颞下颌关节的解剖生理.ppt
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.04 MB
- 文档页数:2


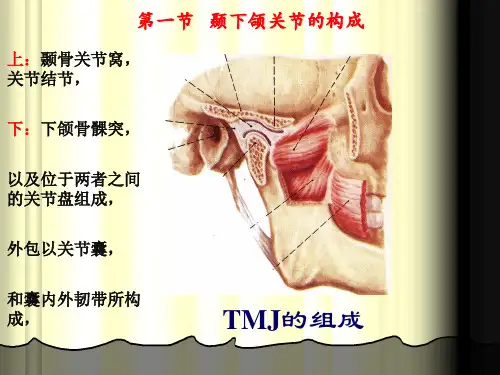
动物解剖生理颞下颌关节的组成英文回答:The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is a synovial joint that connects the mandible (lower jaw) to the temporal bone of the skull. It is responsible for the movement of the jaw, allowing for actions such as opening and closing the mouth, chewing, and speaking.The TMJ is composed of several components. The mandibular condyle, which is the rounded portion of the mandible, fits into the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone. This forms the hinge-like joint that allows for the opening and closing of the mouth. The articular disc, a fibrous cartilage structure, is located between the condyle and the fossa. It acts as a cushion and helps to distribute the forces during jaw movement.The TMJ also has ligaments that provide stability tothe joint. The lateral ligament, also known as thetemporomandibular ligament, connects the condyle to the zygomatic arch. It limits excessive movement of the jaw and helps to maintain proper alignment. The stylomandibular ligament, on the other hand, connects the styloid process of the temporal bone to the angle of the mandible. It provides additional support to the joint.Furthermore, the TMJ is surrounded by a joint capsule, which is a fibrous structure that encloses the joint and helps to maintain its integrity. The capsule is lined with a synovial membrane that produces synovial fluid, which lubricates the joint and reduces friction during movement.In addition to these components, there are also several muscles involved in the movement of the TMJ. The muscles of mastication, such as the temporalis, masseter, and medial pterygoid, are responsible for the opening and closing of the jaw. They work together to provide the necessary force for chewing and biting.中文回答:颞下颌关节(TMJ)是一种滑膜关节,连接下颌骨(下颚)和颞骨。