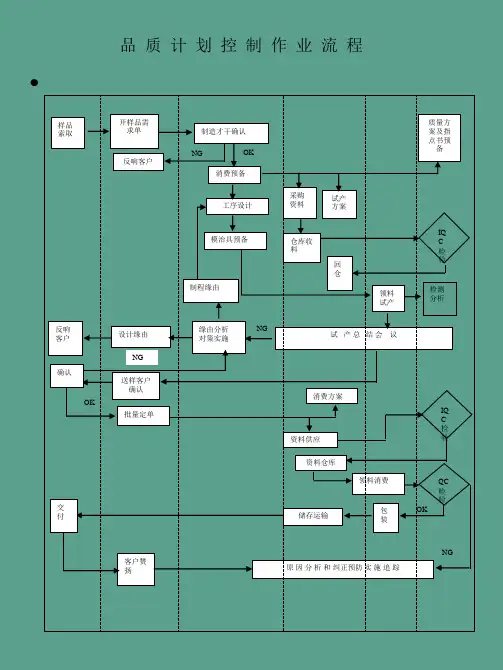
ISO26262 流程图控制计划模板(含全套附属EXCEL表)
- 格式:xls
- 大小:805.00 KB
- 文档页数:2


符合ISO26262标准的软件测试解决方案随着汽车行业的迅速发展,汽车电子电器E/E系统在汽车中的作用不断提高,ECU开发所占用的时间和成本也越来越高。
与此同时,越来越多的电子控制系统(例如车身稳定控制系统ESP,防抱死制动系统ABS,自适应前照明系统AFS等)具有与安全相关的功能,因此对ECU的安全要求也越来越高。
为了减少产品的开发时间和成本,降低由于安全问题而导致的维护甚至召回的风险,越来越多的整车厂和供应商开始重视汽车领域的功能安全问题,ECU软件功能安全的问题也成为汽车行业迫切需要解决的问题,车辆功能安全标准ISO 26262就在这样的环境和需求下应运而生,并于2011年11月正式发布第一版本,该标准是当前汽车业中最流行、最复杂、也是最重要的一份标准。
ISO 26262的目标是通过避免汽车E/E系统故障行为可能导致的危害来提高E/E系统的功能安全。
ISO26262采用车辆安全完整性等级(ASIL)来判断系统的功能安全程度,ASIL由ASILA(最低)、ASILB、ASILC及ASIL D(最高)四个等级组成,ASIL等级越高表示系统的功能安全评估越严格,相应的表示系统正确执行安全功能,或者说的避免该功能出错的概率越高,即系统的安全可靠性越高。
ISO 26262标准的组成架构由十个规范和信息指导文件组成,其中ISO 26262—4/5/6阐述的是系统级/硬件级/软件级的产品开发,使用嵌套的V模型定义了每个开发阶段的过程以及相应的工作产品。
本解决方案主要阐明了在软件级产品开发阶段如何去理解ISO26262的要求,并且指出了在实际的软件开发过程中如何结合ISO 26262的软件测试生命周期,通过包括软件测试工作的执行以及过程控制等方面来确保ECU软件质量满足ISO26262软件级功能安全相应等级的要求。
基于V模式的ISO26262软件测试生命周期如图所示,基于V模式的ISO26262-6软件测试生命周期可以划分为五个阶段:静态分析需求和功能需求:在软件级产品开发初始化阶段和软件安全需求规范制定阶段确定了一些基本的嵌入式软件静态分析需求和功能需求,这部分内容是以后设计和测试的基础;架构验证:在软件架构设计阶段,我们可以使用人工分析的方式来验证和测试软件架构层的内容,但是有条件的话最好使用合适的架构设计工具,在设计的过程中同时进行架构验证;静态测试:在软件单元设计和实现阶段同时进行静态测试,可以使用开发辅助工具来进行静态测试,这样不必因为静态测试的活动而改变开发流程。

ISO26262 电控开发流程概述发表时间:2020-11-05T09:12:46.097Z 来源:《科学与技术》2020年19期作者:王震华赵鲁荣张霞张鲁兵[导读] 功能安全(Functional Safety)的要求是无论零部件或者安全相关控制系王震华赵鲁荣张霞张鲁兵潍柴动力股份有限公司电控研究院,山东潍坊 261061摘要:功能安全(Functional Safety)的要求是无论零部件或者安全相关控制系统发生的失效是硬件随机失效还是系统失效,都需要使受控设备可靠地进入和维持安全状态,避免对人员或者环境产生危害;本文从电控开发流程角度触发,介绍功能安全流程的建立、要求及方法,并结合标准要求,给出完整的电控开发流程体系。
关键词:功能安全;电控单元;ASIL等级引言在过去近40年中,功能安全的理念和技术不断发展,已经在全球范围深入各个行业和领域,成为社会、行业、企业控制各种灾难性事故的有效措施。
ISO26262是欧洲多个知名主机厂及供应商共同讨论制定的,于2005年启动,2011年底发布,2018年发布第二版,加入商用车。
新版ISO26262标准为实现汽车电子系统全生命周期内的功能安全起到了至关重要的指导作用,但对新版标准的详细解读以及如何将其应用到实际的产品中,目前可供参考的应用案例还很少。
因此,以ISO26262新版标准作为指南,进行电控系统的产品开发,对于正确解读和应用ISO 26262 标准具有重大参考意义。
1 标准介绍2018版的ISO 26262 标准主要包括 12 个部分,其体系结构图如图 1所示[1、2]。
图1 ISO26262标准体系结构ISO26262标准的第一部分介绍相关术语;第二部分功能安全管理,定义了涉及安全相关系统开发的组织和人员应满足的要求,定义功能安全管理指南及安全计划,建立公司安全文化;第三部分概念阶段,主要是对危害分析和风险评估的描述,导出功能安全目标,确定功能安全相关概念,导出客户需求;第四部分为系统层面的产品开发,完成系统设计及安全分析,并按要求进行系统相关测试,导出系统需求,FMEA及FTA概念;第五部分为硬件层面的产品开发,确定基于ASIL等级的硬件安全指标,包含SPFM,LFM,PMHF指标,完成硬件安全分析及设计;第六部分为软件层面的产品开发,包含软件开发指南、软件需求、软件实现、软件验证计划、软件验证报告;第七部分为生产、运行、服务和报废过程中功能安全相关的要求和建议;第八部分为是对支持过程的归纳;第九部分为基于汽车安全完整性等级(ASIL)和安全的分析,明确ASIL等级的分配原则;第十部分为对整个ISO26262标准的应用导则。



10-汽车功能安全(ISO26262)系列:软件开发-软件开发模型及安全需求本篇属于汽车功能安全专题系列第10篇内容,我们开始聊汽车功能安全软件开发相关内容。
开始阅读之前强烈建议参考之前系列文章:01 - 汽车功能安全(ISO 26262)系列 - 开篇02 - 汽车功能安全系列之概念阶段开发 - Item Definition & HARA03 - 汽车功能安全(ISO 26262)系列: 概念阶段开发 - 功能安全需求及方案(FSR&FSC)04 - 汽车功能安全(ISO 26262)系列: 系统阶段开发 - 技术安全需求(TSR)及安全机制05 - 汽车功能安全(ISO 26262)系列: 系统阶段开发 - 技术安全方案TSC及安全分析06 - 汽车功能安全(ISO 26262)系列: 系统阶段开发 - 系统安全架构07 - 汽车功能安全(ISO 26262)系列: 硬件开发 - 硬件安全需求,安全设计及安全机制08 - 汽车功能安全(ISO 26262)系列: 硬件开发 - 硬件随机失效概率化评估09 - 汽车功能安全(ISO 26262)系列: 硬件开发 - 随机硬件失效量化FMEDA在功能安全系统开发阶段,我们已经得到了技术层面可实施的技术安全需求TSR,并将其分配至系统架构中的硬件(HW)和软件(SW)组件,接下来以此为基础进行相应硬件和软件功能安全开发。
对于软件功能安全开发而言,具体来讲,主要包括以下内容:•软件开发模型•什么是软件安全需求•软件架构安全设计•软件详细设计•软件安全测试•鉴于内容较多,我们这篇来聊前两部分内容。
01软件开发模型为了更好了解软件及其功能安全开发过程,我们首先来聊聊软件开发模型。
不管是ISO 26262,Aspice还是System Engineering,其开发过程都基于V模型,可以说V模型是汽车工程师必修内容。
对于功能安全而言,软件功能安全开发V模型属于ISO 26262第6部分内容,是系统开发大的V模型中软件开发部分,紧接着第4部分系统开发内容。


Validation Plan <insert project name>Document Control InformationLocation: The version of this document is maintained in folder <fill in folder location> Revision HistoryTable of ContentsContentsDocument Control Information (2)Table of Contents (3)List of Figures (4)List of Tables (5)1Introduction (6)1.1Purpose (6)1.2Scope (6)1.3Definitions, A cronyms, a nd A bbreviations (7)2Inputs and Output (9)2.1Prerequisition (9)2.2Further supporting Information (9)2.3Outputs (9)3Safety Strategy and Processes (10)3.1Overview (10)3.2Validation Test objectives (10)3.3Safety Validation (Item development life cycle) (10)3.4Validation Processes (11)3.5Safety Organization and R&R................................................................ 错误!未定义书签。
3.6Regression strategy (14)4Item Description (15)4.1Item o verview (15)4.1.1System Component (15)4.2Configuration (16)4.3Calibration (16)5Project Development and Validation schedule (17)5.1Validation Test Plan (17)5.1.1HARA Controllability Validation (17)5.1.2Safety Goal Validation (18)5.1.3Long-term test (18)5.2Test Methods information (19)5.3Validation method for safety goal (20)6Test Case and Acceptance Criteria (21)7References (22)List of Figures Figure 1 :List of Tables1Introduction1.1PurposeValidation Plan is planning document which plans validation performance for integrated item at Vehicle level. After HW, SW development, the hardware and software elements are integrated and tested to form an item that is then integrated into a vehicle. Once integrated at the vehicle level, safety validation is performed to provide evidence of functional safety with respect to the safety goals.Therefore the Validation Plan describes all validation activities which shall be carried out for this IWV project. It is fully compliant to the requirements of ISO 26262 Part4 paragraph 5.4.2, 6.4.6 and 9.4.2.The objective of Safety Validation is described in ISO 26262.The first objective is to provide evidence of compliance with the safety goals and that the functional safety concepts are appropriate for the functional safety of the item.The second objective is to provide evidence that the safety goals are correct, complete and fully achieved at the vehicle level.1.2ScopeThis plan is useful for validation activities which should be performed at vehicle level byIWV Development Project.This document describes the following information for IWV validation:Y the configuration of the item subjected to validationY the calibration of the item subjected to validationY Validation proceduresY test casesY driving maneuversY acceptance criteriaY the equipment and required environmental conditions.1.3Definitions, Acronyms, and AbbreviationsAll terms, acronyms and abbreviations which are required to correctly interpret this document are listed as follows.2Inputs and Output2.1PrerequisitionThe following information shall be available.-Safety Plan-Item Definition-Hazard Analysis & Risk Assessment-Safety Goal-Functional Safety Concept-Validation plan (refined)2.2Further supporting Information The following information may be considered -Project plan-Technical Safety Concept-Functional Concept (from external source)-Item Integration and Testing Plan-Safety Analysis Reports2.3OutputsThe following is the deliverable from this phase -Validation Report3Safety Strategy and Processes3.1OverviewThe Validation Plan is a requirement of the Automotive Functional Safety Standard ISO 26262. Internal and external safety inspectors may use this System Validation Plan as the basis for assessing how and to what extent safety-related issues have been addressed and treated during development of a safety critical system in the automotive domain.3.2Validation Test objectivesValidation plan must satisfy the following requirements:- The safety activities for the product development at the system level shall be planed including determination of appropriate methods and measures during design andintegration (5.4.1)- The validation activities shall be planned (5.4.2)3.3Safety Validation (Item development life cycle)Following figure shows that when it must be performed according to safety activity cycle for Safety Validation. Timing for performing according to safety activity cycle for Safety Validation is shown in figure 4-3.Figure 1 : Reference phase of Safety Validation3.4Validation ProcessesThe safety goals of the item shall be validated at the vehicle level by evaluating the controllability, effectiveness of safety measures, external measures and other technologies.And the results of the validation shall be evaluated.Validation process is like below.Safety Goal Validation- Operating scenario - Intended use- Foreseeable misuse - Safety Measure- External Measure- Other Technology- Positive test of Function- Fault Injection Test- Simulation- Fleet Test- User test under real-lifeconditionResultEvaluationValidation ReportFigure 2 : Validation Process3.5Regression strategyRegression test shall be required the quality and performance improvement in case of vehicle structure, mounting position and vehicle communication load changes.4Item Description4.1Item o verview4.1.1System ComponentFigure 3 : Sketch of <fill in system name>4.1.2S afety Goal of <fill in system name>The safety goals for validation test are listed in the following table.SPF shall be documented by reference of FMEA, FTA analysis report.Table 6 Safety goal of <fill in system name>4.2ConfigurationValidation tester shall check configuration of IWV through scanning tool before testing4.3CalibrationFor domestic market, IWV shall use calibration data for domestic market; IWV shall use calibration data for EU and general market because the structure of vehicle is different according to market. Therefore validation tester shall check calibration ID through scanning tool before testing.5Project Development and Validation schedule5.1Validation Test PlanValidation test item and schedule shall be prepared base on above the document.Specific test case of validation in each stage shall be specified in 7. Test Case Clause.Figure 5 : Validation Test schedule5.1.1HARA Controllability ValidationIn case of HARA performance, Severity, Exposure, Controllability shall be driven by statedcritera and other brain-storming on criteria. At this time, high ASIL C,D to allocate forControllability rating shall be needed to verify the rating validity through vehicle test.The validation test such as this Controllability shall be performed in the initialdevelopment, detail content and test case shall be specified in 7. Test case clause.Description of the performance period of Controllability validation test5.1.2Safety Goal ValidationThe final goal of validation is to verify that safety goal shall be accurately implemented at the vehicle level. The evaluation period is (TBD).Test case shall be completed and sample shall be prepared until (TBD).5.1.3Long-term testThe durability test of Safety Goal shall be verified through long-term test.The implementation period is (TBD).5.2Test Methods informationPass/fail criteria and test procedure are regulated in test case.5.3Validation method for safety goal6Test Case and Acceptance CriteriaPass/fail criteria and test procedure are regulated in test case.7References(NOTE) Basically, each referenced document should be listed by specifying the document name, version number, and date. A reference document which is continuously and frequently updated within the project, however, does not need to specify the version and date. If the version and date for a reference document are missing, it means the latest baseline version for that document has been referred to.。
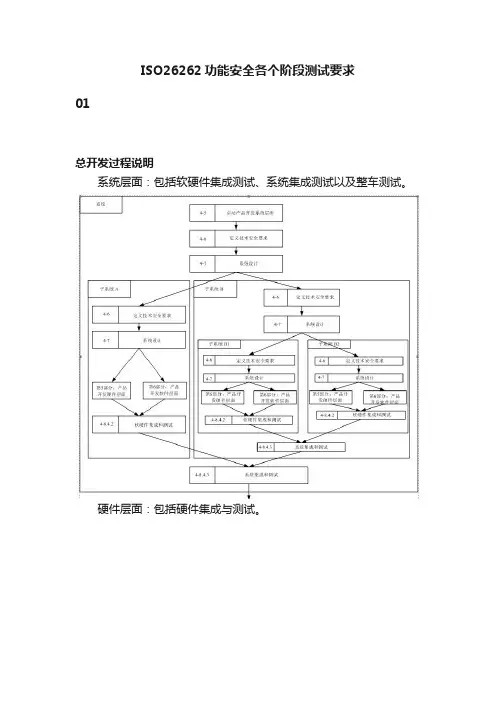
ISO26262功能安全各个阶段测试要求01总开发过程说明系统层面:包括软硬件集成测试、系统集成测试以及整车测试。
硬件层面:包括硬件集成与测试。
软件层面:单元测试、集成测试。
02功能安全总体要求2.1 各项指标2.2 诊断覆盖度举例针对一个信号举例说明:03功能安全测试要求3.1 测试计划核心内容应包括,测试对象:需要测试的对象描述,以及测试的范围描述;测试人员:人员能力、人员职责范围等;测试环境:涉及到的仿真环境(Simulink)、台架环境(HIL、实验台架等)等;测试工具:用到的各种软件以及硬件测试工具,如Canoe、Canape、Inca等,说明工具的型号以及版本信息;测试方法:功能安全表格中提到的针对各个阶段,所需采取的测试手段或方法;测试标准:测试通过以及失败的准则;测试条件:包括测试准入条件、测试准出条件以及测试异常退出条件等;测试回归:定义回归策略,如在产品末期,进行一次全回归测试等;测试时间计划表:针对各个阶段进行详细的测试计划安排,确保各个阶段人、事、物齐全,确保测试按照计划进行。
3.2 测试规格根据不同的测试对象进行分析,选择合适的测试方法、编写测试用例。
测试用例应包括,用例ID:每个测试用例应有唯一的测试ID,方便建立追溯;测试方法:说明测试用例选择的测试方法;测试环境:说明当前用例的环境;测试对象:说明对应的测试对象版本、配置信息;输入条件:说明测试用例的输入条件;测试步骤:说明测试用例的执行步骤;预期结果:说明测试用例执行后预期的输出、输出范围以及功能表现等,说明通过与失败评判标准。
3.3 软件相关测试3.3.1 软件单元测试测试对象:包括软件单元内部的语句、逻辑以及单元给外部调用的接口。
验证方法:表8 可通过静态验证工具来进行验证,表9中,一般需要进行数据流以及控制流分析图。
验证要求:证明软件单元满足软件单元设计规范;证明软件单元符合软硬件接口的定义;证明软件单元具有一定的鲁棒性;证明软件单元不包含非期望的功能,且满足下表覆盖度。
Form No: KOF 1000139502 All information contained herein is confidential and/or proprietary to XxAutomotive and any unauthorized disclosureor utilization is expressly prohibited. The information is legally safeguarded by digital fingerprints and offenders will(PLM version of BL-667) be held liable for any damages suffered. All rights and/or title to any intellectual property are reserved .1(7)Fun cti onal Safety Assessme nt Pla nFunctional Safety Assessment Plan vProject Name>Fun cti onal Safety Assessme nt Pla n1 Table of Contents1TABLE OF CONTENTS (2)2REVISION HISTORY (3)3INTRODUCTION (4)3.1G ENERAL OVERVIEW (4)3.2A BOUT THIS DOCUMENT (4)3.3A BBREVIATIONS (4)4REFERENCES (5)5MAIN CONTENT ............................................................................................................................ 错误!未定义书签。
汽车电子功能安全标准ISO26262解析(八)——ASIL等级分解汽车电子功能安全标准ISO26262解析(八)——ASIL等级分解原创pianpian_zct 最后发布于2018-01-18 11:14:55 阅读数6399 收藏展开ISO 26262-9 Clause 5 Requirements decomposition with respect to ASIL tailoringThe objective of this clause is to provide rules and guidance for decomposing safety requirements into redundant safety requirements to allow ASIL tailoring at the next level of detail.本章节的目的是为安全需求分解提供规则和指导,以便于将需求分解为冗余的安全需求,并使得下一级别的ASIL裁剪成为可能。
The ASIL, as an attribute of the safety goal, is inherited by each subsequent safety requirement.每一条安全需求都从安全目标继承ASIL等级。
The functional and technical safety requirements are allocated to architectural elements, starting with preliminary architectural assumptions and ending with the hardware and software elements.通过最初的架构假设,功能性和技术性的安全需求被分配给架构的每一个硬件和软件模块。
During the allocation process, benefit can be obtained from architectural decisions and the existence of independent architectural elements. This offers the opportunity:在ASIL等级分配的过程中,架构的决定性和架构中每个模块的独立存在性为我们提供了如下机会:1) to implement safety requirements redundantly by these independent architectural elements;通过使用这些独立的架构模块,来冗余地实现安全需求。
BMS功能安全开发流程(六):汽车软件开发在汽车行业软件开发一般遵循V模型,左边是开发过程,右边对应的测试过程。
ISO26262第六部分推荐的软件开发流程也V模型,如下图所示,跟硬件的V模型开发流程基本一样,需求-->架构-->详细设计。
1. 软件架构设计软件开发流程跟硬件开发基本一样,由软件TSR和系统需求可以确定软件基本架构。
软件安全要求需要与软件架构一起实施,以及与安全相关的其它软件要求。
在软件架构中,由于软件单元获得了分配给他们的不同软件安全性要求,因此考虑这些可能与不同ASILs的要求是否可以共存在同一软件单元中也很重要。
如果不符合这些标准,则需要根据所有分配的安全要求的最高ASIL开发和测试软件。
这些标准可能包括内存保护和保证的执行时间。
软件架构包含静态和动态方面的,静态方面的主要和不同软件单元之间的接口:1)软件结构包括其分级层次; 2)数据处理的逻辑顺序; 3) 数据类型和它们的特征参数; 4)软件组件的外部接口; 5)软件的外部接口及约束(包括架构的范围和外部依赖)。
动态方面的涉及:1)功能性和行为;2)控制流和并发进程;3)软件组件间的数据流;4)对外接口的数据流时间的限制。
为了说明这两个方面,软件架构所用到的标记法有,非正式标记法,半正式标记法,正式标记法,ASIL 等级越高,标记法越正式。
在软件架构设计中,需要重点考虑软件的可维护性及可测试性。
在汽车行业,软件在整个产品周期内都应当考虑维护性,同时还要考虑软件架构的设计测试的容易醒,在ISO 26262标准中,测试是非常重要的一方面,任何设计都应该同时考虑到测试的方便性。
为避免高度复杂性导致系统性故障,ISO26262列出来一些推荐的标准:•软件层次性,软件模块的高内聚性,限制软件模块大小•软件模块之间的接口应当尽量少且简单。
这个可以通过限制软件模块的耦合度实现•软件调度应当避免使用中断,如果使用了中断,要注意考虑中断的优先级。