC circuits•Amplifiers and oscillators•Filters and frequency response•Digital logic gates and circuits•Operational amplifiers3.2 Digital Circuits•Number systems and codes•Logic gates and Boolean algebra•Combinational circuits•Sequential circuits•Memory and storage devices3.3 Microprocessors•Introduction to microprocessors and microcontrollers•Assembly language programming•Interfacing with input and output devices•Designing simple embedded systems4. Course Design4.1 Course FormatThe course will be delivered in a combination of lectures, laboratory sessions, and group projects. The lectures will cover the theoretical concepts of electronic technology in English, and the laboratory sessions will give students practical experience by building simple circuits and designing systems using microprocessors. Group projects will provide an opportunity for students to work collaboratively and apply their skills in a real-world context.4.2 AssessmentThe assessment of this course consists of the following components: •Quizzes and exams in English, which will assess stud ents’ understanding of the course content.•Laboratory reports, which will evaluate students’ practical skills in circuit building and microprocessor programming.•Group project presentations, which will assess students’ ability to apply their skills in a real-world context andcommunicate effectively in English.4.3 Resources•Textbook: Electronic Technology Basics – English Edition (ISBN XXXXXXXXX)•Laboratory equipment: Oscilloscopes, signal generators, multimeters, microprocessor development boards, breadboards, andother components.•Software: Proteus, MPLAB X, and Arduino IDE.5. ConclusionThis course is designed to provide Chinese students with an opportunity to learn electronic technology basics in English. By developing their English proficiency and understanding of electronic technology principles, students will be equipped to pursue further study and careers in the global electronics industry.。
10 4.Latin拉丁语5.prolific多产的Notes安培(1775-1836)是一位法国的数学家和物理学家,他奠定了电动力学的基础,发明了电磁铁和安培表。
电流的单位是以他的名字“安培”来命名的。
Reading is to the mind what exercise is to the body.读书有益于身心犹如运动有益于身体。
Richard SteelUnit 3 KeyboardKeyboard(as shown in Fig.3-1), in computer science, a keypad device with buttons or keys that a user presses to enter data characters and commands into a computer. Keyboards emerged from the combination of typewriter and computer-terminal technology. They are one of the fundamental pieces of personal computer (PC) hardware, along with the central processing unit (CPU),the monitor or screen, and the mouse or other cursor device.Fig.3-1 KeyboardThe most common English-language key pattern for typewriters and keyboards is called QWERTY, after the layout of the first six letters in the top row of its keys (from left to right). In the late 1860s, American inventor and printer Christopher Sholes invented the modern form of the typewriter. Sholes created the QWERTY keyboard layout by separating commonly used letters so that typists would type slower and not jam their mechanical typewriters. Subsequent generations of typists have learned to type using QWERTY keyboard, prompting manufacturers to maintain this key orientation on typewriters.Computer keyboards copied the QWERTY key layout and have followed theModule A Fundamentals of Electricity and Electronicsprecedent set by typewriter manufacturers of keeping this convention. Modern keyboards connect with the computer CPU by cable or infrared transmitter. When a key on the keyboard is pressed, a numeric code is sent to the keyboard's driver software and to the computer's operating system software. The driver translates this data into a specialized command that the computer's CPU and application programs understand. In this way, users may enter text, commands, numbers, or other data. The term character is generally reservedfor letters, numbers, and punctuation, but may also include control codes, graphical symbols, mathematical symbols, and graphic images.New Words and Expressionskeypad n.小键盘button n.按钮press v.按下,压下character n.字符command n.命令emerge v.涌现combination n.结合typewriter n.打字机terminal n.终端fundamental a.基本的Central Processing Unit (CPU) 中央处理器cursor n.光标pattern n.式样,模式QWERTY 标准的传统键盘布局layout n.布局inventor n.发明者printer n.印刷工人create v.(创)造出separate v.分开jam v.塞紧,卡住mechanical a.机械的subsequent a.下一(个)prompt v.推动,促使orientation n.方向,定位precedent n.先例,前例convention n.会议,常规infrared a.红外线的11。