句子成分结构讲义
- 格式:docx
- 大小:27.15 KB
- 文档页数:4



英语句子成分“讲义”英语句子看上去纷繁庞杂,但仔细观察不外乎五个基本句式。
这五个基本句式可以演变出多种复杂的英语句子。
换言之,绝大多数英语句子都是由这五个基本句式生成的。
这五个基本句式如下:S十V主谓结构S十V十F主系表结构S十V十O主谓宾结构S十V十O1十O2 主谓双宾结构S十V十O十C 主谓宾补结构说明:S=主语;V=谓语;P=表语;O=宾语;O1=间接宾语;O2=直接宾语;C=宾语补足语五个基本句式详细解释如下:1.S十V句式在此句式中,V是不及物动词,又叫自动词(vi.)。
例如:He runs quickly.他跑得快。
They listened carefully.他们听得很仔细。
He suffered from cold and hunger.他挨冻受饿。
China belongs to the third world country.中国属于第三世界国家。
The gas has given out.煤气用完了。
My ink has run out.我的钢笔水用完了。
2.S十V十P句式在此句式中,V是系动词(link v.),常见的系动词有:look,seem,appear,sound,feel,taste,smell,grow,get,fall ill/asleep,stand/sit still,become,turn等。
例如:He is older than he looks.他比看上去要老。
He seen interested in the book.他似乎对这本书感兴趣。
The story sounds interesting.这个故事听起来有趣。
The desk feels hard.书桌摸起来很硬。
The cake tastes nice.饼尝起来很香。
The flowers smell sweet and nice.花闻起来香甜。
You have grown taller than before.你长得比以前高了。

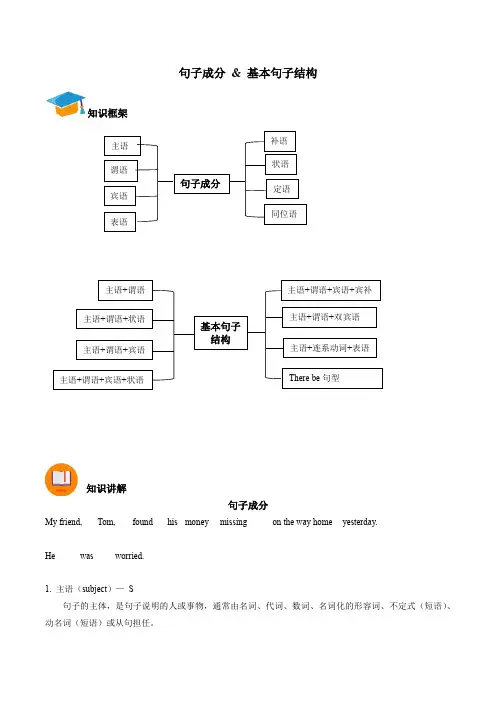
语法精讲:句子成分和基本句子结构知识点1 句子成分句子是表达思想的基本单位,主要句子成分(sentence elements)有主语(S)、谓语(V)、宾语(0)、补语(C)、状语(A)、表语(P)、定语(Attr.)等。
具体如下:1.主语(subject):表示句子所要说明或描述的人或事物,一般由名词、代词或相当于名词的词组或句子充当,置于句首。
如:The students are listening to me carefully. They want to learn English well. Learning English well isn't as hard as you think.学生们在认真听我讲课。
他们想学好英语,学好英语不像你想的那么难。
2.谓语(verb):说明或描述主语的动作、状态或特征,由动词或动词短语充当,位于主语之后。
如:He runs every morning.他每天早上跑步。
You may keep the book for two weeks.这本书你可以借两周。
The students are playing basketball on the playground.学生们正在操场上打篮球。
The film is interesting.这部电影很有趣。
3.宾语(object):指动作所涉及的人或事物。
一般由名词、代词或相当于名词的词组或句子充当,位于动词或介词之后。
有的动词后面可以接两个宾语,通常把其中表示人的宾语称为间接宾语(indirect object),把表示物的宾语称为直接宾语(direct object)。
如:He is going to buy a dictionary.他打算买本词典。
(动词的宾语)We should learn from him.我们应向他学习。
(介词的宾语)Lend me your book,please.请把你的书借给我。
句子成分 & 基本句子结构知识框架知识讲解句子成分My friend,Tom, found his money missing on the way home yesterday.Hewas worried.1. 主语(subject )— S句子的主体,是句子说明的人或事物,通常由名词、代词、数词、名词化的形容词、不定式(短语)、动名词(短语)或从句担任。
句子成分 补语 状语 定语 主语 谓语 宾语 基本句子结构主语+谓语 主语+谓语+宾语主语+连系动词+表语 主语+谓语+双宾语 主语+谓语+宾语+宾补 主语+谓语+状语 主语+谓语+宾语+状语There be 句型 同位语 表语The apple is red.Four and five makes nine.The sick and the old need our help.Running is good for health.2. 谓语(verb)—V表示主语的动作或状态,由动词担任He often reads newspapers.The plane takes off at 8 o’clock.3. 宾语(object)—O表示动作的对象或行为承受者,一般位于及物动词(短语)或介词之后,通常由名词、代词、形容词、数词、名词化的形容词、不定式(短语)、动名词(短语)或从句担任直接宾语:direct object —DO间接宾语:indirect object —IOWhere did you buy that?I wish to call on you.We should help the poor.Do you understand what I mean?4. 表语(predicative)—P位于系动词之后,说明主语的特征、类属、状态或身份,通常由名词、代词、形容词、数词、副词、介词短语、不定式(短语)、分词短语或从句担任Please feel free to say what you really think.e to see me tomorrow when I am at work.She is singing.Dancing is her favorite activity.5. 宾语补足语(object plement)—C位于宾语之后,对宾语进行补充说明的成分,通常由形容词、分词(短语)、不定式(短语)、名词、介词(短语)或副词担任I found the book very interesting.Do you hear Tom singing?Please make yourself at home.Please keep the dog out.注意:主动语态变被动语态后,宾语补足语就变成了主语补足语Someone considered him to have stolen the money.He was considered to have stolen the money by someone.6. 定语(attributive)修饰或限定名词或代词的成分,通常由形容词、代词、数词、名词(所有格)、动名词(短语)、副词、介词短语、不定式(短语)、分词(短语)或从句担任Open your mouth and put on your tongue.It’s a fine day today.Put the child in the sleeping bag.Let’s try another way to do this.7. 状语(Adverbial)—A用来修饰动词、形容词、副词或句子,可以表示时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、比较、程度、条件、方式、让步等。

英语句子结构详细讲解一.句子成分分析1.主语(subject)句子的主体,全句述说的对象。
一般由名词,代词,数词,不定式,动名词,从句担任,常置于句首。
(名词)(主格代词)(数词)(不定式)(动名词)(主语从句)2. 谓语(predicate)对主语加以陈述,表示主语的行为或状态,常用动词或者动词词组担任,放在主语的后面。
谓语分为简单谓语和复合谓语(1).简单谓语由一个动词或者动词短语构成at 6 o?clock.(动词)(动词短语)(2).复合谓语①由情态动词或其他助动词加动词原形构成(情态动词+动词原形)She (助动词do+动词原形)(助动词has+动词原形)补充:协助主要动词构成谓语动词词组的词叫助动词(Auxiliary Verb)。
被协助的动词称作主要动词(Main Verb)。
最常用的助动词有:be, do, have, shall, will, should, would. 助动词自身没有词义,不可单独使用,例如:He doesn't like English. 他不喜欢英语。
(doesn't是助动词,无词义;like是主要动词,有词义)②由系动词加表语构成(即主系表结构)(状态系动词be+表语)(表象系动词look+表语)补充:系动词亦称联系动词(Link Verb),作为系动词。
有些不具词义;有些具有词义,但不能单独用作谓语,后边必须跟表语(亦称补语),构成系表结构说明主语的状况、性质、特征等情况。
1.状态系动词用来表示主语状态,只有be一词,例如:He is a teacher. 他是一名教师。
(is与补足语一起说明主语的身份。
)2.持续系动词用来表示主语继续或保持一种状况或态度,主要有keep, rest, stay, lie, remain, 例如:He always kept silent at meeting. 他开会时总保持沉默。
This matter rests a mystery. 此事仍是一个谜。

英语句子成分结构详解一、英语语句基本结构分析:( 一) 主谓宾结构:1、主语:可以作主语的成分有名词 ( 如 boy) ,主格代词 ( 如 you) ,数词,动词不定式,动名词等。
主语一般在句首。
注意名词单数形式常和冠词不分家 !eg: The boy comes from America.( 名词 )He made a speech.( 主格代词 )Two plus two is four. ( 数词 )To be a teacher is my dream.( 动词不定式 )Doing a research is a necessary step of covering a story.( 动名词 ) 2、谓语:谓语由动词构成,是英语时态、语态变化的主角,一般在主语之后。
谓语可以是不及物动词 (vi.) 没有宾语,形成主谓结构,eg:We come.Many changes took place in my home town.3、宾语:宾语位于及物动词之后,一般同主语构成一样,不同的是构成宾语的代词必须是‘ 代词宾格’,如: me, him,them 等。
除了代词宾格可以作宾语外,名词,动名词,不定式等可以作宾语。
eg:I will do it tomorrow. 代词宾格The boy needs a pen. 名词I like swimming. 动名词I like to swim this afternoon.不定式( 二) 主系表结构:1、主语:同‘主谓宾’结构。
2、谓语:联系动词become成为get 变的turn 变成go 变be 动词am,is,are,was,were,have been感官动词:feel, touch, hear, see 等。
其特点是联系动词与其后的表语没有动宾关系,表语多为形容词或副词,不可能是宾语。
3、表语:说明主语的状态、性质等。
可为形容词、副词、名词、代词、不定式、分词联系动词eg: He becamea teacher at last.His face turned red.感官动词多可用作联系动词eg: He looks well. 他面色好。
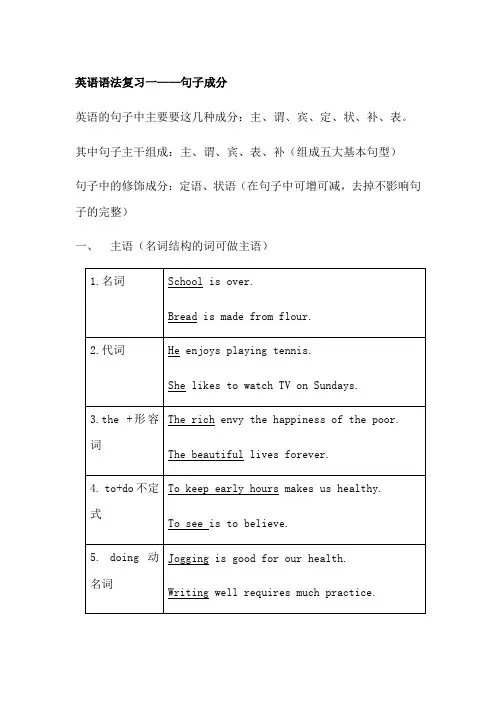
英语语法复习一——句子成分英语的句子中主要要这几种成分:主、谓、宾、定、状、补、表。
其中句子主干组成:主、谓、宾、表、补(组成五大基本句型)句子中的修饰成分:定语、状语(在句子中可增可减,去掉不影响句子的完整)一、主语(名词结构的词可做主语)二、谓语(动词做句子的谓语,谓语往往有时态的变化)三、宾语(请注意:能做主语的词也能做宾语;及物动词有宾语,介词后面也有宾语)四、补语(宾语补足语,对宾语进行解释说明,可和宾语构成有逻辑的句子)五、表语(放在系动词之后,对主语进行说明的成分就是表语)句子修饰成分:定语、状语六、定语:(主要用于修饰主语和宾语的形容词结构,也可理解为修饰名词的形容词结构,限定词,单个形容词,现在分词和过去分词一般放在名词左边;形容词短语、不定式、现在分词短语、过去分词短语、介词短语、定语从句和同位语从句一般放在名词右边)七、状语(用于修饰动词的副词或者相当于副词的结构)Practice:请指出下面文章的句子成分:Americans today have different eating habits. There is a wide selection of food available. They have a broader knowledge of nutrition, so they buy more fresh fruit and vegetables than ever before. At the same time, american purchase increasing quantities of sweets and sodas.Statistics show that the way people live determines the way they eat. American lifestyles have changed. There are now growing numbers ofpeople who live alone. These changing lifestyles are responsible for the increasing number of people who must rush meals or sometimes simply go without them. Many Americans have less time than ever before to spend preparing food. Partly as a consequence of this limited time, ove r half of American houses now have microwave ovens. Moreover, Americans eat out nealy four times a week on average.It is easy to study the amounts and kinds of food that people consume. The United States Department of Agriculture and the food industry collect sales statistics and keep accurate records. This information not only tells us what people are eating, but also tells us about the changes in attitudes and tastes. Beef, which used to be the most popular choice for dinner, is no longer an American favorite. Instead, chicken, turkey and fish have become more popular. Sales of these foods have greatly increased in recent years.。

英语语法之句子成分及句子结构一、句子成分组成句子的各个部分叫句子成分。
句子成分包括主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语、表语和宾语补足语等。
主语和谓语是句子的主体部分(在英文中一般的句子必须有主语和谓语)。
即:句子成分有主要成分和次要成分;主要成分有主语和谓语;次要成分有表语、宾语、定语、状语、补语和同位语1 .主语(subject)主语是一个句子所叙述的主体,一般位于句首。
但在there be结构、疑问句和倒装句中,主语位于谓语、助动词或情态动词后面。
主语可由名词、代词、数词、不定式、动名词、名词化的形容词和主语从句等表示。
找出句中主语The sun rises in the east.名词Twenty years is a short time in history.数词The poor are now living in the shelter名词化的形容词Seeing is believing.动名词To see is to believe.不定式He likes dancing.代词What he needs is a book .句子(主从)It is n ecessary to master a foreig n Ian guage.2谓语::说明主语的动作、状态和特征;动词在句中作谓语,一般放在主语之后。
(1)简单谓语:由动词或动词词组组成I saw the flag on the top of the hill. He looked after two orphans.(2)复合谓语由情态动词或助动词+动词;He can speakEnglish well. Shedoesn' t sedonlike dancing3宾语:动作的对象或承受者一一及物动词或介词的宾语,即动宾&介宾,常用名词或相当于名词的词(动词不定式或动名词)、代词和数词充当Show your passport, please.名词She did n't say anything.代词How many do you want? - I want two.数词I enjoy traveling. 动名词He pretended not to see me 不定式They sent the injured to hospital.名词化的形容词I think (that)he is fit for this job. 句子(宾语从句宾语分为直接宾语和间接宾语.直接宾语指物或事,间接宾语指人或动物.(双宾语结构)He gave me some books. Please passne the book.He bought his girlfriend some flowers /4.宾语补足语有些及物动词除了有一个直接宾语以外,还要有一个宾语补足语,说明宾语的身份和状态以补充其意义不足,使句子的意义完整(宾语的复合结构)。

第一讲句子成分及句子结构第1讲:句子成分和句子结构(一)句子成分定义:组成句子的各个部分叫做句子的成分。
句子成分包括:主语、谓语、宾语、宾语补足语、表语、定语和状语。
主语和谓语是句子的主体部分(在英语中,句子必须有主语和谓语)。
1.主语主语是句子陈述的对象,表示所说的“是什么”或“是谁”。
一般由名词、代词、不定代词或相当于名词的单词或短语来充当,也有从句充当的现象。
大多数主语都在句首。
如:(1) 代词作主语 We work in a big factory.(2) 名词作主语 The classroom is very big.(3) 数词作主语 Three are enough. 三个就够了(4)不定式作主语To learn English well is important.学好英语很重要。
(不定式做主语常用it来代替)It is important to learn English well.(5)动名词作主语Watching TV is bad for your eyes.看电视对眼睛有害。
(6)从句作主语That the earth goes around the sun is true.地球绕着太阳转是事实。
(常用It来代替)。
It is true that the earth goes around the sun.What we need is food. 我们最需要的是食物.(7)在“There be ”句型中,主语在there be 之后。
如:There are some bottles of milk in the box.There is a desk and four chairs in the room(8)在倒装结构中,主语在动词后。
On the wall hang two pictures .墙上挂着两幅图画。
In front of the building stands a tall tree.楼前有一棵大树。

英语句子成分和英语句子结构句子成分分析:(6种:主谓宾定状补)1、主语(Subject):动作的发出者,可由名词、代词、不定式(to do)、或动名词(V-ing)等来充当,通常置于句首。
The sun rises in the east.2、谓语(Predicate): 只有动词或动词短语才能充当,置于主语之后说明主语的动作、状态和特征。
We study English.3、宾语:动作的承受者1)动宾位于谓语动词(vt)之后I like China. (名词)I like listening to classical music.2)双宾语-----间宾(指人)和直宾(指物)He gave me a book yesterday.Give the poor man some money.4、定语:修饰或限制名词或代词的词、词组或句子。
Marry is an English teacher.(名词)Dalian is a beautiful city. (形容词)5、状语。
表示时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、程度、条件、方式和让步等。
He goes to school by bike.6、补语宾补:对宾语的补充,全称为宾语补足语。
We will make them happy. (形容词)7、表语(Predicative)系动词之后的成分,表示主语的性质、状态和特征。
He is a teacher. (名词)Five and five is ten. (数词)He is asleep.(形容词)The picture is on the wall. ( 介词短语)The cleaner's job is to clean the street.(不定式)(常见的系动词有be, sound(听起来), look(看起来), feel(摸起来,smell(闻起来), taste (尝、吃起来), feel(感觉)...It sounds a good idea.The sound sounds strange.Her voice sounds sweet.Tom looks thin.The food smells delicious.The food tastes good.句子结构简单句的五个基本句型主+谓(vi不及物动词) She came./ My head aches.主+谓(vt及物动词)+宾语She likes English.主+谓+间接宾语+直接宾语She gave John a book.She bought a book for me.主+系+表She is happy.主+谓(vt.)+宾+宾补She makes her mother angry.(There +be There lies a book on the desk. )句子的种类:陈述句/ 祈使句/ 感叹句/ 疑问句练习:分析下列句子成分1. Our school is far from my home.2. It is a great pleasure to talk with you3. All of us considered him honest.4. My grandfather bought me a pair of sports shoes.5.He broke a piece of glass.6. Trees turn green when spring comes.7. They pushed the door open. 8. Grandma told me an interesting story last night. 9.He wrote some letters to his friends. 10. We need a place twice larger than this one.11. He asked us to sing an English song. 12. We will make our school more beautiful.13. She showed us many of her pictures.14. The cars made in Japan are better than those in Germany.15. At last he got home, tired and hungry. 16. Would you please pass me the cup?17 Mary handed her homework to the teacher. 18. Do you know the latest news about him?19. I’ll get my hair cut tomorrow.翻译练习:主谓结构(主语+不及物动词)你应当努力学习。
英语句子成分和英语句子结构讲解及练习一、句子成分分析:(6种:主谓宾定状补)1、主语(Subject):动作的发出者,可由名词、代词、不定式(to do)、或动名词(V-ing)等来充当,通常置于句首。
The sun rises in the east.2、谓语(Predicate): 只有动词或动词短语才能充当,置于主语之后说明主语的动作、状态和特征。
We study English.3、宾语:动作的承受者1)动宾位于谓语动词(vt)之后I like China. (名词)I like listen to the classical music.2)双宾语-----间宾(指人)和直宾(指物)He gave me a book yesterday. Give the poor man some money.4、定语:修饰或限制名词或代词的词、词组或句子。
Marry is an English teacher.(名词)5、状语。
表示时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、程度、条件、方式和让步等。
He goes to school by bike.6、补语宾补:对宾语的补充,全称为宾语补足语。
We will make them happy. (形容词)7、表语(Predicative)系动词之后的成分,表示主语的性质、状态和特征。
He is a teacher. (名词)Five and five is ten. (数词)He is asleep.(形容词)The picture is on the wall. ( 介词短语)The cleaner's job is to clean the street.(不定式)(常见的系动词有be, sound(听起来), look(看起来), feel(摸起来,smell(闻起来), taste (尝、吃起来), feel(感觉)...It sounds a good idea. The sound sounds strange.Her voice sounds sweet. Tom looks thin.The food smells delicious. The food tastes good.句子结构简单句的五个基本句型主+谓(vi不及物动词) She came./ My head aches.主+谓(vt及物动词)+宾语She likes English.主+谓+间接宾语+直接宾语She gave John a book.She bought a book for me.主+系+表She is happy.主+谓(vt.)+宾+宾补She makes her mother angry.(There +be There lies a book on the desk. )句子的种类:陈述句/ 祈使句/ 感叹句/ 疑问句练习:分析下列句子成分1. Our school is far from my home.2. It is a great pleasure to talk with you3. All of us considered him honest.4. My grandfather bought me a pair of sports shoes.5.He broke a piece of glass.6. Trees turn green when spring comes.7. They pushed the door open. 8. Grandma told me an interesting story last night. 9.He wrote some letters to his friends. 10. We need a place twice larger than this one.11. He asked us to sing an English song. 12. We will make our school more beautiful.13. She showed us many of her pictures.14. The cars made in Japan are better than those in Germany.15. At last he got home, tired and hungry. 16. Would you please pass me the cup?17 Mary handed her homework to the teacher. 18. Do you know the latest news about him?19. I’ll get my hair cut tomorrow.翻译练习:主谓结构(主语+不及物动词)你应当努力学习。
第四章句子成分一.句子成分的性质(一)配对性句子结构中的直接构成成分,往往是两两相对的,是同现的,相互依存的,这就是句子成分的配对性。
句子成分的配对性通常体现在,具有直接关系的句子成分之间往往是对应关系:句子成分配对性的特点是:具有配对关系的句子成分之间是同现的,相互依存的,离开了一方,另外一方也就无所谓存在了。
这一点,在前边的“语法概说”中,已经有所表述,这里不再讨论。
(二)应对性句子成分的应对性,指的是某些句子成分之间可以互易位置,而句子的意思基本不变。
汉语句子成分应对性通常体现在以下几种情况。
1.主—宾应对:主语、宾语互换位置而句子的意思基本不变。
如:①三个人坐一条凳子。
→一条凳子坐三个人。
②西昌通火车了。
→火车通西昌了。
③自古英雄出少年。
→自古少年出英雄。
2.定—中应对:句子中的定语和中心语互换位置而句子的意思基本不变。
如:①水汪汪的眼睛。
→眼睛水汪汪的。
②朵朵白云,阵阵春风。
→白云朵朵,春风阵阵。
3.状—中应对:句子中状语和中心语互换位置而句子的意思基本不变:①你错写了几个字。
→你写错了几个字。
②四周出奇地肃静。
→四周肃静得出奇。
③车子很慢很慢地开着。
→车子开得很慢很慢。
4.主—谓应对:句子中的主语、谓语互换位置而句子的基本意思不变。
如:①一斤白菜三元钱。
→三元钱一斤白菜。
②一张死契六十块大洋。
→六十块大洋一张死契。
上述各种应对关系的事实都是存在的,语法研究要做的是:进一步找到上述各种易位的条件二.主语、谓语(一)主语的语法构成总体上说,可以充当汉语主语的语言成分很多。
在汉语的词类中,除了副词、叹词和各种虚词之外,其他各类实词和词组都可以充当主语。
就此而言,汉语的“主语”似乎是比较讲究“民主”的——汉语的主语不是“名词性成分”的专利。
从具体情况来看,汉语主语通常由以下各种成分来充当。
1.名词性成分充当主语。
这是汉语最为常见的主语构成形式。
如:①他松了一口气。
②小王走了。
③母亲和宏儿都睡着了。
句子成分分析讲解在语言学中,句子是语言表达的基本单位。
而句子成分分析是对句子的结构进行拆分和分析的过程,通过对句子成分的分析,我们可以更好地理解句子的构成和意义。
本文将对句子成分的分类和分析方法进行讲解,并通过例句来说明。
一、基本成分句子的基本成分包括主语、谓语和宾语。
主语是句子的中心词,通常表示动作的执行者或者是被动的承受者。
谓语是句子的核心部分,用来说明主语的动作或状态。
宾语是谓语动作的对象或者是受事者。
例如,下面是一个简单的句子:他喝咖啡。
在这个句子中,"他"是主语,"喝"是谓语,"咖啡"是宾语。
二、进一步成分除了基本成分,句子中还可以存在进一步的成分,如状语、定语和补语。
1. 状语状语用来修饰动作或状态的描述,可以表示时间、地点、方式、原因等信息。
例如:他昨天在图书馆读书。
在这个句子中,"昨天"是表示时间的状语,"在图书馆"是表示地点的状语。
2. 定语定语用来修饰名词,对名词进行限定或者描述。
例如:我买了一本有趣的小说。
在这个句子中,"有趣的"是修饰名词"小说"的定语。
3. 补语补语用来补充说明主语或宾语的状态或特征。
例如:他变得很自信。
在这个句子中,"很自信"是补语,补充说明主语"他"的状态。
三、成分的判断方法在进行句子成分分析时,可以通过下面的方法来判断句子中的成分。
1. 代换法通过将句子中的某个结构替换为代词或代名词,来判断这个结构是否是某种成分。
例如:他喝咖啡 -> 他喝它。
通过将"咖啡"替换为"它",我们可以判断"咖啡"是宾语。
2. 变换法通过改变句子中的时态、人称等变量,来判断某个结构的成分属性。
例如:他昨天在图书馆读书 -> 他今天在图书馆读书。
一【2 】.英语句子成分和英语句子构造讲授:(一)句子成分1.主语(subject): 句子解释的人或事物.主语可以由名词.代词.数词.不定式.动名词.分词.主语从句和短语等来担任.The sun rises in the east.(名词) He likes dancing. (代词)Twenty years is a short time in history. (数词)Seeing is believing. (动名词)To see is to believe. (不定式) What he needs is a book. (主语从句)It is very clear that the elephant is round and tall like a tree.(It情势主语,主语从句是真正主语)What he has said is true. (句子)2.谓语(predicate): 解释主语的动作.状况和特点.I saw the flag on the top of the hill?He looked after two orphans.复合谓语:由情态动词或助动词+动词;He can speak English well.She doesn’t seem to like dancing.找出下列句中的谓语(注:只有动词才可作谓语.):1. We love China.2. We have finished reading this book.3. He can speak English.4. She seems tired.3.表语(predicative): 系动词之后的成分,表示主语的性质.状况和特点.He is a teacher. (名词) Seventy-four! You don’t look it. (代词)Five and five is ten. (数词) He is asleep. (形容词)His father is in. (副词) The picture is on the wall. ( 介词短语)My watch is gone / missing / lost. (形容词化的分词)To wear a flower is to say “I’m poor, I can’t buy a ring. (不定式)The question is whether they will come. (表语从句)★(常见的系动词有: be, sound(听起来), look(看起来), feel(摸起来,smell(闻起来), taste(尝.吃起来), remain(保持,仍是), feel(感到) ...It sounds a good idea. The sound sounds strange.Her voice sounds sweet. Tom looks thin.The food smells delicious. The food tastes good.The door remains open. Now I feel tired.找出下列句中的表语.1. I am a teacher.2. They are on the playground.3. My job is teaching English.4. It gets cold.5. It sounds interesting.4.宾语:1)动作的推却者-----I like China. (名词) He hates you. (代词)How many do you need? We need two. (数词)We should help the old and the poor. I enjoy working with you. (动名词)I hope to see you again. (不定式) Did you write down what he said? (宾语从句)2)介词后的名词.代词和动名词-----介宾Are you afraid of the snake? Under the snow, there are many rocks.3)双宾语-----间宾(指人)和直宾(指物)宾语分为直接宾语和间接宾语.直接宾语指物或事,间接宾语指人或动物.He gave me a book yesterday. Give the poor man some money.指出下面句子的间接宾语和直接宾语:please pass me the book.He bought his girlfriend some flowers.找出下列句子的宾语部分:1. We often help him.2. He likes to play basketball.3. We enjoy listening to the music.4. She said that he felt sick.5. They are talking about the new student.5.宾补:对宾语的补充,全称为宾语补足语.We elected him monitor. (名词) We all think it a pity that she didn’tcome here. (名)We will make them happy. (形容词) We found nobody in. ( 副词 )Please make yourself at home. 介词短语)Don’t let him do that. (省to不定式)His father advised him to teach the lazy boy a lesson. (带to不定式)Don’t keep the lights burni ng. (如今分词)I’ll have my bike repaired. (曩昔分词)6.主补:对主语的补充,全称为主语补足语.He was elected monitor. She was found singing in the next room.He was advised to teach the lazy boy a lesson.7.定语:润饰或限制名词或代词的词.词组或句子.Ai Yanling is a chemistry teacher.(名词) He is our friend. (代词)We belong to the third world. (数词)He was advised to teach the lazy boy a lesson.(形容词)The man over there is my old friend.(副词)The woman with a baby in her arms is my sister. (介词)The boys playing football are in Class 2. (如今分词)The trees planted last year are growing well now. (曩昔分词)I have an idea to do it well. (不定式)You should do everything that I do. (定语从句)定语后置:假如定语是由一个单词表示时,平日要前置.而由一个词组或一个句子表示时,平日则后置The girl in red is his sister.We have a lot of work to do.The girl standing under the tree is his daughter.Do you know the man who spoke just now?8.状语:用来润饰v., adj., adv., 或句子.表示时光.地点.原因.成果.程度.前提.方法和妥协. (以下例句按上述次序分列)I will go there tomorrow.The meeting will be held in the meeting-room.The meat went bad because of the hot weather.He studies hard to learn English well.He didn’t study hard so that he failed in the exam. I like some of you very much.If you study hard, you will pass the exam. He goes to school by bike.Though he is young, he can do it well.(二)句子构造简单句的五个根本句型1.主语+不及物动词 She came./ My head aches.2.主语+及物动词+宾语 She likes English.3.主语+系动词+表语 She is happy.4.主语+双宾动词+间接宾语+直接宾语 She gave John a book.5.主语+宾补动词+宾语+宾语补语 She makes her mother angry.The teacher asked me to read the passage.★ There +be 句型There are some books on the desk.There lies a book on the desk.Exercises :剖析下列句子成分1. Our school is not far from my home.2. It is a great pleasure to talk with you3. All of us considered him honest.4. My grandfather bought me a pair of sports shoes.5. He broke a piece of glass.6. He made it clear that he would leave the city.翻译演习:主谓构造(主语+不及物动词)1.你应当尽力进修You should study hard.2.他昨天晚上很晚回家She went home very late yesterday evening.演习:1.This box weighs five kilos. 这个盒子重五公斤.2.I lived in Beijing five years ago. 五年前我住在北京.主谓宾构造(主语+及物动词+宾语)1.我昨晚写了一封信I wrote a letter last night.2.我今世界午想和你谈谈I want to talk with you this afternoon.演习:1.All of us believe that Jack is an honest boy. 我们大家都信任Jack 是一个说谎男孩.2.He did not know what to say. 他不知道说什麽好.主系表构造(主语+系动词+表语)1.我的弟弟都是大学生My brothers are all college students.2.在冬天,白天很短夜晚很长In winter, the days are short and the nights are long.3. 布朗密斯看上去很健康Mrs Brown looks very healthy.4.在他15岁那年他成为了有名的画家 At the age of fifteen he became a famous pianist. 演习:1、树叶已经变黄了.The leaves have turned yellow.2.这个报告听起来很有意思.The report sounds interesting.双宾语构造(主语+双宾动词+间接宾语+直接宾语)1.强森师长教师客岁叫我们德语Mr Johnson taught us German last year.2.祖父昨晚给我讲了一个有味的故事Grandma told me an interesting story last night. 演习:1. 请你给我弄一本新的,好吗? Will you please get me a new copy?2.我替你叫辆出租汽车好吗? Shall I call you a taxi?复合宾语构造(主语+动词+宾语+宾语补足语)1.我们叫她爱丽丝We call her Alice.2.他怙恃叫他约翰His parents named him John.演习:1、黉舍定了一条规矩,开端上课时学生要起立.The school made it a rule that the students should stand up when class begins. 2.我以为与那小我谈话是无益的.I thought it no use talking with that manThere be 句型1.今晚不会开会There isn’t going to be a meeting tonight.2.这个村庄里只有一口井There was only a well in the village.演习:1.铃响了.There goes the bell2.一周有七天.There are seven days a week二.英语句子种类讲授:按照句子的用处,英语句子可分为陈述句.疑问句.祈使句和感慨句.按照句子的构造,英语句子可分为简单句.并列句和复合句.中考对句子的考核重要分散在以下几个方面:1. 陈述句的构成情势及根本用法;2. 祈使句的构成情势及根本用法;3. 一般疑问句.特别疑问句.选择疑问句.反意疑问句的构成情势及根本用法;4. 由what, how引诱的感慨句的构成情势.用法及差别对于各类从句的用法我们在后面分离阐述.(一.) 陈述句的构成情势及根本用法1. 陈述句:陈述句是用来陈述一个事实或表达措辞人意见(包括确定和否认)的句子.平日用降调,句末用句号“.”.Tom has a new car.The flower isn’t beautiful.2. 陈述句否认式的构成(1) 假如确定陈述句的谓语部分含有助动词.情态动词或连络动词be,则只需在这些动词后加not即可构成否认式.He is playing the guitar.(确定)He is not playing the guitar.(否认)We can get there before dark.(确定)We can’t get thee before dark.(否认)(2) 假如陈述句的谓语动词是实义动词,而个中又没有情态动词或助动词时,则需依据人称和时态在该实义动词前加don’t, doesn’t或didn’t.同时把该实义动词变为本相.He plays the violin well.(确定)He doesn’t play the violin well.(否认)She won the game.(确定)She didn’t win the game.(否认)(3) 假如句子是there be构造或曰语动词是have(有),除了be和have之后加not之外,句中假如有some要变为any.例如:There is some wate r in the cup. →There is not any water in the cup.He has some books. →He has not any books.(4) 除not以外,否认词no, never, nothing, nobody, few等也可构成否认句.例如:There is something wrong with his bike. →There is nothing wrong with his bike.I have seen the film. →I ha ve never seen the film.(二.) 祈使句的构成情势及根本用法祈使句是用来表示敕令.请求.建议.号令等的句子,谓语动词用本相,句末用感慨号“!”或句号“.”.朗读时一般用降调.1.确定的祈使句:(1)祈使句主语是you时,you常省略,但假如要特别强调对方或表达某种强烈的情感时可以有主语或称呼语.Be quiet.You be quiet!(2)“Do+祈使句”表示一种强烈的情感或请求,do起强调感化.Do come back at once! Do be careful.(3)please用在祈使句中可以表示一种虚心的语气,但please用在句末时,必须用逗号与其余部分离开.Open the window, please.(4)Let引诱祈使句时,后面需跟上人称代词或称呼语,人称代词一般只用第一.第三人称.Let Jack wait a minute.Let’s go to school.(5)在祈使句中,Let’s和 Let us是有差别的.Let’s包括措辞者,而Let us不包括听话者在内.这点从反意疑问句时可显著看出.Let’s go skating, shall we?(表示内部的建议)Let us try again, will you?(表示向别人发出请求)2. 否认祈使句平日以Don’t或Never开首.其构造平日是:“Don’t(Never)+动词本相+其他成分” 例如:Don’t do that again!Never leave today’s work for tomorrow!Don’t be late next time!(三.) 一般疑问句.特别疑问句.选择疑问句.反意疑问句的构成情势及根本用法1. 一般疑问句:(1)一般疑问句的确定情势一般疑问句一般是指以助动词.情态动词.be动词或have(有)开端,平日请求以yes,或no来答复的疑问句,一般疑问句读时平日用升调.Do you know Mr. Smith Can you swim?(2)一般疑问句的否认构造① 在一般疑问句的否认构造中,把副词not放在一般疑问句的主语之后.但假如用not的简单情势-n’t,则须将-n’t与一般疑问句句首的be, have,助动词或情态动词写在一路.在现实应用中,一般都采用简单式.Are you not a footb all fan?Aren’t you a football fan?Will she not like it?Won’t she like it?② 与汉语不同的是,英语一般疑问句否认构造的答语是否认照样确定,全由答语的否认或确定来决议.若答语是确定的,则用yes加确定构造;若答语是否认的,则用no加否认构造.Aren’t you a football fan? 你不是足球迷吗?Yes, I am.\ No, I am not.Won’t she like it?Yes, she will. \ No, she won’t.。
1. 按照结构划分,句子种类可分为简单句、并列句和复杂句。
⑪简单句(Simple Sentence):由一个主语(或并列主语)和一个谓语(或并列谓语)构成的句子。
如:①You cannot make a crab walk straight.②Japanese people are experiencing and suffering from phantom quakes as well as other symptoms of “earthquake sickness.”⑫并列句(Compound Sentence):由and,but,so,or,for等并列连词连接起来的两个或两个以上的简单句,构成并列句。
如:①Take care of your field, and your field will take care of you.②China has been slow to adopt auto recall procedures similar to those in the West, but new regulations are in the works.③A fifth-grader in YuShu wants to become an architect and designer, so she can build fine houses in her hometown.④Some people pay too much attention to making money, for they believe money makes the mare go.⑤Don’t make yourself a mouse, or the cat will eat you.⑬复合句(Complex Sentence):一个主句和一个(或多个)由从属连词引导的从句,构成复合句。
根据从句在主句中所起的作用,从句可以分为状语从句、定语从句和名词性从句(包括主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句)。
①What is done by night appears by day. (主语从句)②Duty is what one expects from others. (表语从句)③A straw shows which way the wind blows. (宾语从句)④To be angry with a weak man is a proof that you are not very strong yourself. (同位语从句)⑤One must drink as one brews. (状语从句)⑥The landscape belongs to the man who looks at it. (定语从句)⑭并列复合句(Compound Complex Sentence):并列句中又内含从句的句子。
如:It started with an earthquake that led to a tsunami and one of the worst nuclear power disasters in history happened.2. 按照功能划分,句子种类可分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。
⑪陈述句(Declarative Sentence或Statement):]用来陈述事实。
如:①All men are poets at heart.②Might is right.⑫疑问句(Interrogative Sentence或Question):用来提出问题。
如:①Is might right?Yes, it is. [一般疑问句(General Question或Yes-No Question)]②What is right?Might is right. [特殊疑问句(Special Question或Wh- Question)]③Is might right or wrong?Might is right.(选择疑问句)④. Might isn’t right, is it?Yes, it is. [反意疑问句或附加疑问句(Tag Question)]⑬祈使句(Imperative Sentence或Command):用来发出命令或请求。
如:①Have an aim in life, or your energies will all be wasted.②Don’t part with your illusions. When they are gone you may still exist, but you have ceased to live.⑭感叹句(Exclamatory Sentence或Exclamation):用来表示惊叹或感叹。
如:①What a fine day it is today!②How fine it is today!组成句子的各个部分叫句子成分。
英语句子成分有主语,谓语、表语、宾语、补语、定语、状语等。
1. 主语(Subject):表示句子主要说明的人或事物,通常由名词(名词短语或名词性从句)、代词、动名词、不定式和数词等担任。
如:①A bad workman always blames his tools.②It rains cats and dogs.③Two in distress makes sorrow less.④Keeping is harder than winning.⑤The poor are rich when they are satisfied.⑥To know how to wait is the great secret of success.⑦What makes life dreary is the want of motive.2. 谓语(Predicate):说明主语的动作、状态或特征,由动词或动词词组担任。
如:①A plant may produce new flowers; man is young but once.②Who makes everything right must rise early.③The fame of great men ought to be judged always by the means they used to acquire it.3. 表语(Predicative):位于连系动词be等之后,说明主语身份、特征、属性或状态。
通常由名词、代词、形容词等充当。
如:①Thought is the seed of action.②Telling your troubles is swelling your troubles.③The important thing in life is to have a great aim, and the determination to attain it.④Happiness is not something you experience; it is something you remember.⑤A disease known is half cured.⑥True friendship is like sound health;the value of it is seldom known until it is lost.⑦A change of work is as good as a rest.⑧All men cannot be first.⑨When the cat is away, the mice will play.⑩Mountains look beautiful from a distance.3. 宾语(Object):跟在及物动词之后,表示动作行为的对象(动宾);或跟在介词之后,表示介词所联系的对象(介宾)。
通常由名词、代词、数词等担任。
有些及物动词可以带两个宾语,往往一个指人,一个指物,指人的叫间接宾语,指物的叫直接宾语。
⑪直接宾语(Direct Object或Od):可单独接在动词后面,往往指物。
如:①Money can buy the devil himself.②Love me, love my dog.⑫间接宾语(Indirect Object或Oi):通常不能单独接在动词后面,而须与直接宾语一起使用,往往指人。
如:①Poverty shows us what we are.②Our best friends are those who tell us our faults and help us to mend them.4. 定语(Attribute):修饰名词或代词,通常由形容词、分词、动词不定式、介词短语等来充当。
如:①Your father’s honor to you but a second-hand honor.② A ready way to lose friends is to lend him money.③A barking dog is better than a sleeping lion.④A burnt child dreads the fire.⑤A friend without faults will never be found.5. 状语(Adverbial):修饰动词、形容词、副词或全句等,通常由副词、分词、介词短语等担任。
如:①Adversity successfully overcome is the highest glory.②Diseases come on horseback, but go away on foot.③Eat to please yourself, but dress to please others.④Man alone is born crying, lives complaining, and dies disappointed.7. 补语(或补足语)(Complement):说明主语或宾语,故可分为主语补足语和宾语补足语,通常由形容词,名词、分词、动词不定式等充当。
⑪主语补语(简称主补)(Subject Complement或Cs):补充说明主语特征。
表语就是位于连系动词之后的主语补语。
The actress is thirty-five years old, but she appears a lot younger.⑫宾语补语(简称宾补)(Object Complement或Co):位于宾语之后,补充说明宾语特征。