(完整版)英语教学论
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:963.47 KB
- 文档页数:12

第四章1.根据卡南尔和斯温纳(Canale and Swain )的论述,交际能力包括语法能力、社会语言能力、篇章能力和—。
A.语汇能力B.词汇能力C.语言能力D.策略能力Key: D (pp. 75)2.英国语言哲学家奥斯汀认为,人在说话的时候同时施行着以言述事、以言成事和三种行为。
A.以言做事B.价值判断C.表情达意D.发出指令Key: A (pp. 77)3.韩礼德认为,语言的微观功能包括工具功能、个人功能、启发功能、想象功能、信息功能和及。
A.策略功能、思维功能B.相互关系功能、规章功能C.篇章功能、人际功能D.思维功能、篇章功能Key: B (pp. 74)4. 一些学者从社会交际功能的角度出发,探讨和的理论。
A.语言学习和交际能力B.语言使用和交际能力C.语言使用者和语言使用D.语言使用者和语言能力Key: C (pp. 75)5.海姆斯的交际能力包括:懂的形式上的可能、能判断语言形式的可行性、和。
A.能在交际中得体地使用;B.拥有社会语言能力;知道某些话语能否实际说出来拥有语篇能力C.拥有策略能力;D.拥有策略能力;拥有篇章能力;拥有社会语言能力;Key: A (pp. 75)6.英国语言哲学家奥斯汀的理论中,可以验证,可以是真实或错误的陈述的句子类型是。
A.行为句B.叙述句C.受约句D.指令句Key: B (pp. 77)7.意念大纲的诞生和理论有密切关系.A.海姆斯的交际能力理论B.奥斯汀的言语行为理论C.韩礼德的功能学派D.卡南尔和斯温纳的理论Key: B (pp. 78)8.外语学习理论可以分为两种,一种是探究外语学习普遍性和规律性的研究,另一种是。
A.从语言本身结构的研究;B.从社会属性方面的研究;C.跟其他学科关系的研究;D.不同类型学习者学习特殊性和规律性的研究;Key: D (pp. 78)9.华生提出的行为主义心理学公式是。
A.刺激---- 反应B.输入---- 反应C.刺激一一理解一一反应D.输入一一理解一一反应Key: A (pp. 79)10.按照行为主义的观点,所有学习,不论是言语还是非言语学习,都要经过一个过程。

《英语教学论》教案一、教学目标:1. 了解英语教学的基本原则和方法。
2. 掌握英语教学过程中的技巧和策略。
3. 培养教师对英语教学的兴趣和热情。
二、教学内容:1. 英语教学的基本原则2. 英语教学方法3. 英语教学技巧4. 英语教学策略5. 英语教学案例分析三、教学方法:1. 讲授法:讲解英语教学的基本原则、方法和技巧。
2. 案例分析法:分析典型的英语教学案例,讨论教学策略的运用。
3. 小组讨论法:分组讨论教学过程中遇到的问题和解决方案。
四、教学准备:1. 教材:《英语教学论》教材。
2. 多媒体设备:投影仪、电脑、音响等。
3. 教学资源:相关英语教学案例、视频、图片等。
五、教学过程:1. 导入:简要介绍英语教学的基本概念和重要性。
2. 讲解:详细讲解英语教学的基本原则、方法和技巧。
3. 案例分析:分析典型的英语教学案例,引导学生讨论教学策略的运用。
4. 小组讨论:分组讨论教学过程中遇到的问题和解决方案。
5. 总结:总结本节课的重点内容,布置课后作业。
六、教学评估:1. 课堂参与度:观察学生在课堂讨论和小组活动中的参与情况。
3. 小组讨论报告:评估学生在小组讨论中的表现和提出的解决方案。
七、教学拓展:1. 组织一次英语教学模拟课堂,让学生亲身体验教学过程。
2. 邀请英语教学专家进行讲座,分享教学经验和心得。
3. 组织学生参观英语教学机构,了解实际教学环境和需求。
八、教学反馈:1. 收集学生对教学内容和教学方法的反馈意见。
2. 根据学生反馈调整教学计划和教学方法。
3. 定期与学生沟通,了解他们的学习进展和需求。
九、教学改进:1. 根据教学评估结果,对教学方法和策略进行调整。
2. 关注学生的学习困难,提供针对性的辅导和支持。
3. 不断更新教学资源,增加教学案例和实际教学经验分享。
十、教学总结:1. 总结整个学期的教学内容和成果。
2. 鼓励学生分享他们的学习心得和收获。
希望对您有所帮助!如有需要,请随时提问。


外国语学院成人教育英语教育特色专业建设教学指导书《英语教学论》课程教学指导书吴曼蕾编写淮阴师范学院外国语学院二0一二年九月课程介绍《英语教学论》是普通高等学校英语(教师教育)本科专业的一门必修课,具有基础理论和基本技能实践相结合的学科特点。
该课程传授英语教育教学基本理论和知识,训练英语教学基本技能,具备较高的英语教育理论素养和较强的教学工作能力,能适应21世纪教育改革发展和新一轮教学改革需要的、具有创新精神及创新能力的中小学英语教师。
学生通过课程学习,能初步形成对语言及语言学习本质的正确认识和科学的外语教学观,认识本课程中英语教学的性质及其发展演变过程,了解二十一世纪的英语课程改革,把握英语课程的理念,理解英语课程的性质及目标,掌握英语课程教学设计的基本原理,对语音、词汇、语法教学,听说读写教学和综合性学习教学等问题有所把握。
本课程还注重英语教学实践能力的培养,指导并帮助学生把教学理论与实践相结合,引导学生树立对外语教学作为一种职业和一门科学的正确态度,为其今后成为具备一定教学实践能力的合格中小学英语教师做好准备。
《英语教学论》是研究英语教学规律的一门科学。
“教学论”的含意是指一种理论“法则”(law) 或“体系”(system),而不是狭义的单纯指具体的教学方式方法。
英语教学论研究英语教学的全过程及其规律。
教学内容主要包括:1、教学理论;2、基本教学理论的教学方法和技巧;3、英语课外活动、教学手段和测试手段。
本自学指导书主要是依据高等教育出版社出版的由王蔷主编的《英语教学法教程》(第二版)而写的,并在此基础上对内容进行了必要的增减。
目的是为了进一步便于学生们自学及教师们安排好各个;教学环节和面授内容。
该门课程的学时分配如下:总学时72,讲授20学时,自学52学时。
面授安排在第三学年进行。
这门课程是考试课程。
对教师布置的作业,学生应独立完成并按时交给教师批改。
由于本人水平有限,书中有不当之处,望使用该书的教师和同学们批评指正。

《英语教学论》教案SYLLABUSCONTENTS一、外语学习论 6课时二、外语教学法流派介绍 6课时三、《新课标》解读 4课时四、任务型教学理论与实践 16课时五、班主任工作管理 2课时六、“三课”活动 2课时Course Requirments:1.attendancy (10%)2.classperformance(10%)3.essays and small writings(20%)4.final exam(60%)主要备课资料:1、张正东:《外语教育学》。
科学出版社,1999年。
2、张正东、李少伶:《英语教学论》。
陕西师范大学出版社,2003年。
3、张正东、杜培俸:《外语立体化教学法的原理与模式》。
科学出版社,1998年。
4、胡春洞:《英语教学法》。
高等教育出版社,1990年。
5、王才仁:《英语教学交际论》。
广西教育出版社,1996年。
6、胡春洞、戴忠信:《英语阅读论》。
广西教育出版社,1998年。
7、高兰生、陈辉岳:《英语测试论》。
广西教育出版社,1996年。
8、聂希庸、曹宝健:《中学英语教学》。
光明日报出版社,1998年。
9、程晓堂:《任务型语言教学》。
高等教育出版社,2004年。
10、田式国:《英语教学理论与实践》。
高等教育出版社,2001年。
11、宋桂月、金莺:《英语课程标准教师读本》。
华中师范大学出版社,2002年。
12、鲁子问:《中小学英语真实任务教学实践论》。
外语教学与研究出版社,2003年。
13、梁祝、卢福波:《小学英语新课程课堂教学案例》。
广东高等教育出版社,2003年。
14、程可拉、刘津开:《中学英语任务型教学理念与教学示例》。
华南理工大学出版社,2005年。
15、张玲棣:《高中英语课堂教学设计与案例》。
高等教育出版社,2004年。
16、于勇:《中小学课堂教学技能训练》。
当代世界出版社,2001年17、顾曰国:《英语教学法》(上下)。
外语教学与研究出版社,1998年。

英语教学论内容一、引言英语教学论是研究英语教学理论和实践的学科,涉及教学方法、教材设计、评估与测试等方面。
本篇文章将详细介绍英语教学论的内容,包括英语教学理论、教学方法和评估与测试。
二、英语教学理论1.语言学习理论语言学习理论研究人类语言习得的规律和过程,对英语教学具有重要的指导意义。
常见的语言学习理论包括行为主义、认知主义、社会交际主义等。
了解不同的语言学习理论,可以帮助教师选择合适的教学策略和方法。
2.语言教学法语言教学法是指用于教授英语的具体方法和技巧。
常见的语言教学法包括直接法、交际法、情境法、任务型教学法等。
每种教学法都有其特点和适用范围,教师可以根据学生的需求和学习目标选择合适的教学法。
3.教学模式和教学策略教学模式和教学策略是在教学过程中组织和安排学习活动的方式和方法。
常见的教学模式包括传统教学、合作学习、项目学习等,而教学策略则包括启发式教学、问题解决教学、个性化教学等。
教师可以根据不同的教学目标和学生特点选择合适的教学模式和策略。
三、教学方法1.教材设计与使用教材是英语教学的重要组成部分,教师可以根据学生的需求和学习目标选择适合的教材。
同时,教师也可以根据教材进行课堂教学设计,结合教材内容和学生实际,设计合适的教学活动和任务,提高学生的语言能力。
2.课堂教学方法课堂教学方法是指教师在课堂上组织和开展教学活动的方式和方法。
常见的课堂教学方法包括讲授法、问答法、小组讨论、角色扮演等。
教师可以根据教学目标和学生特点选择适当的教学方法,并通过多样化的教学活动激发学生的学习兴趣。
3.多媒体技术和教学工具多媒体技术和教学工具在英语教学中扮演着重要的角色。
教师可以使用投影仪、音频设备、电子白板等多媒体设备,辅助教学内容的呈现和理解。
同时,还可以利用各种教学软件和在线资源,丰富课堂教学内容,提高学生的学习效果。
四、评估与测试1.评估方法和工具评估是对学生学习情况进行全面、客观和准确的评价。
常见的评估方法包括作业、考试、口语表达、听力理解、写作等。
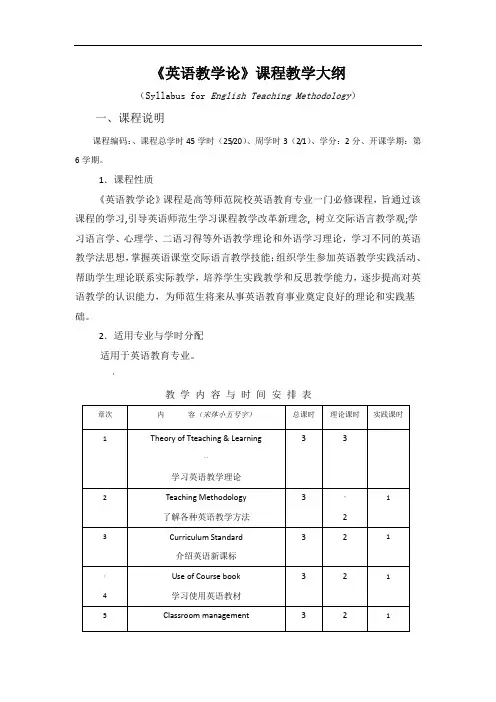
《英语教学论》课程教学大纲(Syllabus for English Teaching Methodology)一、课程说明课程编码:、课程总学时45学时(25/20)、周学时3(2/1)、学分:2分、开课学期:第6学期。
1.课程性质《英语教学论》课程是高等师范院校英语教育专业一门必修课程,旨通过该课程的学习,引导英语师范生学习课程教学改革新理念, 树立交际语言教学观;学习语言学、心理学、二语习得等外语教学理论和外语学习理论,学习不同的英语教学法思想,掌握英语课堂交际语言教学技能;组织学生参加英语教学实践活动、帮助学生理论联系实际教学,培养学生实践教学和反思教学能力,逐步提高对英语教学的认识能力,为师范生将来从事英语教育事业奠定良好的理论和实践基础。
2.适用专业与学时分配适用于英语教育专业。
*教学内容与时间安排表3.课程教学目的与要求:I.教学目的:通过《英语教学论》课程的学习,帮助英语师范生具有新课程教学改革的理念和职业规范与师德,掌握一定的外语教学理论和外语学习理论,了解交互性语言教学的课堂教学理论基础,培养英语教学实践经历和反思教学的的能力,促进师范生在学术上的可持续发展的基本素质。
II.教学要求:教师通过多媒体讲授英语教学理论、教学流派、课程标准和教学原则等知识后,组织师范生进行小组为单位的教学内容演示等教学实践活动,提高师范生对英语教学本质的认识,使他们一定的理论高度,具备反思教学的可持续发展的能力,逐步完善自己的英语教学能力。
4.本门课程与其它课程关系本课程是在第6学期开设的专业基础必修课,学生已经学习了英语专业的一些基础课程以及一些相关的通识课之后才开设,本门课程的开设对巩固和提高英语教师专业学生的专业素质会起到积极作用。
它既能够优化教育理论课程,如心理学、教育学等,同时也能够检验学生对所学英语专业知识的把握程度及综合运用英语语言的能力。
5.推荐教材及参考书推荐教材:Davies, Eric Pearse Success in English Teaching Shanghai Foreign Language Education Press, 20052.王蔷:《英语教学法教程》,高等教育出版社,2000年。

《英语教学论》教案一、前言1. 教学目标:通过本章的学习,使学生了解英语教学的基本概念、教学法及其发展历程,为后续教学实践打下理论基础。
2. 教学内容:英语教学的基本概念、教学法及其发展历程。
3. 教学方法:讲授、讨论、案例分析。
4. 教学重点:英语教学的基本概念、教学法及其在实际教学中的应用。
5. 教学难点:教学法的内涵及其在实际教学中的运用。
二、英语教学的基本概念1. 教学目标:使学生掌握英语教学的基本概念,如教学目标、教学内容、教学过程等。
2. 教学内容:a. 教学目标的制定b. 教学内容的选取与组织c. 教学过程的设计与实施d. 教学评价的方法与原则3. 教学方法:讲授、讨论。
4. 教学重点:教学目标、教学内容、教学过程、教学评价的概念及其相互关系。
5. 教学难点:教学目标、教学内容、教学过程、教学评价在实际教学中的运用。
三、英语教学法及其发展历程1. 教学目标:使学生了解英语教学法的基本类型及其发展历程,掌握各类教学法的特点与应用。
a. 直接法b. 间接法c. 交际法d. 任务型教学法e. 信息技术辅助教学法f. 教学法的发展历程3. 教学方法:讲授、讨论、案例分析。
4. 教学重点:各类教学法的特点与应用。
5. 教学难点:各类教学法在实际教学中的整合与运用。
四、教学计划与教学大纲1. 教学目标:使学生掌握教学计划与教学大纲的编制方法,能够根据教学目标编写教学计划与教学大纲。
2. 教学内容:a. 教学计划的编制b. 教学大纲的编制c. 教学计划与教学大纲的实施与调整3. 教学方法:讲授、讨论、案例分析。
4. 教学重点:教学计划与教学大纲的编制方法及其在实际教学中的应用。
5. 教学难点:教学计划与教学大纲在实际教学中的实施与调整。
五、教学评价1. 教学目标:使学生了解教学评价的基本概念、方法及其在英语教学中的应用。
a. 教学评价的基本概念b. 教学评价的方法c. 教学评价的原则d. 教学评价在英语教学中的应用3. 教学方法:讲授、讨论、案例分析。

1, Communicative language learning (CL T)1,定义CLT is an approach to the teaching second and foreign language that emphasizes interaction as both the means and the ultimate(最终的) goal of learning a language,also can called as Functional Approach(功能法) or National Approach(意念法).2,优点(1), Attaches great importance to the actual needs of the students;(重视学生的实际需要)(2), Attention to the cultivation of communicative competence, which is beneficial to students in a certain social environment properly using the target language for communication.(重视交际能力的培养,有利于学生在一定的社会环境中恰当地使用目的语进行交际)3,缺点(1) It’s not easy to judge and ensure its function and thoughts.(2) It’s not easy to compile(编写) textbook.2, Task-based language teaching (TBLT)1,定义Task-based language teaching (TBLT) refers to an approach based on the use of tasks as the core unit of planning and instruction in language.2,特点1, Emphasis -Target language2, Focus on – the learning Process & language itself3, It is student-centered class4, It pays attention to real situations3,优点(1), c an stimulate students’ interest,2(2), students have more opportunities to express their own opinions and feelings.(3),It can improve their exploration, participation, communication and cooperation ability.4,缺点(1) The classroom efficiency is low.(2) It is difficult to guarantee the big class teaching task.(3) It is rely on teachers’ teaching ability and teaching level.3, The Oral Approach and Situational Language Teaching1, 背景Situational Language Teaching was originally called Oral Approach, which was developed by British applied linguists from the 1930's to 1960’s; the two leaders of this movement were Harold Palmer and A.S. Hornby.2, 定义The Oral Approach and Situational Language Teaching is a languageteaching method derived from the Direct Method and developed by British applied linguists between 1930s and 1960s. The Method is no longer in fashion, but some techniques from the Method can still be found in language teaching activities and especially in many textbooks.3, 目标(1) to teach a practical command of the four basic skills of language, through Structure.(2)accuracy in both pronunciation and grammar.(3) errors to be avoided.(4)automatic control of basic structures and sentence patterns through speech.4, 方法:Theory of Language Behaviorist habit-learning theory:Three conditions:1. Receiving knowledge and materials2. Fixing them in memory by repetition3. Using them in actual practiceLearning language is to learn speech habitsUse of blind imitative drills5, 角色Learner roles: Listen and repeat / more active participationTeacher roles: Serves as a model, Conductor of an orchestraThe roles of instructional materials: SLT is dependent on both a textbook and visual aids.1. Begin with spoken English, oral before written form2. The target language is the language of the classroom3. New language points: Introduced and practiced4. Selection: Cover the general service vocabulary5. Simple forms at first and then complex ones6. Rich vocabulary and basic grammar (Reading and Writing)6, 优点It strong emphasis on oral practice, grammar and sentence patterns conforms to the intuitions of many practically oriented classroom teachers.7, 缺点Children do not acquire their mother tongue through repetition and habit formation.8, 特点The essential features of SLT are seen in the "P-P-P" lesson model that thousands of teachers who studied for the RSA/ Cambridge Certificate in TEFL were required to master in the 1980s and early 1990s, with a lesson having three phrases: Presentation, Practice, and Production.4,The Audio-lingual Method1, 定义The Audio-lingual Method is a method of foreign language teaching which emphasizes the teaching of listening and speaking before writing and reading.2,特点It uses dialogues as the main form of language presentation and drills as the main training techniques. Mother tongue is discouraged in the classroom.3,基本原则(1)Emphasis on the teaching of listening and speaking.(2)Use of dialogues as the chief means of presenting the language.(3)Mainly practice techniques: imitation, memorization, pattern drills.(4)Mother tongue is discouraged in the classroom.5,Total Physical Response (TPR)1,定义In the teaching activities, teacher creates a happy relaxed environment. Meanwhile students respond with whole-body actions. The right brain is silent, nonverbal, but it can make adaptation action to express them through instruction.2,特点TPR emphasizes the importance of listening and watching. The teacher issued instructions and they complete the action.This method is suitable for little children to study foreign language; as a result of they have interests for everything around them.3,优点TPR makes complex knowledge easier than before. For example, teachers can have a dialogue with our students and build the English context in order to simplify knowledge6,暗示法Suggestopedia定义:The approach was based on the effect of suggestion in learning, the concept of which is that positive suggestion would make the learner more receptive to stimulate learning特点1,To create a cheerful, relaxing atmosphere2,The authoritative behavior of the teacher and the authority of the material3,Emphasis on memorization of vocabulary pairs4,Infantilization(稚化): Role playing games, songs and gymnastic exercises help students regain their self-confidence.5,Double-planeness: learners learn from the effect of direct instruction and the environment where the instruction takes place.优点Creating a relaxing and comfortable environmentReducing students’ pressure in learning languageAvoid boredom and making class interestingImp roving students’ motivation of learning缺点Not all teachers are qualified for this methodRequiring money to decorate the classroomThe number of students is limitedLasting a long time for teaching every day8,团体学习法Community Language Learning (CLL)1,定义Community Language Learning is an approach in which students work together to develop what aspects of a language they would like to learn.It is based on the Counseling-approach in which the teacher acts as a counselor and a paraphraser, while the learner is seen as a client and collaborator.2,特点(1)The CLL emphasizes the sense of community in the learning group, it encourages interaction as a vehicle of learning, and it considers as a priority the students' feelings and the recognition of struggles in language acquisition. There is no syllabus or textbook tofollow and it is the students themselves who determine the content of the lesson by means of meaningful conversations in which they discuss real messages. Notably, it incorporates translation, transcription, and recording techniques.(2)Student’s role-client(3)Teacher’s role-counselor3,优点A brave speakerNo fixed teaching materialsAcquire answer the questionsIntrospection4,缺点Demand too high on teacherRely on9,自然学习法The natural approach is a method of language teaching developed by Stephen Krashen and Tracy Terrell in the late 1970s and early 1980s.It aims to foster naturalistic language acquisition in a classroom setting, and to this end it emphasizes communication, and places decreased importance on conscious grammar study and explicit correction of student errors. Efforts are also made to make the learning environment as stress-free as possible.In the natural approach, language output is not forced, but allowed to emerge spontaneously after students have attended to large amounts of comprehensible language input.优点(1)The classroom consisting of acquisition activities can be an excellent environment for beginners.(2)Comprehensible and meaningful practice activities are emphasized and the situation at their level.(3)The teacher creates speeches which enable students to interact using the target language.(4) Communication as the primary function of language and emphasis on meaning.(5)Students are not forced to respond in the target language immediately.(6)The teacher knows students’ needs and concentrates on appropriate and useful areas.(7)Materials come from our daily life rather than from textbooks.缺点(1)It ignores many factors essential in second language course design.(2)It ignores the importance of vocabulary.(3)It not necessary to analyze grammatical structure & rulesautomatically provided in the input.(4)It is suitable for the beginners, not apply to the high level students.。


《英语教学论》教案一、教学目标1. 了解英语教学的基本原则和方法。
2. 掌握英语教学过程中的技巧和策略。
3. 提高英语教学效果,培养学生的英语综合运用能力。
二、教学内容1. 英语教学的基本原则2. 英语教学方法3. 英语教学技巧4. 英语教学策略5. 英语教学评价三、教学重点与难点1. 英语教学的基本原则和方法的运用。
2. 英语教学技巧和策略的实践。
四、教学准备1. 教材:《英语教学论》2. 教学课件3. 教学道具五、教学过程1. 导入:通过一个有趣的英语教学案例,引发学生对英语教学的兴趣和思考。
2. 讲解:介绍英语教学的基本原则和方法,并通过实例进行分析。
3. 实践:分组讨论,学生互相练习英语教学技巧和策略。
4. 展示:每组选出一名代表,进行英语教学演示。
5. 评价:教师对学生的英语教学进行评价和指导。
7. 作业:布置相关的英语教学练习题,让学生进行巩固。
六、教学方法与技巧1. 任务型教学法:通过完成实际任务,激发学生的学习兴趣和积极性。
2. 交际型教学法:注重学生之间的互动和交流,提高口语表达能力。
3. 情境教学法:创造真实的语言环境,提高学生的语言运用能力。
4. 游戏教学法:通过趣味游戏,增加学习的趣味性和互动性。
七、教学评价与反馈1. 形成性评价:关注学生的学习过程,及时给予指导和鼓励。
3. 自我评价:鼓励学生自我反思,提高自主学习能力。
4. 同伴评价:学生之间互相评价,促进互动和共同进步。
八、教学策略与技巧1. 启发式教学:引导学生主动思考和探索,提高学习兴趣。
2. 差异化教学:关注学生的个体差异,满足不同学生的学习需求。
3. 合作学习:鼓励学生合作完成任务,提高团队协作能力。
4. 信息技术辅助教学:利用多媒体和网络资源,丰富教学内容和形式。
九、教学案例分析2. 分析一个失败的英语教学案例,找出问题所在并提出改进措施。
2. 反思教学方法和策略的有效性,提出改进和优化建议。
3. 强调英语教学的实践性和持续性,鼓励学生在实践中不断探索和进步。
湖南师范大学硕士研究生入学考试自命题考试大纲考试科目代码:[971] 考试科目名称:英语教学论一、考试形式与试卷结构1.试卷分值及考试时长本试卷满分为150分,考试时长为180分钟。
2.答题方式答题方式为闭卷、笔试。
3.试卷结构第一部分:英语教学理论基本知识(1)名词解释题:6道题,每题5分,共计30分。
(2)简答题:4道题,每题15分,共计60分。
第二部分:英语教学理论基本知识运用分析论述题:3道题,每题20分,共计60分。
二、考试内容与考试要求1.考试内容(1)学科教学论:优秀教师的基本素养;交际能力、语言教学的交际原则;任务及任务型教学;新课程标准;教案设计;课堂管理;语言知识教学与跨文化意识培养;语言技能教学与综合语言技能教学;形成性评价与终结性评价;教材评估、选择及开发利用;外语教学法主要流派及其发展脉络。
(2)第二语言习得:第二语言习得的定义;一语与二语习得的差异;第二语言习得的途径与习得顺序;中介语;影响第二语言习得的外部因素;输入、互动、输出对习得的影响;母语的作用;学习者差异对二语习得的影响;课堂教学对二语习得的作用;二语习得理论及其发展脉络。
2.考试要求(1)能比较系统地掌握英语学科教学及第二语言习得的核心概念、基本知识、基础理论与基本方法;(2)能熟练运用学科教学论及第二语言习得的基本理论和方法分析、解决教学中的实际问题;三、参考书目1.王蔷:《英语教学法教程》(第二版),高等教育出版社,2006年。
2.束定芳、庄智象:《现代外语教学:理论、实践与方法》(修订版),上海外语教育出版社,2008年。
3.Ellis,R. Understanding Second Language Acquisition(《第二语言习得概论》),上海外语教育出版社,1999年。
《英语教学论》教案一、教学目标:1. 了解并掌握英语教学的基本理论和方法。
2. 培养教师运用英语教学策略进行有效教学的能力。
3. 提高教师对英语教学评价的认识和运用。
二、教学内容:1. 第一章:英语教学论概述英语教学的基本概念英语教学的历史与发展英语教学的重要性2. 第二章:英语教学方法直接法间接法交际法任务型教学法3. 第三章:英语教学策略教学计划与设计课堂教学管理学习动机的激发学习策略的培养4. 第四章:英语教学评价教学评价的类型与方法形成性评价与终结性评价的运用自我评价与同伴评价教学反思与改进5. 第五章:英语教学资源与技术英语教学资源的开发与利用多媒体教学技术的运用网络教学资源的利用教学辅助工具的选择与使用三、教学过程:1. 导学:介绍英语教学论的基本概念和重要性,激发学生的学习兴趣。
2. 教学方法与策略的学习:通过案例分析、讨论和实践,让学生掌握各种教学方法和策略。
3. 教学评价的学习:通过实例分析,让学生了解并掌握各种评价方法的应用。
4. 教学资源的利用:介绍并演示如何利用各种教学资源和辅助工具进行教学。
四、教学评价:1. 平时成绩:学生的课堂参与度、讨论和作业完成情况。
2. 实践报告:学生分组进行教学实践,提交实践报告。
3. 期末考试:闭卷考试,考察学生对英语教学论知识的掌握。
五、教学资源:1. 教材:《英语教学论》教材。
2. 辅助材料:教学案例、教学设计模板、评价工具等。
3. 多媒体教学设备:投影仪、电脑、音响等。
4. 网络资源:英语教学网站、在线课程、教学论坛等。
六、教学活动设计:1. 案例分析:选取典型的英语教学案例,让学生分析并讨论教学方法、策略和评价的应用。
2. 小组讨论:分组讨论教学问题,培养学生的合作能力和解决问题的能力。
3. 教学设计实践:学生分组设计一节英语课,包括教学目标、方法、评价等,并进行展示。
4. 教学模拟:学生模拟教学过程,教师进行评价和指导。
七、教学计划与时间安排:1. 第一周:英语教学论概述2. 第二周:英语教学方法3. 第三周:英语教学策略4. 第四周:英语教学评价5. 第五周:英语教学资源与技术6. 第六周:教学活动设计实践7. 第七周:教学模拟与评价八、教学注意事项:1. 注重理论与实践相结合,提高学生的教学能力。
《英语教学论》教案一、教学目标1. 了解英语教学的基本原则和方法。
2. 掌握英语教学设计的基本步骤。
3. 熟悉英语教学评价的标准和手段。
4. 提高英语教学实践能力。
二、教学内容1. 英语教学的基本原则2. 英语教学方法3. 英语教学设计4. 英语教学评价5. 英语教学实践三、教学方法1. 讲授法:讲解英语教学的基本原则、方法和评价手段。
2. 案例分析法:分析典型英语教学设计案例,讨论其优点和不足。
3. 小组讨论法:分组讨论英语教学实践中遇到的问题,分享经验。
4. 模拟教学法:进行模拟教学,提高学员的英语教学能力。
四、教学安排1. 第一课时:英语教学的基本原则2. 第二课时:英语教学方法3. 第三课时:英语教学设计4. 第四课时:英语教学评价5. 第五课时:英语教学实践五、教学评价1. 课堂参与度:评估学员在课堂讨论、提问和分享经验方面的积极性。
2. 模拟教学效果:评估学员在模拟教学中的表现,包括教学内容、方法和组织能力。
3. 课后作业:评估学员对教学内容的掌握程度,以及运用所学知识解决实际问题的能力。
4. 期末考试:全面测试学员对英语教学理论和实践的掌握程度。
六、教学资源1. 教材:《英语教学论》教材,用于讲解基本理论和知识点。
2. 案例库:收集各类英语教学设计案例,用于分析和讨论。
3. 模拟教学材料:提供模拟教学所需的教材、课件等资源。
4. 视听资料:播放优秀英语教学视频,供学员学习借鉴。
5. 在线资源:推荐相关英语教学网站和论坛,便于学员课后学习和交流。
七、教学过程1. 导入:每节课开始时,用几分钟时间引导学员回顾上节课的内容,为新课的学习做好铺垫。
2. 讲解:详细讲解本节课的教学内容,通过案例分析、互动讨论等方式,帮助学员理解和掌握知识点。
3. 实践:安排模拟教学环节,让学员亲自动手实践,提高教学能力。
4. 总结:每节课结束前,对所学内容进行总结,强调重点和难点。
5. 作业布置:布置课后作业,巩固所学知识,培养学员独立思考和解决问题的能力。
《英语教学论》教案第一章:英语教学论概述1.1 教学论的概念与发展1.2 英语教学论的重要性1.3 英语教学论的研究对象与方法1.4 英语教学论的基本原则与理念第二章:英语教学目标与标准2.1 英语教学目标的制定2.2 英语教学标准的设计2.3 英语教学目标与标准的实施与评估2.4 英语教学目标与标准的调整与更新第三章:英语教学方法与策略3.1 英语教学方法的选择与应用3.2 英语教学策略的制定与实施3.3 英语教学活动设计与组织3.4 英语教学评价与反馈第四章:英语教学资源与材料4.1 英语教学资源的分类与利用4.2 英语教学材料的筛选与评估4.3 英语教学资源的整合与创新4.4 英语教学材料的制作与使用第五章:英语教师专业发展5.1 英语教师的角色与职责5.2 英语教师的专业素养与能力5.3 英语教师培训与进修5.4 英语教师评价与激励机制第六章:英语教学理论与模型6.1 交际语言教学理论6.2 任务型语言教学理论6.3 全身反应法与沉默法6.4 语言学习假设与教学实践第七章:英语课程设计与规划7.1 英语课程目标的设计7.2 英语课程内容的选择与组织7.3 英语课程计划的制定与实施7.4 英语课程的评价与调整第八章:英语教学技巧与艺术8.1 语音教学技巧8.2 词汇教学技巧8.3 语法教学技巧8.4 口语与听力教学技巧第九章:英语教学与文化因素9.1 语言与文化关系探讨9.2 英语教学中的文化导入9.3 跨文化交流能力培养9.4 文化差异对英语教学的影响第十章:英语教学研究与反思10.1 英语教学研究方法与步骤10.2 英语教学研究案例分析10.3 英语教学反思与自我评估10.4 英语教学研究与反思的应用重点和难点解析一、英语教学论概述难点解析:理解英语教学论的定义及其在语言教学领域的作用,掌握英语教学论的历史发展脉络。
二、英语教学目标与标准难点解析:如何确立具体、可操作的英语教学目标,以及如何根据教学目标设计相应的教学标准。