hdu试题分类
- 格式:doc
- 大小:31.00 KB
- 文档页数:7

******** 二分图#include <iostream>#include <cstring>using namespace std;#define maxx 100000;int map[501][501],vis[501],d[501];int n,m;int find_path(int x){for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){if(vis[i] || !map[x][i]) continue;vis[i] = 1;if(!d[i] || find_path(d[i])){d[i]=x;return 1;}}return 0;}int max_match(){int count=0;memset(d,0,sizeof(d));for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));if(find_path(i))count++;}return count;}int main(){int k,a,b;while(cin>>k&&k){cin>>n>>m;memset(map,0,sizeof(map));for(int i=0;i<k;i++){cin>>a>>b;map[a][b]=1;}cout<<max_match()<<endl;}return 0;}****** priority_queue dijkstra#include <iostream>#include <queue>using namespace std;const int MAXN =1000000;int u[MAXN];int v[MAXN];int w[MAXN];int d[MAXN];int first[MAXN];int next[MAXN];bool done[MAXN];typedef pair<int,int> pii;priority_queue<pii,vector<pii>,greater<pii> > q; int n,m;void Dijkstra(){memset(done,0,sizeof(done));for(int i=0;i<n;++i){d[i]=MAXN;}d[0]=0;q.push(make_pair(d[0],0));while(!q.empty()){pii u=q.top();q.pop();int x=u.second;if(done[x]){continue;}done[x]=true;for(int e=first[x];e!=-1;e=next[e]){if(d[v[e]]>d[x]+w[e]){d[v[e]]=d[x]+w[e];q.push(make_pair(d[v[e]],v[e]));}}}}int main(){//输入边,构造出邻接表memset(first,-1,sizeof(first));cin>>n>>m;for(int i=0,j=0;i<m;++i){int a,b,c;cin>>a>>b>>c;u[j]=a;v[j]=b;w[j]=c;next[j]=first[u[j]];first[u[j]]=j;++j;u[j]=b;v[j]=a;w[j]=c;next[j]=first[u[j]];first[u[j]]=j;++j;}Dijkstra();for(int j=0;j<n;++j){cout<<j<<","<<d[j]<<endl;}return 0;}*****matrix__chengfa#include <iostream>#include <cmath>#include <algorithm>#include <cstring>using namespace std;struct node{int mm[10][10];};node l,t;int n,m;node cheng(node a,node b){node c;for(int i=0;i<10;i++)for(int j=0;j<10;j++){c.mm[i][j]=0;for(int k=0;k<10;k++){c.mm[i][j]+=a.mm[i][k]*b.mm[k][j]%m;}c.mm[i][j]%=m;}return c;}node solve(int x){if(x==0) return l;if(x==1) return t;if(x&1){return cheng(solve(x-1),t);}else{node ttt=solve(x/2);return cheng(ttt,ttt);}}int main(){int f[10],num,sum;memset(t.mm,0,sizeof(t.mm));memset(l.mm,0,sizeof(l.mm));for(int i=0,j=1;i<9;i++){t.mm[i][j++]=1;}for(int i=0,j=0;i<10;i++){l.mm[i][j++]=1;}while(cin>>n>>m){sum=0;for(int i=0;i<10;i++){cin>>num;t.mm[9][9-i]=num;}if(n<10) {cout<<n<<endl;continue;}node dd=solve(n-9);for(int i=0;i<10;i++){sum += i*dd.mm[9][i]%m;}cout<<sum%m<<endl;}return 0;}。

hdu试题分类hdu题目分类模拟题, 枚举1002 1004 1013 1015 1017 1020 1022 1029 1031 1033 1034 1035 1036 1037 1039 1042 1047 1048 1049 1050 1057 1062 1063 1064 1070 1073 1075 1082 1083 1084 1088 1106 1107 1113 1117 1119 1128 1129 1144 1148 1157 1161 1170 1172 1177 1197 1200 1201 1202 1205 1209 1212(大数取模) 1216(链表)1218 1219 1225 1228 1229 1230 1234 1235 1236 1237 1239 12501256 1259 1262 1263 1265 1266 1276 1279 1282 1283 1287 1296 1302 1303 1304 1305 1306 1309 1311 1314复杂模拟搜索,递归求解1010 1016 1026 1043(双广) 1044 (BFS+DFS) 1045 1067 1072 1104 1175 1180 1195 1208 1226 1238 1240 1241 1242 1258 1271 1312 1317博奕1079动态规划1003 1024 1025 1028 1051 1058 1059 1069 1074 1078 1080 1081 1085 1087 1114 1158 1159 1160 1171 1176 1181 1203 1224 1227 1231 1244 1248 1253 1254 1283 1300数学,递推,规律1005 1006 1012 1014 1018 1019 1021 1023 1027 1030 1032 1038 1041 1046 1059 1060 1061 1065 1066 1071(微积分) 1097 1098 1099 1100 1108 1110 1112 1124 1130 1131 1132 1134 1141 1143 1152 1155(物理题) 1163 1165 1178 1194 1196(lowbit) 1210 1214 1200 1221 1223 1249 1261 1267 1273 1290 1291 1292 1294 1297 1313 1316数论1164 1211 1215 1222 1286 12991086 1115 1147贪心1009 1052 1055 1257并查集1198 1213 1232 1272线段树,离散化1199 1255图论最短路相关的问题1142 1162 1217 1301二分图问题1054 1068 1150 1151 1281其他1053 (huffman) 1102(MST) 1116(欧拉回路)1233(MST) 1269(强连通)数据结构1103(堆+模拟)1166(数状树组)1247 1251 1285(Topol)1298汉诺塔系列1207最近顶点对10071500 DP1501 DP1502 DP or 记忆化1503 DP1504 模拟1505 DP1506 DP1507 2分匹配1508 记忆化容易点1510 DP1511 搜索可以过1512 左偏树1513 DP1514 DP1515 DFS1516 DP1517 博奕1518 搜索1519 DP(不确定)1520 树状DP1521 数学题,母函数什么的。

hdu 2048 数学题这道题可以认为是一道纯数学题,我竟然半天没推出公式,最后参考了一下别人的解题报告才想清晰,汗颜啊~~ N张票的全部罗列可能自然是Ann = N!种罗列方式现在的问题就是N张票的错排方式有几种。
首先我们考虑,假如前面N-1个人拿的都不是自己的票,即前N-1个人满足错排,现在又来了一个人,他手里拿的是自己的票。
只要他把自己的票与其他N-1个人中的随意一个交换,就可以满足N个人的错排。
这时有N-1种办法。
另外,我们考虑,假如前N-1个人不满足错排,而第N个人把自己的票与其中一个人交换后恰好满足错排。
这种状况发生在原先N-1人中,N-2个人满足错排,有且仅有一个人拿的是自己的票,而第N个人恰好与他做了交换,这时候就满足了错排。
由于前N-1个人中,每个人都有机会拿着自己的票。
所以有N-1种交换的可能。
综上所述:f(n) = (i - 1) * [f(n - 1) + f(n - 2)] 固然最后打完代码后运行一看,发觉题目要求保留两位小数,这样的话当n 6的时候全部的结果都是一样的了(明显嘛,当n无限增大的时候概率会趋于一个稳定值的) /* * h2048/linux.c * Creat on: 2011-7-25 * Author : ben */ilude stdio.h include stdlib.h include sing.h include math.h vo work();int main() {ifndef ONLINE_JUDGEfreopen("data.in", "r", stdin);endif work(); return 0;}void work() { int T, i; double table[10] = { 0, 0, 50, 33.33, 37.5,36.67, 36.81 }, ans; scanf("%d", T); while (T--) { scanf("%d",i); if(i 7) { ans = table[i]; }ee { ans = 36.79; }printf("%.2f%%\n", ans); }}第1页共1页。


HDU100题简要题解(2060~2069)这⼗题感觉是100题内相对较为⿇烦的,好多数学题,有点搞我⼼态...歪⽐巴⼘HDU2060 SnookerProblem Descriptionbackground:Philip likes to play the QQ game of Snooker when he wants a relax, though he was just a little vegetable-bird. Maybe you hadn't played that game yet, no matter, I'll introduce the rule for you first.There are 21 object balls on board, including 15 red balls and 6 color balls: yellow, green, brown, blue, pink, black.The player should use a white main ball to make the object balls roll into the hole, the sum of the ball's fixed value he made in the hole is the player's score. The player should firstly made a red ball into the hole, after that he gains red-ball's value(1 points), then he gets the chance to make a color ball, then alternately. The color ball should be took out until all the red-ball are in the hole. In other word, if there are only color balls left on board, the player should hit the object balls in this order: yellow(2 point), green(3 point), brown(4 point), blue(5 point), pink(6 point), black(7 point), after the ball being hit into the hole, they are not get out of the hole, after no ball left on board, the game ends, the player who hasthe higher score wins the game. PS: red object balls never get out of the hole.I just illustrate the rules that maybe used, if you want to contact more details, visit afterthe contest.for example, if there are 12 red balls on board(if there are still red ball left on board, it can be sure that all the colorballs must be on board either). So suppose Philp can continuesly hit the ball into the hole, he can get the maximun score is12 * 1 (12 red-ball in one shoot) + 7 * 12(after hit a red ball, a black ball which was the most valuable ball should be the target) +2 +3 +4 +5 +6 + 7(when no red ball left, make all the color ball in hole).Now, your task is to judge whether Philip should make the decision to give up when telling you the condition on board(How many object balls still left not in the hole and the other player's score). If Philp still gets the chance to win, just print "Yes", otherwise print "No". (PS: if the max score he could get on board add his current score is equal to the opponent's current score, still output "Yes")InputThe first line contains a numble N indicating the total conditions. Then followed by N lines, each line is made of three integers: Ball_Left P_Score O_Score represeting the ball number left on board, Philp's current score, and the opponent's current score.All the input value are in 32 bit integer value range.OutputYou should caculate the max score left Philp can gain, and judge whether he has the possiblity to win.Sample Input212 1 11 30 39Sample OutputYesNo看到题⽬,脸上笑嘻嘻,⼼⾥......硬着头⽪看完了,发现是道⽔题:)分两种情况,加起来:1、⼤于六个球也就是有红球的情况,每打⼀个红球就紧接着打⼀个⿊球,打完红球再把其他颜⾊的打进去2、少于六个球也就是⽆红球的情况,假装剩下的都是相对较⼤的球#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cmath>#include <cstring>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;int n, x, num1, num2;int main() {while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {while (n--) {scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &num1, &num2);if (x > 6)num1 += (x - 6) * 8 + 27;else {int cnt = 7;while (x--) {num1 += cnt;cnt--;}}if (num1 >= num2) printf("Yes\n");else printf("No\n");}}return 0;}HDU2061 Treasure the new start, freshmen!Problem Descriptionbackground:A new semester comes , and the HDU also meets its 50th birthday. No matter what's your major, the only thing I want to tell youis:"Treasure the college life and seize the time." Most people thought that the college life should be colorful, less presure.But in actual, the college life is also busy and rough. If you want to master the knowledge learned from the book, a great deal of leisure time should be spend on individual study and practise, especially on the latter one. I think the every one of you should take the learning attitude just as you have in senior school."No pain, No Gain", HDU also has scholarship, who can win it? That's mainly rely on the GPA(grade-point average) of the student had got. Now, I gonna tell you the rule, and your task is to program to caculate the GPA.If there are K(K > 0) courses, the i-th course has the credit Ci, your score Si, then the result GPA isGPA = (C1 * S1 + C2 * S2 +……+Ci * Si……) / (C1 + C2 + ……+ Ci……) (1 <= i <= K, Ci != 0)If there is a 0 <= Si < 60, The GPA is always not existed.InputThe first number N indicate that there are N test cases(N <= 50). In each case, there is a number K (the total courses number), then K lines followed, each line would obey the format: Course-Name (Length <= 30) , Credits(<= 10), Score(<= 100).Notice: There is no blank in the Course Name. All the Inputs are legalOutputOutput the GPA of each case as discribed above, if the GPA is not existed, ouput:"Sorry!", else just output the GPA value which is rounded to the 2 digits after the decimal point. There is a blank line between two test cases.Sample Input23Algorithm 3 97DataStruct 3 90softwareProject 4 852Database 4 59English 4 81Sample Output90.10Sorry!头⼤,看完发现⼜是⼀道⽔题,题意的精华在于其中的公式:GPA = (C1 * S1 + C2 * S2 +……+Ci * Si……) / (C1 + C2 + ……+ Ci……) (1 <= i <= K, Ci != 0)然后⽤这个算,并且⽤⼀个flag记录是否存在有不及格科⽬的情况#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cmath>#include <cstring>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;int n, m;double a[101], b[101];int main() {while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {while (n--) {scanf("%d", &m);double sum = 0;double num = 0;int flag = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {string s;cin >> s;scanf("%lf%lf", &a[i], &b[i]);if (b[i] < 60) flag = 1;sum += a[i] * b[i];num += a[i];}if (flag == 1) cout << "Sorry!" << endl;else {double ans = (sum + 0.0) / num;printf("%.2lf\n", ans);}if (n) cout << endl;}}return 0;}HDU2062 Subset sequenceProblem DescriptionConsider the aggregate An= { 1, 2, …, n }. For example, A1={1}, A3={1,2,3}. A subset sequence is defined as a array of a non-empty subset. Sort all the subset sequece of An in lexicography order. Your task is to find the m-th one.InputThe input contains several test cases. Each test case consists of two numbers n and m ( 0< n<= 20, 0< m<= the total number of the subset sequence of An ).OutputFor each test case, you should output the m-th subset sequence of An in one line.Sample Input1 12 12 22 32 43 10Sample Output111 222 12 3 1⼈傻了,康了题解才解决这题,卡这题上了⼀上午...这题我感觉算是这100题⾥思维含量最⾼的⼏个了,反正我是傻了(因为菜借这题终于明⽩了三元运算符,⾼中的时候看学弟⽤过,⼀脸懵逼也没想着去学,终于知道是个啥东西了(求gcd的时候还挺⽅便的,直接⼀⾏解决)题⽬⼤意:考虑⼀个集合 An = { 1, 2, ..., n}。
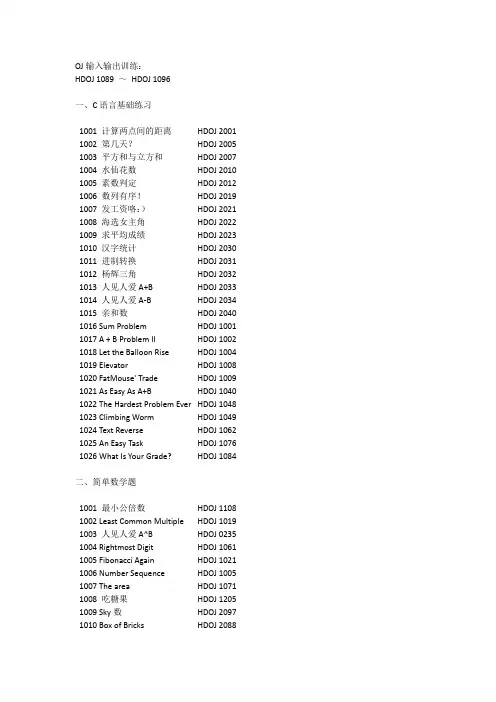
OJ输入输出训练:HDOJ 1089 ~HDOJ 1096一、C语言基础练习1001 计算两点间的距离HDOJ 2001 1002 第几天?HDOJ 2005 1003 平方和与立方和HDOJ 2007 1004 水仙花数HDOJ 2010 1005 素数判定HDOJ 2012 1006 数列有序!HDOJ 2019 1007 发工资咯:)HDOJ 2021 1008 海选女主角HDOJ 2022 1009 求平均成绩HDOJ 2023 1010 汉字统计HDOJ 2030 1011 进制转换HDOJ 2031 1012 杨辉三角HDOJ 2032 1013 人见人爱A+B HDOJ 2033 1014 人见人爱A-B HDOJ 2034 1015 亲和数HDOJ 2040 1016 Sum Problem HDOJ 1001 1017 A + B Problem II HDOJ 1002 1018 Let the Balloon Rise HDOJ 1004 1019 Elevator HDOJ 1008 1020 FatMouse' Trade HDOJ 1009 1021 As Easy As A+B HDOJ 1040 1022 The Hardest Problem Ever HDOJ 1048 1023 Climbing Worm HDOJ 1049 1024 Text Reverse HDOJ 1062 1025 An Easy Task HDOJ 1076 1026 What Is Your Grade? HDOJ 1084二、简单数学题1001 最小公倍数HDOJ 1108 1002 Least Common Multiple HDOJ 1019 1003 人见人爱A^B HDOJ 0235 1004 Rightmost Digit HDOJ 1061 1005 Fibonacci Again HDOJ 1021 1006 Number Sequence HDOJ 1005 1007 The area HDOJ 1071 1008 吃糖果HDOJ 1205 1009 Sky数HDOJ 2097 1010 Box of Bricks HDOJ 20881011 简易版之最短距离HDOJ 20831012 Fibbonacci Number HDOJ 20701013 Coin Change HDOJ 20691014 A + B Again HDOJ 20571015 Lowest Common Multiple Plus HDOJ 20281016 Can you solve this equation? HDOJ 21991017 Strange fuction HDOJ 28991018 Pseudoprime numbers HDOJ 19051019 Delta-wave HDOJ 10301020 月之数HDOJ 25021021 又见GCD HDOJ 25041022 找新朋友HDOJ 12861023 七夕节HDOJ 12151024 完数HDOJ 1406三、递推求解1001 超级楼梯HDOJ 20411002 不容易系列之二HDOJ 20421003 一只小蜜蜂... HDOJ 20441004 不容易系列之(3)——LELE的RPG难题HDOJ 20451005 骨牌铺方格HDOJ 20461006 折线分割平面HDOJ 20501007 母牛的故事HDOJ 20181008 下沙的沙子有几粒?HDOJ 12671009 自共轭Ferrers图HDOJ 12461010 汉诺塔II HDOJ 12071011 悼念512汶川大地震遇难同胞——重建希望小学HDOJ 2190 1012 Children’s Queue HDOJ 12971013 Tiling_easy version HDOJ 25011014 统计问题HDOJ 25631015 Buy the Ticket HDOJ 11331016 Game of Connections HDOJ 11341017 Computer Transformation HDOJ 10411018 Children’s Queue HDOJ 12971019 The Number of Paths HDOJ 12931020 "下沙野骆驼"ACM夏令营HDOJ 129四、简单典型DP1001 数塔HDOJ 20841002 Super Jumping! Jumping! Jumping! HDOJ 10871003 免费馅饼HDOJ 11761004 Common Subsequence HDOJ 11591005 搬寝室HDOJ 14211006 Humble Numbers HDOJ 10581007 Max Sum HDOJ 10031008 Max Sum Plus Plus HDOJ 10241009 FatMouse's Speed HDOJ 11601010 Bone Collector HDOJ 26021011 Piggy-Bank HDOJ 11141012 I NEED A OFFER! HDOJ 12031013 悼念512汶川大地震遇难同胞——珍惜现在,感恩生活HDOJ 2191 1014 Coins HDOJ 2844五、简单博弈1001 Brave Game HDOJ 18461002 Good Luck in CET-4 Everybody! HDOJ 18471003 Fibonacci again and again HDOJ 18481004 Rabbit and Grass HDOJ 18491005 Being a Good Boy in Spring Festival HDOJ 18501006 kiki's game HDOJ 21471007 Public Sale HDOJ 21491008 悼念512汶川大地震遇难同胞——选拔志愿者HDOJ 21881009 丑数游戏1010 YLF's Game六、半程测试1001 CD HDOJ 37631002 Alaska HDOJ 37641003 Celebrity Split HDOJ 37651004 Knight's Trip HDOJ 37661005 Paintball HDOJ 37671006 Shopping HDOJ 37681007 Stack Machine HDOJ 37691008 Ideas HDOJ 37701009 HST HDOJ 37711010 Tunnelling the Earth H DOJ 3772七、母函数1001 Ignatius and the Princess III HDOJ 10281002 Square Coins HDOJ 13981003 Holding Bin-Laden Captive! HDOJ 10851004 Big Event in HDU HDOJ 11711005 Fruit HDOJ 21521006 The Balance HDOJ 1709八、并查集1001 How Many Tables HDOJ 1213 1002 小希的迷宫HDOJ 1272 1003 Is It A Tree? HDOJ 1325 1004 More is better HDOJ 1856 1005 Constructing Roads HDOJ 1102 1006 畅通工程HDOJ 1232 1007 还是畅通工程HDOJ 1233 1008 畅通工程HDOJ 1863 1009 畅通工程再续HDOJ 1875 1010 继续畅通工程HDOJ 1879共26 + 24 + 20 + 14 + 10 + 6 + 10 = 110 题。

hdu前缀和与差分题目【原创版】目录1.概述 hdu 前缀和差分题目2.hdu 前缀和差分题目的解题思路3.hdu 前缀和差分题目的实例解析正文一、概述 hdu 前缀和差分题目在编程竞赛中,我们经常会遇到一些涉及数组和前缀和的问题。
而hdu 前缀和差分题目是这类问题中的一种。
它要求我们根据给定的数组,计算前缀和,并根据前缀和的差分求解一些问题。
这类题目涉及到的知识点主要有前缀和的计算方法,以及如何利用前缀和的差分快速求解问题。
二、hdu 前缀和差分题目的解题思路解决这类问题的一般思路如下:1.首先,我们需要计算数组的前缀和。
前缀和的计算方法有多种,如直接求和、循环求和、利用等差数列求和公式等。
在实际操作中,我们可以根据题目的特点和要求,选择合适的计算方法。
2.其次,我们需要根据前缀和的差分求解问题。
这通常涉及到一些基本的算法,如二分查找、哈希表等。
对于一些复杂的问题,我们还需要结合题目的具体要求,设计合适的算法。
三、hdu 前缀和差分题目的实例解析以一个具体的题目为例,题目描述如下:给定一个长度为 n 的整数数组 a,要求我们计算前缀和数组 s,并根据 s 的差分数组 t 求解一些问题。
其中,前缀和数组 s 满足 s[i] =a[0] + a[1] +...+ a[i],而差分数组 t 满足 t[i] = s[i+1] - s[i]。
针对这个题目,我们可以按照以下步骤进行求解:1.计算前缀和数组 s。
我们可以使用循环求和的方法,时间复杂度为O(n)。
2.计算差分数组 t。
我们可以通过 s 数组求解,时间复杂度为 O(n)。
3.根据差分数组 t 求解问题。
这涉及到一些具体的问题,如求最大值、最小值等。
我们可以根据问题的具体要求,设计合适的算法。
综上所述,解决 hdu 前缀和差分题目,我们需要掌握前缀和的计算方法和差分的求解方法,同时结合题目的具体要求,设计合适的算法。

hdu前缀和与差分题目【实用版】目录1.概述 hdu 前缀和与差分题目2.hdu 前缀和的计算方法3.hdu 差分题目的解题思路4.总结与展望正文一、概述 hdu 前缀和与差分题目在编程竞赛中,我们常常会遇到一些涉及数组、链表等数据结构的题目,其中 hdu 前缀和与差分题目是一类典型的题目。
这类题目要求我们根据给定的数组或链表,计算某些特定元素的和或差分值。
hdu 是“Harvard Data Unit”的缩写,意为哈佛数据单元,是一种常见的数据输入格式。
二、hdu 前缀和的计算方法hdu 前缀和题目要求我们计算一个数组中任意一个元素的前缀和,即该元素以及其前面所有元素的和。
计算前缀和的方法有很多,其中一种比较常见的方法是使用前缀和数组。
1.构建一个与原数组长度相同的前缀和数组,初始值都为 0。
2.遍历原数组,将每个元素的值加入对应的前缀和数组元素。
3.得到前缀和数组,即可计算任意元素的前缀和。
例如,给定数组{1, 2, 3, 4, 5},构建前缀和数组为{0, 1, 3, 6, 10},分别对应原数组每个元素的前缀和。
三、hdu 差分题目的解题思路hdu 差分题目要求我们计算一个数组中任意两个元素的差分值。
这类题目通常需要我们先计算出数组中每个元素的前缀和,然后根据前缀和计算差分值。
1.构建前缀和数组,方法同上。
2.计算差分数组,将原数组每个元素的值减去对应的前缀和数组元素。
3.得到差分数组,即可计算任意两个元素的差分值。
例如,给定数组{1, 2, 3, 4, 5},构建前缀和数组为{0, 1, 3, 6, 10},计算差分数组为{1, 1, 3, 4, 5}。
四、总结与展望hdu 前缀和与差分题目是编程竞赛中的一类基础题目,涉及到数组、链表等基本数据结构的操作。
解决这类题目需要我们熟练掌握前缀和数组、差分数组的计算方法,以及相关的编程技巧。

以下是一个经典的HDU(杭州电子科技大学)在线评测系统中的编程题目:
题目名称:盛最多水的容器
题目描述:
给定n 个非负整数a1,a2,...,an,每个数代表一个坐标点(i, ai)。
在坐标内画n 条线,使得i 垂直于ai。
找出其中的两条线,使得它们与x 轴构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
解题思路:
这道题目可以通过扫描整个数组,同时维护一个当前最大容器的体积来求解。
在每一步中,我们可以计算以当前点为顶点的矩形的体积,并与当前最大体积进行比较。
如果新计算的体积更大,则更新最大体积。
最终返回最大体积即可。
具体实现时,我们可以使用两个变量max_area 和cur_area 来分别表示最大容器体积和当前容器体积。
初始时,将max_area 设置为0,cur_area 设置为0。
然后遍历整个数组,对于每个点(i, ai),计算以该点为顶点的矩形的体积cur_area = min(cur_area * (i - left), ai * (right - i)) + ai * (right - left),其中left 和right 分别表示当前矩形的左边界和右边界。
如果cur_area 大于max_area,则更新max_area。
最终返回max_area 即可。
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)。

hdu算法刷题算法是计算机科学的核心,对于每个计算机科学的学生和专业人士来说,算法题目的刷题是非常重要的。
HDU(Hangzhou Dianzi University)是中国著名的知名高校,其在线评测系统(HDU Online Judge)提供了大量的算法题目,帮助学生和专业人士提升解决实际问题的能力。
本文将介绍HDU算法刷题的一些常见技巧和建议。
首先,要想高效地刷题,掌握基本的算法和数据结构是必不可少的。
常见的算法包括贪心算法、动态规划、深度优先搜索(DFS)、广度优先搜索(BFS)、排序算法等。
掌握这些算法的思想和实现方法,能够帮助我们快速解决问题。
此外,熟悉常见的数据结构如数组、链表、栈、队列、堆、树、图等,也是解决实际问题的基础。
其次,解题过程中要注重理解题目要求和限制条件。
每道题目都有其独特的问题背景和解决方法。
通常,我们需要先读懂题目的意思,并仔细解读题目描述和输入输出格式。
在理解题目后,我们需要分析问题的特点和难点,确定解题的思路和算法。
这个过程需要耐心和细心,有时候需要灵活运用不同的算法思想来解决问题。
在刷题过程中,我们可以按照题目的难易程度进行分类,从简单的题目开始解决。
通过解决一些简单的题目,可以逐渐熟悉题目的解法和代码的写法,提高我们的编程能力。
随着题目的难度逐渐提升,我们也可以学习更多的算法和数据结构,进一步提升自己的解题能力。
此外,HDU Online Judge提供了许多ACM竞赛的模拟题和历年真题。
这些题目的难度较高,但对于挑战性和综合能力的提升非常有帮助。
我们可以尝试解决这些题目,挑战自己的解题能力,并从中学习到更多的知识和技巧。
另外,参加算法竞赛和与他人讨论解题思路也是提高解题能力的好方法。
可以加入一些在线的算法讨论群组,与其他刷题者分享解题思路和经验。
大家可以相互讨论和学习,互相促进进步。
此外,参加一些算法竞赛如ACM ICPC也能提高解题能力,锻炼自己的应变能力和合作精神。

hdu前缀和与差分题目前缀和与差分是一类经典的算法题目,在大部分编程竞赛中都有相关的考察。
这两种算法主要应用于数组的操作和变换,能够高效地解决一些涉及连续子数组的问题。
一、前缀和前缀和是指在数组中,对于每个元素,将其之前的所有元素的和累加起来。
如下所示:前缀和数组:[a1, a2, a3, ..., an]前缀和数组:[0, a1, a1 + a2, a1 + a2 + a3, ..., a1 + a2 + ... + an]对于前缀和数组,我们可以通过O(n)的时间复杂度来计算,即遍历一遍原数组,每次累加之前的和即可得到前缀和数组。
前缀和的应用十分广泛,常用于解决一些与连续子数组相关的问题,例如:1.求解数组中某一区间的和:通过计算前缀和数组的差值,即可得到原数组中某一区间的和。
2.求解数组中的子数组的最大和:通过枚举数组中所有可能的子数组,并利用前缀和数组,可以在O(n)的时间复杂度内求解出最大和。
3.求解数组中某个前缀和为给定值的子数组的个数:通过统计前缀和数组中某个值的出现次数,即可求解出满足条件的子数组个数。
二、差分差分是前缀和的逆运算,常用于解决一些需要对数组的某个区间进行修改的问题。
差分数组的定义如下所示:差分数组:[b1, b2, b3, ..., bn]差分数组:[b1, b2 - b1, b3 - b2, ..., bn - bn-1]对于差分数组,我们可以通过O(n)的时间复杂度来求解原数组,即遍历一遍差分数组,每次累加前面的差值即可得到原数组。
差分的应用也是非常广泛的,常用于解决一些与数组区间修改相关的问题,例如:1.给定一个数组,对于某个区间进行增加/减少操作:通过对差分数组的操作,将增量或减量累加到对应的区间上即可。
2.给定一个数组,求解某个区间内的元素和:通过对差分数组的操作,将差分数组进行前缀和计算,然后再加上原数组对应的值即可求解出原区间的和。
差分数组可以看作是前缀和数组的逆运算,它提供了一种在O(1)时间复杂度内进行单点修改和O(n)时间复杂度内完成数组还原的方法。
hdu前缀和与差分题目在编程竞赛中,前缀和与差分问题是一类非常常见且具有挑战性的题目。
这类题目在HDU(杭电在线编程竞赛平台)上尤为突出。
本文将首先介绍前缀和与差分的概念,然后分析HDU前缀和与差分题目的特点和解题技巧,最后通过典型题目解析来帮助大家更好地理解和掌握这类题目。
## 一、前缀和概念前缀和(Prefix Sum)是一个数学概念,它表示一个数列中,从第一个元素到当前元素的和。
前缀和具有以下性质:1.设数列a1, a2, ..., an,前i个元素的前缀和为Si,则Si = a1 + a2 + ...+ ai。
2.利用前缀和计算数列和:Sn = S1 + S2 + ...+ Sn。
前缀和在诸如区间查询、区间第K小数等应用场景中有着广泛的应用。
## 二、差分概念差分(Difference)是一个数学概念,它表示两个数之间的差。
差分具有以下性质:1.设数列a1, a2, ..., an,第i个元素与第j个元素之间的差为di,j,则di,j = a[i] - a[j]。
2.利用差分计算数列中任意两个元素之间的差:d1,2 = a1 - a2, d2,3 = a2 - a3, ..., dn-1, n = an-1 - an。
差分在诸如区间不同元素个数等应用场景中有着广泛的应用。
## 三、HDU前缀和与差分题目特点HDU前缀和与差分题目具有以下特点:1.题目类型及难度:主要为选择题和填空题,难度从易到难不等。
2.题目涉及的数据范围:数据范围较小,通常不超过10^5。
3.题目解题思路和方法:解题思路和方法通常涉及前缀和与差分的性质,需要灵活运用。
## 四、解题技巧与策略解题技巧与策略包括:1.前缀和与差分的基本思想:熟练掌握前缀和与差分的概念,理解它们在题目中的作用。
2.高效算法与空间优化:在实际解题过程中,要尽量优化算法,减少空间复杂度。
3.边界条件处理:根据题目要求,合理处理边界条件。
## 五、典型题目解析以下是HDU平台上三道典型的前缀和与差分题目:### 题目1:序列和查询给定一个长度为n的序列a,有m个查询。
HDU题目整理【背包问题】2602 Bone Collector1114 Piggy-Bank1203 I NEED A OFFER!1171 Big Event in HDU1059 Dividing2844 Coins2191 悼念512汶川大地震遇难同胞——珍惜现在,感恩生活2159 FATE1561 The more, The Better1011 Starship Troopers2639 Bone Collector II3033 I love sneakers!2955 Robberies2546 饭卡2415 Bribing FIPA1712 ACboy needs your help3535 AreYouBusy3449 Consumer【线段树+树状数组】2688 Rotate2838 Cow Sorting3015 Disharmony Trees3030 Increasing Speed Limits2227 Find the nondecreasing subsequences3450 Counting Sequences3465 Life is a Line1541 Stars2642 Stars1166 敌兵布阵3458 Rectangles Too!1542 Atlantis1828 Picture3016 Man Down1255 覆盖的面积2871 Memory Control1698 Just a Hook1394 Minimum Inversion Number1823 Luck and Love3397 Sequence operation2795 Billboard1540 Tunnel Warfare1779 9-Problem C1543 Paint the Wall3536 Painting【DP优化】2577 How to Type1513 Palindrome1025 Constructing Roads In JGShining's Kingdom3351 Seinfeld1978 How many ways2686 Matrix3376 Matrix Again3392 Pie1422 重温世界杯1505 City Game1506 Largest Rectangle in a Histogram2870 Largest Submatrix2830 Matrix Swapping II1024 Max Sum Plus Plus1244 Max Sum Plus Plus Plus1227 Fast Food1793 Minimal search cost2829 Lawrence3415 Max Sum of Max-K-sub-sequence3401 Trade3276 Star3045 Picnic Cows2993 MAX Average Problem/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemId=3756 有助理解"状态"的推荐题目,今年省赛金牌题Bridging signals /JudgeOnline/problem?id=1631 LIS优化Group /thx/problem.php?id=1351Group2 /thx/problem.php?id=1369 MiniCost /problem.php?pid=1880/JudgeOnline/problem?id=2823学习单调队列的推荐题目Fence /JudgeOnline/problem?id=1821单调队列Batch Scheduling /JudgeOnline/problem?id=1180 单调队列,优化斜率Post office /JudgeOnline/problem?id=1160四边形不等式优化/JudgeOnline/problem?id=3017单调队列优化/JudgeOnline/problem?id=3709单调队列,优化斜率【网络流】1532 Drainage Ditches1533 Going Home1853 Cyclic Tour3081 Marriage Match II3277 Marriage Match III3416 Marriage Match IV3315 My Brute3376 Matrix Again3313 Key Vertex3338 Kakuro Extension1565 方格取数(1)1569 方格取数(2)2686 Matrix3395 Special Fish2448 Mining Station on the Sea3035 War3046 Pleasant sheep and big big wolf3251 Being a Hero1733 Escape2883 kebab2732 Leapin' Lizards3061 Battle3157 Crazy Circuits/JudgeOnline/problem?id=3762/OnlineJudge/index.php/problem/read/id/1491/JudgeOnline/problem?id=2987/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemCode=2314/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemCode=1992Poj2914:/JudgeOnline/problem?id=2914(stoer-Wagner)/JudgeOnline/problem?id=3308SGU 176 http://acm.sgu.ru/problem.php?contest=0&problem=176容量有上下界的网络流问题,有难度/daizhy_acm/blog/item/c3e63252763ae66984352480.html 这里有个题目分类,有兴趣的话,可以去刷~/?p=217胡浩的博客上也有点东西~可以去看看~【字符匹配】1711 Number Sequence1867 A + B for you again3374 String Problem3336 Count the string1075 What Are You Talking About1251 统计难题1671 Phone List1247 Hat’s Words1800 Flying to the Mars2072 单词数2222 Keywords Search2896 病毒侵袭3065 病毒侵袭持续中2243 考研路茫茫——单词情结2825 Wireless Password2296 Ring3341 Lost's revenge3247 Resource Archiver【最短路】2544 最短路2066 一个人的旅行2112 HDU Today1874 畅通工程续1142 A Walk Through the Forest1385 Minimum Transport Cost1548 A strange lift1217 Arbitrage2680 Choose the best route2923 Einbahnstrasse2962 Trucking2722 Here We Go(relians) Again1690 Bus System2482 Transit search1596 find the safest road1598 find the most comfortable road2377 Bus Pass2363 Cycling2433 Travel1688 Sightseeing2833 WuKong3191 How Many Paths Are There【数据结构问题】http://124.205.79.250/JudgeOnline/problem?id=1456 Supermarkethttp://124.205.79.250/JudgeOnline/problem?id=3228 Gold Transportationhttp://124.205.79.250/JudgeOnline/problem?id=1182 食物链http://124.205.79.250/JudgeOnline/problem?id=1733 Parity gamehttp://124.205.79.250/JudgeOnline/problem?id=1417 True Liarshttp://124.205.79.250/JudgeOnline/problem?id=2912 Rochambeau/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemCode=3261 Connections in Galaxy Warhttp://124.205.79.250/JudgeOnline/problem?id=3264 Balanced Lineup(RMQ模板题)1829 A Bug's Life1272 小希的迷宫1325 Is It A Tree?1558 Segment set1598 find the most comfortable road 3461 Code Lock3367 Pseudoforest2473 Junk-Mail Filter3172 Virtual Friends3047 Zjnu Stadium3038 How Many Answers Are Wrong 2818 Building Block3234 Exclusive-OR2586 How far away ?2874 Connections between cities 3486 Interviewe2888 Check Corners【矩阵乘法】1575 Tr A1757 A Simple Math Problem2254 奥运2256 Problem of Precision1558 Gauss Fibonacci2604 Queuing2276 Kiki & Little Kiki 22855 Fibonacci Check-up2971 Tower2294 Pendant3117 Fibonacci Numbers2842 Chinese Rings3519 Lucky Coins Sequence3509 Buge's Fibonacci Number Problem 3524 Perfect Squares3483 A Very Simple Problem【搜索专题】1253 胜利大逃亡1072 Nightmare1495 非常可乐2757 Ocean Currents1026 Ignatius and the Princess I1728 逃离迷宫1401 Solitaire1175 连连看1016 Prime Ring Problem2809 God of War1043 Eight1667 The Rotation Game1547 Bubble Shooter2216 Game III2364 Escape2822 Dogs1983 Kaitou Kid - The Phantom Thief (2) 2821 Pusher2782 The Worm Turns2234 无题I1560 DNA sequence1813 Escape from Tetris2517 棋盘分割2416 Treasure of the Chimp Island 1226 超级密码2579 Dating with girls(2)。
hdu 邻接矩阵最水的题英文版The problem of adjacency matrix in HDU is considered to be one of the easiest problems in the history of competitive programming. The task simply requires the participants to input a number N and then output an N*N adjacency matrix where all elements are 0 except for the diagonal elements, which are 1.Although this problem may seem trivial, it serves as a good warm-up exercise for beginners in the field of competitive programming. It helps them understand the concept of adjacency matrices and how they are used to represent graphs in computer science.In addition, this problem also tests the participants' ability to read input and output data correctly, as well as their proficiency in basic programming skills. Overall, while the adjacency matrix problem in HDU may be the easiest of all, it still serves as a valuable learning opportunity for aspiring competitive programmers.完整中文翻译HDU中的邻接矩阵问题被认为是竞赛编程史上最简单的问题之一。
hdu5459(递推好题)Jesus Is HereTime Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/102400 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 512 Accepted Submission(s): 368Problem DescriptionI've sent Fang Fang around 201314 text messages in almost 5 years. Why can't she make sense of what I mean?``But Jesus is here!" the priest intoned. ``Show me your messages."Fine, the first message is and the second one is .The -th message is afterwards. Let me give you some examples., and .``I found the -th message's utterly charming," Jesus said.``Look at the fifth message". and two appear in it.The distance between the first and the second one we said, is .``You are right, my friend," Jesus said. ``Love is patient, love is kind.It does not envy, it does not boast, it is not proud. It does not dishonor others, it is not self-seeking, it is not easily angered, it keeps no record of wrongs.Love does not delight in evil but rejoices with the truth.It always protects, always trusts, always hopes, always perseveres."Listen - look at him in the eye. I will find you, and count the sum of distance between each two different as substrings of the message.InputAn integer , indicating there are test cases.Following lines, each line contain an integer , as the identifier of message.OutputThe output contains exactly lines.Each line contains an integer equaling to:where as a string corresponding to the -th message.Sample Input9 5 6 7 8 113 1205 199312 199401 201314Sample OutputCase #1: 5 Case #2: 16 Case #3: 88 Case #4: 352 Case #5: 318505405 Case #6: 391786781 Case #7: 133875314 Case #8: 83347132 Case #9: 16520782这个题真的很难想,但是hdu划分其难度只有2,那么肯定要好好总结⼀下了。
hdu2094—看似拓扑实际上是⼀道思维题HDU2094 产⽣冠军题意:中⽂题,就不解释了。
题意已经⾮常清楚了。
这道题的看起来像是⼀个拓扑排序的问题实际上拓扑感觉做不了,可能可以做了吧?但是我没想到,估计也⽐较⿇烦吧。
这⾥介绍⼀种⽐较简单的做法,就是⼀种思维,如果存在冠军(所有⼈都可以被他打败),这个⼈肯定没有败过,⽽其他⼈都败过,所以我们只需要确定所有⼈的⼈数,和败者的⼈数(去重以后,所以需要⽤set,因为⼀个败者会败给多个⼈,所以在多个对局中出现)。
如果所有⼈的数量与败者的数量的差是1,说明存在冠军,否则,不存在,直接看代码吧!//Author: xiaowuga#include <bits/stdc++.h>#define maxx INT_MAX#define minn INT_MIN#define inf 0x3f3f3f3fconst long long N=100;using namespace std;typedef long long L;set<string>a,b;int main() {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);int n;while(cin>>n&&n){a.clear();b.clear();for(int i=0;i<n;i++){string x,y;cin>>x>>y;a.insert(x);a.insert(y);b.insert(y);}if(a.size()-b.size()==1) cout<<"Yes"<<endl;else cout<<"No"<<endl;}return0;}很简单的⼀道题,主要靠思维吧,感觉和拓扑没什么关系。
hdu试题分类hdu题目分类模拟题, 枚举1002 1004 1013 1015 1017 1020 1022 1029 1031 1033 1034 1035 1036 1037 1039 1042 1047 1048 1049 1050 1057 1062 1063 1064 1070 1073 1075 1082 1083 1084 1088 1106 1107 1113 1117 1119 1128 1129 1144 1148 1157 1161 1170 1172 1177 1197 1200 1201 1202 1205 1209 1212(大数取模) 1216(链表)1218 1219 1225 1228 1229 1230 1234 1235 1236 1237 1239 12501256 1259 1262 1263 1265 1266 1276 1279 1282 1283 1287 1296 1302 1303 1304 1305 1306 1309 1311 1314复杂模拟搜索,递归求解1010 1016 1026 1043(双广) 1044 (BFS+DFS) 1045 1067 1072 1104 1175 1180 1195 1208 1226 1238 1240 1241 1242 1258 1271 1312 1317博奕1079动态规划1003 1024 1025 1028 1051 1058 1059 1069 1074 1078 1080 1081 1085 1087 1114 1158 1159 1160 1171 1176 1181 1203 1224 1227 1231 1244 1248 1253 1254 1283 1300数学,递推,规律1005 1006 1012 1014 1018 1019 1021 1023 1027 1030 1032 1038 1041 1046 1059 1060 1061 1065 1066 1071(微积分) 1097 1098 1099 1100 1108 1110 1112 1124 1130 1131 1132 1134 1141 1143 1152 1155(物理题) 1163 1165 1178 1194 1196(lowbit) 1210 1214 1200 1221 1223 1249 1261 1267 1273 1290 1291 1292 1294 1297 1313 1316数论1164 1211 1215 1222 1286 12991086 1115 1147贪心1009 1052 1055 1257并查集1198 1213 1232 1272线段树,离散化1199 1255图论最短路相关的问题1142 1162 1217 1301二分图问题1054 1068 1150 1151 1281其他1053 (huffman) 1102(MST) 1116(欧拉回路)1233(MST) 1269(强连通)数据结构1103(堆+模拟)1166(数状树组)1247 1251 1285(Topol)1298汉诺塔系列1207最近顶点对10071500 DP1501 DP1502 DP or 记忆化1503 DP1504 模拟1505 DP1506 DP1507 2分匹配1508 记忆化容易点1510 DP1511 搜索可以过1512 左偏树1513 DP1514 DP1515 DFS1516 DP1517 博奕1518 搜索1519 DP(不确定)1520 树状DP1521 数学题,母函数什么的。
其实都可以过1522 稳定婚姻1523 DP1524 博弈1525 博弈1526 Maxflow1527 博弈1528 2分匹配1529 简单题1530 最大团1531 差分约束1532 Maxflow 入门题1533 KM Or 最小费用流1534 差分约束1535 差分约束1536 博弈1537 模拟加置换群的理论CODE可以短些,其实没必要。
1538 很有意思的题目。
据说是Microsoft亚洲总裁面试的题目1540 线段树1541 树状数组1542 离散,线段树1543 线段树1544 简单的1545 DP /forum/htm_data/18/0608/2050.html 1546 搜索1547 模拟1548 模拟1551 2分答案155315541555 简单1556 技巧。
数学1557 搜索1558 并查+ 线段判交1559 DP1560 减支+ 搜索1561 树状DP1562 暴力between 1000 and 99991563 简单1564 博弈。
1565 状态DP1566 数学1567 模拟1568 大数1569 最小割1570 数学1571 最段路1573 数学1574 DP1575 2分1576 数论1577 模拟,处理精度1579 记忆化1580 DP1582 搜索1583 模拟1584 搜索158515861587 简单题目1591 模拟1592 简单1593 数学1594 数学1595 图论1596 图论1597 图论1598 图论1599 图论基础题:1000、1001、1004、1005、1008、1012、1013、1014、1017、1019、1021、1028、1029、1032、1037、1040、1048、1056、1058、1061、1070、1076、1089、1090、1091、1092、1093、1094、1095、1096、1097、1098、1106、1108、1157、1163、1164、1170、1194、1196、1197、1201、1202、1205、1219、1234、1235、1236、1248、1266、1279、1282、1283、1302、1303、1323、1326、1330、1334、1335、1339、1390、1391、1393、1395、1397、1405、1406、1407、1408、1412、1418、1420、1465、1491、1555、1562、1563、1570、1587、1673、1678、1708、1718、1720、1785、1799、1859、1862、1877、1898、1976、1977、1985、1994、2000、2001、2002、2003、2004、2005、2006、2007、2008、2009、2010、2011、2012、2013、2014、2015、2016、2017、2018、2019、2020、2021、2022、2023、2024、2025、2026、2027、2028、2029、2030、2031、2032、2033、2034、2035、2039、2040、2042、2043、2048、2049、2051、2053、2055、2056、2057、2060、2061、2071、2073、2075、2076、2078、2081、2083、2088、2090、2092、2093、2095、2096、2097、2098、2099、2101、2103、2106、2107、2109、2113、2114、2115、2123、2131、2132、2133、2135、2136、2137、2138、2139、2143、2148、2153、2156、2161、2162、2164、2178、2186、2192、2200、2201、2212、2304、2309、2317、2401、2500、2502、2503、2504、2519、2520、2521、2523、2524、2535、2537、2539、2547、2548、2549、2550、2551、2552、2555、2560、2561、2562、2566、2567、2568、2700、2710、DP:1003、1024、1029、1069、1074、1087、1114、1159、1160、1171、1176、1203、1231、1257、1260、1284、1421、1789、1978、2059、2084、2159、2191、2544、2571、2602、2709、搜索:1010、1015、1016、1026、1072、1075、1175、1180、1181、1238、1239、1240、1241、1242、1253、1254、1312、1372、1548、1597、1671、1677、1728、1800、1983、2102、2141、2553、2563、2605、2612、2614、1616、2717贪心:1009、1045、1049、1050、1051、1052、1257、1800、2037、2111、2124、2187、2391、2570数学题:1018、1065、1071、1115、1141、1162、1212、1220、1492、1593、1701、1722、1798、1840、1999、2036、2080、2086、2089、2105、2108、2134、2303、2393、2438、2529、2547、2548、2552、2554、2601、2603、2701、递推:1133、1143、1207、1249、1267、1284、1290、1297、1396、1992、1995、1996、2013、2014、2044、2045、2046、2047、2050、2064、2065、2067、2068、2070、2077、2085、2151、2154、2160、2190、2501、2512、2563、2569、2709、2716、字符串:1020、1039、1043、1062、1073、1075、1088、1113、1161、1200、1251、1256、1288、1321、1328、1379、1804、1860、1982、1984、2017、2024、2025、2026、2027、2043、2052、2054、2072、2074、2087、2131、2137、2140、2163、2203、2206、2352、2500、2549、2564、2565、2567、2572、2609、2607、2707、2708、2719、2721、2723、大数:1002、1042、1133、1250、1297、1715、1753、1865、2100、胡搞:1022、1027、1030、1035、1128、1165、1209、1210、1215、1222、1228、1229、1230、1237、1259、1276、1286、1337、1342、1361、1370、1506、1577、1597、1702、1716、1727、1868、1870、1896、1981、1986、1987、1988、1997、1998、1999、2058、2062、2089、2090、2094、2104、2116、2117、2135、2175、2183、2184、2197、2303、2368、2370、2374、2511、2522、2527、2600、2615、2703、2711、2714、2715、2725、博弈:1077、1404、1517、1524、1525、1527、1536、1564、1729、1730、1846、1847、1848、1849、1850、2147、2149、2176、2177、2188母函数:1085、1171、1398、2079、2082、2110、2152、2189、2566、hash:1264、1280、1425、1496、1800、2522、2600、。