信号与系统 奥本海姆 第二章答案
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:133.72 KB
- 文档页数:6

Chapter 22.1解:(a) 1[][][][0][][1][1][3][3]y n x n h n x h n x h n x h n =*=+-+-2[1]4[]2[1]2[2]2[4]n n n n n δδδδδ=+++-+---(图略)(b) 21[][2][][2]y n x n h n y n =+*=+2[3]4[2]2[1]2[]2[2]n n n n n δδδδδ=++++++--(图略)(c) 32[][][2][]y n x n h n y n =*+=(图略)2.5解:9[][][]k y n x k h n k ==-∑,由[4]5y =可知:4N ≥由[14]0y =可知:9114N ++≤,即:4N ≤ 所以:4N =2.11解:(a) 3t ≤时,()0y t =35t <≤时,3()(3)()(3)()ty t u t h t u h t d τττ=-*=--⎰3(3)3()313t tt e ed ττ-----==⎰5t >时,[]()63(5)53()31()(3)(5)()3t t e e y t t u t u h t e d ττ------=---*==⎰因此:()3(3)63(5)0,31(),3531,53t t t e y t t e e t -----⎧⎪≤⎪⎪-=<≤⎨⎪⎪-⎪>⎩(b )()(3)(5)dx t t t dtδδ=--- 3(3)3(5)()()()(3)(5)(3)(5)t t dx t g t h t h t h t e u t e u t dt----∴=*=---=---(c) ()()dy t g t dt=2.13解:(a) 将1[][]5n h n u n ⎛⎫= ⎪⎝⎭代入式子得:111[][1][]55n n u n A u n n δ-⎛⎫⎛⎫--= ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭⎝⎭即:()1[]5[1][]5nu n Au n n δ⎛⎫--= ⎪⎝⎭从而可得:51A =,即:15A = (b)由(a)可知:1[][1][]5h n h n n δ--= 则1S 的逆系统2S 的单位脉冲响应为:11[][][1]5h n n n δδ=--2.16解:(a)对。



第2章线性时不变系统2.1 复习笔记一、离散时间线性时不变系统:卷积和1.用脉冲表示离散时间信号把任意一个序列表示成一串移位的单位脉冲序列δ[n-k]的线性组合,而这个线性组合式中的权因子就是x[k]。
2.线性系统的卷积和(1)输入x[n]表示为一组移位单位脉冲的线性组合。
(2)h k[n]为该线性系统对移位单位脉冲δ[n-k]的响应。
(3)线性系统对输入x[n]的响应y[n]就是系统对这些单个移位脉冲响应的加权线性组合,即3.线性时不变系统的卷积和或叠加和用符号记为意义:既然一个线性时不变系统对任意输入的响应可以用系统对单位脉冲的响应来表示,那么线性时不变系统的单位脉冲响应就完全刻画了系统的特征。
4.用图解的方法来计算卷积和(1)对某一n值,比如n=n0,已求得y[n]画出了信号h[n0-k],将它与x[k]相乘,并对所有的k值将乘积相加。
(2)求下一个n值,即n=n0+1时的y[n]画出信号h[(n0+1)-k],即将信号h[n0-k]右移一点即可;(3)对于接下来的每一个n值,继续上面的过程把h[n-k]一点一点地向右移,再与x[k]相乘,并对所有的k将全部乘积相加。
二、连续时间线性时不变系统:卷积积分1.用冲激表示持续时间信号任意信号x(t)可表示成了一个加权的移位冲激函数的和上式为连续时间冲激函数的筛选性质。
2.连续时间线性时不变系统的单位冲激响应及卷积积分表示(1)单位冲激响应h(t)也就是h(t)是系统对δ(t)的响应。
(2)卷积积分或叠加积分意义:一个连续时间线性时不变系统的特性可以用它的单位冲激响应来刻画。
两个信号x(t)和h(t)的卷积标记为3.求解连续时间信号的卷积的步骤(1)在任意时刻t的输出y(t)是输入的加权积分,对x(τ)其权是h(t-τ)。
(2)为了求出对某一给定t时的这个积分值,首先需要得到h(t-τ)。
(3)h(t-τ)是τ的函数,t为某一固定值,利用h(τ)的反转再加上平移(t>0时就向右移t;t<0时就向左移|t|),就可以求得h(t-τ)。
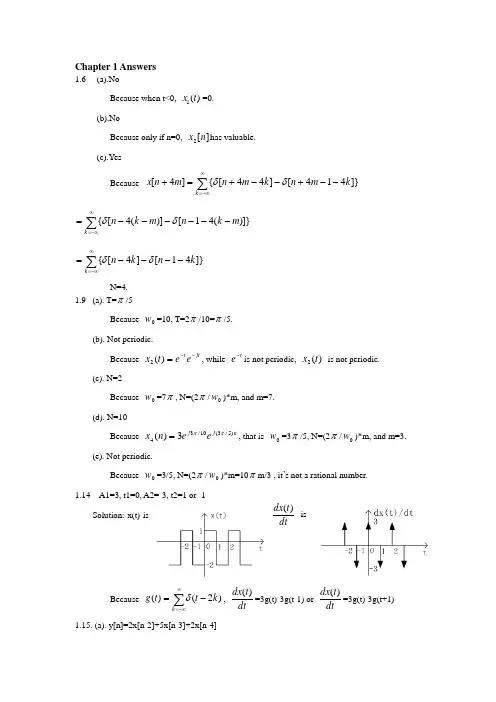
Chapter 1 Answers1.6 (a).NoBecause when t<0, )(1t x =0.(b).NoBecause only if n=0, ][2n x has valuable.(c).Yes Because ∑∞-∞=--+--+=+k k m n k m n m n x ]}414[]44[{]4[δδ ∑∞-∞=------=k m k n m k n )]}(41[)](4[{δδ ∑∞-∞=----=k k n k n ]}41[]4[{δδ N=4.1.9 (a). T=π/5Because 0w =10, T=2π/10=π/5.(b). Not periodic.Because jt t e e t x --=)(2, while t e -is not periodic, )(2t x is not periodic.(c). N=2Because 0w =7π, N=(2π/0w )*m, and m=7.(d). N=10Because n j j e e n x )5/3(10/343)(ππ=, that is 0w =3π/5, N=(2π/0w )*m, and m=3.(e). Not periodic. Because 0w =3/5, N=(2π/0w )*m=10πm/3 , it ’s not a rational number.1.14 A1=3, t1=0, A2=-3, t2=1 or -1dtt dx )( isSolution: x(t) isBecause ∑∞-∞=-=k k t t g )2()(δ, dt t dx )(=3g(t)-3g(t-1) or dtt dx )(=3g(t)-3g(t+1) 1.15. (a). y[n]=2x[n-2]+5x[n-3]+2x[n-4]Solution:]3[21]2[][222-+-=n x n x n y ]3[21]2[11-+-=n y n y ]}4[4]3[2{21]}3[4]2[2{1111-+-+-+-=n x n x n x n x ]4[2]3[5]2[2111-+-+-=n x n x n xThen, ]4[2]3[5]2[2][-+-+-=n x n x n x n y(b).No. For it ’s linearity.the relationship between ][1n y and ][2n x is the same in-out relationship with (a). you can have a try.1.16. (a). No.For example, when n=0, y[0]=x[0]x[-2]. So the system is memory. (b). y[n]=0.When the input is ][n A δ,then, ]2[][][2-=n n A n y δδ, so y[n]=0. (c). No.For example, when x[n]=0, y[n]=0; when x[n]=][n A δ, y[n]=0. So the system is not invertible.1.17. (a). No.For example, )0()(x y =-π. So it ’s not causal.(b). Yes.Because : ))(sin()(11t x t y = , ))(sin()(22t x t y =))(sin())(sin()()(2121t bx t ax t by t ay +=+1.21. Solution:We have known:(a).(b).(c).(d).1.22. Solution:We have known:(a).(b).(e).(g)1.23. Solution:For )]()([21)}({t x t x t x E v -+= )]()([21)}({t x t x t x O d --= then,(a).(b).(c).1.24.For: ])[][(21]}[{n x n x n x E v -+= ])[][(21]}[{n x n x n x O d --=then,(a).(b).1.25. (a). Periodic. T=π/2.Solution: T=2π/4=π/2.(b). Periodic. T=2.Solution: T=2π/π=2.(d). Periodic. T=0.5. Solution: )}()4{cos()(t u t E t x v π=)}())(4cos()()4{cos(21t u t t u t --+=ππ )}()(){4cos(21t u t u t -+=π )4cos(21t π= So, T=2π/4π=0.51.26. (a). Periodic. N=7Solution: N=m *7/62ππ=7, m=3.(b). Aperriodic.Solution: N=ππm m 16*8/12=, it ’s not rational number.(e). Periodic. N=16 Solution as follow:)62cos(2)8sin()4cos(2][ππππ+-+=n n n n x in this equation,)4cos(2n π, it ’s period is N=2π*m/(π/4)=8, m=1.)8sin(n π, it ’s period is N=2π*m/(π/8)=16, m=1.)62cos(2ππ+-n , it ’s period is N=2π*m/(π/2)=4, m=1. So, the fundamental period of ][n x is N=(8,16,4)=16.1.31. SolutionBecause )()1()(),2()()(113112t x t x t x t x t x t x ++=--=. According to LTI property ,)()1()(),2()()(113112t y t y t y t y t y t y ++=--=Extra problems:Sketch ⎰∞-=t dt t x t y )()(. 1. SupposeSolution:2. SupposeSketch:(1). )]1(2)1()3()[(--+++t t t t g δδδ(2). ∑∞-∞=-k k t t g )2()(δ(2).Chapter 22.1 Solution:Because x[n]=(1 2 0 –1)0, h[n]=(2 0 2)1-, then(a).So, ]4[2]2[2]1[2][4]1[2][1---+-+++=n n n n n n y δδδδδ (b). according to the property of convolutioin:]2[][12+=n y n y(c). ]2[][13+=n y n y][*][][n h n x n y =][][k n h k x k -=∑∞-∞= ∑∞-∞=-+--=k k k n u k u ]2[]2[)21(2 ][211)21()21(][)21(12)2(0222n u n u n n k k --==+-++=-∑ ][])21(1[21n u n +-= the figure of the y[n] is:2.5 Solution:We have known: ⎩⎨⎧≤≤=elsewhere n n x ....090....1][,,, ⎩⎨⎧≤≤=elsewhere N n n h ....00....1][,,,(9≤N ) Then, ]10[][][--=n u n u n x , ]1[][][---=N n u n u n h∑∞-∞=-==k k n u k h n h n x n y ][][][*][][ ∑∞-∞=-------=k k n u k n u N k u k u ])10[][])(1[][(So, y[4] ∑∞-∞=-------=k k u k u N k u k u ])6[]4[])(1[][( ⎪⎪⎩⎪⎪⎨⎧≥≤=∑∑==4,...14, (140)0N N k Nk =5, then 4≥N And y[14] ∑∞-∞=------=k k u k u N k u k u ])4[]14[])(1[][(⎪⎪⎩⎪⎪⎨⎧≥≤=∑∑==14,...114, (1145)5N N k Nk =0, then 5<N ∴4=N2.7 Solution:[][][2]k y n x k g n k ∞=-∞=-∑(a )[][1]x n n δ=-,[][][2][1][2][2]k k y n x k g n k k g n k g n δ∞∞=-∞=-∞=-=--=-∑∑(b) [][2]x n n δ=-,[][][2][2][2][4]k k y n x k g n k k g n k g n δ∞∞=-∞=-∞=-=--=-∑∑ (c) S is not LTI system..(d) [][]x n u n =,0[][][2][][2][2]k k k y n x k g n k u k g n k g n k ∞∞∞=-∞=-∞==-=-=-∑∑∑2.8 Solution: )]1(2)2([*)()(*)()(+++==t t t x t h t x t y δδ )1(2)2(+++=t x t xThen,That is, ⎪⎪⎪⎩⎪⎪⎪⎨⎧≤<-≤<-+-=-<<-+=others t t t t t t t t y ,........010,....2201,.....41..,.........412,.....3)(2.10 Solution:(a). We know:Then,)()()(αδδ--='t t t h)]()([*)()(*)()(αδδ--='='t t t x t h t x t y )()(α--=t x t xthat is,So, ⎪⎪⎩⎪⎪⎨⎧+≤≤-+≤≤≤≤=others t t t t t t y ,.....011,.....11,....0,.....)(ααααα(b). From the figure of )(t y ', only if 1=α, )(t y ' would contain merely therediscontinuities.2.11 Solution:(a). )(*)]5()3([)(*)()(3t u et u t u t h t x t y t----==⎰⎰∞∞---∞∞--------=ττττττττd t u e u d t u eu t t )()5()()3()(3)(3⎰⎰-------=tt t t d e t u d et u 5)(33)(3)5()3(ττττ⎪⎪⎪⎪⎩⎪⎪⎪⎪⎨⎧≥+-=-<≤-=<=---------⎰⎰⎰5,.......353,.....313.........,.........0315395)(33)(3393)(3t e e d e d e t e d e t tt t t t t t t t ττττττ(b). )(*)]5()3([)(*)/)(()(3t u e t t t h dt t dx t g t ----==δδ)5()3()5(3)3(3---=----t u e t u e t t(c). It ’s obvious that dt t dy t g /)()(=.2.12 Solution∑∑∞-∞=-∞-∞=--=-=k tk tk t t u ek t t u e t y )]3(*)([)3(*)()(δδ∑∞-∞=---=k k t k t u e)3()3(Considering for 30<≤t ,we can obtain33311])3([)(---∞=-∞-∞=--==-=∑∑ee e ek t u e e t y tk k tk kt. (Because k must be negetive ,1)3(=-k t u for 30<≤t ).2.19 Solution:(a). We have known:][]1[21][n x n w n w +-=(1) ][]1[][n w n y n y βα+-=(2)from (1), 21)(1-=E EE Hfrom (2), αβ-=E EE H )(2then, 212212)21(1)21)(()()()(--++-=--==E E E E E E H E H E H ααβαβ∴][]2[2]1[)21(][n x n y n y n y βαα=-+-+-but, ][]1[43]2[81][n x n y n y n y +-+--=∴⎪⎩⎪⎨⎧=⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛=+=143)21(:....812βααor ∴⎪⎩⎪⎨⎧==141βα(b). from (a), we know )21)(41()()()(221--==E E E E H E H E H21241-+--=E EE E ∴][)41()21(2][n u n h n n ⎥⎦⎤⎢⎣⎡-=2.20 (a). 1⎰⎰∞∞-∞∞-===1)0cos()cos()()cos()(0dt t t dt t t u δ(b). 0dt t t )3()2sin(5+⎰δπ has value only on 3-=t , but ]5,0[3∉-∴dt t t )3()2sin(5+⎰δπ=0(c). 0⎰⎰---=-641551)2cos()()2cos()1(dt t t u d u πτπττ⎰-'-=64)2cos()(dt t t πδ0|)2(s co ='=t t π 0|)2sin(20=-==t t ππ∑∞-∞=-==k t h kT t t h t x t y )(*)()(*)()(δ∑∞-∞=-=k kT t h )(∴2.27Solution()y A y t dt ∞-∞=⎰,()xA x t dt ∞-∞=⎰,()hA h t dt ∞-∞=⎰.()()*()()()y t x t h t x x t d τττ∞-∞==-⎰()()()()()()()()()(){()}y x hA y t dt x x t d dtx x t dtd x x t dtd x x d d x d x d A A ττττττττττξξτττξξ∞∞∞-∞-∞-∞∞∞∞∞-∞-∞-∞-∞∞∞∞∞-∞-∞-∞-∞==-=-=-===⎰⎰⎰⎰⎰⎰⎰⎰⎰⎰⎰(a) ()()(2)tt y t e x d τττ---∞=-⎰,Let ()()x t t δ=,then ()()y t h t =. So , 2()(2)(2)()(2)()(2)t t t t t h t ed e d e u t τξδττδξξ---------∞-∞=-==-⎰⎰(b) (2)()()*()[(1)(2)]*(2)t y t x t h t u t u t e u t --==+---(2)(2)(1)(2)(2)(2)t t u eu t d u e u t d ττττττττ∞∞-------∞-∞=+------⎰⎰22(2)(2)12(1)(4)t t t t u t e d u t e d ττττ---------=---⎰⎰(2)2(2)212(1)[]|(4)[]|t t t t u t e e u t ee ττ-------=--- (1)(4)[1](1)[1](4)t t e u t e u t ----=-----2.46 SolutionBecause)]1([2)1(]2[)(33-+-=--t u dtde t u e dt d t x dt d t t )1(2)(3)1(2)(333-+-=-+-=--t e t x t e t x t δδ.From LTI property ,we know)1(2)(3)(3-+-→-t h e t y t x dtdwhere )(t h is the impulse response of the system. So ,following equation can be derived.)()1(223t u e t h e t --=-Finally, )1(21)()1(23+=+-t u e e t h t 2.47 SoliutionAccording to the property of the linear time-invariant system: (a). )(2)(*)(2)(*)()(000t y t h t x t h t x t y ===(b). )(*)]2()([)(*)()(00t h t x t x t h t x t y --==)(*)2()(*)(0000t h t x t h t x --=012y(t)t4)2()(00--=t y t y(c). )1()1(*)(*)2()1(*)2()(*)()(00000-=+-=+-==t y t t h t x t h t x t h t x t y δ(d). The condition is not enough.(e). )(*)()(*)()(00t h t x t h t x t y --==τττd t h x )()(00+--=⎰∞∞-)()()(000t y dm m t h m x -=--=⎰∞∞-(f). )()]([)](*)([)(*)()(*)()(000000t y t y t h t x t h t x t h t x t y "=''='--'=-'-'==Extra problems:1. Solute h(t), h[n](1). )()(6)(5)(22t x t y t y dt dt y dtd =++ (2). ]1[][2]1[2]2[+=++++n x n y n y n y Solution:(1). Because 3121)3)(2(1651)(2+-++=++=++=P P P P P P P Hso )()()()3121()(32t u e e t P P t h t t ---=+-++=δ (2). Because )1)(1(1)1(22)(22i E i E EE E E E E E H -+++=++=++=iE Eii E E i -+-+++=1212 so []][)1()1(2][1212][n u i i i k i E E i i E E i n h n n +----=⎪⎪⎪⎪⎭⎫⎝⎛-+-+++=δChapter 33.1 Solution:Fundamental period 8T =.02/8/4ωππ==00000000033113333()224434cos()8sin()44j kt j t j t j t j tk k j t j t j t j tx t a e a e a e a e a e e e je je t t ωωωωωωωωωππ∞----=-∞--==+++=++-=-∑3.2 Solution:for, 10=a , 4/2πj ea --= , 4/2πj ea = , 3/42πj ea --=, 3/42πj ea =n N jk k N k e a n x )/2(][π∑>=<=n j n j n j n j e a e a e a e a a )5/8(4)5/8(4)5/4(2)5/4(20ππππ----++++=n j j n j j n j j n j j e e e e e e e e )5/8(3/)5/8(3/)5/4(4/)5/4(4/221ππππππππ----++++= )358cos(4)454cos(21ππππ++++=n n)6558sin(4)4354sin(21ππππ++++=n n3.3 Solution: for the period of )32cos(t πis 3=T , the period of )35sin(t πis 6=Tso the period of )(t x is 6 , i.e. 3/6/20ππ==w)35sin(4)32cos(2)(t t t x ππ++= )5sin(4)2cos(21200t w t w ++=)(2)(21200005522t w j t w j t w j t w j e e j e e ----++=then, 20=a , 2122==-a a , j a 25=-, j a 25-=3.5 Solution:(1). Because )1()1()(112-+-=t x t x t x , then )(2t x has the same period as )(1t x ,that is 21T T T ==, 12w w =(2). 212111()((1)(1))jkw t jkw tk T T b x t e dt x t x t e dt T--==-+-⎰⎰111111(1)(1)jkw tjkw t T Tx t e dt x t e dt T T --=-+-⎰⎰ 111)(jkw k k jkw k jkw k e a a e a e a -----+=+=3.8 Solution:kt jw k k e a t x 0)(∑∞-∞==while:)(t x is real and odd, then 00=a , k k a a --=2=T , then ππ==2/20wand0=k a for 1>kso kt jw k k e a t x 0)(∑∞-∞==t jw t jw e a e a a 00110++=--)sin(2)(11t a e e a t j t j πππ=-=-for12)(2121212120220==++=-⎰a a a a dt t x∴2/21±=a ∴)sin(2)(t t x π±=3.13 Solution:Fundamental period 8T =.02/8/4ωππ==kt jw k k e a t x 0)(∑∞-∞==∴t jkw k k e jkw H a t y 0)()(0∑∞-∞==0004, 0sin(4)()0, 0k k H jk k k ωωω=⎧==⎨≠⎩ ∴000()()4jkw t k k y t a H jkw e a ∞=-∞==∑Because 48004111()1(1)088T a x t dt dt dt T ==+-=⎰⎰⎰So ()0y t =.kt jw k k e a t x 0)(∑∞-∞==∴t jkw k k e jkw H a t y 0)()(0∑∞-∞== ∴dt e jkw H t y Ta t jkw Tk 0)()(10-⎰=for⎪⎩⎪⎨⎧>≤=100, (0100),.......1)(w w jw H ∴if 0=k a , it needs 1000>kwthat is 12100,........1006/2>>k kππand k is integer, so 8>K3.22 Solution:021)(1110===⎰⎰-tdt dt t x Ta Tdt te dt te dt e t x T a t jk t jk t jkw T k ππ-----⎰⎰⎰===1122112121)(10t jk tde jk ππ--⎰-=1121⎥⎥⎦⎤⎢⎢⎣⎡---=----111121ππππjk e te jk t jk tjk ⎥⎦⎤⎢⎣⎡---+-=--ππππππjk e e e e jk jk jk jk jk )()(21⎥⎦⎤⎢⎣⎡-+-=ππππjk k k jk )sin(2)cos(221[]πππππk jk k j k jk k)1()cos()cos(221-==-=0............≠k404402()()1184416tj tj t t j tt j t H j h t edt ee dte edt e e dtj j ωωωωωωωω∞∞----∞-∞∞----∞===+=+=-++⎰⎰⎰⎰A periodic continous-signal has Fourier Series:. 0()j kt k k x t a e ω∞=-∞=∑T is the fundamental period of ()x t .02/T ωπ=The output of LTI system with inputed ()x t is 00()()jk t k k y t a H jk e ωω∞=-∞=∑Its coefficients of Fourier Series: 0()k k b a H jk ω= (a)()()n x t t n δ∞=-∞=-∑.T=1, 02ωπ=11k a T==. 01/221/21()()1jkw t jk tk T a x t e dt t e dt Tπδ---===⎰⎰ (Note :If ()()n x t t nT δ∞=-∞=-∑,1k a T=) So 2282(2)16(2)4()k k b a H jk k k πππ===++ (b)()(1)()n n x t t n δ∞=-∞=--∑ .T=2, 0ωπ=,11k a T== 01/23/21/21/2111()()(1)(1)221[1(1)]2jkw t jk tjk t k T k a x t e dt t e dt t e dtT ππδδ----==+--=--⎰⎰⎰So 24[1(1)]()16()k k k b a H jk k ππ--==+, (c) T=1,02ωπ=01/421/4sin()12()jk t jk tk T k a x t e dt e dt Tk ωπππ---===⎰⎰28sin()2()[16(2)]k k k b a H jk k k ππππ==+ 3.35 Solution: T= /7π,02/14T ωπ==.kt jw k k e a t x 0)(∑∞-∞==∴t jkw k k e jkw H a t y 0)()(0∑∞-∞==∴0()k k b a H jkw =for⎩⎨⎧≥=otherwise w jw H ,.......0250,.......1)(,01,. (17)()0,.......k H jkw otherwise ⎧≥⎪=⎨⎪⎩that is 0250250, (14)k k ω<<, and k is integer, so 18....17k or k <≤. Let ()()y t x t =,k k b a =, it needs 0=k a ,for 18....17k or k <≤.3.37 Solution:11()[]()212()21312411511cos 224nj j nj n n n n j nn j nn n j j j H e h n ee ee e e e ωωωωωωωωω∞∞--=-∞=-∞-∞--=-∞=-===+=+=---∑∑∑∑A periodic sequence has Fourier Series:2()[]jk n Nk k N x n a eπ=<>=∑.N is the fundamental period of []x n .The output of LTI system with inputed []x n is 22()[]()jk jk n NNk k N y n a H eeππ=<>=∑.Its coefficients of Fourier Series: 2()jk Nk k b a H eπ=(a)[][4]k x n n k δ∞=-∞=-∑.N=4, 14k a =.So 2314()524cos()44j k Nk k b a H e k ππ==-3165cos()42k b k π=-3.40 Solution: According to the property of fourier series: (a). )2cos(2)cos(20000000t Tka t kw a e a ea a k k t jkw k t jkw k k π==+='- (b). Because 2)()()}({t x t x t x E v -+=}{2k v k k k a E a a a =+='-(c). Because 2)(*)()}({t x t x t x R e +=2*kk k a a a -+='(d). k k k a Tjka jkw a 220)2()(π=='(e). first, the period of )13(-t x is 3T T ='then 3)(1)13(131213120dme m x T dt e t x T a m T jk T t T jk T k +'--'-'-'⎰⎰'=-'='ππTjkk m T jk T T jk T jk m T jk T ea dm e m x T e dm e e m x T πππππ221122211)(1)(1---------=⎥⎦⎤⎢⎣⎡==⎰⎰3.43 (a) Proof:(i )Because ()x t is odd harmonic ,(2/)()jk T t k k x t a e π∞=-∞=∑,where 0k a = for everynon-zero even k.(2/)()2(2/)(2/)()2T jk T t k k jk jk T tk k jk T tk k T x t a ea e e a e ππππ∞+=-∞∞=-∞∞=-∞+===-∑∑∑It is noticed that k is odd integers or k=0.That means()()2Tx t x t =-+(ii )Because of ()()2Tx t x t =-+,we get the coefficients of Fourier Series222/200/222(/2)/2/20022/2/200111()()()11()(/2)11()()(1)jk t jk t jk t T T T T T T k T jk t jk t T T T T Tjk t jk t T T k TT a x t e dt x t e dt x t e dtT T T x t e dt x t T e dt T T x t e dt x t e dt T T πππππππ-----+--==+=++=--⎰⎰⎰⎰⎰⎰⎰ 2/21[1(1)]()jk t T kT x t e dt T π-=--⎰It is obvious that 0k a = for every non-zero even k. So ()x t is odd harmonic ,(b)Extra problems:∑∞-∞=-=k kT t t x )()(δ, π=T(1). Consider )(t y , when )(jw H ist(2). Consider )(t y , when )(jw H isSolution:∑∞-∞=-=k kT t t x )()(δ↔π11=T , 220==Tw π(1).kt j k k tjkw k k e k j H a ejkw H a t y 20)2(1)()(0∑∑∞-∞=∞-∞===ππ2=(for k can only has value 0)(2).kt j k k tjkw k k e k j H a e jkw H a t y 20)2(1)()(0∑∑∞-∞=∞-∞===πππte e t j t j 2cos 2)(122=+=- (for k can only has value –1 and 1)。
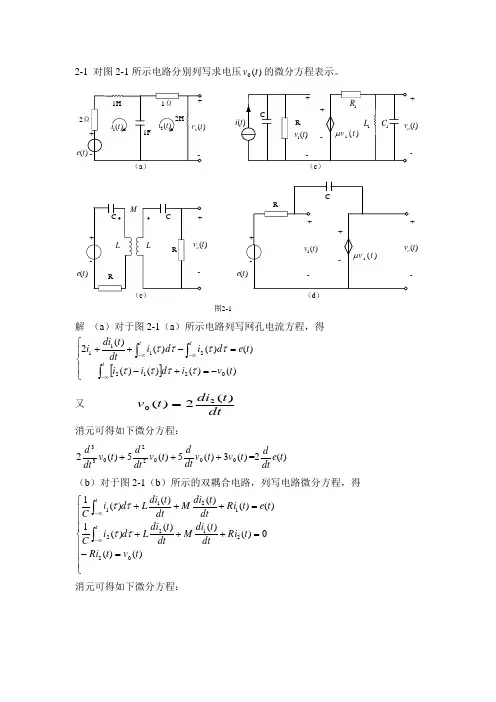
2-1 对图2-1所示电路分别列写求电压)(0t v 的微分方程表示。
2(t ei )(t +-(e )(e )(t +-图2-1解 (a )对于图2-1(a )所示电路列写网孔电流方程,得[]⎪⎩⎪⎨⎧-=+-=-++⎰⎰⎰∞-∞-∞-t t t t v i d i i t e d i d i dt t di i )()()()()()()()(202122111ττττττττ 又 dtt di t v )(2)(20= 消元可得如下微分方程:)(3)(5)(5)(200022033t v t v dt dt v dtd t v dt d +++=2)(te dt d(b )对于图2-1(b )所示的双耦合电路,列写电路微分方程,得⎪⎪⎪⎩⎪⎪⎪⎨⎧=-=+++=+++⎰⎰∞-∞-)()(0)()()()(1)()()()()(10221221211t v t Ri t Ri dt t di M dt t di L d i Ct e t Ri dtt di M dt t di L d i C ttττττ 消元可得如下微分方程:)()(1)(2)(2)(2)()(22020022203304422t e dtd MR t v C t v dt d C R t v dtd R R L t v dtd RL t v dt d M L =++⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛+++- (c )对于图2-1(c )所示电路列写电路方程,得⎪⎪⎩⎪⎪⎨⎧=⎥⎦⎤⎢⎣⎡+++=⎰∞-)()()(1)()()()(10101011t v t v dt d C dt t v L R t v R t v t v dt d C t i t μ 消元可得如下微分方程:)()(1)(1)()(101011022110331t i dt dR t v RL t v dt d R R L C t v dt d R C R C t v dt d CC μ=+⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛++⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛++ (d )对图2-1(d )所示电路列写电路方程,电流)(t i 如图2-2所示,得⎪⎪⎩⎪⎪⎨⎧==+=++⎰∞-)()()()()()()()(1)(1011t v t v t e t v t Ri t e t v d i C t Ri t μμττ 消元可得如下微分方程:(t e )(t +-图2-2)()(1)()1(00t e Rt v R t v dt d Cμμ=+-2-2 图2-3所示为理想火箭推动器模型。

第2章 习 题2-1 求下列齐次微分方程在给定起始状态条件下的零输入响应(1)0)(2)(3)(22=++t y t y dt d t y dt d ;给定:2)0(,3)0(==--y dt dy ; (2)0)(4)(22=+t y t y dt d ;给定:1)0(,1)0(==--y dtd y ;(3)0)(2)(2)(22=++t y t y dt d t y dt d ;给定:2)0(,1)0(==--y dt dy ; (4)0)()(2)(22=++t y t y dt d t y dt d ;给定:2)0(,1)0(==--y dtdy ; (5)0)()(2)(2233=++t y dt d t y dt d t y dt d ;给定:2)0(,1)0(,1)0(22===---y dt d y dt d y 。
(6)0)(4)(22=+t y dt d t y dt d ;给定:2)0(,1)0(==--y dtdy 。
解:(1)微分方程的特征方程为:2320λλ++=,解得特征根:121, 2.λλ=-=- 因此该方程的齐次解为:2()t th y t Ae Be --=+.由(0)3,(0)2dy y dt--==得:3,2 2.A B A B +=--=解得:8, 5.A B ==- 所以此齐次方程的零输入响应为:2()85tty t e e--=-.(2)微分方程的特征方程为:240λ+=,解得特征根:1,22i λ=±.因此该方程的齐次解为:()cos(2)sin(2)h y t A t B t =+.由(0)1,(0)1d y y dx --==得:1A =,21B =,解得:11,2A B ==. 所以此齐次方程的零输入响应为:1()cos(2)sin(2)2y t t t =+.(3)微分方程的特征方程为:2220λλ++=,解得特征根:1,21i λ=-± 因此该方程的齐次解为:()(cos()sin())th y t e A t B t -=+.由(0)1,(0)2dy y dx--==得:1,2,A B A =-= 解得:1,3A B ==.所以齐次方程的零输入响应为:()(cos()3sin())ty t e t t -=+.(4)微分方程的特征方程为:2210λλ++=,解得二重根:1,21λ=-.因此该方程的齐次解为:()()th y t At B e -=+. 由(0)1,(0)2dy y dx--==得:1,2,B A B =-=解得:3, 1.A B == 所以该方程的零输入响应为:()(31)ty t t e -=+.(5)微分方程的特征方程为:3220λλλ++=,解得特征根: 1,21λ=-,30λ=. 因此该方程的齐次解为:()()th y t A Bt C e -=++.由22(0)1,(0)1,(0)2d d y y y dx dt---===得:1,1,22A C B C C B +=-=-=. 解得:5,3,4A B C ==-=-.所以方程的零输入响应为:()5(34)ty t t e -=-+.(6)微分方程的特征方程为:240λλ+=,解得特征根:120,4λλ==-. 因此该方程的齐次解为:4()th y t A Be -=+.由(0)1,(0)2d y y dx --==得:1,42A B B +=-=.解得:31,22A B ==-. 所以此齐次方程的零输入响应为:431()22ty t e -=-.2-2 已知系统的微分方程和激励信号,求系统的零状态响应。
![信号与系统_第二版_奥本海默 _课后答案[1-10章]](https://uimg.taocdn.com/6ff45c8f83c4bb4cf6ecd112.webp)
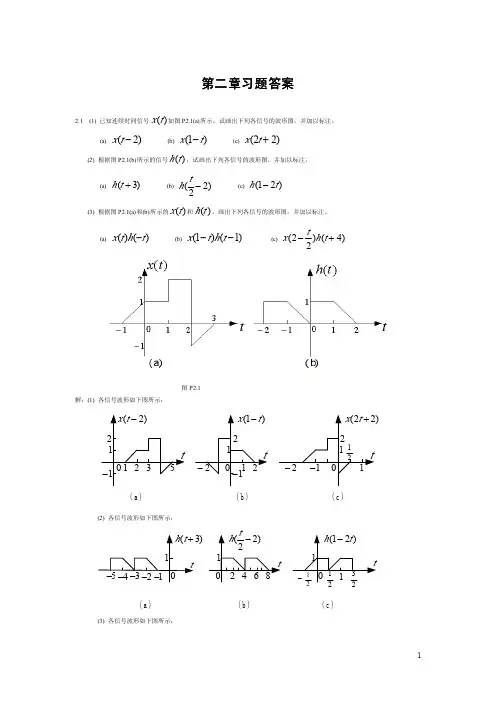

∑ {δ [n + 4m - 4k ] - δ [n + 4m - 1 - 4k ]}∑ {δ [n - 4(k - m )] - δ [n - 1 - 4(k - m )]}∑ {δ [n - 4k ] - δ [n - 1 - 4k ]}s Because g (t ) =∑ δ (t - 2k ) ,Chapter 1 Answers1.6 (a).NoBecause when t<0, x (t ) =0. 1(b).NoBecause only if n=0, x [n ] has valuable.2(c).Y esBecause x[n + 4m ] ===∞ k =-∞ ∞ k =-∞ ∞ k =-∞N=4.1.9 (a). T=π /5Because w =10, T=2π /10= π /5.(b). Not periodic.Because x (t ) = e -t e - jt , while e -t is not periodic, x (t ) is not periodic.2 2(c). N=2Because w =7 π , N=(2 π / w )*m, and m=7.0 0(d). N =10Because x (n) = 3e j 3π / 10 e j (3π / 5)n , that is w =3 π /5, N=(2 π / w )*m, and m=3.4 0(e). Not periodic.Because w =3/5, N=(2 π / w )*m=10π m/3 , it ’not a rational number .1.14 A1=3, t1=0, A2=-3, t2=1 or -1Solution: x(t) isdx(t )dtis∞ k =-∞1.15. (a). y[n]=2x[n-2]+5x[n-3]+2x[n-4]dx(t ) dx(t )=3g(t)-3g(t -1) or =3g(t)-3g(t+1)d t dt2 22 12Solution:y [n ] = x [n - 2] + 1x [n - 3] 2 2 1= y [n - 2] + y [n - 3]1 1= {2 x [n - 2] + 4 x [n - 3]} + {2 x [n - 3] + 4 x [n - 4]}1 1 1 1 =2 x [n - 2] + 5x [n - 3] + 2 x [n - 4]1 11Then, y[n ] = 2 x [n - 2] + 5x[n - 3] + 2 x [n - 4](b).No. For it ’s linearity .the relationship be tw e en y [n ] and x [n ] is the same in-out relationship with (a).1 2you can have a try.1.16. (a). No.For example, when n=0, y[0]=x[0]x[-2]. So the system is memory . (b). y[n]=0.When the input is A δ [n ] ,then, y[n] = A 2δ [n]δ [n - 2] , so y[n]=0.(c). No.For example, when x[n]=0, y[n]=0; when x[n]= A δ [n ] , y[n]=0.So the system is not invertible.1.17. (a). No.For example, y(-π ) = x(0) . So it ’s not causal.(b). Y es.Because : y (t ) = x (sin(t )) ,y (t ) = x (sin(t ))1 122ay (t ) + by (t ) = ax (sin(t )) + bx (sin(t ))1 2121.21. Solution:W e(a).have known:(b).(c).(d).1.22.Solution:W e have known:(a).(b).(e).22 E {x(t )} =(g)1.23. Solution:For1[ x (t ) + x(-t )] v 1O {x(t )} = [ x (t ) - x(-t )] dthen, (a).(b).(c).1.24.2Solution:For:E {x[n ]} = v 1 2( x [n ] + x[-n ])1O {x[n]} = ( x [n ] - x[-n ]) dthen,(a).(b).Solution: x(t ) = E {cos(4π t )u(t )}s(c).1.25. (a). Periodic. T=π /2.Solution: T=2π /4= π /2. (b). Periodic. T=2.Solution: T=2π / π =2. (d). Periodic. T=0.5.v1= {cos(4πt )u (t ) + cos(4π (-t ))u (-t )}2 1= cos(4π t ){u (t ) + u(-t )}2 1= cos(4π t )2So, T=2π /4 π =0.51.26. (a). Periodic. N=7Solution: N= 2π* m =7, m=3.6π / 7(b). Aperriodic.Solution: N= 2π 1/ 8* m = 16m π , it ’not rational number .(e). Periodic. N =16Solution as follow:2 cos( n ) , it ’s period is N=2π *m/( π /4)=8, m=1.sin( n ) , it ’s period is N=2π *m/( π /8)=16, m=1.(2). g (t ) ∑δ (t - 2k )π π π πx[n ] = 2 cos( n ) + sin( n ) - 2 cos( n + 4 8 2 6)in this equation,π4 π8π π- 2 cos( n + 2 6) , it ’s period is N=2π *m/( π /2)=4, m=1.So, the fundamental period of x[n ] is N=(8,16,4)=16.1.31. SolutionBecausex (t ) = x (t ) - x (t - 2), x (t ) = x (t + 1) + x (t ) .2 11311According to LTI property ,y (t ) = y (t ) - y (t - 2), y (t ) = y (t + 1) + y (t )2 11311Extra problems:1. SupposeSketch y(t ) = ⎰t-∞x(t )dt .Solution:2. SupposeSketch:(1). g (t )[δ (t + 3) + δ (t + 1) - 2δ (t - 1)]∞k =-∞Because x[n]=(1 2 0 –1) , h[n]=(2 0 2) , the nSolution: (1).(2).Chapter 22.1 Solution:-1(a).So,y [n ] = 2δ [n + 1] + 4δ [n ] + 2δ [n - 1] + 2δ [n - 2] - 2δ [n - 4]1(b). according to the property of convolutioin:y [n ] = y [n + 2]2 1(c). y [n] = y [n + 2]31=∑ x[k ]h [n - k ]( ) 0 - ( ) (n +2)-2+1= ∑ ( ) k -2 u[n] = 2 u[n]2 ⎩0, elsewhere W e have known: x[n] = ⎨ ⎩0,elsewhere , h[n] = ⎨ ,( N ≤ 9 ), , ∑ h[k ]u[n - k ]∑ (u[k ] - u[k - N - 1])(u[n - k ] - u[n - k - 10])∑ (u[k ] - u[k - N - 1])(u[4 - k ] - u[-k - 6])⎧∑ 1,...N ≤ 4⎪∑1,...N ≥ 4 ⎪⎩∑ (u[k ] - u[k - N - 1])(u[14 - k ] - u[4 - k ])2.3 Solution:y[n ] = x[n ]* h [n ]∞ k =-∞ ∞1= ∑ ( ) k -2 u [k - 2]u [n - k + 2]2k =-∞1 1 n +2 121 k =2 1 -21= 2[1 - ( ) n +1 ]u [n ]2the figure of the y[n] is:2.5 Solution:⎧1 ....0 ≤ n ≤ 9 ....⎧1 0≤ n ≤ N .... Then,x[n] = u[n] - u[n - 10] , h[n] = u[n] - u[n - N - 1]y[n] = x[n]* h[n] =∞k =-∞=∞ k =-∞So, y[4] =∞ k =-∞N⎪ ⎪ = ⎨k =04k =0=5, the n N ≥ 4And y[14] =∞ k =-∞⎧∑ 1,...N ≤ 14⎪∑1,...N ≥ 14 ⎪⎩ ∑ x[k ]g [n - 2k ]∑ x[k ]g [n - 2k ] = ∑ δ [k - 1]g [n - 2k ] = g [n - 2]∑ x[k ]g [n - 2k ] = ∑ δ [k - 2]g [n - 2k ] = g [n - 4]∑ x[k ]g [n - 2k ] = ∑ u[k ]g [n - 2k ] = ∑ g [n - 2k ]N⎪ ⎪= ⎨ k =514k =5∴N = 4=0, the n N < 52.7 Solution:y[n] =∞k =-∞(a ) x[n] = δ [n - 1] , y[n] =∞∞k =-∞ k =-∞ (b)x[n] = δ [n - 2] , y[n] =∞∞k =-∞k =-∞(c) S is not LTI system..(d) x[n] = u[n] , y[n] =∞ ∞∞k =-∞k =-∞ k =02.8 Solution:y(t ) = x(t ) * h (t ) = x(t ) *[δ (t + 2) + 2δ (t + 1)]= x(t + 2) + 2 x (t + 1)Then,⎩ = ⎰ u(τ - 3)e -3(t -τ )u(t - τ )d τ - ⎰ u(τ - 5)e -3(t -τ )u(t - τ )d τ⎩= u(t - 3)⎰ e -3(t -τ ) d τ - u(t - 5)⎰ e -3(t -τ ) d τ⎧t + 3,..... - 2 < t < -1 ⎪4,.......... t = -1 ⎪⎪That is, y(t ) = ⎨t + 4,..... - 1 < t ≤ 0⎪2 - 2t,....0 < t ≤ 1 ⎪ ⎪0,....... others2.10 Solution:(a). W e know:Then,h '(t ) = δ (t ) - δ (t - α )y '(t ) = x(t ) * h '(t ) = x(t ) *[δ (t ) - δ (t - α )]= x(t ) - x(t - α )that is,⎧t,.....0 ≤ t ≤ α ⎪α ,....α ≤ t ≤ 1So, y(t ) = ⎨⎪1 + α - t,.....1 ≤ t ≤ 1 + α ⎪0,.....others(b). From the figure of y '(t ) , only if α = 1 , y '(t ) would contain merely therediscontinuities.2.11 Solution:(a).y(t ) = x(t ) * h(t ) = [u (t - 3) - u (t - 5)]* e -3t u (t )∞ ∞-∞-∞tt35= ⎨⎰ e -3(t -τ ) d τ = ,.....3 ≤ t < 5 ⎪ 3 ⎪⎰ e -3(t -τ ) d τ - ⎰ e -3(t -τ ) d τ = - e ⎪ t9-3t + e 15-3t ⎪⎩ s y(t ) = e -t u (t ) * ∑ δ (t - 3k ) = ∑ [e = ∑ e -(t -3k )u (t - 3k )y(t ) = e -t [ ∑ e 3k u (t - 3k )] = e -t∑ ew [n ] = 1w [n - 1] + x[n ]⎧⎪ ⎪0,................. t < 3⎪ t1 - e 9-3t3t353,...... t ≥ 5(b). g (t ) = (dx(t ) / dt ) * h(t ) = [δ (t - 3) - δ (t - 5)]* e -3t u (t )= e -3(t -3) u (t - 3) - e -3(t -5) u (t - 5)(c). It ’obvious that g (t ) = d y (t ) / dt .2.12 Solution∞∞k =-∞k =-∞∞k =-∞Considering for 0 ≤ t < 3 ,we can obtain-t u (t ) * δ (t - 3k )]∞k =-∞0 k =-∞3k= e -t 11 - e -3.(Because k mu st be negetive , u (t - 3k ) = 1 for 0 ≤ t < 3 ).2.19 Solution:(a). W e have known:2 (1)y[n ] = αy[n - 1] + βw [n ](2)then, H ( E ) = H ( E ) H ( E ) =βE 2= .... or : (α + ) = ∴⎨ 2 8 ⎝ 2 = - E ∴ h [n ] = ⎢2( ) n - ( ) n ⎥u [n ] ⎩Θ⎰⎰ sin(2πt )δ (t + 3)dt has value only on t = -3 , but - 3 ∉ [0,5]⎰ sin(2πt )δ (t + 3)dt =0Θ⎰-4from (1), H ( E ) =E1E -1 2from (2), H ( E ) =2 βEE - α121 ( E - α )(E - )2 = β1 α 1 - (α + ) E -1 + E -22 21 α∴ y[n ] - (α + ) y[n - 1] + y[n - 2] = βx[n ]2 21 3but, y[n ] = - y[n - 2] + y[n - 1] + x[n ]8 4⎧α 1 ⎛1 ⎪ 3 ⎫ ⎪4 ⎭ ⎧ 1 ⎪α = ∴⎨ 4⎪β = 1(b). from (a), we know H ( E ) = H ( E ) H ( E ) =1 22E +1 1 E - E -4 2⎡ 1 1 ⎤ ⎣ 24 ⎦2.20 (a). 1⎪⎩β = 1E 21 1 ( E - )(E - ) 4 2(b). 0∞-∞ u (t ) cos(t )dt =⎰∞ δ (t ) cos(t )dt = cos(0) = 1-∞Θ∴(c). 05 0 5 05-5 u (1 - τ ) cos(2πτ )d τ = -⎰6 u (t ) cos(2πt )dt1 1= -⎰6 δ '(t ) cos(2πt )dt-4= cos '(2π t ) |t =0= -2π sin(2πt ) |t =0= 0∑ δ (t - kT ) * h (t )∑ h (t - kT )⎰ y(t )d t , A = ⎰ x(t )dt ,A = ⎰ h(t )d t .⎰ x(τ ) x (t - τ )d τ⎰ y(t )dt = ⎰ ⎰ x(τ ) x (t - τ )d τd t= ⎰ ⎰ x(τ ) x (t - τ )dtd τ = ⎰ x(τ ) ⎰ x(t - τ )dtd τ⎰ x(τ ) ⎰ x(ξ )d ξ d τ = ⎰ x(τ )d τ{ ⎰ x(ξ )d ξ}2.23 Solution:Θ y(t ) = x(t ) * h (t ) =∞k =-∞=∞ k =-∞∴2.27 SolutionA = y∞ ∞ ∞ x h-∞ y(t ) = x(t )* h(t ) = -∞ -∞ ∞-∞A = y∞ ∞ ∞-∞ -∞ -∞∞ ∞∞∞-∞ -∞-∞ -∞= ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞-∞= A Ax h-∞ -∞ -∞⎰e ⎰ eδ (τ - 2)d τ = ⎰ e⎰ u(τ + 1)eu(t - 2 - τ )d τ - ⎰ u(τ - 2)e= u(t - 1) ⎰ ed τ - u(t - 4) ⎰ e-(t -2-τ )d τ2.40 Solution(a) y(t ) = t-(t -τ) x(τ - 2)d τ ,Let x(t ) = δ (t ) ,then y(t ) = h (t ) .-∞So , h(t ) = t t -2-(t -τ ) -∞-∞-(t -2-ξ )δ (ξ )d ξ = e -(t -2)u(t - 2)(b)y(t ) = x(t )* h(t ) = [u(t + 1) - u(t - 2)]* e -(t -2)u(t - 2)=∞ ∞ -(t -2-τ )-∞-∞-(t -2-τ )u(t - 2 - τ )d τt -2-1-(t -2-τ ) t -2 2= u(t - 1)[e -(t -2) e τ ]| t -2 -u(t - 4)[e -(t -2) e τ ]| t -2-1 2= [1- e -(t -1) ]u(t - 1) - [1- e -(t -4) ]u(t - 4)2.46 SolutionBecaused d dx(t ) = [ 2e -3t ]u (t - 1) + 2e -3t [ u (t - 1)] d t dt d t= -3x(t ) + 2e -3t δ (t - 1) = -3x(t ) + 2e -3δ (t - 1) .From LTI property ,we knowdd tx(t ) → -3 y (t ) + 2e -3 h (t - 1)whereh (t ) is the impulse response of the system.So ,following equation can be derived.2e -3h(t - 1) = e -2t u (t )Finally, h (t ) = 12e 3e -2(t +1)u (t + 1)2.47 SoliutionAccording to the property of the linear time-invariant system:(a). y(t ) = x(t ) * h(t ) = 2 x (t ) * h (t ) = 2 y (t )0 0(b). y(t ) = x(t ) * h(t ) = [ x (t ) - x (t - 2)]* h(t )1y(t)= x (t ) * h (t ) - x (t - 2) * h (t )0 2 4t= [ y (t )] = y (1). Because H ( P ) = 1so h (t ) = (1= 2 + E - E ⎪ [ ]⎪δ [k ] = i (-1 - i) n- (-1 + i) n u [n] so h [n ] = 2 2 i= y (t ) - y (t - 2)0 0(c). y(t ) = x(t ) * h(t ) = x (t - 2) * h (t + 1) = x (t - 2) * h (t ) * δ (t + 1) = y (t - 1)0 0(d). The condition is not enough.(e). y(t ) = x(t ) * h(t ) = x (-t ) * h (-t )0 0= ⎰∞ x (-τ )h (-t + τ )d τ-∞ = ⎰∞x (m )h (-t - m )dm = y (-t )-∞(f). y(t ) = x(t ) * h (t ) = x ' (-t ) * h ' (-t ) = [ x ' (-t ) * h (-t )] ' ' ' " (t )Extra problems:1. Solute h(t), h[n](1). d 2 dy(t ) + 5 y(t ) + 6 y(t ) = x(t )dt 2 dt(2). y[n + 2] + 2 y[n + 1] + 2 y[n ] = x[n + 1]Solution:1 1 - 1= = +P 2 + 5P + 6 ( P + 2)( P + 3) P + 2 P + 3- 1+)δ (t ) = (e -2t - e -3t )u (t )P + 2P + 3(2). Because H ( E ) = E E E= =E 2 + 2E + 2 ( E + 1) 2 + 1 ( E + 1 + i)( E + 1 - i)i i E - E2E + 1 + i E + 1 - i⎛ i ⎫+E + 1 + i E + 1 - i ⎪ 2 ⎪ ⎝ ⎭x(t ) = ∑ for the period of cos( 5πt ) is T = 63the period of sin( 22⎰ x 2 (t )e - jkw 2t d t = ⎰ ( x 1 (1- t ) + x 1 (t - 1))e - jkw 1t dtT T TChapter 33.1 Solution:Fundamental period T = 8 . ω = 2π / 8 = π / 4∞a e j ω0kt = a e j ω0t + a e - j ω0t + a e j 3ω0t + a e - j 3ω0tk 1 -1 3 -3k =-∞ = 2ej ω0t+ 2e - j ω0t + 4 je j 3ω0t - 4 je - j3ω0t π 3π= 4cos( t ) - 8sin( t )4 43.2 Solution:for , a = 1 , a0 -2= e - j π / 4 , a = e j π / 4 , a 2-4= 2e - j π / 3 , a = 2e j π / 34x[n] = ∑ a e jk (2π / N )nkk =< N >= a + a e j (4π / 5)n + a e - j (4π / 5)n + a e j (8π / 5)n + a e - j (8π / 5)n0 2-24-4= 1 + e j π / 4 e j (4π / 5)n + e - j π / 4 e - j (4π / 5)n + 2e j π / 3e j (8π / 5)n + 2e - j π / 3e - j (8π / 5)n4 π 8 π= 1 + 2 cos( πn + ) + 4 cos( πn + )5 4 5 3 4 3π 8 5π= 1 + 2sin( πn + ) + 4sin( πn + )5 4 5 63.3 Solution:2πt ) is T= 3 , 3so the period of x(t ) is 6 , i.e. w = 2π / 6 = π / 32π 5π x(t ) = 2 + cos(t ) + 4sin(t )331= 2 + cos(2w t ) + 4sin(5w t )0 0 1= 2 + (e j 2w 0t + e - j 2w 0t ) - 2 j(e j5w 0t - e - j5w 0t )2 then, a = 2 , a 0 -2 1= a = , a 2 -5 = 2 j , a = -2 j 53.5 Solution:(1). Because x (t ) = x (1 - t ) + x (t - 1) , the n x (t ) has the same period as x (t ) ,21121that is T = T = T ,w = w2121(2). b = 1 k⎰ x 1 (1- t )e - jkw 1t d t + 1 ⎰ x 1 (t - 1)e - jkw 1t dt ∑∑⎰ x(t ) 2 dt = a 0 2 + a -1 2 + a 1 2 = 2 a 1 2 = 1 Fundamental period T = 8 . ω = 2π / 8 = π / 4∑∑ a H ( jkw )ejkw 0tk ω ⎩0,......k ≠ 0⎧ ∑t Because a =⎰ x(t )d t = 1⎰4 1d t + 1 ⎰ 8(-1)d t = 0TT88 4= 1 T T T T= a e - jkw 1 + a e - jkw 1 = (a -k k3.8 Solution:-k+ a )e - jkw 1 kΘx(t ) =∞ k =-∞a e jw 0ktkwhile:andx(t ) is real and odd, the n a = 0 , a = -a 0 kT = 2 , the n w = 2π / 2 = πa = 0 for k > 1k-ksox(t ) =∞ a e jw 0kt = a + a e - jw 0t + a e jw 0tk 0 -1 1k =-∞= a (e j πt - e - j πt ) = 2a sin(π t )11for1 2 2 0∴∴a = ± 2 /21x(t ) = ± 2 sin(π t )3.13 Solution:Θx(t ) =∞ k =-∞a e jw 0ktk∴ y(t ) =∞k 0k =-∞H ( jk ω ) = sin(4k ω0 ) =⎨4,...... k = 00 0 ∴ y(t ) =∞a H ( jkw )e jkw 0= 4a k 00 k =-∞1Soy(t ) = 0 .∑∑a H(jkw)e jkw0tT t H(jw)=⎨if a=0,it needs kw>100T ⎰T⎰t dt=0T ⎰x(t)e-jkw0t dt=⎰te-jk22t dt=1⎰1te-jkπt dt11⎰1tde-jkπt2jkπ⎢-1⎦⎢(e-jkπ+e jkπ)-⎥-jkπ2c os(kπ)+-jkπ⎥⎦[2cos(kπ)]=j cos(kπ)=j(-1)k............k≠03.15Solution:Θx(t)=∞k=-∞a e jw0kt k∴y(t)=∞k=-∞k0∴a=1k ⎰Ty(t)H(jkw)e-jkw0d tfor⎧⎪1,......w≤100⎪⎩0,......w>100∴k0that is k2π100 >100,.......k>π/612and k is integer,so K>8 3.22Solution:a=10x(t)dt=112-1a= k 1T2-12-1π=-1 2jkπ-1=-1⎡⎢te-jkπt⎣1-1-e-jkπt-jkπ1⎤⎥⎥=-=-12jkπ12jkπ⎡(e-jkπ-e jkπ)⎤⎣⎦⎡2sin(kπ)⎤⎢⎣=-12jkπkπkπ⎰ h (t )e - j ωt d t = ⎰ e -4 t e - j ωt d t= ⎰ e e d t + ⎰ e -4t e - j ωt d t∑0 ∑∑Ta = ⎰ x(t )e - jkw 0t d t = ⎰1/ 2 δ(t )e - jk 2πt d t = 1T T-1/ 2 ∑T∑ (-1) δ (t - n ) .T=2, ω = π , a = 1T a = ⎰ x(t )e - jkw 0t d t = ⎰ δ (t )e - jk πt d t + ⎰ 3/ 2 (-1)δ (t - 1)e - jk πt d tT 2 -1/ 2 2 1/ 2 T 16 + (k π )23.34 Solution:∞ ∞H ( j ω ) =-∞-∞0 ∞ 4t - j ωt-∞118=+=4 - j ω 4 + j ω 16 + ω 2A periodic continous-signal has Fourier Series:. x(t ) =T is the fundamental period of x(t ) . ω = 2π / T∞ k =-∞a e j ω ktkThe output of LTI system with inputed x(t ) is y(t ) =Its coefficients of Fourier Series: b = a H ( jk ω )k k 0∞ k =-∞a H ( jk ω )e jk ω tk 0(a) x(t ) =∞ n =-∞ δ (t - n ) .T=1, ω = 2π a = 1 = 1 .0 k1 k(N ot e :If x(t ) =∞ n =-∞δ (t - nT ) , a =1 k)So b = a H ( jk 2π ) = k k 8 2=16 + (2k π )2 4 + (k π )2(b) x(t ) = ∞n =-∞n0 k= 11 1 1/2 1 k1= [1- (-1)k ] 24[1-(-1)k ]So b = a H ( jk π ) = ,k k(c) T=1, ω = 2π⎰ x(t )e - jk ω0t d t = ⎰1/ 4e - jk 2πt d t =∑∑ a H ( jkw )ejkw 0t⎪⎩0,......otherwise ⎩0,......otherwise H ( jw) = ⎨⎪, 14Let y(t ) = x(t ) , b = a , it needs a = 0 ,for k < 18..or .. k ≤ 17 .∑∑∑ 2n e - j ωn + ∑ ( )n e - j ωn1 =2 41 1 5∑a ejk ( N )n .a = k1 T T -1/ 4 k π sin(2 k π)b = a H ( jk π ) =k k k π8sin( )2 k π [16 + (2k π )2 ]3.35 Solution: T= π / 7 , ω = 2π / T = 14 .Θx(t ) =∞a e jw 0ktk∴y(t ) =k =-∞ ∞ k =-∞k 0∴b = a H ( jkw )k k 0for ⎧1,...... w ≥ 250 ⎧1,...... k ≥ 170 that is k ω 0 < 250,....... k < 250, and k is integer , so k < 18..or .. k ≤ 17 .kkk3.37 Solution:H (ej ω) = ∞n =-∞h [n ]e- j ωn=∞ n =-∞1 ( ) ne - j ωn 2-1∞1= 2n =-∞ n =0 1 3e j ω+ =1 - e j ω 1 - e - j ω - cos ω2 2 4A periodic sequen ce has Fourier Series: x [n ] =N is the fundamental period of x[n ] .k =< N >k2πThe output of LTI system with inputed x[n ] is y[n ] =∑ a H (ekj 2π k N)ejk ( 2π )n N .k =< N >∑4 .So b = a H (e j N k ) = 1 4 45 - cos( 2π k ) k =2 21 T ' 1 3T '-1 = ⎰ x(3t - 1)e T ' dt = ⎰ x(m )e = ⎰ x(m )e e⎡ 1T -1 T ⎢⎰∑a e jk (2π/T )t ,where a = 0 for every2π Its coefficients of Fourier Series: b = a H (ejN k )kk3(a) x[n ] =∞ k =-∞δ [n - 4k ] .N=4, a = 1 k k k 2π 4 4b =k3 165 π- cos( k ) 4 23.40 Solution:According to the property of fourier series:(a). a k '= a e - jkw 0t 0 + a e jkw 0t 0 = 2a cos(kw t ) = 2a cos(k k k k 0 0 k 2π t )T 0(b). Because E {x(t )} =v x(t ) + x(-t )2a ' a + a k 2-k= E {a }v k(c). Because R {x(t )} = x(t ) + x * (t )e'a + a *a = k-k k(d). a '= ( jkw ) 2 a = ( jk k 0 k 2πT) 2 ak(e). first, the period of x(3t - 1) is T ' =T3th e n ak ' 2π - jk t T ' 0 T ' -11 T -12π 2π - jkm - jk dmT TT -1- jk 2π m +1 dm T ' 3 3= e- jk 2π ⎣ T -1x(m )e2π- jk m T⎤dm ⎥⎦2π = a e- jk Tk3.43 (a) Proof:( i ) Because x(t ) is odd harmonic , x(t ) =non-zer o even k.∞ k =-∞k kx(t + ) = ∑ a e jk (2π /T )(t + 2 )T 2∑= - ∑ a e jk (2π /T )t(ii )Because of x(t ) = - x (t + ) ,we get the coefficients of Fourier Seriesa = ⎰ x(t )e - jk 2T π t d t = 1 ⎰ T / 2 x(t )e - jk 2T π t d t + 1 ⎰ T x(t )e - jk 2T π t d tT 0 T 0 T T /2 1 T /2 1 T /2 = ⎰ T dt + ⎰ x(t + T / 2)e x(t )e 1 T /2 1 T /2 = ⎰ x(t )eT dt - ⎰ x(t )(-1)k e T dt 1T /2It is obvious that a = 0 for every non-zer o even k. So x(t ) is odd harmonic ,-11x(t ) = ∑ δ (t - kT ) , T = π∞ T k k =-∞= ∞a e jk π e jk (2π /T )tkk =-∞∞kk =-∞It is noticed that k is odd integers or k=0.That meansTx(t ) = - x (t + )2T21 T k2π - jk t T 0 T 0 2π- jk (t +T / 2) Tdt2π 2π- jk t - jk t T 0 T 0= [1- (-1)k ] ⎰T 02π x(t )e- jk Tt d tk(b) x(t )1......-2-12 tExtra problems:∞ k =-∞(1). Consider y(t ) , when H ( jw) isx(t ) = ∑ δ (t - kT ) ↔T π T∑ a H ( jkw )ejkw 0t=1k =-∞ π∑∑π∑1(2). Consider y(t ) , when H ( jw) isSolution:∞k =-∞ 1 1 2π= , w = = 2 0(1).y(t ) =∞k 0∞k =-∞a H ( j 2k )e j 2ktk=2π (for k can only has value 0)(2).y(t ) =∞ k =-∞a H ( jkw )e jkw 0t =1k 0∞k =-∞a H ( j 2k )e j 2ktk=1π (e - j 2t + e j 2t ) =2 cos 2tπ(for k can only has value – and 1)。

信号与系统 奥本海姆第二版 习题解答Department of Computer Engineering2005.12ContentsChapter 1 (2)Chapter 2 (17)Chapter 3 (35)Chapter 4 (62)Chapter 5 (83)Chapter 6 (109)Chapter 7 (119)Chapter 8 (132)Chapter 9 (140)Chapter 10 (160)Chapter 1 Answers1.1 Converting from polar to Cartesian coordinates:111cos 222j eππ==- 111c o s ()222j e ππ-=-=- 2cos()sin()22jj j eπππ=+=2c o s ()s i n ()22jjj eπππ-=-=- 522j jj eeππ==4c o s ()s i n ())144jjj πππ+=+9441j jj ππ=-9441j j j ππ--==-41jj π-=-1.2 055j=, 22j e π-=,233jj e π--=212je π--=, 41j j π+=, ()2221jj eπ-=-4(1)j je π-=, 411j je π+=-12e π-1.3. (a) E ∞=4014tdt e∞-=⎰, P ∞=0, because E ∞<∞ (b) (2)42()j t t x eπ+=, 2()1t x =.Therefore, E ∞=22()dt t x +∞-∞⎰=dt +∞-∞⎰=∞,P ∞=211limlim222()TTTTT T dt dt TTt x --→∞→∞==⎰⎰lim11T →∞=(c) 2()t x =cos(t). Therefore, E ∞=23()dt t x +∞-∞⎰=2cos()dt t +∞-∞⎰=∞, P ∞=2111(2)1lim lim 2222cos()TTTTT T COS t dt dt T Tt --→∞→∞+==⎰⎰(d)1[][]12nn u n x =⎛⎫ ⎪⎝⎭,2[]11[]4nu n n x =⎛⎫ ⎪⎝⎭. Therefore, E ∞=24131[]4nn n x +∞∞-∞===⎛⎫∑∑ ⎪⎝⎭P ∞=0,because E ∞<∞.(e) 2[]n x =()28n j e ππ-+,22[]n x =1. therefore, E ∞=22[]n x +∞-∞∑=∞,P ∞=211limlim1122121[]NNN N n Nn NN N n x →∞→∞=-=-==++∑∑.(f) 3[]n x =cos 4nπ⎛⎫ ⎪⎝⎭. Therefore, E ∞=23[]n x +∞-∞∑=2cos()4n π+∞-∞∑=2cos()4n π+∞-∞∑,P ∞=1limcos 214nNN n NN π→∞=-=+⎛⎫∑ ⎪⎝⎭1cos()112lim ()2122NN n Nn N π→∞=-+=+∑ 1.4. (a) The signal x[n] is shifted by 3 to the right. The shifted signal will be zero for n<1, And n>7. (b) The signal x[n] is shifted by 4 to the left. The shifted signal will be zero for n<-6. And n>0. (c) The signal x[n] is flipped signal will be zero for n<-1 and n>2.(d) The signal x[n] is flipped and the flipped signal is shifted by 2 to the right. The new Signal will be zero for n<-2 and n>4.(e) The signal x[n] is flipped and the flipped and the flipped signal is shifted by 2 to the left. This new signal will be zero for n<-6 and n>0.1.5. (a) x(1-t) is obtained by flipping x(t) and shifting the flipped signal by 1 to the right. Therefore, x (1-t) will be zero for t>-2. (b) From (a), we know that x(1-t) is zero for t>-2. Similarly, x(2-t) is zero for t>-1, Therefore, x (1-t) +x(2-t) will be zero for t>-2. (c) x(3t) is obtained by linearly compression x(t) by a factor of3. Therefore, x(3t) will be zero for t<1.(d) x(t/3) is obtained by linearly compression x(t) by a factor of 3. Therefore, x(3t) will bezero for t<9.1.6(a) x1(t) is not periodic because it is zero for t<0.(b) x2[n]=1 for all n. Therefore, it is periodic with a fundamental period of 1.(c) x3[n1.7. (a)()1[]vnxε={}1111[][]([][4][][4])22n n u n u n u n u nx x+-=--+----Therefore, ()1[]vnxεis zero for1[]nx>3.(b) Since x1(t) is an odd signal, ()2[]vnxεis zero for all values of t.(c)(){}11311[][][][3][3]221122vn nn n n u n u nx x xε-⎡⎤⎢⎥=+-=----⎢⎥⎢⎥⎣⎦⎛⎫⎛⎫⎪ ⎪⎝⎭⎝⎭Therefore, ()3[]vnxεis zero when n<3 and when n→∞.(d) ()1554411()(()())(2)(2)22vt tt t t u t u tx x x e eε-⎡⎤=+-=---+⎣⎦Therefore, ()4()vtxεis zero only when t→∞.1.8. (a) ()01{()}22cos(0)tt tx eπℜ=-=+(b) ()02{()}cos()cos(32)cos(3)cos(30)4tt t t tx eππℜ=+==+(c) ()3{()}sin(3)sin(3)2t tt t tx e eππ--ℜ=+=+(d) ()224{()}sin(100)sin(100)cos(100)2t t tt t t tx e e eππ---ℜ=-=+=+1.9. (a)1()tx is a periodic complex exponential.101021()j t j tt jx e eπ⎛⎫+⎪⎝⎭==(b)2()tx is a complex exponential multiplied by a decaying exponential. Therefore,2()tx is not periodic.(c)3[]nx is a periodic signal. 3[]n x=7j neπ=j neπ.3[]nx is a complex exponential with a fundamental period of 22ππ=.(d)4[]nx is a periodic signal. The fundamental period is given by N=m(23/5ππ)=10().3mBy choosing m=3. We obtain the fundamental period to be 10.(e)5[]nx is not periodic. 5[]nx is a complex exponential with 0w=3/5. We cannot find any integer m such that m(2wπ) is also an integer. Therefore,5[]nxis not periodic.1.10. x(t)=2cos(10t+1)-sin(4t-1)Period of first term in the RHS =2105ππ=.Period of first term in the RHS =242ππ=.Therefore, the overall signal is periodic with a period which the least commonmultiple of the periods of the first and second terms. This is equal toπ.1.11. x[n] = 1+74j n e π−25j n e πPeriod of first term in the RHS =1. Period of second term in the RHS =⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛7/42π=7 (when m=2)Period of second term in the RHS =⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛5/22ππ=5 (when m=1)Therefore, the overall signal x[n] is periodic with a period which is the least common Multiple of the periods of the three terms inn x[n].This is equal to 35.1.12. The signal x[n] is as shown in figure S1.12. x[n] can be obtained by flipping u[n] and thenShifting the flipped signal by 3 to the right. Therefore, x[n]=u[-n+3]. This implies that M=-1 and no=-3.1.13y (t)=⎰∞-tdt x )(τ =dt t))2()2((--+⎰∞-τδτδ=⎪⎩⎪⎨⎧>≤≤--<2,022,12,0,t t tTherefore ⎰-==∞224d t E∑∑∞-∞=∞-∞=----=k k k t k t t g 12(3)2(3)(δδ)This implies that A 1=3, t 1=0, A 2=-3, and t 2=1.1.15 (a) The signal x 2[n], which is the input to S 2, is the same as y 1[n].Therefore ,y 2[n]= x 2[n-2]+21x 2[n-3] = y 1[n-2]+ 21y 1[n-3]=2x 1[n-2] +4x 1[n-3] +21( 2x 1[n-3]+ 4x 1[n-4]) =2x 1[n-2]+ 5x 1[n-3] + 2x 1[n-4] The input-output relationship for S isy[n]=2x[n-2]+ 5x [n-3] + 2x [n-4](b) The input-output relationship does not change if the order in which S 1and S 2 are connected series reversed. . We can easily prove this assuming that S 1 follows S 2. In this case , the signal x 1[n], which is the input to S 1 is the same as y 2[n].Therefore y 1[n] =2x 1[n]+ 4x 1[n-1]= 2y 2[n]+4 y 2[n-1]=2( x 2[n-2]+21 x 2[n-3] )+4(x 2[n-3]+21x 2[n-4]) =2 x 2[n-2]+5x 2[n-3]+ 2 x 2[n-4]The input-output relationship for S is once againy[n]=2x[n-2]+ 5x [n-3] + 2x [n-4]1.16 (a)The system is not memory less because y[n] depends on past values of x[n].(b)The output of the system will be y[n]= ]2[][-n n δδ=0(c)From the result of part (b), we may conclude that the system output is always zero for inputs of the form ][k n -δ, k ∈ ґ. Therefore , the system is not invertible .1.17 (a) The system is not causal because the output y(t) at some time may depend on future values of x(t). For instance , y(-π)=x(0).(b) Consider two arbitrary inputs x 1(t)and x 2(t).x 1(t) →y 1(t)= x 1(sin(t)) x 2(t) → y 2(t)= x 2(sin(t))Let x 3(t) be a linear combination of x 1(t) and x 2(t).That is , x 3(t)=a x 1(t)+b x 2(t)Where a and b are arbitrary scalars .If x 3(t) is the input to the given system ,then the corresponding output y 3(t) is y 3(t)= x 3( sin(t))=a x 1(sin(t))+ x 2(sin(t)) =a y 1(t)+ by 2(t)Therefore , the system is linear.1.18.(a) Consider two arbitrary inputs x 1[n]and x 2[n].x 1[n] → y 1[n] =][01k x n n n n k ∑+-=x 2[n ] → y 2[n] =][02k x n n n n k ∑+-=Let x 3[n] be a linear combination of x 1[n] and x 2[n]. That is :x 3[n]= ax 1[n]+b x 2[n]where a and b are arbitrary scalars. If x 3[n] is the input to the given system, then the corresponding outputy 3[n] is y 3[n]=][03k x n n n n k ∑+-==])[][(2100k bx k ax n n n n k +∑+-==a ][001k x n n n n k ∑+-=+b ][02k x n n n n k ∑+-== ay 1[n]+b y 2[n]Therefore the system is linear.(b) Consider an arbitrary input x 1[n].Lety 1[n] =][01k x n n n n k ∑+-=be the corresponding output .Consider a second input x 2[n] obtained by shifting x 1[n] in time:x 2[n]= x 1[n-n 1]The output corresponding to this input isy 2[n]=][02k x n n n n k ∑+-== ]n [1100-∑+-=k x n n n n k = ][01011k x n n n n n n k ∑+---=Also note that y 1[n- n 1]=][01011k x n n n n n n k ∑+---=.Therefore , y 2[n]= y 1[n- n 1] This implies that the system is time-invariant.(c) If ][n x <B, then y[n]≤(2 n 0+1)B. Therefore ,C ≤(2 n 0+1)B.1.19 (a) (i) Consider two arbitrary inputs x 1(t) and x 2(t). x 1(t) → y 1(t)= t 2x 1(t-1)x 2(t) → y 2(t)= t 2x 2(t-1)Let x 3(t) be a linear combination of x 1(t) and x 2(t).That is x 3(t)=a x 1(t)+b x 2(t)where a and b are arbitrary scalars. If x 3(t) is the input to the given system, then the corresponding output y 3(t) is y 3(t)= t 2x 3 (t-1)= t 2(ax 1(t-1)+b x 2(t-1))= ay 1(t)+b y 2(t)Therefore , the system is linear.(ii) Consider an arbitrary inputs x 1(t).Let y 1(t)= t 2x 1(t-1)be the corresponding output .Consider a second input x 2(t) obtained by shifting x 1(t) in time:x 2(t)= x 1(t-t 0)The output corresponding to this input is y 2(t)= t 2x 2(t-1)= t 2x 1(t- 1- t 0)Also note that y 1(t-t 0)= (t-t 0)2x 1(t- 1- t 0)≠ y 2(t) Therefore the system is not time-invariant.(b) (i) Consider two arbitrary inputs x 1[n]and x 2[n]. x 1[n] → y 1[n] = x 12[n-2]x 2[n ] → y 2[n] = x 22[n-2].Let x 3(t) be a linear combination of x 1[n]and x 2[n].That is x 3[n]= ax 1[n]+b x 2[n]where a and b are arbitrary scalars. If x 3[n] is the input to the given system, then the corresponding output y 3[n] is y 3[n] = x 32[n-2]=(a x 1[n-2] +b x 2[n-2])2=a 2x 12[n-2]+b 2x 22[n-2]+2ab x 1[n-2] x 2[n-2]≠ ay 1[n]+b y 2[n]Therefore the system is not linear.(ii) Consider an arbitrary input x 1[n]. Let y 1[n] = x 12[n-2]be the corresponding output .Consider a second input x 2[n] obtained by shifting x 1[n] in time:x 2[n]= x 1[n- n 0]The output corresponding to this input isy 2[n] = x 22[n-2].= x 12[n-2- n 0]Also note that y 1[n- n 0]= x 12[n-2- n 0] Therefore , y 2[n]= y 1[n- n 0] This implies that the system is time-invariant.(c) (i) Consider two arbitrary inputs x 1[n]and x 2[n].x 1[n] →y 1[n] = x 1[n+1]- x 1[n-1] x 2[n ]→y 2[n] = x 2[n+1 ]- x 2[n -1]Let x 3[n] be a linear combination of x 1[n] and x 2[n]. That is :x 3[n]= ax 1[n]+b x 2[n]where a and b are arbitrary scalars. If x 3[n] is the input to the given system, then the corresponding output y 3[n] is y 3[n]= x 3[n+1]- x 3[n-1]=a x 1[n+1]+b x 2[n +1]-a x 1[n-1]-b x 2[n -1]=a(x 1[n+1]- x 1[n-1])+b(x 2[n +1]- x 2[n -1])= ay 1[n]+b y 2[n]Therefore the system is linear.(ii) Consider an arbitrary input x 1[n].Let y 1[n]= x 1[n+1]- x 1[n-1]be the corresponding output .Consider a second input x 2[n] obtained by shifting x 1[n] in time: x 2[n]= x 1[n-n 0]The output corresponding to this input isy 2[n]= x 2[n +1]- x 2[n -1]= x 1[n+1- n 0]- x 1[n-1- n 0] Also note that y 1[n-n 0]= x 1[n+1- n 0]- x 1[n-1- n 0] Therefore , y 2[n]= y 1[n-n 0] This implies that the system is time-invariant.(d) (i) Consider two arbitrary inputs x 1(t) and x 2(t).x 1(t) → y 1(t)= d O {}(t) x 1 x 2(t) → y 2(t)= {}(t) x 2d OLet x 3(t) be a linear combination of x 1(t) and x 2(t).That is x 3(t)=a x 1(t)+b x 2(t)where a and b are arbitrary scalars. If x 3(t) is the input to the given system, then the corresponding output y 3(t) is y 3(t)= d O {}(t) x 3={}(t) x b +(t) ax 21d O=a d O {}(t) x 1+b {}(t) x 2d O = ay 1(t)+b y 2(t)Therefore the system is linear.(ii) Consider an arbitrary inputs x 1(t).Lety 1(t)= d O {}(t) x 1=2)(x -(t) x 11t -be the corresponding output .Consider a second input x 2(t) obtained by shifting x 1(t) in time:x 2(t)= x 1(t-t 0)The output corresponding to this input isy 2(t)= {}(t) x 2d O =2)(x -(t) x 22t -=2)(x -)t -(t x 0101t t --Also note that y 1(t-t 0)= 2)(x -)t -(t x 0101t t --≠ y 2(t)Therefore the system is not time-invariant.1.20 (a) Givenx )(t =jt e 2 y(t)=t j e 3x )(t =jt e 2- y(t)=t j e 3- Since the system liner+=tj e t x 21(2/1)(jt e 2-))(1t y =1/2(tj e 3+tj e 3-)Thereforex 1(t)=cos(2t))(1t y =cos(3t)(b) we know thatx 2(t)=cos(2(t-1/2))= (j e -jte 2+je jt e 2-)/2Using the linearity property, we may once again writex 1(t)=21( j e -jt e 2+j e jte 2-))(1t y =(j e -jt e 3+je jte 3-)= cos(3t-1)Therefore,x 1(t)=cos(2(t-1/2)))(1t y =cos(3t-1)1.21.The signals are sketched in figure S1.21.1.24 The even and odd parts are sketched in Figure S1.24 1.25 (a) periodic period=2π/(4)= π/2 (b) periodic period=2π/(4)= 2(c) x(t)=[1+cos(4t-2π/3)]/2. periodic period=2π/(4)= π/2 (d) x(t)=cos(4πt)/2. periodic period=2π/(4)= 1/2 (e) x(t)=[sin(4πt)u(t)-sin(4πt)u(-t)]/2. Not period. (f) Not period.1.26 (a) periodic, period=7.(b) Not period.(c) periodic, period=8.(d) x[n]=(1/2)[cos(3πn/4+cos(πn/4)). periodic, period=8. (e) periodic, period=16. 1.27 (a) Linear, stable(b) Not period. (c) Linear(d) Linear, causal, stable(e) Time invariant, linear, causal, stable (f) Linear, stable(g) Time invariant, linear, causal 1.28 (a) Linear, stable(b) Time invariant, linear, causal, stable (c)Memoryless, linear, causal (d) Linear, stable (e) Linear, stable(f) Memoryless, linear, causal, stable (g) Linear, stable1.29 (a) Consider two inputs to the system such that[][][]{}111.S e x n y n x n −−→=ℜand [][][]{}221.Se x n y n x n −−→=ℜNow consider a third inputx3[n]=x2[n]+x 1[n]. The corresponding system outputWill be [][]{}[][]{}[]{}[]{}[][]33121212e e e e y n x n x n x n x n x n y n y n ==+=+=+ℜℜℜℜtherefore, we may conclude that the system is additive Let us now assume that inputs to the system such that [][][]{}/4111.Sj e x n y n e x n π−−→=ℜand[][][]{}/4222.Sj e x n y n e x n π−−→=ℜNow consider a third input x 3 [n]= x 2 [n]+ x 1 [n]. The corresponding system outputWill be[][]{}()[]{}()[]{}()[]{}()[]{}()[]{}()[]{}[]{}[]{}[][]/433331122/4/41212cos /4sin /4cos /4sin /4cos /4sin /4j e m e m e m e j j e e y n e x n n x n n x n n x n n x n n x n n x n e x n e x n y n y n πππππππππ==-+-+-=+=+ℜℜI ℜI ℜI ℜℜ therefore, we may conclude that the system is additive (b) (i) Consider two inputs to the system such that()()()()211111Sdx t x t y t x t dt ⎡⎤−−→=⎢⎥⎣⎦and ()()()()222211S dx t x t y t x t dt ⎡⎤−−→=⎢⎥⎣⎦ Now consider a third input x3[t]=x2[t]+x 1[t]. The corresponding system outputWill be()()()()()()()()()2333211111211dx t y t x t dt d x t x t x t x t dt y t y t ⎡⎤=⎢⎥⎣⎦⎡⎤+⎡⎤⎣⎦=⎢⎥+⎢⎥⎣⎦≠+ therefore, we may conclude that the system is not additiveNow consider a third input x 4 [t]= a x 1 [t]. The corresponding system output Will be()()()()()()()()2444211211111dx t y t x t dt d ax t ax t dt dx t a x t dt ay t ⎡⎤=⎢⎥⎣⎦⎡⎤⎡⎤⎣⎦=⎢⎥⎢⎥⎣⎦⎡⎤=⎢⎥⎣⎦=Therefore, the system is homogeneous.(ii) This system is not additive. Consider the fowling example .Let δ[n]=2δ[n+2]+2δ[n+1]+2δ[n] andx2[n]=δ[n+1]+ 2δ[n+1]+ 3δ[n]. The corresponding outputs evaluated at n=0 are [][]120203/2y andy ==Now consider a third input x 3 [n]= x 2 [n]+ x 1 [n].= 3δ[n+2]+4δ[n+1]+5δ[n]The corresponding outputs evaluated at n=0 is y 3[0]=15/4. Gnarly, y 3[0]≠ ]0[][21y y n +.This[][][][][]444442,1010,x n x n x n y n x n otherwise ⎧--≠⎪=-⎨⎪⎩[][][][][][]4445442,1010,x n x n ax n y n ay n x n otherwise ⎧--≠⎪==-⎨⎪⎩Therefore, the system is homogenous.1.30 (a) Invertible. Inverse system y(t)=x(t+4)(b)Non invertible. The signals x(t) and x 1(t)=x(t)+2πgive the same output (c) δ[n] and 2δ[n] give the same output d) Invertible. Inverse system; y(t)=dx(t)/dt(e) Invertible. Inverse system y(n)=x(n+1) for n ≥0 and y[n]=x[n] for n<0 (f) Non invertible. x (n) and –x(n) give the same result (g)Invertible. Inverse system y(n)=x(1-n) (h) Invertible. Inverse system y(t)=dx(t)/dt(i) Invertible. Inverse system y(n) = x(n)-(1/2)x[n-1] (j) Non invertible. If x(t) is any constant, then y(t)=0 (k) δ[n] and 2δ[n] result in y[n]=0 (l) Invertible. Inverse system: y(t)=x(t/2)(m) Non invertible x 1 [n]= δ[n]+ δ[n-1]and x 2 [n]= δ[n] give y[n]= δ[n] (n) Invertible. Inverse system: y[n]=x[2n]1.31 (a) Note that x 2[t]= x 1 [t]- x 1 [t-2]. Therefore, using linearity we get y 2 (t)= y 1 (t)- y 1 (t-2).this is shown in Figure S1.31(b)Note that x3 (t)= x1 [t]+ x1 [t+1]. .Therefore, using linearity we get Y3 (t)= y1 (t)+ y1 (t+2). this is2(4) y 2(t) periodic, period T; x(t) periodic, period T/2;1.33(1) True x[n]=x[n+N ]; y 1 (n)= y 1 (n+ N 0)i.e. periodic with N 0=n/2if N is even and with period N 0=n if N is odd.(2)False. y 1 [n] periodic does no imply x[n] is periodic i.e. Let x[n] = g[n]+h[n] where0,1,[][]0,(1/2),nn even n even g n and h n n odd n odd⎧⎧==⎨⎨⎩⎩ Then y 1 [n] = x [2n] is periodic but x[n] is clearly not periodic. (3)True. x [n+N] =x[n]; y 2 [n+N 0] =y 2 [n] where N 0=2N (4) True. y 2 [n+N] =y 2 [n]; y 2 [n+N 0 ]=y 2 [n] where N 0=N/2 1.34. (a) ConsiderIf x[n] is odd, x[n] +x [-n] =0. Therefore, the given summation evaluates to zero. (b) Let y[n] =x 1[n]x 2[n] .Theny [-n] =x 1[-n] x 2[-n] =-x 1[n]x 2[n] =-y[n]. This implies that y[n] is odd.(c)ConsiderUsing the result of part (b), we know that x e [n]x o [n] is an odd signal .Therefore, using the result of part (a) we may conclude thatTherefore,(d)ConsiderAgain, since x e (t) x o (t) is odd,Therefore,1.35. We want to find the smallest N 0 such that m(2π /N) N 0 =2πk or N 0 =kN/m,{}1[][0][][]n n x n x x n x n ∞∞=-∞==++-∑∑22[][]e o n n n n x x ∞∞=-∞=-∞=+∑∑222[][][]e on n n n n n x x x∞∞∞=-∞=-∞=-∞==+∑∑∑2[][]0eon n n x x ∞=-∞=∑222[][][].e on n n n n n xx x ∞∞∞=-∞=-∞=-∞==+∑∑∑2220()()()2()().eoet dt t dt t dt t t dt x x x x x ∞∞∞∞-∞-∞-∞-∞=++⎰⎰⎰⎰0()()0.et t dt x x ∞-∞=⎰222()()().e ot dt t dt t dt xx x ∞∞∞-∞-∞-∞=+⎰⎰⎰()()()()()().xy yx t x t y d y t x d t φττττττφ∞-∞∞-∞=+=-+=-⎰⎰where k is an integer, then N must be a multiple of m/k and m/k must be an integer .this implies that m/k is a divisor of both m and N .Also, if we want the smallest possible N 0, then m/k should be the GCD of m and N. Therefore, N 0=N/gcd(m,N). 1.36.(a)If x[n] is periodic0(),0..2/j n N T o e where T ωωπ+= This implies that022o T kNT k T T Nππ=⇒==a rational number . (b)T/T 0 =p/q then x[n] =2(/)j n p q e π,The fundamental period is q/gcd(p,q) and the fundmental frequencyis(c) p/gcd(p,q) periods of x(t) are needed .1.37.(a) From the definition of ().xy t φWe havepart(a) that()().xx xx t t φφ=-This implies that()xy t φis(b) Note from even .Therefore,the odd part of().xx t φis zero.(c) Here, ()().xy xx t t T φφ=-and ()().yy xx t t φφ= 1.38.(a) We know that /22(2)().t t δδ=ThereforeThis implies that1(2)().2t t δδ=(b)The plot are as shown in Figure s3.18. 1.39 We havelim ()()lim (0)()0.u t t u t δδ→→==Also,0022gcd(,)gcd(,)gcd(,)gcd(,).T pp q p q p q p q q p q p pωωππ===/21lim (2)lim ().2t t δδ→∞→∞=01lim ()()().2u t t t δδ→=u Δ'(t ) 1 1/2Δ/2-Δ/2t 0tu Δ'(t )12Δ t 0tu Δ'(t ) 1 1/2Δ-Δttu Δ'(t )1 1/2Δ-Δt 0t⎰⎰∞∞∞--=-=0)()()()()(ττδτττδτd t u d t u t gTherefore,0,0()1,00t g t t undefined for t >⎧⎪=<⎨⎪=⎩()0()()()t u t t δττδτδτ-=-=-1.40.(a) If a system is additive ,then also, if a system is homogeneous,then(b) y(t)=x 2(t) is such a systerm . (c) No.For example,consider y(t) ()()ty t x d ττ-∞=⎰with ()()(1).x t u t u t =--Then x(t)=0for t>1,but y(t)=1 for t>1.1.41. (a) y[n]=2x[n].Therefore, the system is time invariant.(b) y[n]=(2n-1)x[n].This is not time-invariant because y[n- N 0]≠(2n-1)2x [n- N 0]. (c) y[n]=x[n]{1+(-1)n +1+(-1)n-1}=2x[n].Therefore, the system is time invariant .1.42.(a) Consider two system S 1 and S 2 connected in series .Assume that if x 1(t) and x 2(t) arethe inputs to S 1..then y 1(t) and y 2(t) are the outputs.respectively .Also,assume thatif y 1(t) and y 2(t) are the input to S 2 ,then z 1(t) and z 2(t) are the outputs, respectively . Since S 1 is linear ,we may write()()()()11212,s ax t bx t ay t by t +→+where a and b are constants. Since S 2 is also linear ,we may write()()()()21212,s ay t by t az t bz t +→+We may therefore conclude that)()()()(212121t b t a t b t a z z x x s s +−→−+Therefore ,the series combination of S 1 and S 2 is linear. Since S 1 is time invariant, we may write()()11010s x t T y t T -→-and()()21010s y t T z t T -→-Therefore,()()121010s s x t T z t T -→-Therefore, the series combination of S 1 and S 2 is time invariant.(b) False, Let y(t)=x(t)+1 and z(t)=y(t)-1.These corresponds to two nonlinear systems. If these systems are connected in series ,then z(t)=x(t) which is a linear system.00.()().00x t y t =→=0()()()()0x t x t y t y t =-→-=(c) Let us name the output of system 1 as w[n] and the output of system 2 as z[n] .Then11[][2][2][21][22]24y n z n w n w n w n ==+-+-[][][]241121-+-+=n x n x n xThe overall system is linear and time-invariant.1.43. (a) We have())(t y t x s−→−Since S is time-invariant.())(T t y T t x s-−→−-Now if x (t) is periodic with period T. x{t}=x(t-T). Therefore, we may conclude that y(t)=y(t-T).This impliesthat y(t) is also periodic with T .A similar argument may be made in discrete time . (b)1.44 (a) Assumption : If x(t)=0 for t<t 0 ,then y(t)=0 for t< t 0.To prove That : The system is causal.Let us consider an arbitrary signal x 1(t) .Let us consider another signal x 2(t) which is the same as x 1(t)fort< t 0. But for t> t 0 , x 2(t) ≠x 1(t),Since the system is linear,()()()()1212,x t x t y t y t -→-Since ()()120x t x t -=for t< t 0 ,by our assumption =()()120y t y t -=for t< t 0 .This implies that()()12y t y t =for t< t 0 . In other words, t he output is not affected by input values for 0t t ≥. Therefore, thesystem is causal .Assumption: the system is causal . To prove that :If x(t)=0 for t< t 0 .then y(t)=0 for t< t 0 .Let us assume that the signal x(t)=0 for t< t 0 .Then we may express x(t) as ()()12()x t x t x t =-, Where()()12x t x t = for t< t 0 . the system is linear .the output to x(t) will be()()12()y t y t y t =-.Now ,since the system is causal . ()()12y t y t = for t< t 0 .implies that()()12y t y t = for t< t 0 .Therefore y(t)=0 for t< t 0 .(b) Consider y(t)=x(t)x(t+1) .Now , x(t)=0 for t< t 0 implies that y(t)=0 for t< t 0 .Note that the system is nonlinear and non-causal .(c) Consider y(t)=x(t)+1. the system is nonlinear and causal .This does not satisfy the condition of part(a). (d) Assumption: the system is invertible. To prove that :y[n]=0 for all n only if x[n]=0 for all n . Consider[]0[]x n y n =→. Since the system is linear :2[]02[]x n y n =→.Since the input has not changed in the two above equations ,we require that y[n]= 2y[n].This implies that y[n]=0. Since we have assumed that the system is invertible , only one input could have led to this particular output .That input must be x[n]=0 .Assumption: y[n]=0 for all n if x[n]=0 for all n . To prove that : The system is invertible . Suppose that11[][]x n y n → and21[][]x n y n →Since the system is linear ,1212[][][][]0x n x n y n y n -=→-=By the original assumption ,we must conclude that 12[][]x n x n =.That is ,any particular y 1[n] can be produced that by only one distinct input x 1[n] .Therefore , the system is invertible. (e) y[n]=x 2[n]. 1.45. (a) Consider ,()111()()shx x t y t t φ→= and()222()()shx x t y t t φ→=.Now, consider ()()()312x t ax t bx t =+. The corresponding system output will be()()12331212()()()()()()()()()hx hx y t x h t d a x h t d b x t h t d a t b t ay t by t ττττττττφφ∞-∞∞∞-∞-∞=+=+++=+=+⎰⎰⎰Therefore, S is linear .Now ,consider x 4(t)=x 1(t-T).The corresponding system output will be()14411()()()()()()()hx y t x h t d x T h t d x h t T d t T τττττττττφ∞-∞∞-∞∞-∞=+=-+=++=+⎰⎰⎰Clearly, y 4(t)≠ y 1(t-T).Therefore ,the system is not time-invariant.The system is definitely not causal because the output at any time depends on future values of the input signal x(t).(b) The system will then be linear ,time invariant and non-causal. 1.46. The plots are in Figure S1.46.1.47.(a) The overall response of the system of Figure P1.47.(a)=(the response of the system to x[n]+x 1[n])-the response of the system to x 1[n]=(Response of a linear system L to x[n]+x 1[n]+zero input response of S)- (Response of a linear system L to x 1[n]+zero input response of S)=( (Response of a linear system L to x[n]).Chapter 2 answers2.1 (a) We have know that 1[]*[][][]k y x n h n h k x n k ∞=-∞==-∑1[][1][1][1][1]y n h x n h x n =-++-2[1]2[1]x n x n =++-This gives1[]2[1]4[]2[1]2[2]2[4]y n n n n n n δδδδδ=+++-+--- (b)We know that2[][2]*[][][2]k y n x n h n h k x n k ∞=-∞=+=+-∑Comparing with eq.(S2.1-1),we see that21[][2]y n y n =+(c) We may rewrite eq.(S2.1-1) as1[][]*[][][]k y n x n h n x k h n k ∞=-∞==-∑Similarly, we may write3[][]*[2][][2]k y n x n h n x k h n k ∞=-∞=+=+-∑Comparing this with eq.(S2.1),we see that31[][2]y n y n =+2.2 Using given definition for the signal h[n], we may write{}11[][3][10]2k h k u k u k -⎛⎫=+-- ⎪⎝⎭The signal h[k] is non zero only in the rang 1[][2]h n h n =+. From this we know that the signal h[-k] is non zero only in the rage 93k -≤≤.If we now shift the signal h[-k] by n to the right, then the resultant signal h[n-k] will be zero in the range (9)(3)n k n -≤≤+. Therefore ,9,A n =- 3B n =+ 2.3 Let us define the signals11[][]2nx n u n ⎛⎫= ⎪⎝⎭and1[][]h n u n =. We note that1[][2]x n x n =- and 1[][2]h n h n =+ Now,。
第二章第二章 课后题答案课后题答案2-1.1.图题2-1所示电路,求响应u 2(t)对激励f(t)的转移算子H(p)及微分方程。
解 其对应的算子电路模型如图题2.1(b )所示,故对节点①,②可列出算子形式的KCL 方程为= +++−=−+0)(111)(1)()(1)(1312121t u p p t u p t f t u p t u p即()=+++−=−+0)(1)()()()(13122121t u p p t u t pf t u t u p联解得)()()(443)(22t f p H t f p p t u =++=故得转移算子为443)()()22++==p p t f t u p H (u 2(t)对f(t)的微分方程为())()(t f t u p p 34422=++即)(t f t u t u dt d t u dt d 3)(4)(4)(22222=++2-2图题2-2所示电路,求响应i(t)对激励f(t)的转移算子H(p)及微分方程。
解 其对应的算子电路模型如图2.2(b)所示。
故得)()(t f p p p p pp t f t i 3011101022221.01)(2+++=+×++=故得转移算子为30111010)()()(2+++==p p p t f t i p Hi(t)对f(t)的微分方程为)()1010()()3011(2t f p t i p p +=++即)(10)(10)(30)(11)(22t f t f dt d t i t i dt d t i dt d +=++2-3图题2-3所示电路,已知u C (0-)=1 V, i(0-)=2 A。
求t>0时的零输入响应i(t)和u C (t)。
解 其对应的算子电路模型如图题2.3(b)所示。
故对节点N 可列写出算子形式的KCL 方程为0)(2312= ++t u p p C又有uc(t)=pi(t),代入上式化简,即得电路的微分方程为=====++−+−+1)0()0(2)0()0(0)()23(2c cu u i i t i p p电路的特征方程为0232=++p p故得特征根(即电路的自然频率)为p 1=-1,p 2=-2。
第1章信号与系统1.1复习笔记1,连续时间和离散时间信号1个连续时间信号和离散时间信号(1)连续时间信号(图1-1(a))①定义连续时间信号是指自变量是连续变量的信号,并且该信号是在自变量的连续值上定义的。
②代表自变量由T表示,表示连续时间。
连续时间信号表示为X(T)。
(2)离散时间信号(图1-1(b))①定义离散时间信号的自变量仅在一组离散值中选择,并且仅在离散时间点定义信号。
②代表自变量由N表示,N表示离散时间。
离散时间信号表示为x [n]。
说明:hwocrtemp_ ROC60图1-1信号的图形表示(a)连续的时间表示;(b)离散时间信号2.信号能量和功率(1)有限间隔内信号的总能量和功率①描述中的连续时间信号x(T):hwocrtemp_ roc120中的总能量说明:hwocrtemp_ ROC130哪里x |是X的模块(可能是复数)。
通过将上述公式除以长度t2-t1,可以获得平均功率。
②描述中的离散时间信号x [n]:hwocrtemp_ roc140中的总能量说明:hwocrtemp_ ROC150将其除以interval_中的点数即可。
Roc160获得该范围内的平均功率。
(2)无限间隔内信号的总能量和功率①无限时间连续时间信号的总能量x(T)说明:hwocrtemp_ ROC180无限时间连续时间信号x(T)的平均功率说明:hwocrtemp_ ROC220②无限时间中离散时间信号x [n]的总能量说明:hwocrtemp_ ROC190无限时间间隔内离散时间信号x [n]的平均功率说明:hwocrtemp_ ROC230(3)根据信号能量和功率的限制进行分类①该信号的总能量有限,即:hwocrtemp_ Roc240,该信号的平均功率为零。
②如果平均功率P∞是有限的,则其能量是无限的。
③具有无限大的P∞和E∞的信号。
2,自变量的变换基本转型(1)时移①X(t-t0)表示具有延迟|的X(T)。
Signals & Systems(Second Edition)—Learning Instructions(Exercises Answers) Department of Computer Engineering2005.12ContentsChapter 1 (2)Chapter 2 (17)Chapter 3 (53)Chapter 4 (80)Chapter 5 (101)Chapter 6 (127)Chapter 7 (137)Chapter 8 (150)Chapter 9 (158)Chapter 10 (178)Chapter 1 Answers1.1 Converting from polar to Cartesian coordinates:111cos 222j e ππ==-111c o s ()222j e ππ-=-=- 2cos()sin()22jj j eπππ=+=2c o s ()s i n ()22jjj eπππ-=-=- 522j jj eeππ==4c o s ()s i n ())144jjj πππ+=+9441j jj ππ=-91j jj ππ--=-41jj π-=-1.2 055j=, 22j e π-=,233jj e π--=212je π--=, 41j j π+=, ()2221jj eπ-=-4(1)j j eπ-=, 411j je π+=-12e π-=1.3. (a) E ∞=4014tdt e∞-=⎰, P ∞=0, because E ∞<∞ (b) (2)42()j t t x e π+=, 2()1t x =.Therefore, E ∞=22()dt t x +∞-∞⎰=dt +∞-∞⎰=∞,P ∞=211lim lim 222()TTT TT T dt dt T Tt x --→∞→∞==⎰⎰lim11T →∞= (c) 2()t x =cos(t). Therefore, E ∞=23()dt t x +∞-∞⎰=2cos()dt t +∞-∞⎰=∞,P ∞=2111(2)1lim lim 2222cos()TTTTT T COS t dt dt T T t --→∞→∞+==⎰⎰(d) 1[][]12nn u n x =⎛⎫ ⎪⎝⎭, 2[]11[]4nu n n x =⎛⎫ ⎪⎝⎭. Therefore, E ∞=204131[]4nn n x +∞∞-∞===⎛⎫∑∑ ⎪⎝⎭P ∞=0,because E ∞<∞.(e) 2[]n x =()28n j e ππ-+, 22[]n x =1. therefore, E ∞=22[]n x +∞-∞∑=∞,P ∞=211limlim1122121[]NNN N n Nn NN N n x →∞→∞=-=-==++∑∑.(f). Therefore, E ∞=23[]n x +∞-∞∑=2cos()4n π+∞-∞∑=2cos()4n π+∞-∞∑,P ∞=1limcos 214nNN n NN π→∞=-=+⎛⎫∑ ⎪⎝⎭1cos()112lim ()2122NN n Nn N π→∞=-+=+∑ 1.4. (a) The signal x[n] is shifted by 3 to the right. The shifted signal will be zero for n<1, And n>7. (b) The signal x[n] is shifted by 4 to the left. The shifted signal will be zero for n<-6. And n>0. (c) The signal x[n] is flipped signal will be zero for n<-1 and n>2.(d) The signal x[n] is flipped and the flipped signal is shifted by 2 to the right. The new Signal will be zero for n<-2 and n>4.(e) The signal x[n] is flipped and the flipped and the flipped signal is shifted by 2 to the left. This new signal will be zero for n<-6 and n>0.1.5. (a) x(1-t) is obtained by flipping x(t) and shifting the flipped signal by 1 to the right. Therefore, x (1-t) will be zero for t>-2. (b) From (a), we know that x(1-t) is zero for t>-2. Similarly, x(2-t) is zero for t>-1, Therefore, x (1-t) +x(2-t) will be zero for t>-2. (c) x(3t) is obtained by linearly compression x(t) by a factor of3. Therefore, x(3t) will be zero for t<1.(d) x(t/3) is obtained by linearly compression x(t) by a factor of 3. Therefore, x(3t) will bezero for t<9.1.6(a) x1(t) is not periodic because it is zero for t<0.(b) x2[n]=1 for all n. Therefore, it is periodic with a fundamental period of 1.(c) x3[n1.7. (a)()1[]vnxε={}1111[][]([][4][][4])22n n u n u n u n u nx x+-=--+----Therefore, ()1[]vnxεis zero for1[]nx>3.(b) Since x1(t) is an odd signal, ()2[]vnxεis zero for all values of t.(c)(){}11311[][][][3][3]221122vn nn n n u n u nx x xε-⎡⎤⎢⎥=+-=----⎢⎥⎢⎥⎣⎦⎛⎫⎛⎫⎪ ⎪⎝⎭⎝⎭Therefore, ()3[]vnxεis zero when n<3 and when n→∞.(d) ()1554411()(()())(2)(2)22vt tt t t u t u tx x x e eε-⎡⎤=+-=---+⎣⎦Therefore, ()4()vtxεis zero only when t→∞.1.8. (a) ()01{()}22cos(0)tt tx eπℜ=-=+(b) ()02{()}cos()cos(32)cos(3)cos(30)4tt t t tx eππℜ=+==+(c) ()3{()}sin(3)sin(3)2t tt t tx e eππ--ℜ=+=+(d) ()224{()}sin(100)sin(100)cos(100)2t t tt t t tx e e eππ---ℜ=-=+=+1.9. (a)1()txis a periodic complex exponential.101021()j t j tt jx e eπ⎛⎫+⎪⎝⎭==(b)2()txis a complex exponential multiplied by a decaying exponential. Therefore,2()tx is not periodic.(c)3[]nx is a periodic signal. 3[]n x=7j neπ=j neπ.3[]nx is a complex exponential with a fundamental period of 22ππ=.(d)4[]nxis a periodic signal. The fundamental period is given by N=m(23/5ππ)=10().3mBy choosing m=3. We obtain the fundamental period to be 10.(e)5[]nxis not periodic.5[]nx is a complex exponential with 0w=3/5. We cannot find any integer m such that m(2wπ) is also an integer. Therefore, 5[]nxis not periodic.1.10. x(t)=2cos(10t+1)-sin(4t-1)Period of first term in the RHS =2105ππ=.Period of first term in the RHS =242ππ= .Therefore, the overall signal is periodic with a period which the least commonmultiple of the periods of the first and second terms. This is equal to π . 1.11.x[n] = 1+74j n e π−25j n ePeriod of first term in the RHS =1. Period of second term in the RHS =⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛7/42π=7 (when m=2)Period of second term in the RHS =⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛5/22ππ=5 (when m=1)Therefore, the overall signal x[n] is periodic with a period which is the least commonMultiple of the periods of the three terms inn x[n].This is equal to 35.1.12. The signal x[n] is as shown in figure S1.12. x[n] can be obtained by flipping u[n] and thenShifting the flipped signal by 3 to the right. Therefore, x[n]=u[-n+3]. This implies that M=-1 and no=-3.1.13y (t)=⎰∞-t dt x )(τ =dt t))2()2((--+⎰∞-τδτδ=⎪⎩⎪⎨⎧>≤≤-2,022,1,t t Therefore ⎰-==∞224dt E∑∑∞-∞=∞-∞=----=k k k t k t t g 12(3)2(3)(δδ)This implies that A 1=3, t 1=0, A 2=-3, and t 2=1.1.15 (a) The signal x 2[n], which is the input to S 2, is the same as y 1[n].Therefore ,y 2[n]= x 2[n-2]+21x 2[n-3] = y 1[n-2]+ 21y 1[n-3]=2x 1[n-2] +4x 1[n-3] +21( 2x 1[n-3]+ 4x 1[n-4]) =2x 1[n-2]+ 5x 1[n-3] + 2x 1[n-4] The input-output relationship for S isy[n]=2x[n-2]+ 5x [n-3] + 2x [n-4](b) The input-output relationship does not change if the order in which S 1and S 2 are connected series reversed. . We can easily prove this assuming that S 1 follows S 2. In this case , the signal x 1[n], which is the input to S 1 is the same as y 2[n].Therefore y 1[n] =2x 1[n]+ 4x 1[n-1]= 2y 2[n]+4 y 2[n-1]=2( x 2[n-2]+21 x 2[n-3] )+4(x 2[n-3]+21x 2[n-4]) =2 x 2[n-2]+5x 2[n-3]+ 2 x 2[n-4]The input-output relationship for S is once againy[n]=2x[n-2]+ 5x [n-3] + 2x [n-4]1.16 (a)The system is not memory less because y[n] depends on past values of x[n].(b)The output of the system will be y[n]= ]2[][-n n δδ=0(c)From the result of part (b), we may conclude that the system output is always zero for inputs of the form ][k n -δ, k ∈ ґ. Therefore , the system is not invertible .1.17 (a) The system is not causal because the output y(t) at some time may depend on future values of x(t). For instance , y(-π)=x(0).(b) Consider two arbitrary inputs x 1(t)and x 2(t).x 1(t) →y 1(t)= x 1(sin(t))x 2(t)→ y 2(t)= x 2(sin(t))Let x 3(t) be a linear combination of x 1(t) and x 2(t).That is , x 3(t)=a x 1(t)+b x 2(t)Where a and b are arbitrary scalars .If x 3(t) is the input to the given system ,then the corresponding output y 3(t) is y 3(t)= x 3( sin(t))=a x 1(sin(t))+ x 2(sin(t)) =a y 1(t)+ by 2(t)Therefore , the system is linear.1.18.(a) Consider two arbitrary inputs x 1[n]and x 2[n].x 1[n] → y 1[n] =][01k x n n n n k ∑+-=x 2[n ]→ y 2[n] =][02k x n n n n k ∑+-=Let x 3[n] be a linear combination of x 1[n] and x 2[n]. That is :x 3[n]= ax 1[n]+b x 2[n]where a and b are arbitrary scalars. If x 3[n] is the input to the given system, then the corresponding outputy 3[n] is y 3[n]=][03k x n n n n k ∑+-==])[][(2100k bx k ax n n n n k +∑+-==a ][001k x n n n n k ∑+-=+b ][02k x n n n n k ∑+-== ay 1[n]+b y 2[n]Therefore the system is linear.(b) Consider an arbitrary input x 1[n].Lety 1[n] =][01k x n n n n k ∑+-=be the corresponding output .Consider a second input x 2[n] obtained by shifting x 1[n] in time:x 2[n]= x 1[n-n 1]The output corresponding to this input isy 2[n]=][02k x n n n n k ∑+-== ]n [1100-∑+-=k x n n n n k = ][01011k x n n n n n n k ∑+---=Also note that y 1[n- n 1]=][01011k x n n n n n n k ∑+---=.Therefore , y 2[n]= y 1[n- n 1] This implies that the system is time-invariant.(c) If ][n x <B, then y[n]≤(2 n 0+1)B. Therefore ,C ≤(2 n 0+1)B.1.19 (a) (i) Consider two arbitrary inputs x 1(t) and x 2(t). x 1(t)→ y 1(t)= t 2x 1(t-1)x 2(t) → y 2(t)= t 2x 2(t-1)Let x 3(t) be a linear combination of x 1(t) and x 2(t).That is x 3(t)=a x 1(t)+b x 2(t)where a and b are arbitrary scalars. If x 3(t) is the input to the given system, then the corresponding output y 3(t) is y 3(t)= t 2x 3 (t-1)= t 2(ax 1(t-1)+b x 2(t-1))= ay 1(t)+b y 2(t)Therefore , the system is linear.(ii) Consider an arbitrary inputs x 1(t).Let y 1(t)= t 2x 1(t-1)be the corresponding output .Consider a second input x 2(t) obtained by shifting x 1(t) in time:x 2(t)= x 1(t-t 0)The output corresponding to this input is y 2(t)= t 2x 2(t-1)= t 2x 1(t- 1- t 0)Also note that y 1(t-t 0)= (t-t 0)2x 1(t- 1- t 0)≠ y 2(t) Therefore the system is not time-invariant.(b) (i) Consider two arbitrary inputs x 1[n]and x 2[n]. x 1[n] → y 1[n] = x 12[n-2]x 2[n ]→ y 2[n] = x 22[n-2].Let x 3(t) be a linear combination of x 1[n]and x 2[n].That is x 3[n]= ax 1[n]+b x 2[n]where a and b are arbitrary scalars. If x 3[n] is the input to the given system, then the corresponding output y 3[n] is y 3[n] = x 32[n-2]=(a x 1[n-2] +b x 2[n-2])2=a 2x 12[n-2]+b 2x 22[n-2]+2ab x 1[n-2] x 2[n-2]≠ ay 1[n]+b y 2[n]Therefore the system is not linear.(ii) Consider an arbitrary input x 1[n]. Let y 1[n] = x 12[n-2]be the corresponding output .Consider a second input x 2[n] obtained by shifting x 1[n] in time:x 2[n]= x1[n- n]The output corresponding to this input isy 2[n] = x22[n-2].= x12[n-2- n]Also note that y1[n- n]= x12[n-2- n]Therefore , y2[n]= y1[n- n]This implies that the system is time-invariant.(c) (i) Consider two arbitrary inputs x1[n]and x2[n].x1[n] →y1[n] = x1[n+1]- x1[n-1]x2[n ]→y2[n] = x2[n+1 ]- x2[n -1]Let x3[n] be a linear combination of x1[n] and x2[n]. That is :x3[n]= ax1[n]+b x2[n]where a and b are arbitrary scalars. If x3[n] is the input to the given system, then thecorresponding output y3[n] is y3[n]= x3[n+1]- x3[n-1]=a x1[n+1]+b x2[n +1]-a x1[n-1]-b x2[n -1]=a(x1[n+1]- x1[n-1])+b(x2[n +1]- x2[n -1])= ay1[n]+b y2[n]Therefore the system is linear.(ii) Consider an arbitrary input x1[n].Let y1[n]= x1[n+1]- x1[n-1]be the corresponding output .Consider a second input x2[n] obtained by shifting x1[n] in time: x2[n]=x 1[n-n]The output corresponding to this input isy 2[n]= x2[n +1]- x2[n -1]= x1[n+1- n]- x1[n-1- n]Also note that y1[n-n]= x1[n+1- n]- x1[n-1- n]Therefore , y2[n]= y1[n-n]This implies that the system is time-invariant.(d) (i) Consider two arbitrary inputs x1(t) and x2(t).x 1(t) →y1(t)= dO{}(t)x1x 2(t) →y2(t)= {}(t)x2dOLet x3(t) be a linear combination of x1(t) and x2(t).That is x3(t)=a x1(t)+b x2(t)where a and b are arbitrary scalars. If x3(t) is the input to the given system, then the corresponding outputy 3(t) is y3(t)= dO{}(t)x3={}(t)xb+(t)ax21dO=a dO{}(t)x1+b{}(t)x2dO= ay1(t)+b y2(t)Therefore the system is linear.(ii) Consider an arbitrary inputs x1(t).Lety 1(t)= dO{}(t)x1=2)(x-(t)x11t-be the corresponding output .Consider a second input x2(t) obtained by shifting x1(t) in time:x 2(t)= x1(t-t)The output corresponding to this input isy 2(t)= {}(t)x2dO=2)(x-(t)x22t-=2)(x -)t -(t x 0101t t --Also note that y 1(t-t 0)= 2)(x -)t -(t x 0101t t --≠ y 2(t)Therefore the system is not time-invariant. 1.20 (a) Givenx )(t =jt e 2 y(t)=t j e 3x )(t =jt e 2- y(t)=t j e 3- Since the system liner+=t j e t x 21(2/1)(jte 2-))(1t y =1/2(t j e 3+tj e 3-)Thereforex 1(t)=cos)(1t y =cos(3t)(b) we know thatx 2(t)=cos(2(t-1/2))= (j e -jte 2+jejt e 2-)/2Using the linearity property, we may once again writex 1(t)=21( j e -jt e 2+j e jte 2-))(1t y =(j e -jt e 3+je jte 3-)= cos(3t-1)Therefore,x 1(t)=cos(2(t-1/2)))(1t y =cos(3t-1)1.21.The signals are sketched in figure S1.21.1.24 The even and odd parts are sketched in Figure S1.24 1.25 (a) periodic period=2π/(4)= π/2 (b) periodic period=2π/(4)= 2(c) x(t)=[1+cos(4t-2π/3)]/2. periodic period=2π/(4)= π/2 (d) x(t)=cos(4πt)/2. periodic period=2π/(4)= 1/2 (e) x(t)=[sin(4πt)u(t)-sin(4πt)u(-t)]/2. Not period. (f) Not period.1.26 (a) periodic, period=7.(b) Not period.(c) periodic, period=8.(d) x[n]=(1/2)[cos(3πn/4+cos(πn/4)). periodic, period=8. (e) periodic, period=16. 1.27 (a) Linear, stable(b) Not period. (c) Linear(d) Linear, causal, stable(e) Time invariant, linear, causal, stable (f) Linear, stable(g) Time invariant, linear, causal 1.28 (a) Linear, stable(b) Time invariant, linear, causal, stable (c)Memoryless, linear, causal (d) Linear, stable (e) Linear, stable(f) Memoryless, linear, causal, stable (g) Linear, stable1.29 (a) Consider two inputs to the system such that[][][]{}111.S e x n y n x n −−→=ℜand [][][]{}221.Se x n y n x n −−→=ℜNow consider a third inputx 3[n]= x2[n]+x 1[n]. The corresponding system outputWill be [][]{}[][]{}[]{}[]{}[][]33121212e e e e y n x n x n x n x n x n y n y n ==+=+=+ℜℜℜℜtherefore, we may conclude that the system is additive Let us now assume that inputs to the system such that [][][]{}/4111.Sj e x n y n e x n π−−→=ℜand[][][]{}/4222.Sj e x n y n e x n π−−→=ℜNow consider a third input x 3 [n]= x 2 [n]+ x 1 [n]. The corresponding system outputWill be[][]{}()[]{}()[]{}()[]{}()[]{}()[]{}()[]{}[]{}[]{}[][]/433331122/4/41212cos /4sin /4cos /4sin /4cos /4sin /4j e m e m e m e j j e e y n e x n n x n n x n n x n n x n n x n n x n e x n e x n y n y n πππππππππ==-+-+-=+=+ℜℜI ℜI ℜI ℜℜ therefore, we may conclude that the system is additive (b) (i) Consider two inputs to the system such that()()()()211111Sdx t x t y t x t dt ⎡⎤−−→=⎢⎥⎣⎦and ()()()()222211S dx t x t y t x t dt ⎡⎤−−→=⎢⎥⎣⎦ Now consider a third input x 3[t]= x2[t]+x 1[t]. The corresponding system outputWill be()()()()()()()()()2333211111211dx t y t x t dt d x t x t x t x t dt y t y t ⎡⎤=⎢⎥⎣⎦⎡⎤+⎡⎤⎣⎦=⎢⎥+⎢⎥⎣⎦≠+ therefore, we may conclude that the system is not additiveNow consider a third input x 4 [t]= a x 1 [t]. The corresponding system output Will be()()()()()()()()2444211211111dx t y t x t dt d ax t ax t dt dx t a x t dt ay t ⎡⎤=⎢⎥⎣⎦⎡⎤⎡⎤⎣⎦=⎢⎥⎢⎥⎣⎦⎡⎤=⎢⎥⎣⎦=Therefore, the system is homogeneous.(ii) This system is not additive. Consider the fowling example .Let δ[n]=2δ[n+2]+ 2δ[n+1]+2δ[n] andx2[n]= δ[n+1]+ 2δ[n+1]+ 3δ[n]. The corresponding outputs evaluated at n=0 are[][]120203/2y andy ==Now consider a third input x 3 [n]= x 2 [n]+ x 1 [n].= 3δ[n+2]+4δ[n+1]+5δ[n] The corresponding outputs evaluated at n=0 is y 3[0]=15/4. Gnarly, y 3[0]≠ ]0[][21y y n +.This[][][][][]444442,1010,x n x n x n y n x n otherwise ⎧--≠⎪=-⎨⎪⎩ [][][][][][]4445442,1010,x n x n ax n y n ay n x n otherwise ⎧--≠⎪==-⎨⎪⎩Therefore, the system is homogenous.1.30 (a) Invertible. Inverse system y(t)=x(t+4)(b)Non invertible. The signals x(t) and x 1(t)=x(t)+2πgive the same output (c) δ[n] and 2δ[n] give the same output d) Invertible. Inverse system; y(t)=dx(t)/dt(e) Invertible. Inverse system y(n)=x(n+1) for n ≥0 and y[n]=x[n] for n<0(f) Non invertible. x (n) and –x(n) give the same result (g)Invertible. Inverse system y(n)=x(1-n) (h) Invertible. Inverse system y(t)=dx(t)/dt(i) Invertible. Inverse system y(n) = x(n)-(1/2)x[n-1] (j) Non invertible. If x(t) is any constant, then y(t)=0 (k) δ[n] and 2δ[n] result in y[n]=0 (l) Invertible. Inverse system: y(t)=x(t/2)(m) Non invertible x 1 [n]= δ[n]+ δ[n-1]and x 2 [n]= δ[n] give y[n]= δ[n] (n) Invertible. Inverse system: y[n]=x[2n]1.31 (a) Note that x 2[t]= x 1 [t]- x 1 [t-2]. Therefore, using linearity we get y 2 (t)= y 1 (t)- y 1 (t-2).this is shown in Figure S1.31(b)Note that x3 (t)= x1 [t]+ x1 [t+1]. .Therefore, using linearity we get Y3 (t)= y1 (t)+ y1 (t+2). this is2(4) y 2(t) periodic, period T; x(t) periodic, period T/2;1.33(1) True x[n]=x[n+N ]; y 1 (n)= y 1 (n+ N 0)i.e. periodic with N 0=n/2if N is even and with period N 0=n if N is odd.(2)False. y 1 [n] periodic does no imply x[n] is periodic i.e. Let x[n] = g[n]+h[n] where0,1,[][]0,(1/2),nn even n even g n and h n n odd n odd⎧⎧==⎨⎨⎩⎩ Then y 1 [n] = x [2n] is periodic but x[n] is clearly not periodic. (3)True. x [n+N] =x[n]; y 2 [n+N 0] =y 2 [n] where N 0=2N (4) True. y 2 [n+N] =y 2 [n]; y 2 [n+N 0 ]=y 2 [n] where N 0=N/2 1.34. (a) ConsiderIf x[n] is odd, x[n] +x [-n] =0. Therefore, the given summation evaluates to zero. (b) Let y[n] =x 1[n]x 2[n] .Theny [-n] =x 1[-n] x 2[-n] =-x 1[n]x 2[n] =-y[n]. This implies that y[n] is odd.(c)ConsiderUsing the result of part (b), we know that x e [n]x o [n] is an odd signal .Therefore, using the result of part (a) we may conclude thatTherefore,{}1[][0][][]n n x n x x n x n ∞∞=-∞==++-∑∑[][]e o n n n n x x ∞∞=-∞=-∞=+∑∑222[][][]e on n n n n n x x x∞∞∞=-∞=-∞=-∞==+∑∑∑eon nn xx∞=-∞=∑()()()()()().xy yx t x t y d y t x d t φττττττφ∞-∞∞-∞=+=-+=-⎰⎰(d)ConsiderAgain, since x e (t) x o (t) is odd,Therefore,1.35. We want to find the smallest N 0 such that m(2π /N) N 0 =2πk or N 0 =kN/m,where k is an integer, then N must be a multiple of m/k and m/k must be an integer .this implies that m/k is a divisor of both m and N .Also, if we want the smallest possible N 0, then m/k should be the GCD of m and N. Therefore, N 0=N/gcd(m,N).1.36.(a)If x[n] is periodic 0(),0..2/j n N T o ewhere T ωωπ+= This implies that 022o T kNT k T T Nππ=⇒==a rational number . (b)T/T 0 =p/q then x[n] =2(/)j n p q e π,The fundamental period is q/gcd(p,q) and the fundmental frequencyis(c) p/gcd(p,q) periods of x(t) are needed .1.37.(a) From the definition of ().xy t φWe havepart(a) that()().xx xx t t φφ=-This implies that()xy t φis(b) Note from even .Therefore,the odd part of().xx t φis zero.(c) Here, ()().xy xx t t T φφ=-and ()().yy xx t t φφ= 1.38.(a) We know that /22(2)().t t δδ= ThereforeThis implies that1(2)().2t t δδ=(b)The plot are as shown in Figure s3.18. 1.39 We havelim ()()lim (0)()0.u t t u t δδ→→==Also,222[][][].eon n n n n n x x x ∞∞∞=-∞=-∞=-∞==+∑∑∑222()()()2()().e o et dt t dt t dt t t dt xx x x x ∞∞∞∞-∞-∞-∞-∞=++⎰⎰⎰⎰()()0.et t dt x x ∞-∞=⎰222()()().e ot dt t dt t dt xx x ∞∞∞-∞-∞-∞=+⎰⎰⎰0022gcd(,)gcd(,)gcd(,)gcd(,).T pp q p q p q p q q p q p pωωππ===/21lim (2)lim ().2t t δδ→∞→∞= 01lim ()()().2u t t t δδ→= u Δ'(t )u Δ'⎰⎰∞∞∞--=-=0)()()()()(ττδτττδτd t u d t u t gTherefore,0,0()1,00t g t t undefined for t >⎧⎪=<⎨⎪=⎩()0()()()t u t t δττδτδτ-=-=-1.40.(a) If a system is additive ,then also, if a system is homogeneous,then(b) y(t)=x 2(t) is such a systerm . (c) No.For example,consider y(t) ()()ty t x d ττ-∞=⎰with ()()(1).x t u t u t =--Then x(t)=0for t>1,but y(t)=1 for t>1.1.41. (a) y[n]=2x[n].Therefore, the system is time invariant.(b) y[n]=(2n-1)x[n].This is not time-invariant because y[n- N 0]≠(2n-1)2x [n- N 0]. (c) y[n]=x[n]{1+(-1)n +1+(-1)n-1}=2x[n].Therefore, the system is time invariant .1.42.(a) Consider two system S 1 and S 2 connected in series .Assume that if x 1(t) and x 2(t) arethe inputs to S 1..then y 1(t) and y 2(t) are the outputs.respectively .Also,assume thatif y 1(t) and y 2(t) are the input to S 2 ,then z 1(t) and z 2(t) are the outputs, respectively . Since S 1 is linear ,we may write()()()()11212,s ax t bx t ay t by t +→+where a and b are constants. Since S 2 is also linear ,we may write()()()()21212,s ay t by t az t bz t +→+We may therefore conclude that00.()().00x t y t =→=0()()()()0x t x t y t y t =-→-=u Δ'(t ) 1 1/2 Δ-Δttu Δ'(t ) 1 1/2Δ-Δt 0t)()()()(212121t b t a t b t a z z x x s s +−→−+Therefore ,the series combination of S 1 and S 2 is linear. Since S 1 is time invariant, we may write()()11010s x t T y t T -→-and()()21010s y t T z t T -→-Therefore,()()121010s s x t T z t T -→-Therefore, the series combination of S 1 and S 2 is time invariant.(b) False, Let y(t)=x(t)+1 and z(t)=y(t)-1.These corresponds to two nonlinear systems. If these systems are connected in series ,then z(t)=x(t) which is a linear system.(c) Let us name the output of system 1 as w[n] and the output of system 2 as z[n] .Then11[][2][2][21][22]24y n z n w n w n w n ==+-+-[][][]241121-+-+=n x n x n xThe overall system is linear and time-invariant.1.43. (a) We have())(t y t x s−→−Since S is time-invariant.())(T t y T t x s-−→−-Now if x (t) is periodic with period T. x{t}=x(t-T). Therefore, we may conclude that y(t)=y(t-T).This impliesthat y(t) is also periodic with T .A similar argument may be made in discrete time . (b)1.44 (a) Assumption : If x(t)=0 for t<t 0 ,then y(t)=0 for t< t 0.To prove That : The system is causal.Let us consider an arbitrary signal x 1(t) .Let us consider another signal x 2(t) which is the same as x 1(t)fort< t 0. But for t> t 0 , x 2(t) ≠x 1(t),Since the system is linear,()()()()1212,x t x t y t y t -→-Since ()()120x t x t -=for t< t 0 ,by our assumption =()()120y t y t -=for t< t 0 .This implies that()()12y t y t =for t< t 0 . In other words, t he output is not affected by input values for 0t t ≥. Therefore, thesystem is causal .Assumption: the system is causal . To prove that :If x(t)=0 for t< t 0 .then y(t)=0 for t< t 0 .Let us assume that the signal x(t)=0 for t< t 0 .Then we may express x(t) as ()()12()x t x t x t =-, Where()()12x t x t = for t< t 0 . the system is linear .the output to x(t) will be()()12()y t y t y t =-.Now ,since the system is causal . ()()12y t y t = for t< t 0 .implies that()()12y t y t = for t< t 0 .Therefore y(t)=0 for t< t 0 .(b) Consider y(t)=x(t)x(t+1) .Now , x(t)=0 for t< t 0 implies that y(t)=0 for t< t 0 .Note that the system is nonlinear and non-causal .(c) Consider y(t)=x(t)+1. the system is nonlinear and causal .This does not satisfy the condition of part(a). (d) Assumption: the system is invertible. To prove that :y[n]=0 for all n only if x[n]=0 for all n . Consider[]0[]x n y n =→. Since the system is linear :2[]02[]x n y n =→.Since the input has not changed in the two above equations ,we require that y[n]= 2y[n].This implies that y[n]=0. Since we have assumed that the system is invertible , only one input could have led to this particular output .That input must be x[n]=0 .Assumption: y[n]=0 for all n if x[n]=0 for all n . To prove that : The system is invertible . Suppose that11[][]x n y n → and21[][]x n y n →Since the system is linear ,1212[][][][]0x n x n y n y n -=→-=By the original assumption ,we must conclude that 12[][]x n x n =.That is ,any particular y 1[n] can be produced that by only one distinct input x 1[n] .Therefore , the system is invertible. (e) y[n]=x 2[n]. 1.45. (a) Consider ,()111()()shx x t y t t φ→= and()222()()s hx x t y t t φ→=.Now, consider ()()()312x t ax t bx t =+. The corresponding system output will be()()12331212()()()()()()()()()hx hx y t x h t d a x h t d b x t h t d a t b t ay t by t ττττττττφφ∞-∞∞∞-∞-∞=+=+++=+=+⎰⎰⎰Therefore, S is linear .Now ,consider x 4(t)=x 1(t-T).The corresponding system output will be()14411()()()()()()()hx y t x h t d x T h t d x h t T d t T τττττττττφ∞-∞∞-∞∞-∞=+=-+=++=+⎰⎰⎰Clearly, y 4(t)≠ y 1(t-T).Therefore ,the system is not time-invariant.The system is definitely not causal because the output at any time depends on future values of the input signal x(t).(b) The system will then be linear ,time invariant and non-causal. 1.46. The plots are in Figure S1.46.1.47.(a) The overall response of the system of Figure P1.47.(a)=(the response of the system to x[n]+x 1[n])-the response of the system to x 1[n]=(Response of a linear system L to x[n]+x 1[n]+zero input response of S)- (Response of a linear system L to x 1[n]+zero input response of S)=( (Response of a linear system L to x[n]).。