化合物英文命名
- 格式:pptx
- 大小:1.49 MB
- 文档页数:36



常见分子式及化学反应式的读法字母部分均按字母名称读出;化学反应式中的符号→,读作yields 或forms ,意即生成: A) H 2O, [eit ʃ] [tu:] [əu] B) C 6H 12O 6 → 2C 2H 5OH + 2CO 2C six H twelve O six yields two C two H five O H plus two C O two. C) NaOH → Na ++ OH -N sub a O H yields N sub a positive plus O H negative.D)1、Nitrogen reacts with hydrogen to form ammonia at high temperature and pressure with the presence of a catalyst.2、1 mol nitrogen reacts with 3 mol hydrogen to form 2 mol ammonia at high temperature and pressure with the presence of a catalyst.3、 Nitrogen combines with hydrogen to form ammonia at high temperature and pressure with the presence of a catalyst.4、Reaction between nitrogen and hydrogen at high temperature and pressure with the presence of a catalyst gives ammonia.5、At high temperature and pressure, reaction of nitrogen with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst takes place. E)Zinc treated with hydrochloric acid forms hydrogen and zinc chloride. F)Calcium carbonate when heated produces calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. Calcium carbonate is heated to yield calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. Calcium carbonate decomposes to calcium oxide and carbon dioxide when it is heated.N 2+3 H 22 NH 3高温,高压催化剂Zn+2 HClZnCl 2+H 2CaCO 3CaO+CO 2Δ化合物命名1、无机物命名无机化合物英文名称的基本构词规律:◆在化合物命名时常用的英文数目词头:•mono-(1), ['mɒnəʊ]•di-(2), [dai]•tri-(3), [trai]•Tetra-(4), ['tetrə]•penta-(5), ['pentə]•hexa-(6),•hepta-(7),•Octa-(8),•nona-(9), ['nəunə]•deca-(10),•undeca-(11),•dodeca-(12)。

有机化合物的英文命名法有机化学是研究碳和氢的化合物的化学性质和反应的一门学科。
有机化合物的英文命名法是一个非常重要的知识点,它不仅是有机化学的基础,更是解决有机化学问题的关键。
本文将介绍有机化合物的英文命名法。
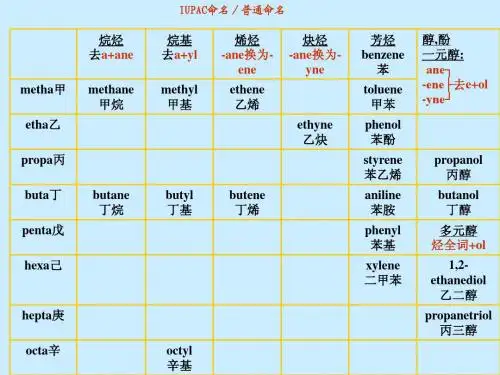
1.直链烷基直链烷基是由碳原子构成的连续直线状的碳氢电子单价基团,命名时采用构成它的烷基名前面加上数字表示碳原子数目。
例如,分别为1、2、3、4个碳原子的直链烷基分别命名为甲基(methyl)、乙基(ethyl)、丙基(propyl)、丁基(butyl)等。
2.环烷基环烷基是由碳原子构成的进环状的碳氢电子单价基团,命名时,采用构成它的烷基名前面加上“环”字表示它是环状的,再用数字表示环上碳原子的数目。
例如,五元环状烷基的命名为环戊基(cyclopentyl)。
3.取代基取代基是在直链烷基或环烷基上去除一个氢原子后加入的其他原子团,命名时先根据取代基所连着的基团(主链)的数目命名取代基的烷基名,然后把烷基名中字母“e”变为字母“y”,最后在主链名前使用编号表示它在主链上的位置。
例如,取代基官能团为氯的命名为氯代烷基(chloroalkyl)时,氯代基中的字母“e”变为字母“y”,主链名前加上编号“1”,得到1-氯代烷基(1-chloroalkyl)。
4.功能基团功能基团是影响有机化合物化学性质的中心部分,能够表现特有的化学性质,命名时首先识别出它的种类,然后根据它的特有性质命名。
例如,酯官能团的命名为alkoxy(由烷基和氧原子构成,其中不含羟基的一种官能团),表示是烷基与氧原子结合的化学实体。
有机化合物的英文命名法是解决有机化学问题的基础,也是有机化学的进一步发展的必要条件。
掌握有机化合物的英文命名法可以让我们更深入地了解有机化学的理论和知识,为我们的学习和应用有机化学知识提供更多的便利条件。



Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds无机化合物的命名(Prefix词头,前缀Suffix词尾,后缀Stem词根)1.Trivial Names俗名H2O water不说dihydrogen oxideNH3 ammonia不说nitrogen trihydrideCaO quicklimeCaCO3 limestone2.Systematic Nomenclature系统命名1)Oxide氧化物——先命名非氧元素ZnOzinc oxideCaO calcium oxideCO carbon oxideNa2O2 sodium peroxideH2O2hydrogen peroxide 注:peroxide过氧化物2)Hydroxide氢氧化物(base碱)Ba(OH)2 barium hydroxideKOH potassium hydroxide3)Acid酸Hydro acid氢酸General formula通式:HnX 命名:hydro- + stem of X + -ic acid H2S hydrosulfuric acid(英) hydrosulphuric(美) 氢硫酸S:sulfur(英)、sulphur(美) HBr 氢溴酸hydrobromic acidBr: bromine HCl 氢氯酸(盐酸)hydrochloric acidCl: chlorine HF 氢氟酸hydrofluoric acidF: fluorineOxoacid or Oxyacid含氧酸General formula通式:HnXOm 命名:Stem of X + -ic acid 注:oxo- (oxy-) 含氧, 氧代H2SO4 sulfuric acid(英) sulphuric acid(美)H2CO3 carbonic acidH3PO4 phosphoric acid P: phosphorus H3BO3 boric acid B: boron HNO3 nitric acid N: nitrogen If X has two oxidation states:-ic:the higher oxidation state-ous:the lower oxidation stateH2SO4 sulfuric acidH2SO3 sulfurous acid1/5HNO3 nitric acidHNO2 nitrous acidIf X (such as halogens) has more than two oxidation states:halogen卤素per- (过,高) + -ic:the still higher oxidation statehypo- (次,在…下) + -ous:the still lower oxidation stateHClO3 chloric acidHClO2 chlorous acidHClO4 perchloric acidHClO hypochlorous acidHIO hypoiodous acid4)Salt盐General formula通式:MnXm 命名:Name of M stem of X + -ide(-ide…化物)Oxide、chloride、nitride、hydrideKI potassium iodideAl2S3 aluminum sulfideLiH lithium hydrideOxysalt含氧酸盐Name the metal ion first and then the anionNaming anions:-ate anions derived from the -ic acid(the higher oxidation state of X)-ite anions derived from the -ous acid (the lower oxidation state of X)HNO3 nitric acidNaNO3 sodium nitrateHNO2 nitrous acidNaNO2 sodium nitriteSO42- sulfateSO32- sulfiteAgClO4 silver perchlorateNaIO3 sodium iodateKClO2 potassium chloriteKBrO potassium hypobromiteMnO42- manganateMnO4- permanganateAcid salt 酸式盐Using “hydrogen” to specify “H”NaHSO4 sodium hydrogen sulfateNaH2PO4 sodium dihydrogen phosphateNa2HPO4 disodium hydrogen phosphate P: phosphorus phosphate磷酸盐(根) Using prefix bi- + name of anion if only one acid salt existsNaHSO4 sodium bisulfateNaHSO3 sodium bisulfiteKHCO3 potassium bicarbonate5)Metals(M)with more than one oxidation state2/5Two methods:①后缀法: 早期使用stem of M + -ic the higher oxidation state of Mstem of M + -ous the lower oxidation state of MHgI2 mercuric iodideHg2I2 mercurous iodide Hg:mercury Cr2+ chromousCr3+ chromic Cr: chromium注:In most cases, Latin stem is used if the metal has symbol derived from itsLatin name.(mercury is an exception)Cu:cuprum (拉丁),copper (英)Cu+ cuprousCu2+ cupricCuI cuprous iodideCuS cupric sulfideSn:stannum (拉丁), tin (英)SnCl2 stannous chlorideSnO2 stannic oxideFe:ferrum (拉丁), iron (英)Fe(OH)2 ferrous hydroxideFeBr3 ferric bromide②IUPAC Rule 1957年开始使用English name of metal(Roman numeral)CuBr copper(I) bromideCuF2 copper(II) fluorideSnO tin(II) oxideSnS2 tin(IV) sulfideFe(NO3)2 iron(II) nitrateFe2(SO4)3 iron(III) sulfateUse Greek prefixes希腊文前缀Mon(o)一di二tri三tetr(a)四pent(a)五hex(a)六hepta七octa八nona九1.to specify the number of each atom in the chemical formula.NO2 nitrogen dioxidePCl5 phosphorus pentachlorideCO2 carbon dioxide2.to specify the number of identical central atoms in condensed acids and their corresponding anions.condensed acid缩酸H3PO4 (mono)phosphoric acidH4P2O7 diphosphoric acid3/5H2SO4 sulfuric acidH2S3O10 trisulfuric acidCrO42- 铬酸盐(根) chromateCr2O72- 重铬酸盐(根)dichromate3. to indicate extent of substitutionPO43- phosphatePS2O23- dithiophosphate thio-硫代…,硫的,含硫的注:The prefixes ortho- and meta- have been used to distinguish acids differingin the “content of water.”ortho- [希腊词头] 正、原(无机酸用)邻(位)(有机化合物命名)meta- [希腊词头] 偏(无机酸用)间(位)(有机化合物命名)ortho-acid 原酸;meta-acid 偏酸H3BO3 orthoboric acid(or boric acid)(原)硼酸(HBO3)n metaboric acid偏硼酸H4SiO4 orthosilicic acid(or silicic acid)原硅酸H2SiO3 metasilicic acid 硅酸(习惯上不叫偏硅酸)H3PO4 orthophosphoric acid (or phosphoric acid)(正)磷酸(HPO3)n metaphosphoric acid 偏磷酸。



常见化合物命名H hydrogen [ˈhaidrədʒən] He helium ['hi:liəm]Li lithium ['liθiəmBe beryllium [be'riliəm]B boron ['bɔ:rɔn]C carbon [ˈkɑ:bən]N nitrogen [ˈnaitrədʒən] O oxygen [ˈɔksidʒən]F fluorine ['fluəri:n]Ne neon [ˈni:ɔn ˈni:ən]Na sodium ['səudiəm]Mg magnesium [mægˈni:ziəm]Al aluminum [ˈæljuˈminiəm, ˈæləˈminiəm] Si silicon [ˈsilikən]P phosphorus ['fɔsfərəs]S sulfur [ ['sʌlfə]Cl chlorine ['klɔ:ri:n]Ar argon ['ɑ:gɔn]Ca calcium [ˈkælsiəm] Rb rubidium [ru:'bidiəm] K potassium [pə'tæsiəm] Br bromine ['brəumi:n] I iodine [ˈaiədi:n]Ba barium ['bɛəriəm其他常有元素Fe : iron ['aiən]Mn : manganese [ˈmæŋgə'ni:z]Cu: copper [ˈkɔpə] 拉丁语:Cuprum Zn: zinc [ziŋk]Hg: mercury [ˈmə:kjuri] 来源于古希腊人对它的称呼hydor argyros (水银)Ag: silver [ˈsilvə] 拉丁名Argentum 即来自希腊文argyros (明亮) , 元素符号Ag ,与英文名silver 毫不相干;Au: gold [gəuld] 金的拉丁名Aurum 来自希腊文aurora (灿烂) ,元素符号Au ,与英文名gold 也无关系。
有机化合物英文命名法
有机化合物英文命名法主要分为以下几种:
1. 烷基命名法:对于链状和支链状化合物,以主链为基础,用烷基来修饰分支部分。
2. 双键位置编号法:对于双键存在的化合物,以主链为基础,通过给双键编号来表示双键的位置。
3. 双键立体异构体命名法:对于含有双键的不对称化合物,根据E、Z规则来区分双键两侧基团的位置关系。
4. 羟基官能团命名法:对于含有羟基(-OH)的化合物,以主链为基础,通过在名称中加入“ol”来表示羟基的存在。
5. 醛、酮官能团命名法:对于含有醛(-CHO)或酮(-CO-)官能团的化合物,以主链为基础,在名称中加入相应的前缀或后缀来表示其存在。
6. 氨基官能团命名法:对于含有氨基(-NH2)的化合物,以主链为基础,在名称中加入“amine”来表示氨基的存在。
以上是常见的有机化合物英文命名法,需要根据具体情况选择适当的命名方法。