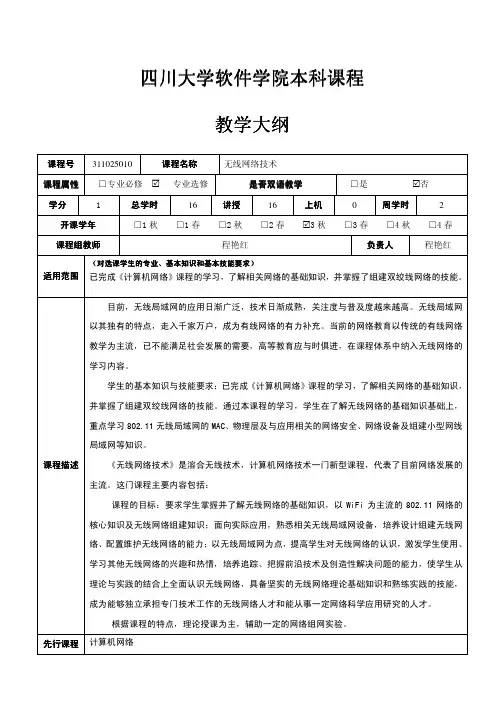
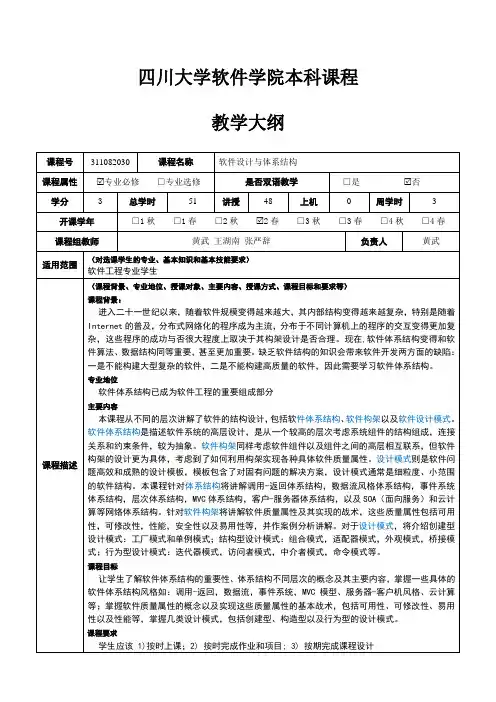
四川大学软件学院本科课程教学大纲
- 格式:doc
- 大小:61.50 KB
- 文档页数:4

四川大学本科实验教学大纲课程名称:数字信号处理英文名称:digital signal processing课程性质:讲/习课程代码:20118630本大纲主笔人:董重明面向专业:(信息专业、统计专业,计算专业等)实验指导书名称:数字信号处理(第十章上机实验)出版单位:西安电子科技大学出版社出版日期:2000。
12 主编:丁玉美高西全实验讲义名称:编写单位:编写日期:主编:一、课程学时学分课程总学时:51学时课程总学分:3学分实验总学时:4学时实验总学分:0学分二、实验的地位、作用和目的数字信号处理是一门理论和试验并重的学科。
上机试验有自己独立的意义。
本身可以作为单列的课程。
但对本课程而言,由于是本科阶段的基础课程,受课时和课程内容的限制上机实验主要还是课程中基础理论的补充。
通过上机,不仅可以帮助同学门加深对理论内容的理解和消化,而且能锻炼独立解决问题的能力,对以后的进不步学习和利用所学解决实际问题都是必不可少的。
三、基本原理及课程简介数字信号处理是诞生于上世纪六十年代的一门学科。
至今在各个方面多现代人的生活产生了极为深刻的影响。
随着各种数码产品的问世和发展,这门学科的已经成为现代社会的标志性学科之一。
它的本质就是用计算机(或者各种芯片)把各种已经数码化的信号加工后,再输出。
从各种原始信号中提取有用的信息为人类服务。
而对数字信号加工和处理的都是通过数字计算进行的。
其中标志性的计算之一就是通过各种快速算法实现的DFT,既FFT。
四、实验方式及基本要求一人一机,按指导教师的指导打开软件,按要求完成具体的相关操作。
五、基本设备与器材配置(名称及数量)普通的个人微机(奔腾Ⅲ以上),windows操作系统,。
安装有mathwork公司的mathlab软件。
一人一机六、实验项目及内容提要说明:上机实验的具体内容暂时定为三个,每个内容两个学时,累计比总学时多两个学时。
原因如下:现在学校有些学院开设有matlab选修课程作为一门计算机语言来学习,如果学习本课程的同学的多数对mathlab的基本内容已经有一定了解,本大纲的第一部分内容就不必要了,可以削减,这时用第三个内容--数字滤波器的设计来补充。

软件工程理论课教学大纲软件工程理论课教学大纲软件工程是计算机科学与工程学科中的重要分支,旨在研究和应用一系列原则、方法和工具,以提高软件开发和维护的效率和质量。
软件工程理论课作为软件工程专业的核心课程之一,对于培养学生的软件开发能力和工程思维具有重要意义。
本文将从课程目标、教学内容、教学方法和评价方式等方面探讨软件工程理论课的教学大纲。
一、课程目标软件工程理论课的主要目标是培养学生掌握软件工程的基本理论和方法,具备软件开发和项目管理的基本能力。
具体包括以下几个方面:1. 理解软件工程的基本概念和原理,包括软件生命周期、需求分析、设计、编码、测试、维护等各个阶段的基本原则和方法。
2. 掌握软件开发过程中的常用工具和技术,如需求管理工具、版本控制工具、测试工具等,能够灵活运用这些工具解决实际问题。
3. 培养学生的团队合作和沟通能力,使其能够参与到实际的软件开发项目中,理解软件开发过程中的团队协作和项目管理的重要性。
4. 培养学生的自学能力和持续学习的意识,使其能够不断跟进软件工程领域的最新发展和技术变化。
二、教学内容软件工程理论课的教学内容应包括以下几个方面:1. 软件工程基本概念和原理:介绍软件工程的基本概念、软件生命周期、软件过程模型等,让学生了解软件工程的基本理论基础。
2. 软件需求分析与规格说明:介绍软件需求分析的基本方法和技术,包括需求获取、需求建模、需求规格说明等,让学生掌握如何正确理解和表达软件需求。
3. 软件设计与架构:介绍软件设计的基本原则和方法,包括面向对象设计、设计模式、架构模式等,让学生了解如何进行软件设计和系统架构设计。
4. 软件测试与质量保证:介绍软件测试的基本原则和方法,包括测试策略、测试用例设计、测试工具等,让学生了解如何进行软件测试和质量保证。
5. 软件项目管理:介绍软件项目管理的基本概念和方法,包括项目计划、进度管理、风险管理等,让学生了解如何进行软件项目管理和团队协作。
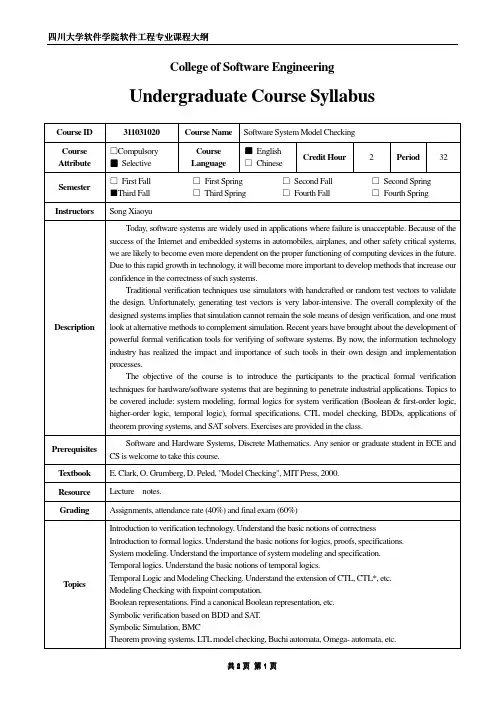
College of Software EngineeringUndergraduate Course Syllabus Course ID 311031020 Course Name Software System Model CheckingCourse Attribute □Compulsory■SelectiveCourseLanguage■English□ChineseCredit Hour 2 Period 32Semester □First Fall □First Spring □Second Fall □Second Spring ■Third Fall □Third Spring □Fourth Fall □Fourth SpringInstructors Song XiaoyuDescriptionToday, software systems are widely used in applications where failure is unacceptable. Because of the success of the Internet and embedded systems in automobiles, airplanes, and other safety critical systems, we are likely to become even more dependent on the proper functioning of computing devices in the future. Due to this rapid growth in technology, it will become more important to develop methods that increase our confidence in the correctness of such systems.Traditional verification techniques use simulators with handcrafted or random test vectors to validate the design. Unfortunately, generating test vectors is very labor-intensive. The overall complexity of the designed systems implies that simulation cannot remain the sole means of design verification, and one must look at alternative methods to complement simulation. Recent years have brought about the development of powerful formal verification tools for verifying of software systems. By now, the information technology industry has realized the impact and importance of such tools in their own design and implementation processes.The objective of the course is to introduce the participants to the practical formal verification techniques for hardware/software systems that are beginning to penetrate industrial applications. Topics to be covered include: system modeling, formal logics for system verification (Boolean & first-order logic, higher-order logic, temporal logic), formal specifications, CTL model checking, BDDs, applications of theorem proving systems, and SA T solvers. Exercises are provided in the class.PrerequisitesSoftware and Hardware Systems, Discrete Mathematics. Any senior or graduate student in ECE and CS is welcome to take this course.T extbook E. Clark, O. Grumberg, D. Peled, "Model Checking", MIT Press, 2000. Resource Lecture notes.Grading Assignments, attendance rate (40%) and final exam (60%)T opics Introduction to verification technology. Understand the basic notions of correctness Introduction to formal logics. Understand the basic notions for logics, proofs, specifications. System modeling. Understand the importance of system modeling and specification. Temporal logics. Understand the basic notions of temporal logics.Temporal Logic and Modeling Checking. Understand the extension of CTL, CTL*, etc. Modeling Checking with fixpoint computation.Boolean representations. Find a canonical Boolean representation, etc.Symbolic verification based on BDD and SA T.Symbolic Simulation, BMCTheorem proving systems. L TL model checking, Buchi automata, Omega- automata, etc.T ools & Environment Projects SAT-based verification Version No Version No:: 1.0 Author Author:: Date Date:: 20020099-6-10 Auditor Auditor:: Mei Hong Date Date:: 20020099-6-1010Signature of leader Signature of leader:: Date Date::20020099-6-1010。

软件工程教学大纲《软件工程》课程教学大纲一、课程的基本情况课程中文名称:软件工程课程英文名称:softwareengineering课程代码:1302031课程类别:专业基础课课程学分:2.5课程学时:44讲课对象:计算机科学与技术专业、软件工程专业前导课程:高级语言程序设计、数据结构、数据库原理二、教学目的《软件工程》是计算机专业的一门必修的专业课程,通过本课程的学习,要求学生掌握软件工程的基本概念、基本原理、实用的开发方法和技术;了解软件工程各领域的发展方向;如何用工程化的方法开发软件项目,以及开发过程中应遵循的流程、准则、标准和规范。
《软件工程》是一门综合性和实践性很强的专业课程。
应注重方法、技术的实际应用,能应用相应的图形工具开发小型软件项目,为更深入地学习和今后从事软件工程实践打下良好的基础。
三、教学基本建议ch1introduction基本要求:§1.1softwarecrisis§1.2softwareengineering§1.3lifespan§1.4softwareprocess重点与难点:lifespanch2feasibilitystudy基本要求:§2.1task§2.2process§2.3systemflowdiagram§2.4dataflowdiagram§2.5datadictionary§2.6cost/benefit重点与难点:dataflowdiagram,datadictionarych3requirementsanalysis基本建议:§3.1task§3.2process§3.3conceptionmodel&e-rdiagrams§3.4otherdiagramtools重点与难点:conceptionmodel&e-rdiagramsch4formalspecificationmethods基本建议:§4.1statemachine§4.2petrinetwork§4.3zspecificationlanguage重点与难点:statemachinech5systemdesign基本建议:§5.1designprocess§5.2designconcepts§5.3designprinciples§5.4diagramtoolsofsoftwarearchitecture§5.5datafloworienteddesignmethods:transform&transactionmapping重点与难点:datafloworienteddesignmethods:transform&transactionmappingch6programdesign基本要求:§6.1structuredprogramdesign§6.2interfacedesign§6.3proceduredesigntools§6.4datastructureorienteddesignmethods重点与难点:datastructureorienteddesignmethodsch7implementation基本要求:§7.1coding§7.2softwaretestingfundamentals§7.3unittesting§7.4integrationtesting§7.5va lidationtesting§7.6white-boxtesting§77black-boxtesting重点与难点:ch8maintenance基本建议:softwaretestingfundamentals§8.1definitions§8.2softwareevolution§8.3maintainabil ity-softwaremeasurement重点与难点:softwareevolutionch9object-orientedmethodology基本要求:§9.1introduction§9.2concepts§9.3objectmodelingtechniques-3models(object,dynamic,function)重点与难点:3models(object,dynamic,function)ch10object-orientedanalysis基本要求:§10.1modelingprocess§10.2requirementspresentation§10.3createobjectmodel§10.4createdynamicmodel§10.5createfunctionmodel重点与难点:modelingprocess,requirementspresentationch12object-orientedimplement基本要求:§12.1programminglanguages§12.2programmingstyles§12.3ootestingstrategies§12.4testcasedesignforoosoftware重点与难点:ootestingstrategiesch13softwareprojectmanagement基本建议:§13.1softwaresizing§13.2costestimation§13.3softwareplan§13.4personnel§13.5qualityassurance§13.6.projectplan重点与难点:softwareplan,projectplan四、课程内容与学时分配课程内容与学时分配表中内容ch1introductionch2feasibilitystudych3requirementsanalysisch4formalspecificatio nmethodsch5systemdesignch6programdesignch7implementationch8maintenancech9object-orientedmethodologych10object-orientedanalysisch12object-orientedimplementch13softwareprojectmanagement总学时4444426462242444学时五、教材与参考书教材:张海藩主编,《软件工程导论(第四版)》,清华大学出版社,2021参考书:[1]rogers.pressman,《softwareengineeringapractitioner’sapproach》5edition,chinamachinepress,2000[2]rogers.pressman著,梅宏译,《软件工程-实践者的研究方法》原书第5版,机械工业出版社,2002th六、教学方式和考核方式1、教学方式课程的讲授应当将理论教学与实验教学紧密结合,并使之相互辅助,提升教学效率。

软件工程教学大纲[简介]软件工程是计算机科学中的一门学科,旨在教授学生软件开发以及项目管理的理论和实践知识。
本文将介绍软件工程教学大纲的内容和目标,以及教学方法和评估方式。
[第一部分:引言]1. 软件工程的定义:软件工程是一种系统化、规范化和可重复的方法,用于开发高质量的软件。
2. 软件工程的重要性:软件在现代社会中的应用广泛,软件工程的实践能够提高软件开发的效率和质量。
[第二部分:教学目标]1. 理论知识:学生应该掌握软件工程的基本原理和方法,包括需求分析、设计、开发、测试和维护等方面的知识。
2. 实践能力:学生应该能够应用软件工程的理论知识解决实际问题,包括软件开发过程中的各个环节。
3. 团队合作:软件开发是一项团队活动,学生应该培养良好的沟通和协作能力。
[第三部分:教学内容]1. 需求分析:介绍需求工程的基本概念和方法,包括需求获取、分析和规格说明等内容。
2. 软件设计:讲解软件设计的原理和方法,包括结构化设计、面向对象设计以及设计模式等知识。
3. 软件开发:介绍软件开发的流程和方法,包括编码、调试、版本控制和软件测试等。
4. 质量保证:教授软件质量保证的理论知识和实践方法,包括软件测试、代码审查和性能优化等。
5. 项目管理:介绍项目管理的基本知识和技巧,包括项目计划、资源管理和风险管理等。
[第四部分:教学方法]1. 理论讲授:通过课堂讲解,向学生传授软件工程知识和理论。
2. 实践操作:安排实践环节,让学生亲自参与软件开发项目,提高他们的实践能力。
3. 小组讨论:组织小组讨论,让学生共同解决软件工程中的问题,培养他们的团队合作能力。
4. 项目实践:安排真实的软件开发项目,让学生在实际环境中应用所学知识,提高他们的实践能力。
[第五部分:评估方式]1. 考试:通过理论考试,评估学生对软件工程理论知识的掌握情况。
2. 项目评估:对学生在实际项目中的表现进行评估,包括项目成果和团队合作能力等方面。

四川大学本科实验教学大纲课程号:课程名称:软件工程英文名称:Software Engineering课程性质:选修本大纲主笔人:余勇面向专业:(信息与计算科学专业)实验指导书名称:+sql server 动态网站开发案例精选出版单位:清华大学出版日期:2005年10月主编:刘斌实验讲义名称:软件工程编写单位:人民邮电出版社编写日期:2002年主编:张海藩一、课程学时学分课程总学时:68学时课程总学分:4学分实验总学时:17学时实验总学分:1学分二、实验的地位、作用和目的辅助教学。
对课程中所涉及到的具体技术和方法进行上机实践,使学生能充分理解和灵活掌握这些技术,加深对课程中概念的认识。
三、基本原理及课程简介软件工程是指导计算机软件开发和维护的工程学科,它采用工程的概念、原理、技术和方法来开发与维护软件,把经过时间考验而证明正确的管理技术和当前能够得到的最好技术方法结合起来,以便经济地开发出高质量的软件并有效地维护它。
四、实验方式及基本要求3~5人分成一组,在其中选出组织能力强、计算机技术较好的同学作为组长,包括组长在内的所有同学进行角色扮演,分别担任,系统分析员,程序员,测试员。
每组分配给1个实习题目。
五、实验报告要求在需求分析阶段:绘制ER图,数据流图,状态转换图。
软件设计阶段:绘制软件结构图,NS盒图。
编码设计阶段:提供完整可以运行的程序代码。
软件测试阶段:提供测试报告。
六、考核与考试上机演示30分,提交完整项目报告70分。
(组长:可以适当加5分) 七、基本设备与器材配置(名称及数量)计算机与计算机局域网络。
八、实验项目及内容提要实验题目:学生信息管理系统校友管理系统网络商城系统网络论坛系统客户关系管理系统网络投稿系统网络考试系统。
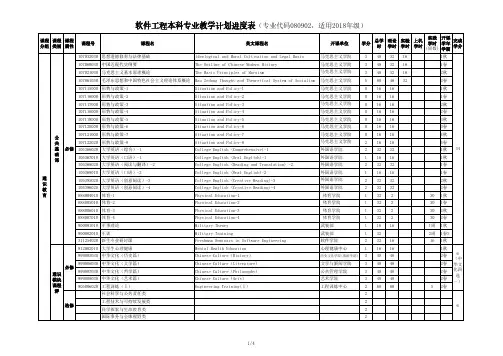
软件工程本科专业教学计划进度表(专业代码080902,适用2018年级)
备注:
1.每学期必选“形势与政策”课程,每期合格后,毕业时共计2学分。
2.《中华文化》课程分为《中华文化(文学篇)》、《中华文化(历史篇)》、《中华文化(艺术篇)》、《中华文化(哲学篇)》四门课程,要求任选一门,至少选修3学分。
3.“社会科学与公共责任类”、“ 工程技术与可持续发展类”、“ 科学探索与生命教育类”、“ 国际事务与全球视野类”通识课程,至少选修4学分。
4.其他通识课程中,要求选修“实践及国际课程周”本专业开设的外教课程,至少选修2学分。
5.专业选修课中,“软件工程通用”课程模块为必选模块,至少选修14学分;其它专业方向课程模块,要求任选其中一个方向模块,至少选修10学分,不得跨方向选修课程。
6.跨学科专业类课程,要求必修两门以上其它专业的专业核心课程,至少6学分。
7.创新创业教育学分要求至少4学分,学分认定方式参见川大教〔2017〕130号文件,包括社会实践、创新创业活动;学科竞赛;特长与技能;科技成果等。
8.实践教育中的“IT企业实习”学分的认定条件是:企业是学院认可的知名IT企业,获得企业的“实习鉴定意见”,评价达到优良,实习所获得的8学分可用于替代专业方向选修课程模块的学分。
9.毕业要求最低学分为167学分,并达到各项课程必修和选修要求。

College of Computer(Software Engineering) Undergraduate Course Syllabus Course ID:31110320Course Name:Software Development Practice Instructors:Guo Bing He Jun Zuo Hang Shu LiDecember 2007First. Course InformationCourse ID31110320 Course Name Software Development PracticeCourse Attribute █Practice □Selective □Compulsory Professional Software EngineeringCredit Hour 2Period 36 Experimental Period Semester Spring2009 Enactment Timing 2008.12 Submission Time 2009.1TextbookSoftware Development Practice (self-edited), 2008 Case Set of Software Development Practice (self-edited), 2008 C++ University Tutorial (Fifth Edition), H.M.Deitel, Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2006Software Development Management Practice----Enterprise Case Analysis ofBeyond CMM5, Zhang Shao-zhong, Li Yuan-ming, Tsinghua University Press,2005BibliographyJournalsWebsite Science and Art of Software Development, Chen Hong-gang, Lin Bin, PublishingHouse of Electronics Industry, 2002Second. Related Course Information, Teaching Purposes, Requirements and ExaminationsTeaching purposes and requirements(It includes the teaching purposes and requirements of basic theory, Relatedtechnologies, development capability, design capability, management capabilitywhich should be achieved.)Course teaching purposes:1) As a independent, practical and comprehensive software development practicecourse, by developing actual software project, it can improves the students’professional knowledge which has been learned in the last two years (forexample Software Engineering, Advanced Programming Language, etc ) andthe capability of using software tools in order to build the foundation for thefollow-up course learning, off-campus training, undergraduate design andsuccessful employment.2) Through guiding students to determine the market-oriented and interestedsoftware project and combined with the direction of teachers in scientificresearch, it trains the students’ awareness of market, project managementcapacity and capabilities of software products, and theoretical and practical’sorganic combination3)In the end of course,we select the excellent practice results as case set, recommend to the budding college funds and undergraduate research training’s alternative projects, and subsidize student continuous R & D to further take part in a number of domestic and international software contests, and by the tempering of graduation project, gradually become one of the real software products, and improve students’ c ultivation effects and quality.Course teaching requirements:1)Students in a class is divided into multiple project teams, the number of personsin each team can’t be more than 5 persons, and one is elected as the team leader.2)Based on students’ ideas, teacher only give some guiding and discussion, atmost extent stimulus the enthusiasm and the development interest of students, and determine the content, objectives, assignment and planning of development project.3)According to the flow of software engineering and the actual engineeringstandards, reasonably organize implementation of the project. According to the four phases of requirements analysis, system design, coding and testing and documentation, and strengthen the daily project management and inspect the results of project in each week.Examinations:By testing to evaluate the practice results of each project team and each student.Teaching content 1.Introductionsoftware technology, software projects, software products, software industry, software technology patents and standards2.Utility software product development process and norms3.Real-time operating system Product case4.Software Engineering Environment Product Casermation Security Product Case6.Digital Entertainment Products Case7.E-Product Case8.E-commerce Product Case9.Embedded Software Product Caseputer Network and Communication Products Case11.IC Design Product CaseAppendix CD Supplementary software and source codeExaminations/testGradingattendance rate (40%) final examinations or test (60%) Prevocational curriculum Advanced Programming Language and Software EngineeringTools & EnvironmentPC and its corresponding software toolsSimulation issues and development projects (the curriculum-related simulation issues, development projects, necessary development tools and technical training, etc)Medium target’s researchsituation of refresher coursesbeen learned(the name of refresher courses been learned, textbook)Medium target’s researchsituation of other courses(course name, textbook, instructors)Relationship with therelevant certificationThird. Teaching ProgramTeaching content 1Introduction to Software Development Practice Hours distribution2Stage goalfamiliar with basic goal and content of the coursePracticeTeaching content 2~18Discussion and check of the project situation in each week Hours distribution34Stage goal Each team member should present their project progress by PPT in turn each week. In the end of course, each team member also should submit their own, independent final project report.Practice。
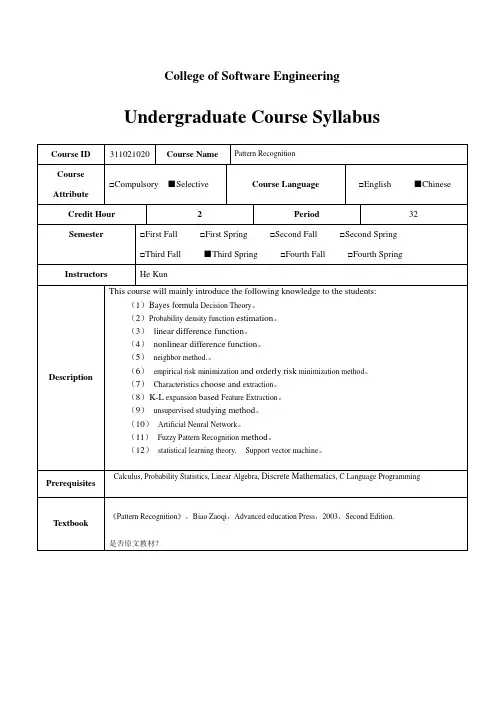
College of Software EngineeringUndergraduate Course SyllabusCourse ID 311021020 Course Name Pattern RecognitionCourseAttribute□Compulsory ■Selective Course Language□English ■Chinese Credit Hour 2 Period32Semester□First Fall □First Spring □Second Fall □Second Spring□Third Fall ■Third Spring □Fourth Fall □Fourth Spring Instructors He KunDescription This course will mainly introduce the following knowledge to the students: (1)Bayes formula Decision Theory。
(2)Probability density function estimation。
(3)linear difference function。
(4)nonlinear difference function。
(5)neighbor method.。
(6)empirical risk minimization and orderly risk minimization method。
(7)Characteristics choose and extraction。
(8)K-L expansion based Feature Extraction。
(9)unsupervised studying method。
(10)Artificial Neural Network。
(11)Fuzzy Pattern Recognition method。