tcp、ip协议栈移植
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:377.67 KB
- 文档页数:15

LWIP协议栈详解LWIP(Lightweight IP)是一个轻量级的开源 TCP/IP 协议栈,旨在为嵌入式系统提供网络连接功能。
它非常适合资源受限的系统,如单片机和小型处理器,因为它非常小巧且具有很好的可移植性。
首先,让我们来看看LWIP的核心协议。
LWIP提供了IP协议、ARP协议、ICMP协议和UDP协议的实现。
IP协议层负责数据包的路由和分段,ARP协议层负责解析IP地址和MAC地址的映射,ICMP协议用于网络探测和错误报告,UDP协议提供简单的不可靠数据传输。
除了核心协议,LWIP还提供了一些可选的协议功能,如TCP协议和DHCP协议的实现。
TCP协议提供了可靠的数据传输,而DHCP协议用于自动获取IP地址。
LWIP的另一个重要特性是它的可移植性。
LWIP设计了一个适配层,将操作系统相关的功能与核心协议分离开来。
适配层提供了一组标准的API,操作系统只需要实现这些API就可以使用LWIP协议栈。
LWIP支持的平台非常广泛,包括常见的操作系统如Windows、Linux和FreeRTOS,以及嵌入式系统如ARM Cortex-M和Microchip PIC等。
最后,让我们来看看LWIP的应用协议扩展能力。
应用协议可以通过注册回调函数来扩展LWIP的功能。
例如,应用程序可以注册一个回调函数来处理HTTP请求,或者注册一个回调函数来处理自定义的应用层数据。
这种扩展机制使得LWIP非常灵活,可以满足各种应用需求。
总结起来,LWIP是一个轻量级的开源TCP/IP协议栈,适用于资源受限的嵌入式系统。
它将TCP/IP协议栈分为核心协议和应用协议两层,提供了IP、ARP、ICMP、UDP等核心协议的实现,并通过可移植的适配层支持各种平台。
此外,LWIP还提供了应用协议扩展的能力,通过注册回调函数来扩展功能。
无论是大型操作系统还是小型嵌入式系统,LWIP都是一个很好的选择。
下载到源码之后
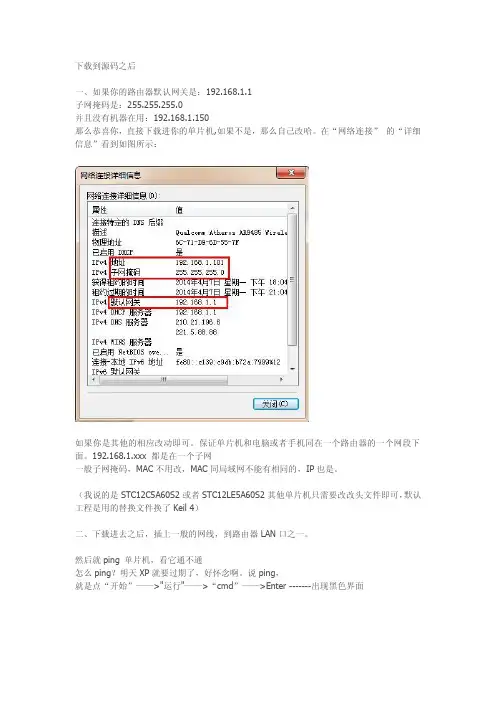
一、如果你的路由器默认网关是:192.168.1.1
子网掩码是:255.255.255.0
并且没有机器在用:192.168.1.150
那么恭喜你,直接下载进你的单片机,如果不是,那么自己改哈。
在“网络连接”的“详细信息”看到如图所示:
如果你是其他的相应改动即可。
保证单片机和电脑或者手机同在一个路由器的一个网段下面。
192.168.1.xxx都是在一个子网
一般子网掩码,MAC不用改,MAC同局域网不能有相同的,IP也是。
(我说的是STC12C5A60S2或者STC12LE5A60S2其他单片机只需要改改头文件即可,默认工程是用的替换文件换了Keil4)
二、下载进去之后,插上一般的网线,到路由器LAN口之一。
然后就ping单片机,看它通不通
怎么ping?明天XP就要过期了,好怀念啊。
说ping,
就是点“开始”——>"运行"——>“cmd”——>Enter-------出现黑色界面
输入:ping192.168.1.150按——>Enter(PS:如果你的IP改成别的,就写别的)
出现这个回应,那么一切都通了。
下一步就是看你想做什么了
三、如果是手机下载TCP/UDP调试APP如果是电脑用TCP/UDP调试助手发送命令
命令解析是在fu_app.c里面函数里面。
默认示例是点亮,关闭led等
接收UDP数据的,有效数据从DATA[42]开始
接收TCP数据的,有效数据从DATA[54]开始
收到什么数据,该做什么都是你自己的事情了。
若不明白?那看视屏教程更直观哈。

1、引言为了实现嵌入式系统终端连入互联网,而有必要为其引入了网络功能。
μC/OS II 是一个源代码开放的实时操作系统,但是它只是一个实时的任务调度及通信内核,并没有集成TCP/IP 通信协议,为了实现网络功能,需要在μC/OS II 移植一个轻量级的TCP/IP 通信协议LwIP。
本文主要论述μC/OS II 下通信协议LwIP 的移植以及测试。
2、LwIP 简介LwIP ( light weight IP)是瑞士计算机科学院的Adam Dunkels 等开发的一套开放TCP/IP 协议栈源代码。
LwIP 既可以移植到操作系统上,又可以在无操作系统的情况下独立运行。
LwIP 实现的重点是在保持TCP/IP 协议主要功能的基础上减少对RAM 的占用,这使LwIP 适合在低端嵌入式系统中使用。
其主要特点如下:(1)支持多网络接口下IP 转发;(2)支持ICMP 协议;(3)包括试验性扩展的UDP;(4)包括简单的拥塞控制,RTT 估算和快速恢复和快速转发的TCP;(5)提供专门的内部回调接口(Raw API)用于提高应用程序性能;(6)可选择的Berkeley 接口API;3、LwIP 协议栈移植到μC/OS II 操作系统的具体实现3.1 嵌入式系统结构和LwIP 接口整个嵌入式系统的结构如图 1 所示,由ARM 微处理器、网卡、网络设备驱动、μC/OSII 操作系统、LwIP 协议栈和应用程序组成。
图 1 嵌入式系统结构图LwIP 在设计时为了适应不同的操作系统,并没有在代码中使用和某个特定的操作系统相关的系统调用和数据结构,而是在LwIP 和操作系统之间提供了一个接口层(sys_arch interface),该接口主要实现的功能包括数据类型的定义、存储模式的选择、任务间的同步、时间和内存的管理等。
因此,完成LwIP 在μC/OS II 移植,我们就是要通过修改这个接口层来实现。
同时,还要根据自己所要实现的具体目的,可以对LwIP 协议栈进行一定的裁减。

lwip移植说明及心得lwIP(lightweight IP)是一个轻量级的TCP/IP协议栈,适用于嵌入式系统。
它提供了TCP/IP协议的核心功能,包括IP、TCP、UDP和ICMP等。
在移植lwIP协议栈时,需要完成以下几个步骤:1. 硬件适配:lwIP协议栈需要根据具体硬件平台进行适配。
首先需要根据硬件平台的网络接口驱动,实现lwIP的网络接口层接口函数,包括接收和发送数据包的函数。
其次,还需要完成其他硬件相关的初始化工作,例如中断初始化、时钟初始化等。
2. 内存管理:lwIP协议栈需要进行内存管理,包括分配、释放和管理数据包的内存。
移植lwIP时,可以根据实际需求选择适合的内存管理方式,例如使用静态内存池或者动态内存分配算法。
3. 系统接口:lwIP需要与操作系统进行交互,包括线程管理、时间管理和互斥锁等。
在移植lwIP时,需要实现与目标操作系统相关的系统接口函数,并将其注册给lwIP。
4. 配置参数:lwIP协议栈有许多配置选项,可以根据实际的应用需求进行设置。
移植lwIP时,需要根据实际需求修改lwipopts.h文件中的配置选项,例如内存池的大小、TCP和UDP的最大连接数等。
在移植lwIP协议栈的过程中,我总结了以下几点心得:1. 在移植过程中,应该尽量保持lwIP协议栈的轻量级特性,避免不必要的代码和功能。
这样可以降低存储和计算资源的消耗,提高系统的性能和效率。
2. 在进行硬件适配时,需要仔细阅读lwIP的文档和源代码,了解其网络接口层的要求和接口函数的使用方式。
同时,还要根据硬件平台的特点做相应的调整和优化,以确保网络数据的稳定和高效传输。
3. 内存管理是lwIP移植的一个关键问题。
根据实际需求选用适合的内存管理方式,并进行合理的内存优化。
例如,可以通过调整内存池的大小、采用更高效的内存分配算法等方式,减小内存的占用和碎片化。
4. 系统接口的实现需要与目标操作系统紧密结合。
在实现系统接口函数时,要充分考虑操作系统的特点和限制,例如线程管理方式、时间管理方式和互斥锁的实现等。


一步步移植uCOS-IIandLwIP(一)STM32F103ZE下移植uCOS-II and LwIP 汇总本文主要记录嵌入式实时操作系统uCOS-II(Ver 2.85)和轻量型TCP/IP协议栈LwIP(Ver 1.4.1)在32bit单片机STM32F103ZE上的移植过程,并列举几个simple examples说明两者工作原理。
本文的叙述原则是“用到什么知识点,就查阅相关资料”,对于其它延伸知识点不再概述。
所需物资:- 硬件开发平台,本平台网卡为DM9000A- uCOS-II(Ver 2.85)源码,可直接从Micrium官网下载uCOS 在cortex-M3上的移植例程uCOSII-ST-STM32F103ZE-SK - LwIP(Ver 1.4.1)源码,下载链接LwIP1.4.1一、Lwip移植TCP/IP协议分为网络链路层、网络层、传输层和应用层四个部分,网络链路层主要涉及底层硬件驱动的编写,另外三个上次协议一般采用协议栈的方式软件实现。
要实现与其它网络设备通信,首当其冲的是要移植好底层网卡驱动。
LwIP协议栈已经为我们提供了网络链路底层接口,我们要做到主要工作涉及到以下几个方面:- 单片机与网卡DM9000芯片的通信;- 完善LwIP协议栈文件ethernetif.c接口函数,该部分的难点在于实现LwIP规定的struct pbuf类型的数据包与网卡数据之间相互转换;- 上层软件协议的simple explain;1、网卡DM9000底层驱动的编写首先查阅DM9000的Datasheet(建议直接从芯片官网上查找,一般会有该芯片的Application note or Demo)本文主要是运用DM9000的16-bit mode,其总线形式类似与intel 8080总线,涉及读写指令和数据的控制引脚为CS#、IOW#、IOR#、CMD,数据总线引脚SD0~SD15,中断引脚INT。


tcpip协议栈TCP/IP协议栈是当前网络通信中最基础和最重要的协议栈之一,它由四层组成,分别是网络接口层、网络层、传输层和应用层。
首先是网络接口层,它负责将数据从传输层传送到物理网络。
在这一层,数据被封装成数据帧,然后通过物理层的网卡发送出去。
常见的协议有以太网、Wi-Fi等。
接下来是网络层,主要负责寻址和路由功能。
数据在这一层被封装成数据包,其中包含源地址和目的地址。
在网络层,数据包通过IP协议进行传输,并依靠路由器等设备进行转发和寻址。
传输层负责数据的可靠传输。
常见的传输层协议有TCP和UDP。
TCP协议提供可靠的连接和流式传输,通过数据的分段、排序和检验,确保数据的可靠性。
而UDP协议则是一种无连接的传输协议,它不保证数据的可靠性,但传输效率较高。
最后是应用层,它是网络应用程序和用户之间的接口。
应用层协议有很多,例如HTTP、FTP、SMTP等。
HTTP协议是Web浏览器和服务器之间传输超文本的协议,FTP协议是用于文件传输的协议,SMTP协议是用于发送电子邮件的协议,它们都是基于TCP协议的。
TCP/IP协议栈的设计使得不同的网络设备和应用程序可以互相交互和通信。
它的优点是灵活性高,可扩展性强,同时在各个层次上实现了分层的模块化设计。
当然,它也存在一些缺点,如复杂性较高,协议过程中的开销较大。
总的来说,TCP/IP协议栈是现代网络通信的基石,它通过网络接口层、网络层、传输层和应用层的协同工作,实现了数据的封装、路由和传输,提供了可靠和高效的网络通信服务。
随着互联网的发展,TCP/IP协议栈也在不断演进和完善,为网络通信提供了更好的基础支撑。

详解uIP TCPIP协议栈在51单片机上的设计实现一引言随着信息技术的不断发展,以及人们对日常生活舒适度、方便度要求的提高,信息家电、智能仪表等产品越来越频繁的出现在我们的生活当中;人们也越来越热衷于把家电、仪表等设备连接到Internet 中,从而可以方便、及时的对它们进行远程察看、远程控制。
把这些设备接入Internet ,就需要考虑TCP/IP 网络协议的实现。
51单片机是对目前所有兼容Intel 8031指令系统的单片机的统称。
该系列单片机的始祖是Intel的8031单片机,后来随着Flash rom技术的发展,8031单片机取得了长足的进展,成为目前应用最广泛的8位单片机之一,其代表型号是ATMEL公司的AT89系列,它广泛应用于工业测控系统之中。
目前很多公司都有51系列的兼容机型推出,在目前乃至今后很长的一段时间内将占有大量市场。
51单片机是基础入门的一个单片机,还是应用最广泛的一种。
需要注意的是52系列的单片机一般不具备自编程能力。
本文将简要描述uIP的实现方法,分析uIP协议栈的应用接口,并讨论如何将其应用到51系列单片机上。
二uIP协议栈的实现方法简述uIP协议栈主要提供了三个函数供系统底层调用。
即uip_init(),uip_input()和uip_periodic()。
其与应用程序的主要接口是UIP_APPCALL()。
ip_init()是系统初始化时调用的,主要初始化协议栈的侦听端口和默认所有连接是封闭的。
当网卡驱动收到一个输进包时,将放进全局缓冲区uip_buf中,包的大小由全局变量uip_len约束。
同时将调用uip_input ()函数,这个函数将会根据包首部的协议处理这个包和需要时调用应用程序。
当uip_input ()返回时,一个输出包同样放在全局缓冲区uip_buf里,大小赋给uip_len.假如uip_len是0,则说明没有包要发送。
否则调用底层系统的发包函数将包发送到网络上。

tcpip协议栈TCP/IP协议栈。
TCP/IP协议栈是互联网的基础协议,它是一组用于互联网的通信协议。
TCP/IP 协议栈由四层构成,分别是网络接口层、网络层、传输层和应用层。
每一层都有其特定的功能和作用,下面将对TCP/IP协议栈的每一层进行详细介绍。
首先是网络接口层,它负责将数据包从一个主机传输到另一个主机。
在这一层,数据包被封装成帧,并通过物理介质进行传输。
网络接口层的协议有以太网、无线局域网等,它们定义了数据在物理介质上传输的格式和规则。
接下来是网络层,网络层主要负责数据包的路由和转发。
在网络层,数据包被封装成数据报,并通过IP地址进行传输。
网络层的主要协议是IP协议,它定义了数据包的格式和路由规则,确保数据包能够在网络中正确地传输到目的地。
然后是传输层,传输层主要负责端到端的通信。
在传输层,数据被封装成报文,并通过端口号进行传输。
传输层的主要协议有TCP和UDP,它们定义了数据的传输方式和可靠性,确保数据能够在源主机和目的主机之间可靠地传输。
最后是应用层,应用层是用户直接使用的层。
在应用层,数据被封装成消息,并通过应用层协议进行传输。
应用层的协议有HTTP、FTP、SMTP等,它们定义了不同应用程序之间的通信规则,确保不同应用程序之间能够正确地交换数据。
总的来说,TCP/IP协议栈是互联网的基础协议,它定义了数据在网络中的传输方式和规则,确保数据能够在不同主机和不同应用程序之间正确地传输和交换。
通过网络接口层、网络层、传输层和应用层的协同工作,TCP/IP协议栈实现了互联网的可靠和高效通信。
除了以上介绍的四层,TCP/IP协议栈还包括了一些辅助协议,如ARP、ICMP、DHCP等,它们在协议栈中起着重要的作用,保证了网络的正常运行和通信的顺利进行。
总的来说,TCP/IP协议栈是互联网的基础,它定义了数据在网络中的传输方式和规则,保证了网络的正常运行和通信的顺利进行。
了解TCP/IP协议栈的结构和功能对于理解互联网的工作原理和网络通信的过程具有重要意义。

TCPIP协议进行数据传输TCP/IP协议是一组用于在网络上进行数据传输的通信协议。
它由两个协议组成:传输控制协议(TCP)和互联网协议(IP)。
TCP/IP协议是互联网的基础,它为数据在网络上的传输提供了可靠性、有序性和高效性。
下面是关于TCP/IP协议进行数据传输的详细介绍。
TCP/IP协议是一个层次化的协议栈,由四个层次组成:网络接口层、网络层、传输层和应用层。
1.网络接口层:网络接口层是TCP/IP协议栈的最底层,它与底层硬件设备(如网卡)进行通信。
它主要负责将数据从主机转发到网络或从网络接收到主机。
在数据传输过程中,网络接口层将数据封装成数据帧,并添加源地址和目标地址等信息。
2.网络层:网络层负责将数据从源主机发送到目标主机。
它使用IP地址来标识网络中的不同主机和路由器。
网络层使用IP协议将数据分割成小的数据包,每个数据包都包含源IP地址和目标IP地址。
同时,它还负责数据包的路由选择和转发。
3.传输层:传输层提供了可靠的端到端数据传输服务。
它使用TCP协议和UDP协议来实现数据的传输。
TCP协议提供面向连接的可靠数据传输,并确保数据的有序性和完整性。
UDP协议则提供无连接的不可靠数据传输,适用于对数据传输实时性要求较高的应用。
4.应用层:应用层是TCP/IP协议栈的最上层,它提供了各种应用程序和网络服务。
常见的应用层协议有HTTP、FTP、SMTP等。
这些协议通过TCP/IP协议栈进行数据传输,实现了各种功能,如网页浏览、文件传输、电子邮件发送等。
在数据传输过程中,TCP/IP协议通过三次握手建立连接、数据分割、数据重组、流量控制、拥塞控制等机制保证数据的可靠传输。
它还通过IP地址和端口号来唯一标识主机和应用程序,以实现数据的正确路由和传递。
总的来说,TCP/IP协议是一套功能完善的网络通信协议,它提供了可靠性、有序性和高效性的数据传输服务。
它是互联网的基础,使得不同主机和应用程序能够在全球范围内进行通信和数据交换。
lwip tcp包处理流程lwIP(轻量级IP)是一个用于嵌入式系统的开源TCP/IP协议栈。
它被设计为可移植且具有较小的内存占用,适用于资源受限的设备。
lwIP实现了传输层的TCP和UDP协议,以及网络层的IP协议。
在lwIP中,TCP包的处理流程可以分为以下几个步骤:1.接收数据包:首先,lwIP需要从硬件层接收到TCP包。
硬件层可以是以太网、Wi-Fi、蓝牙等的驱动程序。
接收到TCP包后,硬件层会通过设备适配层将数据包传递给lwIP协议栈。
2.处理数据包头部:lwIP会解析TCP包的头部信息,包括源端口号、目标端口号、序号、确认号等。
根据这些信息,lwIP可以确定TCP包的接收方是哪个连接。
3.查找TCP连接:在接收到TCP包后,lwIP需要查找该包所属的TCP连接。
如果连接已经存在,lwIP将继续处理该连接的数据包。
如果连接不存在,lwIP会将TCP包丢弃,或者根据需要创建新的连接。
4.状态机处理:处理TCP连接的核心是状态机。
lwIP根据RFC 793中提供的TCP 状态机定义,管理TCP连接的状态转换。
在不同的状态下,lwIP将根据接收到的TCP包执行相应的操作,如发送ACK确认包、处理数据、重传数据等。
5.处理数据:如果接收到的TCP包携带有有效数据,lwIP会将数据复制到缓冲区中,以便应用程序读取。
6.发送ACK确认包:当lwIP接收到一个新的TCP包,它将发送一个ACK(确认)包给发送方。
ACK包的确认号等于接收到的TCP包的序号加上接收到的数据长度。
这样,发送方可以根据ACK包进行传输速度的控制。
7.处理应用程序请求:lwIP将接收到的数据包的有效数据提供给应用程序。
应用程序可以根据自己的需要处理数据,如解析HTTP请求、处理文件等。
8.发送数据:当应用程序需要发送数据时,它将调用lwIP的发送接口。
lwIP将数据复制到缓冲区中,并将数据包发送给目标IP地址和端口号。
9.重传机制:如果发送方发送的TCP包在一定时间内没有收到接收方的ACK确认,lwIP将触发重传机制。
lwip移植一、lwIP 概述lwIP是瑞士计算机科学院(Swedish Institute of Computer Science)的Adam Dunkels等开发的一套用于嵌入式系统的开放源代码TCP/IP协议栈。
Lwip 既可以移植到操作系统上,又可以在无操作系统的情况下独立运行.LwIP的特性如下:(1) 支持多网络接口下的IP转发(2) 支持ICMP协议(3) 包括实验性扩展的的UDP(用户数据报协议)(4) 包括阻塞控制,RTT估算和快速恢复和快速转发的TCP(传输控制协议)(5) 提供专门的内部回调接口(Raw API)用于提高应用程序性能(6) 可选择的Berkeley接口API(多线程情况下)(7) 在最新的版本中支持ppp(8) 新版本中增加了的IP fragment的支持.(9) 支持DHCP协议,动态分配ip地址.以上内容摘自网络关于ucos 上的lwip移植二、移植介绍整个移植过程主要参考网络上关于移植到ucos 的说明和源码。
1.目录及文件介绍原版的lwIP1.1.0包含两个目录src 和 doc移植后增加如下文件和目录[Arch]Lib_arch.c本系统没用,系统中没有实现的C库函数可以写到这里Sys_arch.c 移植的主要工作在这里,关于信号量、消息队列、任务创建 [RX4000] 项目目录[Include][Arch]cc.h 类型定义大小端设置 PACK定义等init.hlib.h 跟Lib_arch.c对应函数声明perf.h 没用sys_arch.h 跟Sys_arch.c对应的一些类型定义和宏定义[Netif]Dm9000a.hNe2kif.h[Netif]Dm_netif.c 网卡驱动与系统关联的抽象层Dm9000a.c网卡的硬件操作函数Ne2kif.c 没用[Init]Lwip.c 协议栈初始化和DHCP初始化Lwipopts.h 协议栈相关参数设置[Dns]Dns.c 增加域名解析函数 gethostbyname (非可重入函数)Dns.h2.移植相关函数介绍1) sys_init这个很简单,就是一些全局量的初始化2) sys_thread_new sys_arch_timeouts相关的三个全局变量如下struct sys_timeouts lwip_timeouts[LWIP_TASK_MAX];为每一个由sys_thread_new创建的任务分配一个存放信号量超时信息的列表struct sys_timeouts null_timeouts;为一个超过任务上限数的任务和不是由sys_thread_new创建的任务取超时列表时返回使用。
飞行模拟器的座舱通信技术运用(全文)在现代航空工业领域当中,现代飞机要求大量数据信息能够快速、有效地在飞机系统与系统、系统与部件之间进行高速传递。
目前相当数量的军用机、民用机及运输机的数据通信都采用美国航空无线电公司(ARINC)制定的民用航空数字总线传输标准ARINC429,它定义了航空电子设备和系统之间相互通信的一种规范。
飞行模拟器是能够复现飞行器及空中环境并能够进行操作的模拟装置。
模拟器上集成了许多数字仪表,可以按照ARINC429总线协议标准实现仪表与飞行模拟控制计算机间的数据传输。
构建ARINC429总线络可使用ARINC429总线控制芯片。
但是考虑到经济因素,ARINC429总线控制芯片具有通用性即不够灵活、飞行模拟控制计算机无相应接口与之直接通信。
文中提出在航空仪表周围开发出将以太数据转化为ARINC429总线标准数据的模块。
这样飞行模拟控制计算机就可以通过络快速与航空仪表进行数据通信。
文中给出了以数字信号处理器(DSP)、FPGA、RTL8019AS以太控制器、TCP/IP协议栈等构成的以太转ARINC4299总线协议标准数据模块。
1飞行模拟器座舱仪表通信系统总体结构本系统如图1所示主要由交换机、以太转ARINC429总线控制模块、航空仪表、仪表控制计算机组成,系统中的交换机、航空仪表是现成的,因而本系统所要解决的主要问题即为以太转ARINC429总线控制模块如图2所示。
该模块主要由DSP、FPGA、RTL8019AS、络变压器等器件组成。
核心器件的主要功能及作用:主控芯片采用的是TI公司的TMS320LF2407A数字信号处理器,该芯片采用3.3V供电电压,最高主频可达40MHz,芯片具有丰富的片内外设,如异步串行口、AD、CAN 总线、看门狗、事件管理器等。
在本系统中DSP2407主要的功能是实现对以太控制器数据进行接收处理,最后将数据发送给FPGA进行处理。
以太控制芯片采用的是台湾瑞昱公司生产的RTL8019AS,具有8/16位总线模式,集成了IEEE802.3协议标准的介质访问控制子层(MAC)和物理层的性能,收发可同时达到10Mbps的速率。
TCPIP协议栈lwip的移植TCP/IP协议栈lwip的移植新建几个头文件Include/lwipopts・ hInclude/arch/cc・ hInclude/arch/perf. hInclude/arch/sysearch・ h除头文件外还需要添加一个C文件:sys_arch. c°说明在doc/sys_arch. txt 中。
修改netif/Ethernetif. Co结构对齐的儿个宏对于一个结构下载下來的LWIP的通用定义如下:PACK_STRCCT_BEGIN structicmp.echo.hdr { PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(u8_t type); PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(u8_t code);PACK.STRUCT.FIELD(ul6_t chksum); PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(ul6_t id):PACK.STRUCT.FIELD(ul6_t seqno): } PACK_STRUCT_STRUCT; PACK.STRUCT.EN #definePACK_STRUCT_FIELD(x) 这个宏是为了字节序的转换,由于是用的小端,就不用转换了直接定义为^define PACK_STRUCT_FIELD (x) x ^define PACK.STRUCT.STRUCT #definePACK_STRUCT_BEGIN #define PACK_STRUCT_END以上三个宏都是为了做结构体对齐用:对r gcc的编译器在结构体后跟个关键字就ok struct ip_hdr { } ;_attribute— ((_packed_))因此可以定义为#define PACK_STRUCT_STRl;CT _attribute_ ((_packed_)) ^definePACK_STRUCT_BEGIN ^define PACK_STRUCT_END 对丁rc 的编译器就郁闷了,vc做结构体对齐是这样做的^pragma pack(l) 〃结构体按照1字节对齐struct ip_hdr { } ; #pragmapackO //结构体按照编译器默认值对齐但是VC 的编译器不允许将预处理做为宏,也就是不允许这种宏替代^define PACK_STRUCT_BEGIN#pragma pack(l)所以想靠宏替换來完成字节对齐是不行了,于是就动了大工夫做了如下处理#ifdef WIN32 #define PACK_STRUCT_STRUCT #define PACK_STRUCT_BEGIN ^definePACK.STRUCT.END #else #define PACK_STRUCT_STRUCT _attribute_ ((_packed_)) ^definePACK_.STRUCT.BEGIN ^define PACK.STRUCT.END endif PACK_STRUCT_BEGIN #ifdef WIN32rlpragma pack(l) #endif struct icmp_echo_hdr{ PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(u8_t type); PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(u8_t code);PACK.STRUCT.FIELD(ul6_t chksum); PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(ul6_t id):PACK.STRUCT.FIELD(ul6_t seqno): } PACK_STRUCT_STRUCT; #ifdef WIN32 ^pragma packO#endif PACK_STRUCT_END这样一改在VC下和GCC都可以了,不过每个结构上都要修改一下,这个是黑郁闷黑郁闷啊“轻量级”保护\SYS_ARCH_DECL_PROTECT(x) - declare a protection state variable・SYS_ARCH_PROTECT(x) 一ent erprotec t ion mode.SYS_ARCH_UNPROTECT(x) 一leaveprotection mode.这三个宏定义一个快速的“保护”和“解除保护”操作。
This article was downloaded by: [University of Jiangnan]On: 27 March 2015, At: 06:51Publisher: Taylor & FrancisInforma Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office: Mortimer House, 37-41 Mortimer Street, London W1T 3JH, UKJournal of Discrete Mathematical Sciences andCryptographyPublication details, including instructions for authors and subscription information:/loi/tdmc20An abridged protocol stack for micro controller inplace of TCP/IPR. Seshadri aa Computer Centre, S.V. University , Tirupati , 517 502 , IndiaPublished online: 03 Jun 2013.PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLEAn abridged protocol stack for micro controller in place of TCP/IP R.Seshadri ∗Computer CentreS.V .UniversityTirupati 517502IndiaAbstractThe existing TCP/IP protocol stack running in hosts takes lot of overhead while the node in network is for a specific purpose.For example transferring simple messages across network.If the node in the network is not a PC but,some thing like a micro controller,which measures some values and stores in its local memory,then it becomes lavishness in using the micro controller’s memory.As it is a node in a network,working with TCP/IP ,it should be able to transfer those values in the form of messages to other hosts which are in either local network or global network.But in micro controller terms the memory is expensive and compact.The existing TCP/IP stack consumes a few mega bytes of memory.Therefore it can’t be accommodated in the memory of micro controller.Hence one needs to reduce the memory consumption.In this regard,an abridged protocol which replaces the existing TCP/IP has been designed to suit the above needs.For this purpose,the TCP/IP have been combined with KEIL C51features for 8051micro controller to make it work in transferring messages in local area network as well as global network.The above scheme was implemented and tested and the system was working satisfac-torily.The results are found to be more effective in communicating information/message from the micro controller to a PC.Keywords :Ethernet,stack,Transmission Control Protocol (TCP ),Internet Protocol (IP ).Introduction to TCP/IPThe name TCP/IP refers to a suite of communication protocols.The name is misleading because TCP and IP are the only two of the dozens of protocols that compose the suite.Its name comes from two of the most ∗E-mail :ravalaseshadri@yahoo.co.in—————————————————–Journal of Discrete Mathematical Sciences &CryptographyVol.9(2006),No.3,pp.523–536c Taru Publications D o w n l o ade d b y [U n i v e r s i t y of J i a ng n a n ] a t 06:51 27 M a r ch 2015524R.SESHADRI important protocols in the suite,the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)and the Internet Protocol (IP).TCP/IP originated out of the investigative research into networking protocols that the Department of Defense (DOD)initiated in 1969.In 1968,the DOD Advanced Research Projects Agency (APRA)began researching the network technology that is now called packet switching.The original focus of this research was to facilitate communication among the DOD community.However,the network that was initially constructed as a result of this research,then called ARPANET,gradually became known as the internet.In the early 1980’s,the TCP/IP protocols were developed.In 1983,they became standard protocols for ARPANET.It is often referred to as DOD protocol suite or the internet protocol suite.When two computers wish to exchange information over a network,there are several components that must be in place before the data can actually be sent and received.Ofcourse,the physical hardware must exist,which is typically either a Network Interface Card (NIC)or a serial communications port for dial-up network connections.Beyond this phys-ical connection,however computers also need to use a protocol,which defines the parameters of the communication between them.In short,a protocol defines “rules of the road”that each computer must follow so that all the systems in the network can exchange data.One of the most popular protocols is use today is TCP/IP ,which stands for transmission control/internet protocol.KEIL C51compiler basicsThe KEIL C51compiler has been written to allow C programmers to get code running quickly on 8051systems with little or no learning curve.However,to get the best from it,some appreciation of the under-lying hardware is desirable.The most basic decision to be made is which memory model to use.Implementation of abridged TCP/IP in C51[1]The conceptual overview and infrastructure of TCP/IP will be very immensive and fuzzy.Each protocol in the stack has its own functional ually Programmers choose a powerful high level language for implementation.High level language like ‘C’provides dynamic mem-ory allocation,buffer maintenance strong type checking etc.,which are useful in implementing protocols in an optimized way.D o w n l o a d e d b y [U n i v e r s i t y o f J i a n g n a n ] a t 06:51 27 M a r c h 2015MICRO CONTROLLER IN PLACE OF TCP/IP 525Existing paradigmThe native TCP/IP in the Linux system implements several features:Internet ProtocolIn the TCP ,UDP ,ICMP ,IGMP data gets transmitted as IP datagrams,so it is called as workhorse protocol.Currently,IP is implemented with the following features:IP routing:This provides the basic mechanism for routers to interconnectdifferent physical networks.IP routing is done by hop-by-hop basis.It uses a data structure called routing table which maintains source and destination addresses and the next hop router to which the datagram is to be sent.IP multicasting:This feature enables the IP to send the datagrams to theselective destination addresses.IP tunneling:This feature lets the other protocols to use the IP .Forexample IPX protocol can make use if IP tunneling to send its data.IP masquerading:If a Linux host is connected to the internet with IPmasquerade enabled,then computers connecting to it either on the same LAN or connected with modems can reach the internet as well,even though they have no officially assigned IP addresses.IP accounting:This keeps track of IP network traffic,performs packetlogging and produces some statistics.IP aliasing:This provides the possibility of setting multiple networkaddresses on the same low-level network device driver.It is typically used for services that act differently based on the address they listen on.Address Resolution ProtocolCurrently ARP implements two featuresGratuitous ARP:It occurs when a host sends an ARP request looking for its own IP address.This is done when the interface is configured at bootstrap time.Transmission Control Protocol:Currently TCP is implemented with the following features [2]:•Handle multiple simultaneous connections D o w n l o a d e d b y [U n i v e r s i t y o f J i a n g n a n ] a t 06:51 27 M a r c h 2015526R.SESHADRI•Hold sent segments until ack is received•Resend segments if no ack is received•Handle TCP options•Handle passive open (act as a server)•Handle active open (act as a client)•Assemble multiple segments•Assemble out-of-order segments•Discard duplicate received segments•Nagle algorithm•Van Jacobsen’s algorithm•Respect other end’s max segment size•Slow start on new connection•Estimate round trip time•Kam’s algorithm•Congestion avoidance algorithm•Handle urgent mode Code Description Code Description0Echo reply 3Destination unreachable 4Source quench 5Redirect8Echo 9Router advertisement10Router solicitation 11Time exceeded12Parameter problem 13Timestamp request14Timestamp reply 15Information request16Information reply 17Address mask request 18Address mask reply 30Traceroute31Datagram conversion errorProblems in existing paradigmThe above mentioned protocols and its feature are efficient in terms of functionality when the PC to PC communication is concerned.It took few Mbytes of memory in a x86system.As in case of micro controller the memory model is very compact when compared with the PC.Now our existing system can not be suited for porting in to micro controller,because it’s a spacious one.D o w n l o a d e d b y [U n i v e r s i t y o f J i a n g n a n ] a t 06:51 27 M a r c h 2015MICRO CONTROLLER IN PLACE OF TCP/IP 527Proposed paradigm [3]Not all the features mentioned above are required in terms of micro-controller.So we abridged them and implemented the following protocols and its features.The model for the proposed system is shown in Figure1.Figure 1Layers of the proposed systemInternet ProtocolIP routing:This provides the basic mechanism for routers to interconnect different physical networks.IP routing is done by hop-by-hop basis.It uses a datastructure called routing table which maintains source and destination addresses and the next hop router to which the datagram is to be sent.Address Resolution ProtocolARP will translate the IP address to the physical address of the destination host.It uses a lookup table (some times referred to as the ARP cache)to perform this translation.D o w n l o a d e d b y [U n i v e r s i t y o f J i a n g n a n ] a t 06:51 27 M a r c h 2015528R.SESHADRI Transmission Control ProtocolCurrently TCP is implemented with the following features:Handle multiple simultaneous connectionsHold sent segments until ack is receivedHandle TCP optionsHandle passive openInternet Control Message ProtocolIt is an interactive error reporting protocol.Currently it handles the following message types:Code Description0Echo reply3Destination unreachableImplementationSequence ofsteps followed toimplement an abridgedprotocol stack inplace of TCP/IP isshown in Figure2.Figure 2Sequence of steps D o w n l o a d e d b y [U n i v e r s i t y o f J i a n g n a n ] a t 06:51 27 M a r c h 2015MICRO CONTROLLER IN PLACE OF TCP/IP 529The following are the protocols,which has been implemented so as to reach the desired goal.ARP (Address Resolution Protocol )ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol )IP (Internet Protocol )TCP (Transmission Control Protocol )HTTP (Hyper Text Transmission Protocol )ETH (Ethernet Protocol )Now let us see on by one protocol.Implementation of ARP [4]The data structures used in this protocol are as follows:typedef struct{ULONG ipaddr;UCHAR hwaddr[6];UCHAR timer;}ARP CACHE;This cache maintains the recent mappings from internet addresses to hardware addresses.The normal expiration time of entry in a cache is 0.5seconds from the time the entry was created.This time value is represented using the timer template member in the structure.typedef struct{UINT hardware type;UINT protocol type;UCHAR hwaddr len;UCHAR ipaddr len;UINT message type;UCHAR source hwaddr[6];ULONG source ipaddr;UCHAR dest hwaddr[6];ULONG dest ipaddr;}ARP HEADER;D o w n l o a d e d b y [U n i v e r s i t y o f J i a n g n a n ] a t 06:51 27 M a r c h 2015530R.SESHADRI This represents the ARP header.The methods which I used in this are as follows:UCHAR*arp resolve(ULONG)This method finds the ethernet hardware address for the given IP address,if destination IP is on the subnet then we want the eth address of destination,otherwise we want eth address of gateway.This will look in ARP cache first.If not found there,this will send ARP request.This will return pointer to the hardware address or NULL if not found.void arp rcve(UCHAR*)This handles incoming ARP messages.void arp send(UINT8*,UINT32,UINT8)This allocates memory for the entire outgoing message,including Ethernet and ip headers,then builds an outgoing ARP response message.void age arp cache(void)This is called every 60seconds to age the ARP cache.If an entry times out then it is deleted from the cache.void arp retransmit(void)This resends an ARP request if there was no response to the first one.It is called every 0.5seconds.If there is no response after 2retries,the datagram that IP was trying to send is deleted.Implementation of ICMPThe data structure used in this protocol is as follows:typedef struct{UCHAR msg type;UCHAR msg code;UINT checksum;ULONG msg data;UCHAR echo data;}ICMP ERR HEADER;typedef struct{UCHAR ver len;D o w n l o a d e d b y [U n i v e r s i t y o f J i a n g n a n ] a t 06:51 27 M a r c h 2015MICRO CONTROLLER IN PLACE OF TCP/IP 531UCHAR type of service;UINT total length;UINT identifier;UINT fragment info;UCHAR time to live;UCHAR protocol id;UINT header cksum;ULONG source ipaddr;ULONG dest ipaddr;}IP HEADER;typedef struct{UCHAR msg type;UCHAR msg code;UINT checksum;UINT identifier;UINT sequence;UCHAR echo data;}PING HEADER;ICMP messages are usually acted on by the IP layer,when an ICMP error message is sent,the message always contains the IP header and the first eight bytes of IP datagram that caused the ICMP error to be generated.So used the above two data structures.The methods which were used in this are as follows:void ping send(UCHAR*,ULONG,UINT)This builds a ping response message.It allocates memory for the entire outgoing message,including Eth and IP headers.void dest unreach send(UCHAR*,ULONG)This builds an outgoing ICMP destination port unreachable response message.void icmp rcve(UCHAR*,UINT)This handles incoming ICMP messages.And displays what type of error it is.D o w n l o a d e d b y [U n i v e r s i t y o f J i a n g n a n ] a t 06:51 27 M a r c h 2015Implementation of IPThe data structure used in this protocol is as follows:typedef struct{UCHAR ver len;UCHAR type of service;UINT total length;UINT identifier;UINT fragment info;UCHAR time to live;UCHAR protocol id;UINT header cksum;ULONG source ipaddr;ULONG dest ipaddr;}IP HEADER;This represents the IP header.The methods followed are as follows:void ip send(UCHAR*,ULONG,UCHAR,UINT)This builds outgoing IP datagrams.It adds the 20byte IP header and checksum then forwards the IP datagram to the Ethernet layer for sending.void ip rcve(UCHAR*)This handles incoming IP datagrams from the Ethernet layer.Implementation of TCP [5]The data structure used in this protocol is as follows:typedef struct{UINT source yort;UINT dest yort;ULONG sequence;ULONG ack number;UINT flags;UINT window;UINT checksum;D o w n l o a d e d b y [U n i v e r s i t y o f J i a n g n a n ] a t 06:51 27 M a r c h 2015UINT urgent ytr;UCHAR options;}TCP HEADER;This represents the TCP header.typedef struct{UCHAR ver len;UCHAR type of service;UINT total length;UINT identifier;UINT fragment info;UCHAR time to live;,UCHAR protocol id;UINT header cksum;ULONG source ipaddr;ULONG dest ipaddr;}IF HEADER;The methods which I used in this are as follows:void TCP send(UINT,UNIT,UCHAR)This sends a TCP segments that do not include any data.void TCP rcve(UCHAR*,UINT)This handles incoming TCP messages and manages the TCP state ma-chine.void TCP retransmit(void)This runs every 0.5seconds.If the other end has not acknowledged everything we have sent,resends it.To save RAM space,we regenerate a segment rather than keeping a bunch segments hanging around eating up RAM.A connection should not be in an opening or closing state when this timer expires,so we simply send a reset.If a connection is in the ESTABLISHED state when the timer expires then we have just sent a web page so resend the page.void TCP inactivity(void)This runs every 0.5seconds.If the connection has had no activity it initiates closing the connection.D o w n l o a d e d b y [U n i v e r s i t y o f J i a n g n a n ] a t 06:51 27 M a r c h 2015Implementation of HTTPThe data structure used in this protocol is as follows:typedef struct{UCHAR ver len;UCHAR type of service;UINT total length;UINT identifier;UINT fragment info;UCHAR time to live;UCHAR protocol id;UINT header cksum;ULONG source ipaddr;ULONG dest ipaddr;}IP HEADER;typedef struct{UINT source-port;UINT dest-port;ULONG sequence;ULONG ack number;UINT flags;UINT window;UINT checksum;UINT urgent-ptr;UCHAR options;}TCP HEADER;The methods which I used in this are as follows:void init http(void)UINT http server(UCHAR*,UINT,UCHAR,UCHAR)This serves up either a HTML page,a JPEG image,or controls an LED,depending what it gets from the browser.The received header must contain the word “GET”or “POST”)to be considered a valid request.Implementation of ethernet protocolThe data structure used in this protocol is as follows:D o w n l o a d e d b y [U n i v e r s i t y o f J i a n g n a n ] a t 06:51 27 M a r c h 2015typedef struct{UCHAR dest hwaddr[6];UCHAR source hwaddr[6];UINT frame type;}ETH HEADER;The methods which I used in this are as follows:void eth rcve(UCHAR*)This is the handler for incoming Ethernet frames.This is designed to handle standard Ethernet frames.void eth send(UCHAR*,UCHAR*,UINT,UIN1)This adds the ethernet header and sends completed Ethernet frame to micro controller.Testing•Here the test case is the acquisition of power measurement in the micro controller in the form of HTTP reply.•For this we initialized the microcontroller with the IP address 192.168.0.15and passed the HTTP request.•The HTTP request is passed from another host in the network through the internet explorer.•HTTP reply from the micro controller is as given below.D o w n l o a d e d b y [U n i v e r s i t y o f J i a n g n a n ] a t 06:51 27 M a r c h 2015Conclusion•This paper clearly shown that it is possible to implement “An Abridged Protocol Stack for Micro Controller in place of TCP/IP”using KEIL C51in Windows operating system.•The Micro Controller is made itself to work in a Network instead of PC’s.Now some of the cost based measures like space,complexity,effort are reduced.Micro Controller is highly economical when com-pared with PC’s.Future enhancements•This can be enhanced to support Wireless communication over Eth-ernet by implementing the 802.11standards.This can be done easily because this abridged stack can adapt a new protocol easily.•Right now there is no any security for the data in the micro controller,i.e any body can have access to it.In future this can be avoided by implementing authentication methods like LDAP etc.•We can enhance this abridged protocol stack by adding some extra features to current protocols,so that it can be more efficient in communicating data,while the configuration of the system also upgraded.•In future this can be enhanced and implement for Linux and other operating systems also.References[1]M.Beach,C51Primer .[2][3]W.Richard Stevens,TCP/IP Illustrated ,Vol.1.[4] C.Hunt,TCP/IP Network Administration .[5]W.R.Stevens,TCP/IP Illustrated ,Vol.1.Received April,2006D o w n l o a d e d b y [U n i v e r s i t y o f J i a n g n a n ] a t 06:51 27 M a r c h 2015。