USP87细胞毒性体外试验
- 格式:docx
- 大小:13.32 KB
- 文档页数:5

医疗器械生物学评价第 5 局部:体外细胞毒性试验1范围GB/T 16886 的本局部阐述了评价医疗器械体外细胞毒性的试验方法。
这些方法规定了以下供试品以直接或通过集中的方式与培育细胞接触和进展孵育;a〕用器械的浸提液,和/或b〕与器械接触。
这些方法是用相应的生物参数测定哺乳动物细胞的体外生物学反响。
2标准性引用文件以下文件中的条款通过GB/T 16886 的本局部的引用而成为本局部的条款。
但凡注日期的引用文件,其随后全部的修改单〔不包括订正的内容〕或均不适用于本局部,然而,鼓舞依据本局部达成协议的各方争论是否可使用这些文件的最版本。
但凡不注日期的引用文件,其最版本适用于本局部。
GB/T 16886. 1 医疗器械生物学评价第1 局部:评价与试验〔GB/T 16886.1-2023,idt ISO 10993- 1:1997〕CB/ T 16886. 12-2023 医疗器械生物学评价第12 局部:样品制备和参照材料〔idt ISO 10993-12 :1996〕3术语与定义GB/ T 16886. 1/ ISO 1993-1 中确立的以及以下术语和定义适用于本局部。
3.13.2 阴性比照材料negative control material依据本局部试验时不产生细胞毒性反响的材料。
注:阴性比照的目的是验证背景反响,例如高密度聚乙烯1〕牙科材料的阴性比照物。
阳性比照材料 pos itive control material依据本局部试验时可重现细胞毒性反响的材料。
已作为合成聚合物的阴性比照材料,氧化陶瓷棒则用作注:阳性比照的白目的是验证相应试验系统的反响,例如用有机锡作稳定剂的聚氯乙烯的阳性比照,酚的稀释液用于浸提液的阳性比照。
2)已用作固体材料和浸提液1)高密度聚乙烯可从美国药典委员会〔Rockvillie, Maryland, USA〕和Hatano 争论所食品和药品安全中心〔Ochiai 729-5 ,Hanagawa.257-Japan〕获得。


87BIOLOGICAL REACTIVITY TESTS, IN VITROThe following tests are designed to determine the biological reactivity of mammalian cell cultures following contact with the elastomeric plastics and other polymeric materials with direct or indirect patient contact or of specific extracts prepared from the materials under test. It is essential that the tests be performed on the specified surface area. When the surface area of the specimen cannot be determined, use 0.1 g of elastomer or 0.2 g of plastic or other material for every mL of extraction fluid. Exercise care in the preparation of the materials to prevent contamination with microorganisms and other foreign matter.Three tests are described (i.e., the Agar Diffusion Test, the Direct Contact Test, and the Elution Test).1 The decision as to which type of test or the number of tests to be performed to assess the potential biological response of a specific sample or extract depends upon the material, the final product, and its intended use. Other factors that may also affect the suitability of sample for a specific use are the polymeric composition; processing and cleaning procedures; contacting media; inks; adhesives; absorption, adsorption, and permeability of preservatives; and conditions of storage. Evaluation of such factors should be made by appropriate additional specific tests before determining that a product made from a specific material is suitable for its intended use. Materials that fail the in vitro tests are candidates for the in vivotests described in Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo 88.USP R EFERENCE S TANDARDS 11— USP High-Density Polyethylene RS. USP Positive Bioreaction RS.Cell Culture Preparation— Prepare multiple cultures of L-929 (ATCC cell line CCL 1, NCTC clone 929; alternative cell lines obtained from a standard repository may be used with suitable validation) mammalian fibroblast cells inserum-supplemented minimum essential medium having a seeding density of about 105 cells per mL. Incubate the cultures at 37 ± 1in a humidified incubator for NLT 24 h in a 5 ± 1% carbon dioxide atmosphere until a monolayer, with greater than 80% confluence, is obtained. Examine the prepared cultures under a microscope to ensure uniform, near-confluent monolayers. [NOTE—The reproducibility of the In Vitro Biological Reactivity Tests depends upon obtaining uniform cell culture density. ]Extraction Solvents—Sodium Chloride Injection (see monograph—use Sodium Chloride Injection containing 0.9% of NaCl). Alternatively, serum-free mammalian cell culture media or serum-supplemented mammalian cell culture media may be used. Serum supplementation is used when extraction is done at 37for 24 h.Apparatus—Autoclave— Employ an autoclave capable of maintaining a temperature of 121 ± 2, equipped with a thermometer, a pressure gauge, a vent cock, a rack adequate to accommodate the test containers above the water level, and a water cooling system that will allow for cooling of the test containers to about 20, but not below 20, immediately following the heating cycle.Oven— Use an oven, preferably a mechanical convection model, that will maintain operating temperatures in the range of 50–70within ± 2. Incubator— Use an incubator capable of maintaining a temperature of 37 ± 1 and a humidified atmosphere of 5 ± 1% carbon dioxide in air.Extraction Containers— Use only containers, such as ampuls or screw-cap culture test tubes, or their equivalent, of Type I glass. If used, culture test tubes, or their equivalent, are closed with a screw cap having a suitable elastomeric liner. The exposed surface of the elastomeric liner is completely protected withan inert solid disk 50–75 µm in thickness. A suitable disk can be fabricated from polytef.Preparation of Apparatus— Cleanse all glassware thoroughly with chromic acid cleansing mixture and, if necessary, with hot nitric acid followed by prolonged rinsing with Sterile Water for Injection. Sterilize and dry by a suitable process for containers and devices used for extraction, transfer, or administration of test material. If ethylene oxide is used as the sterilizing agent, allow NLT 48 h for complete degassing.Procedure—Preparation of Sample for Extracts— Prepare as directed in the Procedureunder Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo 88.Preparation of Extracts— Prepare as directed for Preparation of Extracts inBiological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo 88using either Sodium Chloride Injection (0.9% NaCl) or serum-free mammalian cell culture media as Extraction Solvents. [NOTE—If extraction is done at 37for 24 h in an incubator, use cell culture media supplemented by serum. The extraction conditions should not in any instance cause physical changes, such as fusion or melting of the material pieces, other than a slight adherence. ]Agar Diffusion TestThis test is designed for elastomeric closures in a variety of shapes. The agar layer acts as a cushion to protect the cells from mechanical damage while allowing the diffusion of leachable chemicals from the polymeric specimens. Extracts of materials that are to be tested are applied to a piece of filter paper. Sample Preparation— Use extracts prepared as directed, or use portions of the test specimens having flat surfaces NLT 100 mm2 in surface area. Positive Control Preparation— Proceed as directed for Sample Preparation. Negative Control Preparation— Proceed as directed for Sample Preparation.Procedure— Using 7 mL of cell suspension prepared as directed under Cell Culture Preparation, prepare the monolayers in plates having a 60-mm diameter. Following incubation, aspirate the culture medium from the monolayers, and replace it with serum-supplemented culture medium containing NMT 2% of agar. [NOTE—The quality of the agar must be adequate to support cell growth. The agar layer must be thin enough to permit diffusion of leached chemicals. ] Place the flat surfaces ofSample Preparation, Negative Control Preparation, and Positive Control Preparation or their extracts in an appropriate extracting medium, in duplicate cultures in contact with the solidified agar surface. Use no more than three specimens per prepared plate. Incubate all cultures for NLT 24 h at 37 ± 1, preferably in a humidified incubator containing 5 ± 1% of carbon dioxide. Examine each culture around each Sample, Negative Control, and Positive Control, under a microscope, using a suitable stain, if desired.Interpretation of Results— The biological reactivity (cellular degeneration and malformation) is described and rated on a scale of 0–4 (see Table 1). Measure the responses of the cell cultures to the Sample Preparation, the Negative Control Preparation, and the Positive Control Preparation. The cell culture test system is suitable if the observed responses to the Negative Control Preparation is grade 0 (no reactivity) and to the Positive Control Preparation is at least grade 3 (moderate). The Sample meets the requirements of the test if the response to the Sample Preparation is not greater than grade 2 (mildly reactive). Repeat the procedure if the suitability of the system is not confirmed. Table 1. Reactivity Grades for Agar Diffusion Test and Direct Contact TestGrade Reactivity Description of Reactivity Zone0 None No detectable zone around or under specimen1 Slight Some malformed or degenerated cells under specimen2 Mild Zone limited to area under specimen and less than 0.45 cm beyond specimen3 Moderate Zone extends 0.45 to 1.0 cm beyond specimen4 Severe Zone extends greater than 1.0 cm beyondGrade Reactivity Description of Reactivity ZonespecimenDirect Contact TestThis test is designed for materials in a variety of shapes. The procedure allows for simultaneous extraction and testing of leachable chemicals from the specimen with a serum-supplemented medium. The procedure is not appropriate for very low- or high-density materials that could cause mechanical damage to the cells.Sample Preparation— Use portions of the test specimen having flat surfaces NLT 100 mm2 in surface area.Positive Control Preparation— Proceed as directed for Sample Preparation. Negative Control Preparation— Proceed as directed for Sample Preparation. Procedure— Using 2 mL of cell suspension prepared as directed under Cell Culture Preparation, prepare the monolayers in plates having a 35-mm diameter. Following incubation, aspirate the culture medium from the cultures, and replace it with 0.8 mL of fresh culture medium. Place a single Sample Preparation, a Negative Control Preparation, and a Positive Control Preparation in each of duplicate cultures. Incubate all cultures for NLT 24 h at 37 ± 1in a humidified incubator containing 5 ± 1% of carbon dioxide. Examine each culture around each Sample, Negative Control, and Positive Control Preparation, under a microscope, using a suitable stain, if desired. Interpretation of Results— Proceed as directed for Interpretation of Results under Agar Diffusion Test. The Sample meets the requirements of the test if the response to the Sample Preparation is not greater than grade 2 (mildly reactive). Repeat the procedure if the suitability of the system is not confirmed.Elution TestThis test is designed for the evaluation of extracts of polymeric materials. The procedure allows for extraction of the specimens at physiological ornonphysiological temperatures for varying time intervals. It is appropriate for high-density materials and for dose-response evaluations.Sample Preparation— Prepare as directed in Preparation of Extracts, using either Sodium Chloride Injection (0.9% NaCl) or serum-free mammalian cell culture media as Extraction Solvents. If the size of the Sample cannot be readily measured, a mass of NLT 0.1 g of elastomeric material or 0.2 g of plastic or polymeric material per mL of extraction medium may be used. Alternatively, use serum-supplemented mammalian cell culture media as the extracting medium to simulate more closely physiological conditions. Prepare the extracts by heating for 24 h in an incubator containing 5 ± 1% of carbon dioxide. Maintain the extraction temperature at 37 ± 1, because higher temperatures may cause denaturation of serum proteins.Positive Control Preparation— Proceed as directed for Sample Preparation. Negative Control Preparation— Proceed as directed for Sample Preparation. Procedure— Using 2 mL of cell suspension prepared as directed under Cell Culture Preparation, prepare the monolayers in plates having a 35-mm diameter. Following incubation, aspirate the culture medium from the monolayers, and replace it with extracts of the Sample Preparation, Negative Control Preparation, or Positive Control Preparation. The serum-supplemented and serum-free cell culture media extracts are tested in duplicate without dilution (100%). The Sodium Chloride Injection extract is diluted withserum-supplemented cell culture medium and tested in duplicate at 25% extract concentration. Incubate all cultures for 48 h at 37 ± 1in a humidified incubator preferably containing 5 ± 1% of carbon dioxide. Examine each culture at 48 h, under a microscope, using a suitable stain, if desired. Interpretation of Results— Proceed as directed for Interpretation of Results under Agar Diffusion Test but use Table 2. The Sample meets the requirements of the test if the response to the Sample Preparation is not greater than grade 2 (mildly reactive). Repeat the procedure if the suitability ofthe system is not confirmed. For dose-response evaluations, repeat the procedure, using quantitative dilutions of the sample extract.Table 2. Reactivity Grades for Elution TestGrade Reactivity Conditions of All Cultures0 None Discrete intracytoplasmic granules; no cell lysis1 Slight Less than or equal to 20% of the cells are round, loosely attached, and without intracytoplasmic granules; occasional lysed cells are present2 Mild Greater than 20% to less than or equal to 50% of the cells are round and devoid of intracytoplasmic granules; no extensive cell lysis and empty areas between cells3 Moderate Greater than 50% to less than 70% of the cell layers contain rounded cells or are lysed4 Severe Nearly complete destruction of the cell layers1Further details are given in the following publications of the American Society for Testing and Materials, 1916 Race St., Philadelphia, PA 19103: “Standard Test Method for Agar Diffusion Cell Culture Screening for Cytotoxicity,” ASTM Designat ion F 895-84; “Standard Practice for Direct Contact Cell Culture Evaluation of Materials for Medical Devices,” ASTM Designation F 813-83.Auxiliary Information—Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.Topic/Question Contact Expert CommitteeGeneral Chapter Desmond G. Hunt,Ph.D.Senior ScientificLiaison(301) 816-8341 (GCPS2010) General Chapters - Packaging Storage and DistributionReference Standards RS Technical Services1-301-816-8129 rstech@USP38–NF33 Page 156 Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 38(2)(专业文档是经验性极强的领域,无法思考和涵盖全面,素材和资料部分来自网络,供参考。
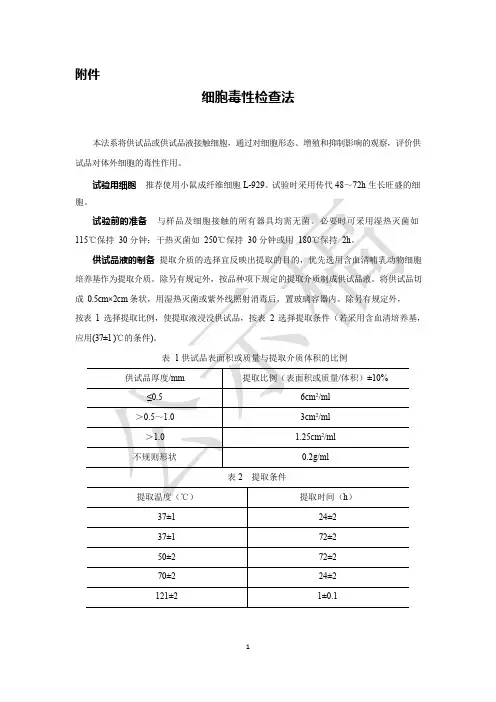
附件细胞毒性检查法本法系将供试品或供试品液接触细胞,通过对细胞形态、增殖和抑制影响的观察,评价供试品对体外细胞的毒性作用。
试验用细胞推荐使用小鼠成纤维细胞L-929。
试验时采用传代48~72h 生长旺盛的细成1相对增殖度法阴性对照液制备为不加供试品的细胞培养液。
阳性对照液制备取生物毒性阳性参比物质,照供试品制备项下的规定进行,如6.3%苯酚的细胞培养液。
检查法取33 个培养瓶,分别加入4×10 4 个/ml 浓度细胞悬液1ml,细胞培养液4ml,置(37±1 )℃,(5±1 )%CO2的条件下培养24h。
培养24h 后弃去原培养液。
阴性对照组:取13 个培养瓶加入5ml 阴性对照液;阳性对照组取10 个培养瓶加入5ml根据各组细胞浓度按下式计算细胞相对增殖度(RGR):RGR =供试品组(或阳性对照组)细胞浓度平均值⨯100阴性对照组细胞浓度平均值结果评价试验组相对增殖度(以第7 天的细胞浓度计算)为0 级或1 级判为合格。
试验组相对增殖度为2 级,应结合形态综合评价,轻微毒或无毒的判为合格。
试验组相对增殖度为3 级~5 级判为不合格。
2琼脂扩散法供试品制备将样品用纯化水冲洗干净(根据实际情况需要),用滤纸吸干。
若用供试品液进行试验,将制备的供试品液附着到生物惰性吸收性的基质﹙例如超细硼硅玻璃纤维滤纸﹚上,制成面积不少于100mm2 的圆形供试品。
阴性对照制备取无生物毒性阴性参比物质,例如高密度聚乙烯。
按照供试品制备项下的规定进行。
阳性对照制备取生物毒性阳性参比物质,例如含二乙基二硫代氨基甲酸锌的聚氨酯(ZDEC)。
按照供试品制备项下的规定进行。
可采用10%二甲基亚砜(DMSO)溶液,附着到生物惰性吸收性(例如超细硼硅玻璃纤维滤纸)的基质上。
检查法取细胞悬浮液(1×10 5个/ml)7ml,均匀分散至直径60mm 的培养皿中。
置于含(5±1 )%CO2气体的细胞培养箱中培养24h 至近汇合单层细胞,弃去培养皿中培养基,将溶化琼脂冷却至48℃左右与含20%血清的2 倍新鲜哺乳动物细胞培养基混合,使琼脂最终质量浓度不大于2%,在每只培养皿内加入新制备的含琼脂培养基(要足够薄以利于可沥滤物的扩散)。



vivi2010-10-02USP总目录:修订文件1 New Official Text,修订公告。
勘误表,临时修订声明,修)加快修订过程包括勘误表,临时修订声明(IRAS上刊部分刊出,勘误表,临时修订公告也会在订公告在USP网站上New Official Text PF出前言2front matter药典与处方集增补删减情况,审核人员,辅料收录情况3凡例药典,标题和修订1 2 药典地位和法律认可 3标准复合性专论和通则45 专论组成6 检验规范和检验方法7 测试结果8 术语和定义处方和配药 910 包装存储与标签4通则章节列表)一般检查和含量测定(章节编号小于1000检查和含量分析的一般要求检查和含量分析的仪器,微生物检查,生物检查和含量测定,化学检查和含量测定,物理检查和测定1000一般信息(章节号大于)5食物补充剂通则试剂(试剂,指示剂,溶液等)6.参考表7性状描述和溶解性查询表(按字母顺序)食品补充剂各论(字母顺序)8各论(辅料标准)9NF10 USP各论11术语附件:通则的章节中文目录(使用起来比较方便,直接找对应章节号即可)一、通用试验和检定(1)试验和检定的总要求1 注射剂11 参比标准物(2)试验和检定的装置16 自动分析方法21 测温仪31 容量装置,如容量瓶、移液管、滴定管,各种规格的误差限度41 砝码和天平(3)微生物学试验51 抗菌效力试验55 生物指示剂:耐受性能试验61 微生物限度试验61 非灭菌制品的微生物检查:计数试验62 非灭菌制品的特定菌检查,如大肠杆菌、金葡菌、沙门氏菌等71 无菌试验(4)生物学试验和检定81 抗生素微生物检定85 细菌内毒素试验87 体外生物反应性试验:检查合成橡胶、塑料、高聚物对哺乳类细胞培养的影响88 体内生物反应性试验:检查上述物质对小鼠、兔iv、ip或肌内植入的影响泛酸钙检定91111 生物检定法的设计和分析115 右泛醇检定121 胰岛素检定141 蛋白质——生物适应试验,用缺蛋白饲料大鼠,观察水解蛋白注射液和氨基酸混合物的作用151 热原检查法161 输血、输液器及类似医疗装置的内毒素、热原、无菌检查171 维生素B活性检定12(5)化学试验和检定A 鉴别试验181 有机含氮碱的鉴别191 一般鉴别试验193 四环素类鉴别197 分光光度法鉴别试验201 薄层色谱鉴别试验B 限量试验206 铝211 砷221 氯化物和硫酸盐223 二甲基苯胺226 4-差向脱水四环素231 重金属241 铁251 铅261 汞271 易炭化物试验281 炽灼残渣291 硒C 其他试验和检定中和酸能力301311 藻酸盐检定331 苯丙胺检定341 多剂量容器注射剂中所加防腐剂含量的气相色谱或极谱法测定345 枸橼酸与其盐以及磷酸盐检定351 甾体检定361 巴比妥酸盐检定371 维生素B放射示踪物检定12381 注射剂橡胶塞检查391 肾上腺素检定401 脂肪和固定油检查411 叶酸检定425 抗生素碘量法检定429 微粒大小的光衍射测量431 甲氧基测定441 烟酸或烟酰胺检定451 亚硝酸盐滴定461 氮测定466 普通杂质的薄层色谱法检查467 有机挥发性杂质检查法467 残留溶剂测定471 氧瓶燃烧法481 核黄素检定501 有机含氮碱的盐511 单一甾醇检定521 磺胺类的色谱法检定531 硫胺检定541 滴定法554 α-生育酚检定561 植物来源物品的一般检查项目植物来源物品的各种鉴别项目(植物学部分、显微鉴别、化学鉴别)563 565 植物提取物的一般提取方法和要求571 维生素A检定:化学法、色谱法581 维生素D检定:色谱法、化学法、生物法591 锌测定(6)物理试验和测定601 气雾剂、鼻喷雾剂、计量吸入剂和干粉吸入剂的各项检测611 乙醇含量测定:蒸馏法、气一液色谱法616 固体的疏松密度和叩击密度测定621 色谱法631 色度检查和标准641 溶解的完全性检查643 总有机炭测定645 水导电性测定651 冻凝温度的测定661 药用容器的检测项目要求671 盛装胶囊和片剂容器加盖后对湿气的通透性试验691 棉花吸附性和纤维长度测定695 结晶性检查696 用溶液测热法测定结晶度698 装量检查699 固体密度(粉粒密度测定法)701 崩解试验711 溶出试验721 蒸馏温度范围(馏程)测定724 通过透皮转运系统药物的释放726 电泳727 毛细管电泳730 等离子体光谱化学检查法731 干燥失重炽灼失重733736 质谱法741 熔点范围或温度的测定751 眼膏中的金属颗粒测定755 最低装量检查法761 核磁共振771 眼用软膏的要求776 光学显微镜微粒检查法781 旋光度检查785 渗透压摩尔浓度测定法786 用分析筛测量颗粒大小的分布788 注射液中微粒物质测定法789 眼用溶液中微粒物质测定法791 PH测定法795 非灭菌制剂的药物配制要求797 灭菌制剂的药物配制要求801 极谱法811 粉末细度测定821 放射活性药物823 正电子发射层析X线摄影(PET)所用放射性药物的配制831 折光指数测定841 比重测定846 粉末的比表面积测定851 分光光度法与光散射861 外科缝合线直径检查871 附有针的缝合线检查881 外科缝合线、纺织品与膜片的弹力强度检查891 热分析:温度变化、热解重量分析、易熔杂质分析等905 剂量单位的均匀性检查(含量均匀度、装量差异)911 黏度测定药品含水量的测定921941 结晶型药物的X线衍射分析二、通用资料1010 数据分析方法1015 诊断用放射药的自动合成装置1031 药用容器、医用装置和植入物所用材料的生物相容性检查1035 灭菌用生物指示剂1041 生物制品的批签发1043 细胞、基因和组织工程产品的辅助材料1045 生物技术产品1046 细胞和基因治疗产品1047 生物技术产品的检验法1048 生物技术产品的质量——重组DNA蛋白质产品生产所用细胞表达构成的分析1049 生物技术产品的稳定性试验1050 人或动物来源的细胞系所得生物技术产品的病毒安全性评价1051 玻璃仪器清洗方法1061 颜色的仪器测量1065 离子色谱1072 消毒剂与防腐剂1074 赋形剂生物学安全性评价指导原则1075 复方药物配制质量规范1078 大批量药用赋形剂的生产质量规范1079 储存与运输的质量规范1081 明胶的凝胶强度1086 药品中的杂质来源1087 特性溶出1088 剂型的体外和体内评价1090 体内生物等效性试验指导原则1091 剂型中含有无活性组分的标示1092 溶出试验方法的发展和验证药用滴管11011111 非灭菌药品的微生物特征1111 非灭菌药品的微生物特征检查:药用原料和药物制剂的判定标准1112 非灭菌药品中的水活性测定,即在同一温度时,药品中水的蒸气压与纯水蒸气压之比,它等于药品在密闭系统中产生相对湿度的1%1116 清洁室和其他受控环境的微生物评价1117 微生物实验室的质量规范(GLP)1118 监控装置:时间、温度、湿度1119 近红外分光光度法1120 拉曼(Raman)分光光度法1121 药品命名法1136 药品包装:应用单元1146 口服固体药分装在单疗程剂量容器中的检查方法1150 药物剂型的稳定性1151 药物剂型1160 处方调配的药学计算1171 原料药的位相溶解度分析1174 粉末流动性测定1176 处方天平和容量装置1177 包装质量规范1178 分装质量规范1181 扫描电子显微镜1191 调剂工作中的药品稳定性保持1196 药典协调(指欧洲药典、美国药典、日本药局方三方机构讨论协调的原则和方法)1207 灭菌产品包装:完整性评价1208 灭菌试验:隔离系统的验证1209 灭菌:化学和物理化学的指示剂与积分仪1211 药典收载品种的灭菌和灭菌保证1216 片剂脆性检查1221 茶匙(家用标准为5 ml,可作为病人口服液体药物的量具,误差应小于10%)药品灭菌终点的放行参数12221223 微生物替代方法的验证1225 药典方法的验证1227 在抗菌效力、微生物限度、灭菌等试验中,微生物的恢复验证1230 血液透析用水1231 药用水的制备和要求1241 在制药系统中,水—固体的相互作用1251 用分析天平称量的要求1265 书写药物处方的指导原则三、饮食增补剂2021 营养和饮食增补剂的微生物计数试验2022 营养和饮食增补剂中不允许存在的微生物(如金葡菌、沙门氏菌、大肠杆菌、梭状芽胞杆菌属)检查法2023 非灭菌的营养和饮食增补剂中的微生物特征2030 植物来源物品的增补资料2040 饮食增补剂的崩解和溶出检查2091 饮食增补剂的重(装)量差异检查2750 饮食增补剂的生产条件与质量要求(与药品有别)。

一次性使用医用注射器活塞体外细胞毒性检测
何华红;李薇;吴婷
【期刊名称】《中国医疗器械杂志》
【年(卷),期】2010(034)002
【摘要】检测机构对一次性使用医用注射器活塞进行生物学评价时,多发现其呈细胞毒性.我们按卫生部提出的生物学评价试验选择指南及样品提供方意见,选取了基本生物学评价中的5项试验,对一批一次性使用医用注射器活塞进行了系统生物学评价,发现其有细胞毒性.进一步对其进行综合检测和分析后,发现原因可能是厂家清洗活塞后的洗液残留所致.此研究为客观评价一次性使用医用注射器活塞的产品质量,督促厂家改进生产工艺,保证产品安全提供了参考.
【总页数】3页(P123-125)
【作者】何华红;李薇;吴婷
【作者单位】广州市药品检验所医疗器械及药包材室,广州,510160;广州市药品检验所医疗器械及药包材室,广州,510160;广州市药品检验所医疗器械及药包材室,广州,510160
【正文语种】中文
【中图分类】TH77
【相关文献】
1.一次性使用无菌注射器细胞毒性检测 [J], 朱碧君;袁兴东;罗丹;刘波
2.一次性使用注射器用活塞溶血试验的探讨 [J], 严小莉;王莎莎;刘茜;高静贤
3.不同厂家一次性使用医用注射器及活塞体外细胞毒性的质量考察 [J], 王文佳;何华红;李薇;吴婷;庞智慧
4.不同来源一次性使用无菌注射器用活塞体外细胞毒性的比较研究 [J], 陈志勇;肖佳音;王宗尉;刘海疆;刘凯;李庆忠
5.一次性使用无菌注射器用橡胶活塞的化学分析方法的改进 [J], 陈慧君
因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。

87BIOLOGICAL REACTIVITY TESTS, IN VITROThe following tests are designed to determine the biological reactivity of mammalian cell cultures following contact with the elastomeric plastics and other polymeric materials with direct or indirect patient contact or of specific extracts prepared from the materials under test. It is essential that the tests be performed on the specified surface area. When the surface area of the specimen cannot be determined, use 0.1 g of elastomer or 0.2 g of plastic or other material for every mL of extraction fluid. Exercise care in the preparation of the materials to prevent contamination with microorganisms and other foreign matter.Three tests are described (i.e., the Agar Diffusion Test, the Direct Contact Test, and the Elution Test).1 The decision as to which type of test or the number of tests to be performed to assess the potential biological response of a specific sample or extract depends upon the material, the final product, and its intended use. Other factors that may also affect the suitability of sample for a specific use are the polymeric composition; processing and cleaning procedures; contacting media; inks; adhesives; absorption, adsorption, and permeability of preservatives; and conditions of storage. Evaluation of such factors should be made by appropriate additional specific tests before determining that a product made from a specific material is suitable for its intended use. Materials that fail the in vitro tests are candidates for the in vivotests described in Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo 88.USP R EFERENCE S TANDARDS 11— USP High-Density Polyethylene RS. USP Positive Bioreaction RS.Cell Culture Preparation— Prepare multiple cultures of L-929 (ATCC cell line CCL 1, NCTC clone 929; alternative cell lines obtained from a standard repository may be used with suitable validation) mammalian fibroblast cells inserum-supplemented minimum essential medium having a seeding density of about 105 cells per mL. Incubate the cultures at 37 ± 1in a humidified incubator for NLT 24 h in a 5 ± 1% carbon dioxide atmosphere until a monolayer, with greater than 80% confluence, is obtained. Examine the prepared cultures under a microscope to ensure uniform, near-confluent monolayers. [NOTE—The reproducibility of the In Vitro Biological Reactivity Tests depends upon obtaining uniform cell culture density. ]Extraction Solvents—Sodium Chloride Injection (see monograph—use Sodium Chloride Injection containing 0.9% of NaCl). Alternatively, serum-free mammalian cell culture media or serum-supplemented mammalian cell culture media may be used. Serum supplementation is used when extraction is done at 37for 24 h.Apparatus—Autoclave— Employ an autoclave capable of maintaining a temperature of 121 ± 2, equipped with a thermometer, a pressure gauge, a vent cock, a rack adequate to accommodate the test containers above the water level, and a water cooling system that will allow for cooling of the test containers to about 20, but not below 20, immediately following the heating cycle.Oven— Use an oven, preferably a mechanical convection model, that will maintain operating temperatures in the range of 50–70within ± 2. Incubator— Use an incubator capable of maintaining a temperature of 37 ± 1 and a humidified atmosphere of 5 ± 1% carbon dioxide in air.Extraction Containers— Use only containers, such as ampuls or screw-cap culture test tubes, or their equivalent, of Type I glass. If used, culture test tubes, or their equivalent, are closed with a screw cap having a suitable elastomeric liner. The exposed surface of the elastomeric liner is completely protected withan inert solid disk 50–75 µm in thickness. A suitable disk can be fabricated from polytef.Preparation of Apparatus— Cleanse all glassware thoroughly with chromic acid cleansing mixture and, if necessary, with hot nitric acid followed by prolonged rinsing with Sterile Water for Injection. Sterilize and dry by a suitable process for containers and devices used for extraction, transfer, or administration of test material. If ethylene oxide is used as the sterilizing agent, allow NLT 48 h for complete degassing.Procedure—Preparation of Sample for Extracts— Prepare as directed in the Procedureunder Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo 88.Preparation of Extracts— Prepare as directed for Preparation of Extracts inBiological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo 88using either Sodium Chloride Injection (0.9% NaCl) or serum-free mammalian cell culture media as Extraction Solvents. [NOTE—If extraction is done at 37for 24 h in an incubator, use cell culture media supplemented by serum. The extraction conditions should not in any instance cause physical changes, such as fusion or melting of the material pieces, other than a slight adherence. ]Agar Diffusion TestThis test is designed for elastomeric closures in a variety of shapes. The agar layer acts as a cushion to protect the cells from mechanical damage while allowing the diffusion of leachable chemicals from the polymeric specimens. Extracts of materials that are to be tested are applied to a piece of filter paper. Sample Preparation— Use extracts prepared as directed, or use portions of the test specimens having flat surfaces NLT 100 mm2 in surface area. Positive Control Preparation— Proceed as directed for Sample Preparation. Negative Control Preparation— Proceed as directed for Sample Preparation.Procedure— Using 7 mL of cell suspension prepared as directed under Cell Culture Preparation, prepare the monolayers in plates having a 60-mm diameter. Following incubation, aspirate the culture medium from the monolayers, and replace it with serum-supplemented culture medium containing NMT 2% of agar. [NOTE—The quality of the agar must be adequate to support cell growth. The agar layer must be thin enough to permit diffusion of leached chemicals. ] Place the flat surfaces ofSample Preparation, Negative Control Preparation, and Positive Control Preparation or their extracts in an appropriate extracting medium, in duplicate cultures in contact with the solidified agar surface. Use no more than three specimens per prepared plate. Incubate all cultures for NLT 24 h at 37 ± 1, preferably in a humidified incubator containing 5 ± 1% of carbon dioxide. Examine each culture around each Sample, Negative Control, and Positive Control, under a microscope, using a suitable stain, if desired.Interpretation of Results— The biological reactivity (cellular degeneration and malformation) is described and rated on a scale of 0–4 (see Table 1). Measure the responses of the cell cultures to the Sample Preparation, the Negative Control Preparation, and the Positive Control Preparation. The cell culture test system is suitable if the observed responses to the Negative Control Preparation is grade 0 (no reactivity) and to the Positive Control Preparation is at least grade 3 (moderate). The Sample meets the requirements of the test if the response to the Sample Preparation is not greater than grade 2 (mildly reactive). Repeat the procedure if the suitability of the system is not confirmed. Table 1. Reactivity Grades for Agar Diffusion Test and Direct Contact TestGrade Reactivity Description of Reactivity Zone0 None No detectable zone around or under specimen1 Slight Some malformed or degenerated cells under specimen2 Mild Zone limited to area under specimen and less than 0.45 cm beyond specimen3 Moderate Zone extends 0.45 to 1.0 cm beyond specimen4 Severe Zone extends greater than 1.0 cm beyondGrade Reactivity Description of Reactivity ZonespecimenDirect Contact TestThis test is designed for materials in a variety of shapes. The procedure allows for simultaneous extraction and testing of leachable chemicals from the specimen with a serum-supplemented medium. The procedure is not appropriate for very low- or high-density materials that could cause mechanical damage to the cells.Sample Preparation— Use portions of the test specimen having flat surfaces NLT 100 mm2 in surface area.Positive Control Preparation— Proceed as directed for Sample Preparation. Negative Control Preparation— Proceed as directed for Sample Preparation. Procedure— Using 2 mL of cell suspension prepared as directed under Cell Culture Preparation, prepare the monolayers in plates having a 35-mm diameter. Following incubation, aspirate the culture medium from the cultures, and replace it with 0.8 mL of fresh culture medium. Place a single Sample Preparation, a Negative Control Preparation, and a Positive Control Preparation in each of duplicate cultures. Incubate all cultures for NLT 24 h at 37 ± 1in a humidified incubator containing 5 ± 1% of carbon dioxide. Examine each culture around each Sample, Negative Control, and Positive Control Preparation, under a microscope, using a suitable stain, if desired. Interpretation of Results— Proceed as directed for Interpretation of Results under Agar Diffusion Test. The Sample meets the requirements of the test if the response to the Sample Preparation is not greater than grade 2 (mildly reactive). Repeat the procedure if the suitability of the system is not confirmed.Elution TestThis test is designed for the evaluation of extracts of polymeric materials. The procedure allows for extraction of the specimens at physiological or。

生物学评价之细胞毒性试验1范围细胞毒性试验是利用细胞体外培养方法来评价医疗器械或其浸提液可滤出成分中急性细胞毒性的潜在性。
2 试验项目选择(推荐)根据GB/T16886.5-1997标准中有关细胞毒性试验的要求,现推荐下面任何一种细胞毒性试验方法评价医疗器械的细胞毒性,即琼脂覆盖法,分子滤过法,生长抑制法。
3 试验条件(1)细胞株可以使用已建立的细胞株,目前我国使用较多的是L-929(小鼠结缔组织成纤维细胞)和V-79(中国地鼠肺成纤维细胞)。
(2)培养基培养基及其血清浓度的含量应能适合所选择细胞株的生长,满足细胞生长的需要。
培养基内含抗生素的量应不引起细胞毒性,以免影响材料的评价,含血清和谷氨酰胺的培养基在2~8℃贮存不能超过一周,只含谷氨酰胺不含血清的培养基在2~8℃贮存不能超过一个月,培养基的pH值在7.2~7.4之间,所有培养用液都应是无菌的。
(3)样品的制备•试验样品的制备。
试验样品应选择材料本身或其浸提液进行。
试验材料应用最终产品。
制备材料浸提液的条件往往是夸大临床应用的条件来评价样品潜在的细胞毒性,但不能引起样品严重的变化(如溶解或其化学结构改变),浸提液应在制备后的24h内使用;固体材料应至少有一个平面使其利于在细胞层或琼脂层相接触,各种试验样品在试验时均应经无菌处理。
•阴性对照。
应是已知无细胞毒性的物质。
对于合成高分子材料,高密度聚乙烯较为适宜,牙科材料则可用氧化铝陶瓷作为阴性对照。
•阳性对照。
是已知的有一定细胞毒性的物质。
推荐含锡的聚氯乙烯作为固体材料或浸提液的阳性对照。
稀释苯酚亦可作为浸提液的阳性对照。
4 试验方法1)琼脂覆盖法•目的:本试验是为了评价医疗器械科浸提成分的急性细胞毒性。
•范围:本试验方法适用于固体(粉末,纤维状,金属),液体等试验材料。
•试验样品的制备。
试验样品:将试验样品制成100mm2的圆形,要求边缘光滑整齐。
液体材料用0.1mL的样品吸收在同面积的无菌滤纸片或纤维素上。

医疗器械生物学评价第5部分:体外细胞毒性试验1 范围GB/T 16886 的本部分阐述了评价医疗器械体外细胞毒性的试验方法。
这些方法规定了下列供试品以直接或通过扩散的方式与培养细胞接触和进行孵育;a)用器械的浸提液,和/或b)与器械接触。
这些方法是用相应的生物参数测定哺乳动物细胞的体外生物学反应。
2 规范性引用文件下列文件中的条款通过GB/T 16886 的本部分的引用而成为本部分的条款。
凡是注日期的引用文件,其随后所有的修改单(不包括勘误的内容)或修订版均不适用于本部分,然而,鼓励根据本部分达成协议的各方研究是否可使用这些文件的最新版本。
凡是不注日期的引用文件,其最新版本适用于本部分。
GB/T 16886. 1 医疗器械生物学评价第1部分:评价与试验(GB/T 16886.1-2001,idt ISO 10993- 1:1997)CB/ T 16886. 12-2000 医疗器械生物学评价第12部分:样品制备和参照材料(idt ISO 10993-12 :1996)3 术语与定义GB/ T 16886. 1/ ISO 1993-1中确立的以及下列术语和定义适用于本部分。
3.1阴性对照材料negative control material按照本部分试验时不产生细胞毒性反应的材料。
注:阴性对照的目的是验证背景反应,例如高密度聚乙烯1)已作为合成聚合物的阴性对照材料,氧化陶瓷棒则用作牙科材料的阴性对照物。
3.2阳性对照材料 pos itive control material按照本部分试验时可重现细胞毒性反应的材料。
注:阳性对照的白目的是验证相应试验系统的反应,例如用有机锡作稳定剂的聚氯乙烯2)已用作固体材料和浸提液的阳性对照,酚的稀释液用于浸提液的阳性对照。
_____________________________________1)高密度聚乙烯可从美国药典委员会(Rockvillie, Maryland, USA)和Hatano研究所食品和药品安全中心(Ochiai 729-5 ,Hanagawa.257-Japan)获得。
细胞毒性实验设计方案1.2. 准备材料: DMEM(高糖)胰酶双抗(青霉素/链霉素)DAPI MTT(5mg/mL) DMSO PBS 4%多聚甲醛 指甲油6孔培养板 96孔培养板超薄载玻片培养瓶(25mL)一包0.45μm 滤膜灭菌: 50mL ,10mL ,5mL 离心管两种枪头2.实验方案本实验所用的材料为载药的通过二硫键桥连透明质酸的夹心二氧化硅(SiO 2-SS-HA/DOX ),在高谷胱甘肽条件下,二硫键断裂,透明质酸脱离,同时夹心二氧化硅中药物得以释放。
本实验的目的为测定透明质酸修饰的夹心二氧化硅(SiO 2-SS-HA/DOX )的细胞毒性。
实验组为SiO 2-SS-HA/DOX 、SiO 2-SS-HA 、DOX ,空白对照组为纯细胞,分别采用HepG2人肝癌细胞为肿瘤细胞模型和L929成纤维细胞为正常细胞模型。
采用HepG2人肝癌细胞为肿瘤细胞模型,实验组为SiO 2-SS-HA/DOX 、SiO 2-SS-HA 、DOX ,空白对照组为纯细胞。
培养基中含有10% (v/v) FBS 和1% (w/v) 双抗(青霉素/链霉素)。
配制不同浓度的SiO 2-SS-HA/DOX 、SiO 2、HA 、DOX 药物载体培养基溶液。
(1).以HepG2人肝癌细胞为肿瘤细胞模型:培养基的配置:双抗 1% 血清12% DMEM 87%具体操作步骤:细胞的复活:①将冻存于液氮中的细胞取出,迅速放入37℃温水中,使细胞快速溶解。
②将悬浮的细胞移至离心管中,加5mL 无血清培养基,1000rmp,5min 离心去上清,再加5mL 有血清培养基,转移至培养瓶中。
(每次转移时,将之前的离心管洗涤,并用移液枪来回吸,使液体混合均匀。
)③将培养瓶放入培养箱中培养。
细胞的传代:将0.25%的胰酶分装至小离心管中,每个管中2mL,冻存于-20℃,每次使用一管,避免反复冻融。
①将培养瓶从培养箱中取出,盖子旋紧,喷75%的酒精放入超净台。
国家食品药品监督管理局关于认可上海生物材料研究测试中心体外细胞毒性试验等项目检测资格的通知
【法规类别】医疗器械药品药材进出口
【发文字号】国食药监械[2006]212号
【发布部门】国家食品药品监督管理局(原国家药品监督管理局)(已撤销)
【发布日期】2006.05.22
【实施日期】2006.05.22
【时效性】现行有效
【效力级别】部门规范性文件
国家食品药品监督管理局关于认可上海生物材料研究测试中心体外细胞毒性试验等项目
检测资格的通知
(国食药监械[2006]212号)
上海市食品药品监督管理局:
根据《医疗器械监督管理条例》及《医疗器械检测机构资格认可办法》(国药监械〔2003〕125号)的规定,国家局医疗器械检测机构资格认可审查组于2006年3月28至29日,对上海生物材料研究测试中心的医疗器械检测能力进行了现场评审。
经审查,国家局认可该中心对体外细胞毒性试验等9个项目(见附件)进行检测的资格。
有效期5年。
附件:认可的医疗器械受检目录
国家食品药品监督管理局
二○○六年五月二十二日
附件:
认可的医疗器械受检目录。
细胞毒性实验细胞毒性实验是一种常见的生物学实验方法,用于评估各种物质对细胞的毒性和影响。
通过细胞毒性实验可以研究药物的安全性、环境污染物的危害性以及化学物质的毒理学特性。
本文将介绍细胞毒性实验的基本原理、常用方法以及结果的解读。
基本原理细胞毒性实验基于细胞生物学的基本原理,利用细胞在体外的培养条件下对外界刺激的反应来评估物质的毒性。
在细胞毒性实验中,通常选用肿瘤细胞株或非肿瘤细胞株作为实验对象,通过给细胞暴露于不同浓度的待测物质,观察其对细胞形态、生长、代谢等方面的影响,从而判断其毒性程度。
常用方法MTT法MTT法是一种常用的细胞毒性实验方法,通过将细胞与MTT染料反应产生紫色的甲苯胺酚盐,用来反映细胞的代谢活性,从而评估细胞的存活率。
该方法操作简单、灵敏度高,常用于筛选化合物的毒性作用。
LDH释放法LDH释放法是测定细胞膜通透性的一种方法,通过测定培养基中LDH的释放量来评估细胞的损伤程度。
在细胞受到毒性物质的作用后,细胞膜破裂导致LDH的释放,因此LDH释放量的增加可以反映细胞膜的破损情况。
结果解读在细胞毒性实验中,通常会得到一系列不同浓度下的实验数据,如细胞存活率、LDH释放量等。
通过对这些数据进行统计分析和比较,可以得出物质对细胞毒性的评估结果。
一般情况下,细胞存活率越低,LDH释放量越高,说明物质对细胞的毒性越大。
细胞毒性实验是评估化合物毒性的重要手段,通过该实验可以为药物研发、环境保护和毒理学研究提供重要参考。
科学家们不断改进细胞毒性实验的方法,提高其准确性和灵敏度,希望能够为人类健康和环境保护作出更大的贡献。
细胞毒性试验评价一次性使用无菌注射器的生物安全性朱勤;刘骅;武谷【摘要】Objective Biological security of the disposable sterilized syring is evaluated by cytotoxicity.Method The cytotoxicity ex-periment was made according to the GB/T14233.2-2005 about forty groups of eight factoris of the Disposable Sterilized Syring in 2010 national spot check.Result The pinhead has no cytotoxicity,but some syringe has cytotoxicity.Conclusion There is requirement to strengthen the research of the cytotoxicity evaluation of the disposable sterilized syring.%目的:通过体外细胞毒性试验评价一次性使用无菌注射器的生物安全性。
方法按照GB/T14233.2-2005对2010年国家抽验的8个厂家40批次一次性使用无菌注射器进行了体外细胞毒性试验。
结果注射针的细胞毒性均符合要求,部分注射器的细胞毒性较大。
结论需要加强对一次性使用无菌注射器的细胞毒性评价。
【期刊名称】《安徽医药》【年(卷),期】2015(000)004【总页数】3页(P649-650,651)【关键词】一次性使用无菌注射器;细胞毒【作者】朱勤;刘骅;武谷【作者单位】安徽省食品药品检验研究院,安徽合肥 230051;安徽省食品药品检验研究院,安徽合肥 230051;安徽省食品药品检验研究院,安徽合肥 230051【正文语种】中文一次性使用无菌注射器是临床上广泛使用的医疗器械,与血液或人体直接接触,是属于国家重点监管的医疗器械产品之一,与人民医疗健康息息相关。
避孕套的体外细胞毒性检测实验
付海洋;奚廷斐
【期刊名称】《中国计划生育学杂志》
【年(卷),期】2008(016)007
【摘要】目的:通过两种避孕套的体外细胞毒性实验,探讨适合避孕套的细胞毒性检测方法.方法:按照GB/T16886.5的体外细胞毒性评价方法要求,用琼脂覆盖法和MTT比色法检测两种避孕套的细胞毒性.结果:用琼脂覆盖法检测出两种避孕套的细胞毒性均为2级;用MTT比色法检测时,在浸提液浓度为50%时,相对增值率(RGR)避孕套A为5%,避孕套B为7%,两者差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);在浸提液浓度为10%时,避孕套A的RGR为87%,避孕套B为99%,两者差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);在浸提液浓度为20%时,避孕套A的RGR为42%,避孕套B为77%,两者有统计学差异(P<0.05).结论:由于MTT比色法具有定量评价的优点,更适合避孕套的细胞毒性检测.
【总页数】3页(P408-410)
【作者】付海洋;奚廷斐
【作者单位】中国药品生物制品检定所,北京,100050;中国药品生物制品检定所【正文语种】中文
【中图分类】R1
【相关文献】
1.壳聚糖抗菌喷膜体外细胞毒性检测的探讨 [J], 田胜慧;郑保婷;柯军;颜林
2.医用超声耦合剂体外细胞毒性检测的探讨 [J], 高静贤;王莎莎;金梦;严小莉
3.一次性使用医用注射器活塞体外细胞毒性检测 [J], 何华红;李薇;吴婷
4.组织工程用猪膀胱无细胞基质的体外细胞毒性检测 [J], 张玉石;李汉忠;张锐强
5.异叶败酱化学成分的研究及体外细胞毒性检测 [J], 丁兰;徐福春;王瀚;欧巧明因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。
两种体外细胞毒性检测方法的比较研究黄哲玮;孙皎;孟爱英【期刊名称】《生物医学工程学进展》【年(卷),期】2005(026)004【摘要】目的比较两种常用的细胞毒性检测方法在医疗器械生物学评价中的相关性.方法分别采用MTT比色法和细胞增殖度法,在37℃条件下,将五种医疗器械/生物材料的浸提液分别与小鼠成纤维细胞(L-929)接触2天和2,4,7天,比较材料对细胞的毒性影响.结果 5种不同的材料浸提液分别表现出不同程度的细胞毒性反应(0~2级).将MTT比色法与细胞增殖度法(2天)的实验数据进行相关性分析,显示两者之间具有良好的相关性(R=0.977).结论 MTT比色法由于其检测所需的细胞量相对较少,试验步骤相对简便、检测周期短,因此具有一定的优越性,是个值得推荐的细胞毒性检测方法.【总页数】3页(P205-207)【作者】黄哲玮;孙皎;孟爱英【作者单位】上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院/上海生物材料研究测试中心,上海,200023;上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院/上海生物材料研究测试中心,上海,200023;上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院/上海生物材料研究测试中心,上海,200023【正文语种】中文【中图分类】R3【相关文献】1.特异性细胞毒性T淋巴细胞体外检测方法的进展 [J], 王锦彤;卢贤瑜2.贻贝粘蛋白创面修复敷料体外细胞毒性的检测方法 [J], 刘茜;兰华林;顾铭;高敏;王召旭3.贻贝粘蛋白创面修复敷料体外细胞毒性的检测方法 [J], 刘茜;兰华林;顺铭;高敏;王召旭;4.两种不同细胞毒性检测方法的比较 [J], 田林奇;韩颖;魏聪;徐玉茵;周静;张娟丽;郭艳5.两种不同盖髓剂对人牙髓细胞毒性的体外研究 [J], 古丽努尔·阿吾提;古丽波斯坦·吐尔逊;阿尔孜古丽·吐尔逊;居来提·吐尔逊因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。
87 BIOLOGICAL REACTIVITY TESTS, IN VITROThe following tests are designed to determine the biological reactivity of mammalia n cell cultures followi ng con tact with the elastomeric plastics and other polymeric materials with direct or in direct patie nt con tact or of specific extracts prepared from the materials under test. It is essential that the tests be performed on the specified surface area. When the surface area of the specime n cannot be determ in ed, use 0.1 g of elastomer or 0.2 g of plastic or other material for every mL of extraction fluid. Exercise care in the preparation of the materials to preve nt con tam in ati on with microorga nisms and other foreign matter. Three tests are described (i.e., the Agar Diffusi on Test , the Direct Con tact Test and the Elution Test ).1 The decision as to which type of test or the number of tests to be performed to assess the potential biological response of a specific sample or extract depends upon the material, the final product, and its inten ded use. Other factors that may also affect the suitability of sample for a specific use are the polymeric composition; processing and cleaning procedures; con tact ing media; in ks; adhesives; absorptio n, adsorptio n, and permeability of preservatives; and con diti ons of storage. Evaluatio n of such factors should be made by appropriate additi onal specific tests before determining that a product made from a specific material is suitable for its in ten ded use. Materials that fail the in vitro tests are can didates for the in vivotests described in Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo 88 .USP R EFERENCE S TANDARDS 11 —USP High-Density Polyethylene RS.USP Positive Bioreaction RS.Cell Culture Preparation —Prepare multiple cultures of L-929 (ATCC cell lineCCL 1, NCTC clone 929; alternative cell lines obtained from a standard repository may be used with suitable validation) mammalian fibroblast cells inserum-suppleme nted minimum esse ntial medium hav ing a seedi ng den sity of about 10 5 cells per mL. Incubate the cultures at 37 1 一in a h±midifiedin cubator for NLT 24 h in a 5 1% c±b on dioxide atmosphere un til amono layer, with greater tha n 80% con flue nee, is obta in ed. Exam ine the prepared cultures un der a microscope to en sure uniform, n ear-c on flue ntmono layers. [NOTE ——The reproducibility of the In Vitro Biological Reactivity Tests depends upon obtaininguniform cell culture density. ]Extractio n Solvents —Sodium Chloride Injectio n (see mono graph —useSodium Chloride Injection containing 0.9% of NaCl). Alternatively, serum-free mammalia n cell culture media or serum-suppleme nted mammalia n cell culture media may be used. Serum suppleme ntati on is used whe n extracti on is done at 37 - for 24 h.Apparatus —Autoclave —Employ an autoclave capable of maintaining a temperature of 121±2 -, equipped with a thermometer, a pressure gauge, a vent cock, a rack adequate to accommodate the test containers above the water level, and a water cooling system that will allow for cooling of the test containers to about20 -, but not below 20 -, immediately following the heating cycle.Oven —Use an ove n, preferably a mecha ni cal con vect ion model, that will maintain operating temperatures in the range of 50 -刁0 within ±.In cubator —Use an in cubator capable of maintaining a temperature of 37 1土and a humidified atmosphere of 5 1% carbon dioxide in air.Extracti on Containers —Use only contain ers, such as ampuls or screw-cap culture test tubes, or their equivale nt, of Type I glass. If used, culture test tubes, or their equivale nt, are closed with a screw cap hav ing a suitable elastomeric liner. The exposed surface of the elastomeric liner is completely protected with an inert solid disk 50 —5 m in thickness. A suitable disk can be fabricated from polytef.Preparati on of Apparatus ——Clea nse all glassware thoroughly with chromic acid clea nsing mixture an d, if n ecessary, with hot n itric acid followed by proIon ged rinsing with Sterile Water for Injectio n. Sterilize and dry by a suitable process for containers and devices used for extracti on, tran sfer, or adm ini strati on of test material. If ethyle ne oxide is used as the steriliz ing age nt, allow NLT 48 h for complete degass ing.Procedure —Preparati on of Sample for Extracts —Prepare as directed in the Procedure under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo 88 .Preparati on of Extracts ——Prepare as directed for Preparati on of Extracts inBiological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo 88 using either Sodium Chloride Injection (0.9% NaCl) or serum-free mammalia n cell culture media asExtraction Solvents. [NOTE —If extraction is done at 37 U for 24 h in an incubator, use cell culture media supplemented by serum. The extraction conditions should not in any instance cause physical changes, such as fusion or melting of the material pieces, other than a slight adherence. ]Agar Diffusi on TestThis test is desig ned for elastomeric closures in a variety of shapes. The agar layer acts as a cushion to protect the cells from mechanical damage while allow ing the diffusi on of leachable chemicals from the polymeric specime ns. Extracts of materials that are to be tested are applied to a piece of filter paper. Sample Preparati on —Use extracts prepared as directed, or use porti ons of the test specime ns hav ing flat surfaces NLT 100 mm in surface area. Positive Control Preparation —Proceed as directed for Sample Preparation . Negative Con trol Preparatio n ——Proceed as directed for Sample Preparati on Procedure —Using 7 mL of cell suspe nsion prepared as directed un der CellCulture Preparati on , prepare the mono layers in plates hav ing a 60-mm diameter. Following incubation, aspirate the culture medium from the mono layers, and replace it withserum-suppleme nted culture medium con tai ning NMT 2% of agar. [NOTE—The quality of the agar must be adequate to support cell growth.The agar layer must be thin enough to permit diffusion of leached chemicals. ] Place the flat surfaces ofSample Preparati on, Negative Con trol Preparati on , and Positive Con trolPreparation or their extracts in an appropriate extracting medium, in duplicate cultures in con tact with the solidified agar surface. Use no more tha n threespecimens per prepared plate. Incubate all cultures for NLT 24 h at 37 1- ,±preferably in a humidified in cubator containing 5 1% of carbb n dioxide.Examine each culture around each Sample, Negative Control , and PositiveControl, under a microscope, using a suitable stain, if desired.In terpretati on of Results ——The biological reactivity (cellular dege nerati on and malformati on) is described and rated on a scale of 0 — (see Table 1). Measurethe responses of the cell cultures to the Sample Preparation , the NegativeControl Preparation , and the Positive Control Preparation . The cell culture test system is suitable if the observed resp on ses to the Negative Con trolPreparation is grade 0 (no reactivity) and to the Positive Control Preparation isat least grade 3 (moderate). The Sample meets the requireme nts of the test if the response to the Sample Preparation is not greater than grade 2 (mildly reactive). Repeat the procedure if the suitability of the system is not con firmed.Table 1. Reactivity Grades for Agar Diffusio n Test and Direct Con tact TestGrade Reactivity Descripti on of Reactivity Zone0 None No detectable zone around or un der specime nSome malformed or dege nerated cells un der1 Slight specime nZone limited to area un der specime n and lesstha n2 Mild 0.45 cm bey ond specime n3 Moderate Zone exte nds 0.45 to 1.0 cm bey ond specime n4 Severe Zone exte nds greater tha n 1.0 cm bey ondspecime nDirect Con tact TestThis test is desig ned for materials in a variety of shapes. The procedure allows for simulta neous extract ion and testi ng of leachable chemicals from the specime n with a serum-suppleme nted medium. The procedure is not appropriate for very low- or high-de nsity materials that could cause mecha ni cal damage to the cells.Sample Preparati on —Use porti ons of the test specime n hav ing flat surfaces2NLT 100 mm in surface area.Positive Control Preparation —Proceed as directed for Sample Preparation . Negative Con trol Preparatio n ——Proceed as directed for Sample Preparati on Procedure —Using 2 mL of cell suspe nsion prepared as directed un der Cell Culture Preparati on , prepare the mono layers in plates hav ing a 35-mm diameter. Following incubation, aspirate the culture medium from the cultures, and replace it with 0.8 mL of fresh culture medium. Place a single Sample Preparation , a Negative Control Preparation , and a Positive Control Preparation in each of duplicate cultures. Incubate all cultures for NLT 24 h at 37 ±1〕in a humidified in cubator containing 5 1% of carb on dioxide.Examine each culture around each Sample, Negative Control , and Positive Control Preparation , under a microscope, using a suitable stain, if desired.In terpretati on of Results —Proceed as directed for In terpretati on of Results under Agar Diffusion Test . The Sample meets the requirements of the test if the response to the Sample Preparation is not greater than grade 2 (mildly reactive). Repeat the procedure if the suitability of the system is not con firmed.Eluti on TestThis test is designed for the evaluation of extracts of polymeric materials. The procedure allows for extract ion of the specime ns at physiological or。